Similar presentations:
Modern view at asphaltenes. (Lecture 4)
1. Modern view at asphaltenes
• The basic idea about the PDS dispersed phase resins, asphaltenes, carbenes and carboids• Separating crude oil (SARA)
• Definition onset
• The various models of a structure asphaltenes :
packing (onion), continental (or island) and fractal
14/09/16
lecture 4
1
2. Component analysis
• Paraffines [alkanes]:n-/izostructure
Naphthenes: [cycloalkanes]
• Aromatic hydrocarbons [arenes]
• Hydrocarbons of mixed structure: in Diesel fraction and above
• Non-hydrocarbon oil components: S, N, O
• Mineral components: H2O, salts
• Macromolecular components
14/09/16
lecture 4
2
3. High-molecular oil components
• Wax:– С18-С35 (300-450 а.е.)
• Cerezines:
– С36-С55 (500-700 а.е.)
• Resins-asphaltenic substances (RAS):
– Resines:
– Asphaltenes:
14/09/16
< 1000 а.е.
> 1000 а.е.
lecture 4
3
4. RAS classification
• Resins:• M <1000
• soluble in alkanes
• condensed systems related with aliphatic chains
• Asphaltenes:
14/09/16
M > 1000
≈ 1 D and above
insoluble in alkanes
soluble in benzene,CS2, CCl4, etc.
tend to associations, define the structure of oil disperse systems
lecture 4
4
5.
14/09/16lecture 4
5
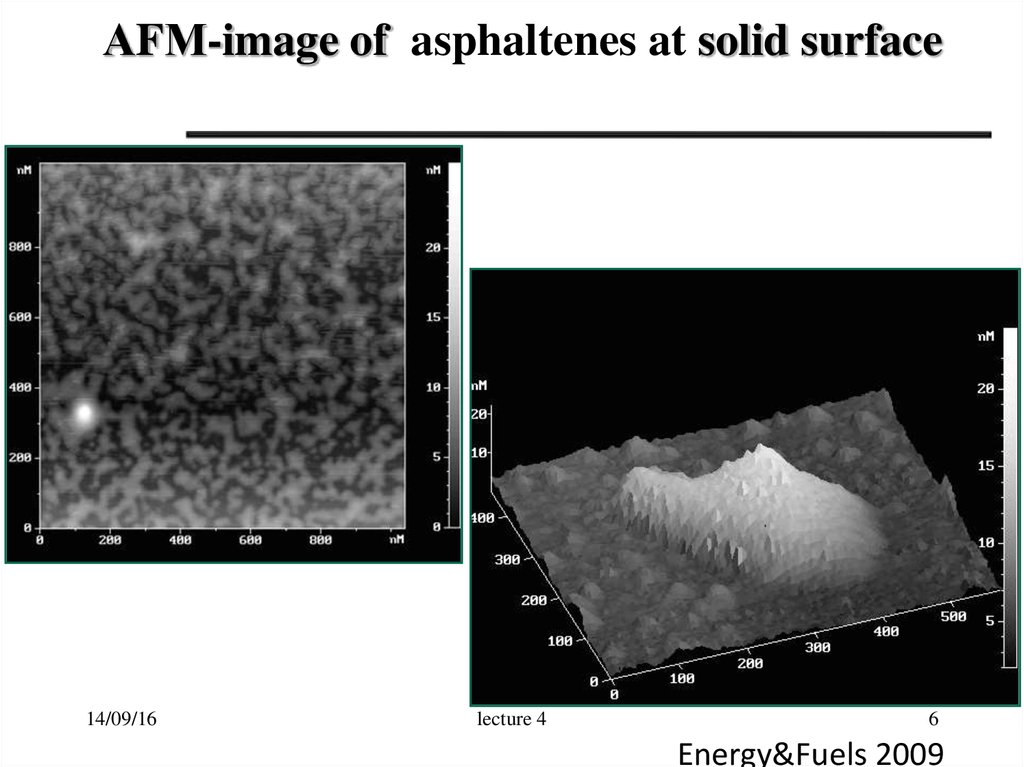
6.
АFМ-image of asphaltenes at solid surface14/09/16
lecture 4
6
Energy&Fuels 2009
7.
Two approaches in development ofrepresentations about structure RA
• Chemical
- structural formulas of molecules of resins and
asphaltenes СnH2n-z NpSqOr
(The calculated values z for resins 40-50,
for asphaltenes- 130-140)
• Physical
- packing model of asphaltene structure(Yen,1961);
- a scale sedimentators and solvents in relation to
asphaltene (Hotier, 1980);
- fractal model of a structure asphaltene(1994).
14/09/16
lecture 4
7
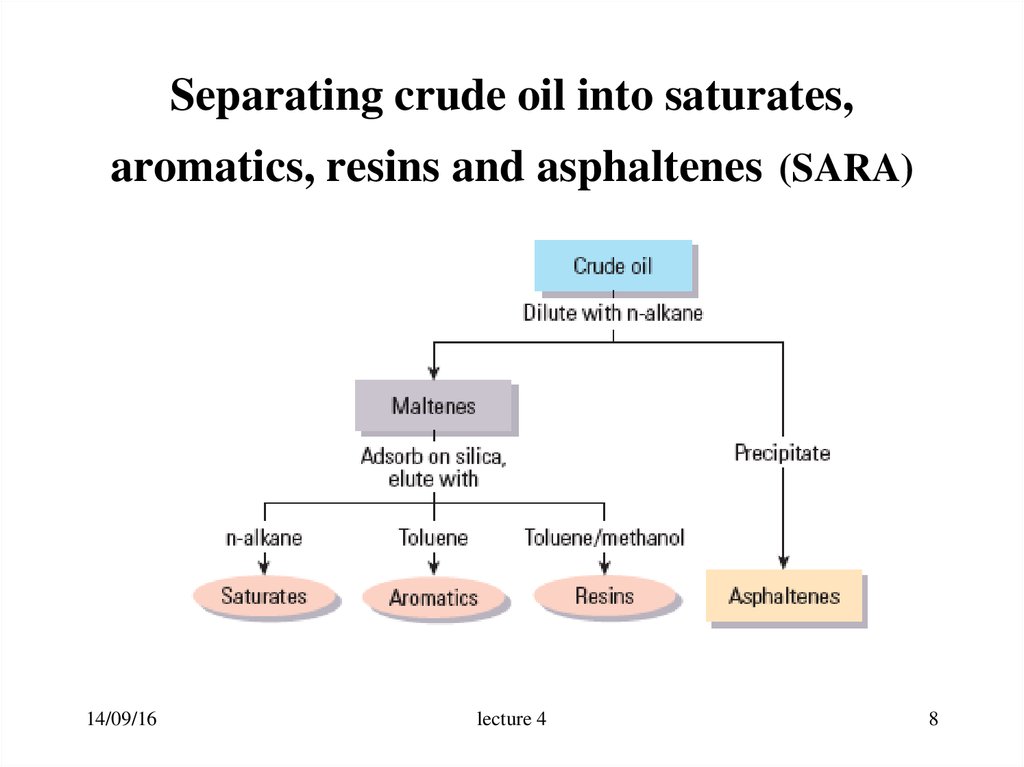
8. Separating crude oil into saturates, aromatics, resins and asphaltenes (SARA)
14/09/16lecture 4
8
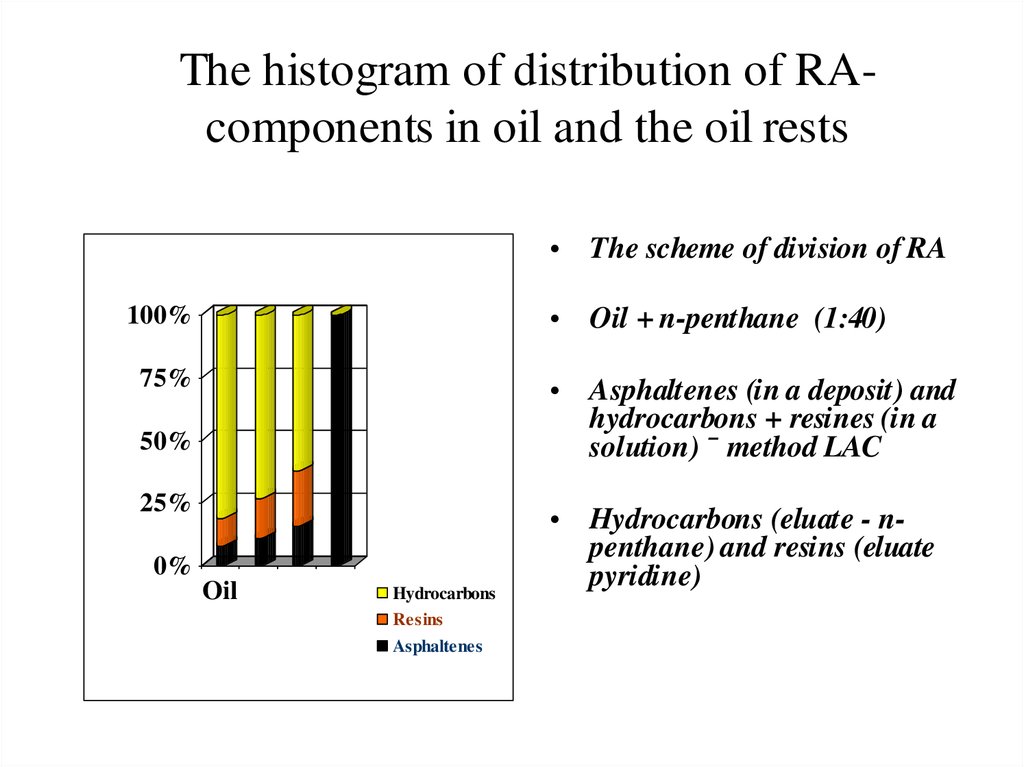
9.
The histogram of distribution of RAcomponents in oil and the oil rests• The scheme of division of RA
• Oil + n-penthane (1:40)
100%
75%
• Asphaltenes (in a deposit) and
hydrocarbons + resines (in a
solution) ¯ method LAC
50%
25%
0%
Oil
Hydrocarbons
• Hydrocarbons (eluate - npenthane) and resins (eluate
pyridine)
Resins
Asphaltenes
14/09/16
lecture 4
9
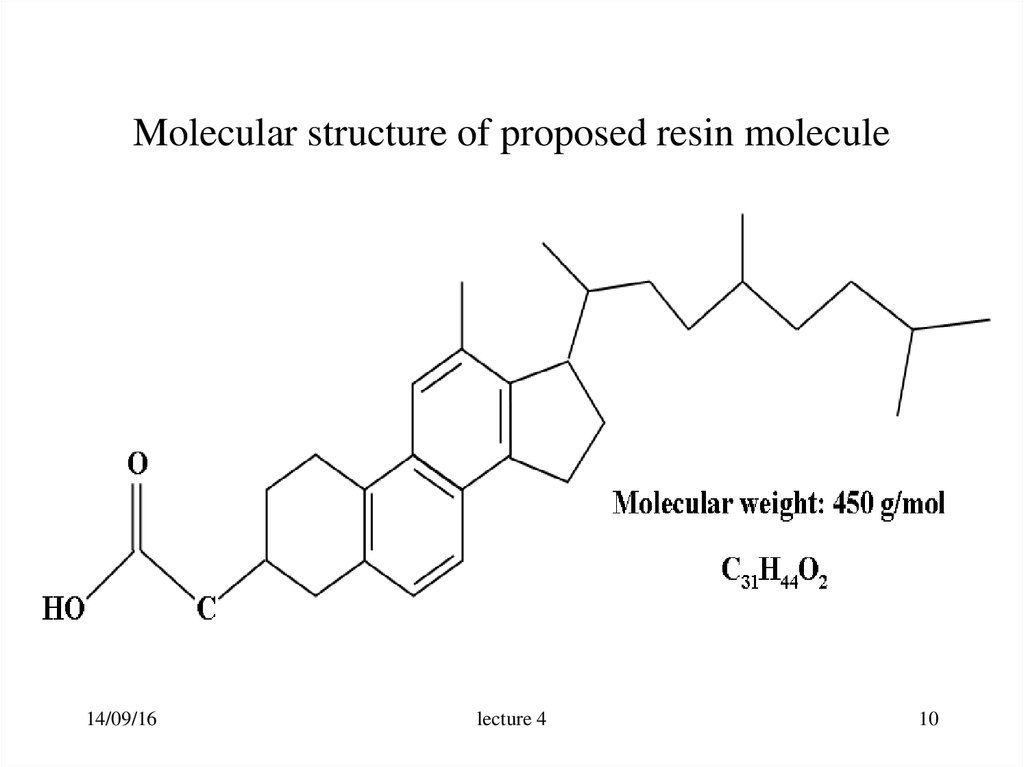
10. Molecular structure of proposed resin molecule
14/09/16lecture 4
10
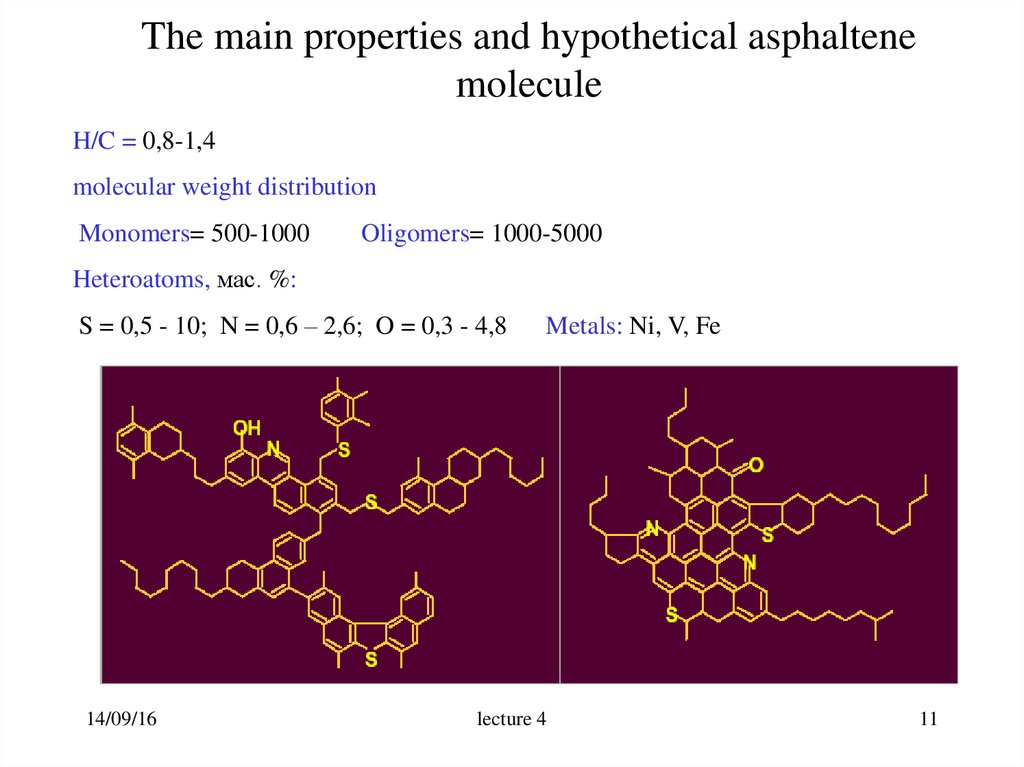
11. The main properties and hypothetical asphaltene molecule
H/C = 0,8-1,4molecular weight distribution
Monomers= 500-1000
Oligomers= 1000-5000
Heteroatoms, мас. %:
S = 0,5 - 10; N = 0,6 – 2,6; O = 0,3 - 4,8
14/09/16
Metals: Ni, V, Fe
lecture 4
11
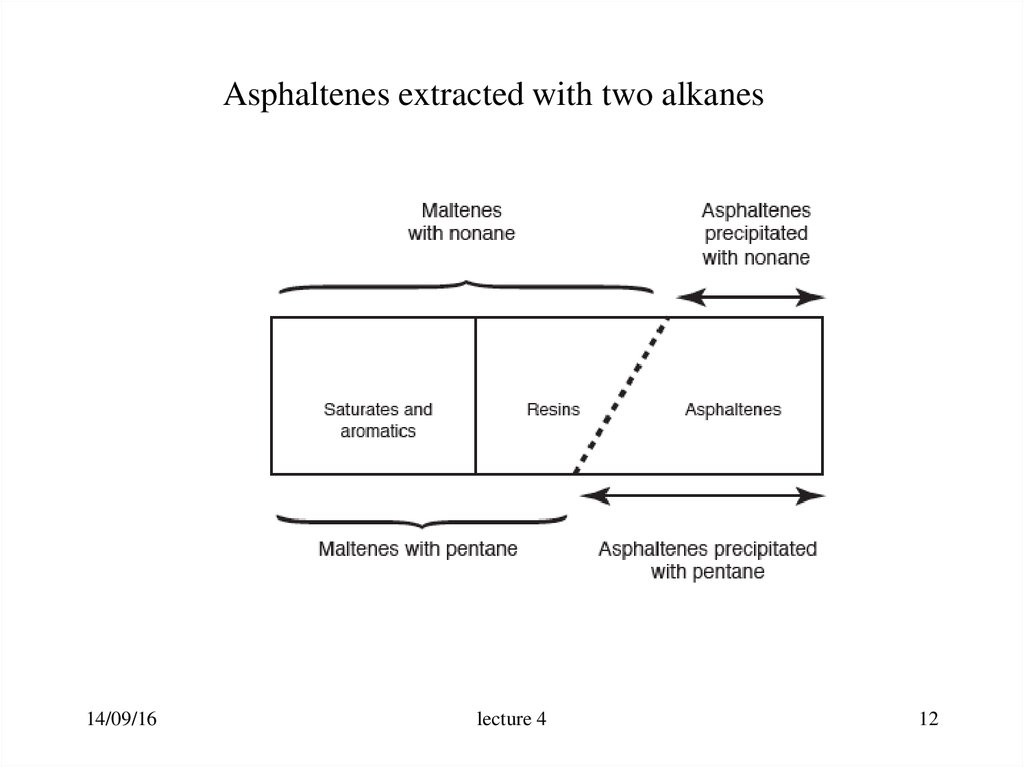
12.
Asphaltenes extracted with two alkanes14/09/16
lecture 4
12
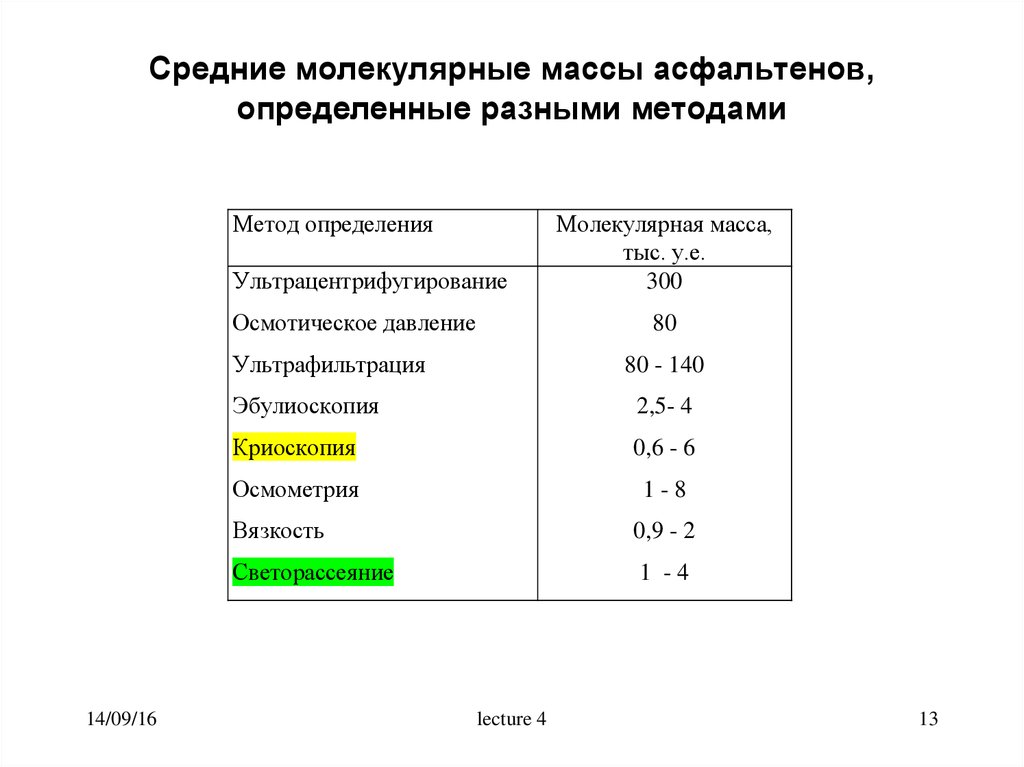
13.
Средние молекулярные массы асфальтенов,определенные разными методами
Метод определения
Ультрацентрифугирование
Осмотическое давление
80
Ультрафильтрация
14/09/16
Молекулярная масса,
тыс. у.е.
300
80 - 140
Эбулиоскопия
2,5- 4
Криоскопия
0,6 - 6
Осмометрия
1-8
Вязкость
0,9 - 2
Светорассеяние
1 -4
lecture 4
13
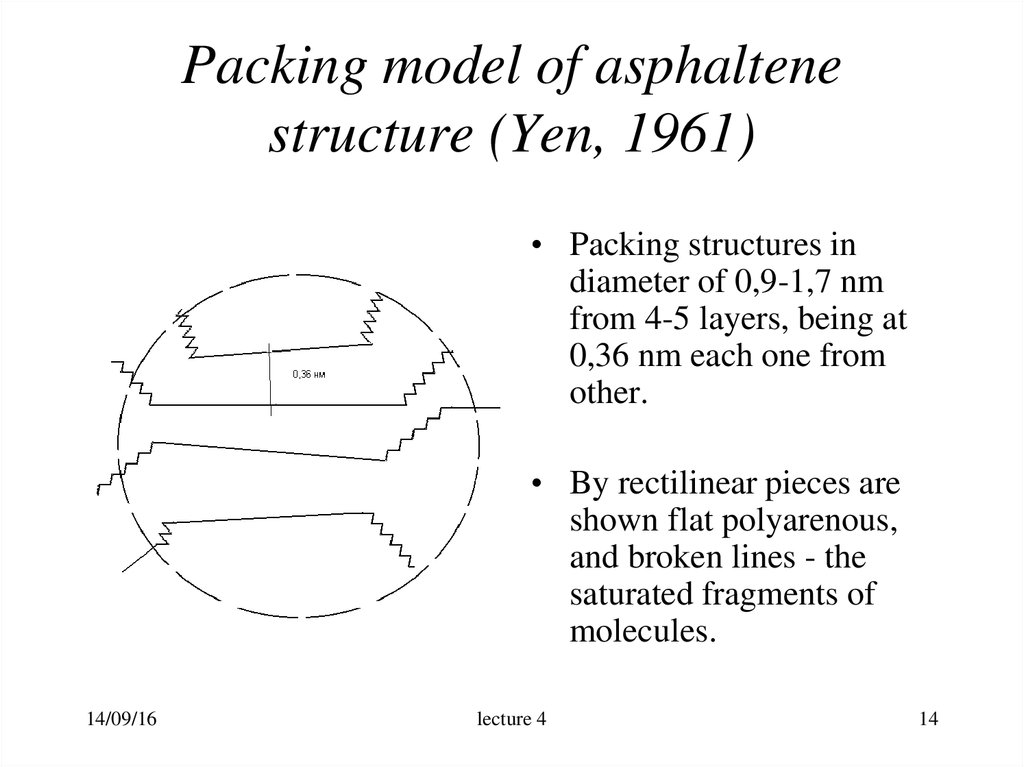
14. Packing model of asphaltene structure (Yen, 1961)
• Packing structures indiameter of 0,9-1,7 nm
from 4-5 layers, being at
0,36 nm each one from
other.
• By rectilinear pieces are
shown flat polyarenous,
and broken lines - the
saturated fragments of
molecules.
14/09/16
lecture 4
14
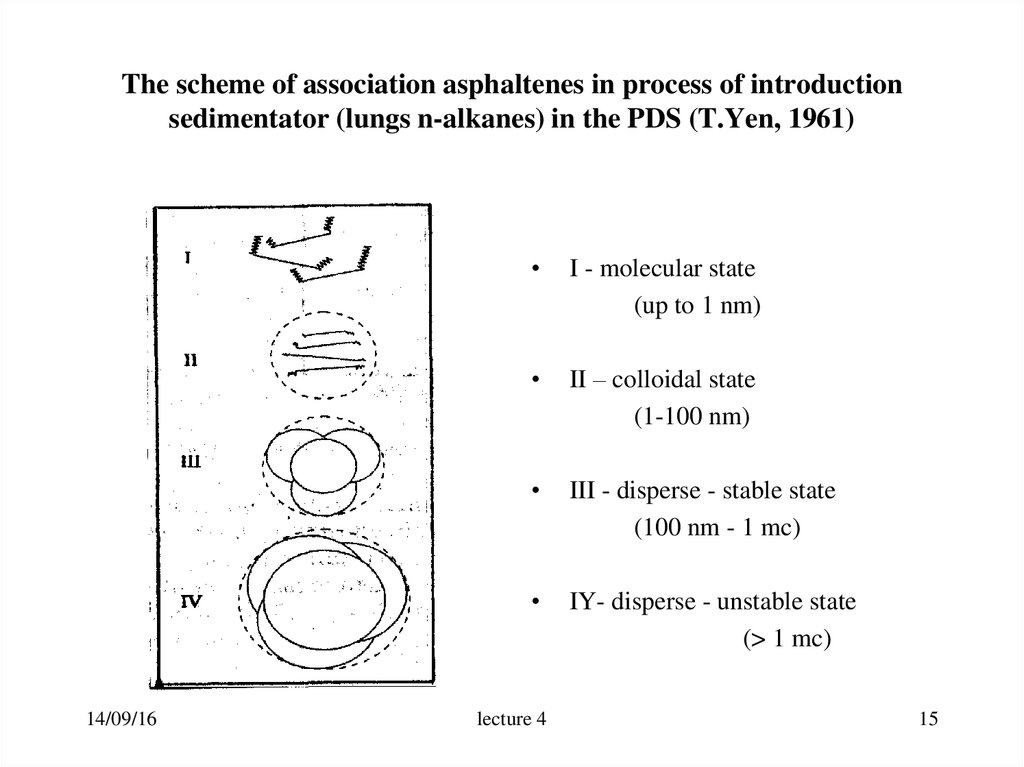
15. The scheme of association asphaltenes in process of introduction sedimentator (lungs n-alkanes) in the PDS (T.Yen, 1961)
14/09/16I - molecular state
(up to 1 nm)
II – colloidal state
(1-100 nm)
III - disperse - stable state
(100 nm - 1 mc)
IY- disperse - unstable state
(> 1 mc)
lecture 4
15
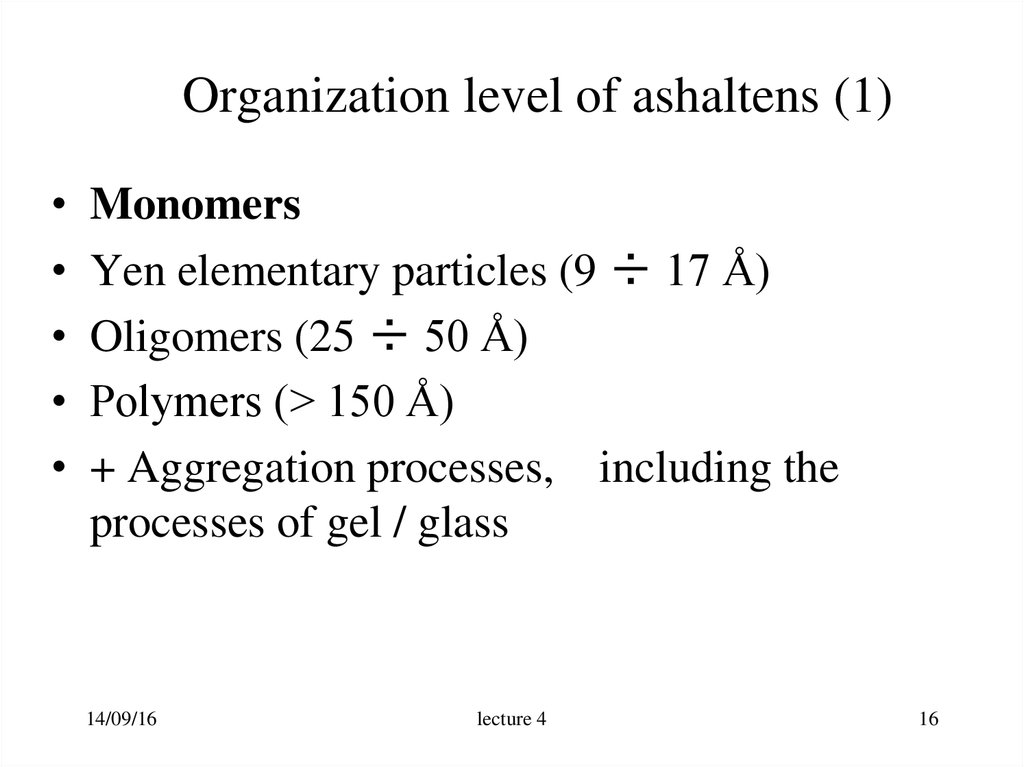
16. Organization level of ashaltens (1)
Monomers
Yen elementary particles (9 ÷ 17 Å)
Oligomers (25 ÷ 50 Å)
Polymers (> 150 Å)
+ Aggregation processes, including the
processes of gel / glass
14/09/16
lecture 4
16
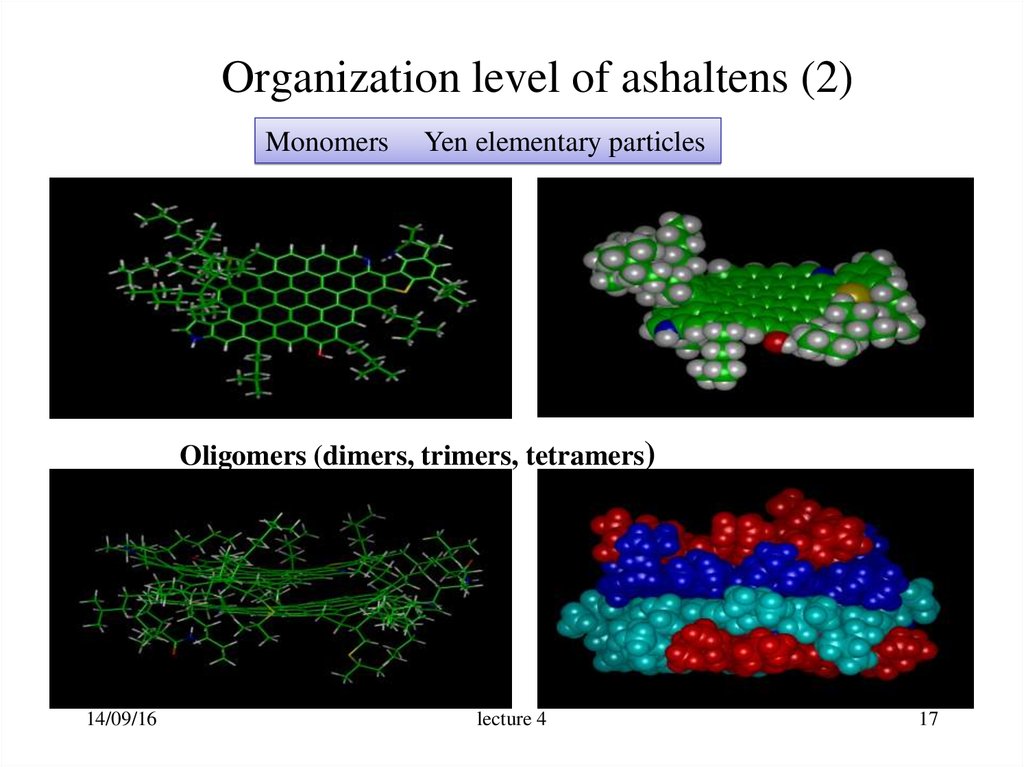
17. Organization level of ashaltens (2)
MonomersYen elementary particles
Oligomers (dimers, trimers, tetramers)
14/09/16
lecture 4
17
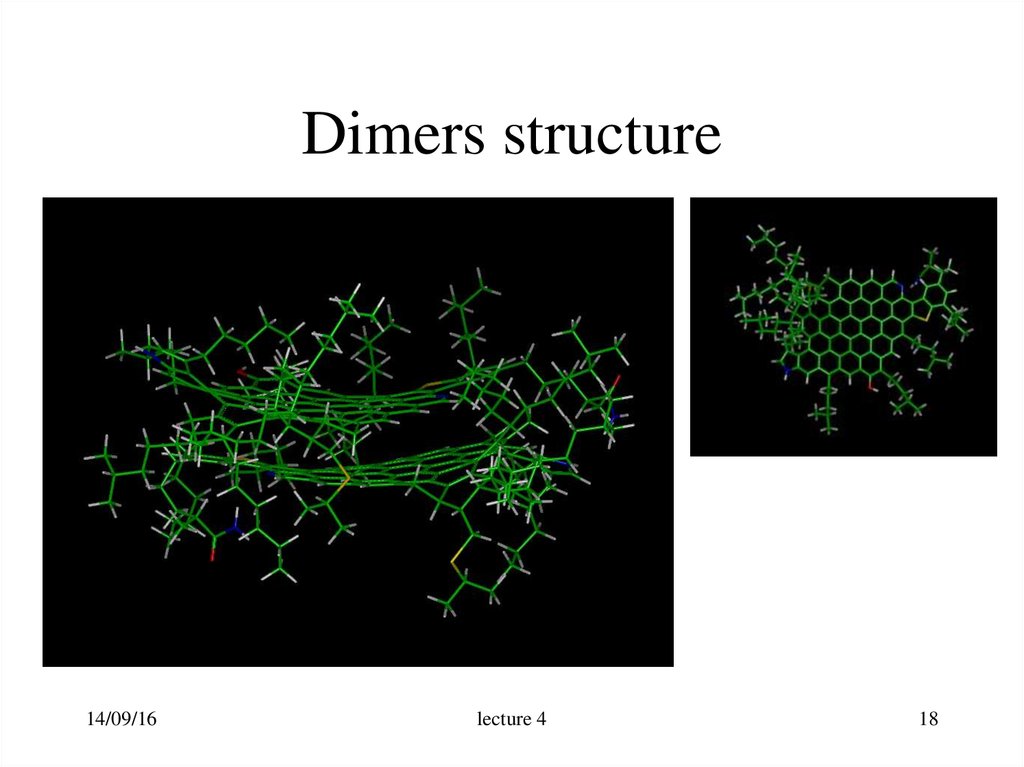
18. Dimers structure
14/09/16lecture 4
18
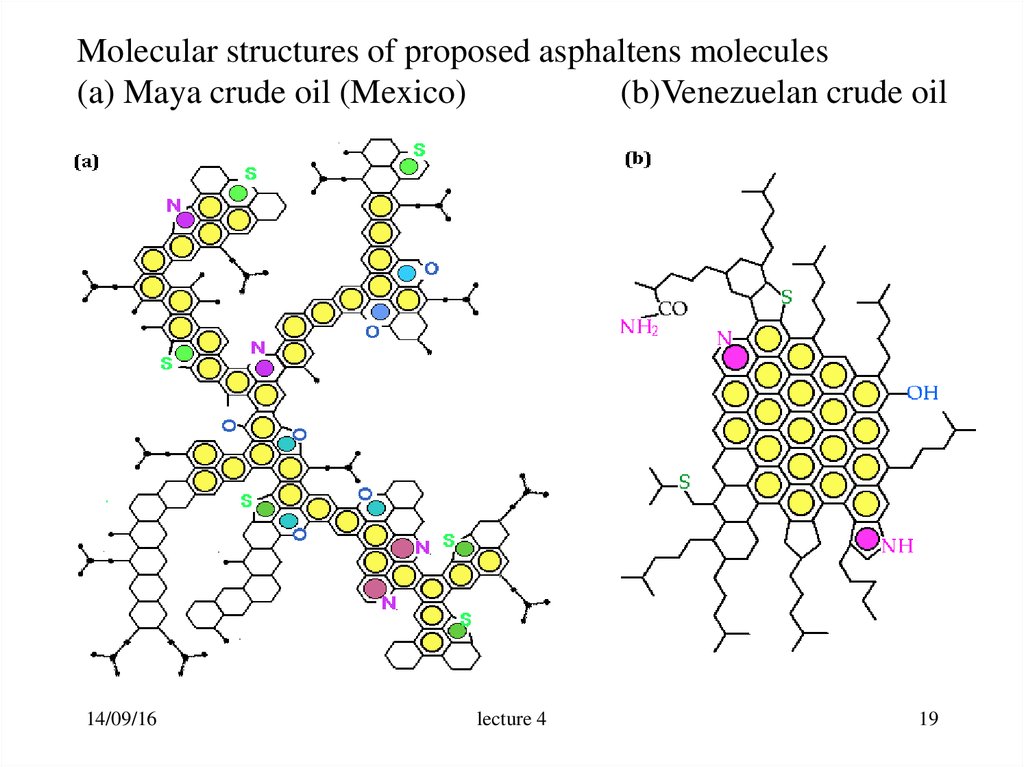
19.
Molecular structures of proposed asphaltens molecules(a) Maya crude oil (Mexico)
(b)Venezuelan crude oil
14/09/16
lecture 4
19
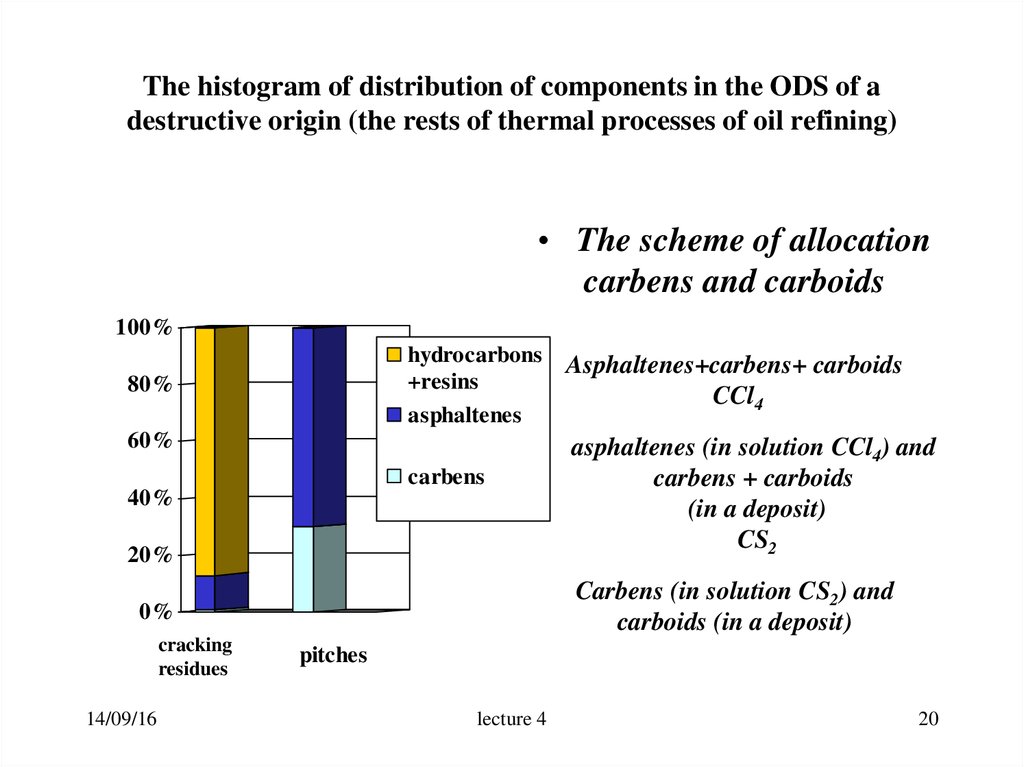
20. The histogram of distribution of components in the ODS of a destructive origin (the rests of thermal processes of oil refining)
• The scheme of allocationcarbens and carboids
100%
hydrocarbons
+resins
asphaltenes
80%
60%
carbens
40%
20%
14/09/16
asphaltenes (in solution CCl4) and
carbens + carboids
(in a deposit)
CS2
Carbens (in solution CS2) and
carboids (in a deposit)
0%
cracking
residues
Asphaltenes+carbens+ carboids
CCl4
pitches
lecture 4
20
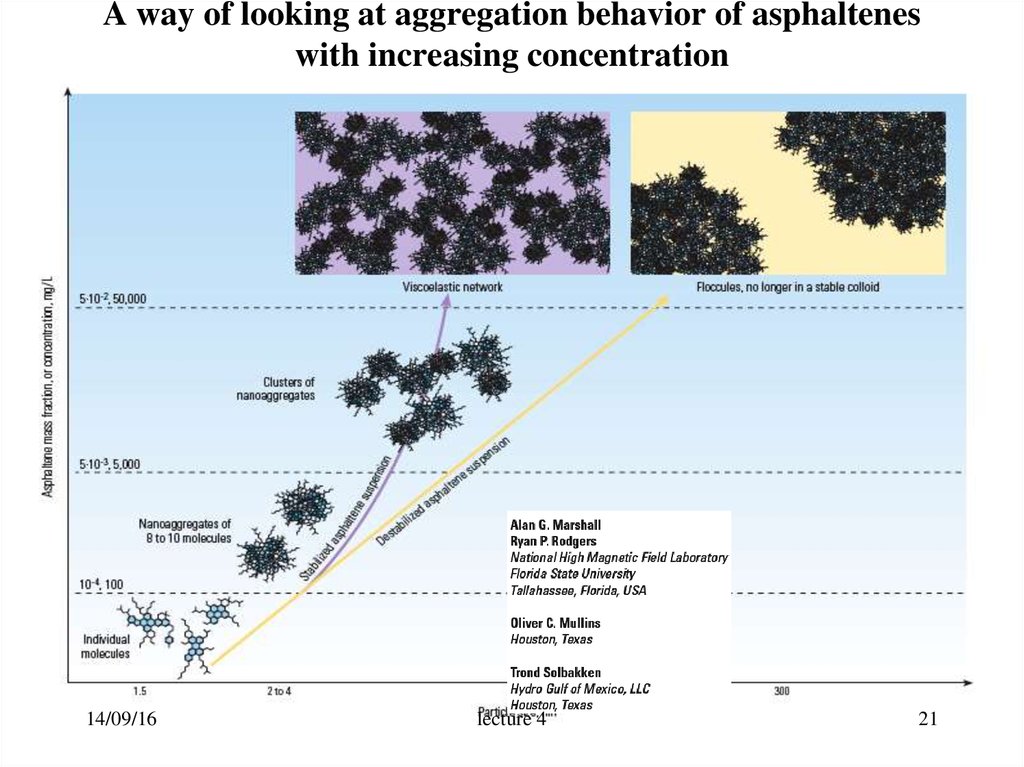
21. A way of looking at aggregation behavior of asphaltenes with increasing concentration
14/09/16lecture 4
21
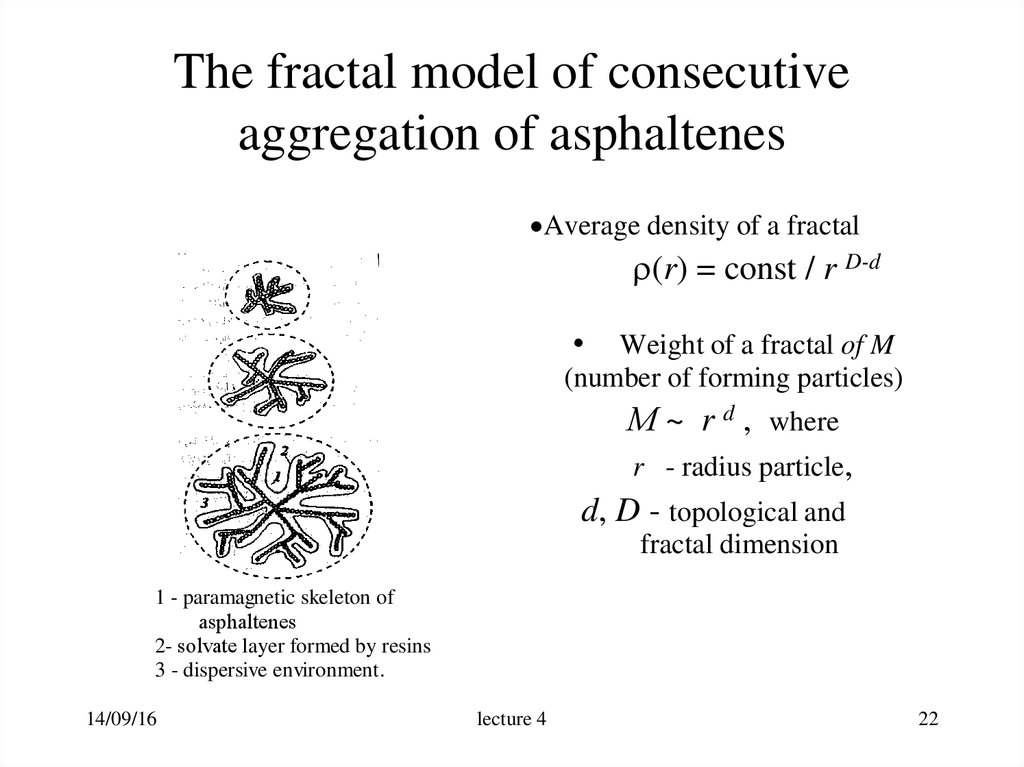
22. The fractal model of consecutive aggregation of asphaltenes
Average density of a fractal(r) = const / r D-d
• Weight of a fractal of M
(number of forming particles)
М ~ r d , where
r - radius particle,
d, D - topological and
fractal dimension
1 - paramagnetic skeleton of
asphaltenes
2- solvate layer formed by resins
3 - dispersive environment.
14/09/16
lecture 4
22



 industry
industry








