Similar presentations:
Petroleum disperse systems. (Lecture 3)
1. Petroleum disperse systems
• The PDS classification• Nanoparticles in PDS
• Lyophilic and lyophobic PDS. Shchukin-Rehbinder criterion
• Some challenges of Petroleum Industry, connected with PDS
exploitation, treatment, transport and refining
14/09/16
lecture 3
1
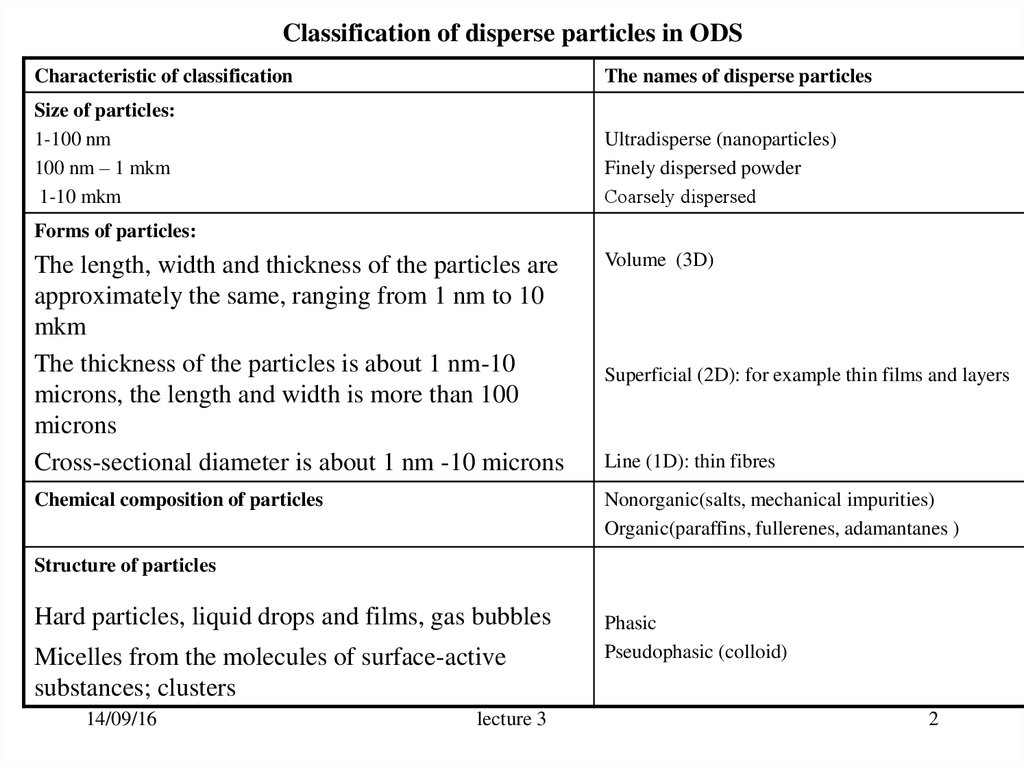
2. Classification of disperse particles in ODS
Characteristic of classificationThe names of disperse particles
Size of particles:
1-100 nm
100 nm – 1 mkm
1-10 mkm
Ultradisperse (nanoparticles)
Finely dispersed powder
Сoarsely dispersed
Forms of particles:
The length, width and thickness of the particles are
approximately the same, ranging from 1 nm to 10
mkm
The thickness of the particles is about 1 nm-10
microns, the length and width is more than 100
microns
Cross-sectional diameter is about 1 nm -10 microns
Volume (3D)
Chemical composition of particles
Nonorganic(salts, mechanical impurities)
Organic(paraffins, fullerenes, adamantanes )
Superficial (2D): for example thin films and layers
Line (1D): thin fibres
Structure of particles
Hard particles, liquid drops and films, gas bubbles
Micelles from the molecules of surface-active
substances; clusters
14/09/16
lecture 3
Phasic
Pseudophasic (colloid)
2
3.
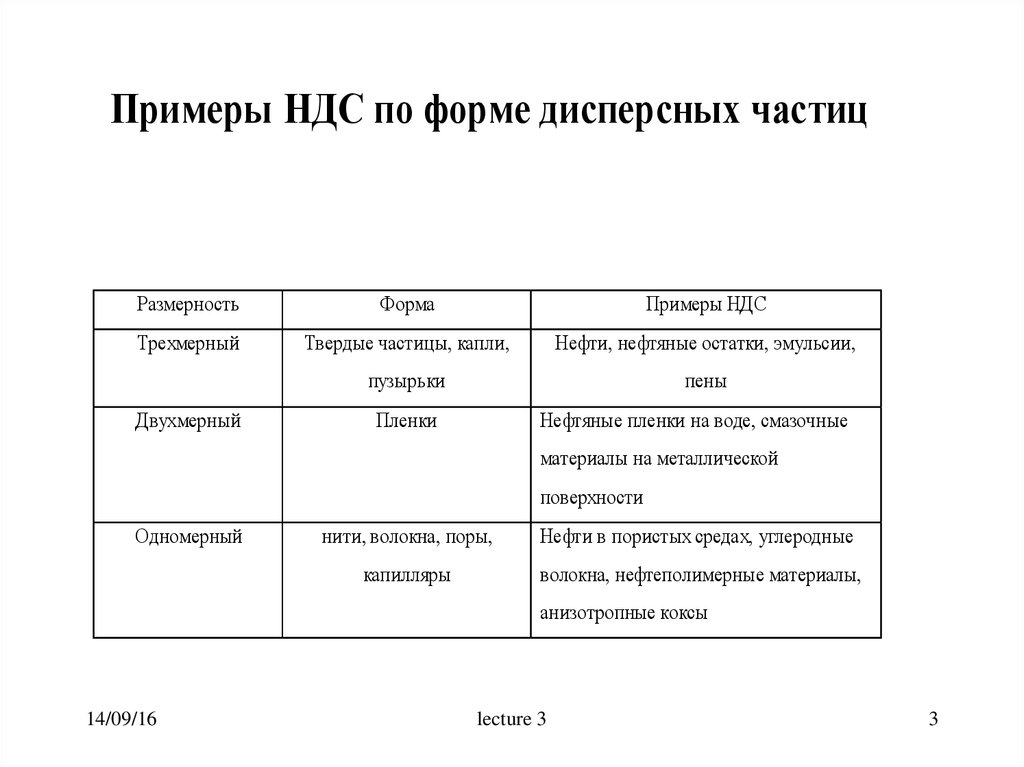
Примеры НДС по форме дисперсных частицРазмерность
Форма
Примеры НДС
Трехмерный
Твердые частицы, капли,
Нефти, нефтяные остатки, эмульсии,
пузырьки
пены
Двухмерный
Пленки
Нефтяные пленки на воде, смазочные
материалы на металлической
поверхности
Одномерный
нити, волокна, поры,
Нефти в пористых средах, углеродные
капилляры
волокна, нефтеполимерные материалы,
анизотропные коксы
14/09/16
lecture 3
3
4.
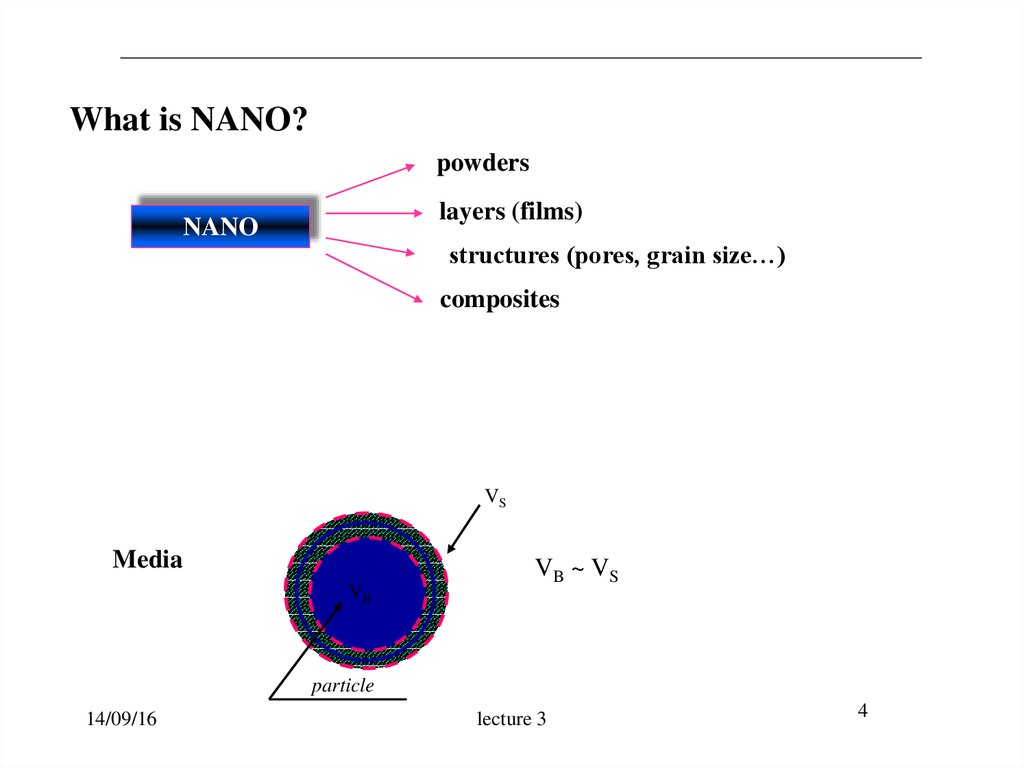
What is NANO?powders
layers (films)
NANO
structures (pores, grain size…)
composites
VS
Media
VB
VB ~ VS
particle
14/09/16
lecture 3
4
5. Energy and power aspects of surface (interfacial)* tension
The compensate of intermolecular interactionson the phase boundary leads to the fact that the
phase boundary surface has an uncompensated
excess energy (energy aspect), σ [erg/cm2, J/m2]
and causes the appearance of a tangential force
(power aspect), σ [din/cm, N/m]
*
The term "interphase boundary" is usually attributed to the
boundary between two immiscible phases, the term "surface" indicates
that one of the phases is a gas, usually air
14/09/16
lecture 3
5
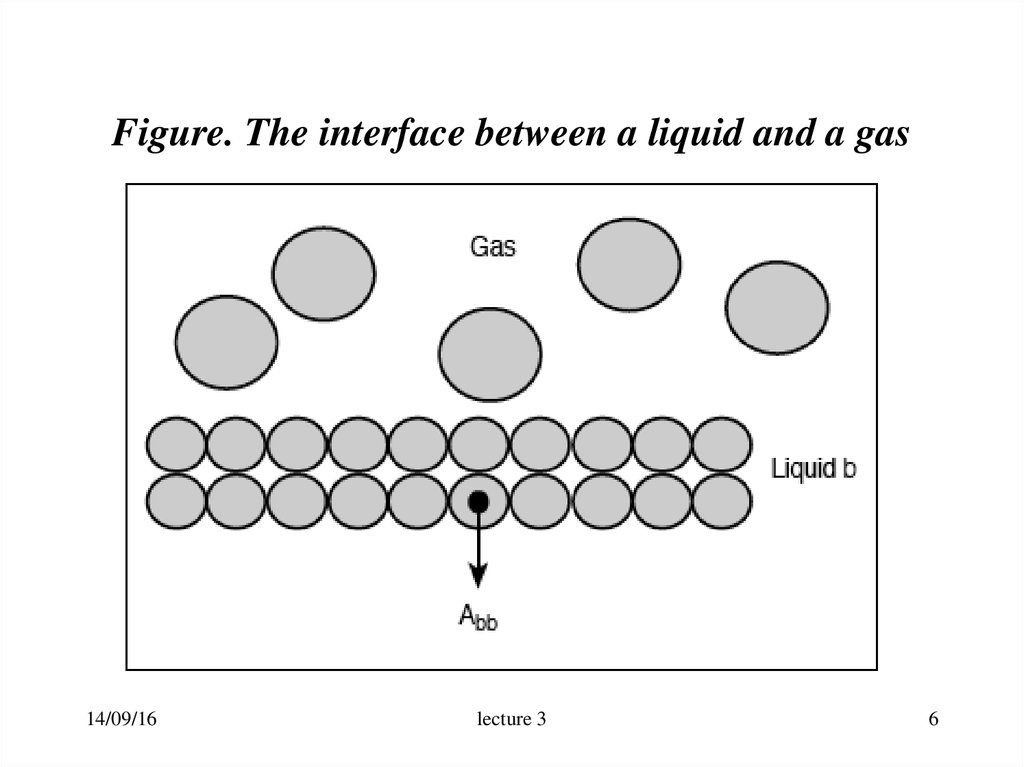
6. Figure. The interface between a liquid and a gas
14/09/16lecture 3
6
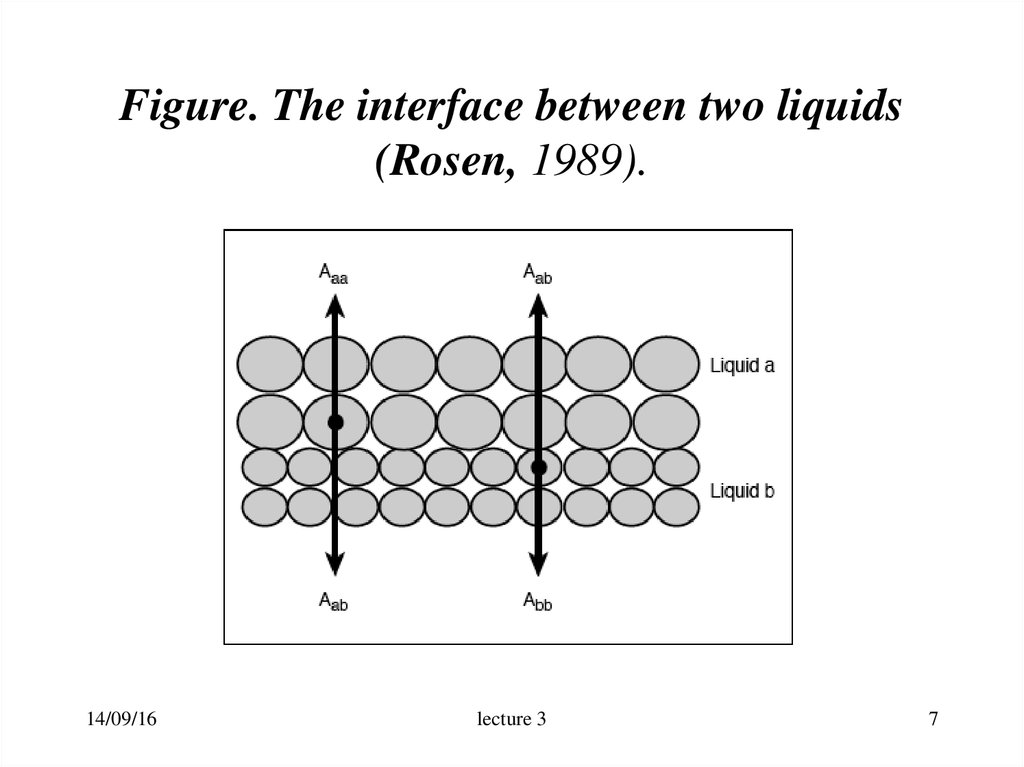
7. Figure. The interface between two liquids (Rosen, 1989).
14/09/16lecture 3
7
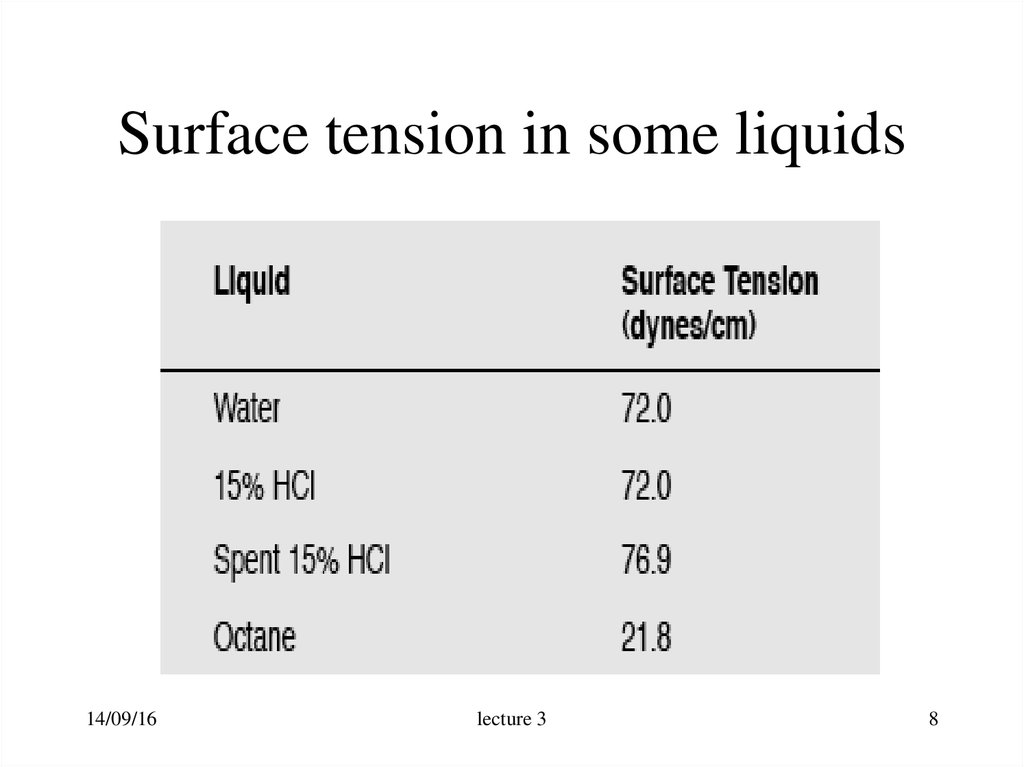
8. Surface tension in some liquids
14/09/16lecture 3
8
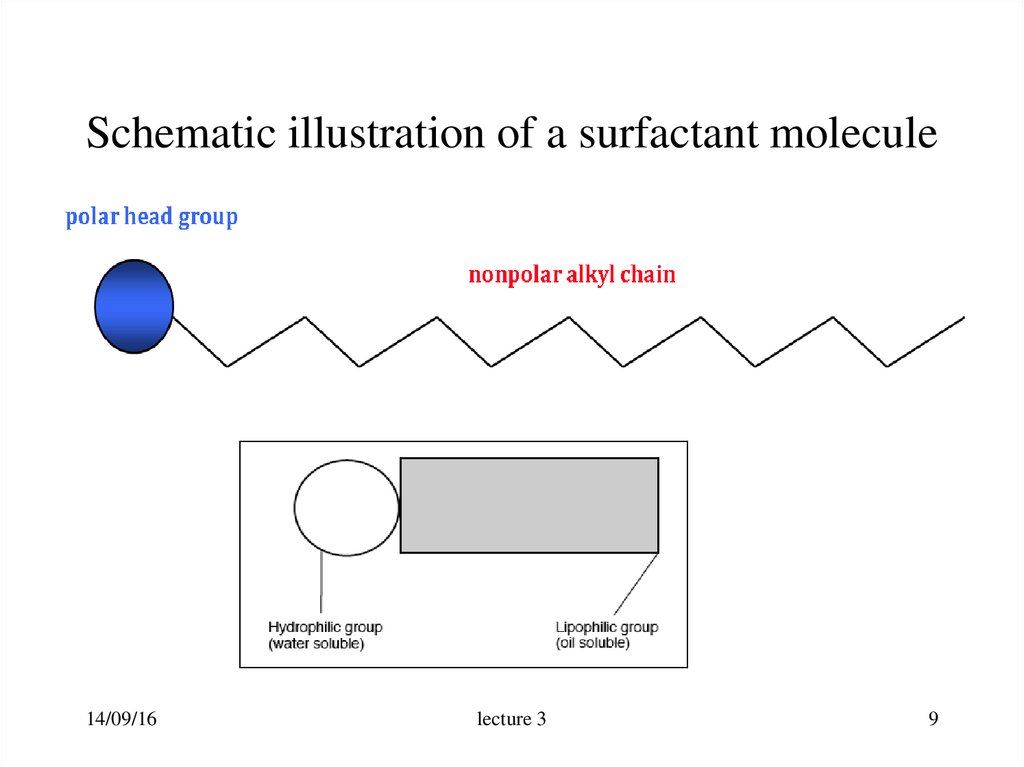
9. Schematic illustration of a surfactant molecule
14/09/16lecture 3
9
10. Lyophilic and lyophobic ODS
ODS can be divided on lyophilic and lyophobic due to value
of interfacial interactions at the interface
Shchukin-Rehbinder criterion 4πr2σ ~ γkT,where
r - particle size,
T-temperature,
K - Boltzmann constant,
- dimensionless coefficient
Calculation shows, that at standart conditions
σcrit~ 0,01-0,1 mN/m
Lyophilic ODS σ < σcrit
Lyophobic ODS σ > σcrit
14/09/16
lecture 3
10
11. Composite ODS
Five interfaces:Solid body – gas (surface)
Solid body - liquid (interphase boundary)
Solid body – solid body
liquid – gas (surface)
liquid-liquid (interphase boundary)
14/09/16
lecture 3
11
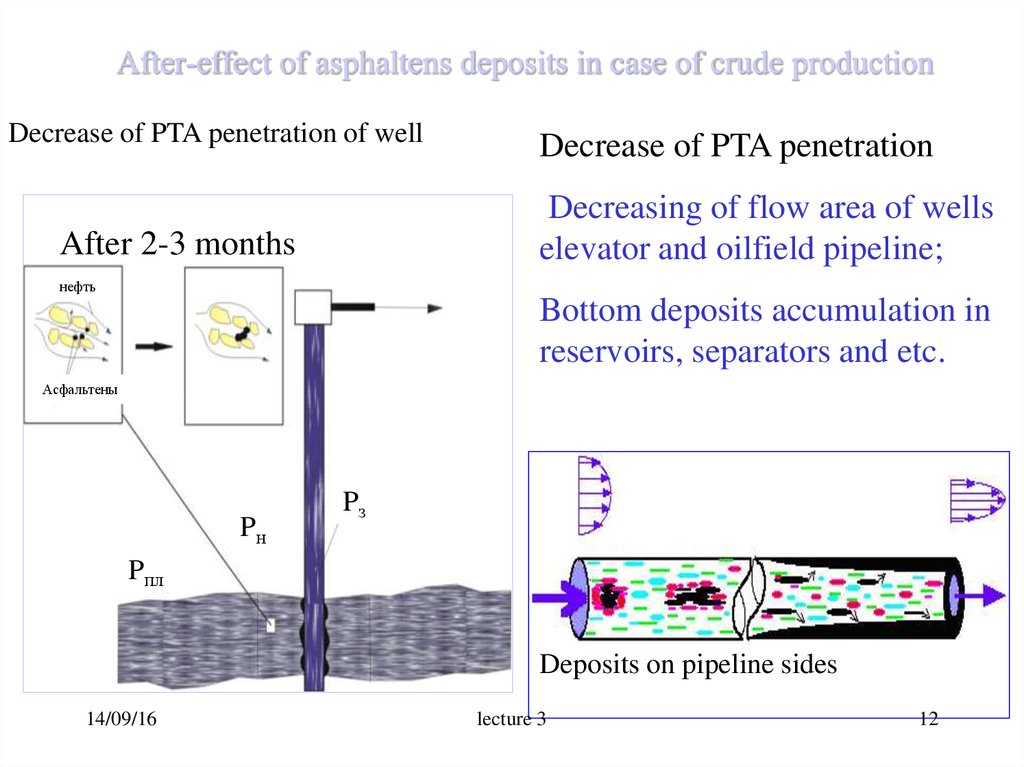
12. After-effect of asphaltens deposits in case of crude production
Decrease of PTA penetration of wellDecrease of PTA penetration
Decreasing of flow area of wells
elevator and oilfield pipeline;
After 2-3 months
нефть
Bottom deposits accumulation in
reservoirs, separators and etc.
Асфальтены
Pн
Pз
Pпл
Deposits on pipeline sides
14/09/16
lecture 3
12
13. Basic conditions, which determine risk of asphaltens setting out in PTA (pig trap area)
Changing of thermobaricе conditions in PTA;
Рпл – Рн > 8 – 10 МPа;
Presence of contamination;
Formation of trolly-oil;
Practice of incongruent chemicals (isopropil alcohol,
methanol, propanone, solvents);
• Acid treatment and other chemical methods of
intensification of oil inflow from the bench
14/09/16
lecture 3
13
14. Deposition of asphaltenes in a pipeline wall
14/09/16lecture 3
14
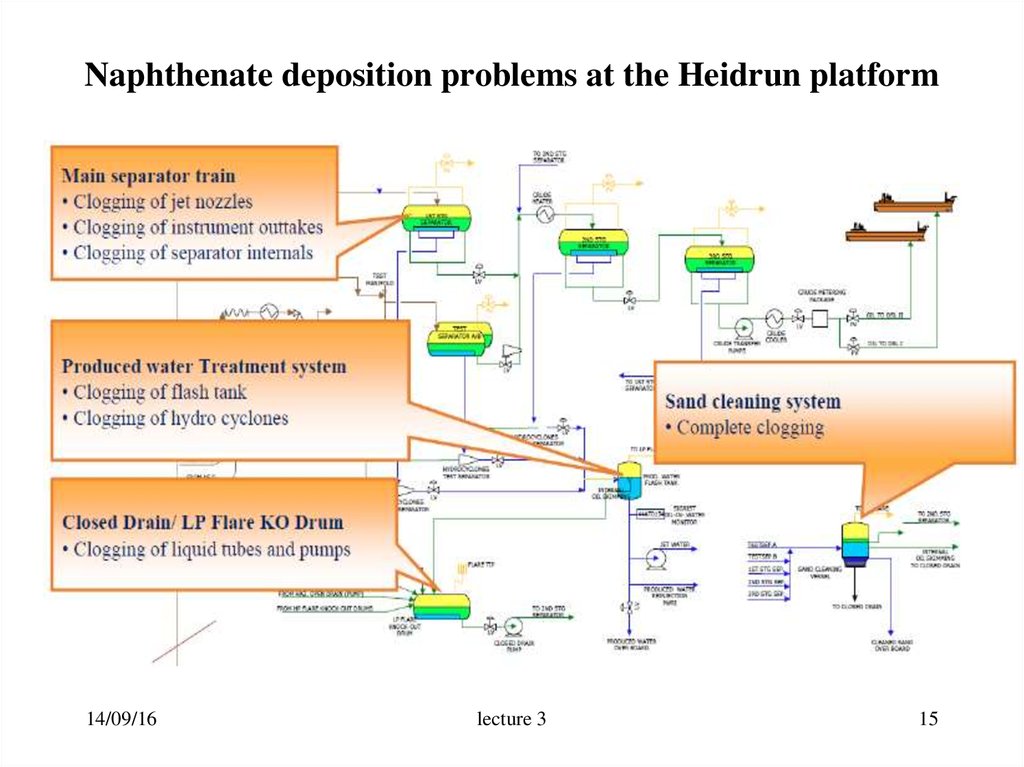
15. Naphthenate deposition problems at the Heidrun platform
14/09/16lecture 3
15
16. Pigging operation to remove wax from the Norwegian shelf
14/09/16lecture 3
16
17. Production
• Asphaltum-resinsparaffin deposit(ARPD)
• Clogging of oil
reservoir pores
(skin-effect)
14/09/16
lecture 3
17
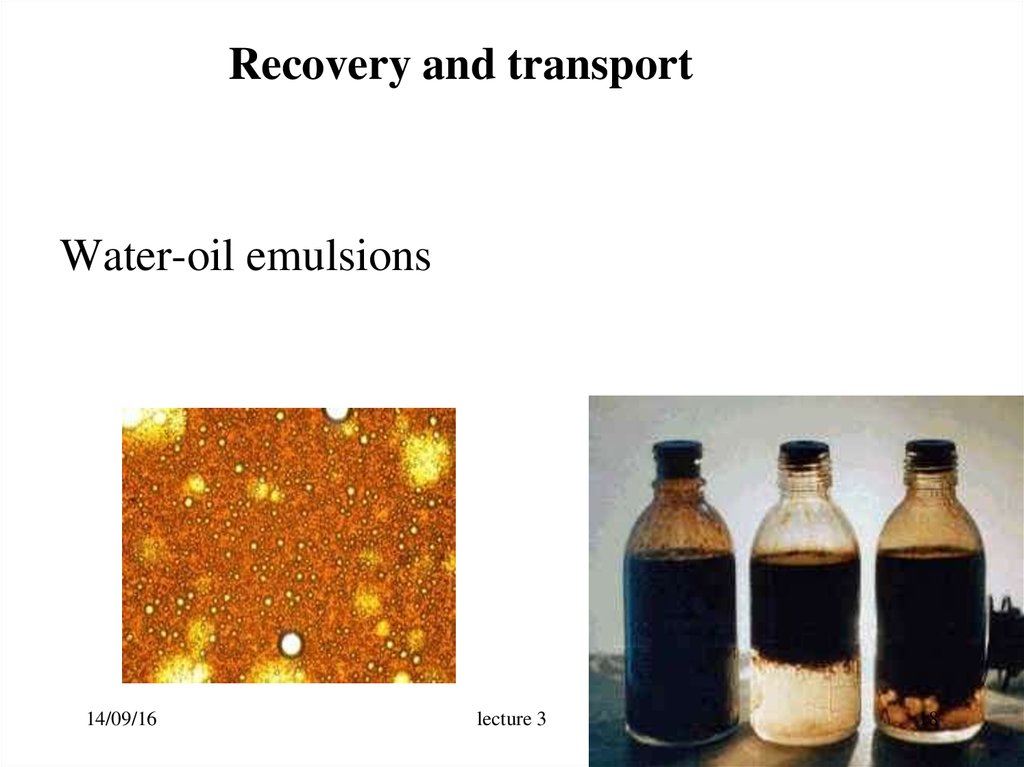
18. Recovery and transport
Water-oil emulsions14/09/16
lecture 3
18
19. Refining
Change of states inprocessing vessels and in
coilers of pipe heaters
14/09/16
lecture 3
19







 industry
industry








