Similar presentations:
Protein Chemistry
1. Protein Chemistry
2.
3. Essential amino acids
• valine, leucine, isoleucine,lysine, methionine, threonine,
tryptophan, phenylalanine
Semi-essential amino acids
arginine and histidine
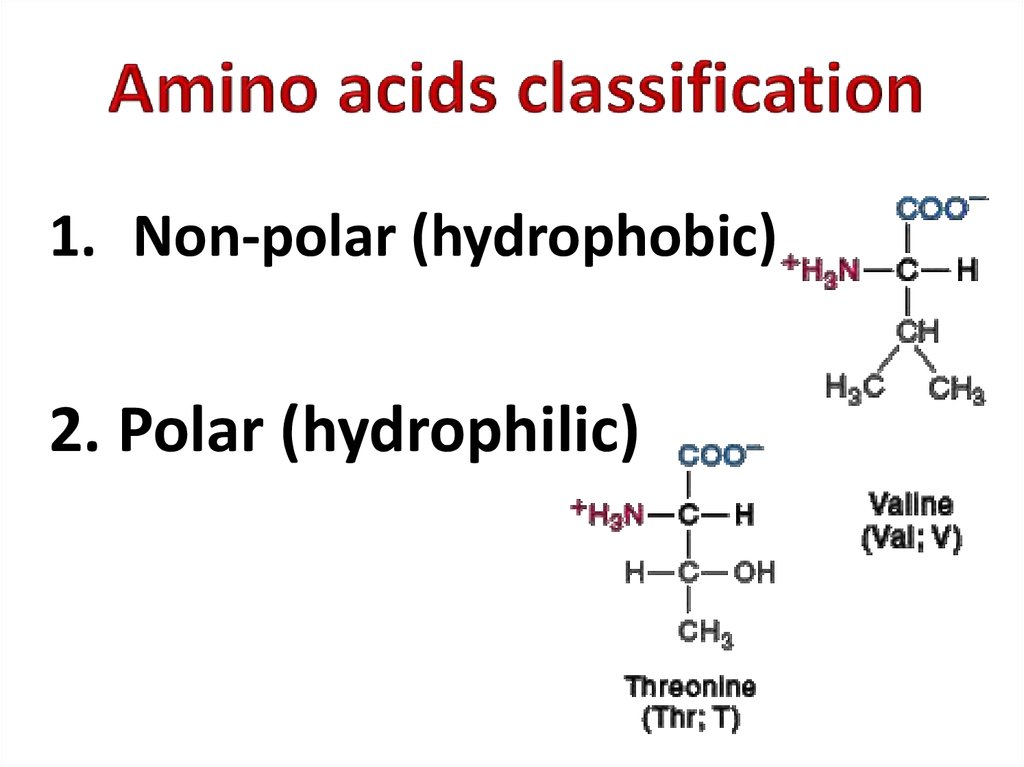
4. Amino acids classification
1. Non-polar (hydrophobic)2. Polar (hydrophilic)
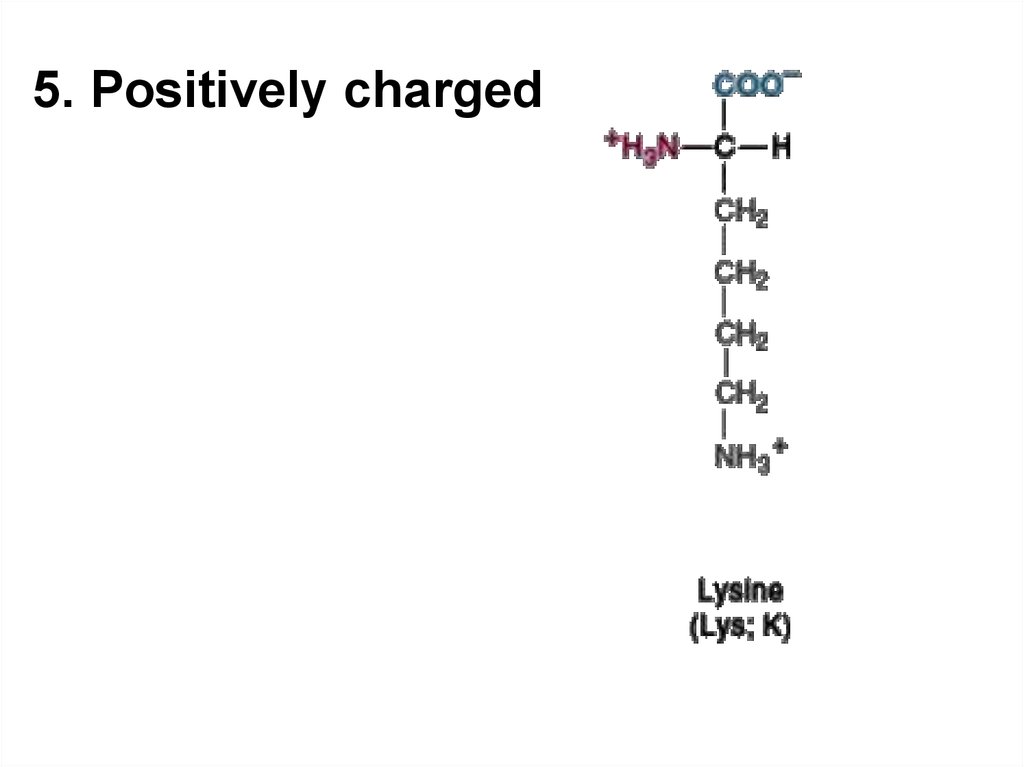
5.
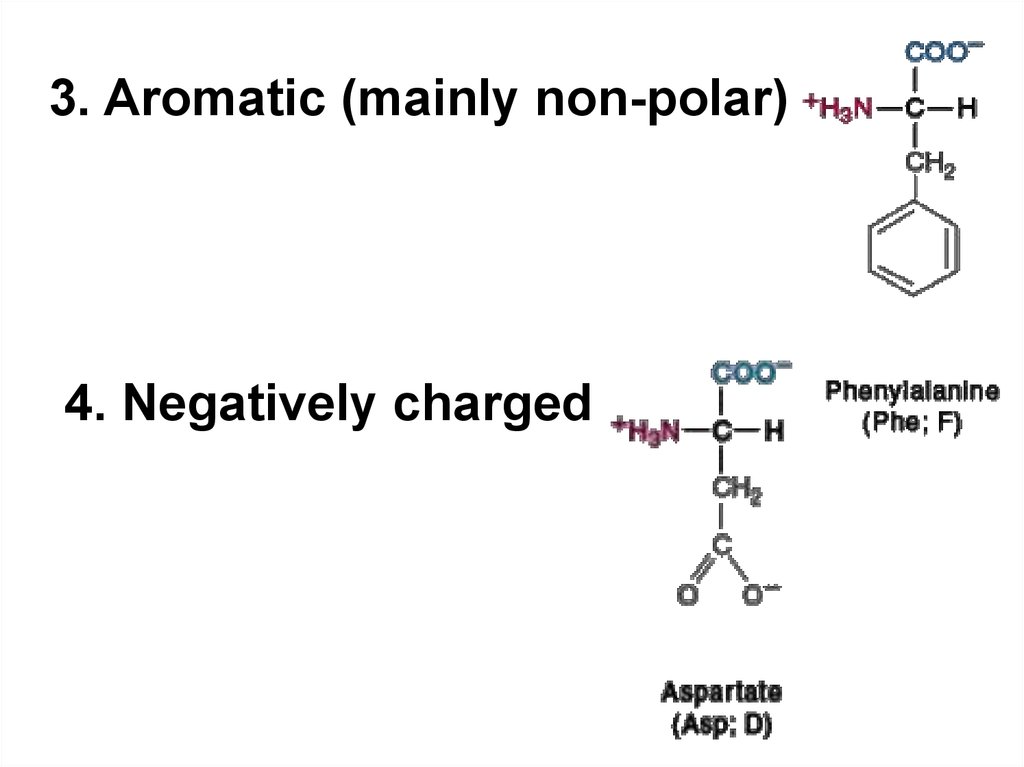
3. Aromatic (mainly non-polar)4. Negatively charged
6.
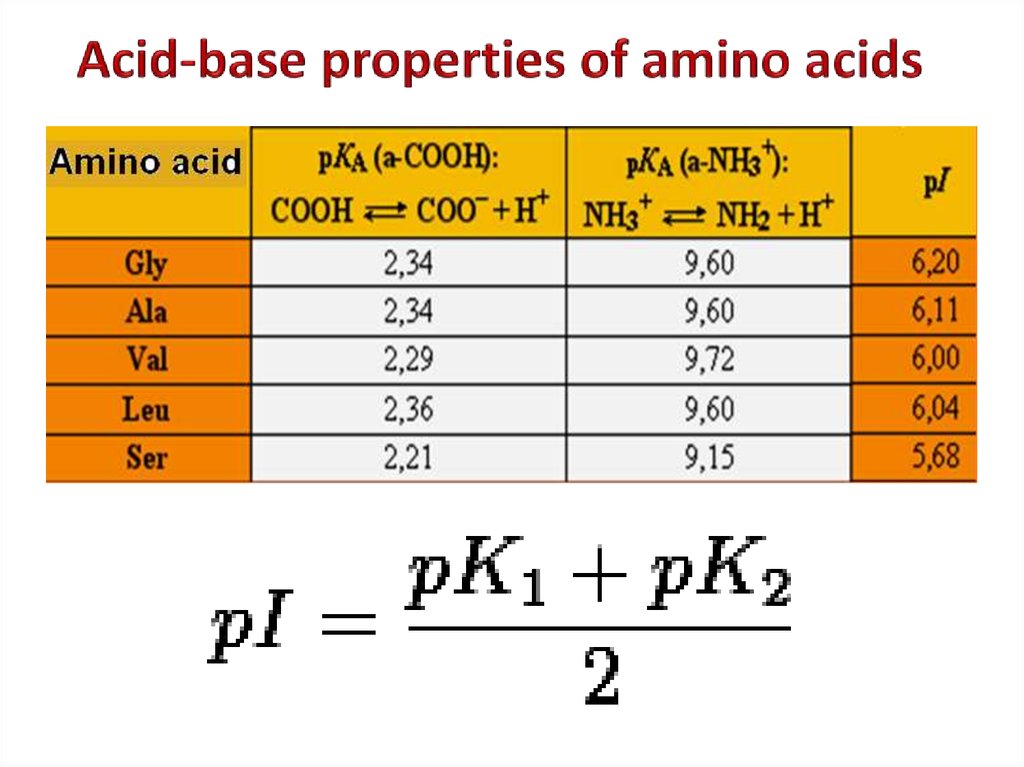
5. Positively charged7. Acid-base properties of amino acids
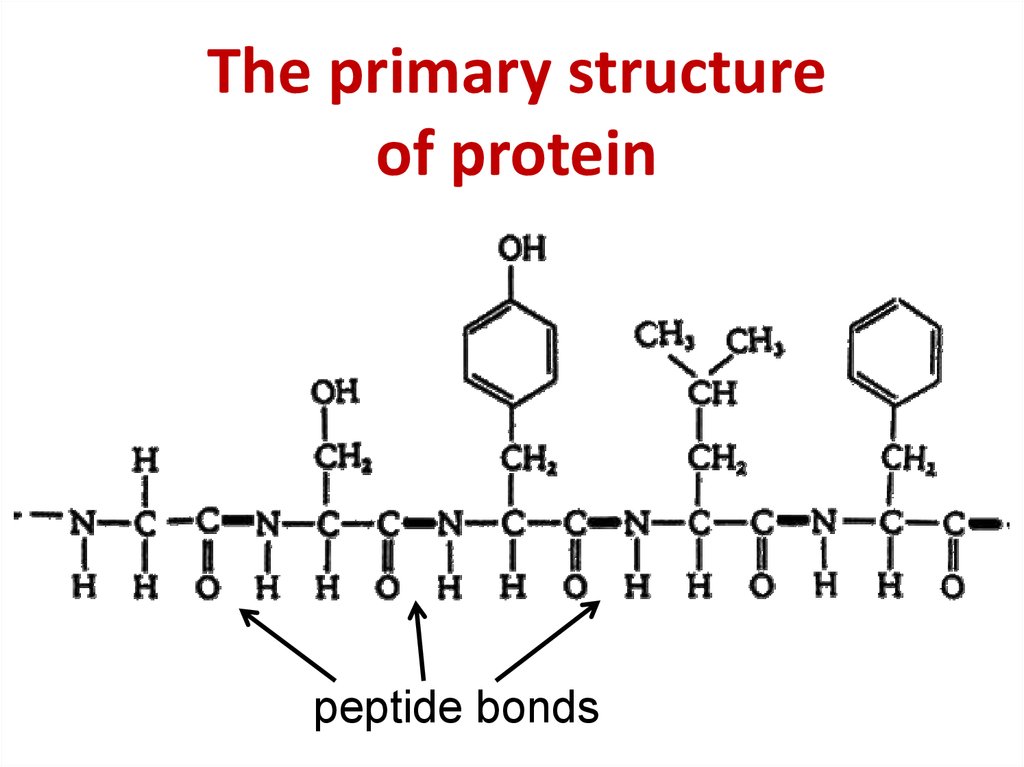
8. The primary structure of protein
The primary structureof protein
peptide bonds
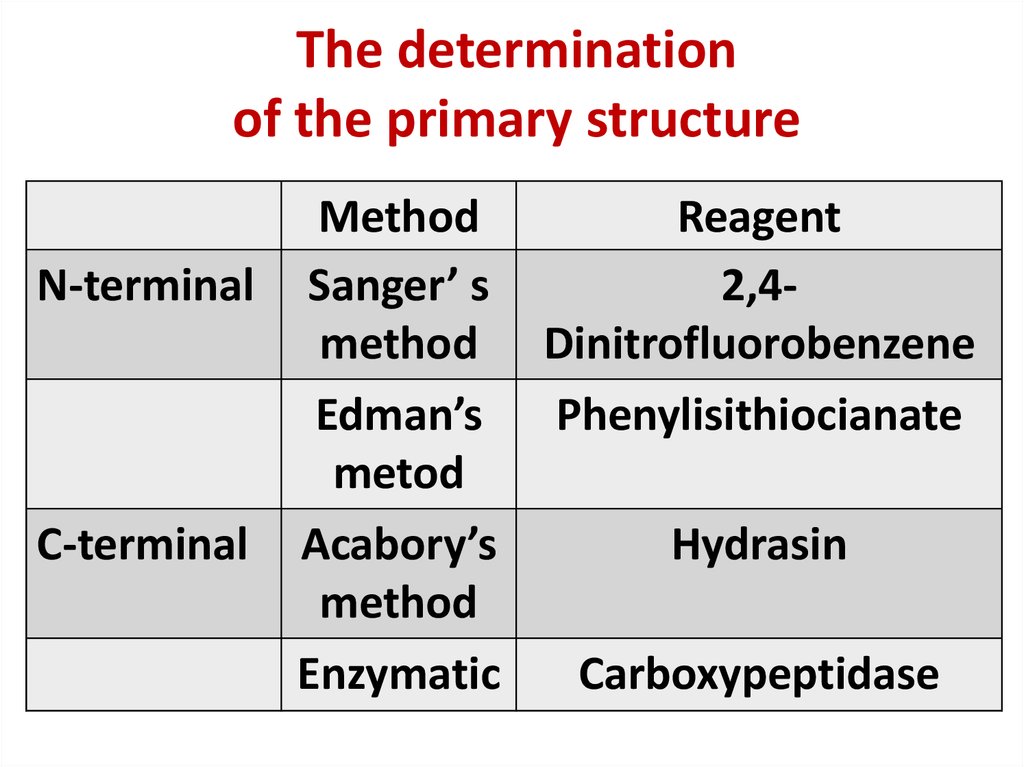
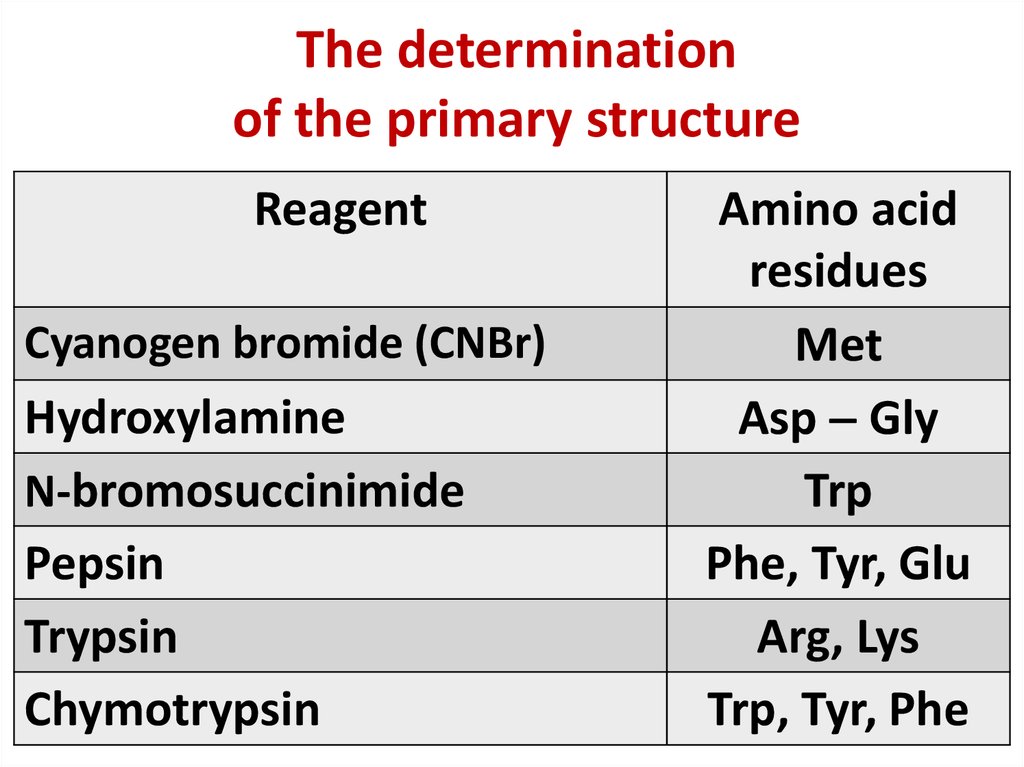
9. The determination of the primary structure
MethodReagent
N-terminal Sanger’ s
2,4method Dinitrofluorobenzene
Edman’s
Phenylisithiocianate
metod
C-terminal Acabory’s
Hydrasin
method
Enzymatic
Carboxypeptidase
10. The determination of the primary structure
ReagentCyanogen bromide (CNBr)
Hydroxylamine
N-bromosuccinimide
Pepsin
Trypsin
Chymotrypsin
Amino acid
residues
Met
Asp Gly
Trp
Phe, Tyr, Glu
Arg, Lys
Trp, Tyr, Phe
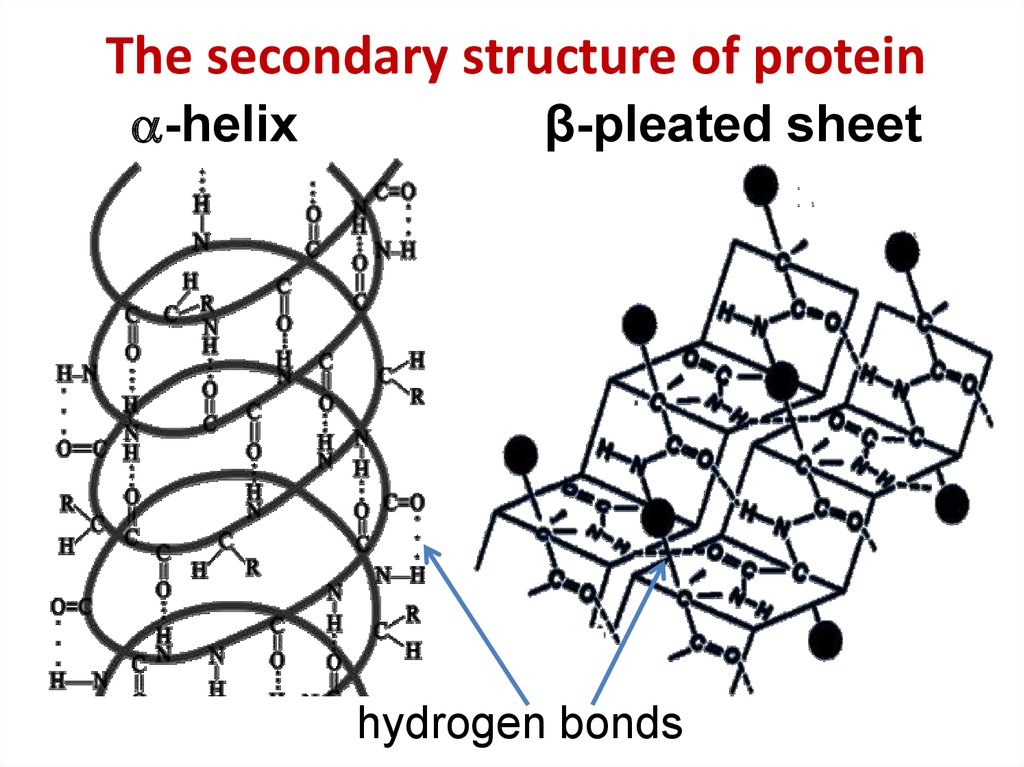
11. The secondary structure of protein
The secondary structure of protein-helix
β-pleated sheet
hydrogen bonds
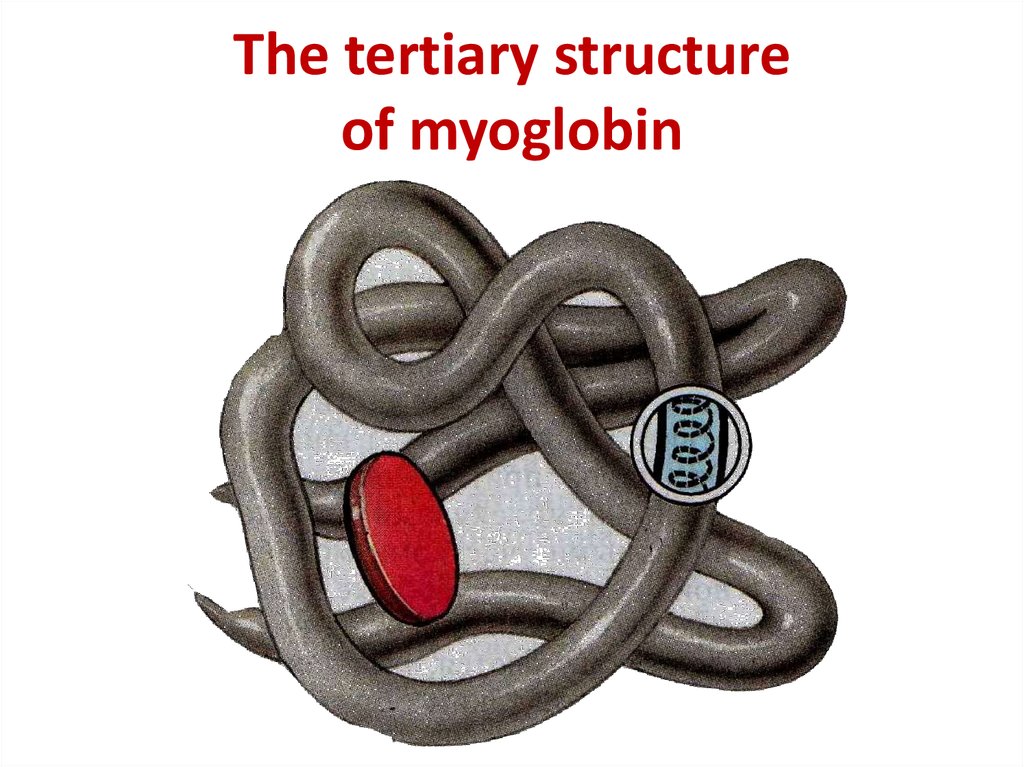
12. The tertiary structure of myoglobin
The tertiary structureof myoglobin
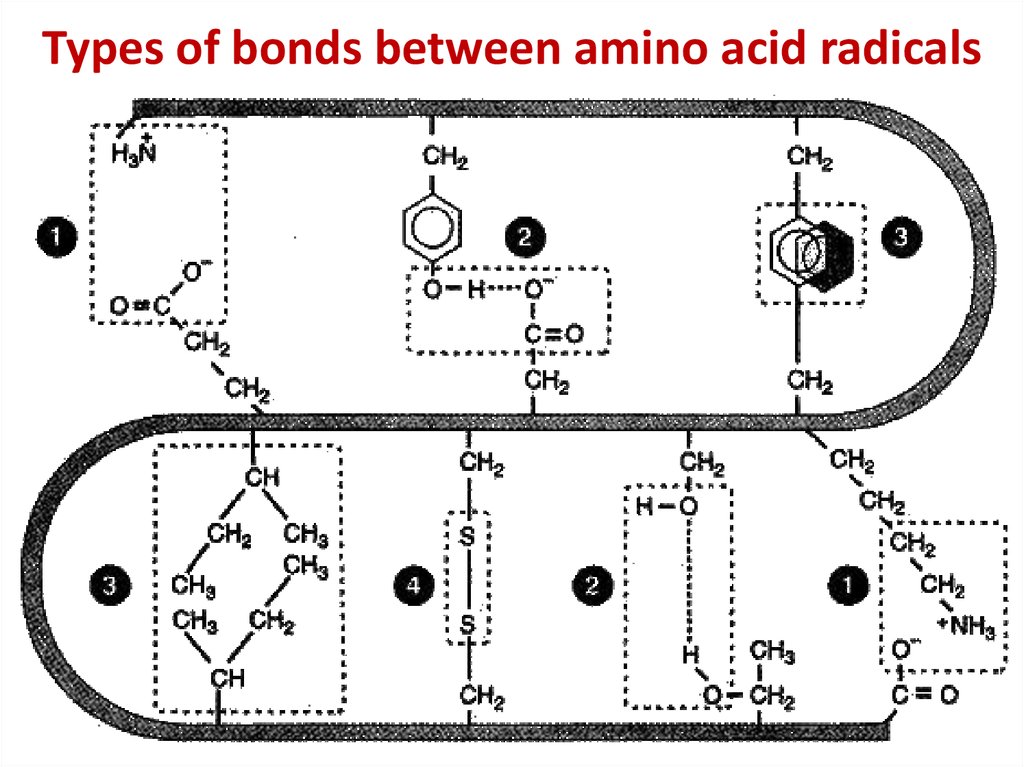
13. Types of bonds between amino acid radicals
Types of bonds between amino acid radicals14. Chaperone
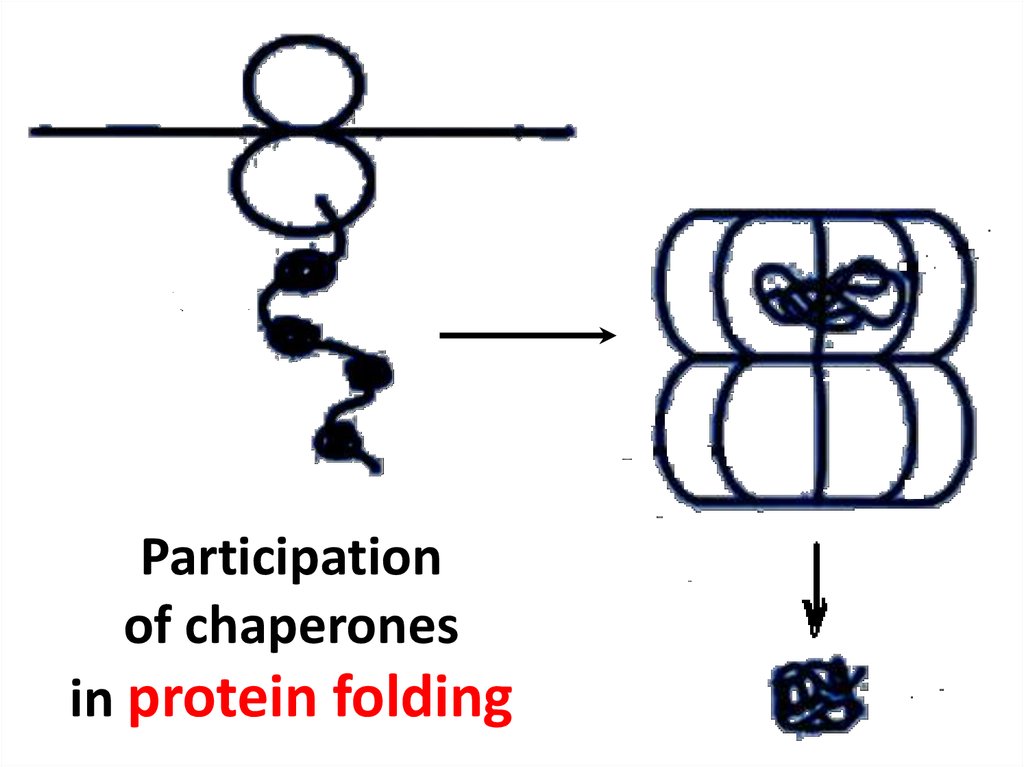
15. Participation of chaperones in protein folding
Participationof chaperones
in protein folding
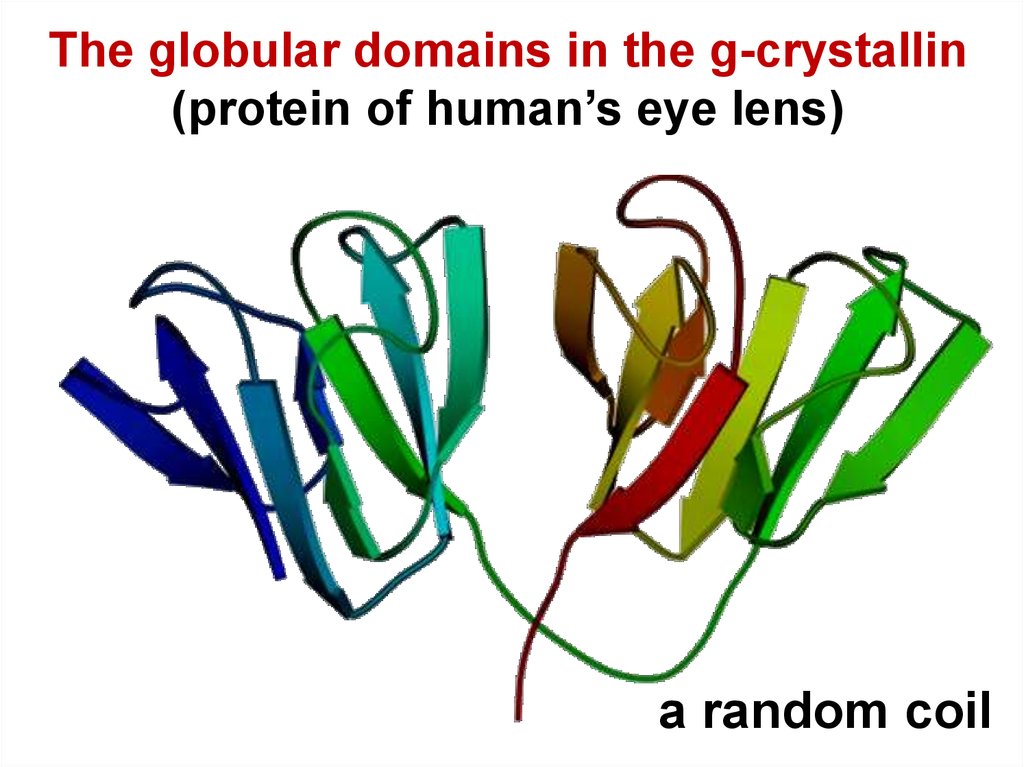
16.
The globular domains in the g-crystallin(protein of human’s eye lens)
a random coil
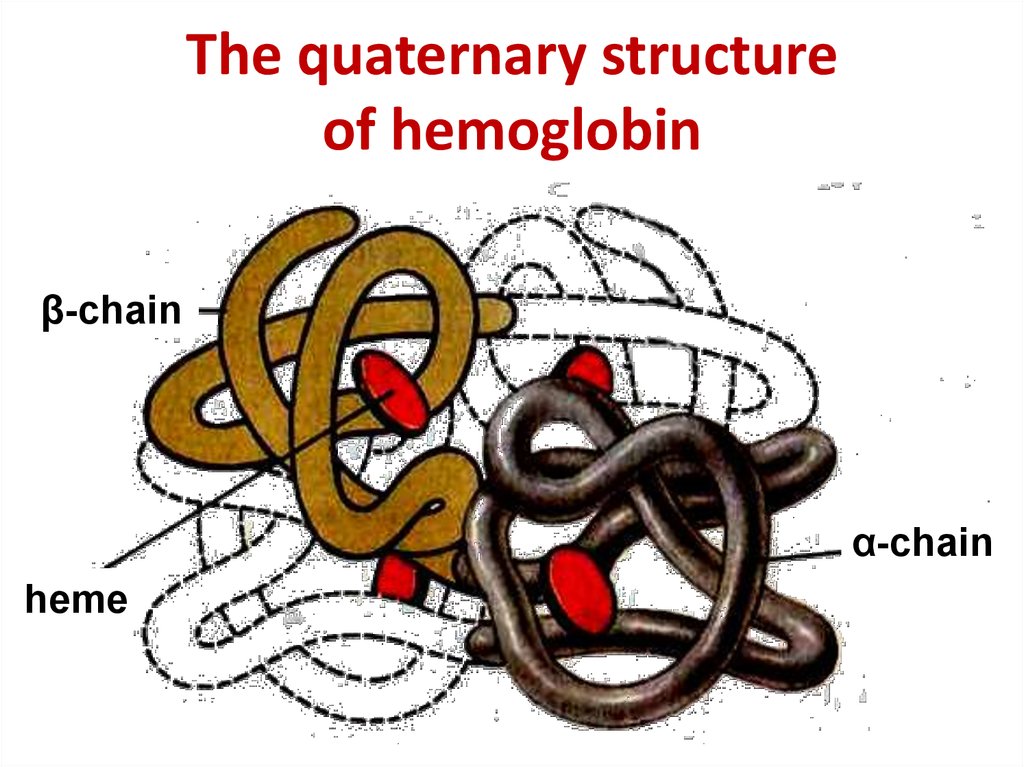
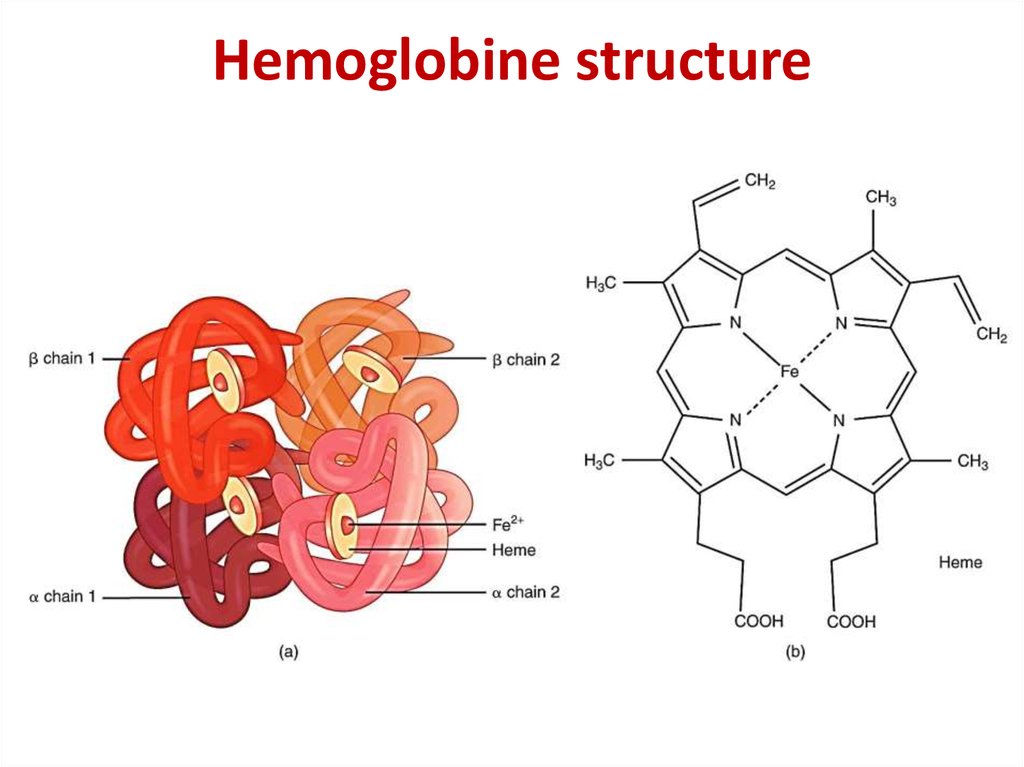
17. The quaternary structure of hemoglobin
The quaternary structureof hemoglobin
β-chain
α-chain
heme
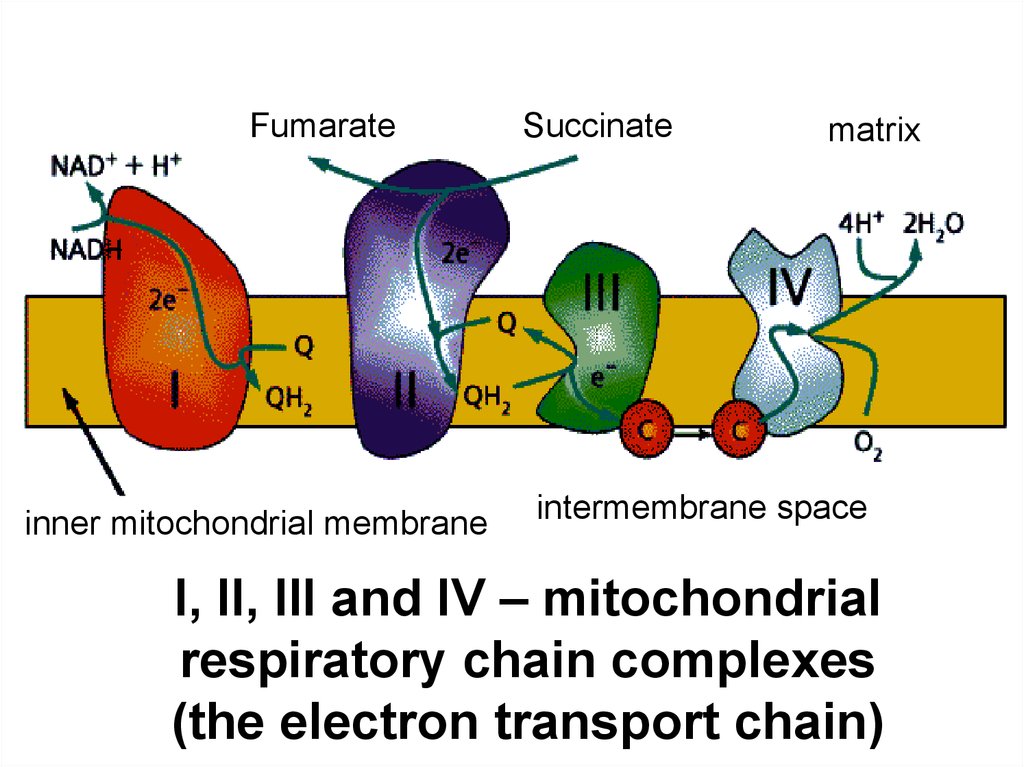
18.
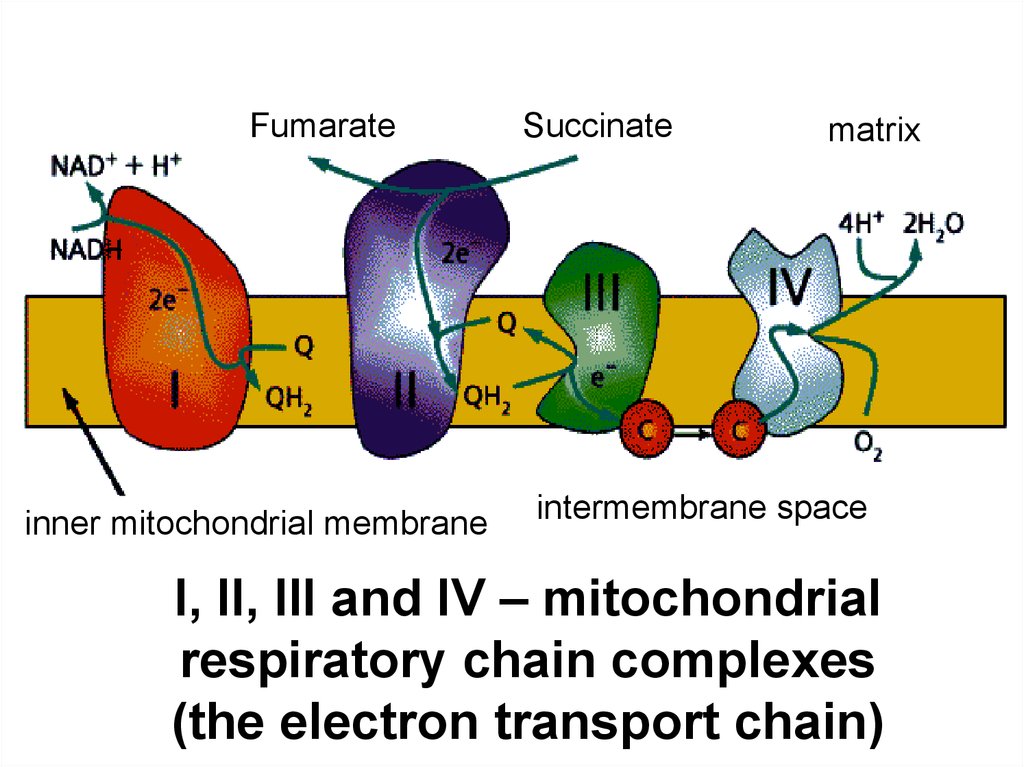
Fumarateinner mitochondrial membrane
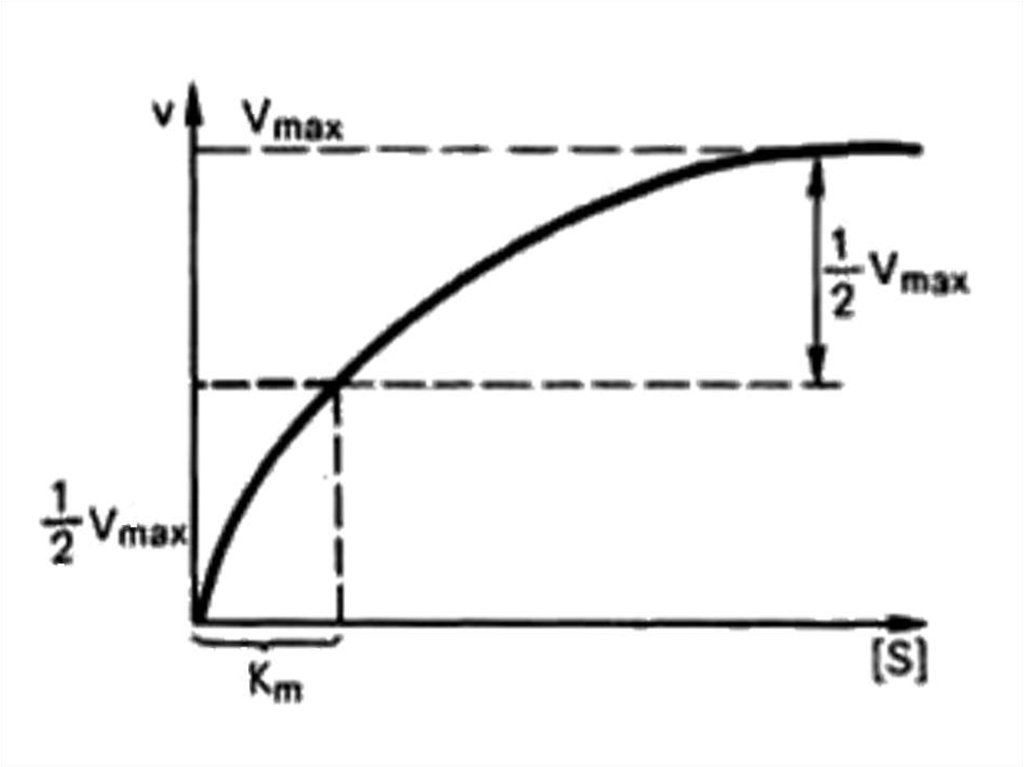
Succinate
matrix
intermembrane space
I, II, III and IV – mitochondrial
respiratory chain complexes
(the electron transport chain)
19. Classification of proteins Simple proteins
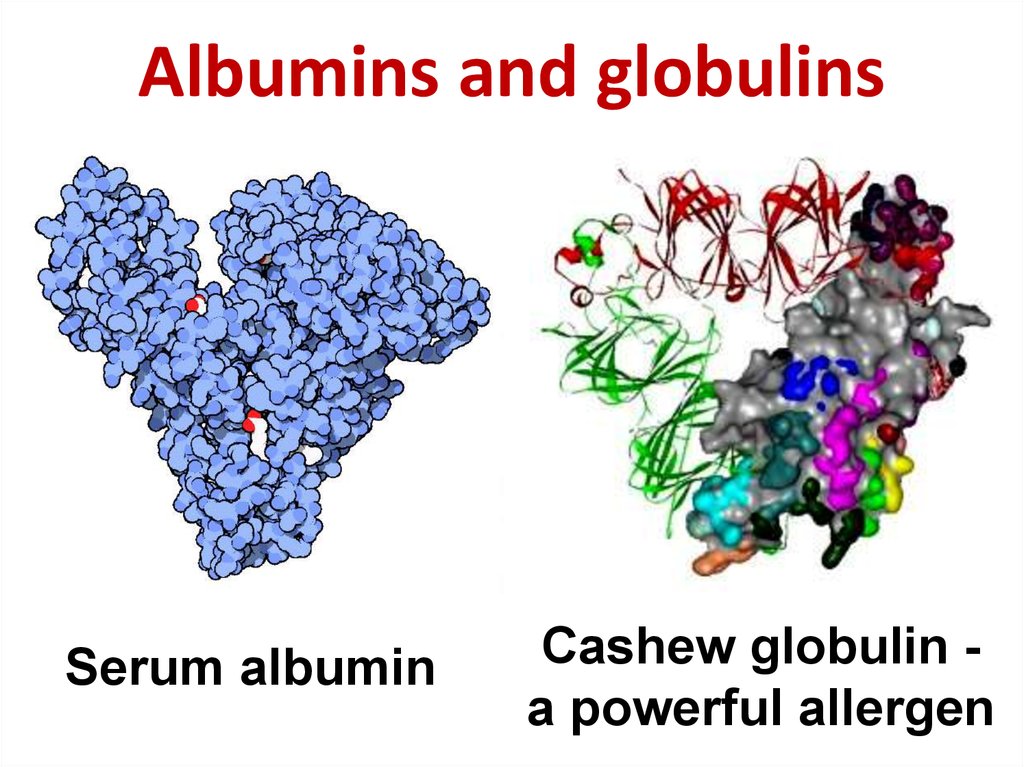
20. Albumins and globulins
Serum albuminCashew globulin a powerful allergen
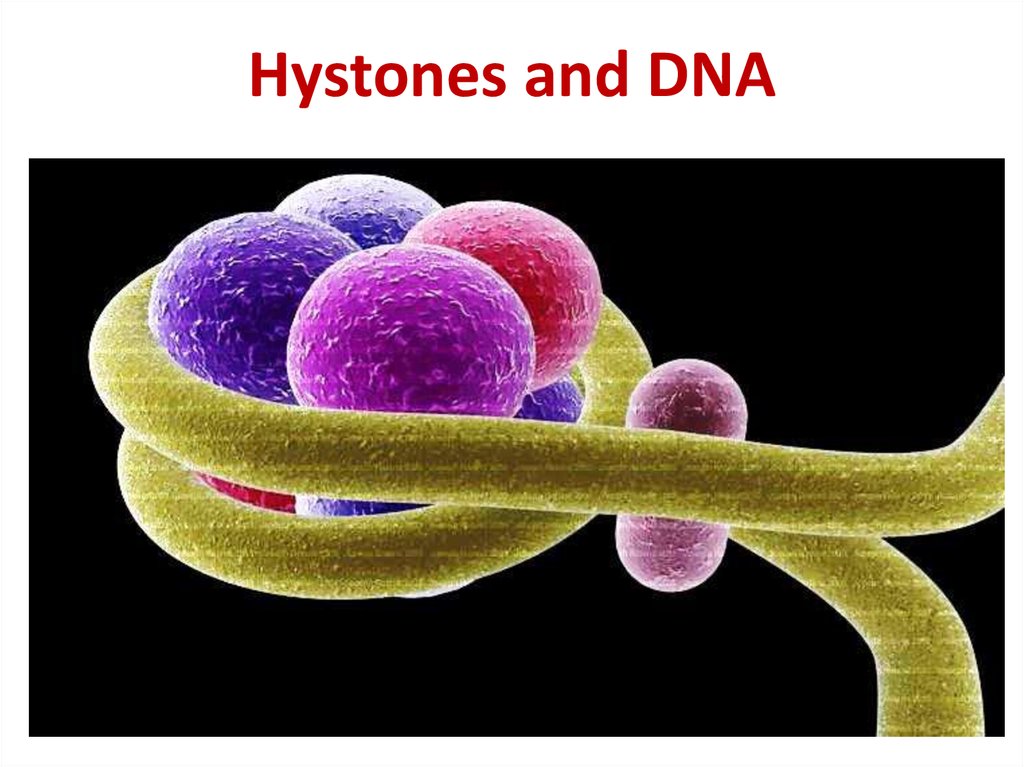
21. Hystones and DNA
22. Prolamin
23. Conjugative proteins
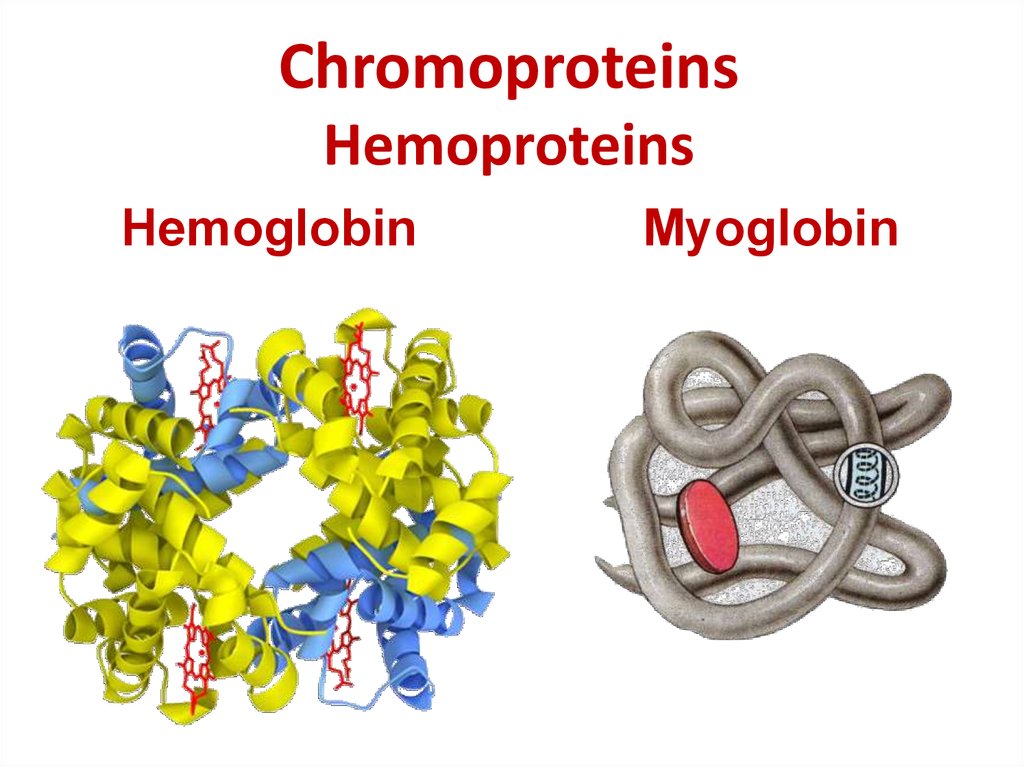
24. Chromoproteins Hemoproteins
HemoglobinMyoglobin
25. Hemoglobine structure
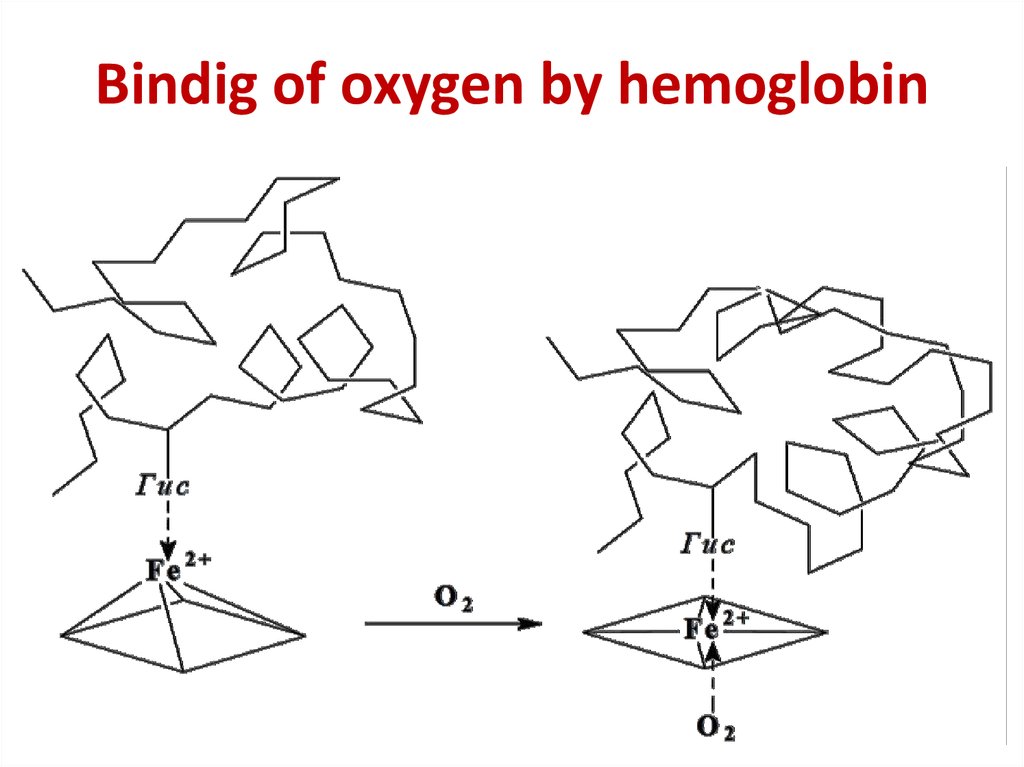
26. Bindig of oxygen by hemoglobin
Bindig of oxygen by hemoglobin27.
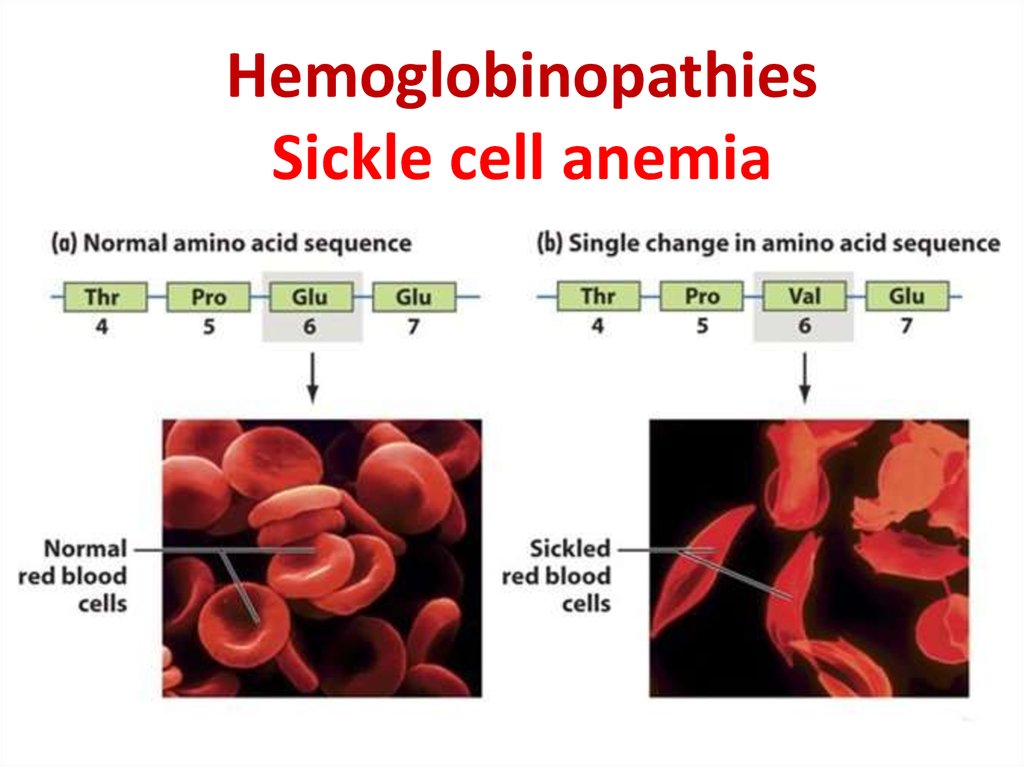
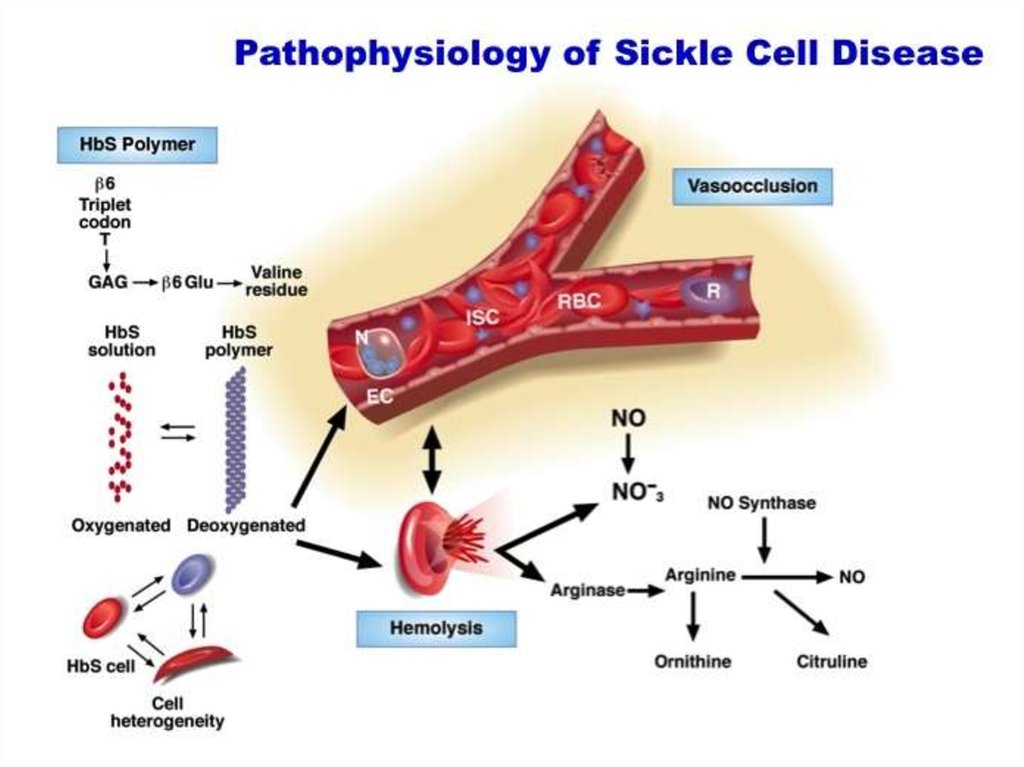
28. Hemoglobinopathies Sickle cell anemia
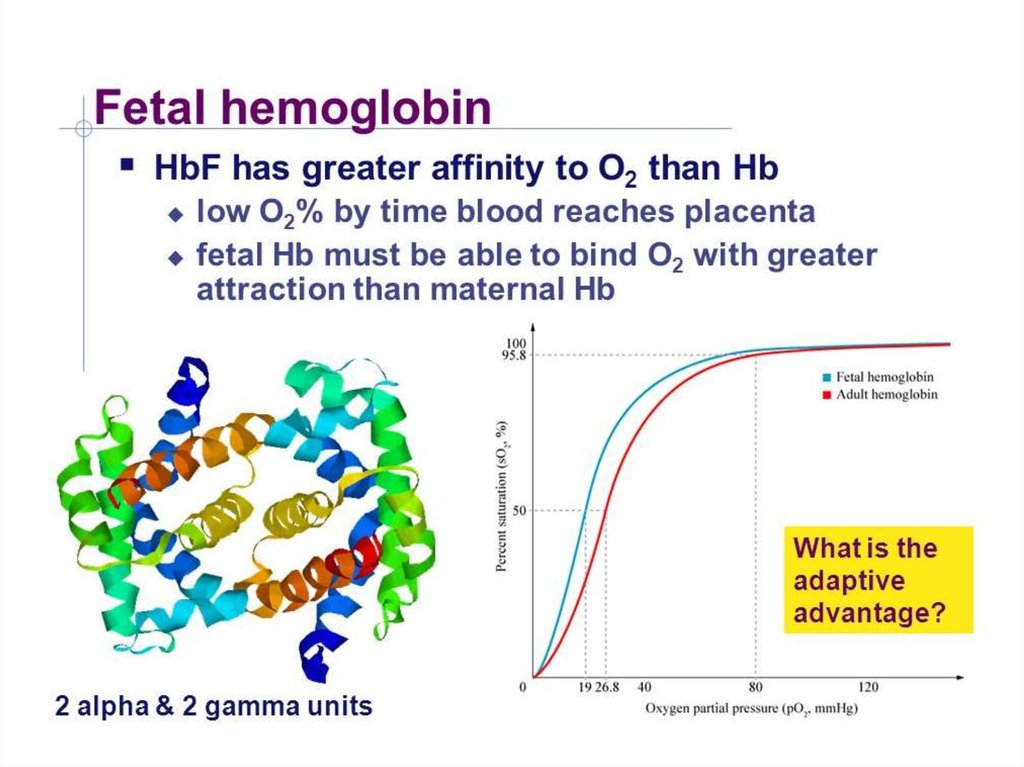
29.
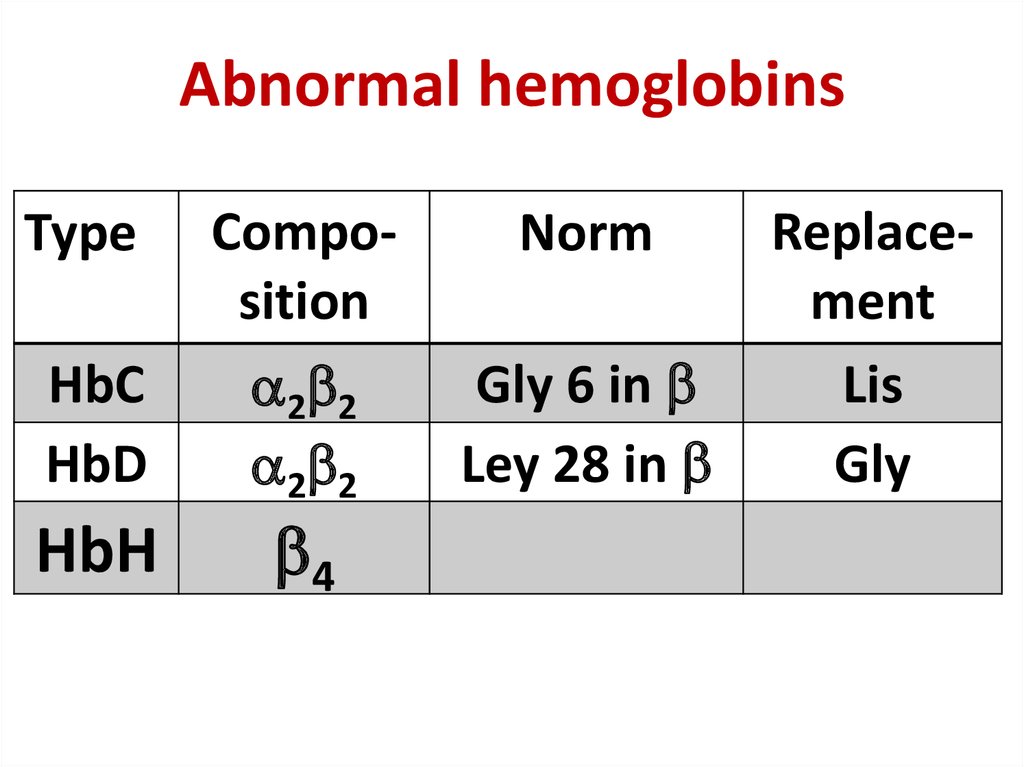
30. Abnormal hemoglobins
Abnormal hemoglobinsType
Composition
Norm
HbС
HbD
2 2
2 2
Gly 6 in
Ley 28 in
HbН
4
Replacement
Lis
Gly
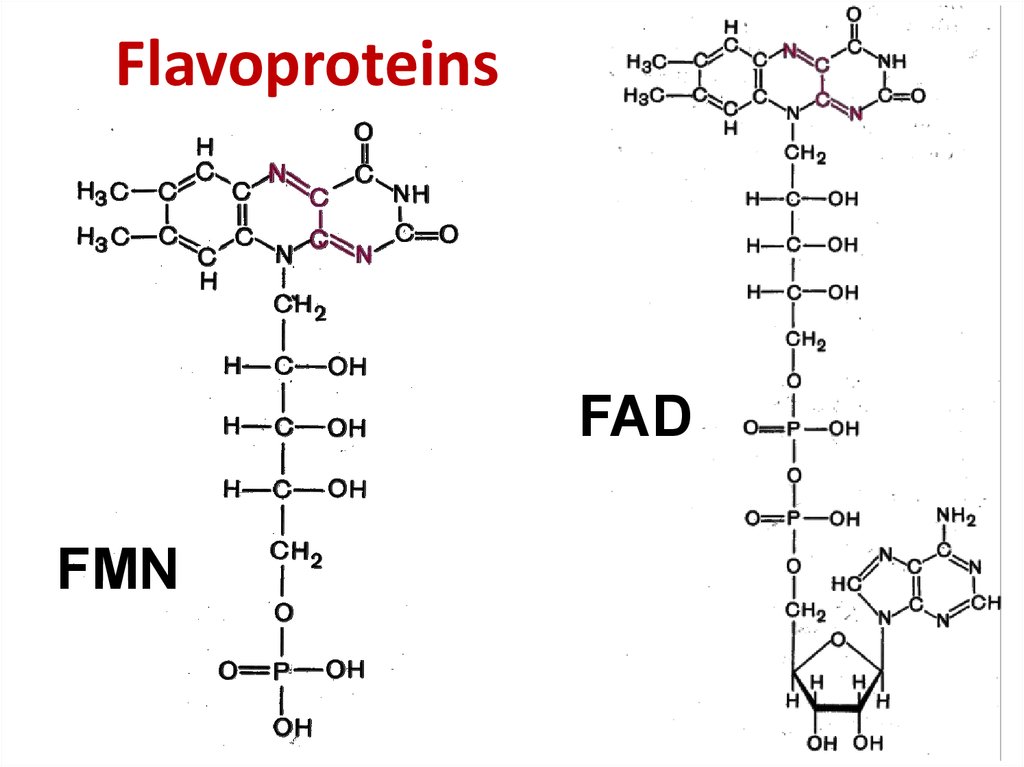
31. Flavoproteins
FADFMN
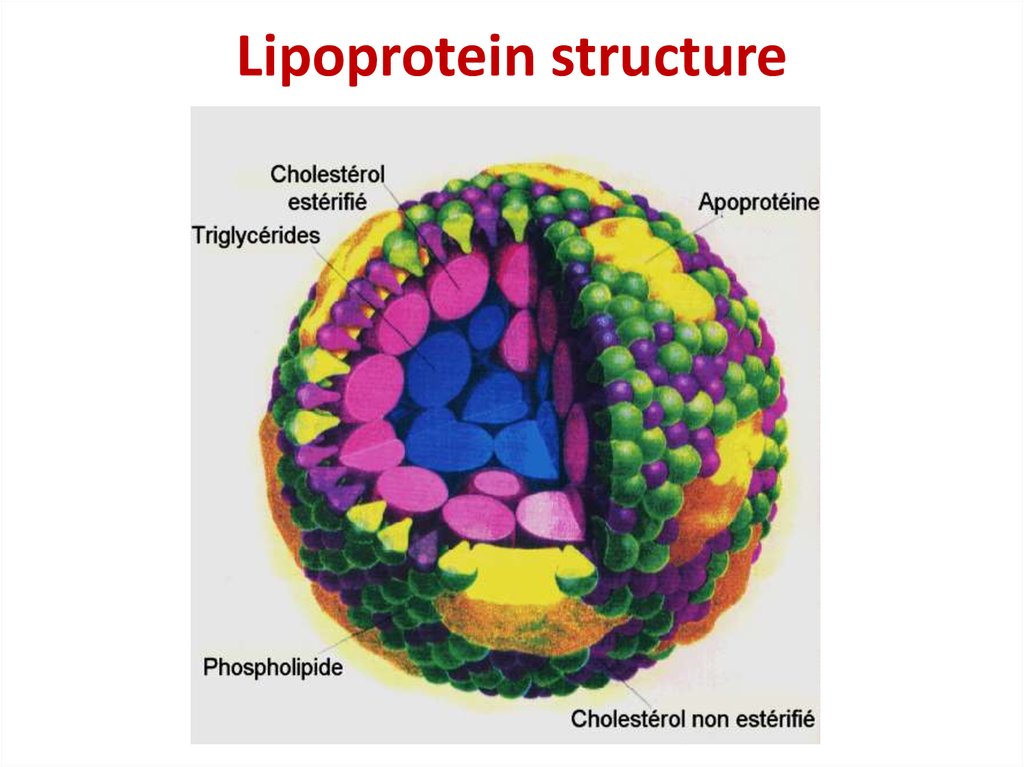
32. Lipoprotein structure
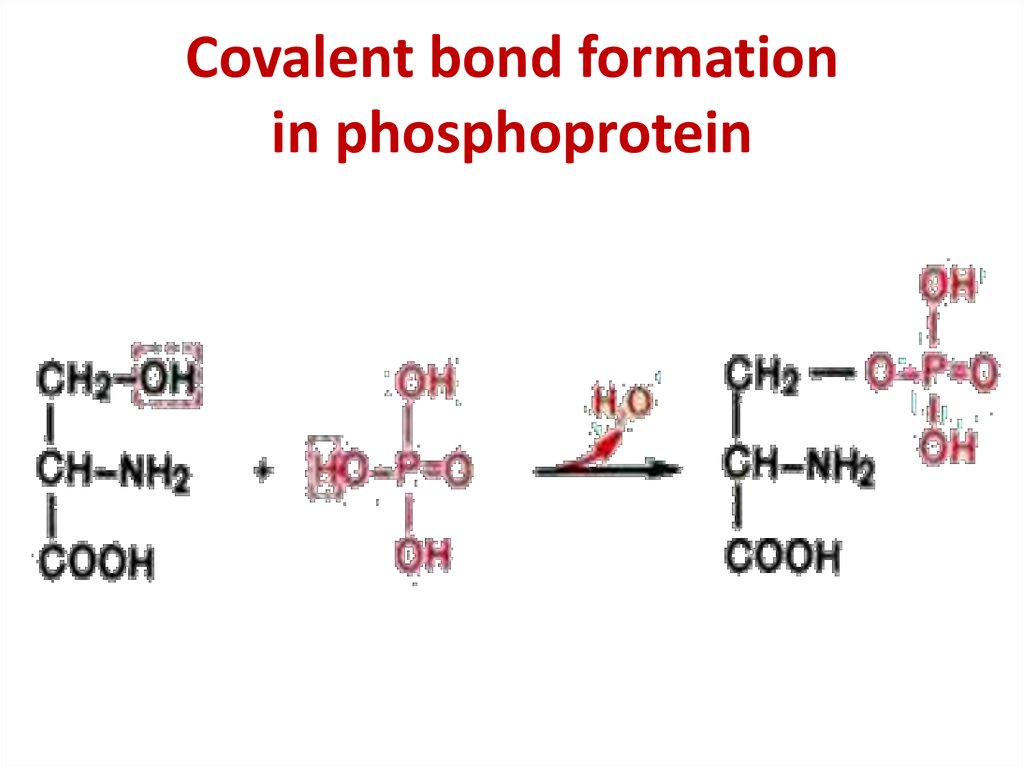
Lipoprotein structure33. Covalent bond formation in phosphoprotein
Covalent bond formationin phosphoprotein
34. Ionic bond formation in phosphoprotein
Ionic bond formationin phosphoprotein
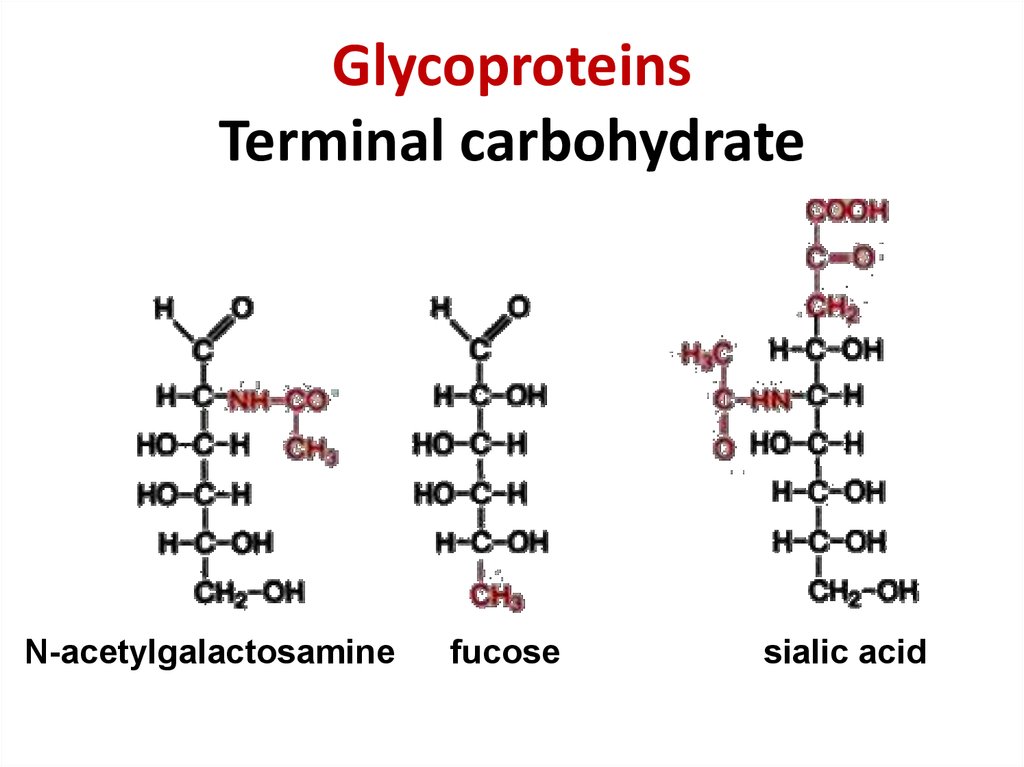
35. Glycoproteins Terminal carbohydrate
GlycoproteinsTerminal carbohydrate
N-acetylgalactosamine
fucose
sialic acid
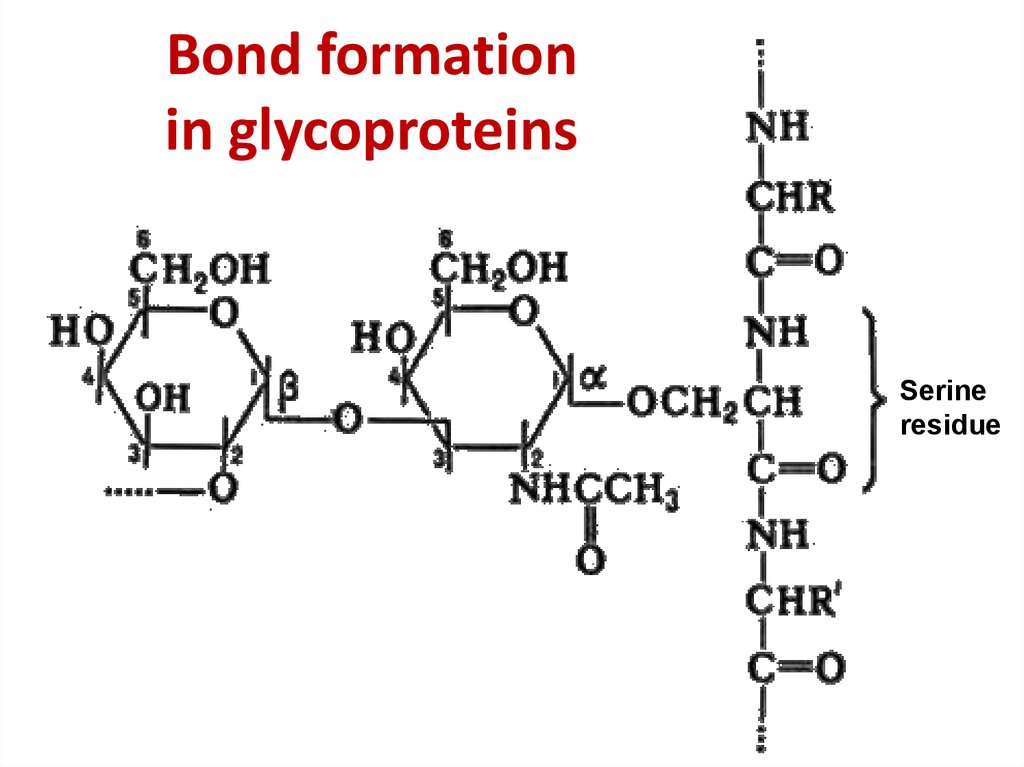
36. Bond formation in glycoproteins
Bond formationin glycoproteins
Serine
residue
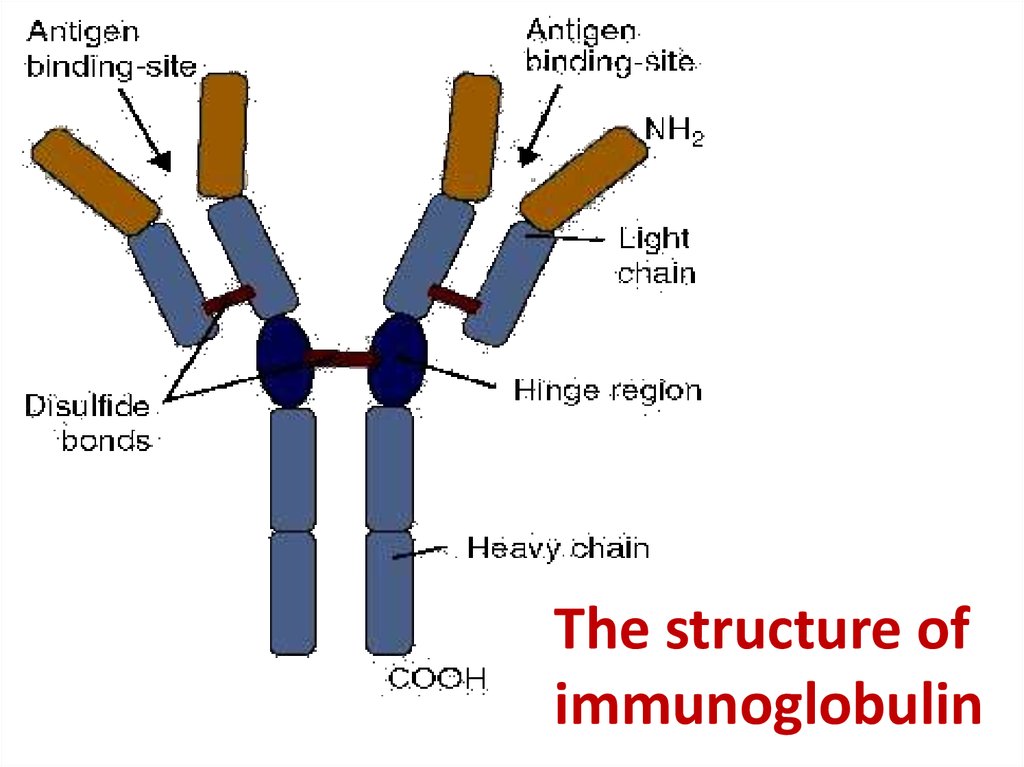
37. The structure of immunoglobulin
The structure ofimmunoglobulin
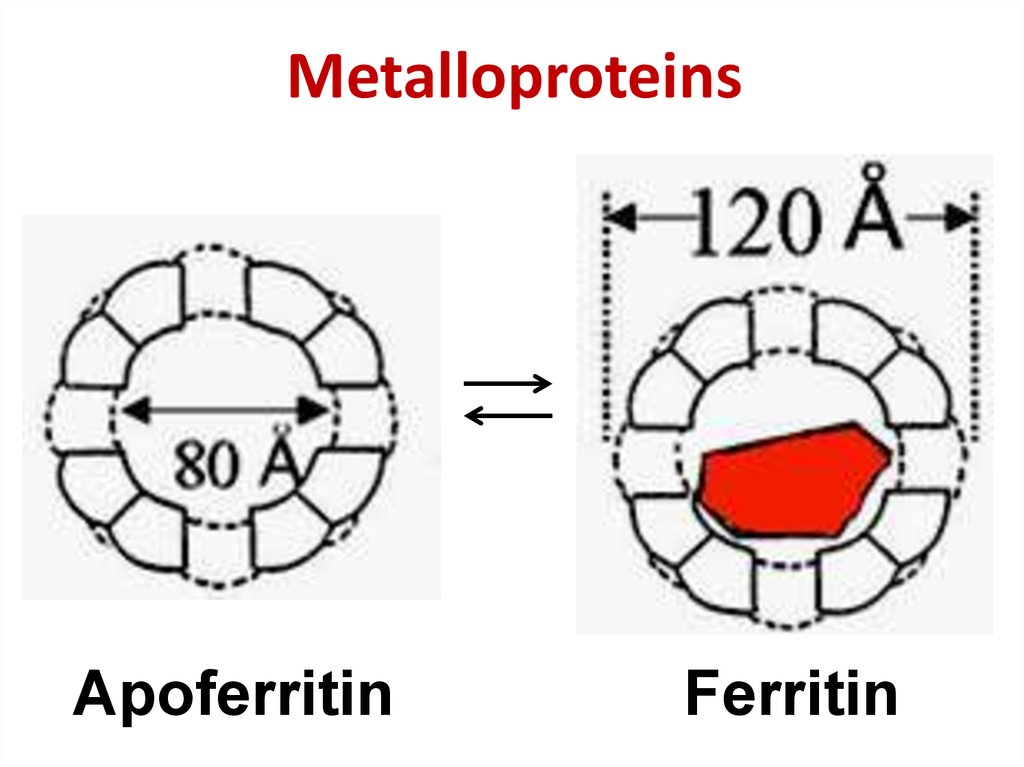
38. Metalloproteins
ApoferritinFerritin
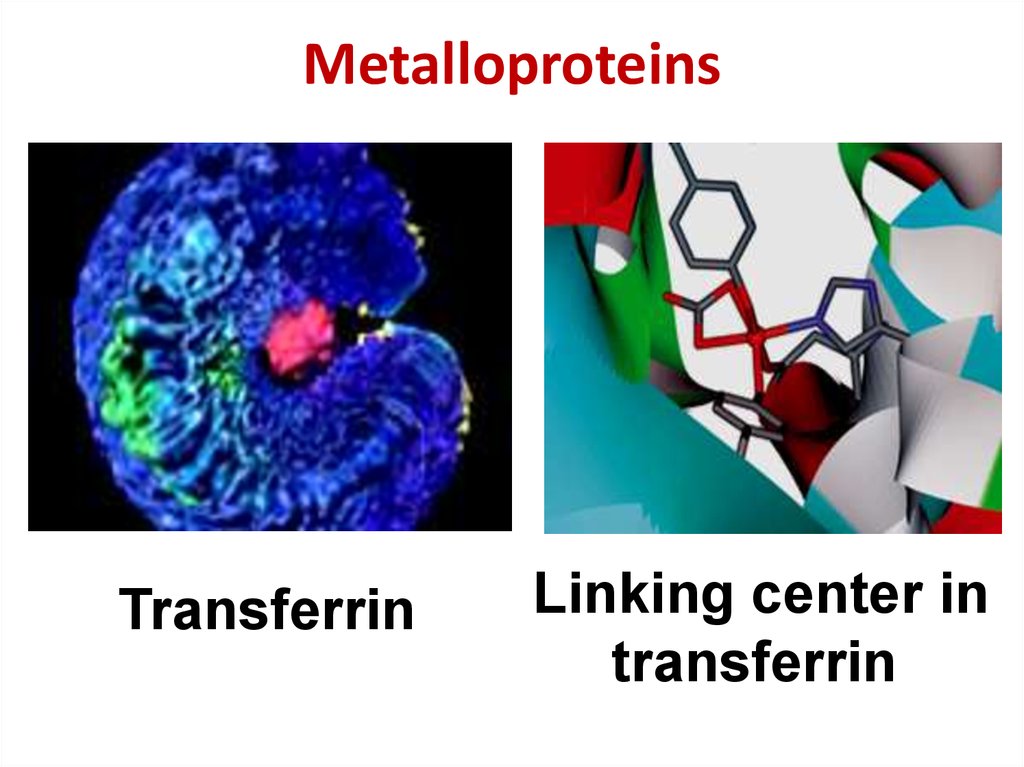
39. Metalloproteins
TransferrinLinking center in
transferrin
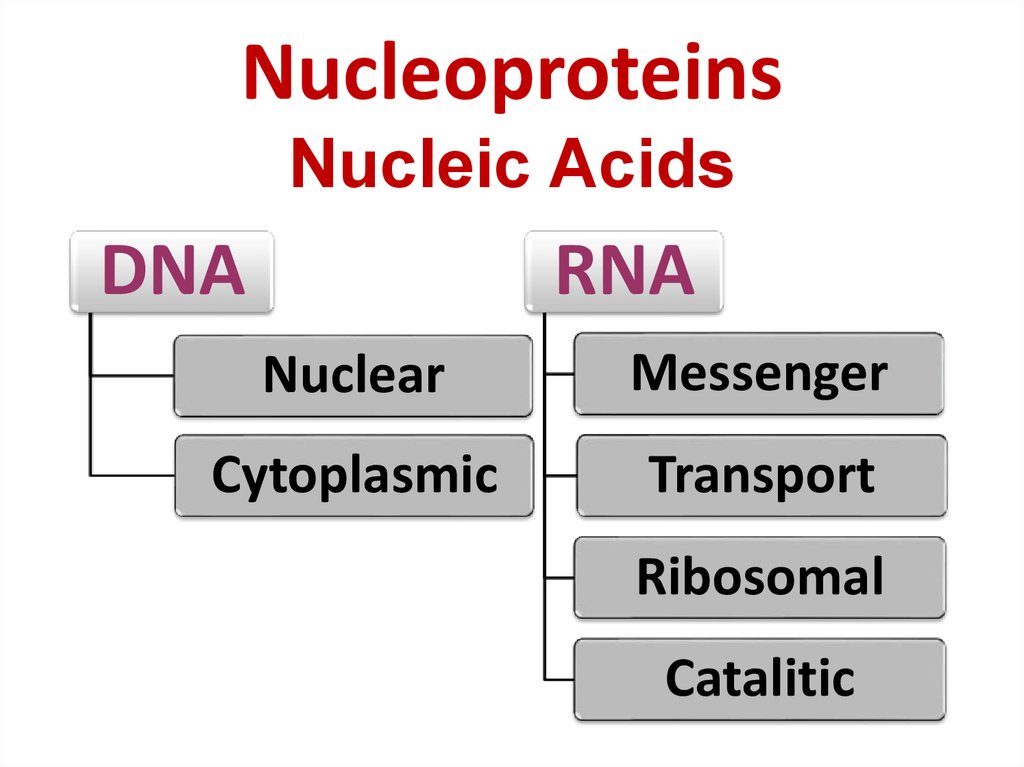
40. Nucleoproteins Nucleic Acids
DNARNA
Nuclear
Messenger
Cytoplasmic
Transport
Ribosomal
Catalitic
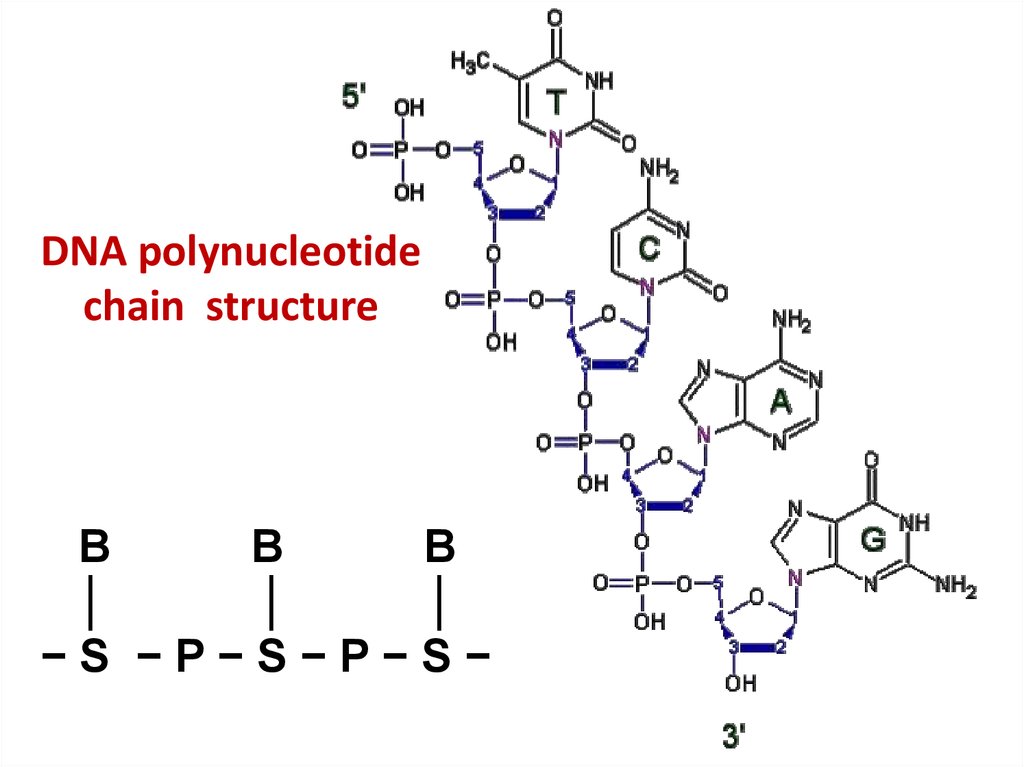
41. DNA polynucleotide chain structure
BB
B
│
│
│
−S −P−S−P−S−
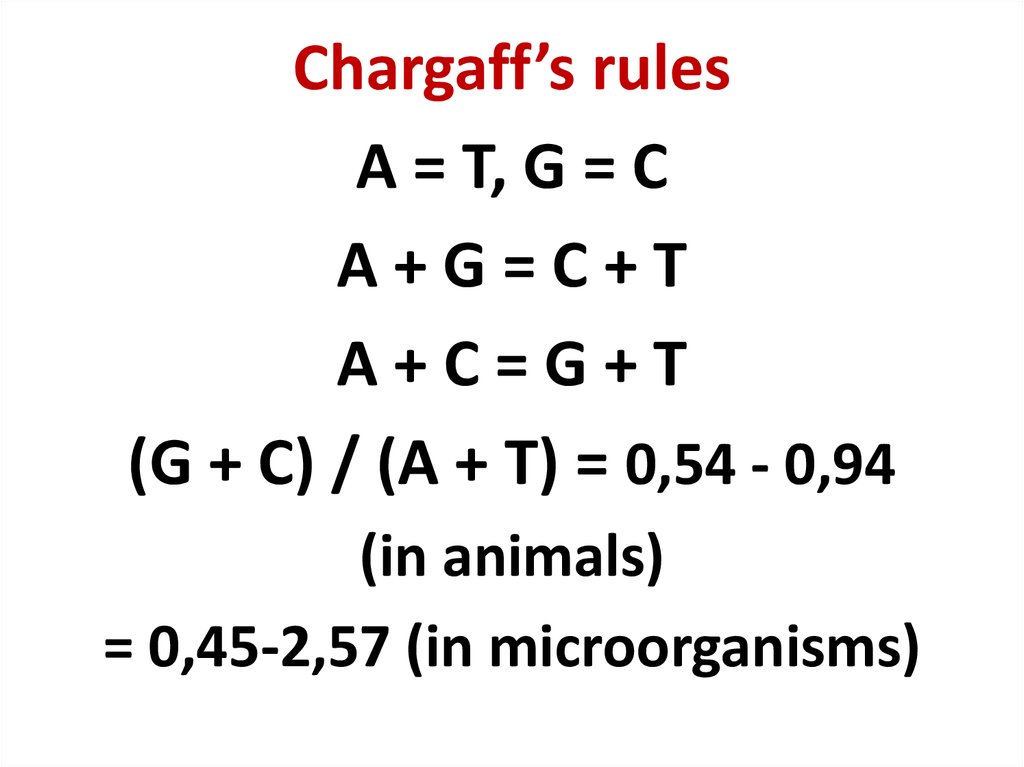
42. Chargaff’s rules
A = T, G = CA+G=C+T
A+C=G+T
(G + C) / (A + T) = 0,54 - 0,94
(in animals)
= 0,45-2,57 (in microorganisms)
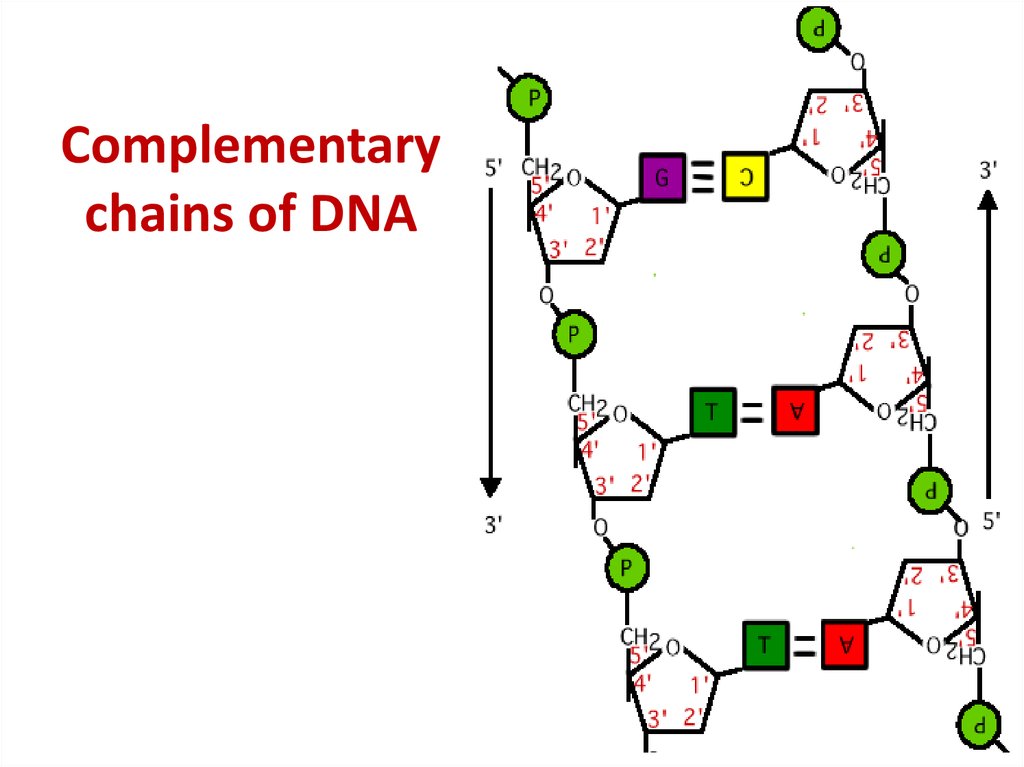
43. Complementary chains of DNA
Complementarychains of DNA
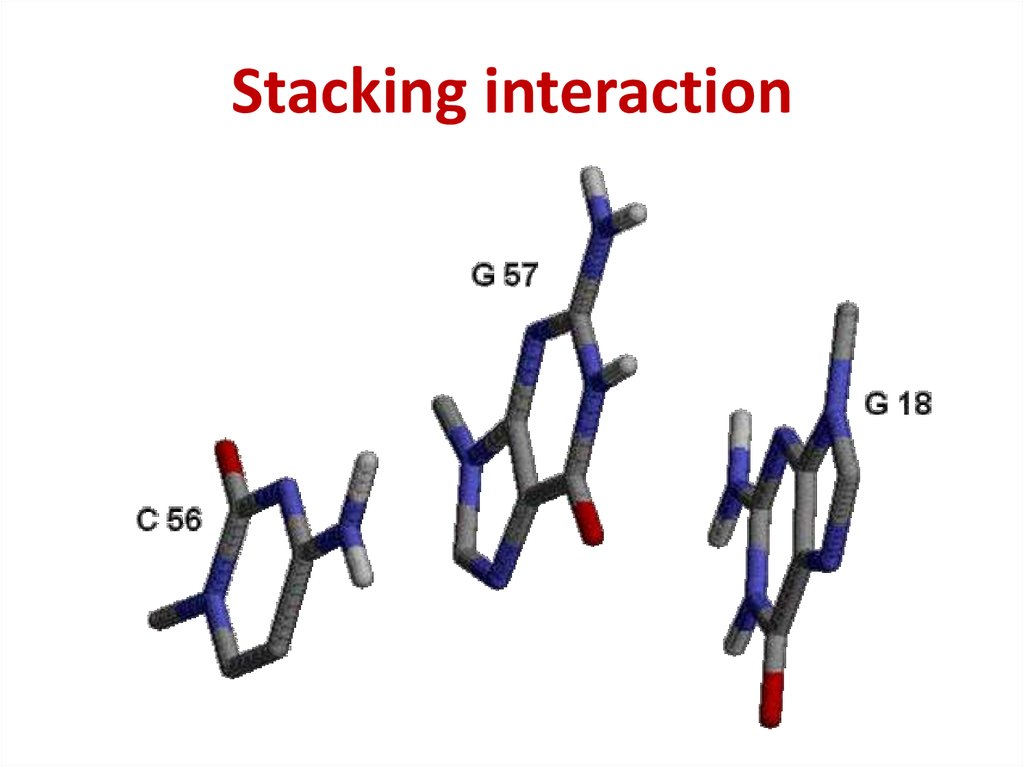
44. Stacking interaction
Stacking interaction45. The intensity of stacking
Purine – Purine >> Pyrimidine – Purine >
> Pyrimidine – Pyrimidine
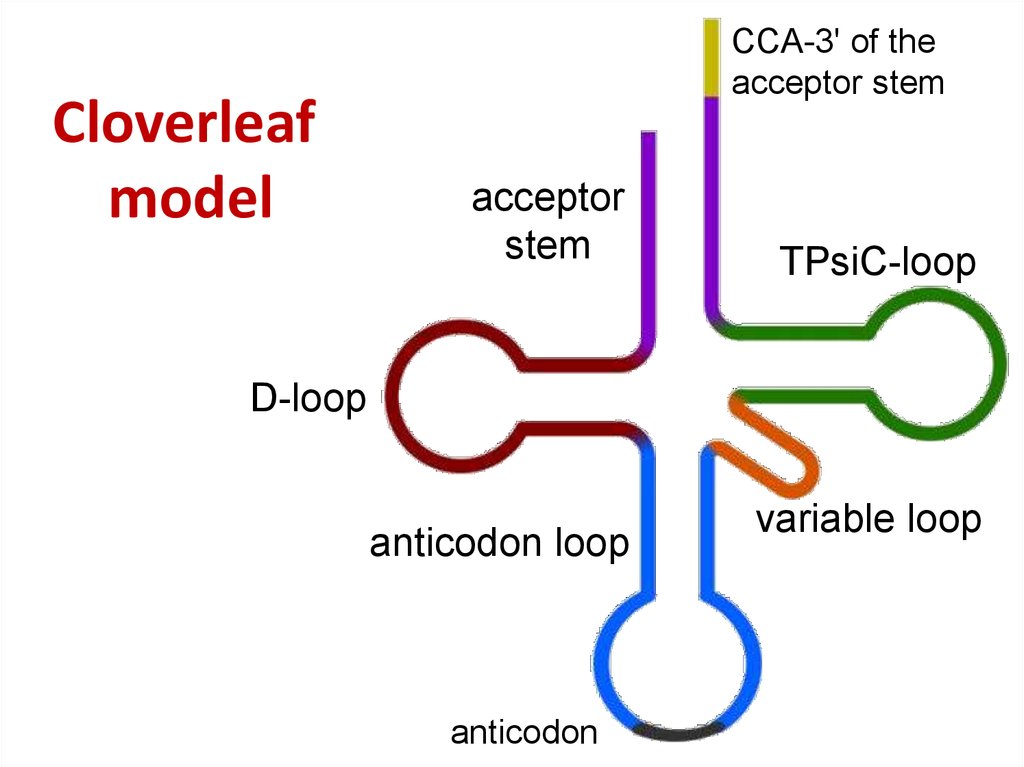
46. Cloverleaf model
Cloverleafmodel
CCA-3' of the
acceptor stem
acceptor
stem
TPsiC-loop
D-loop
anticodon loop
anticodon
variable loop
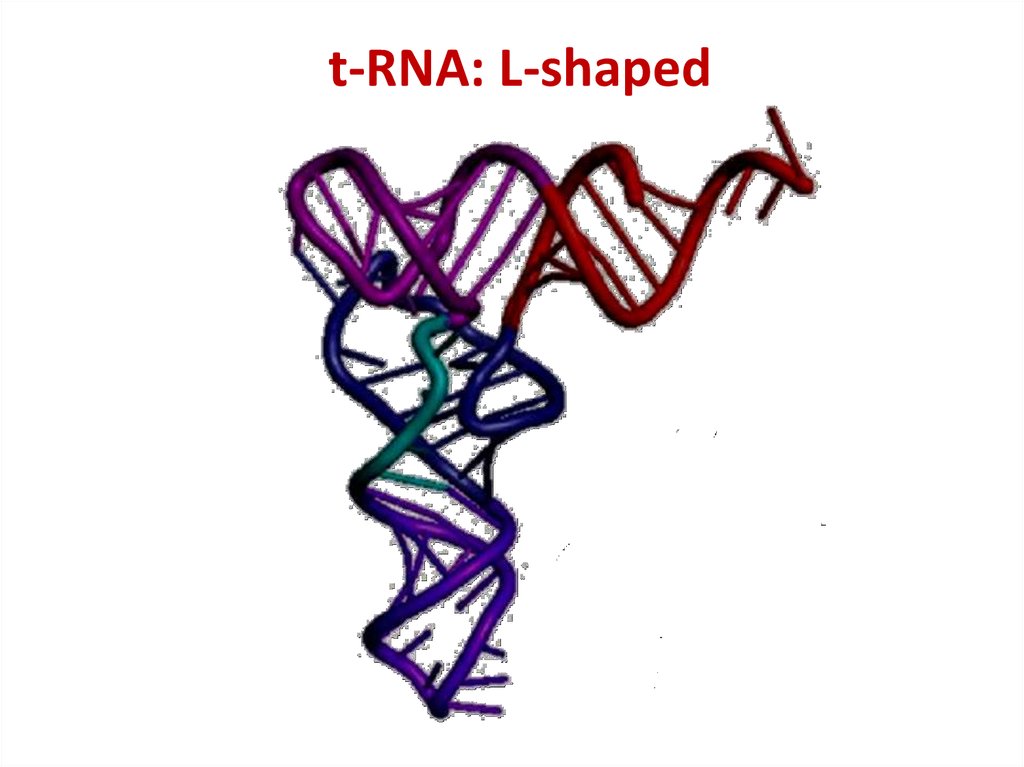
47. t-RNA: L-shaped
48. Вiochemistry of enzymes
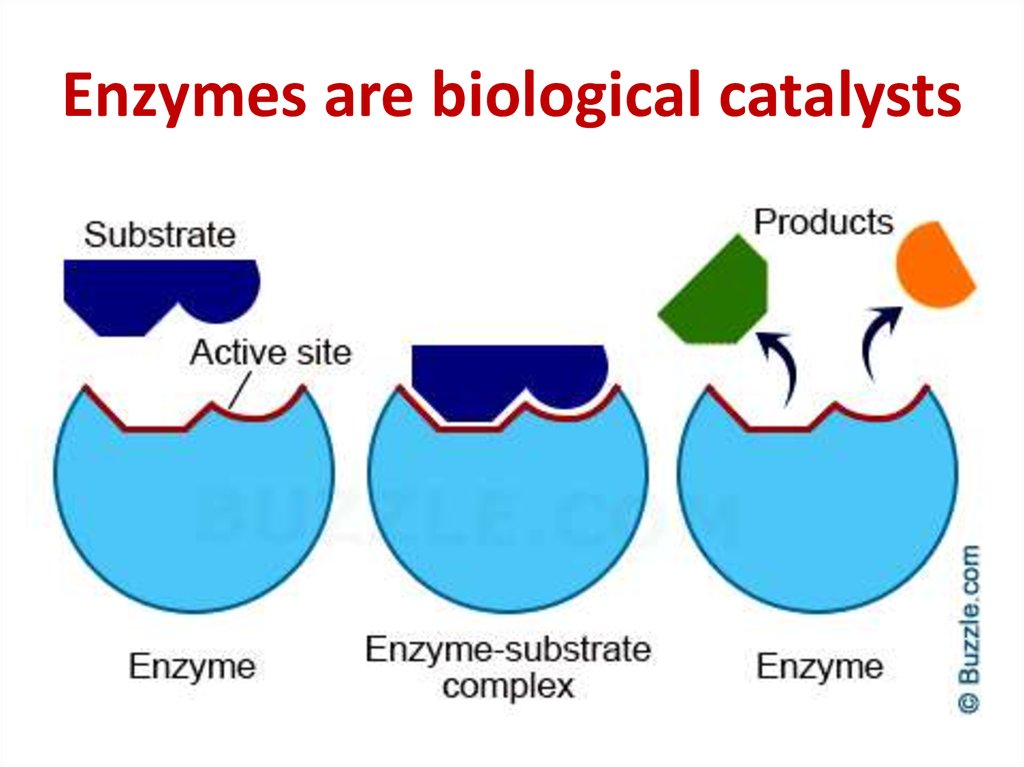
49. Enzymes are biological catalysts
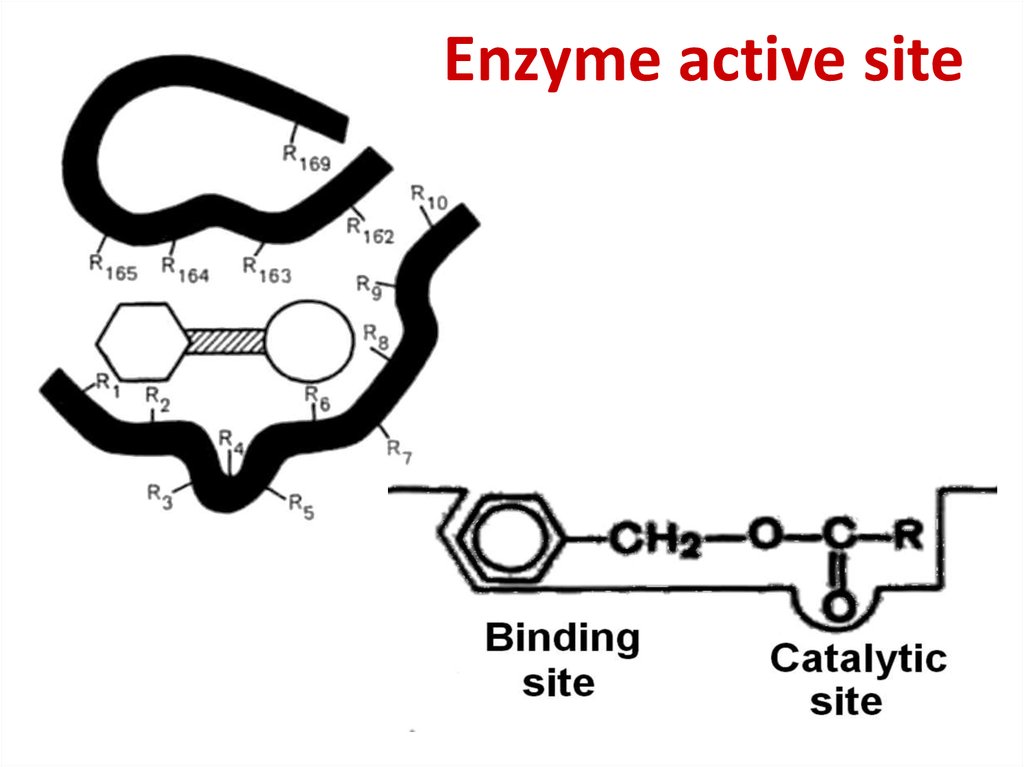
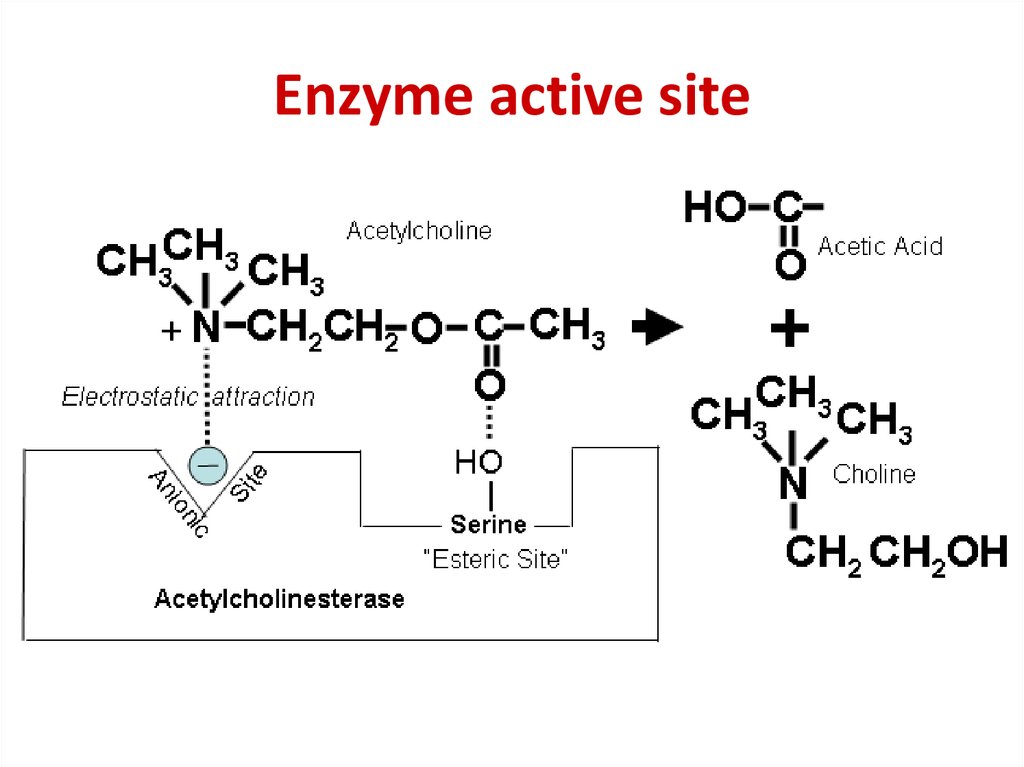
50. Enzyme active site
51. Enzyme active site
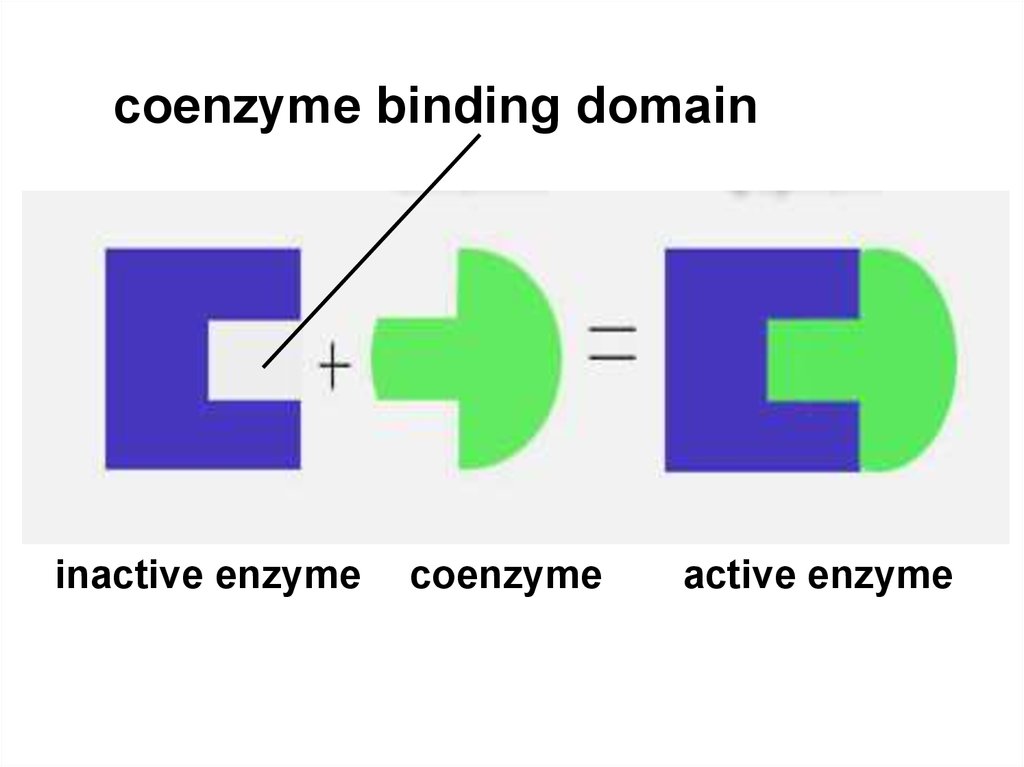
52.
coenzyme binding domaininactive enzyme
coenzyme
active enzyme
53.
The overallCoenzyme
role
Coenzyme A Activation and
transfer of
acyl groups
Pyridoxal
transfer
of amino
phosphate
groups
Transfer of
FAD
hydrogen
(electrons)
Vitamin
precursor
Pantothenic
acid
Pyridoxine Vitamin B6
Riboflavin Vitamin B2
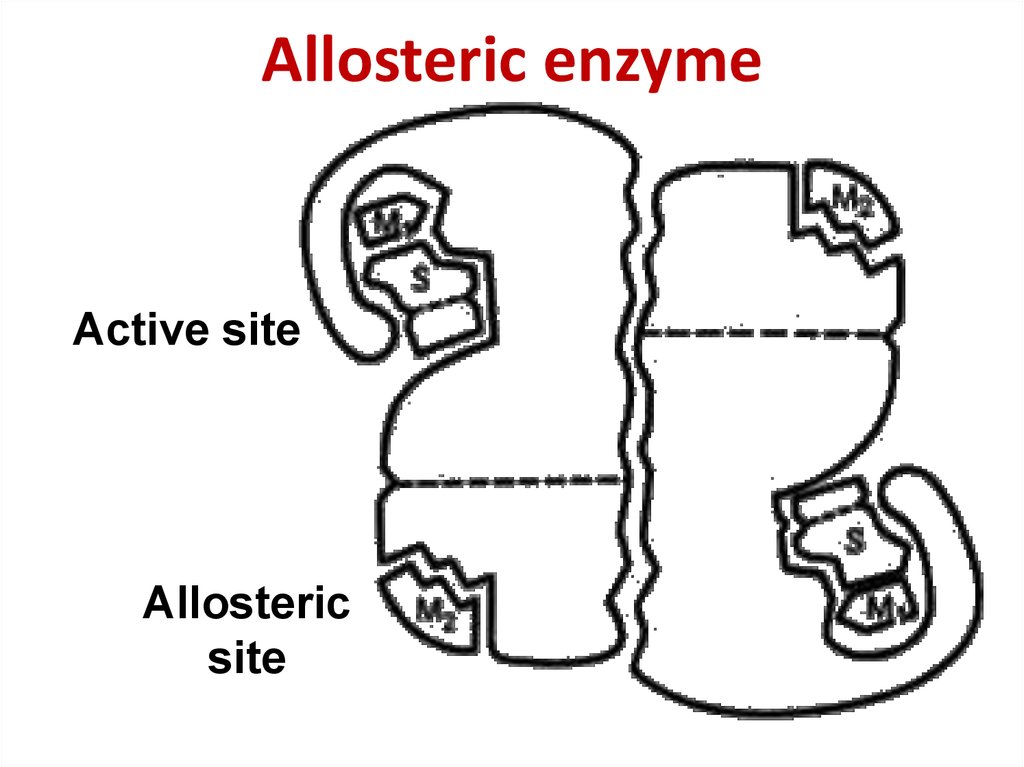
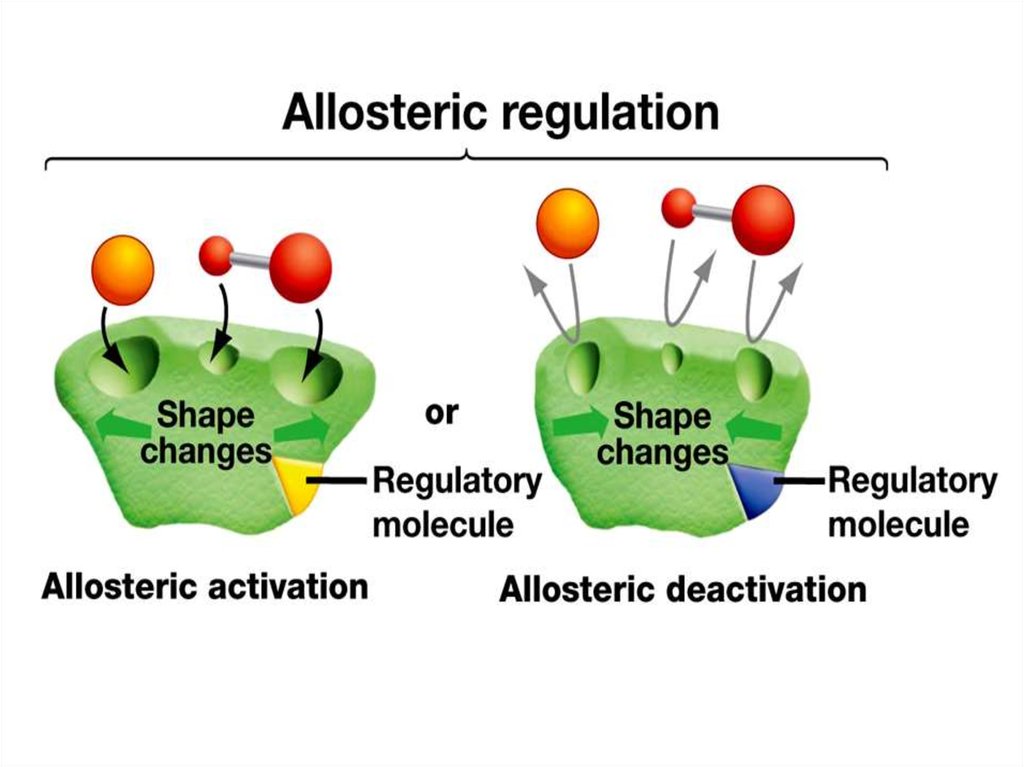
54. Allosteric enzyme
Allosteric enzymeActive site
Allosteric
site
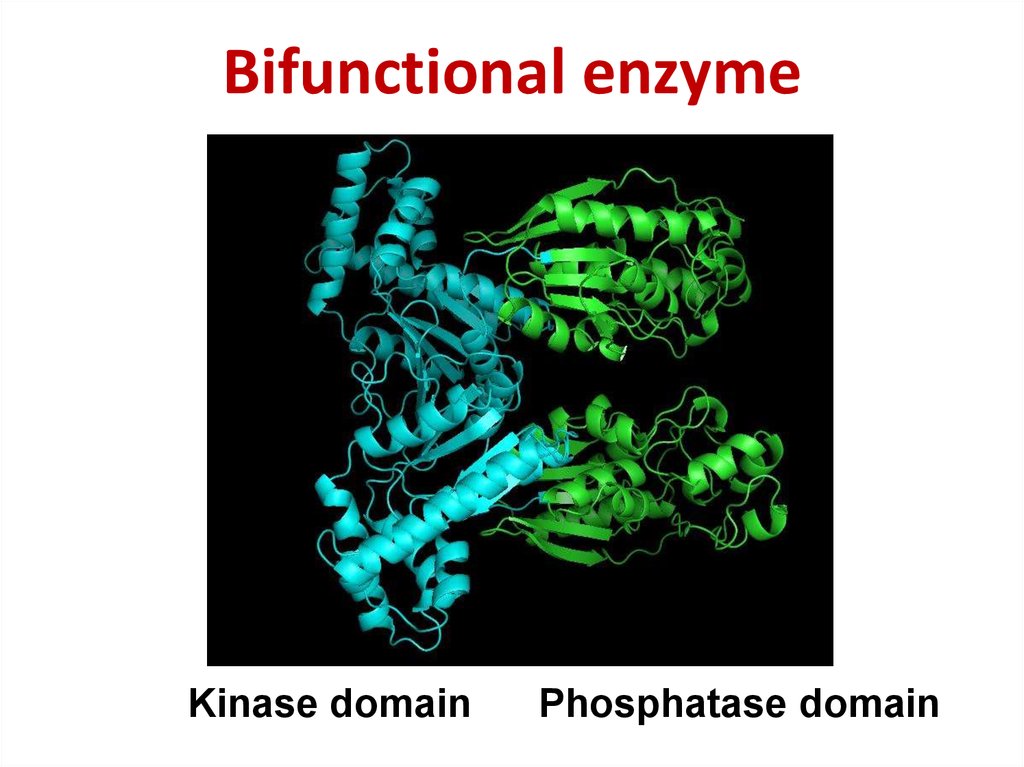
55. Bifunctional enzyme
Bifunctional enzymeKinase domain
Phosphatase domain
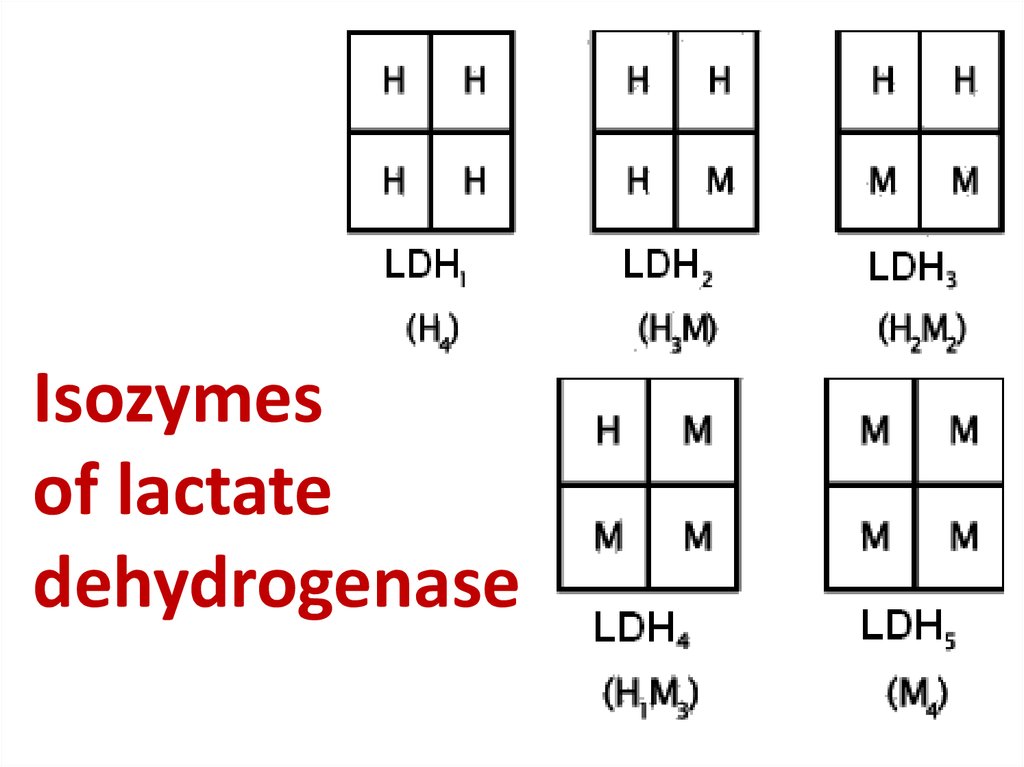
56. Isozymes of lactate dehydrogenase
57. Multimolecular enzyme systems
Multimolecular enzyme systemsNADPH oxidase
58.
Fumarateinner mitochondrial membrane
Succinate
matrix
intermembrane space
I, II, III and IV – mitochondrial
respiratory chain complexes
(the electron transport chain)
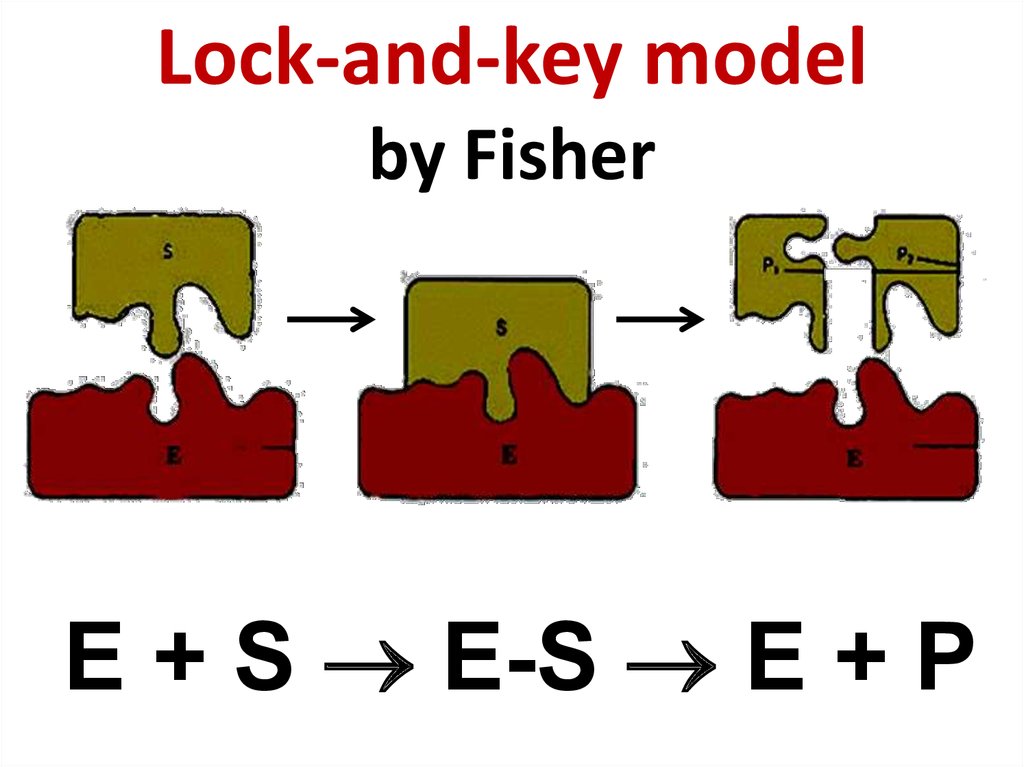
59. Hermann Emil Fischer (1852 - 1919)
Hermann Emil Fischer (1852 - 1919)60. Lock-and-key model by Fisher
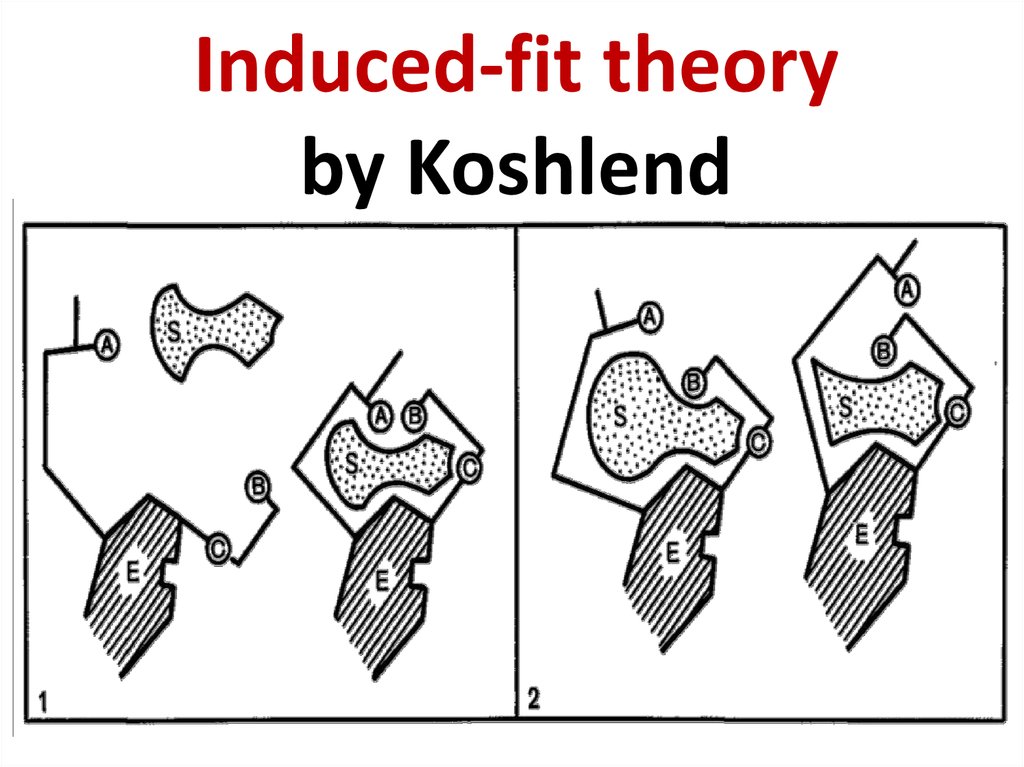
E + S E-S E + P61. Daniel Koshland (1920 - 2007)
Daniel Koshland (1920 - 2007)62. Induced-fit theory by Koshlend
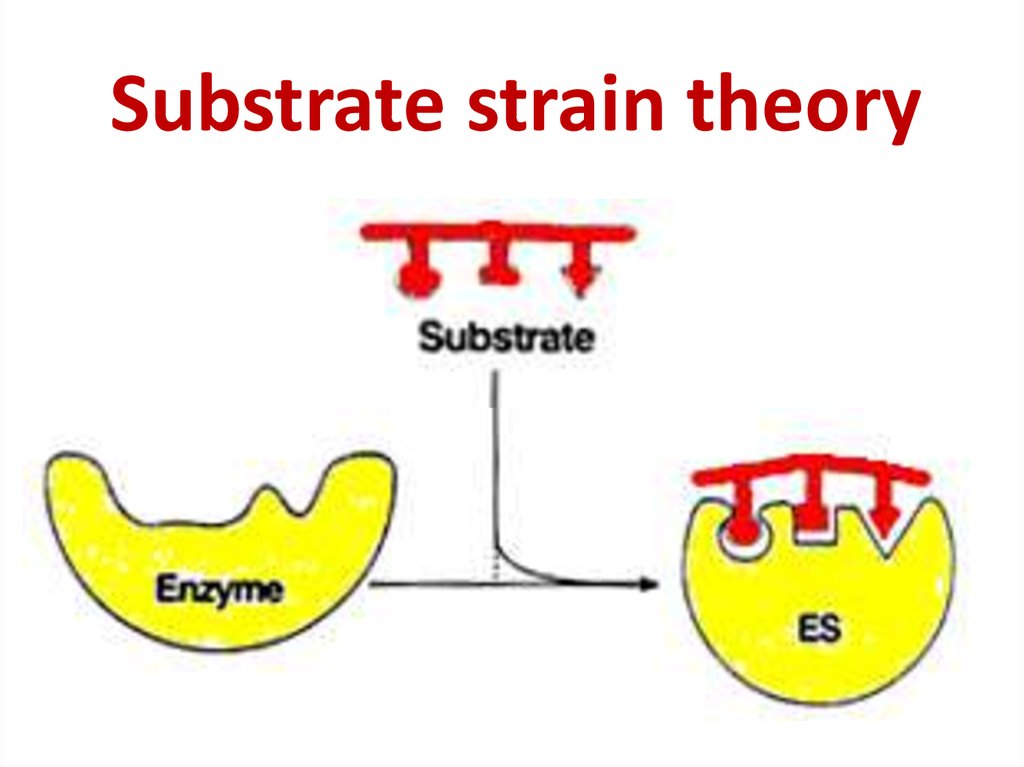
63. Substrate strain theory
64.
65. Leonor Michaelis
Enzyme kineticsLeonor Michaelis
Maud Leonora Menten
66.
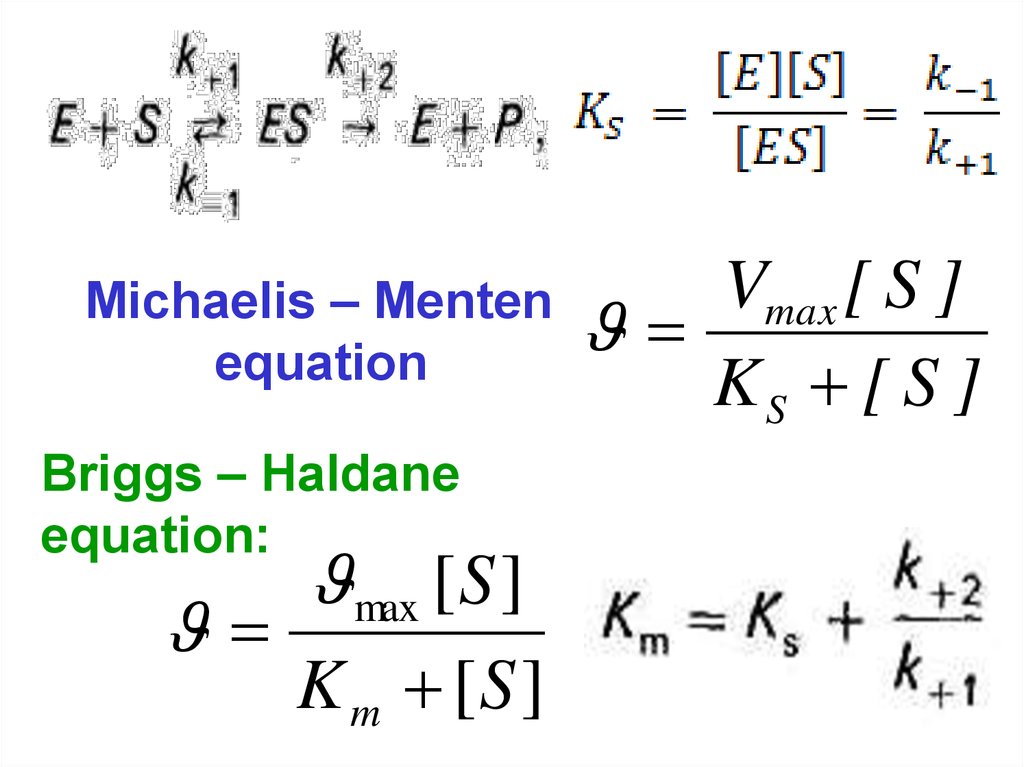
Michaelis – Mentenequation
Briggs – Haldane
equation:
max [ S ]
K m [S ]
Vmax [ S ]
KS [ S ]
67.
68. Lineweaver – Burk plot
69.
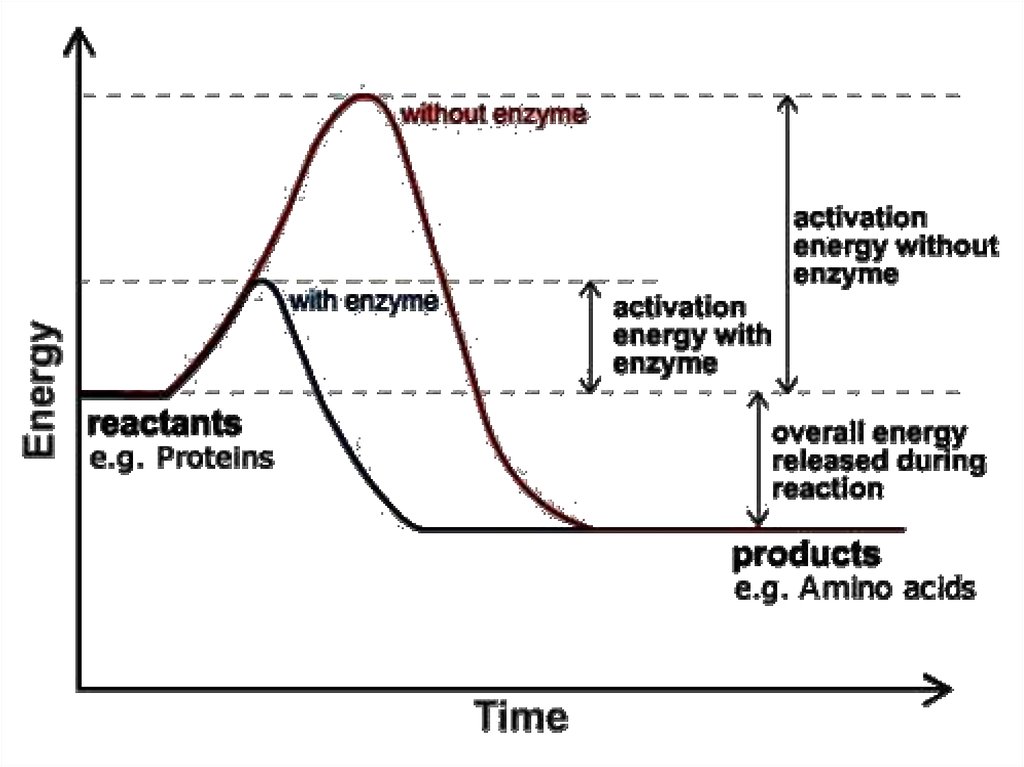
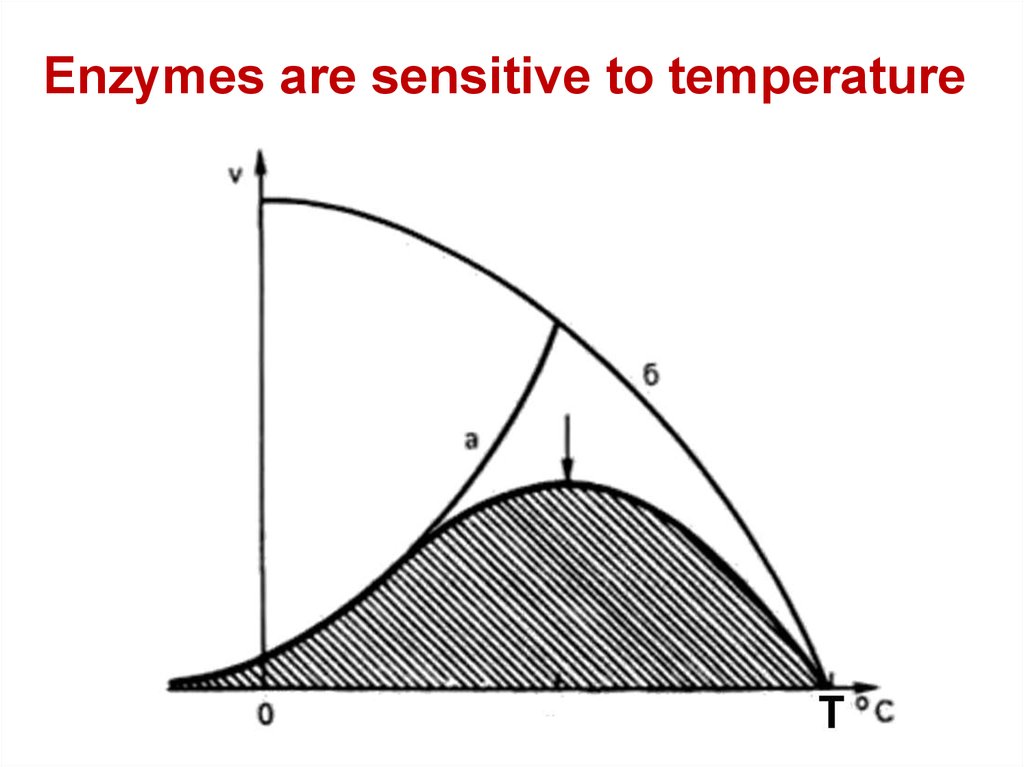
Enzymes are sensitive to temperature70.
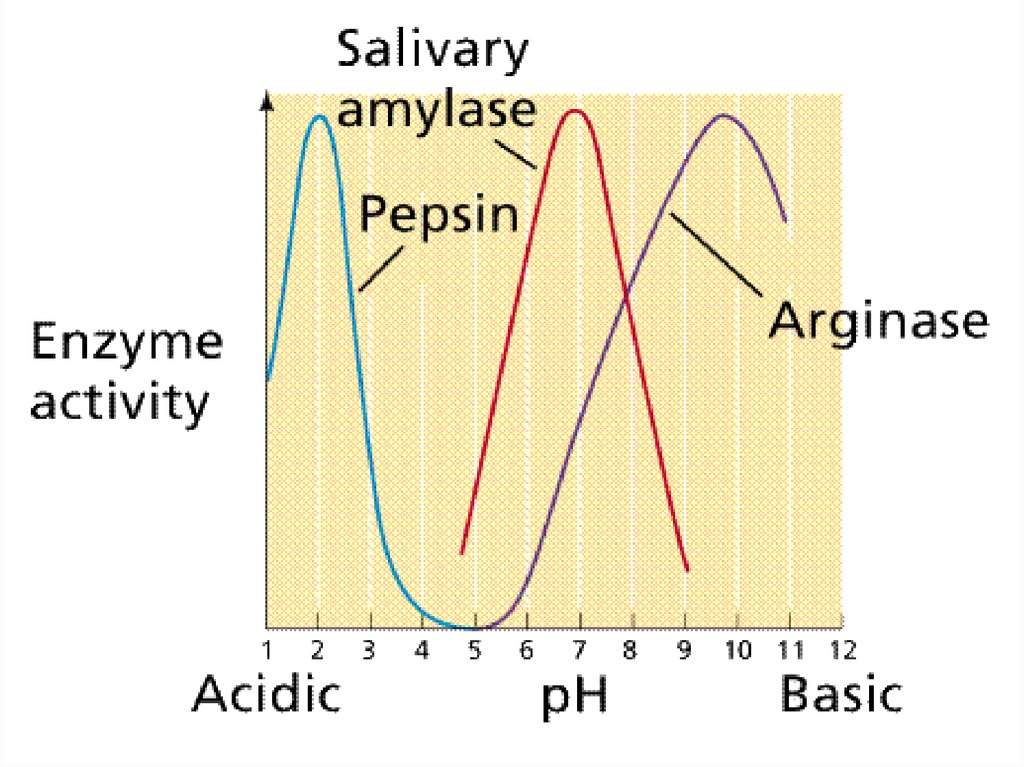
Enzymes are sensitive to pH71.
72.
Enzymes are very specific andonly work with certain substrates
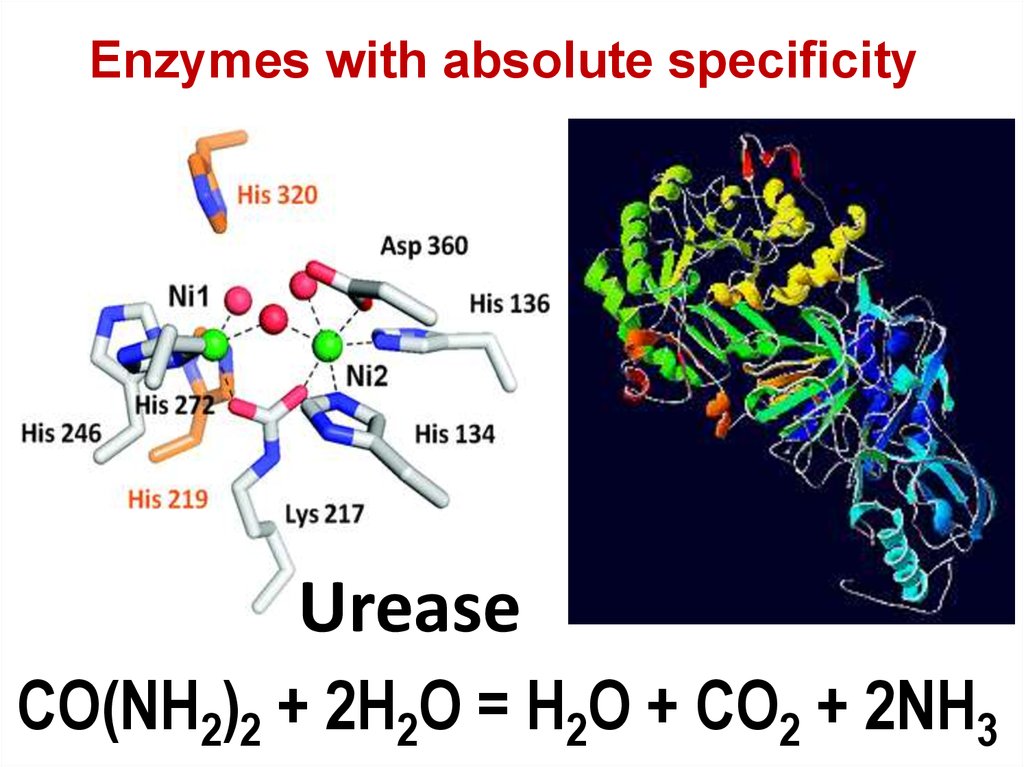
73. Urease
Enzymes with absolute specificityUrease
CO(NH2)2 + 2H2O = H2O + CO2 + 2NH3
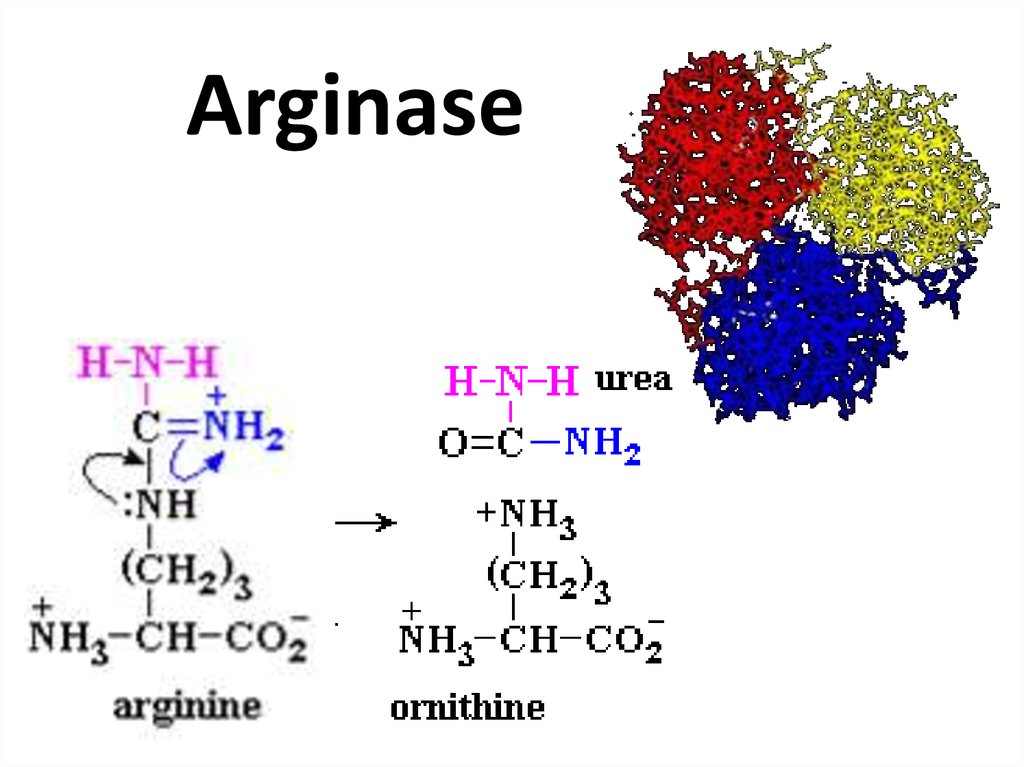
74. Arginase
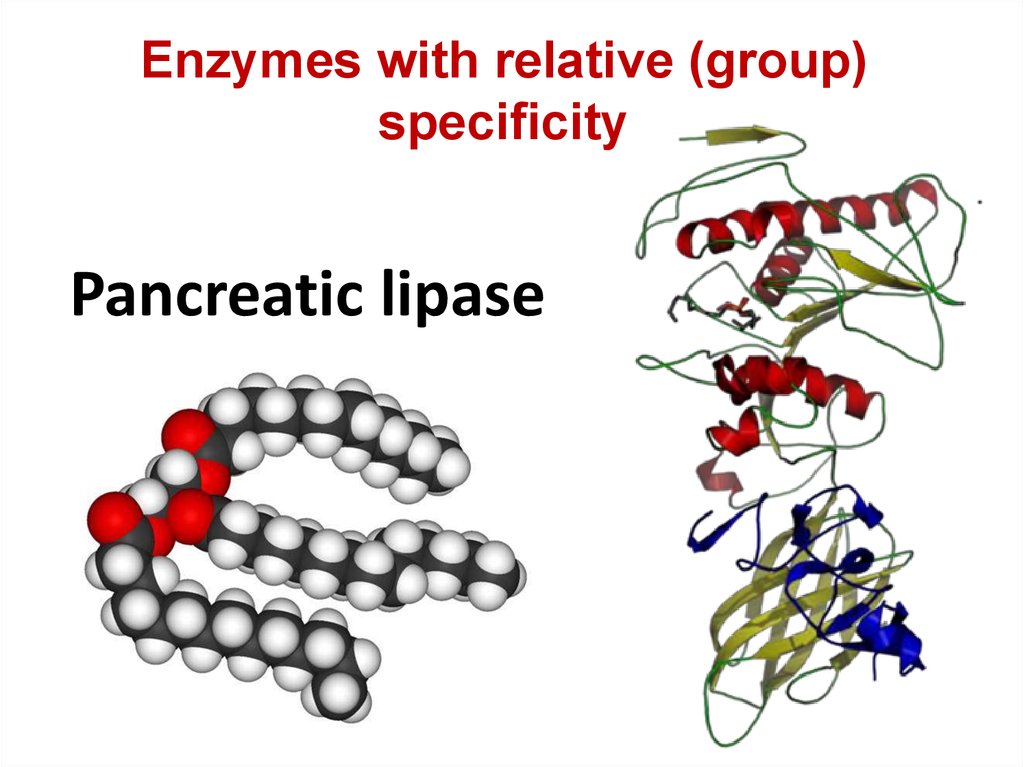
75. Pancreatic lipase
Enzymes with relative (group)specificity
Pancreatic lipase
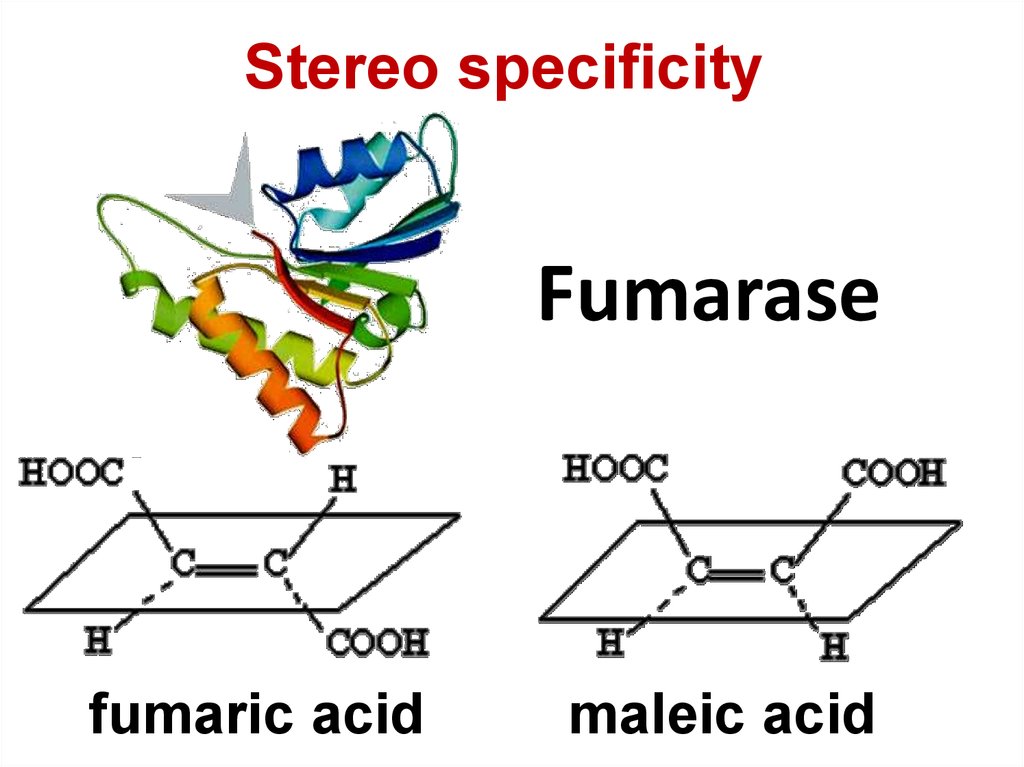
76. Fumarase
Stereo specificityFumarase
fumaric acid
maleic acid
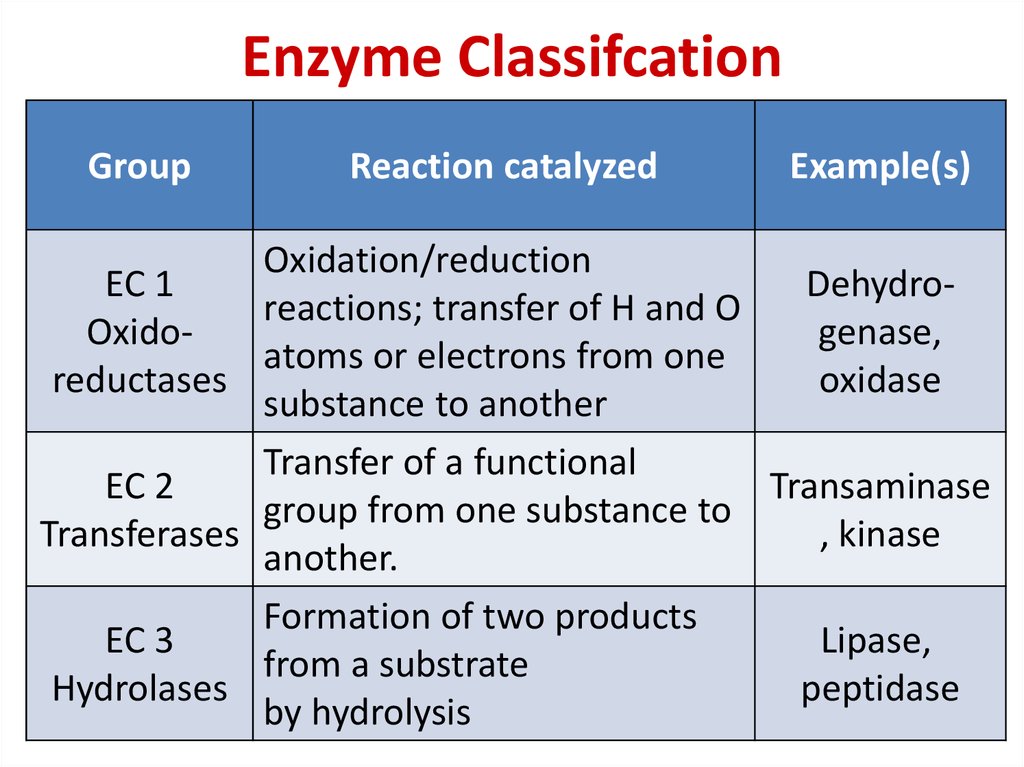
77. Enzyme Classifcation
GroupReaction catalyzed
Example(s)
Oxidation/reduction
EC 1
Dehydroreactions; transfer of H and O
Oxidogenase,
atoms or electrons from one
reductases
oxidase
substance to another
Transfer of a functional
EC 2
Transaminase
group from one substance to
Transferases
, kinase
another.
Formation of two products
EC 3
Lipase,
from a substrate
Hydrolases
peptidase
by hydrolysis
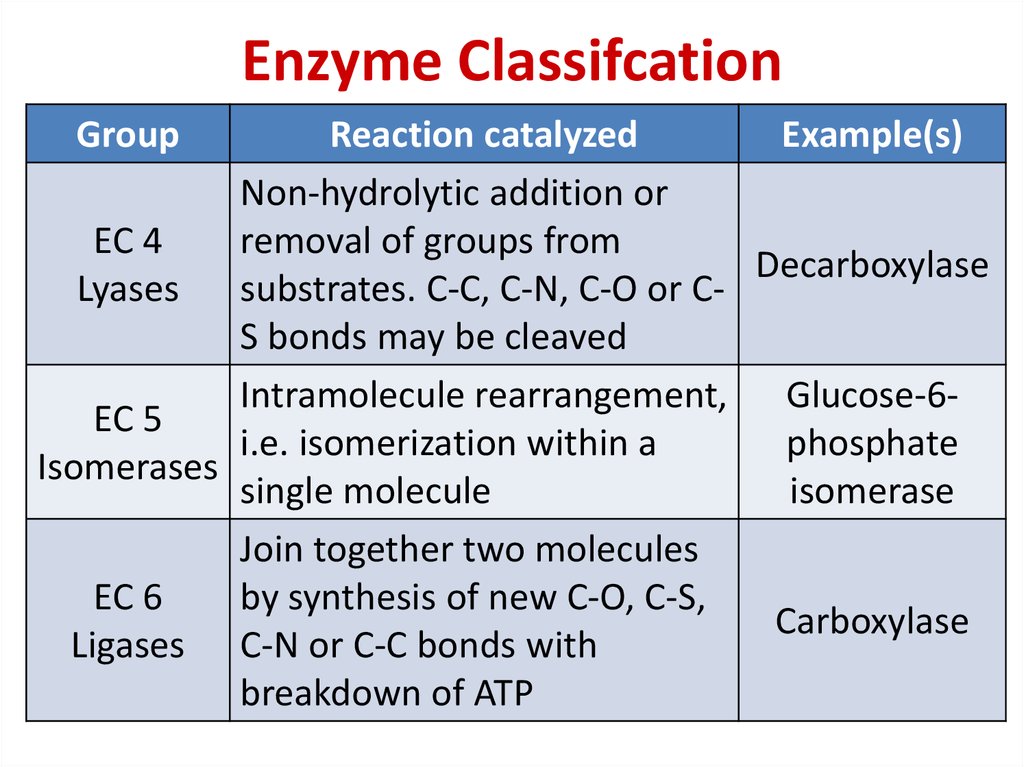
78. Enzyme Classifcation
GroupReaction catalyzed
Example(s)
Non-hydrolytic addition or
EC 4
removal of groups from
Decarboxylase
Lyases
substrates. C-C, C-N, C-O or CS bonds may be cleaved
Intramolecule rearrangement, Glucose-6EC 5
i.e. isomerization within a
phosphate
Isomerases
single molecule
isomerase
Join together two molecules
EC 6
by synthesis of new C-O, C-S,
Carboxylase
Ligases C-N or C-C bonds with
breakdown of ATP
79. Enzyme Classifcation
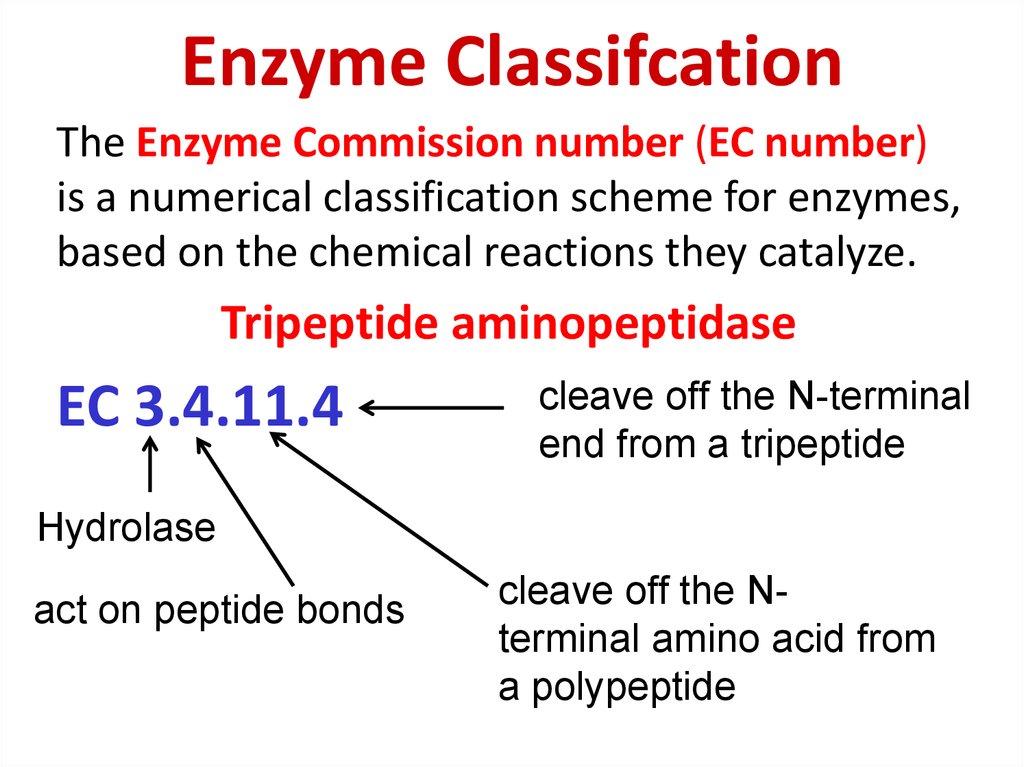
The Enzyme Commission number (EC number)is a numerical classification scheme for enzymes,
based on the chemical reactions they catalyze.
Tripeptide aminopeptidase
EC 3.4.11.4
cleave off the N-terminal
end from a tripeptide
Hydrolase
act on peptide bonds
cleave off the Nterminal amino acid from
a polypeptide
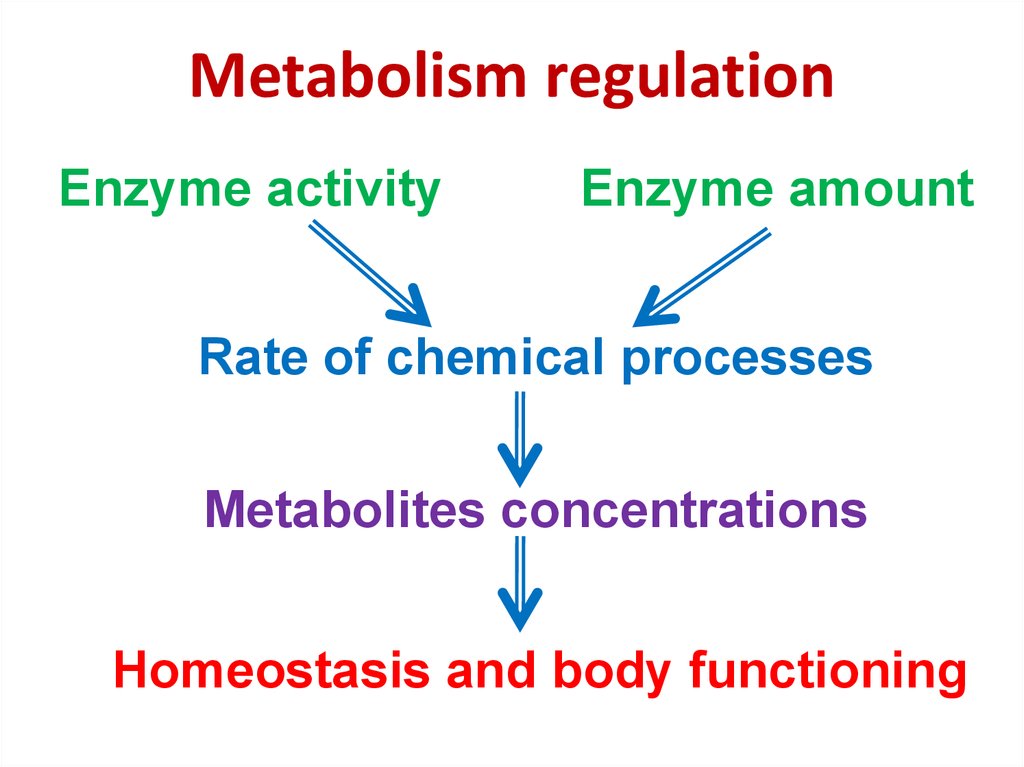
80. Metabolism regulation
Enzyme activityEnzyme amount
Rate of chemical processes
Metabolites concentrations
Homeostasis and body functioning
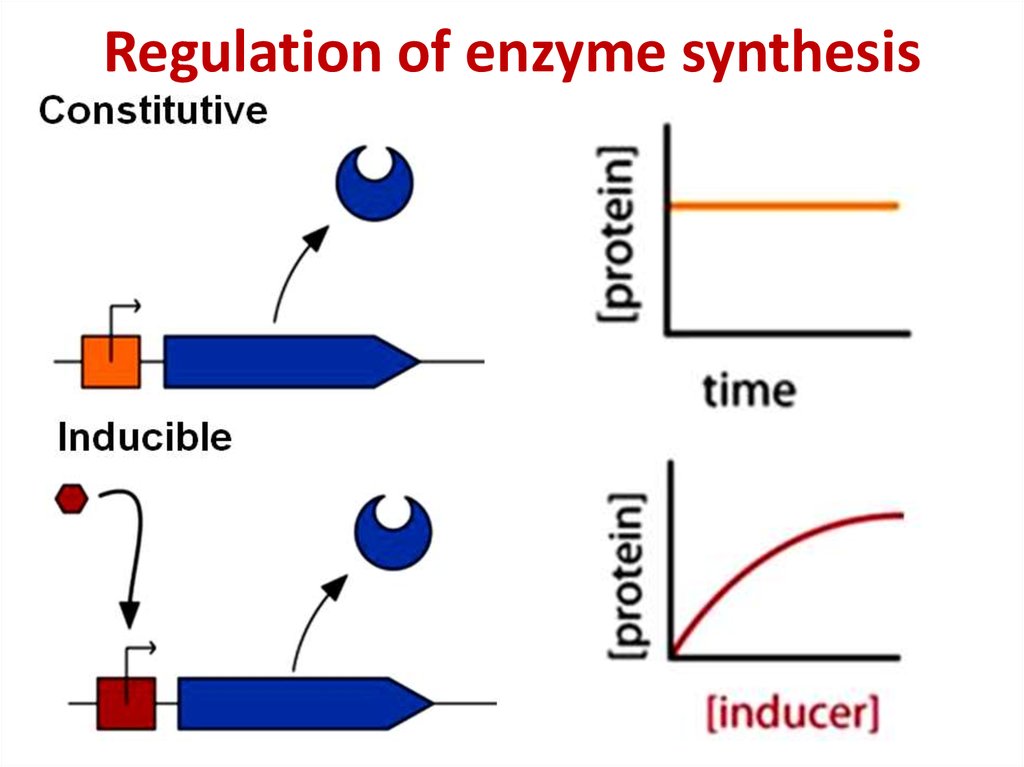
81. Regulation of enzyme synthesis
82. Regulation of enzyme activity
Regulation ofenzyme activity
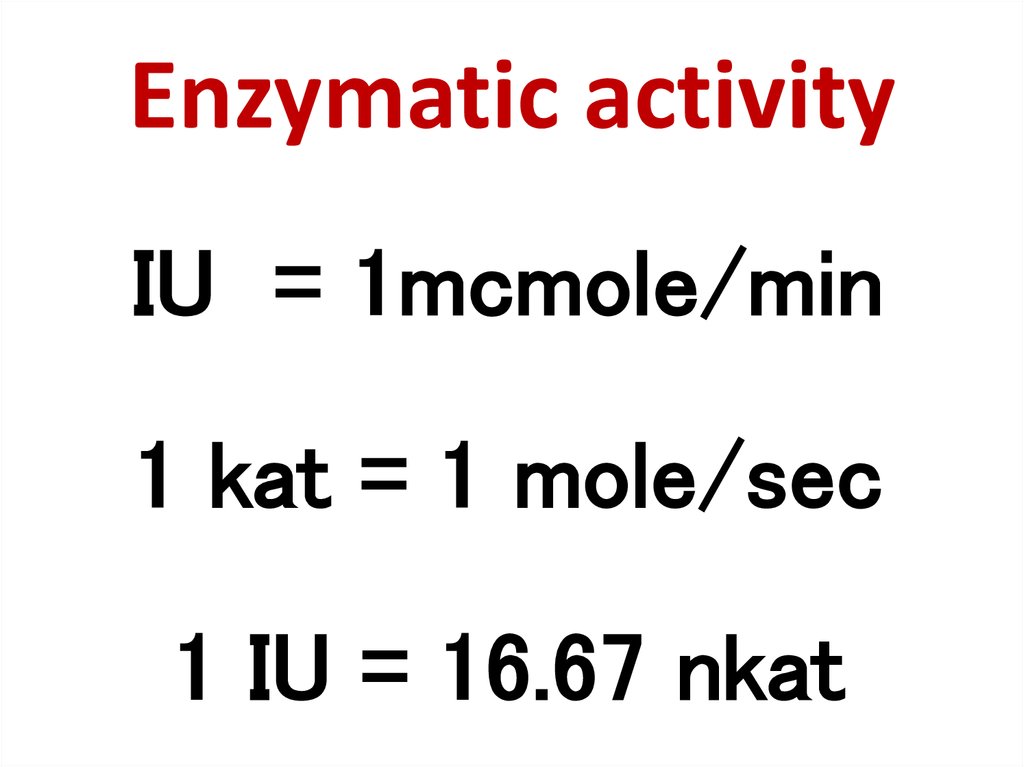
83. Enzymatic activity
IU = 1mcmole/min1 kat = 1 mole/sec
1 IU = 16.67 nkat
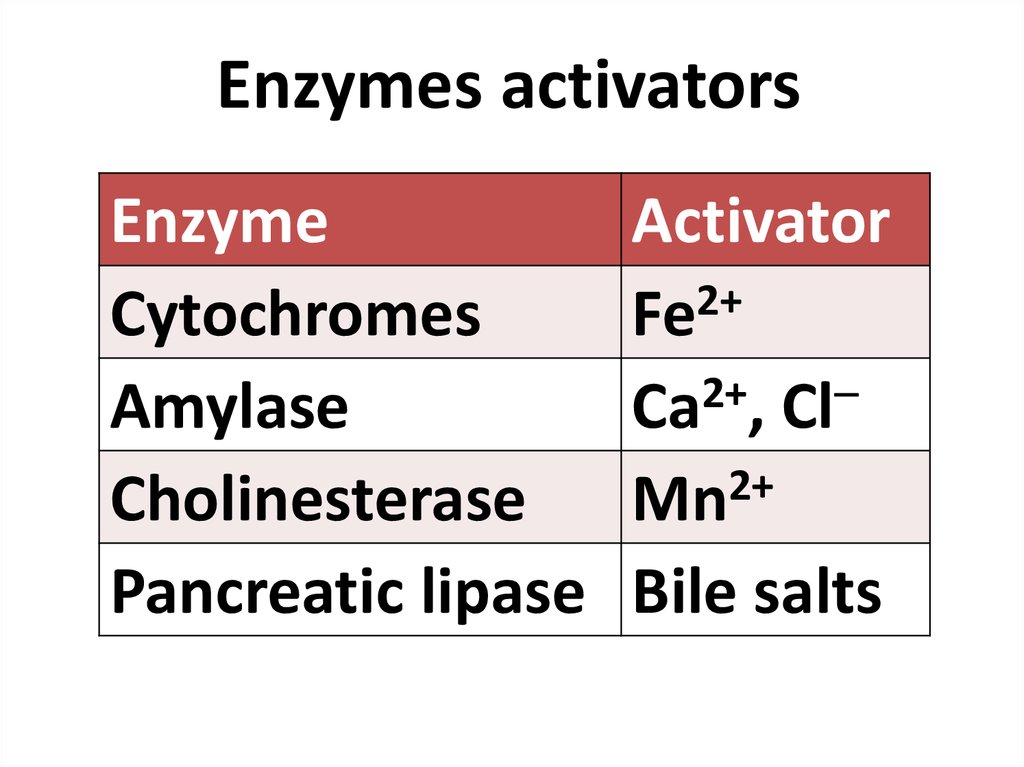
84. Enzymes activators
Enzymes activatorsEnzyme
Cytochromes
Amylase
Cholinesterase
Pancreatic lipase
Activator
Fe2+
2+
Ca , Cl
2+
Mn
Bile salts
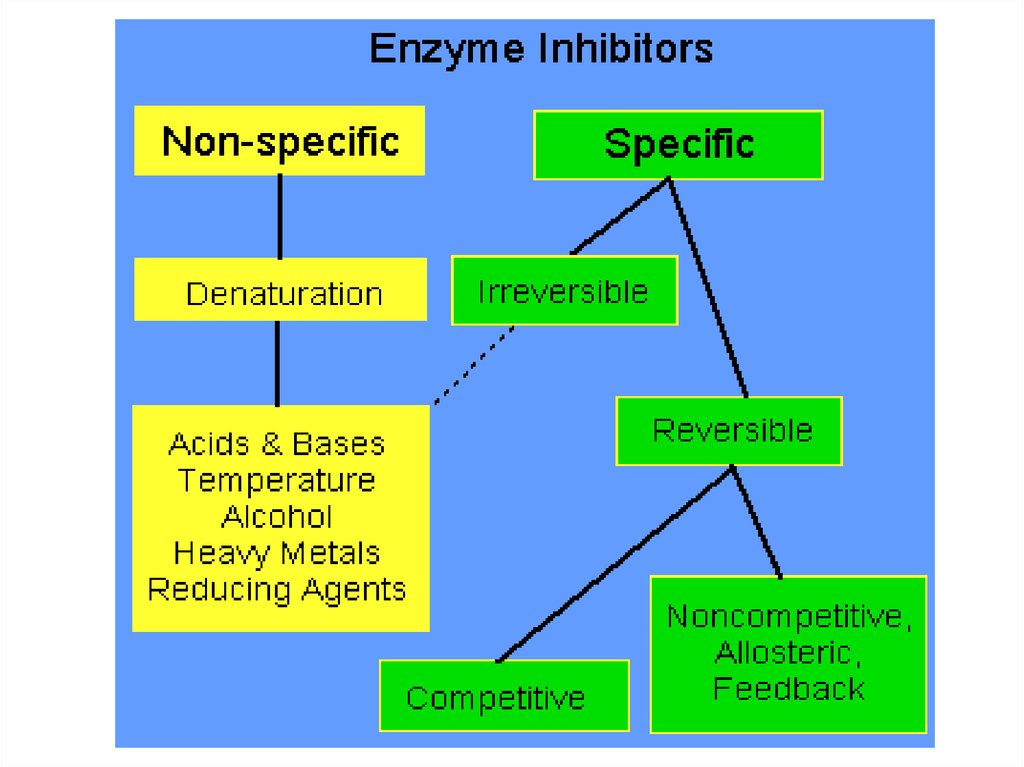
85.
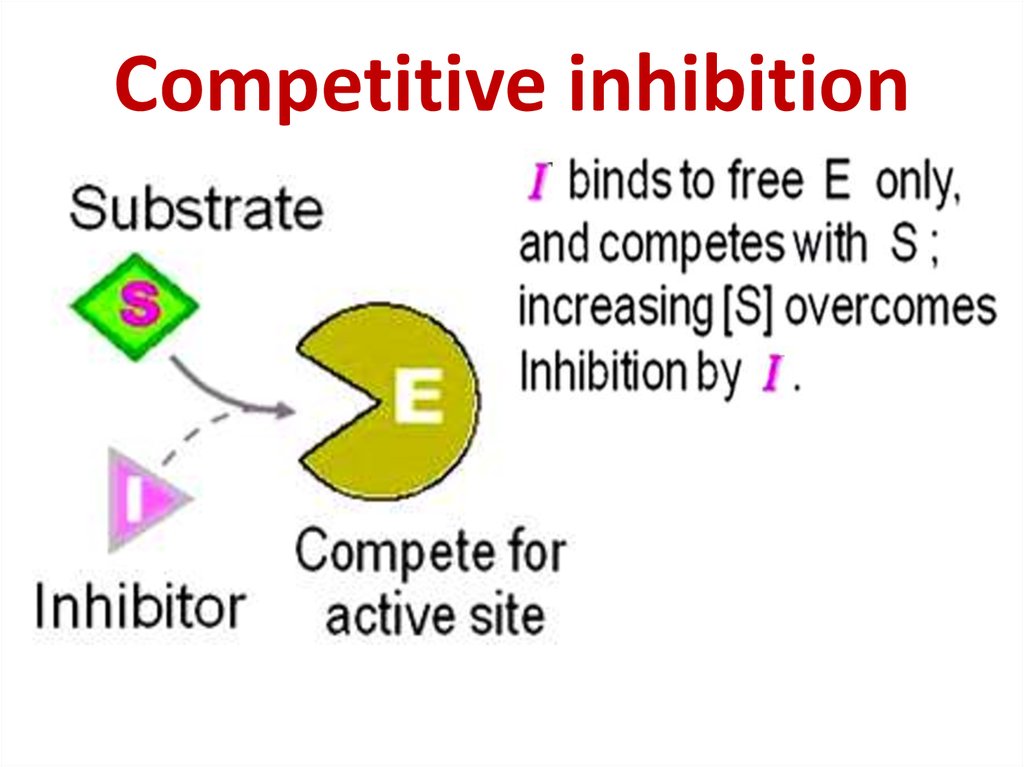
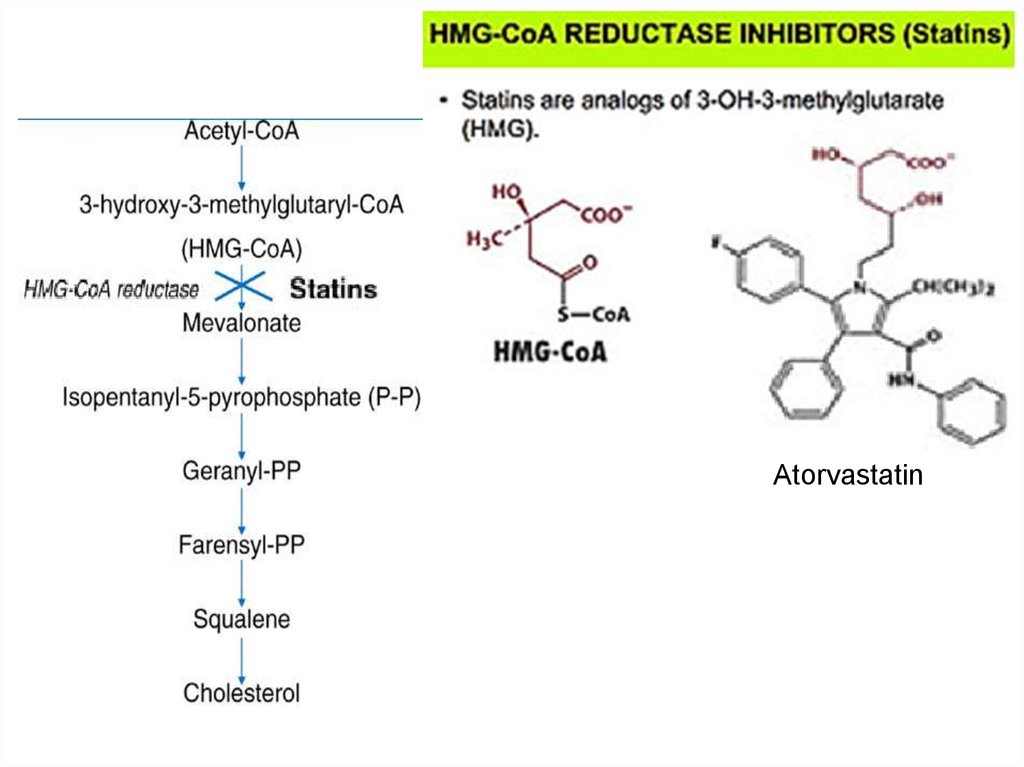
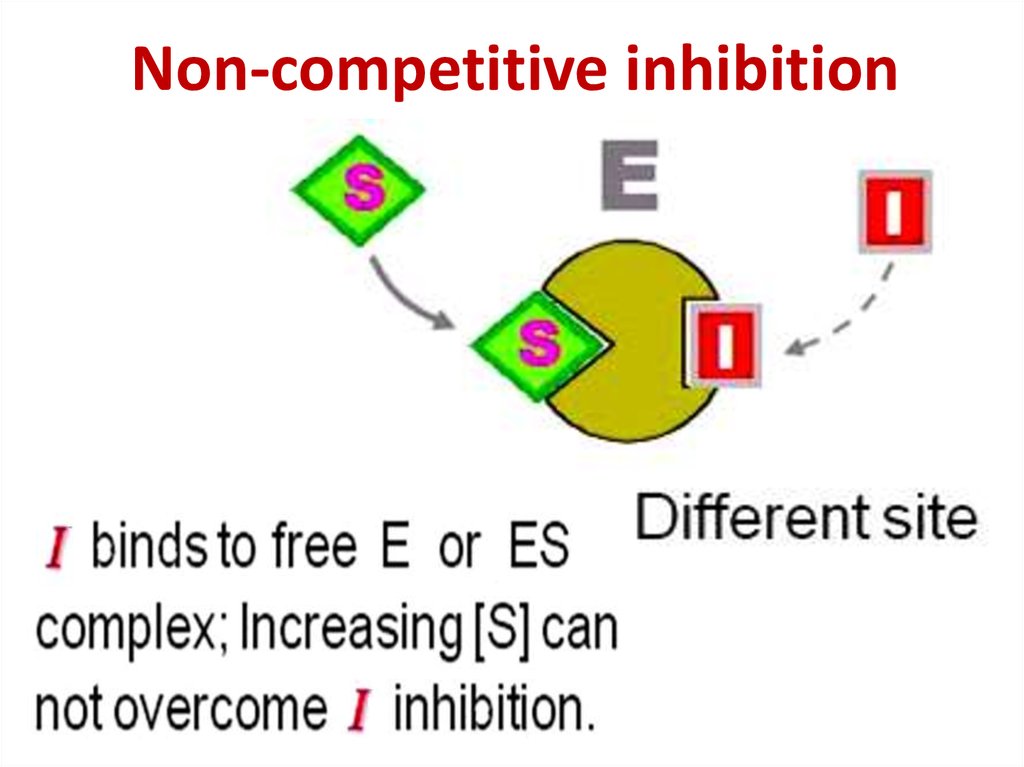
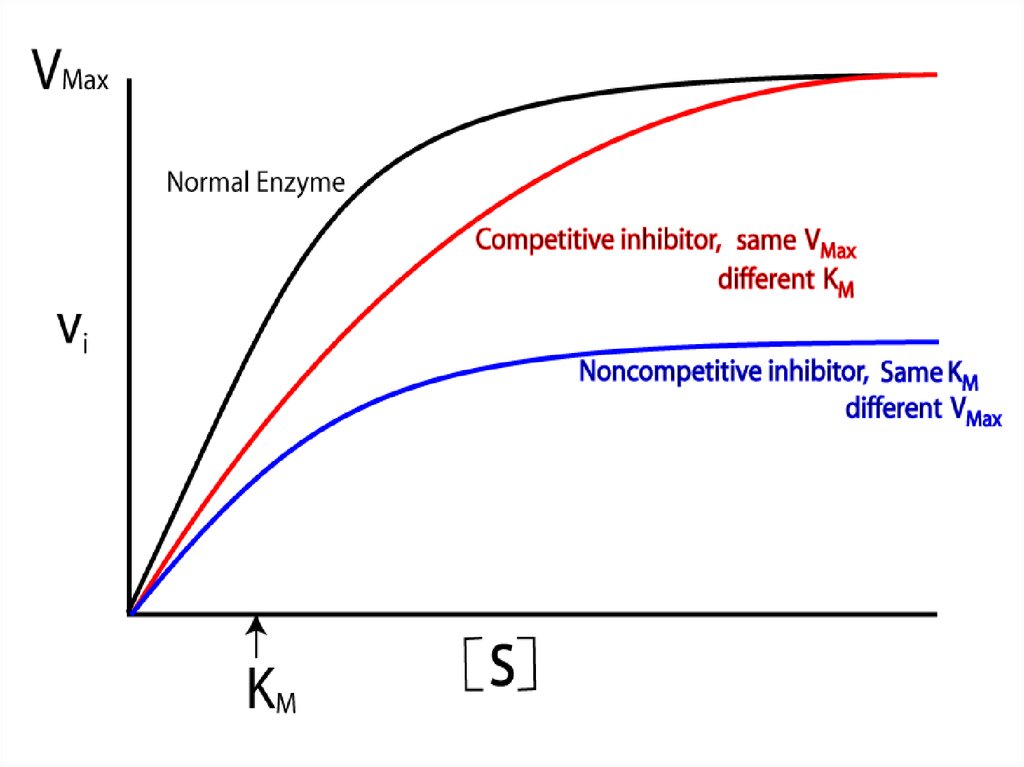
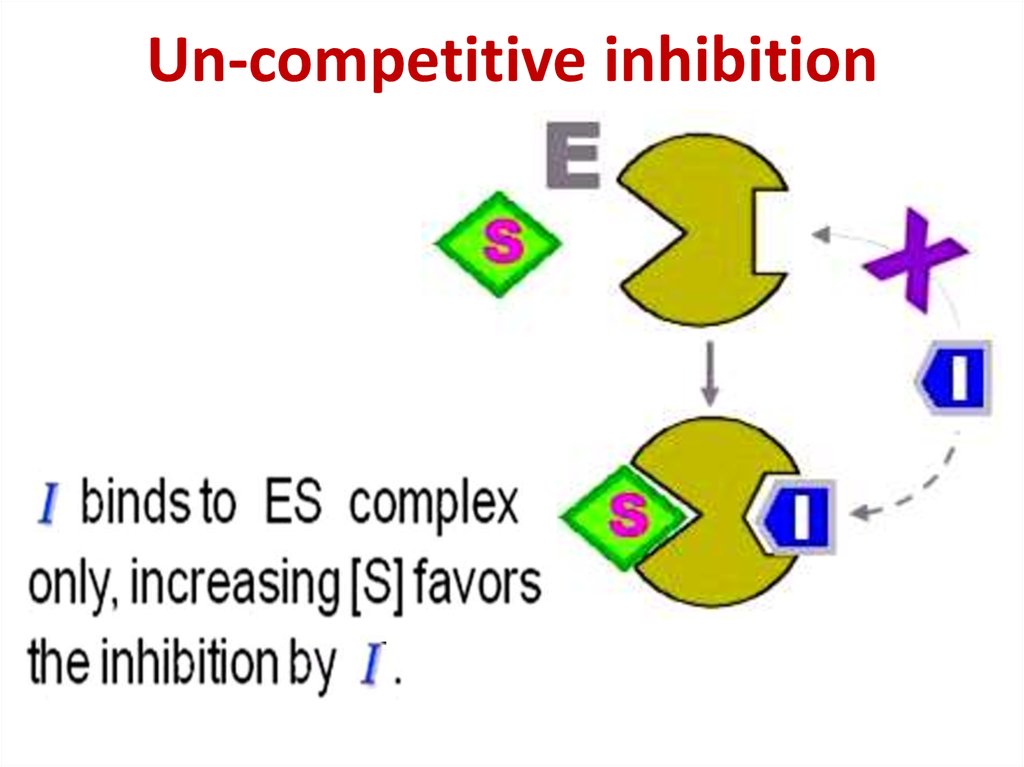
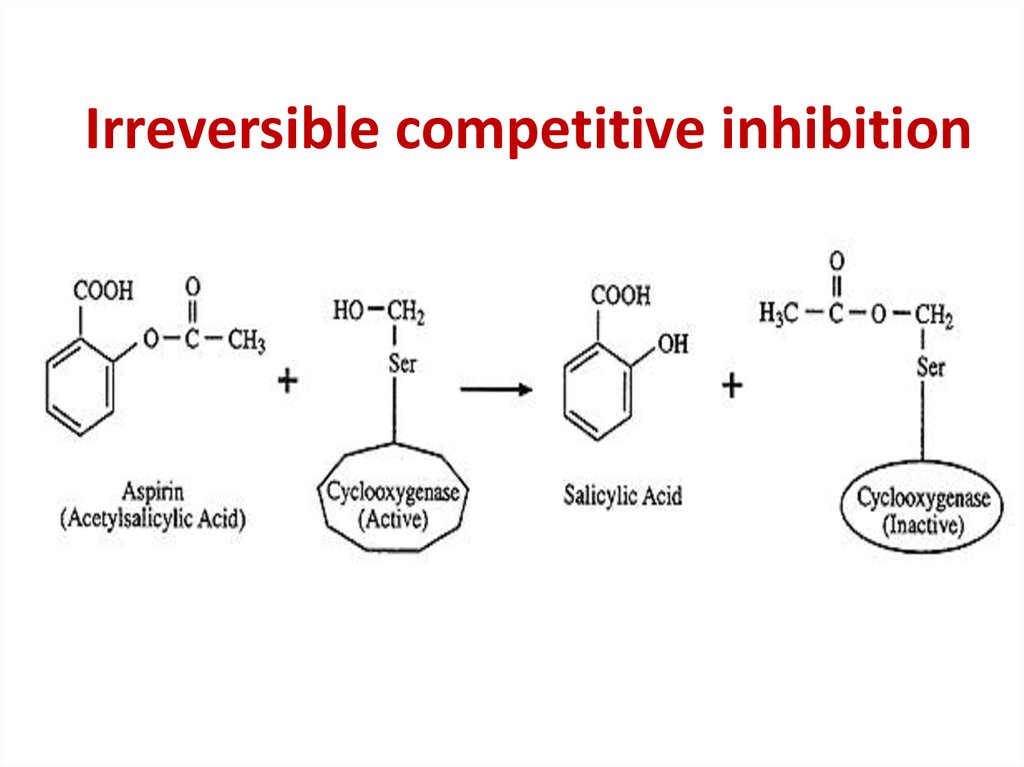
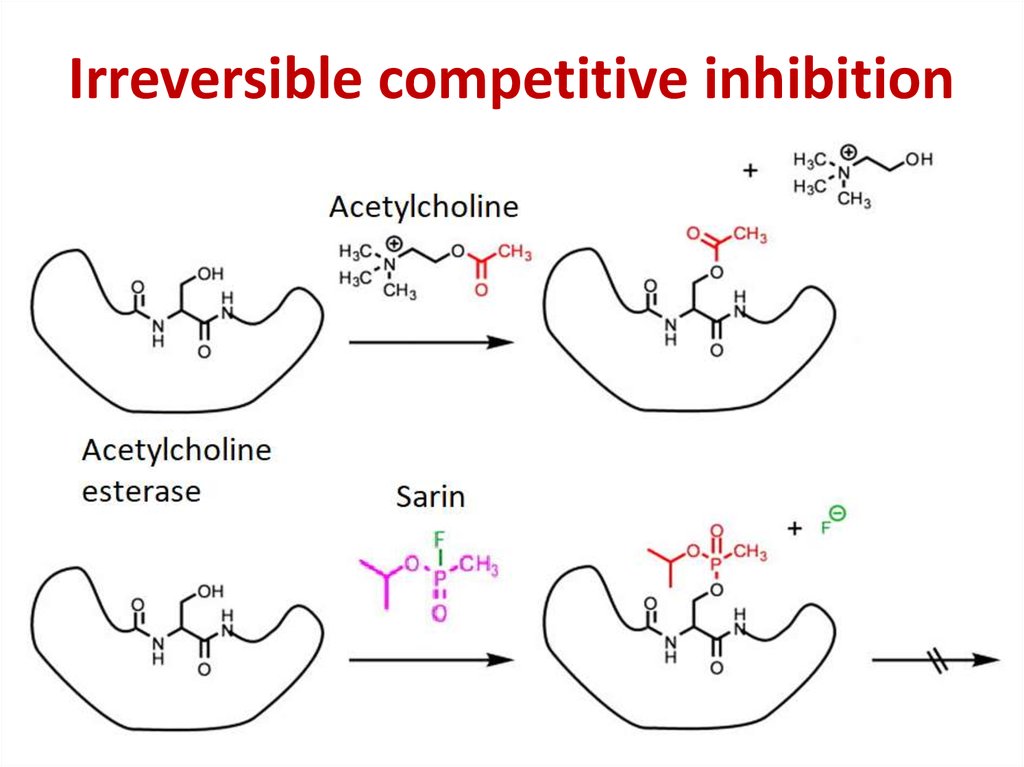
86. Competitive inhibition
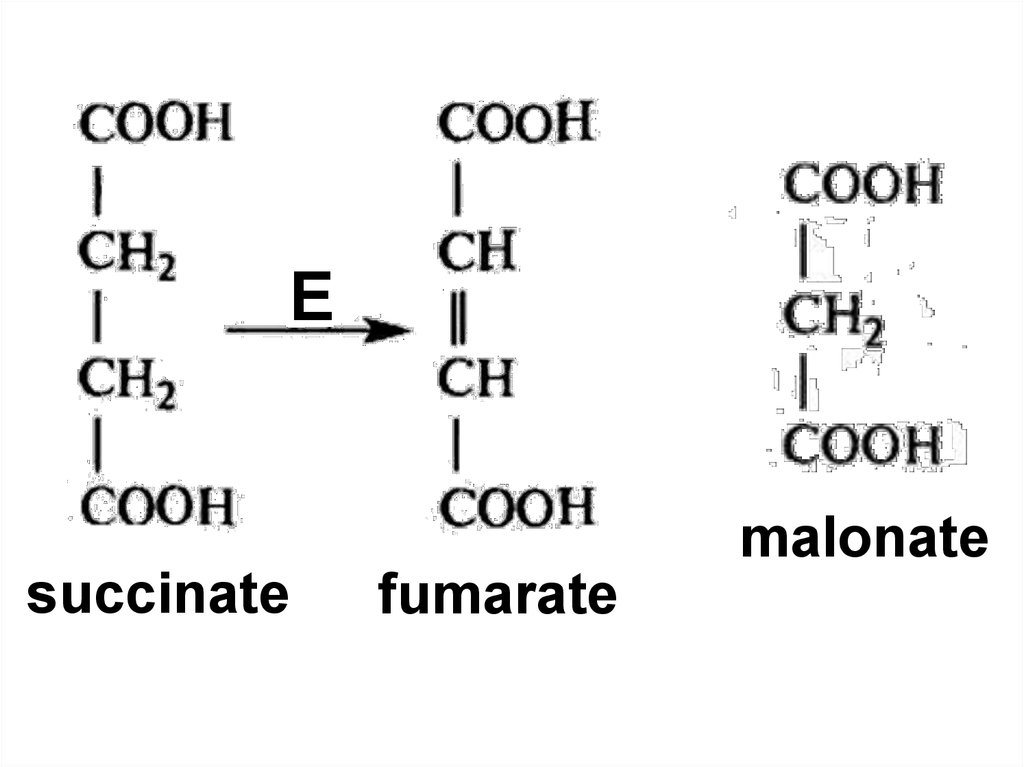
Competitive inhibition87.
malonatesuccinate
fumarate
88.
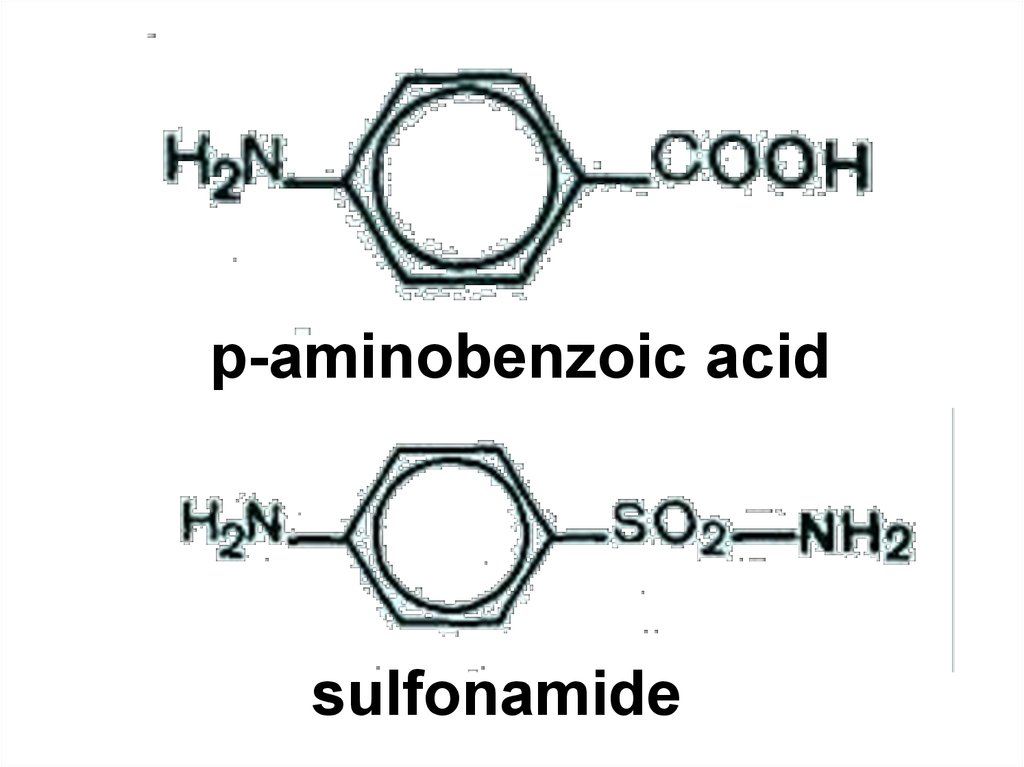
p-aminobenzoic acidsulfonamide















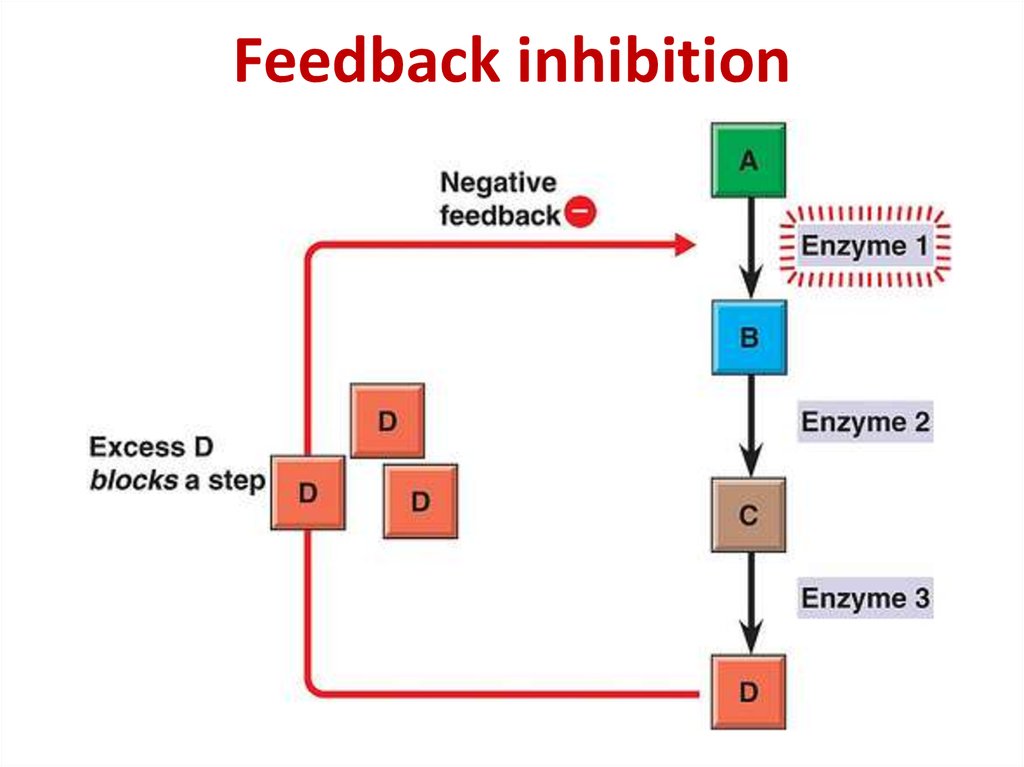
 chemistry
chemistry








