Similar presentations:
Lipid metabolism
1. LIPID METABOLISM
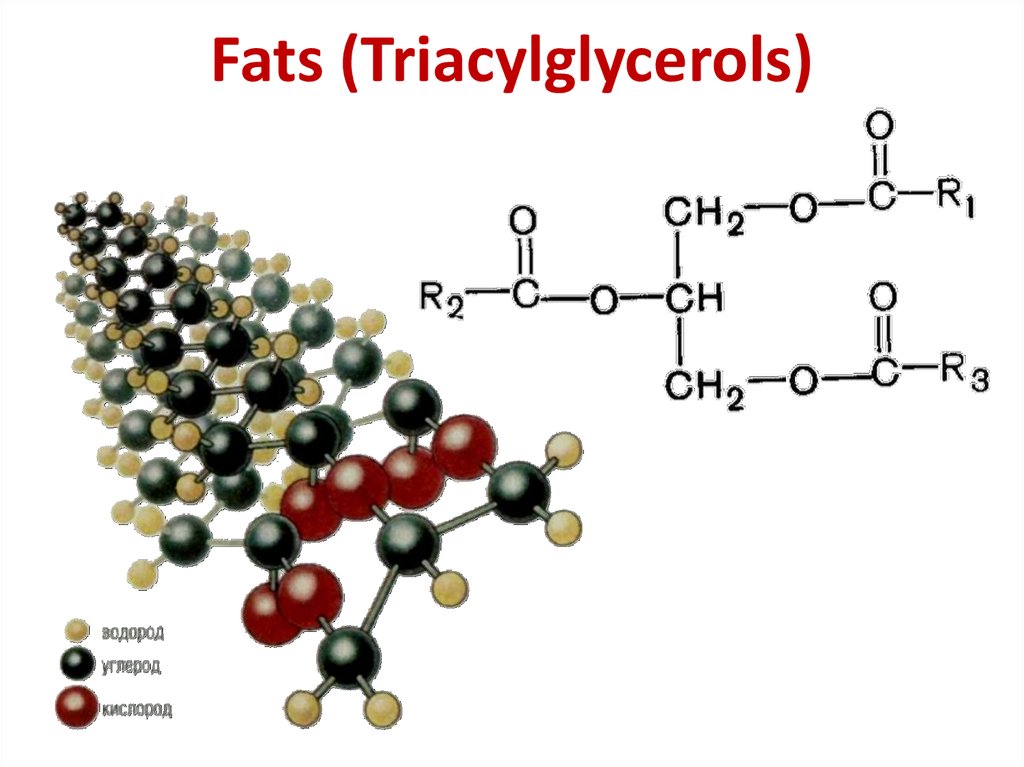
2. Fats (Triacylglycerols)
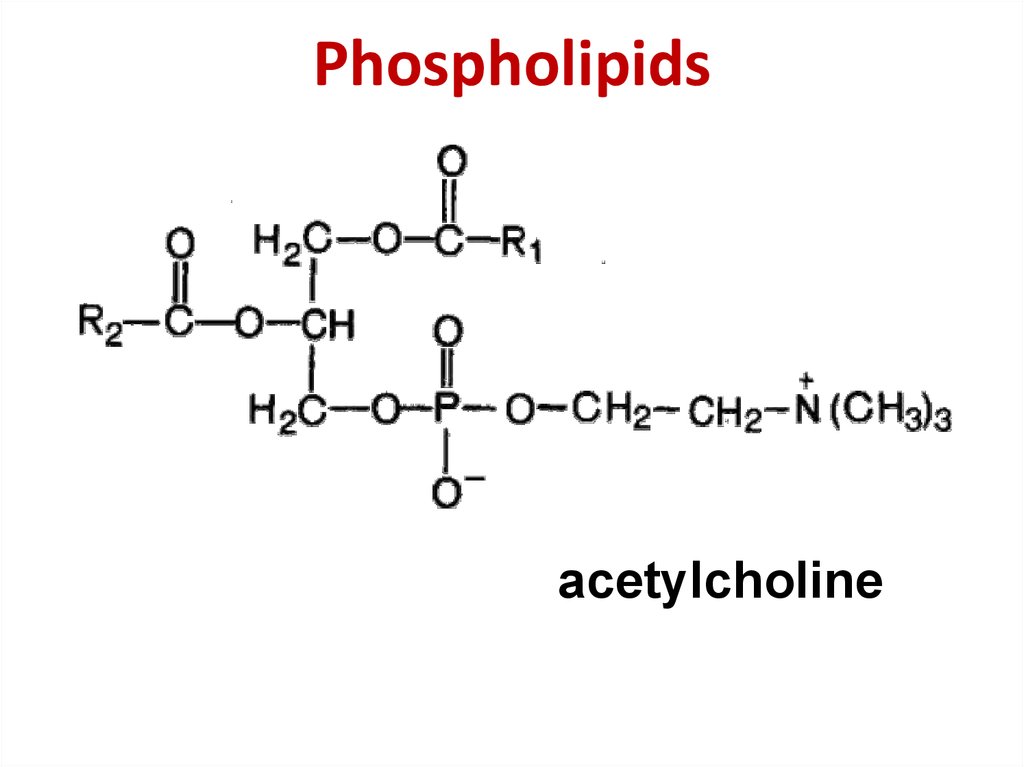
3. Phospholipids
acetylcholine4. Sphingophospholipids
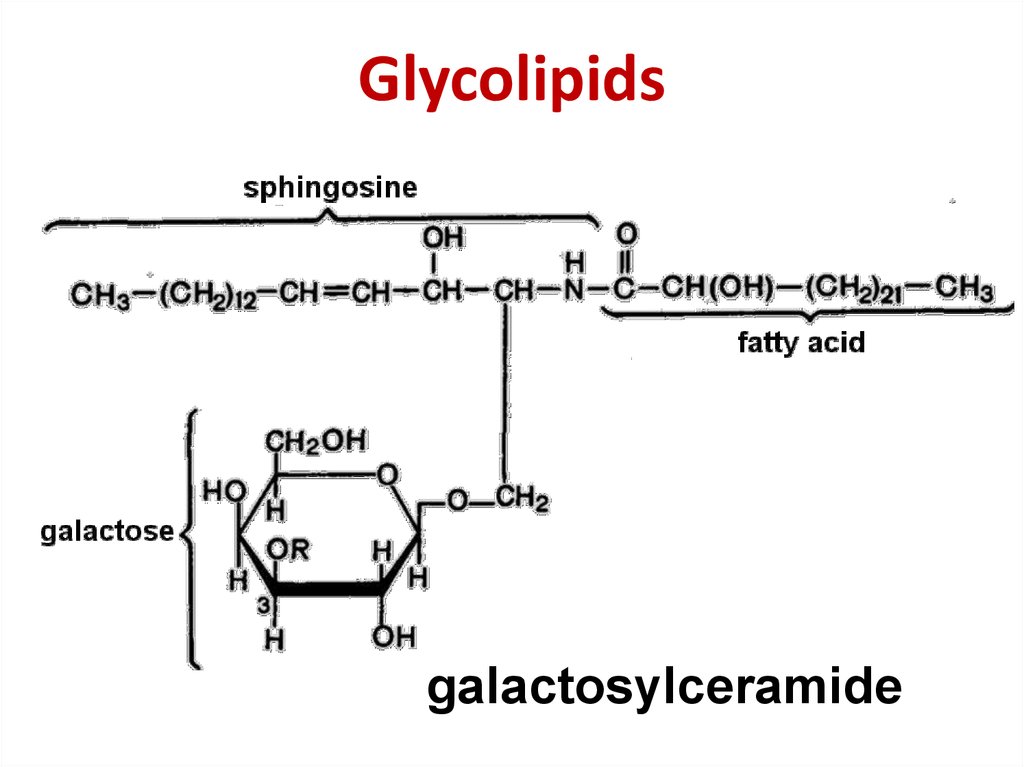
sphingomyelin5. Glycolipids
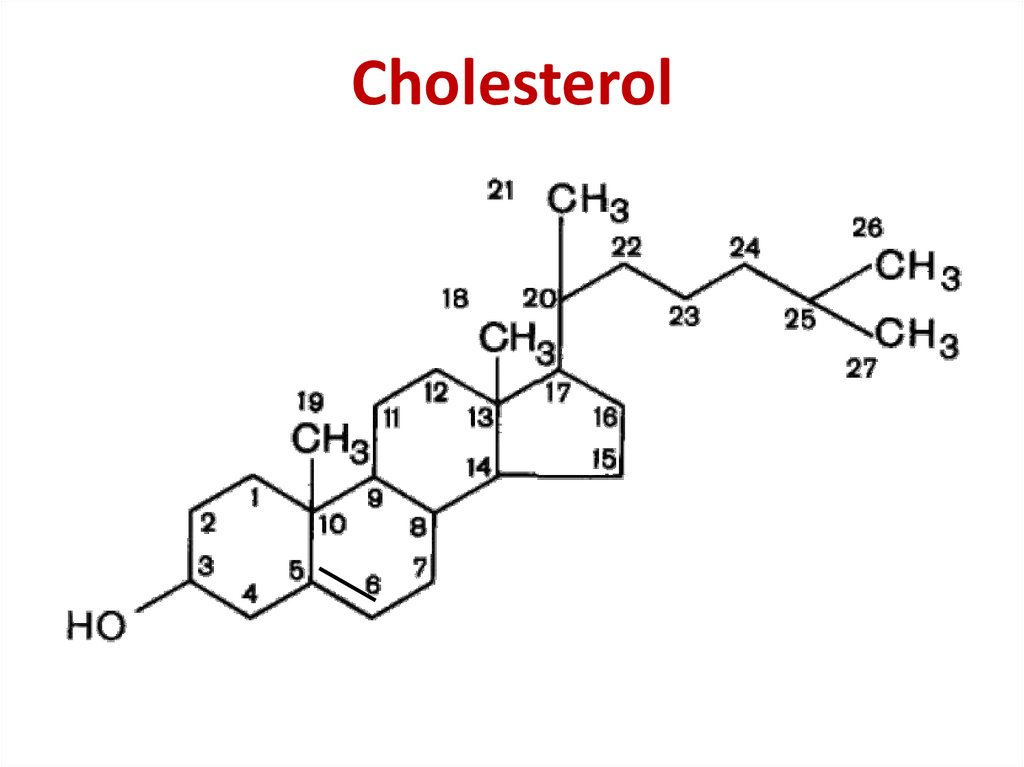
galactosylceramide6. Cholesterol
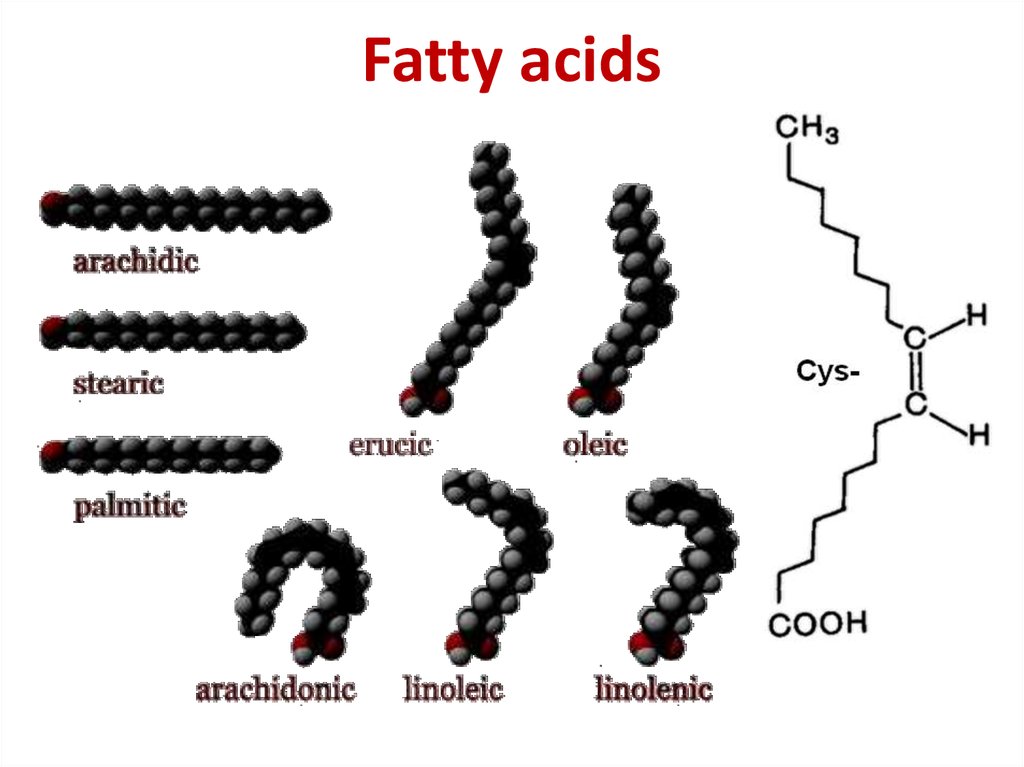
7. Fatty acids
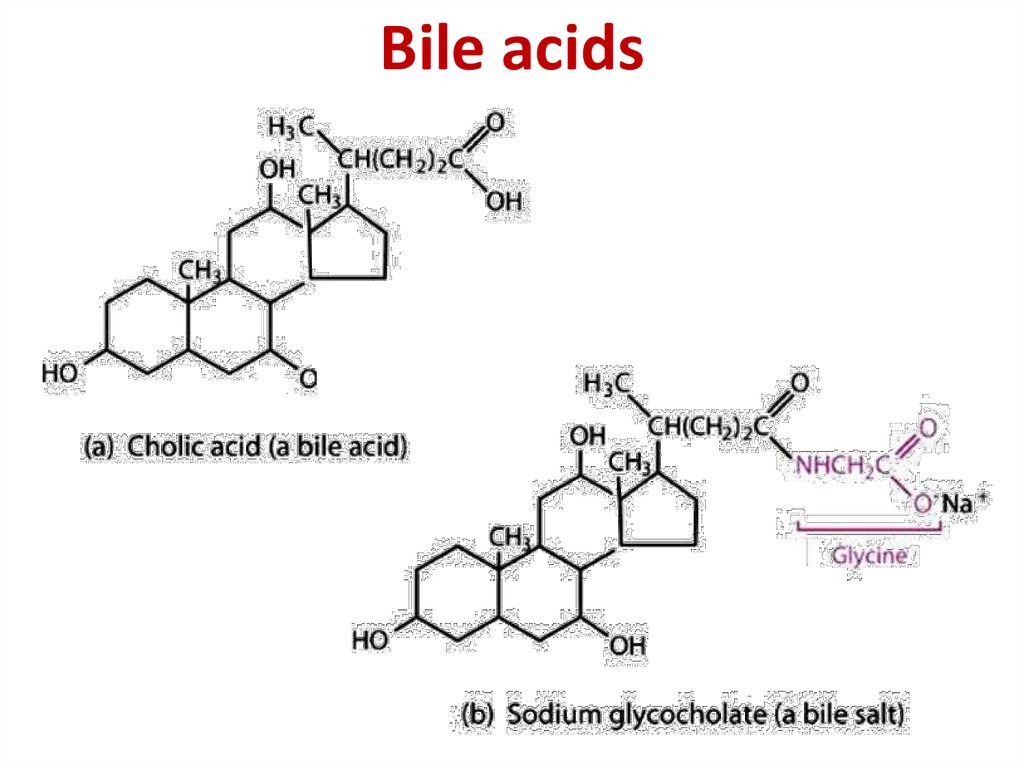
8. Bile acids
9. Lipid functions
Storage form of energy
Supply essential fatty acids
Structural components of cell membranes
Electrical insulation
Protect body from cold
Mechanical protection of internal organs
Metabolic regulators (hormones)
Help transport fat soluble vitamins
10. Human pancreatic lipase (activation by colipase)
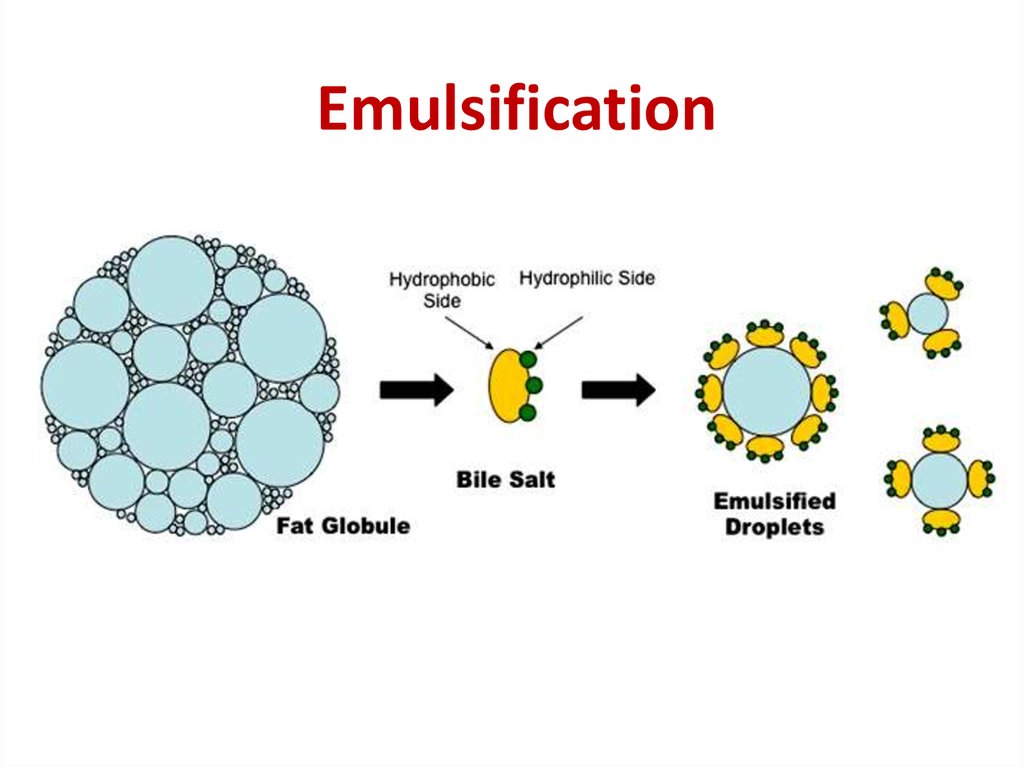
Colipase is colored in blue11. Emulsification
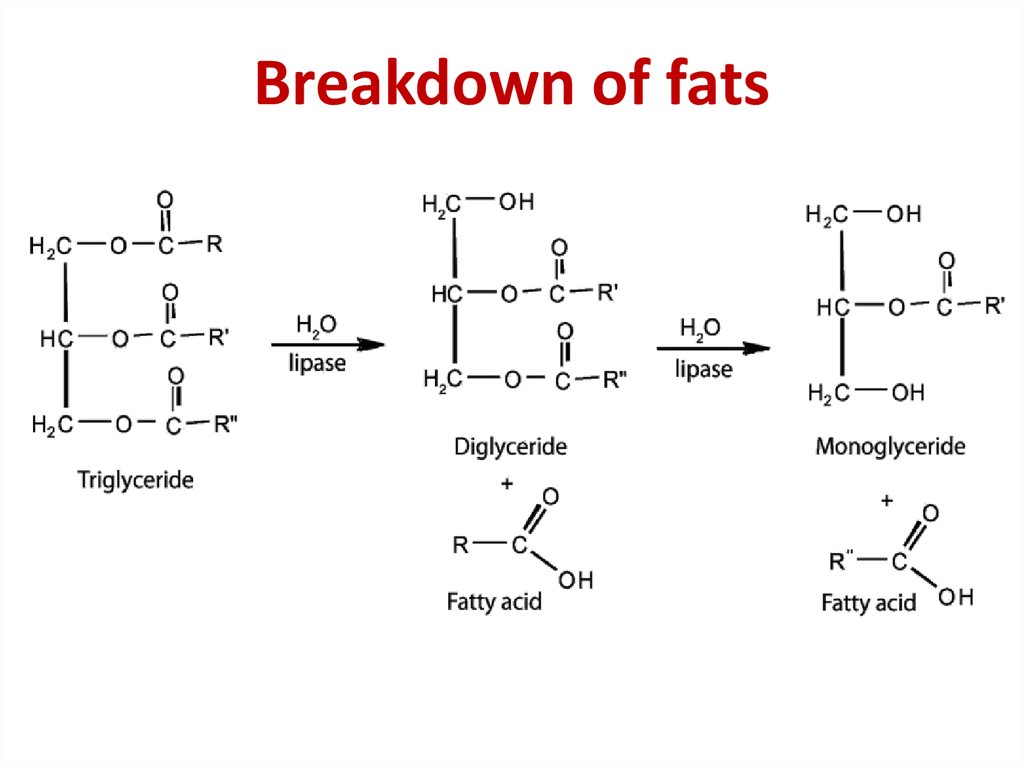
12. Breakdown of fats
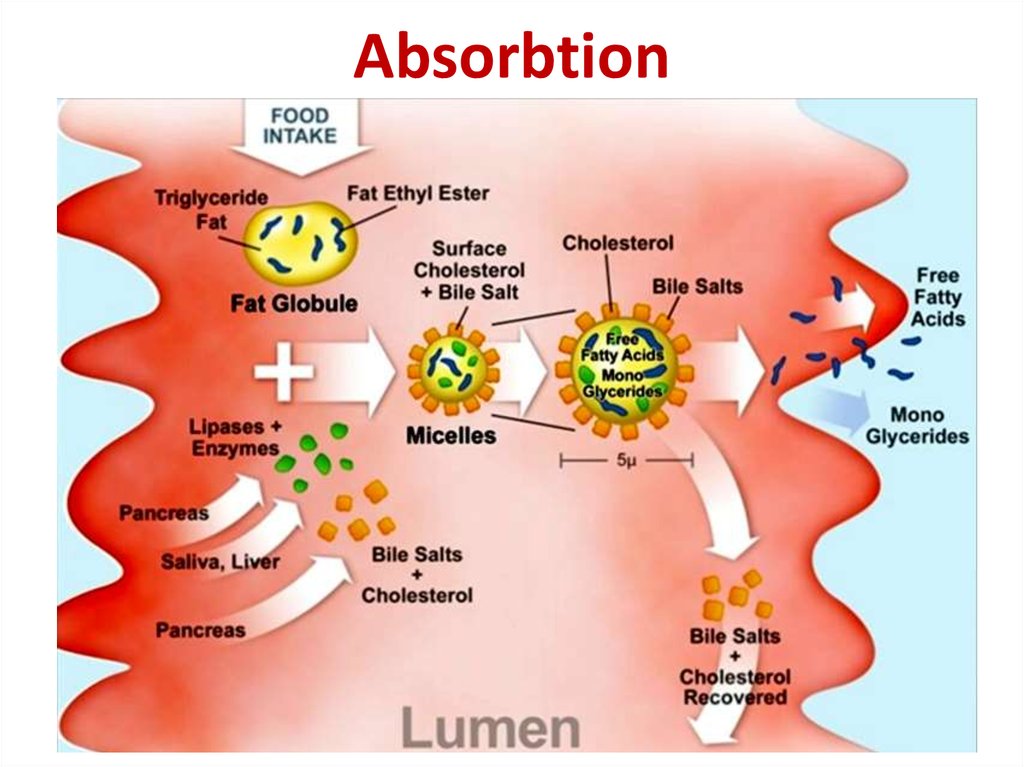
13. Absorbtion
14.
SteatorrheaIncreased
excretion of
neutral fat
Increased
excretion of fatty
acids
Pancreatic
exocrine
insufficiency
Intestinal
pathology
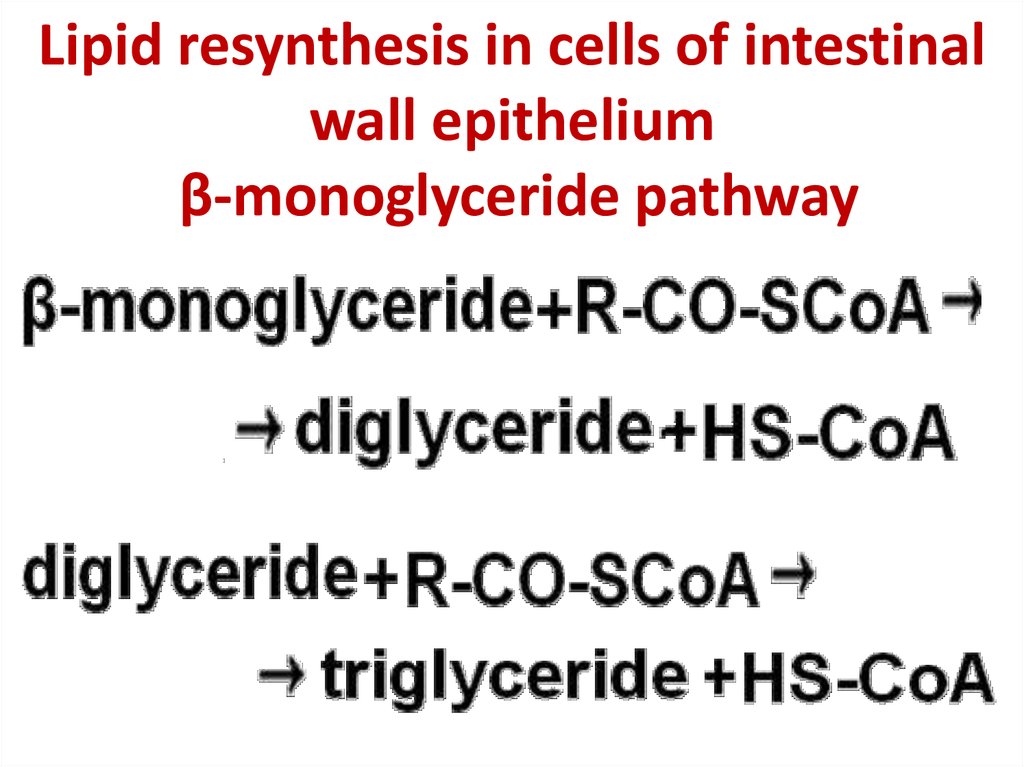
15. Lipid resynthesis in cells of intestinal wall epithelium β-monoglyceride pathway
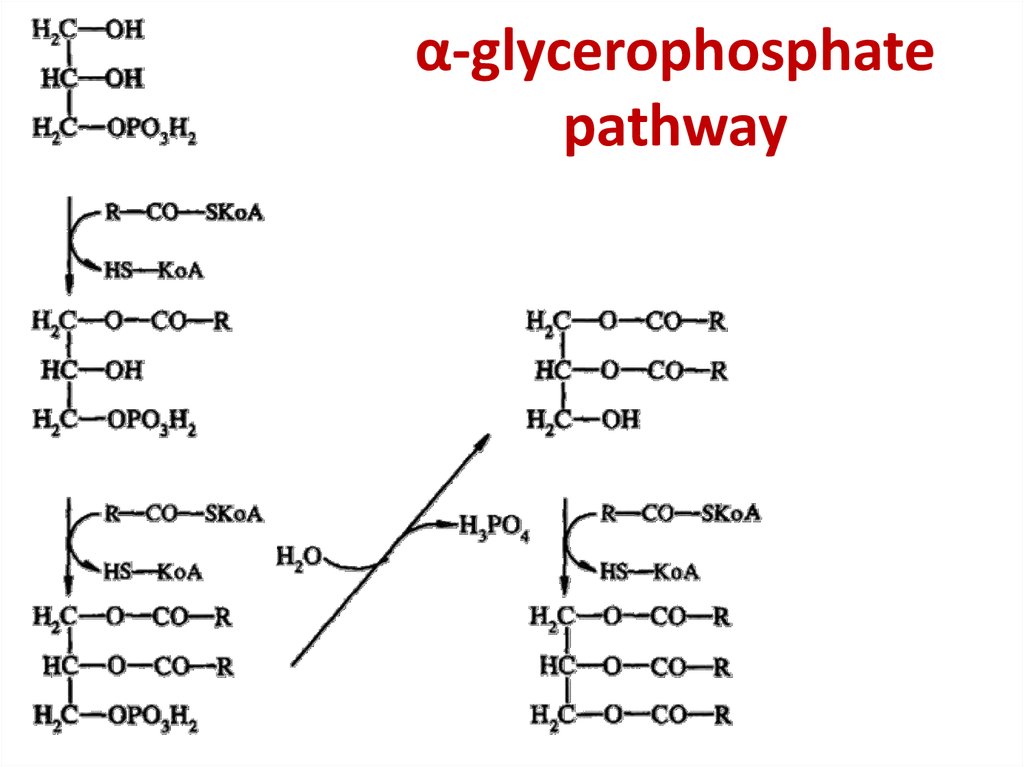
16. α-glycerophosphate pathway
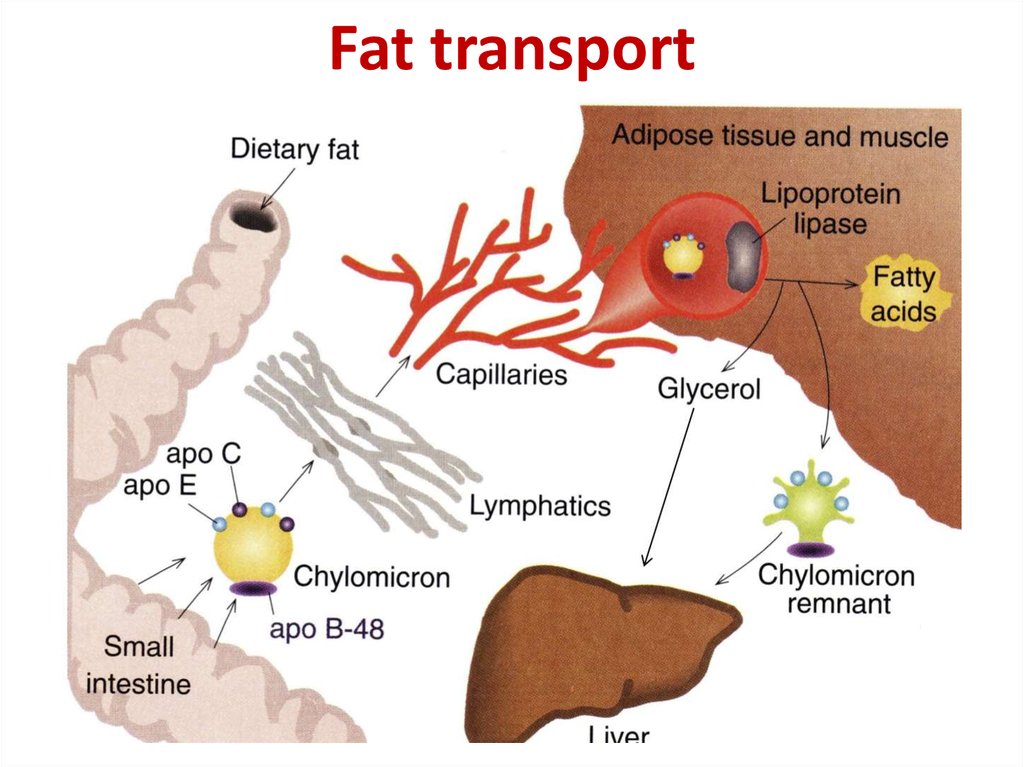
17. Formation of chylomicrons
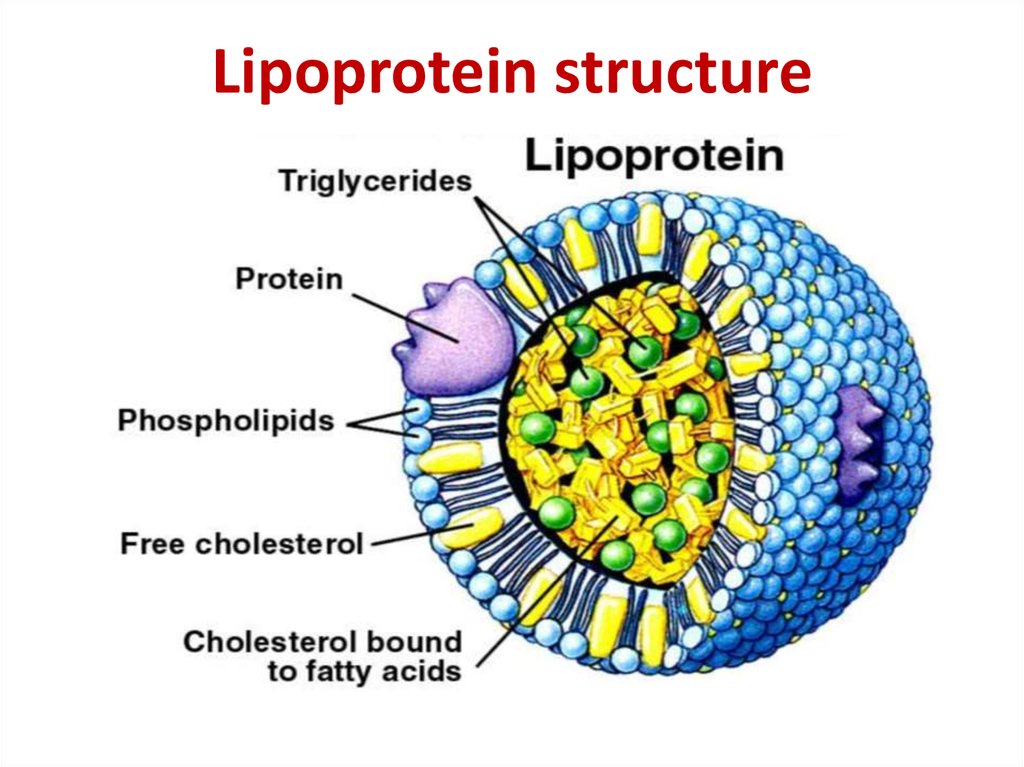
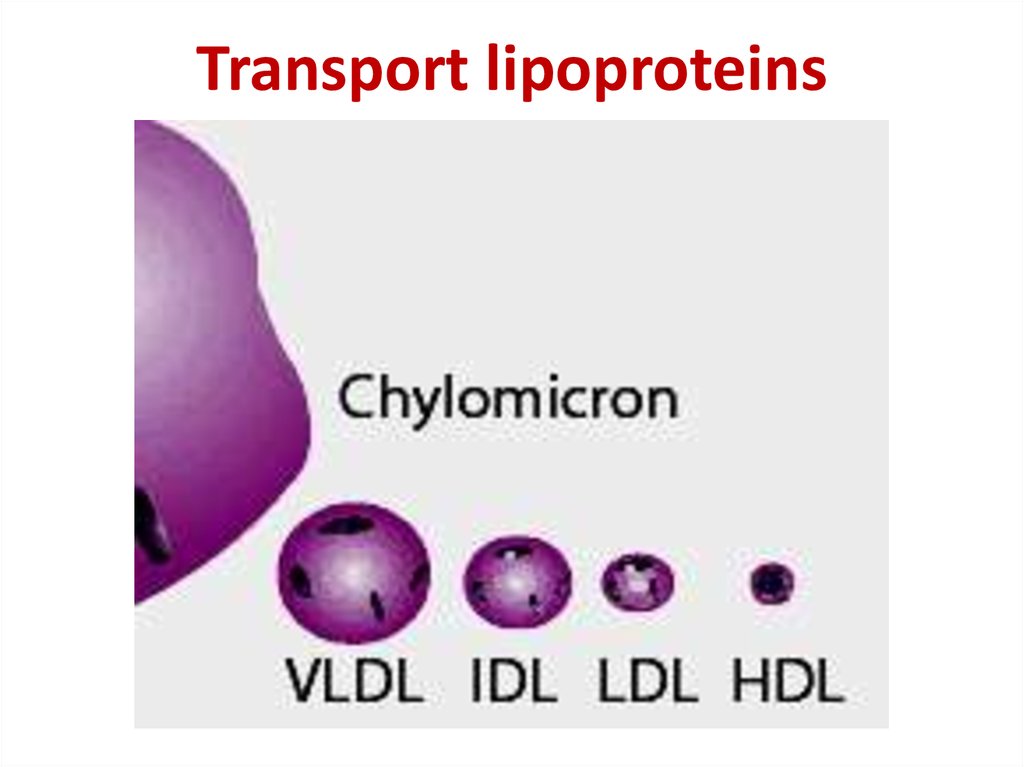
18. Lipoprotein structure
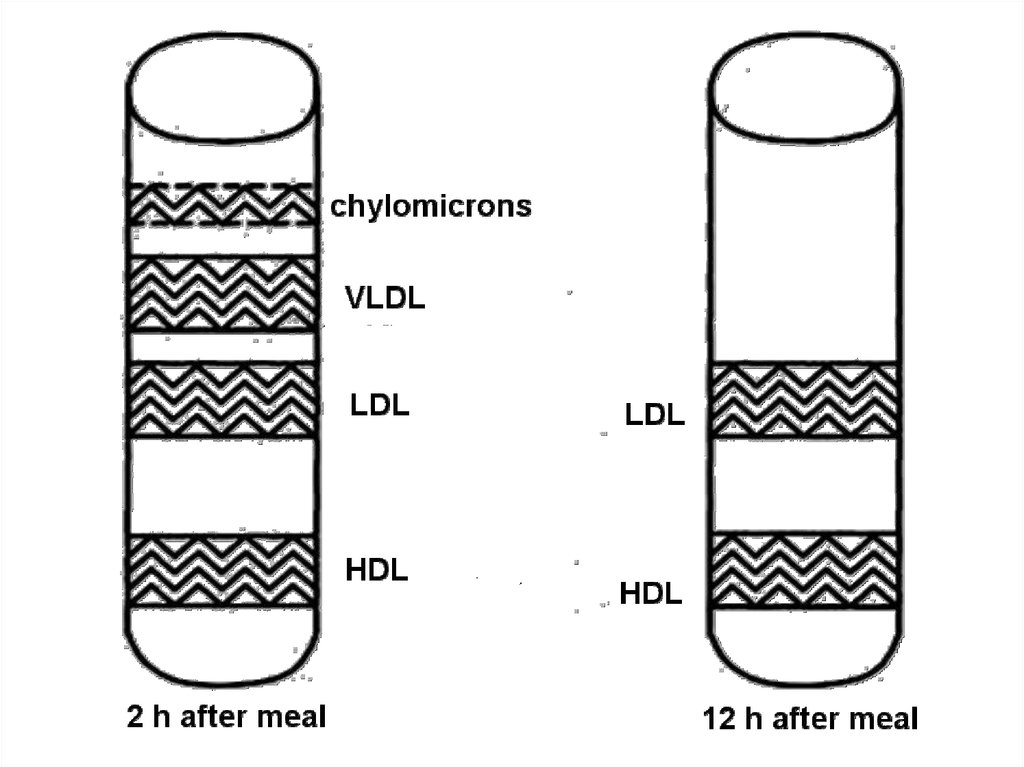
19. Transport lipoproteins
20. Fat transport
21. Artery section
RBCChylomicron
22.
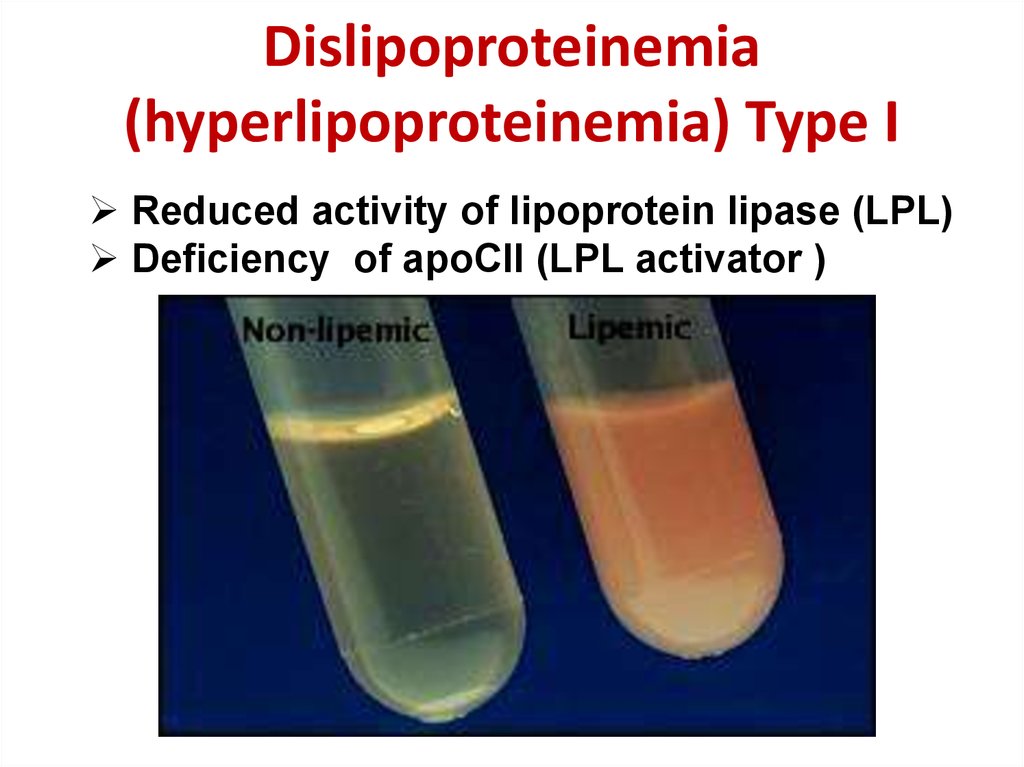
23. Dislipoproteinemia (hyperlipoproteinemia) Type I
Reduced activity of lipoprotein lipase (LPL)Deficiency of apoCII (LPL activator )
24. Tissue lipase activation
adipocyteProteinkinase
inactive
АТP
cАМP
Proteinkinase
active
ТАG-lipase
inactive
ТАG
ТАG-lipase
active
Tissue lipase
activation
Glucagon
Adrenalin
blood
Glycerol
Glycerol
Fatty
acids
Fatty
acids
Oxidation
in tissues
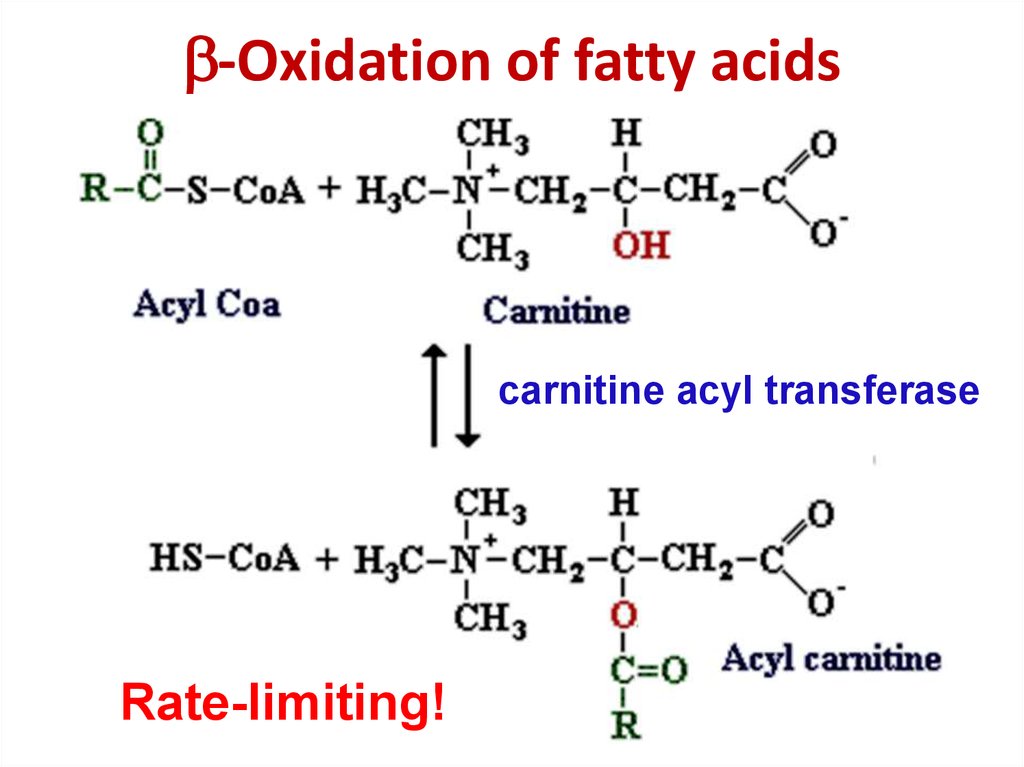
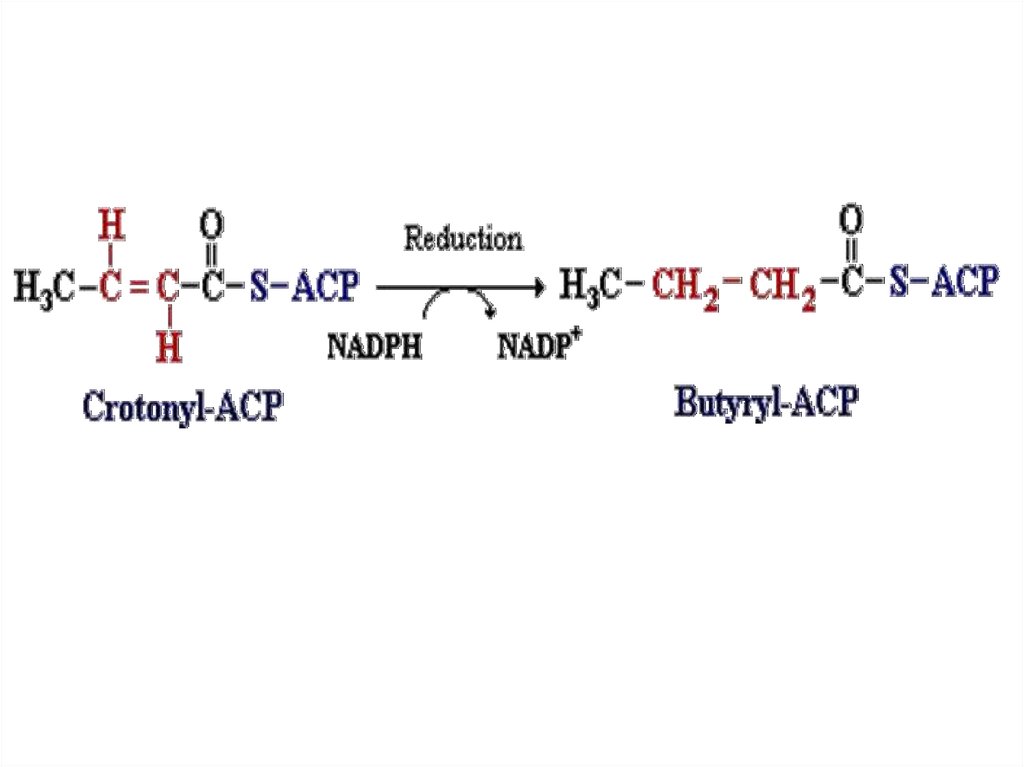
25. -Oxidation of fatty acids
-Oxidation of fatty acidscarnitine acyl transferase
Rate-limiting!
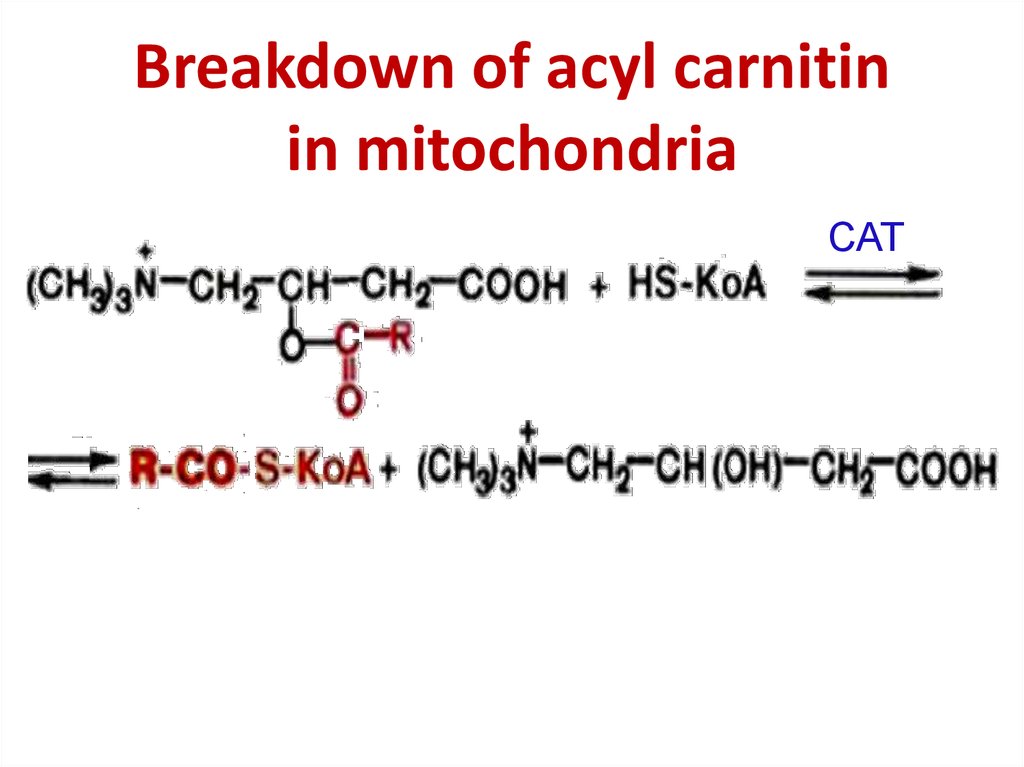
26. Breakdown of acyl carnitin in mitochondria
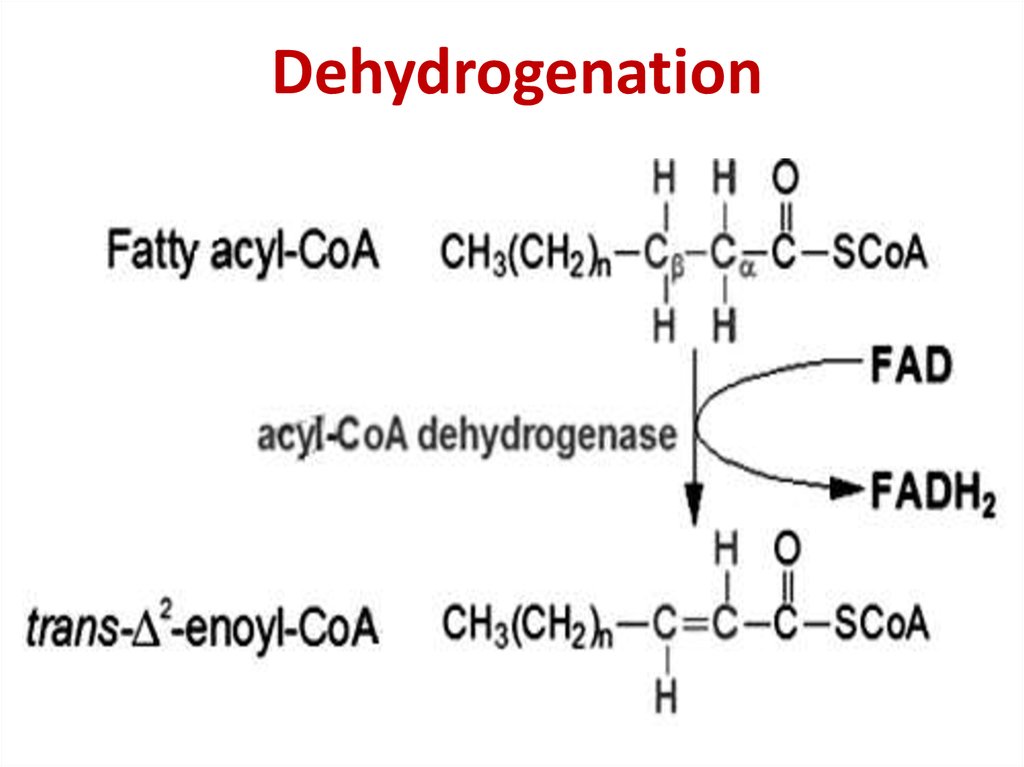
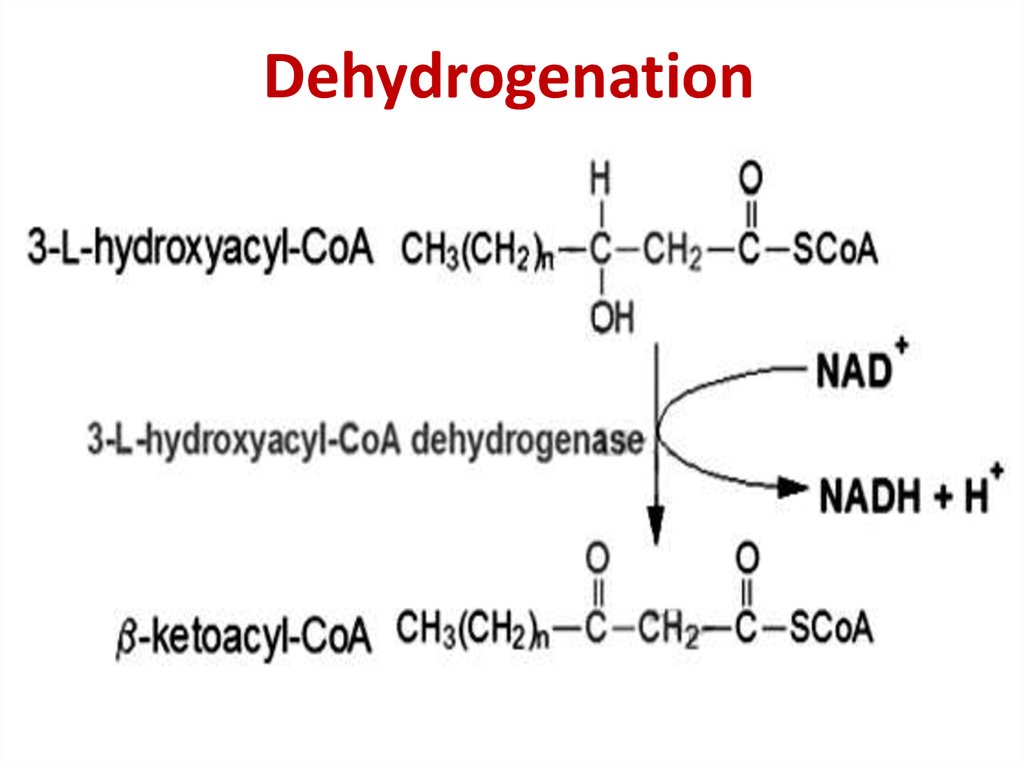
CAT27. Dehydrogenation
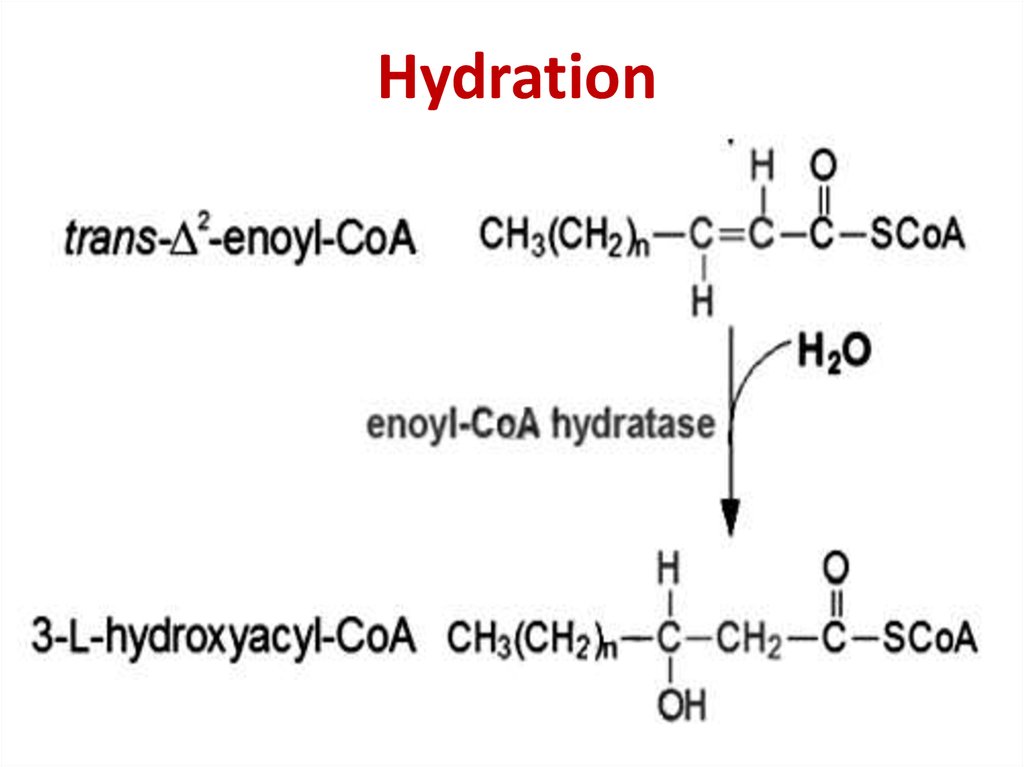
28. Hydration
29. Dehydrogenation
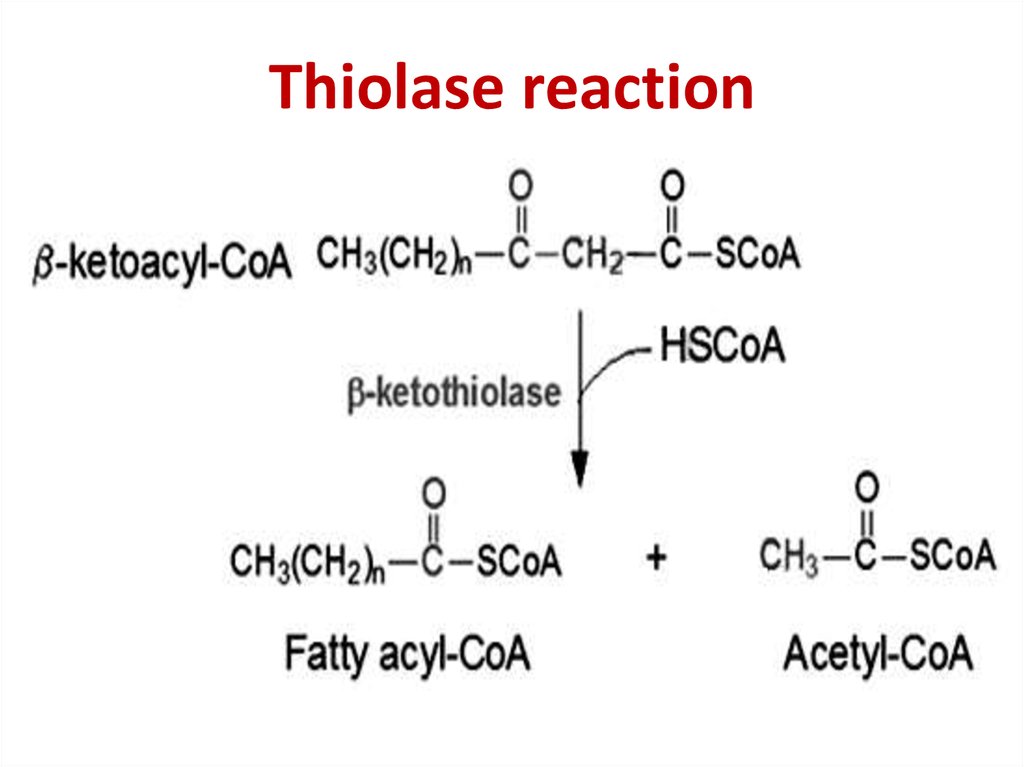
30. Thiolase reaction
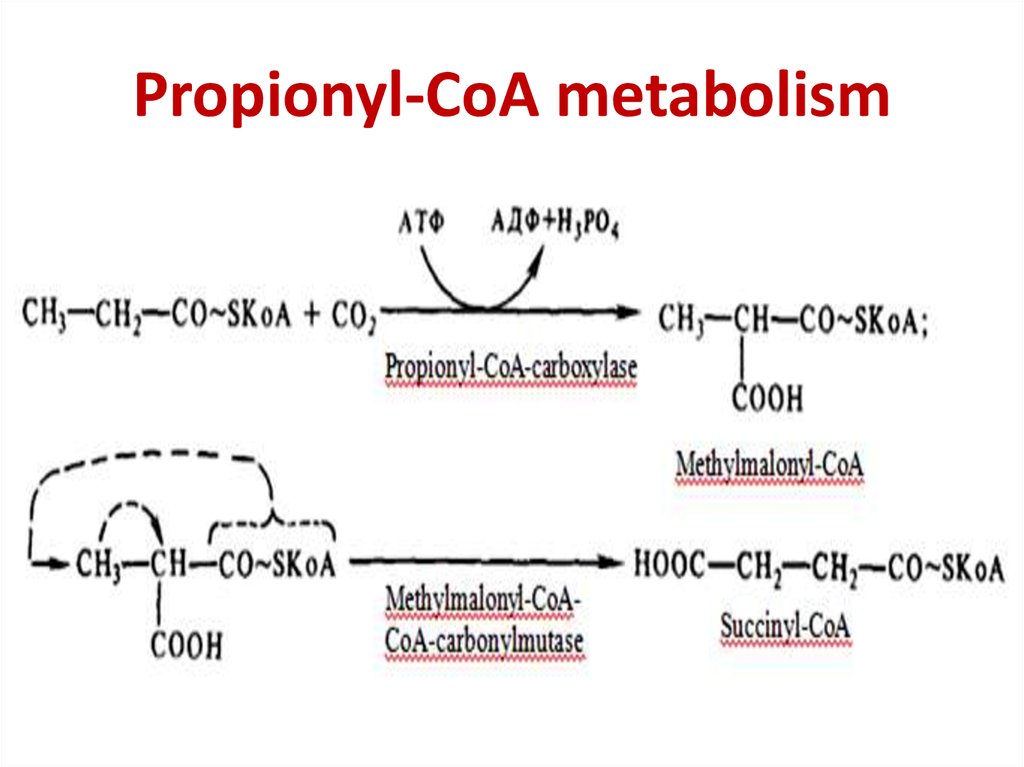
31. Propionyl-CoA metabolism
32. Oxidadion of unsaturated fatty acids
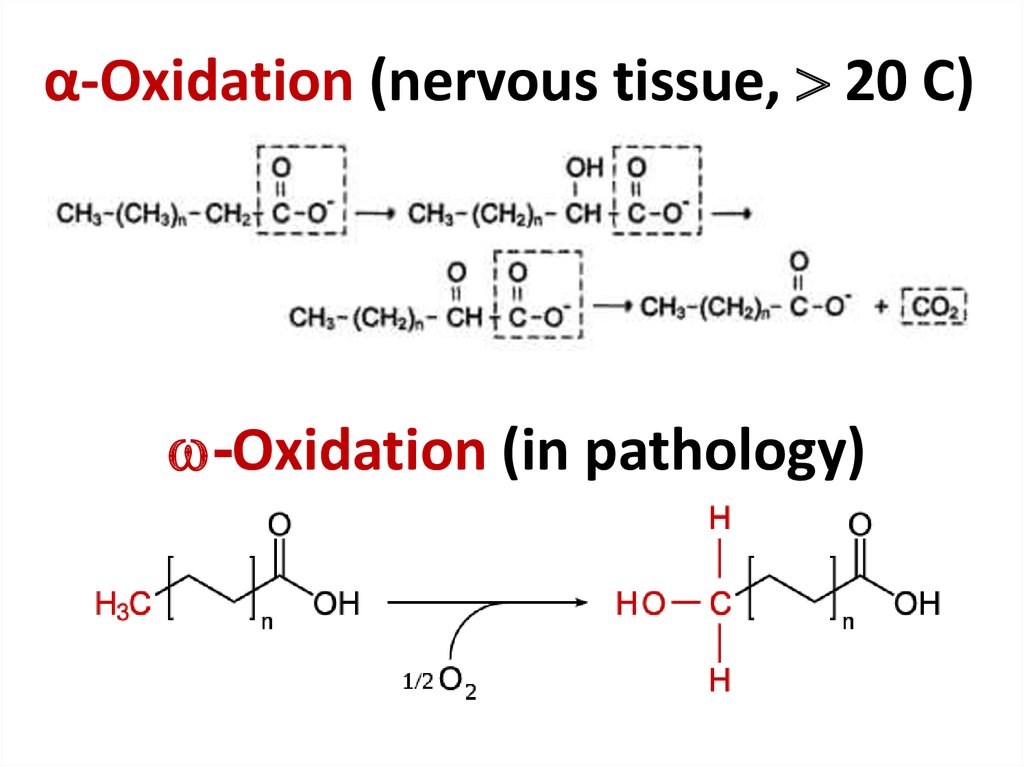
33. α-Oxidation (nervous tissue, 20 С)
α-Oxidation (nervous tissue, 20 С)-Oxidation (in pathology)
34. Violations of fatty acid oxidation
• Hereditary defects of carnitineacyl transferase I or enzymes of
carnitine synthesis
• Genetic defect of dehydrogenase
of fatty acids with medium chain
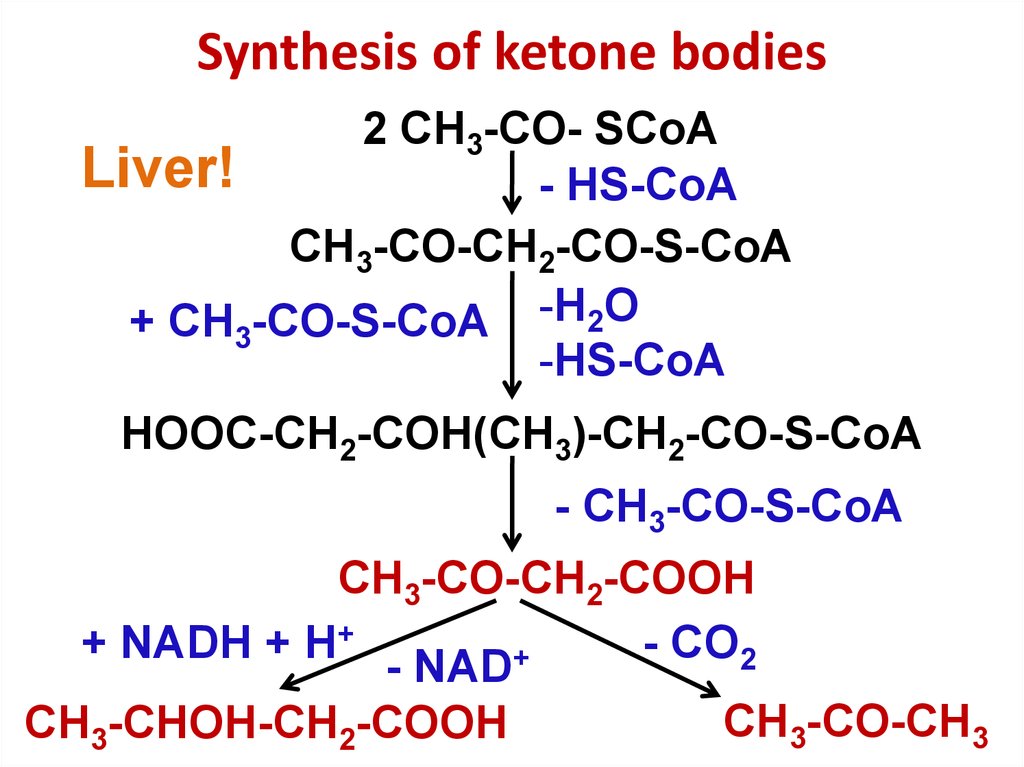
35. Synthesis of ketone bodies
Synthesis of ketone bodies2 CH3-CO- SCоА
Liver!
- HS-CоА
CH3-CO-CH2-CO-S-CоА
+ CH3-CO-S-CоА -Н2О
-HS-CоА
HOOC-CH2-COH(CH3)-CH2-CO-S-CоА
- CH3-CO-S-CоА
CH3-CO-CH2-COOH
+ NАDН + Н+
- CO2
+
- NАD
CH3-CO-CH3
CH3-CHOH-CH2-COOH
36.
Oxidation of ketone bodiesacetoacetate
succinyl-CoA
CoA-transferase
succinate
acetoacetyl-CoA
thiolase
Myocardium
Renal cortex
+ НS-КоА
2 acetyl-CoA
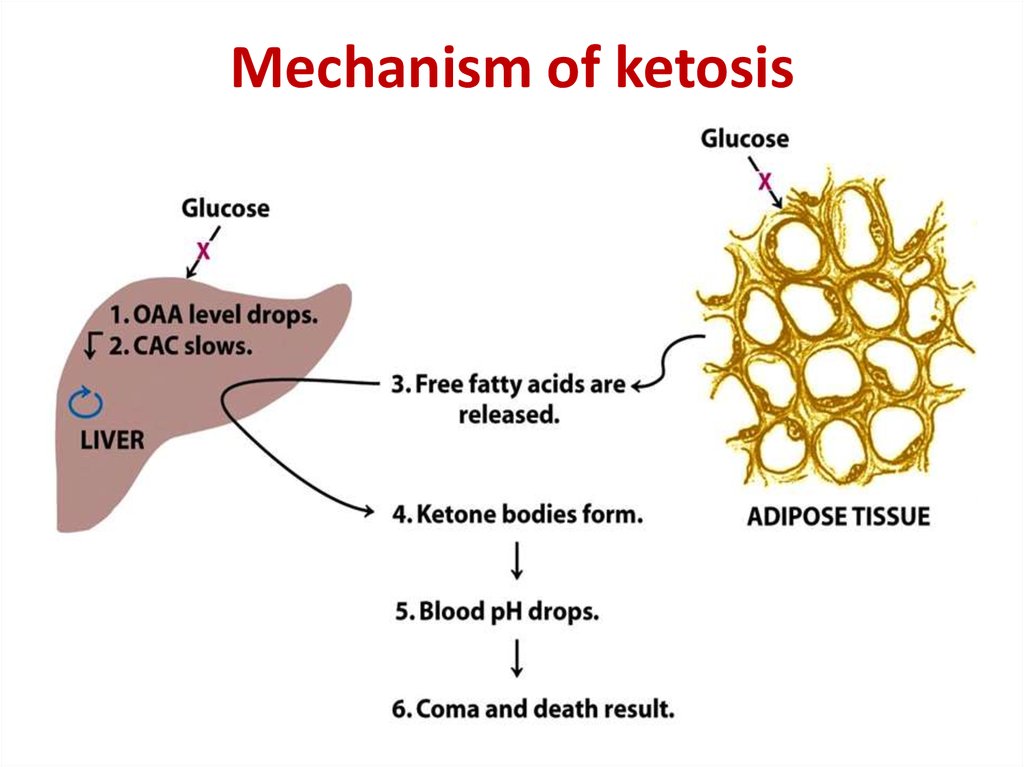
37. Mechanism of ketosis
38. Lipogenesis Acetyl-CoA transport
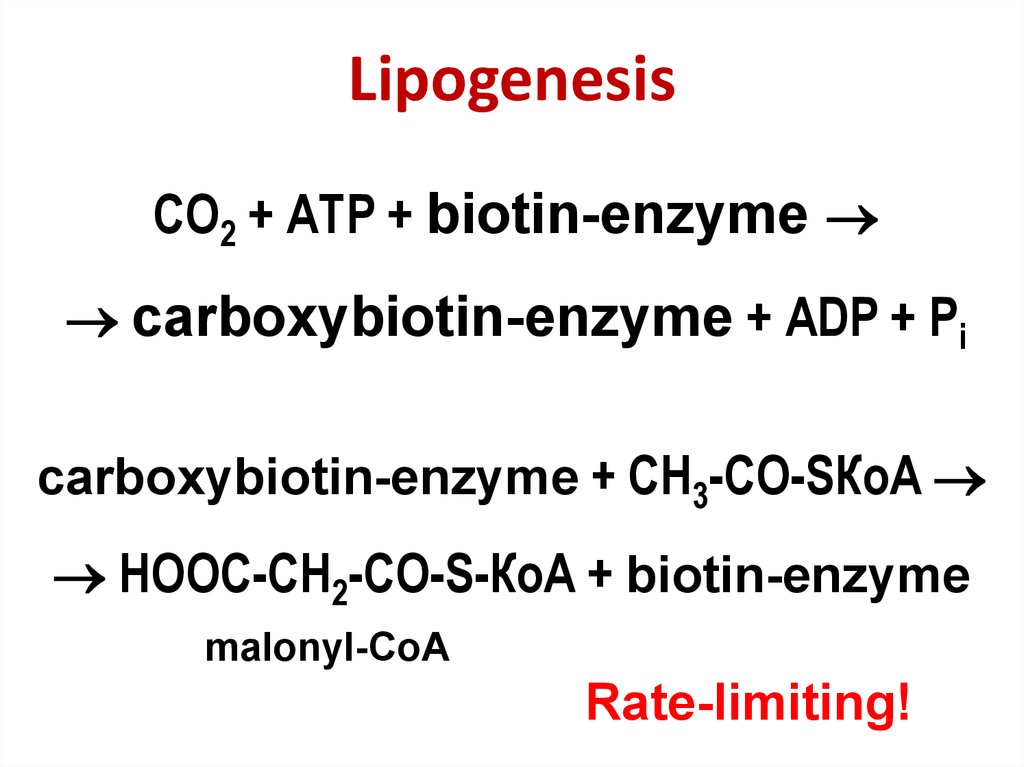
39. Lipogenesis
СО2 + АТP + biotin-enzymecarboxybiotin-enzyme + АDP + Pi
carboxybiotin-enzyme + СН3-СО-SКоА
НООС-СН2-СО-S-КоА + biotin-enzyme
malonyl-CoA
Rate-limiting!
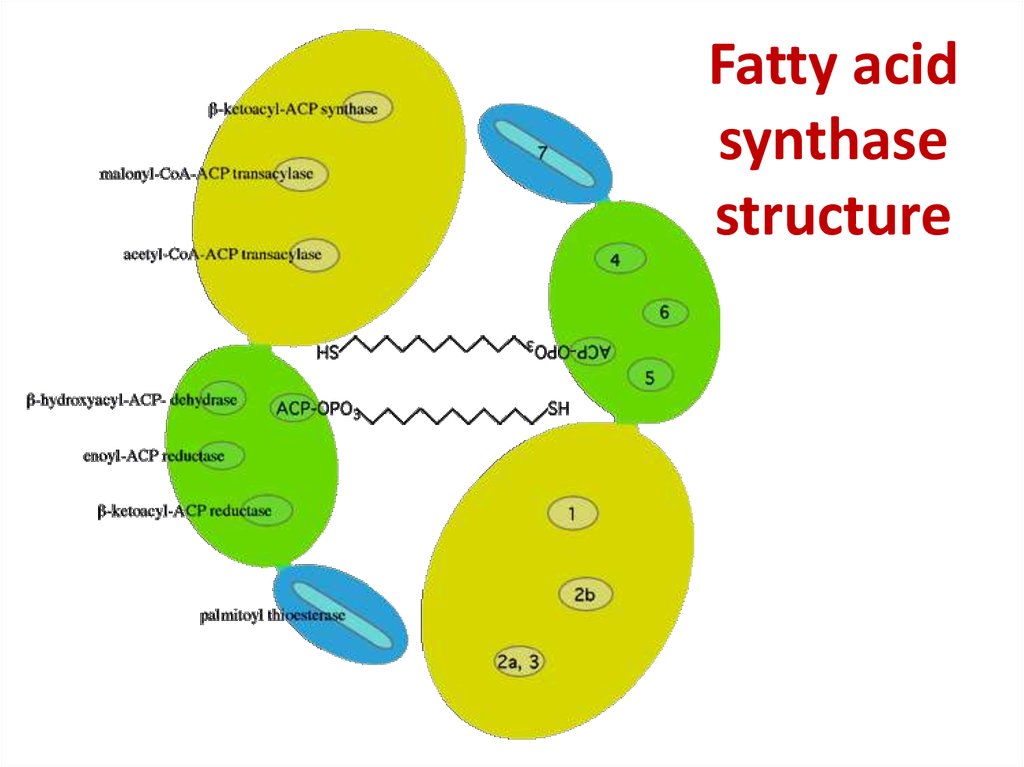
40. Fatty acid synthase structure
41.
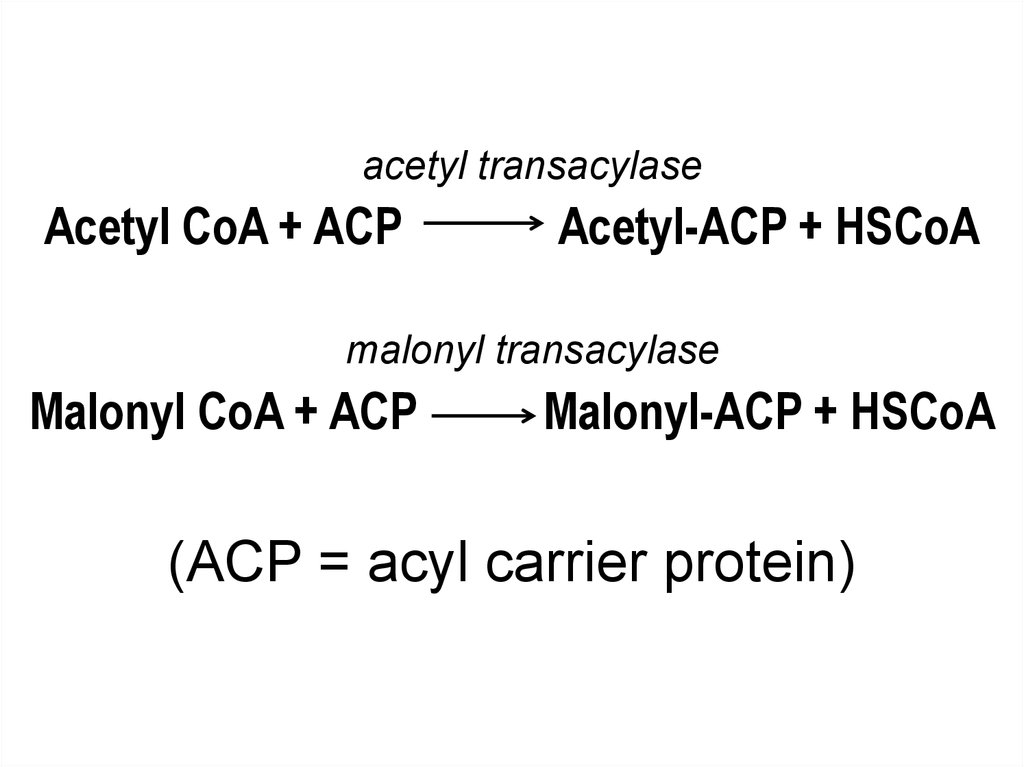
acetyl transacylaseAcetyl CoA + ACP
Acetyl-ACP + HSCoA
malonyl transacylase
Malonyl CoA + ACP
Malonyl-ACP + HSCoA
(ACP = acyl carrier protein)
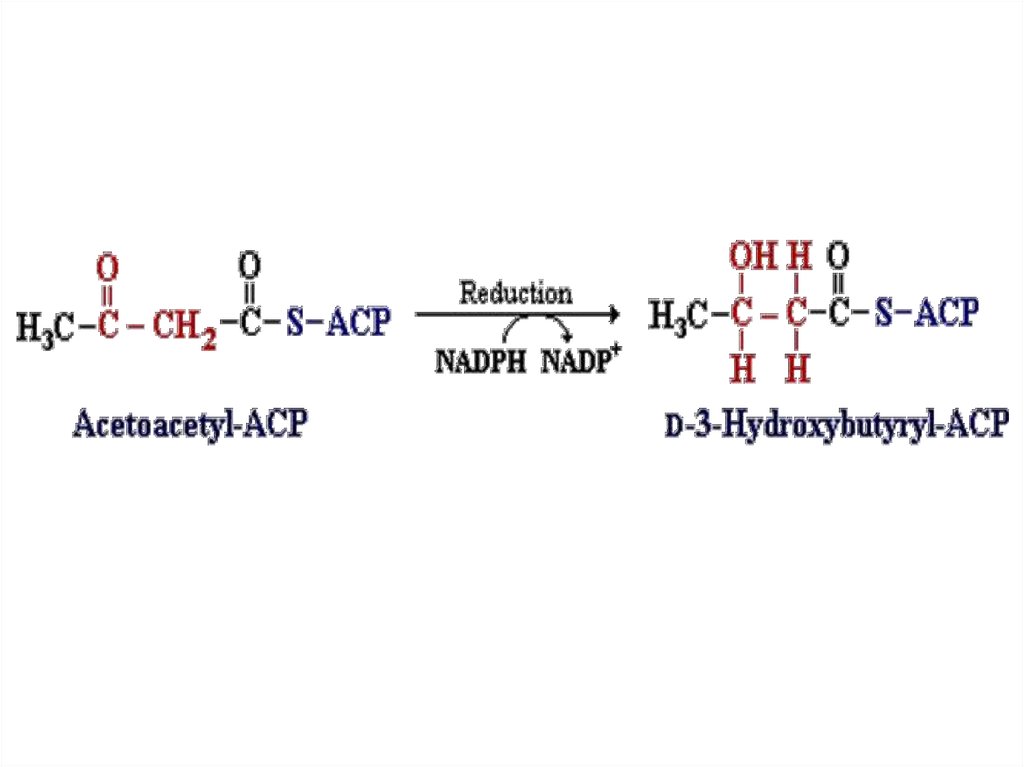
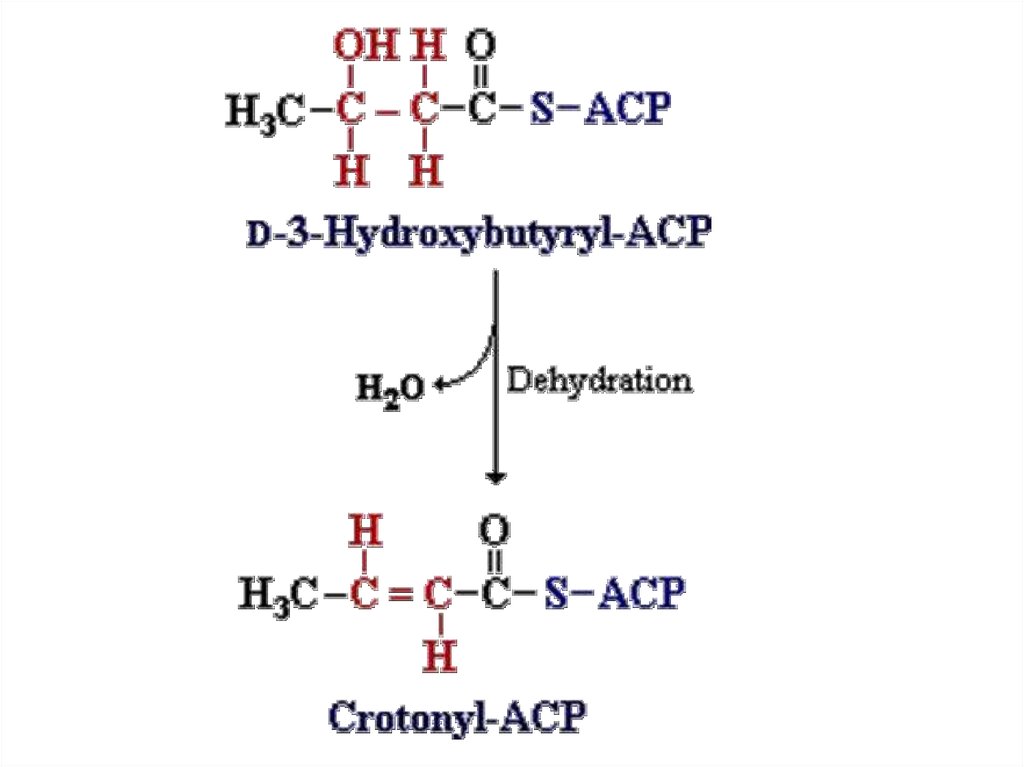
42.
43.
44.
45.
46. Formation of other fatty acids
Formation of other fatty acidsPalmitic acid 16:0
desaturase
Palmitoleic
Acid 16:1 (9)
elongase
Stearic acid 18:0
desaturase
Oleic acid
18:1(9)
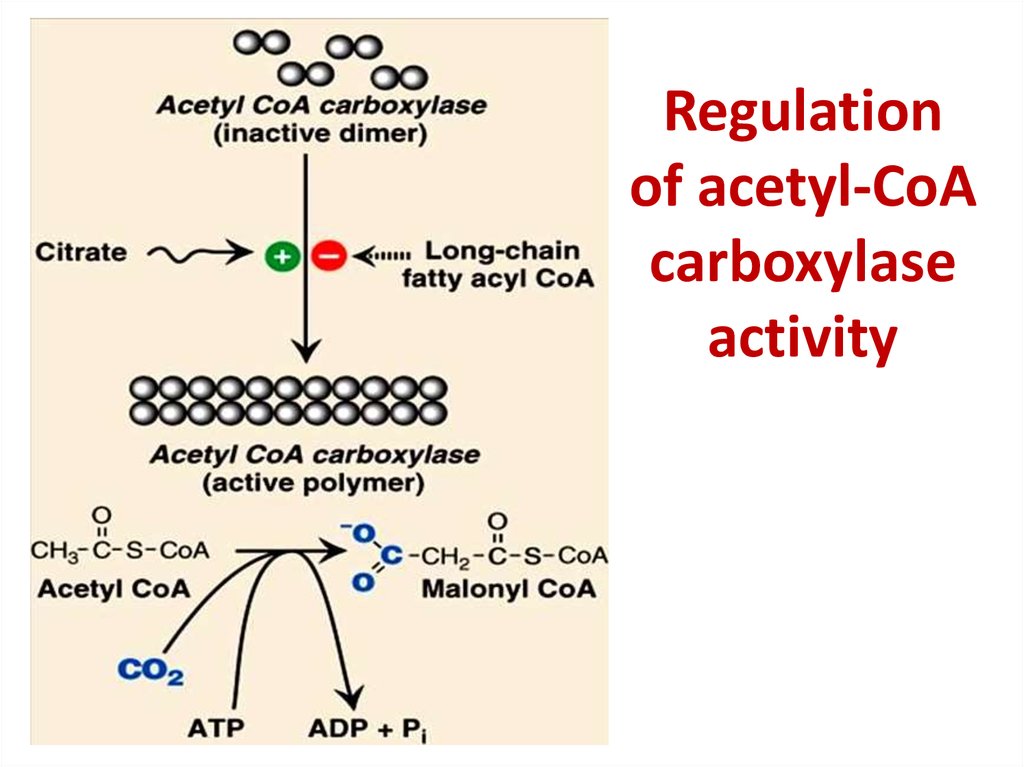
47. Regulation of acetyl-CoA carboxylase activity
Regulationof acetyl-CoA
carboxylase
activity
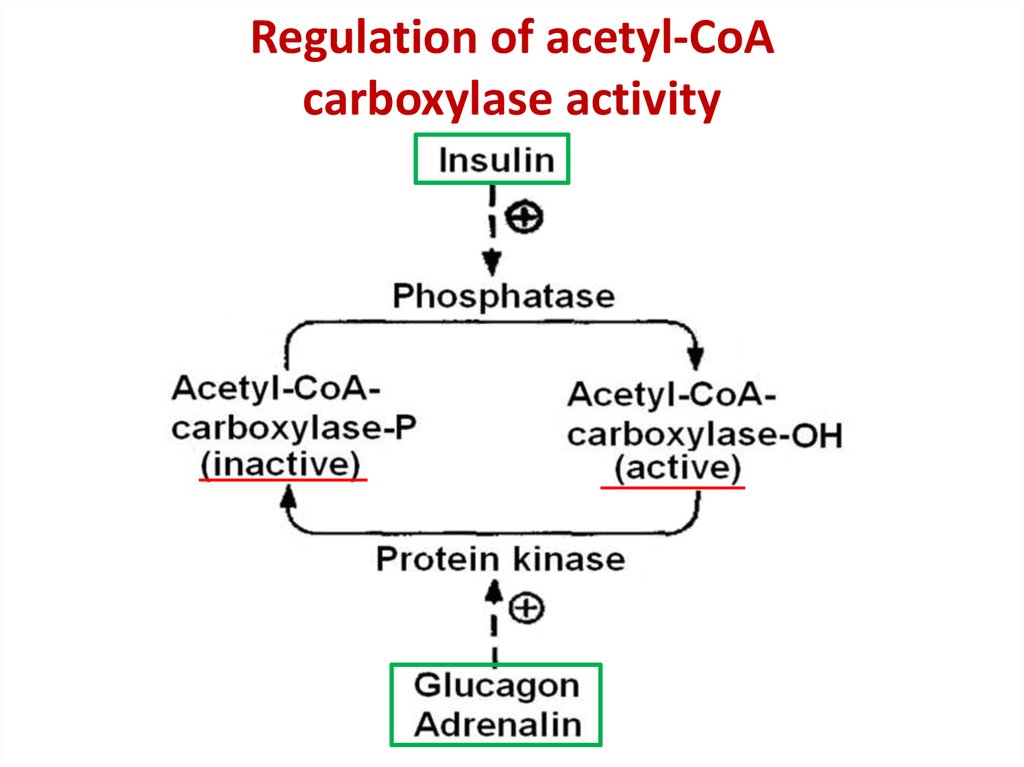
48. Regulation of acetyl-CoA carboxylase activity
Regulation of acetyl-CoAcarboxylase activity













 chemistry
chemistry








