Similar presentations:
Carbohydrate metabolism
1. Carbohydrate metabolism
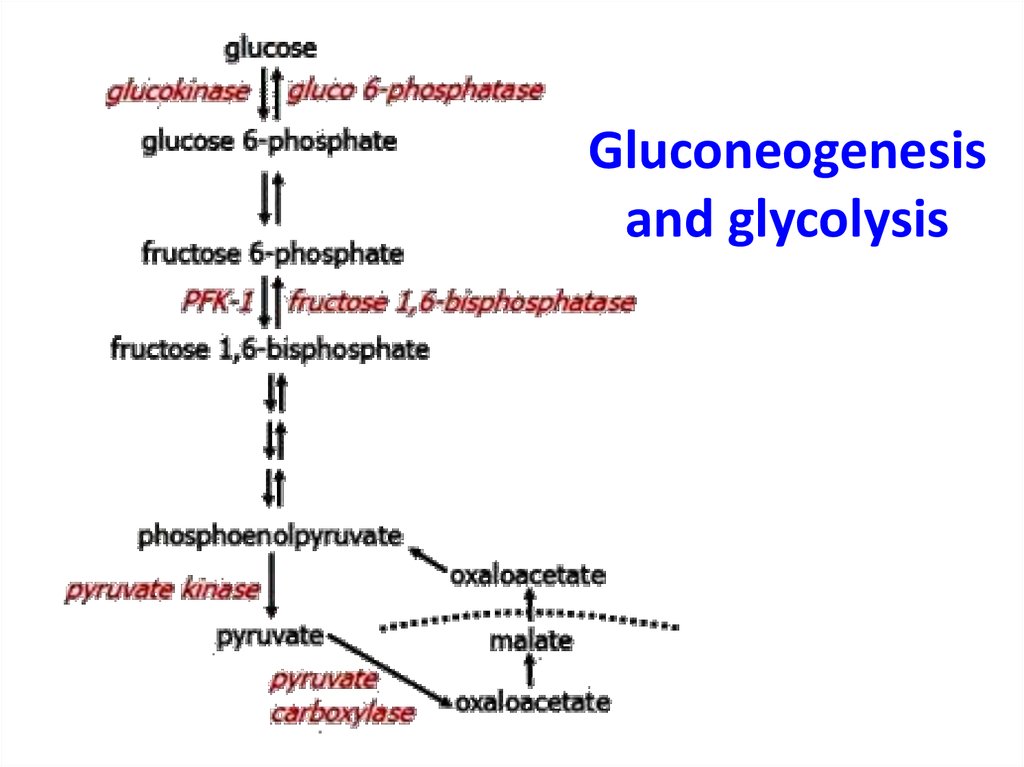
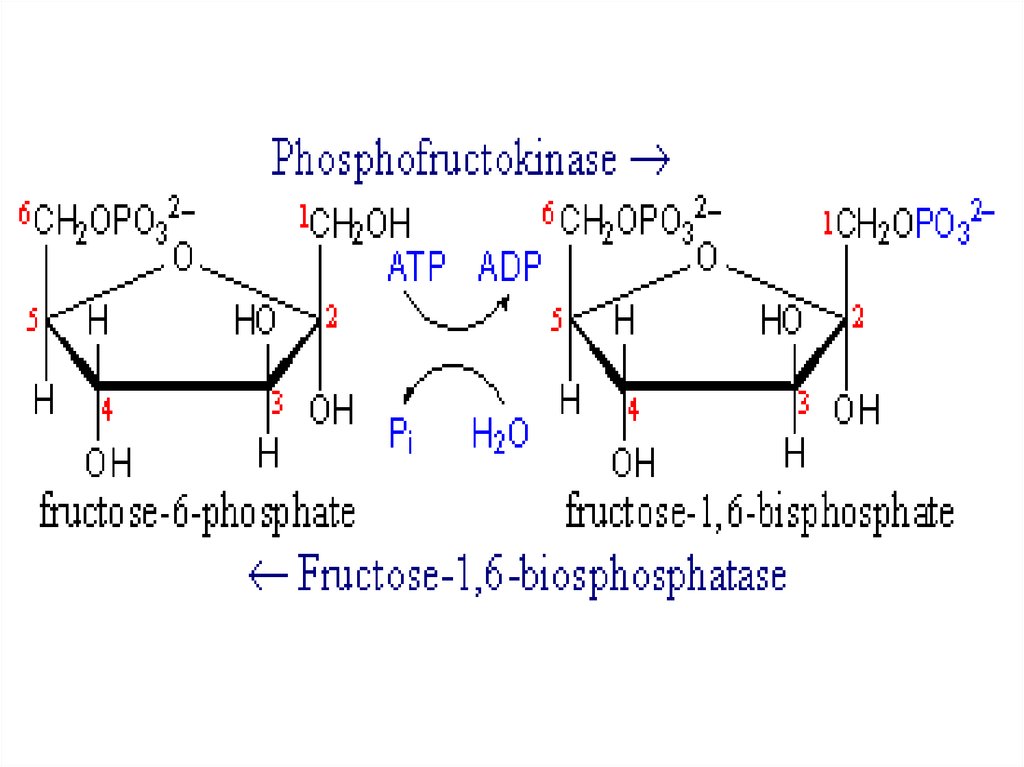
2. Gluconeogenesis and glycolysis
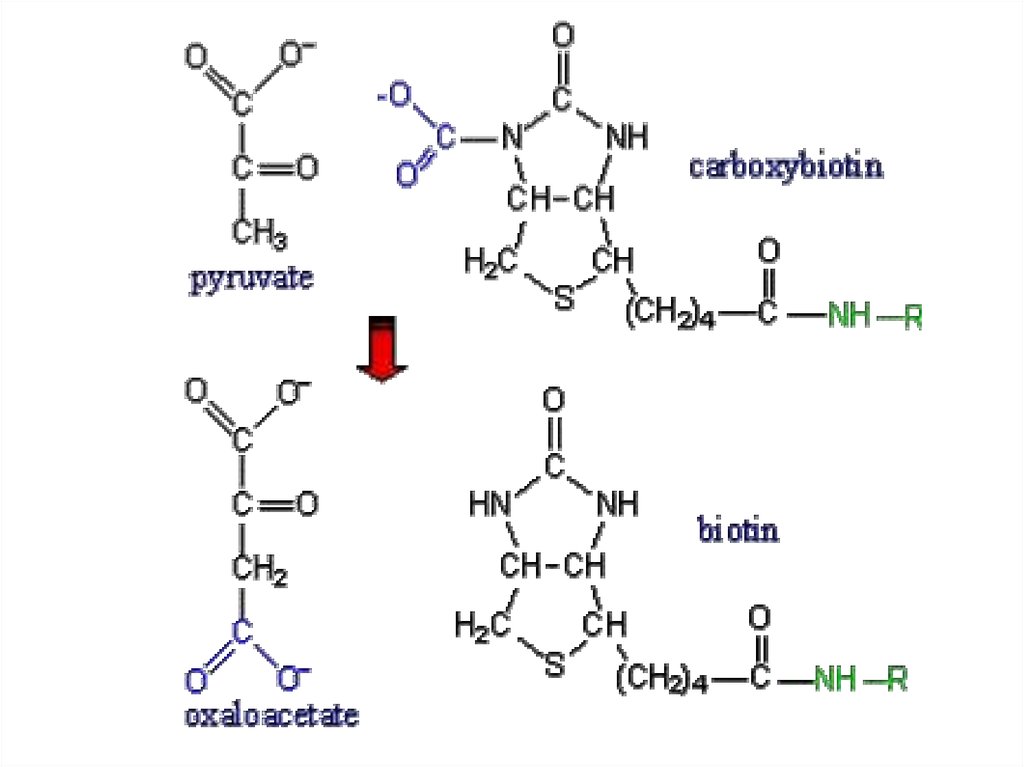
3. Gluconeogenesis
4.
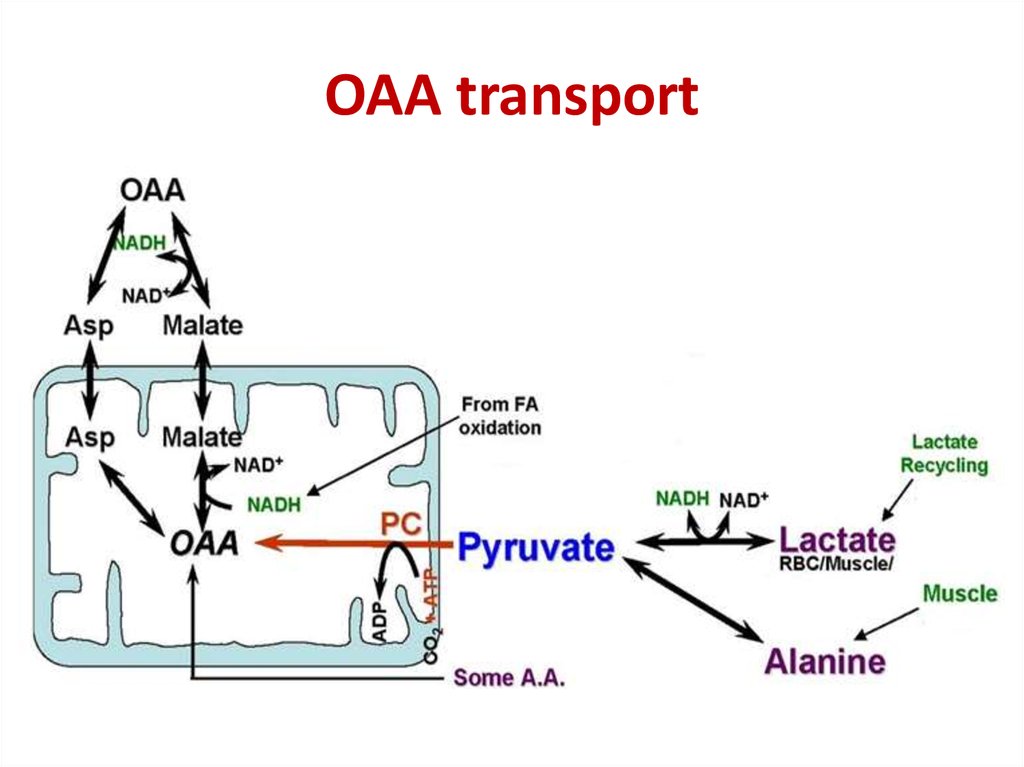
5. OAA transport
6.
7.
8.
9. The overall equation:
2 pyruvate + 2 NADH + H+ + 4 ATP + 2 GTPglucose + 2 NAD+ + 4 ADP + 2 GDP + 6 Pi
10.
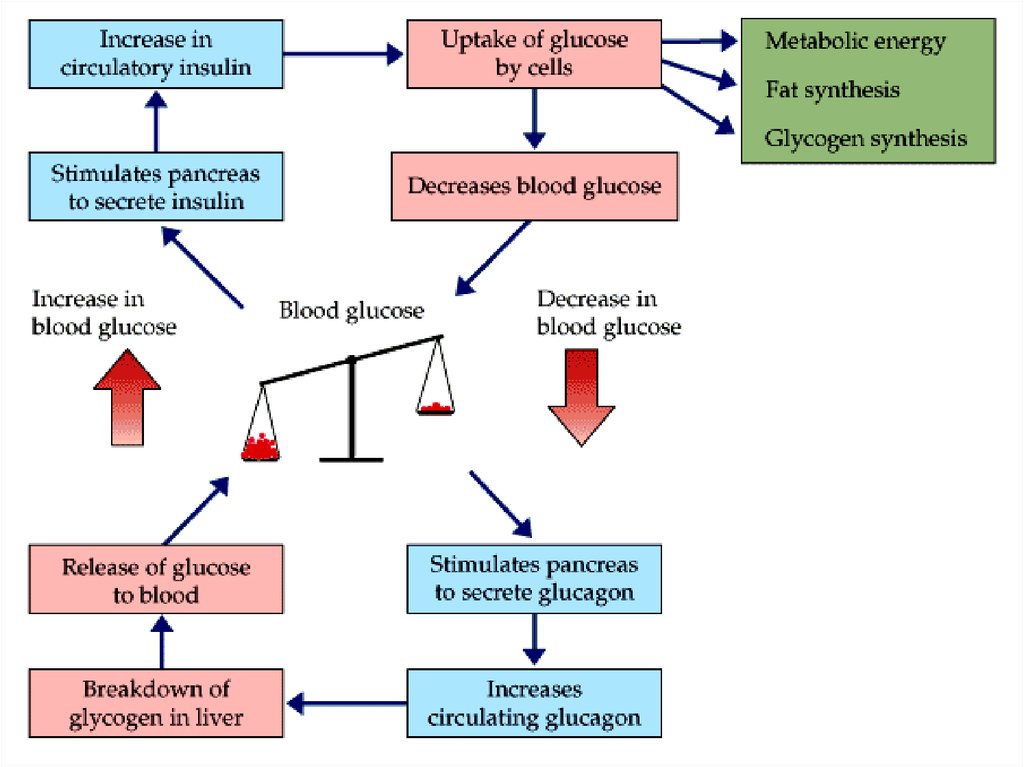
11. Insulin
• Stimulate glucose transport into cells• Induses synthesis of glucokinase,
phosphofructokinase, pyruvate
kinase
• Activates protein phosphatase
pyruvate kinase
12. Glycolysis and gluconeogenesis regulation
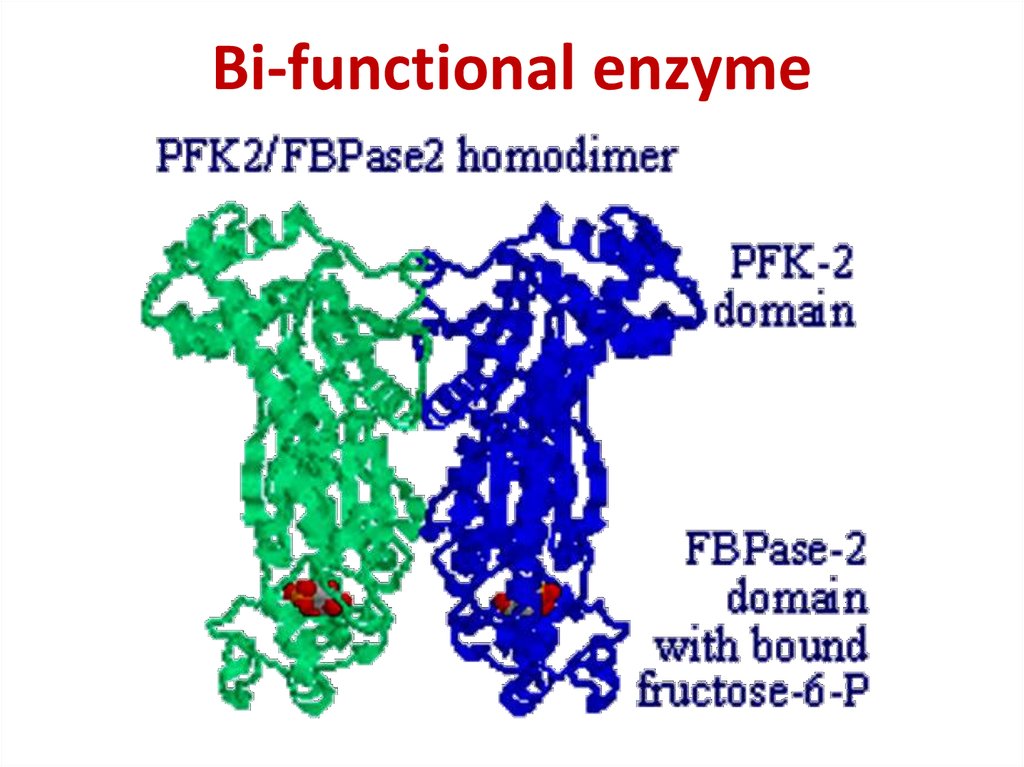
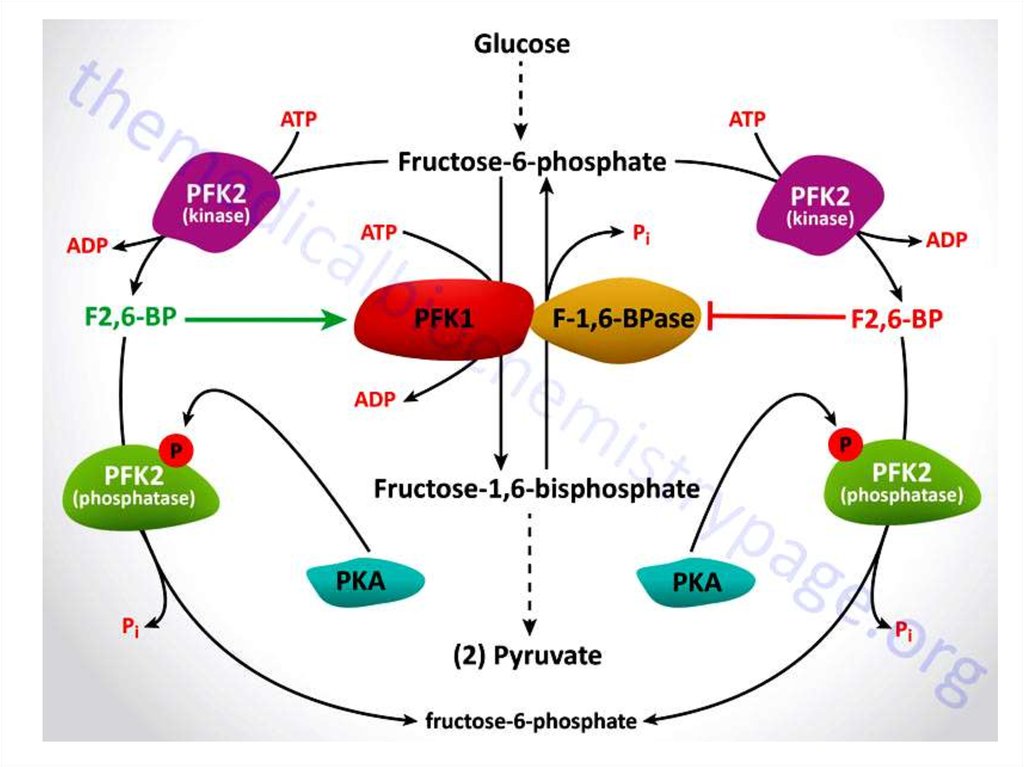
13. Bi-functional enzyme
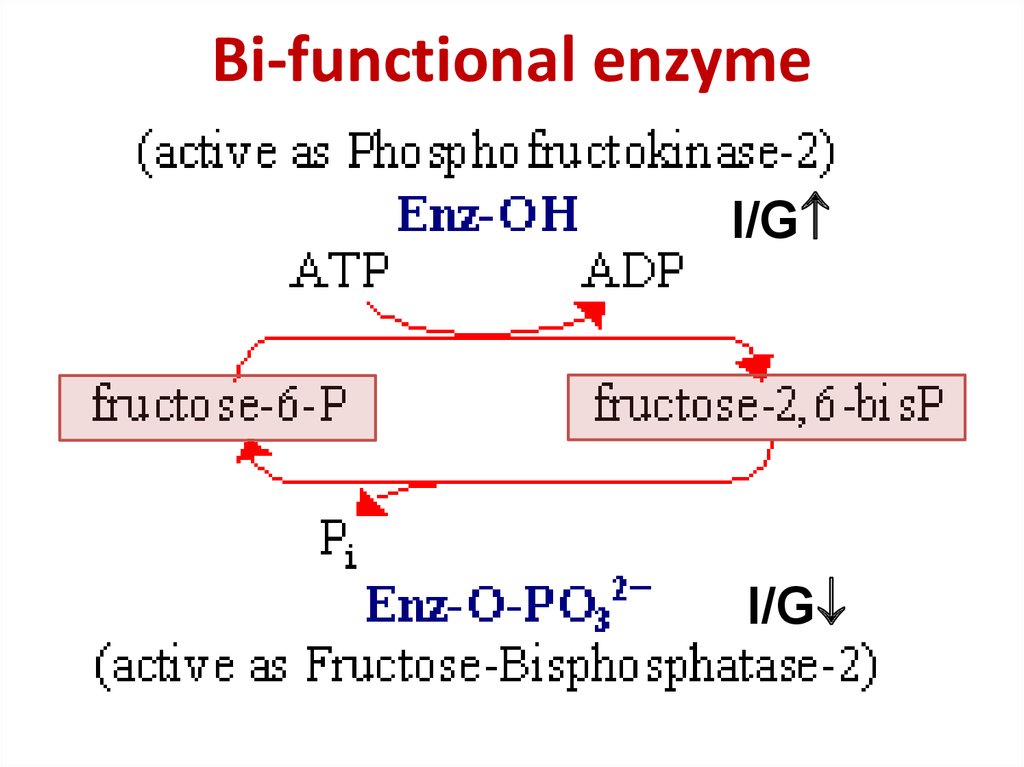
Bi-functional enzyme14. Bi-functional enzyme
Bi-functional enzymeI/G
I/G
15.
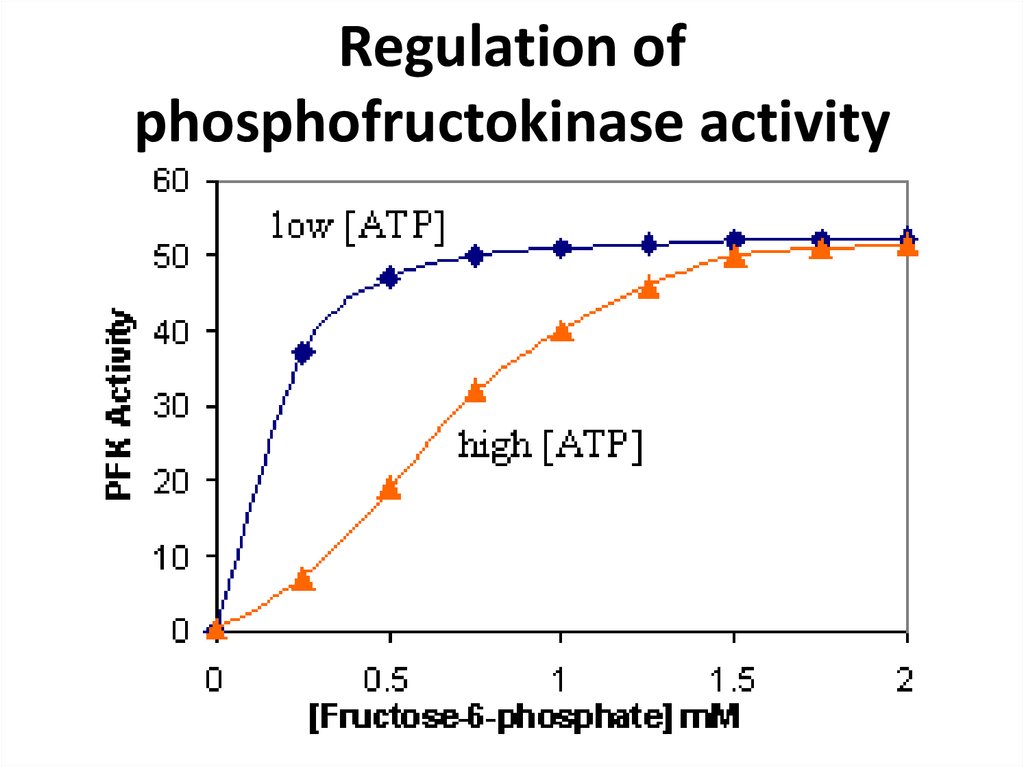
16. Regulation of phosphofructokinase activity
17.
Regulation ofpyruvate kinase activity
18. Glycogen Metabolism Glycogen in the cell
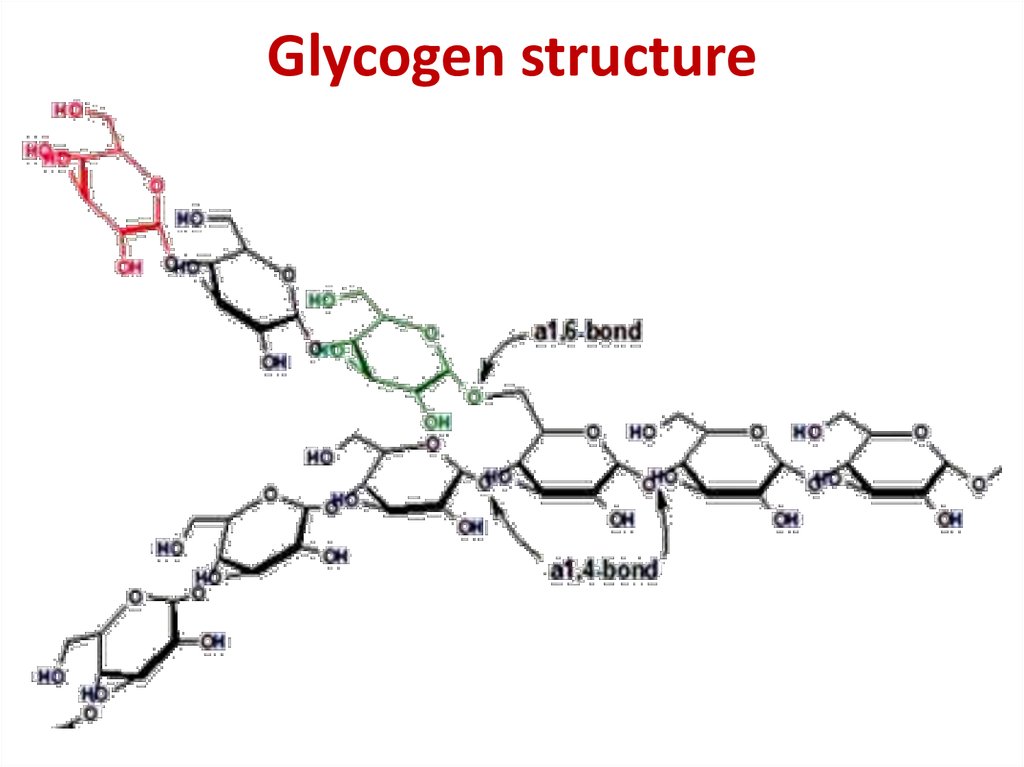
19. Glycogen structure
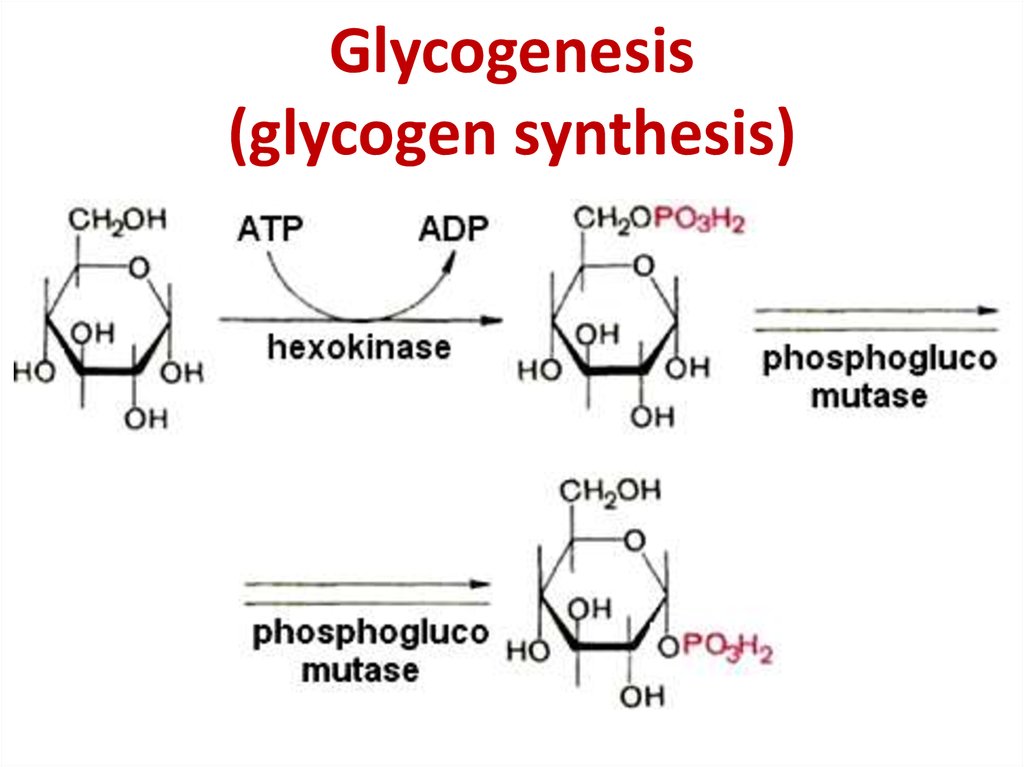
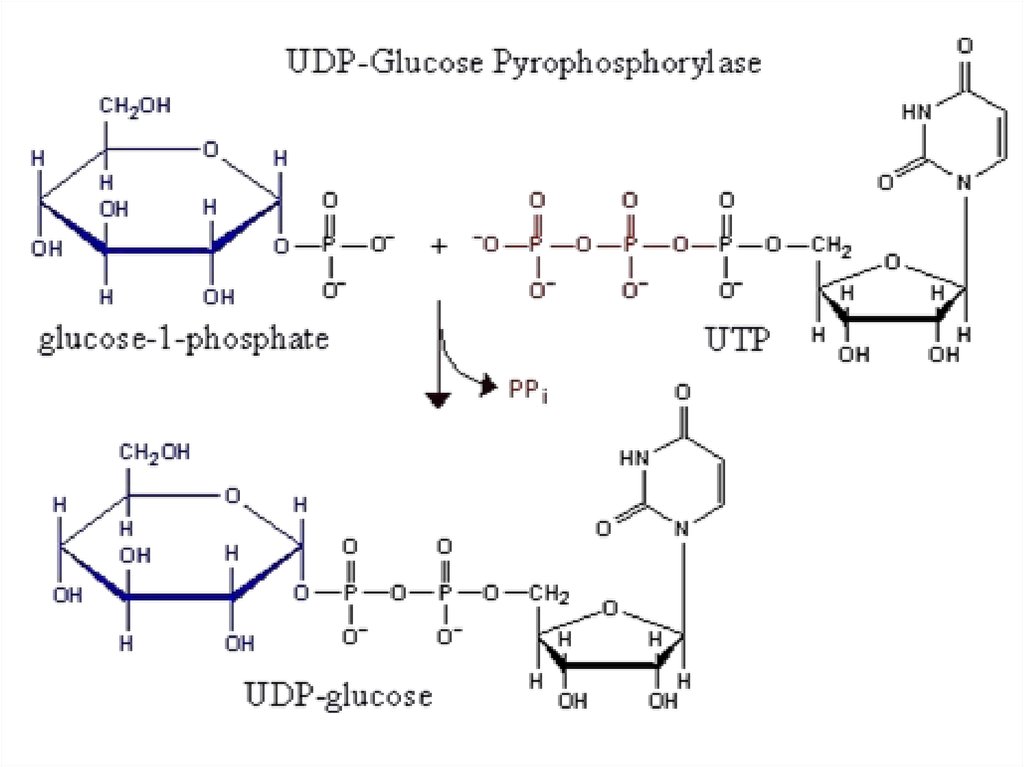
20. Glycogenesis (glycogen synthesis)
21.
22. Glycogen syntase
23.
24.
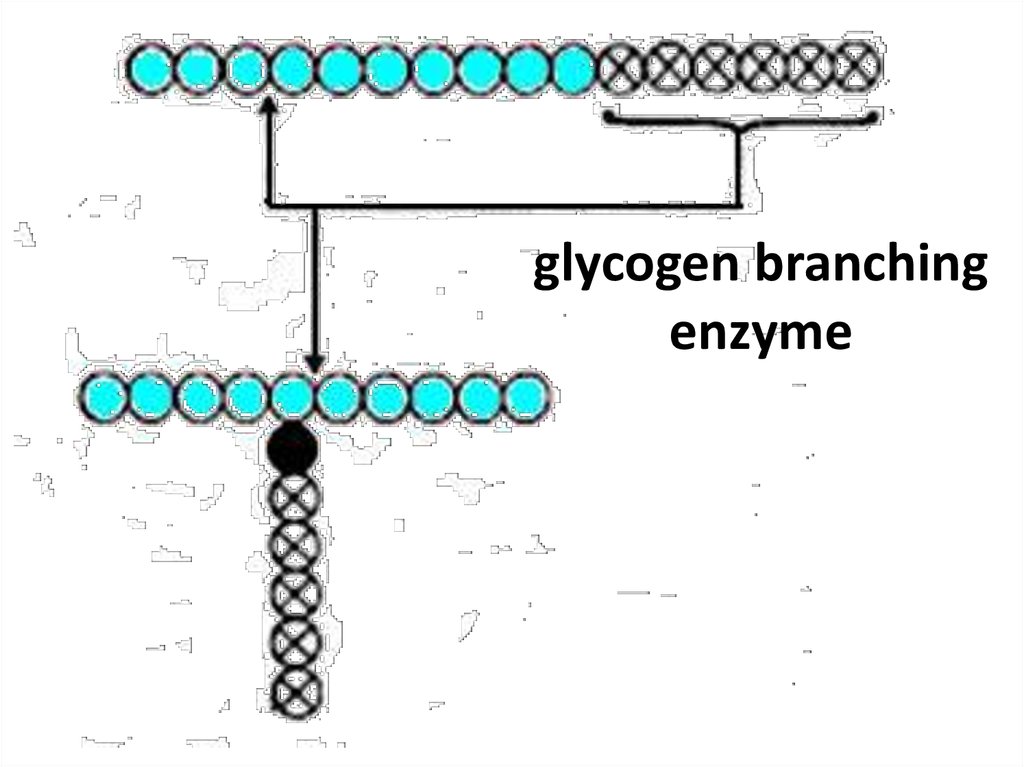
25. glycogen branching enzyme
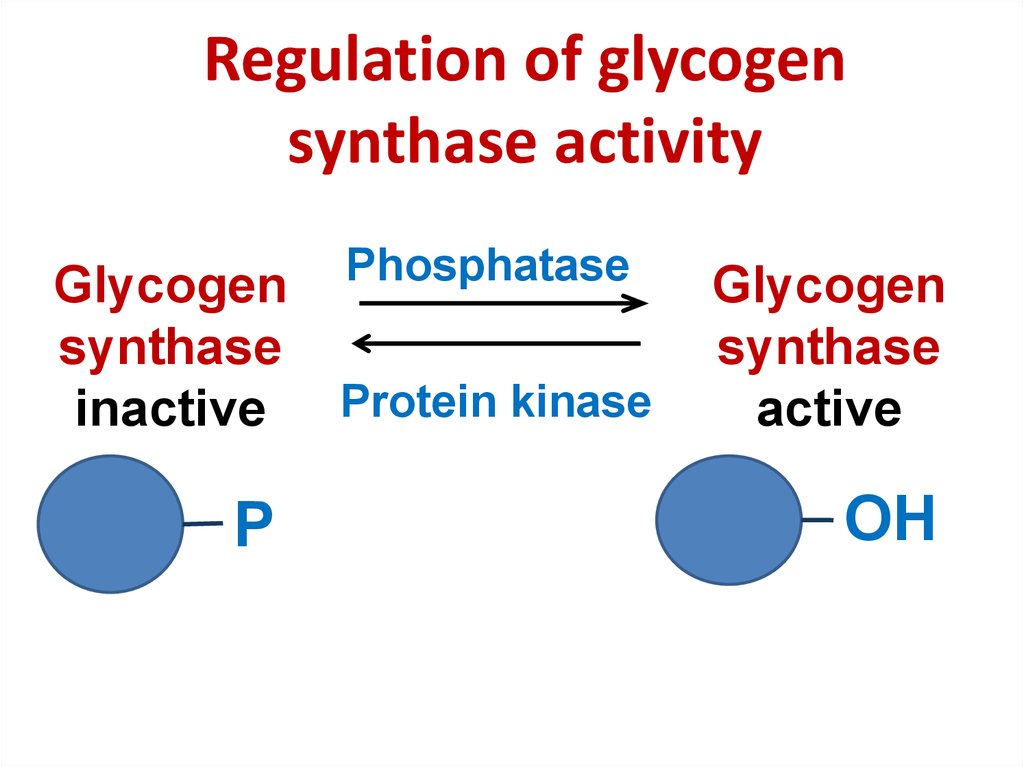
26. Regulation of glycogen synthase activity
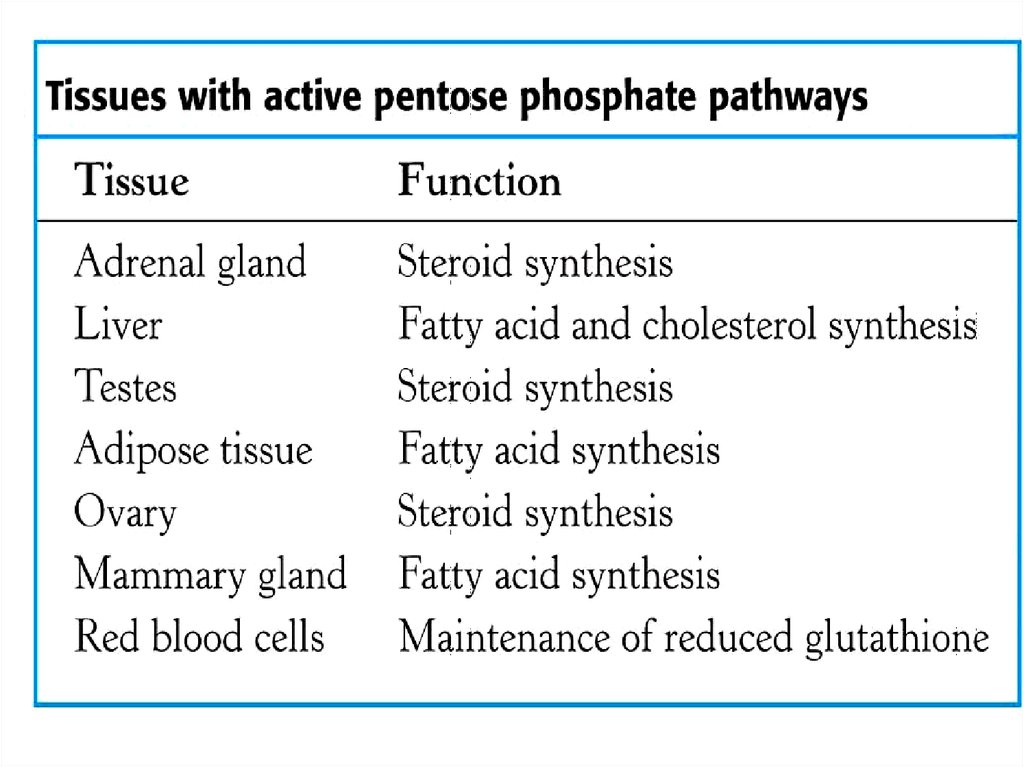
Glycogensynthase
inactive
P
Phosphatase
Protein kinase
Glycogen
synthase
active
OH
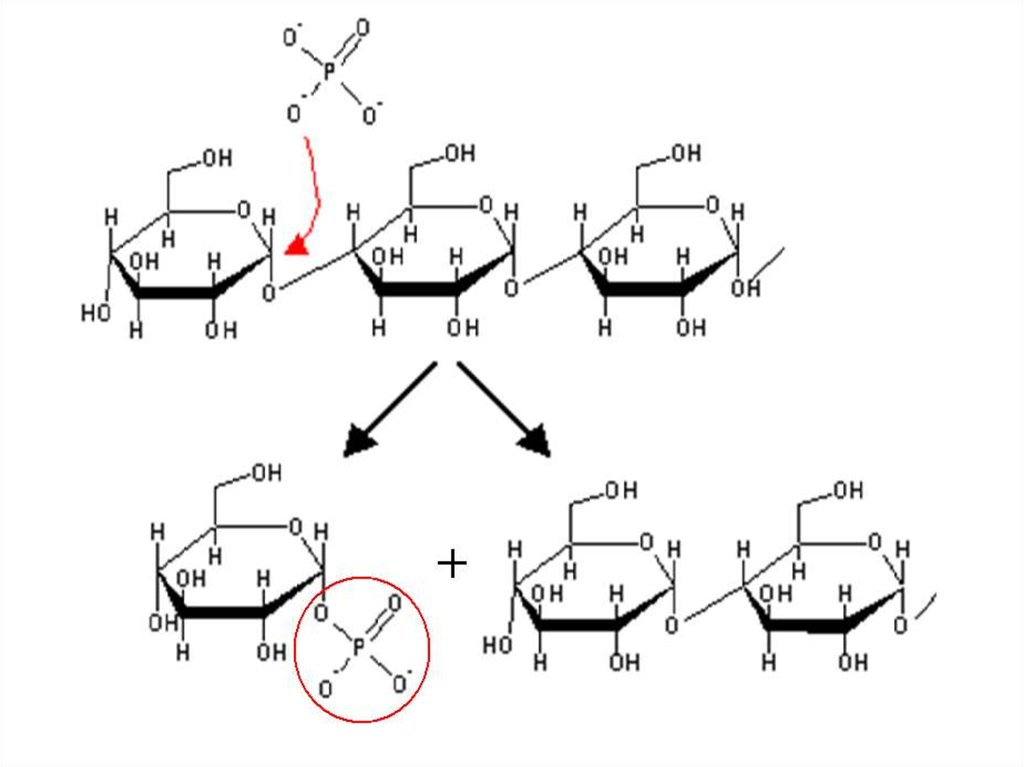
27. Degradation of glycogen Glycogen phosphorylase
28.
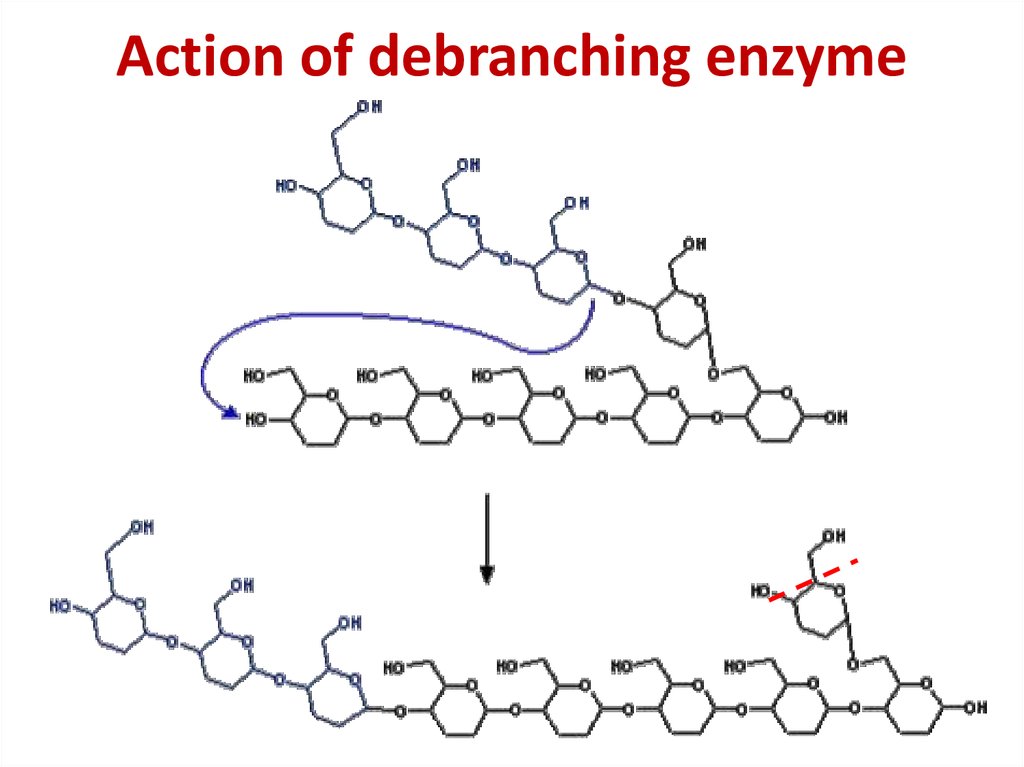
29. Action of debranching enzyme
30. Glycogen metabolism regulation
31.
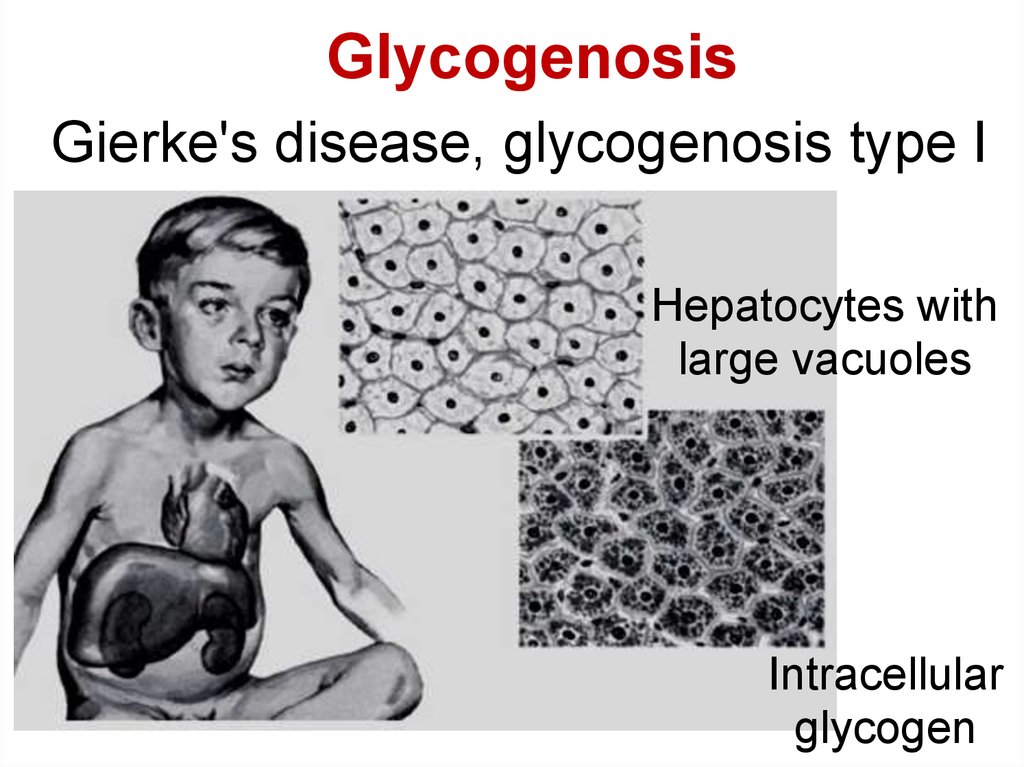
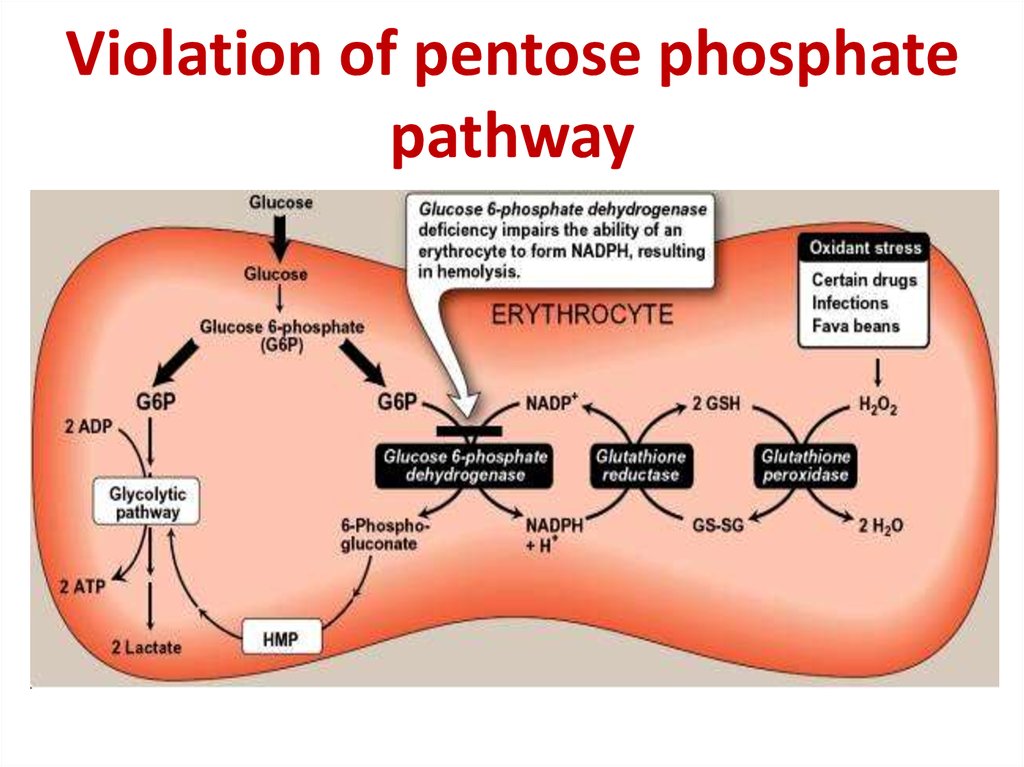
GlycogenosisGierke's disease, glycogenosis type I
Hepatocytes with
large vacuoles
Intracellular
glycogen
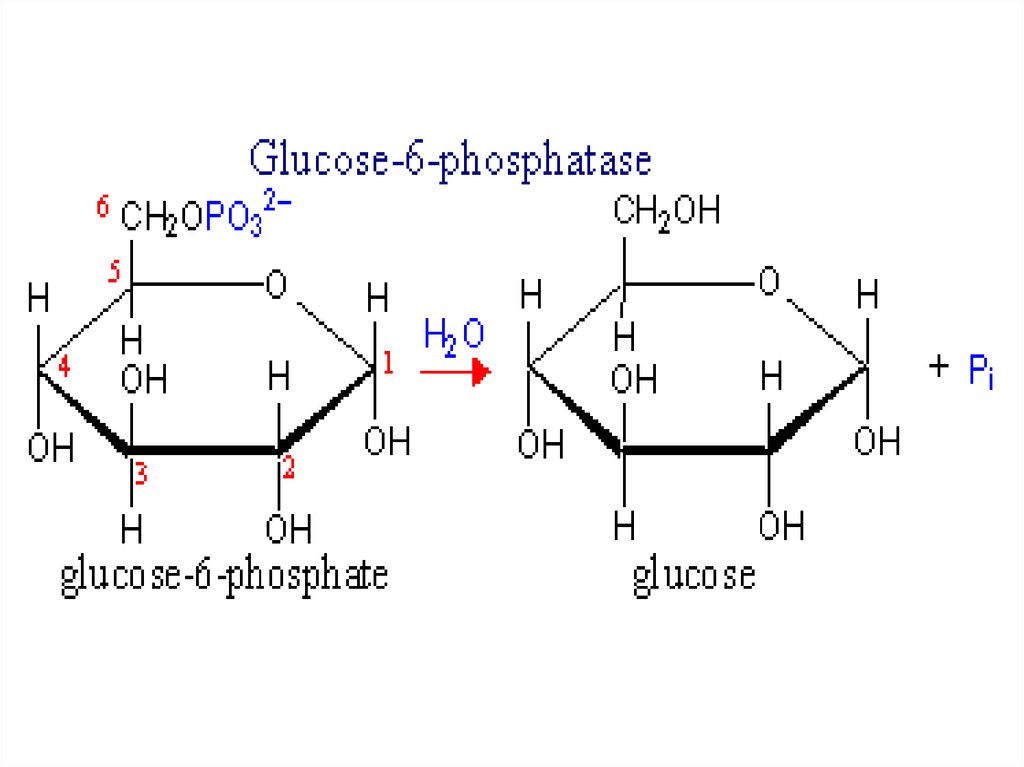
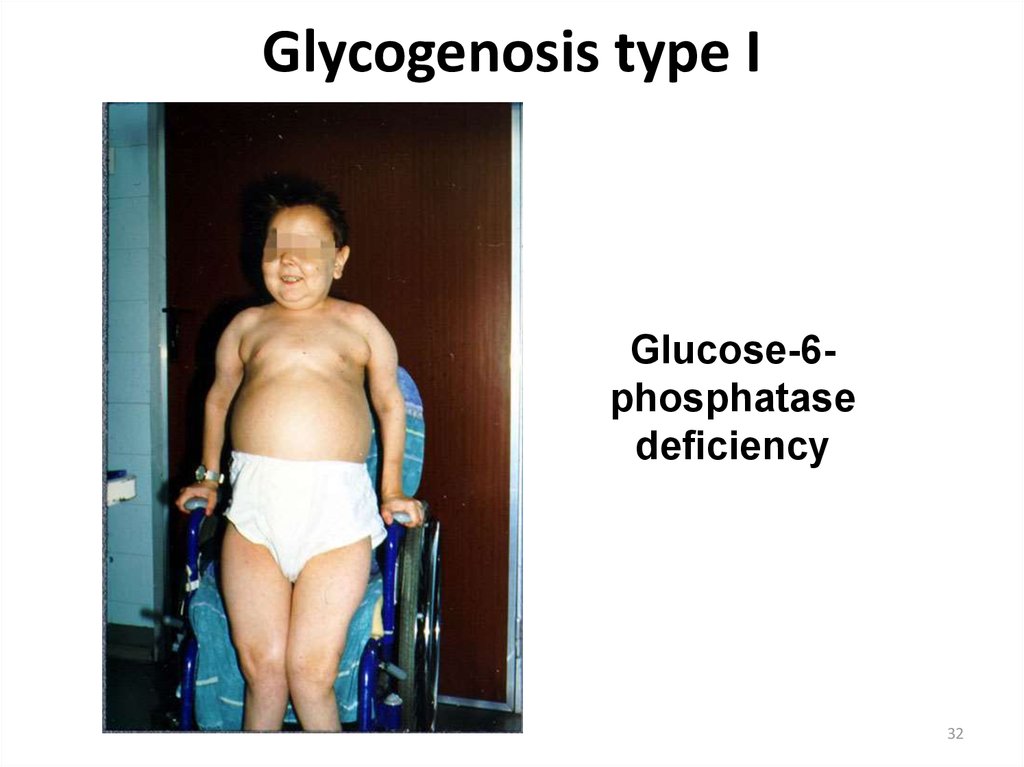
32. Glycogenosis type I
Glucose-6phosphatasedeficiency
32
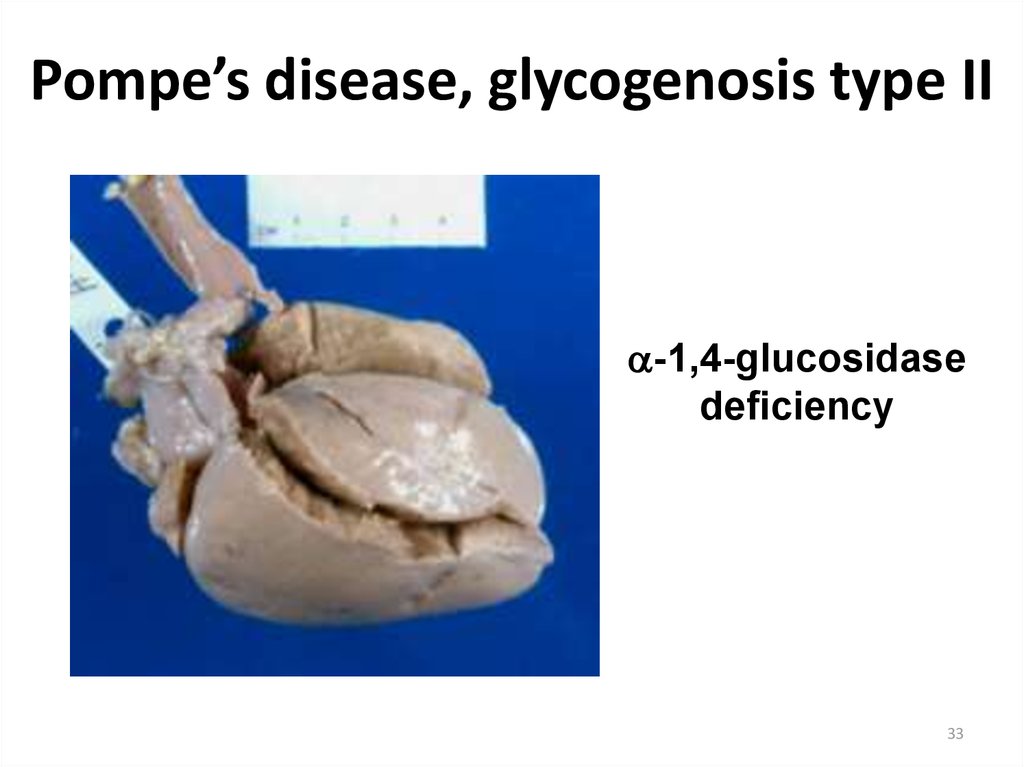
33. Pompe’s disease, glycogenosis type II
-1,4-glucosidasedeficiency
33
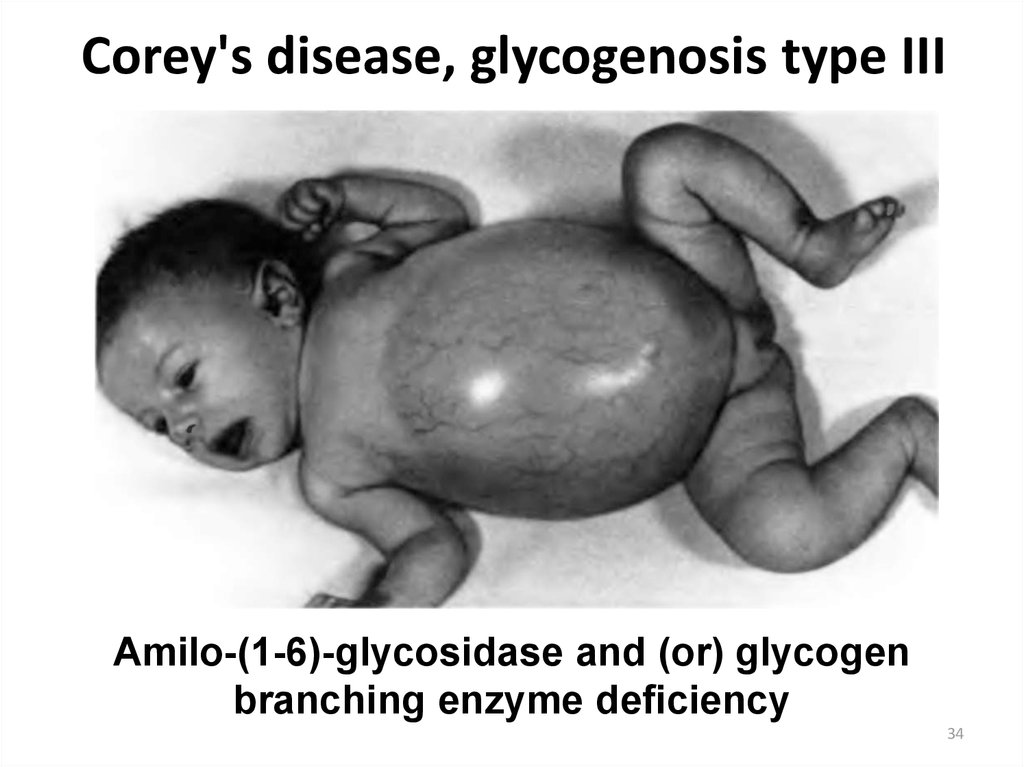
34. Corey's disease, glycogenosis type III
Amilo-(1-6)-glycosidase and (or) glycogenbranching enzyme deficiency
34
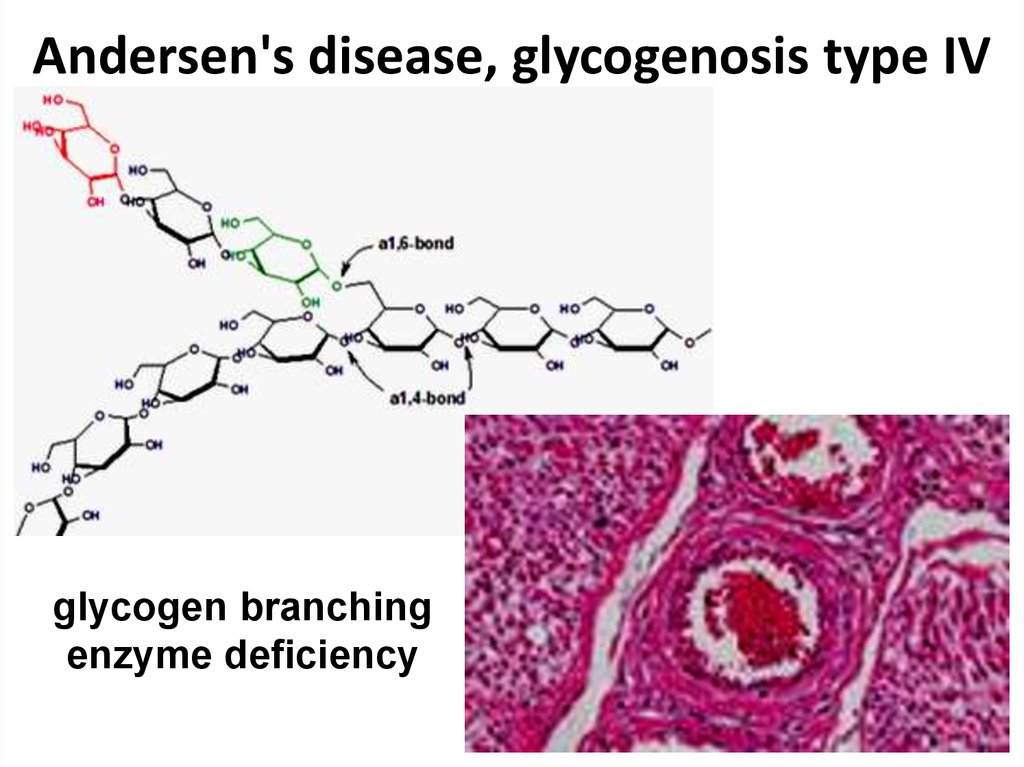
35. Andersen's disease, glycogenosis type IV
glycogen branchingenzyme deficiency
35
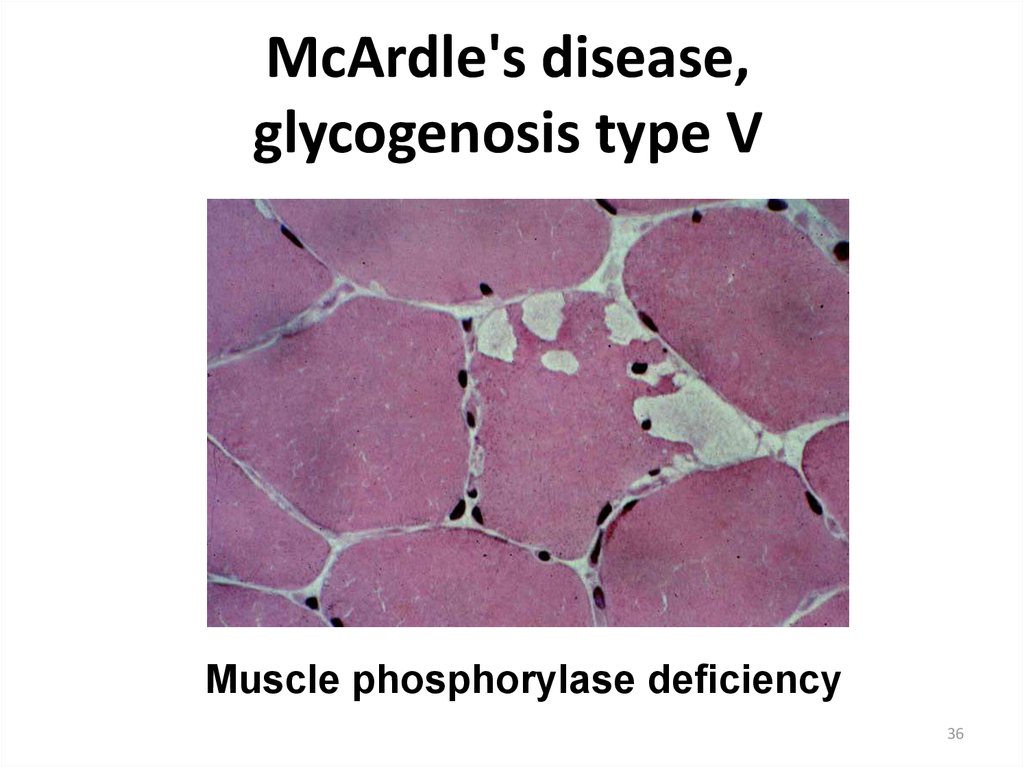
36. McArdle's disease, glycogenosis type V
Muscle phosphorylase deficiency36
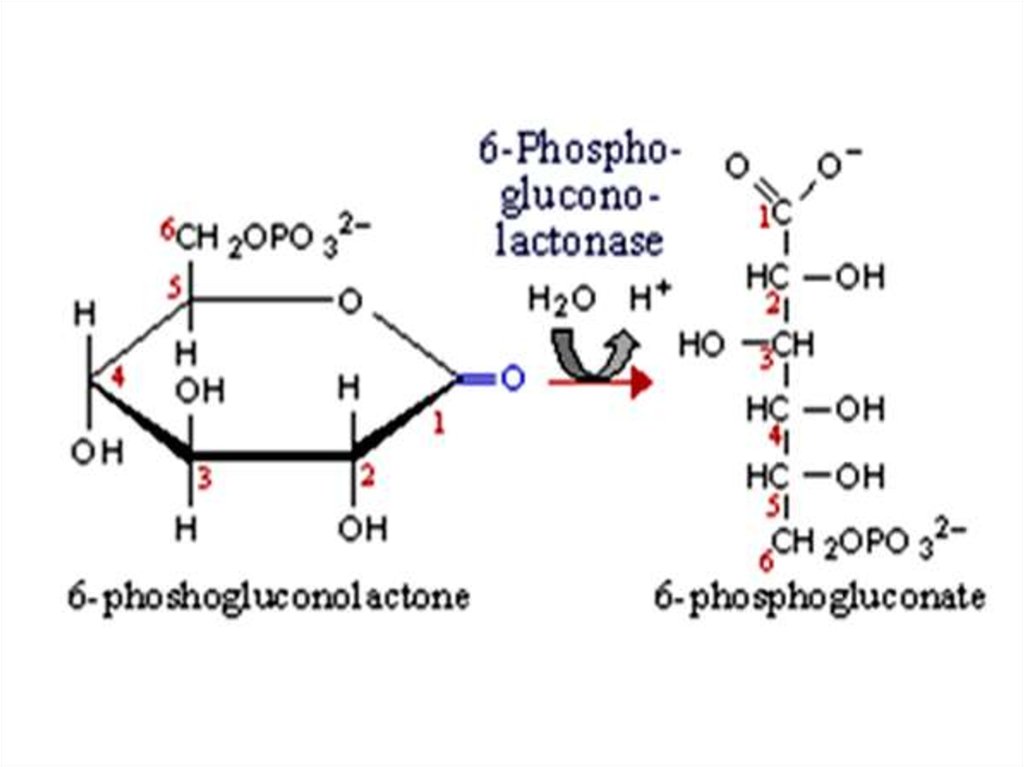
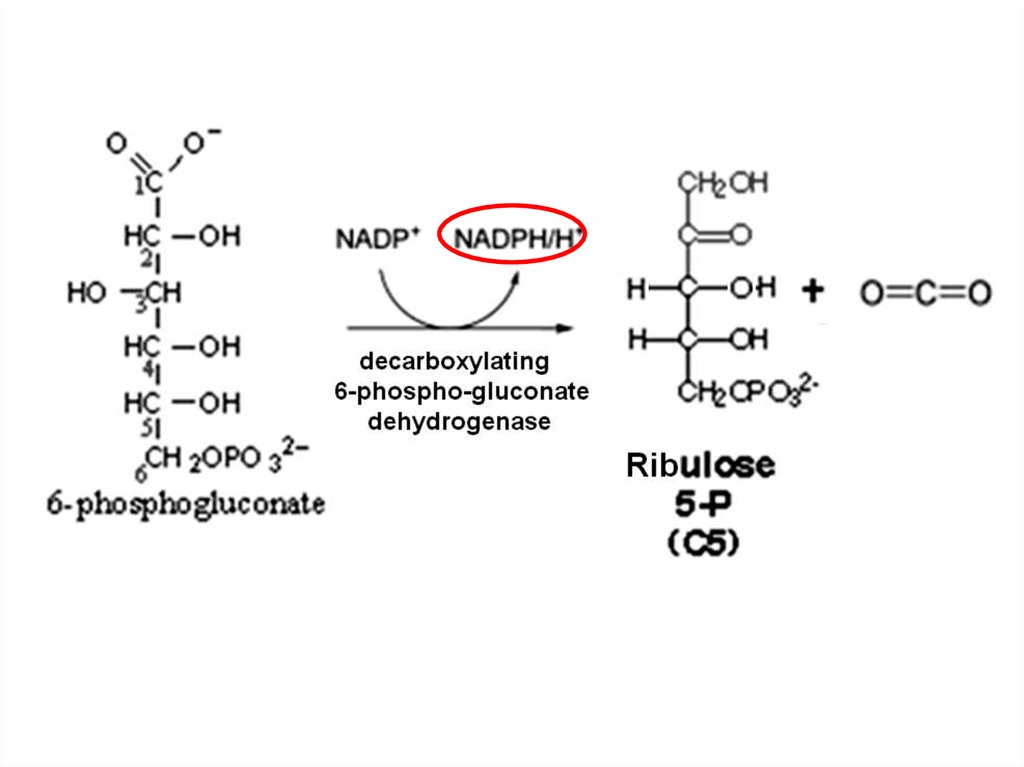
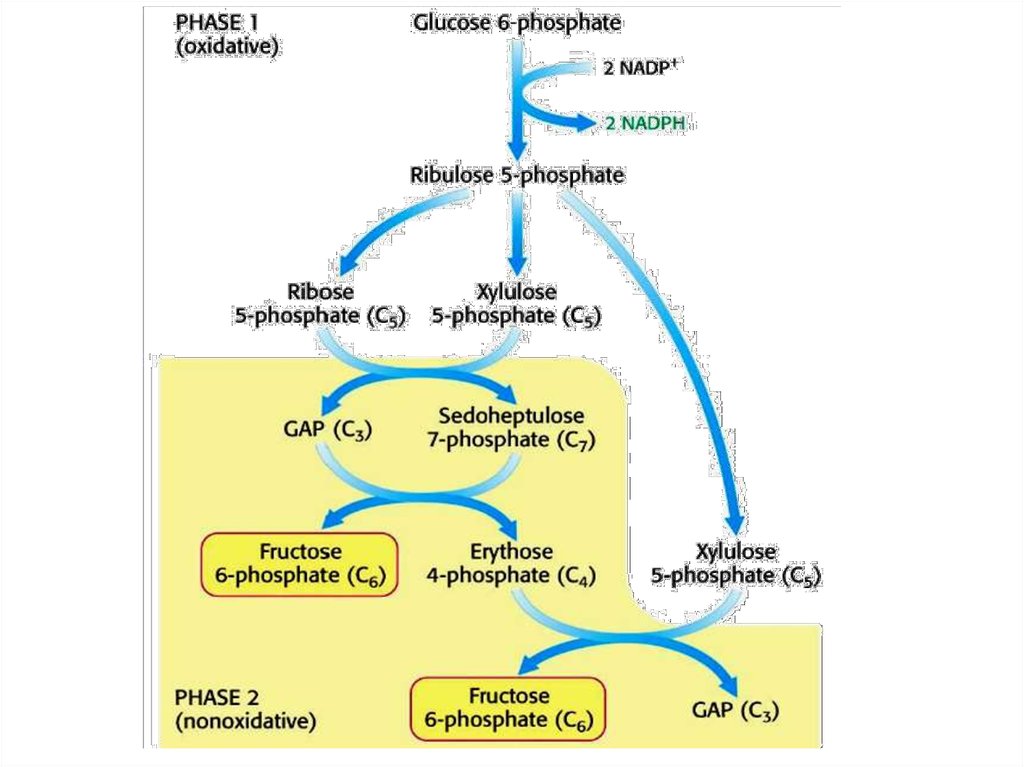
37. PENTOSE PHOSPHATE PATHWAY (HEXOSE MONOPHOSPHATE SHUNT) Oxidative phase
38.
39.
40.
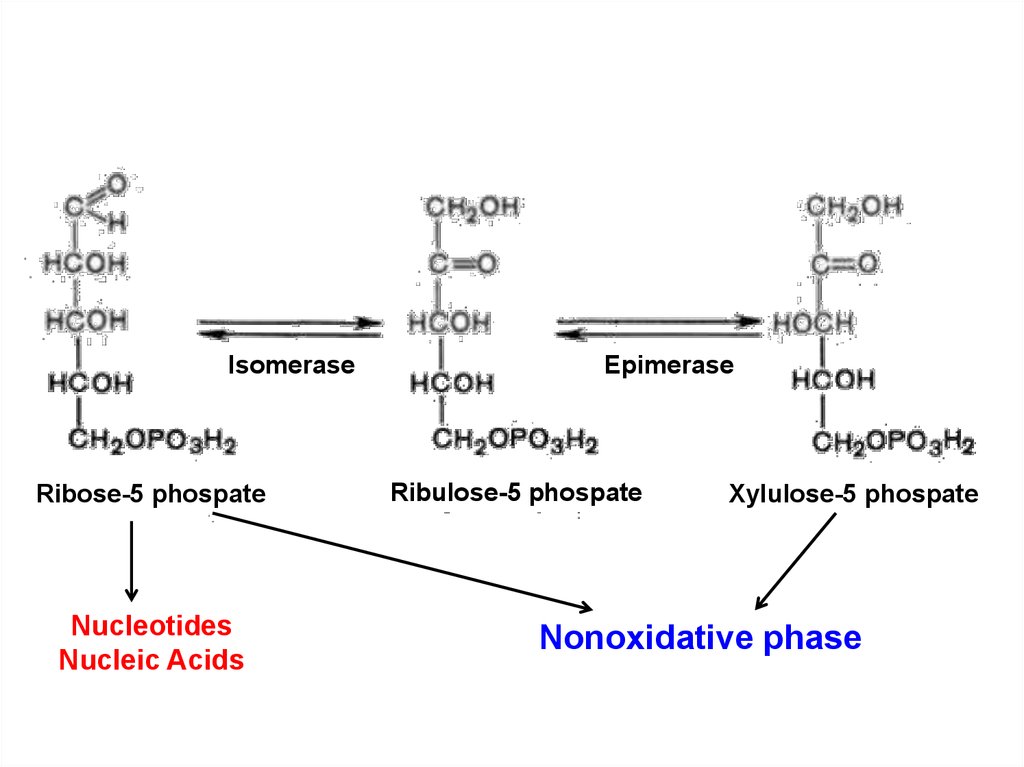
IsomeraseRibose-5 phospate
Nucleotides
Nucleic Acids
Epimerase
Ribulose-5 phospate
Xylulose-5 phospate
Nonoxidative phase
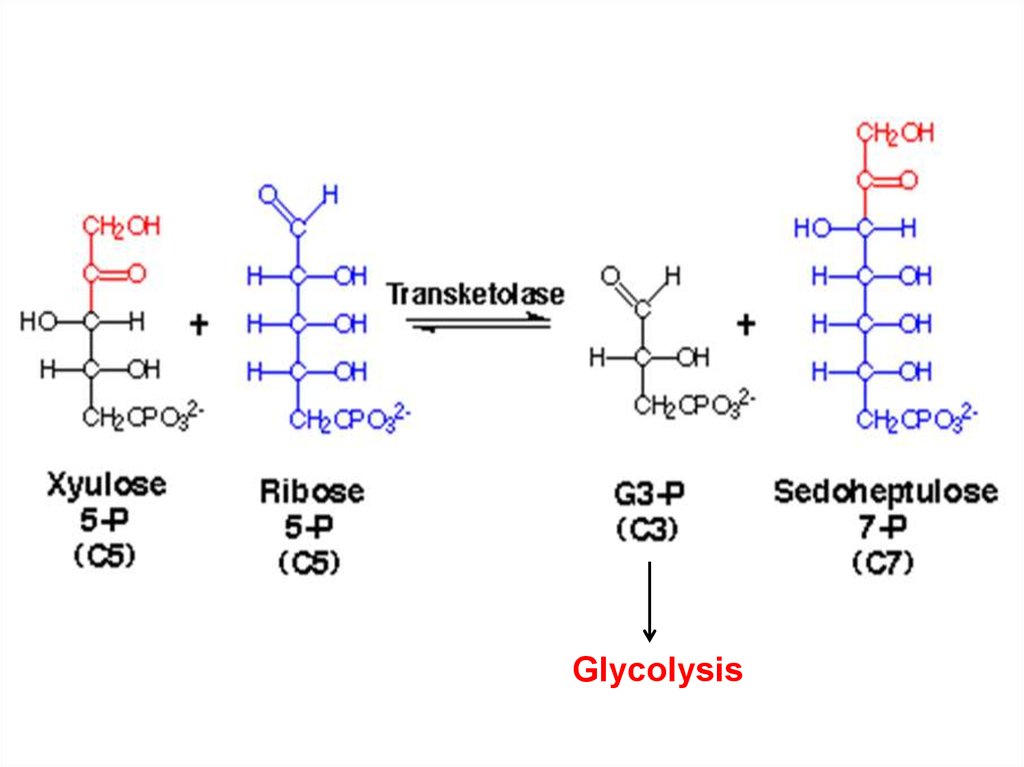
41.
Glycolysis42.
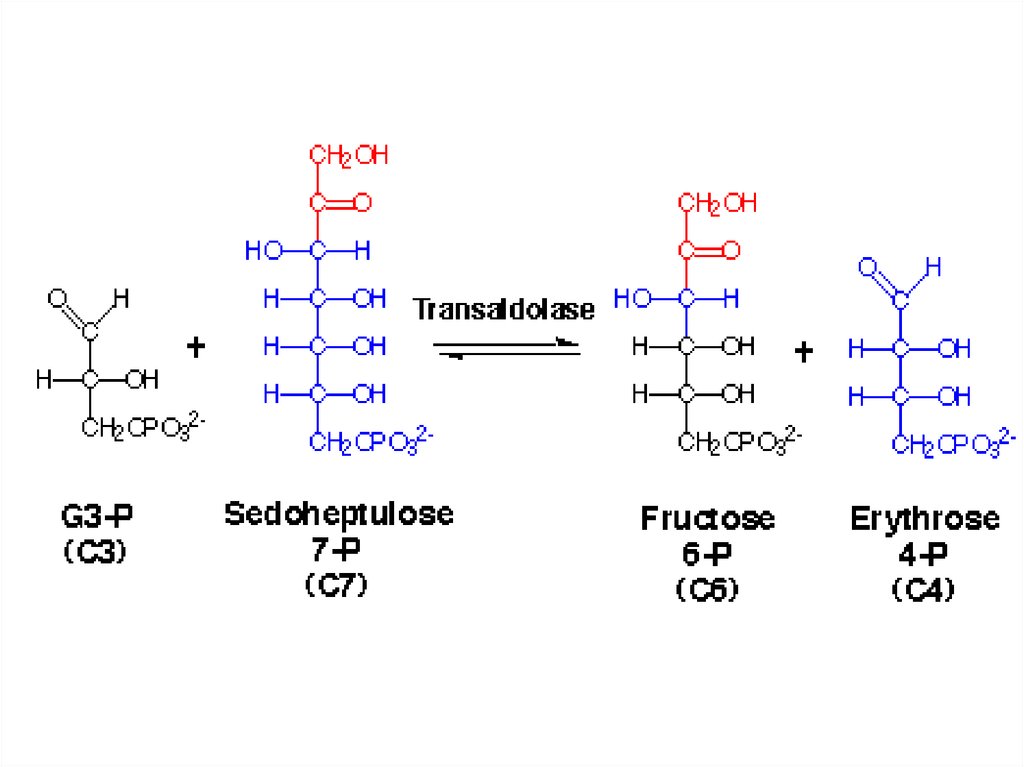
43.
Glycolysis44.
45. The overall equation:
6 G-6-P + 12+
NADP
+ 7 H2O
5 G-6-P + 12 NADPH + 12H+ + 6 CO2
















 chemistry
chemistry








