Similar presentations:
Protein and amino acid metabolism
1. Protein and amino acid metabolism
2. Protein-rich products
3. Essential amino acids
valine, leucine, isoleucine,lysine, methionine, threonine,
tryptophan, phenylalanine
arginine and histidine
4. Proteases
Serine proteasesCysteine proteases
Aspartic proteases
Metalloproteases
Treonine proteases
Glutamic proteases
5.
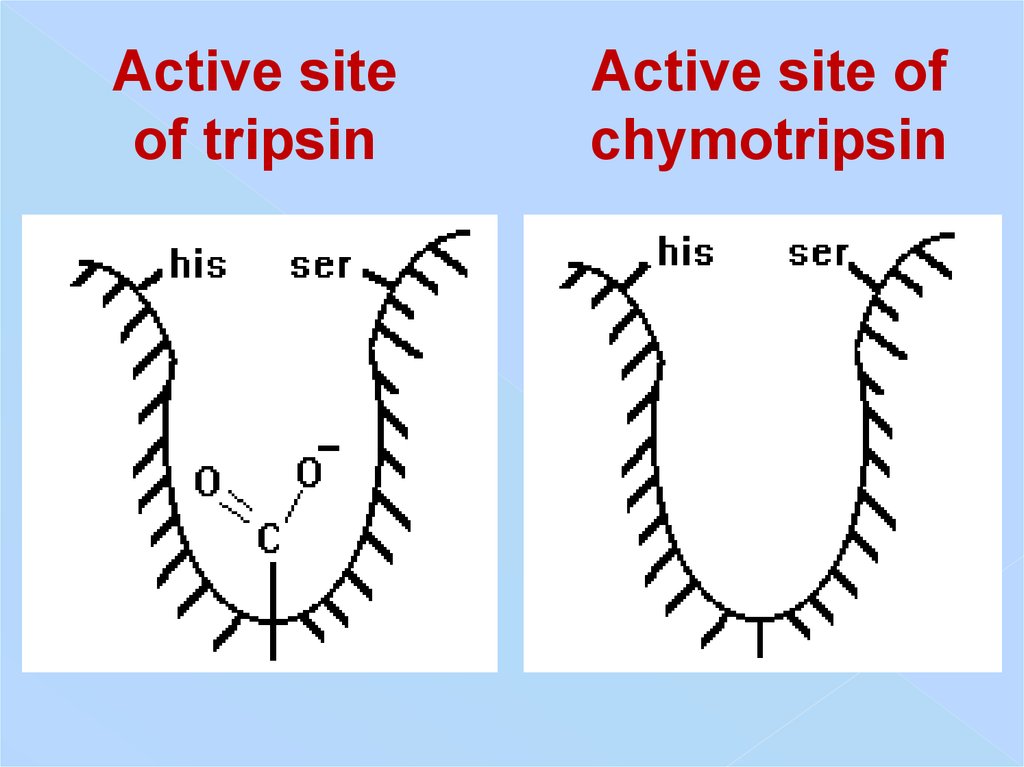
Active siteof tripsin
Active site of
chymotripsin
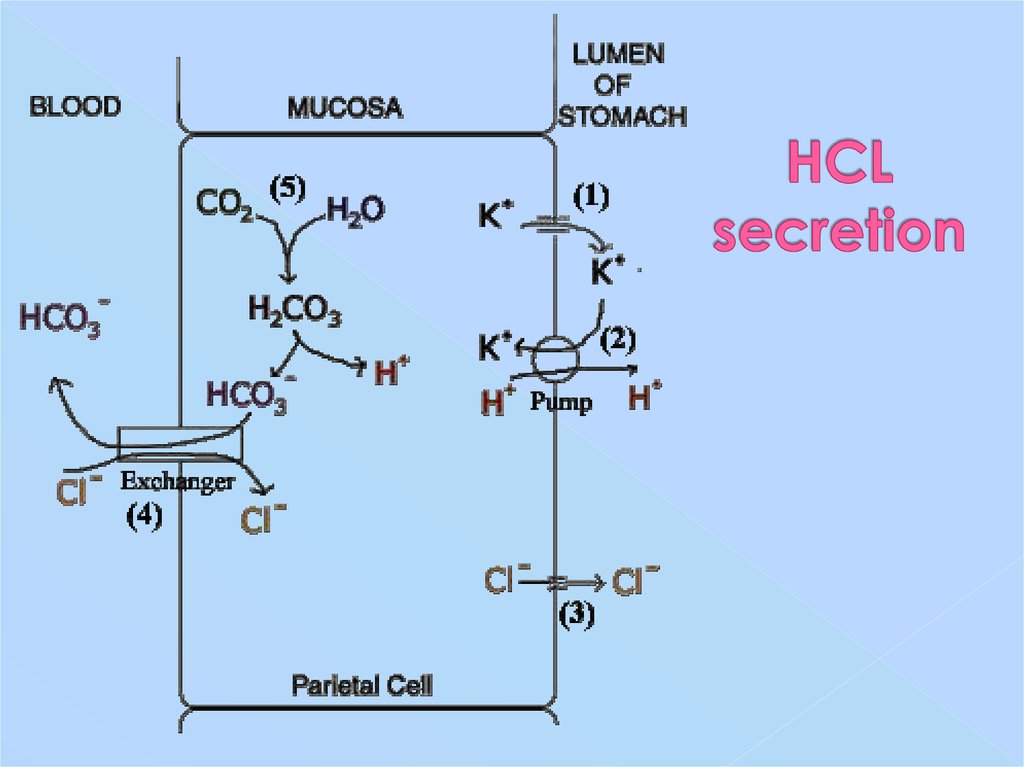
6. HCL secretion
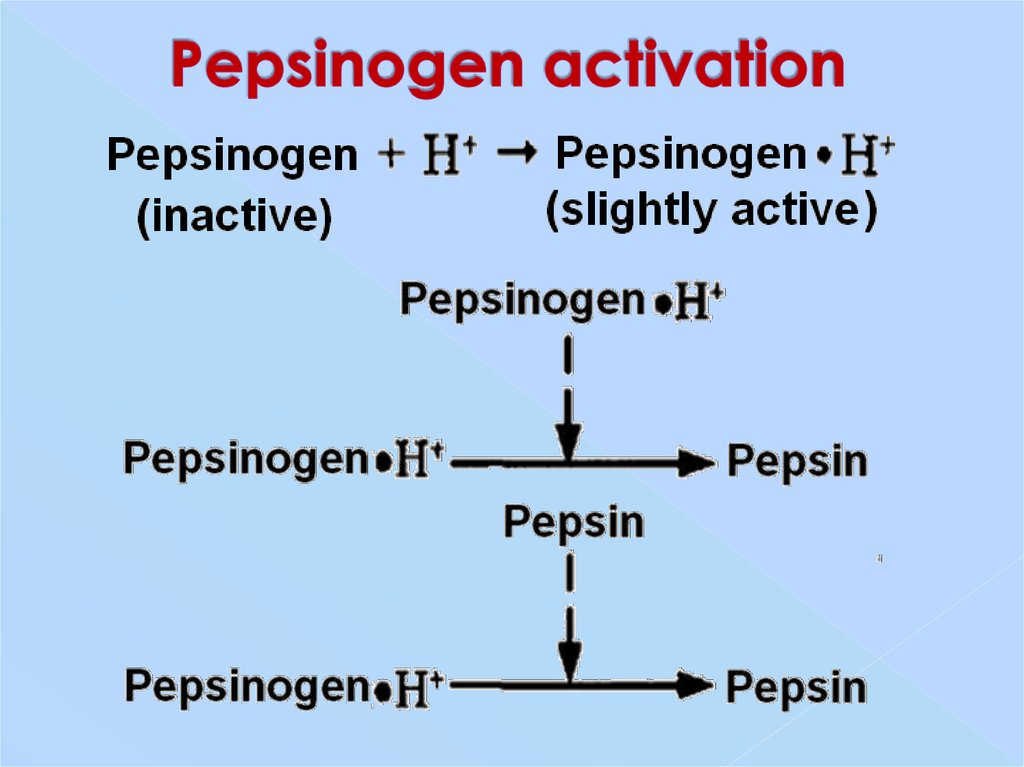
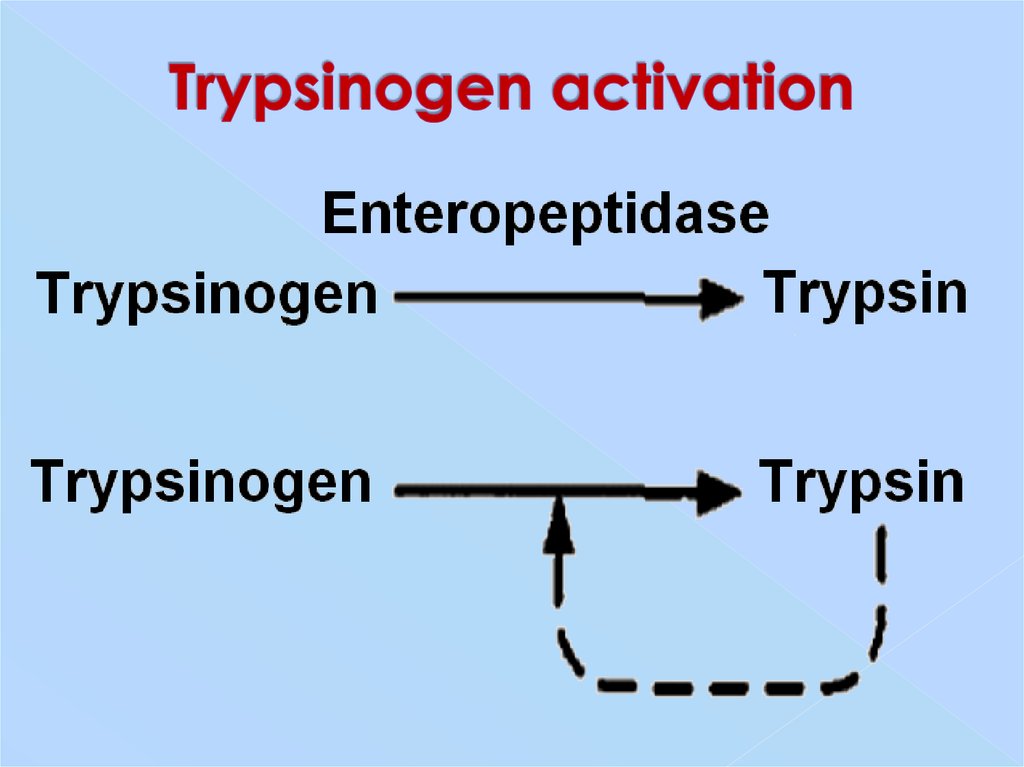
7. Pepsinogen activation
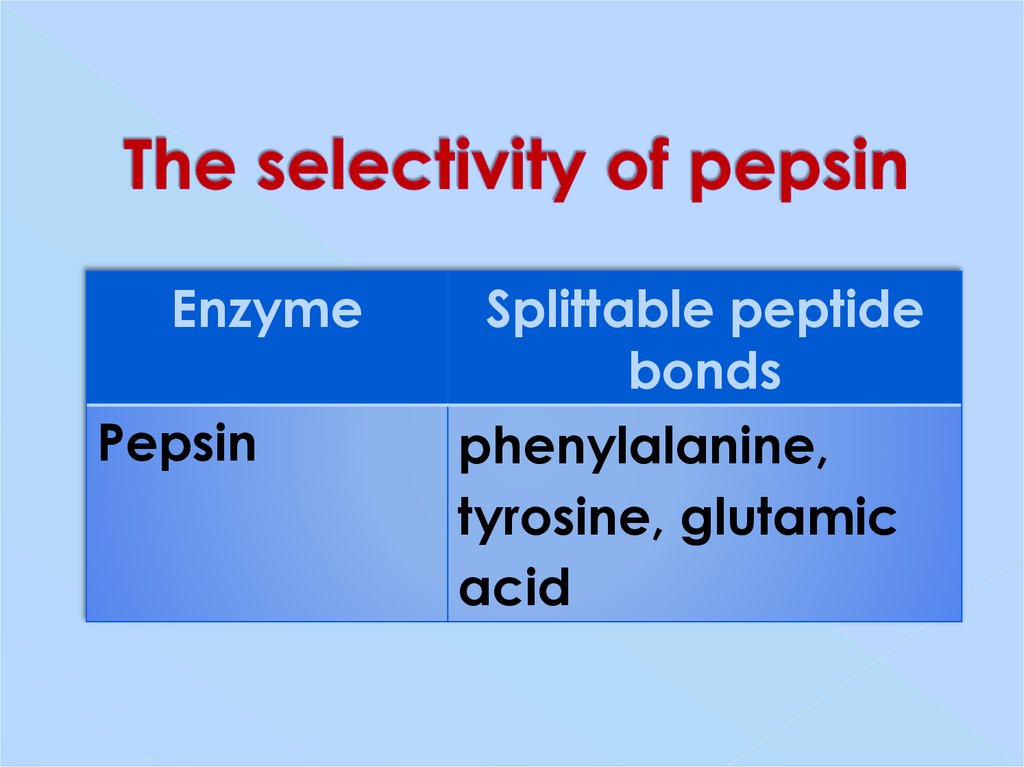
8. The selectivity of pepsin
EnzymePepsin
Splittable peptide
bonds
phenylalanine,
tyrosine, glutamic
acid
9. Trypsinogen activation
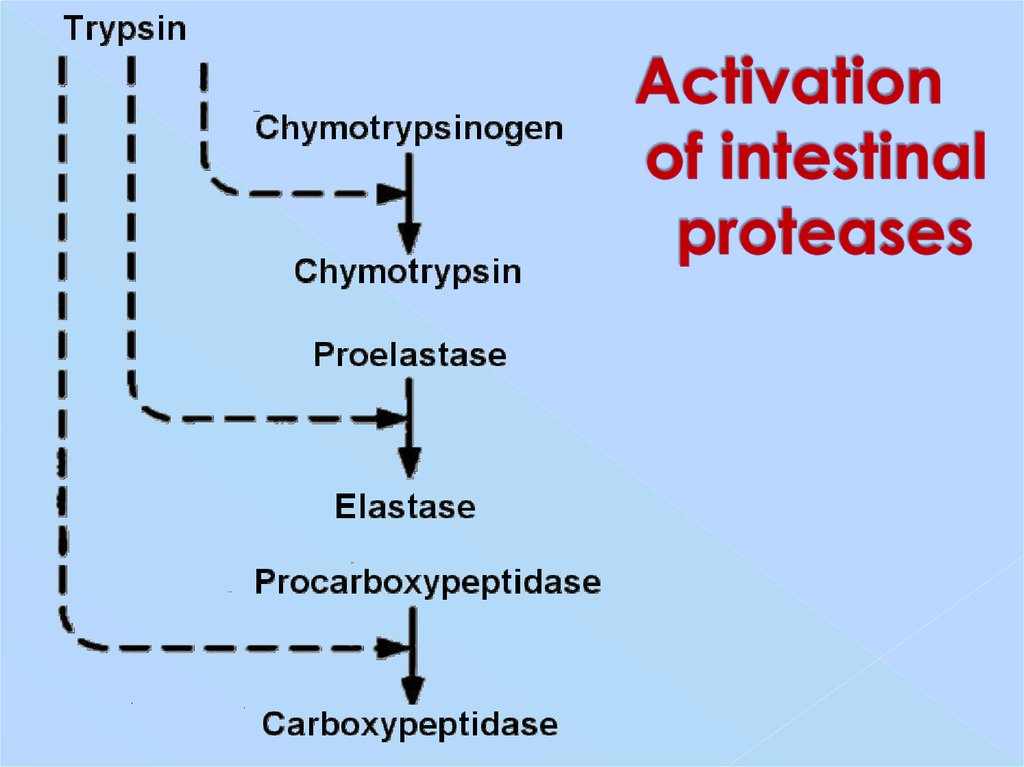
10. Activation of intestinal proteases
11. The selectivity of peptidases
EnzymeSplittable peptide
bonds
Trypsin
Chymotrypsin
lysine, arginine
Elastase
alanine, serine, glycine
Carboxypeptidase A
alanine, leucine, valine
Carboxypeptidase В
lysine, arginine
tryptophan,
phenylalanine, tyrosine
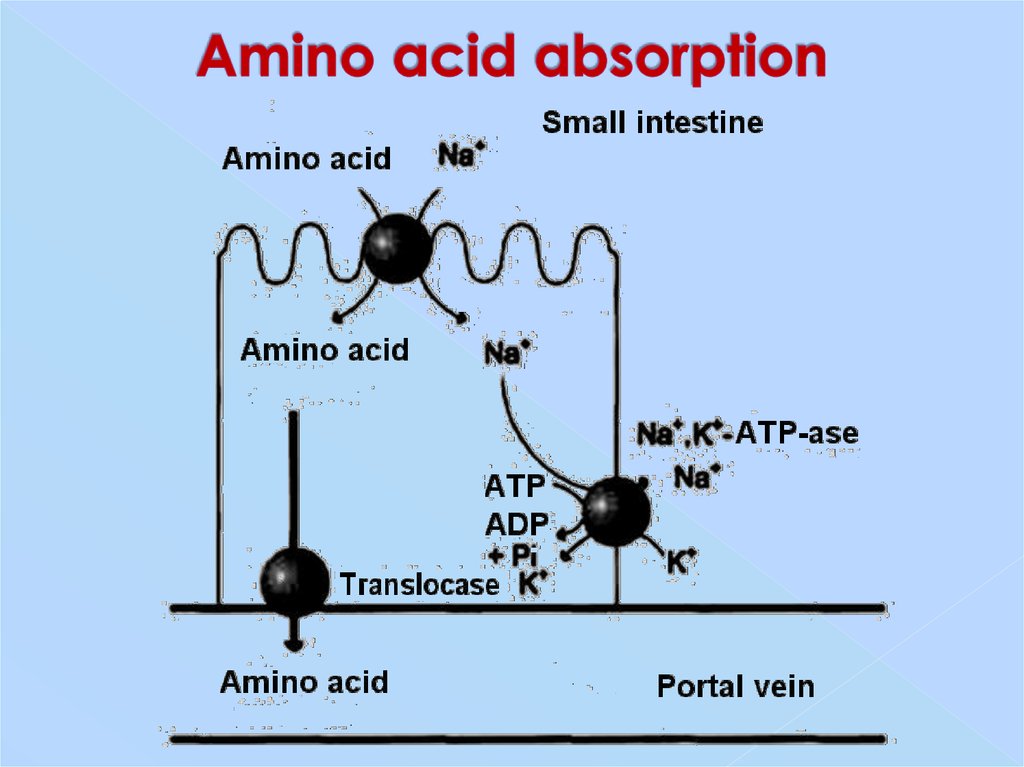
12. Amino acid absorption
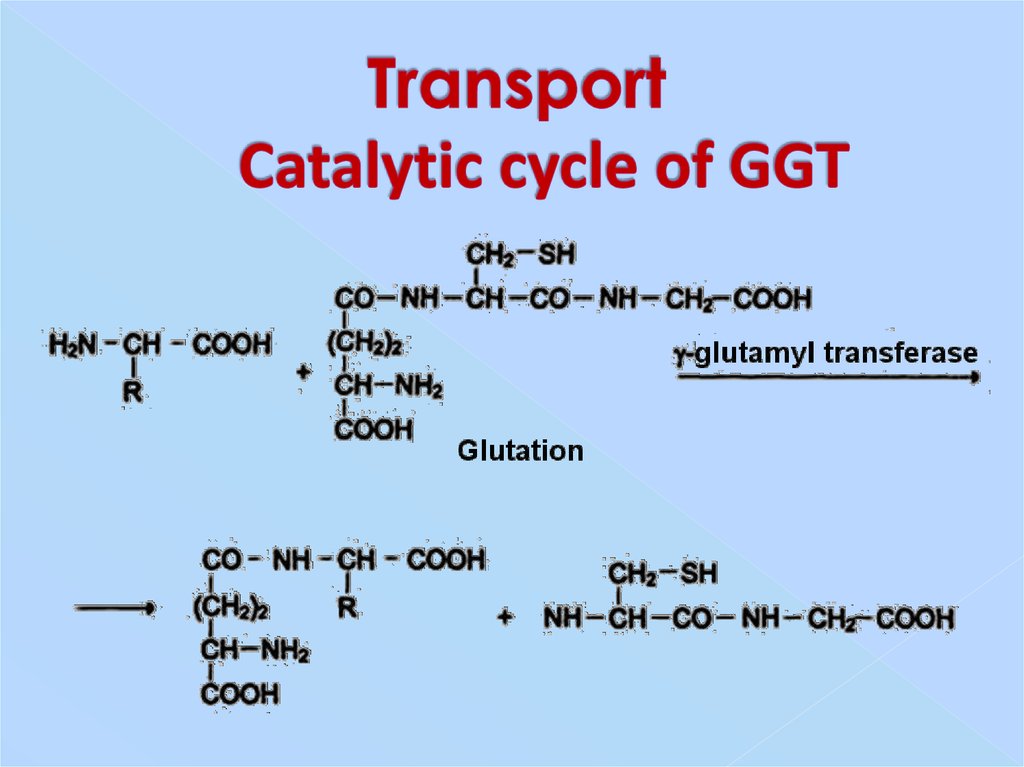
13. Transport Catalytic cycle of GGT
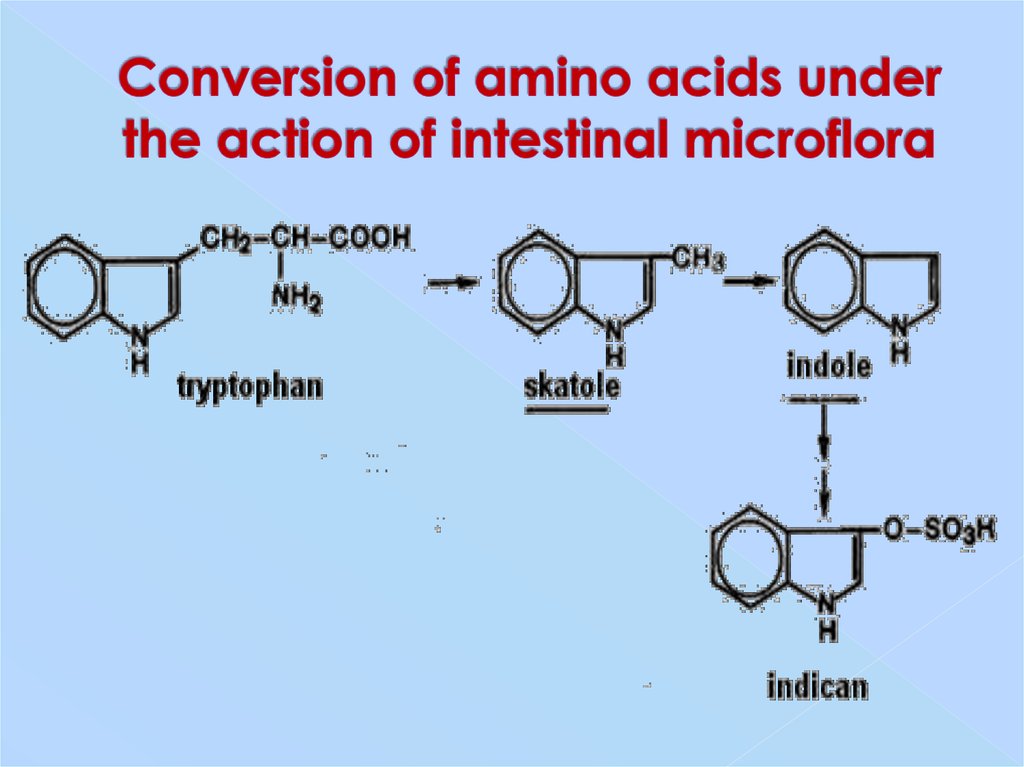
14. Conversion of amino acids under the action of intestinal microflora
15. Proteolysis in tissues
16.
Avram Hershko,Aaron Ciechanover and Irwin Rose
Nobel Prize in Chemistry, 2004
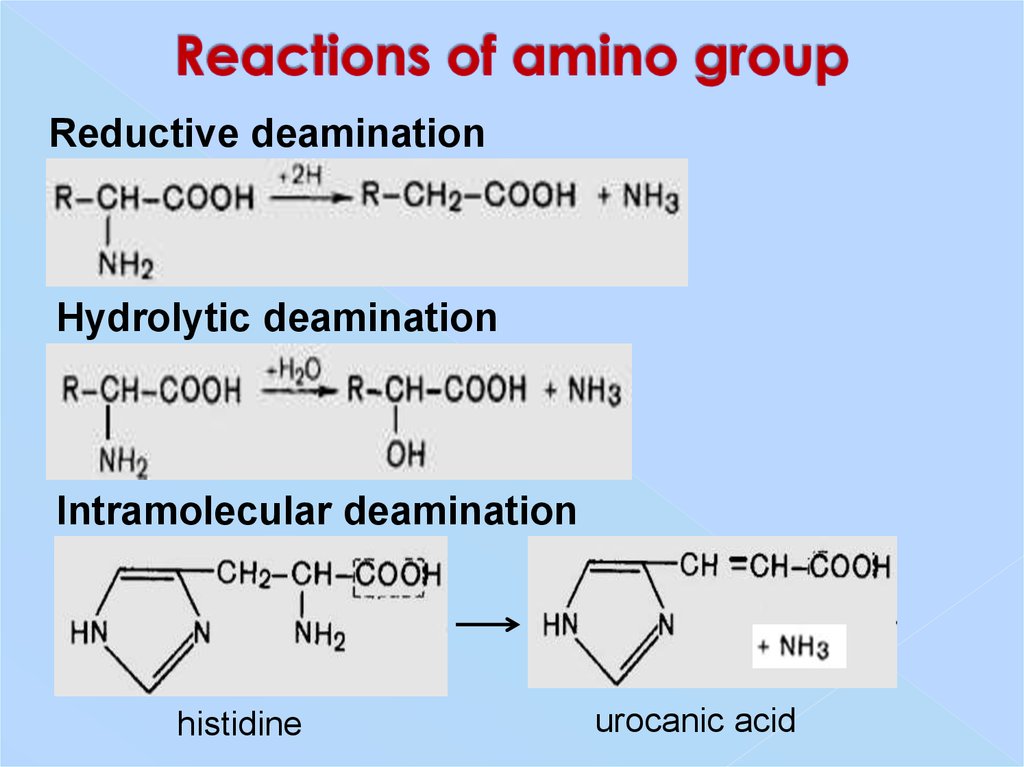
17. Reactions of amino group
Reductive deaminationHydrolytic deamination
Intramolecular deamination
histidine
urocanic acid
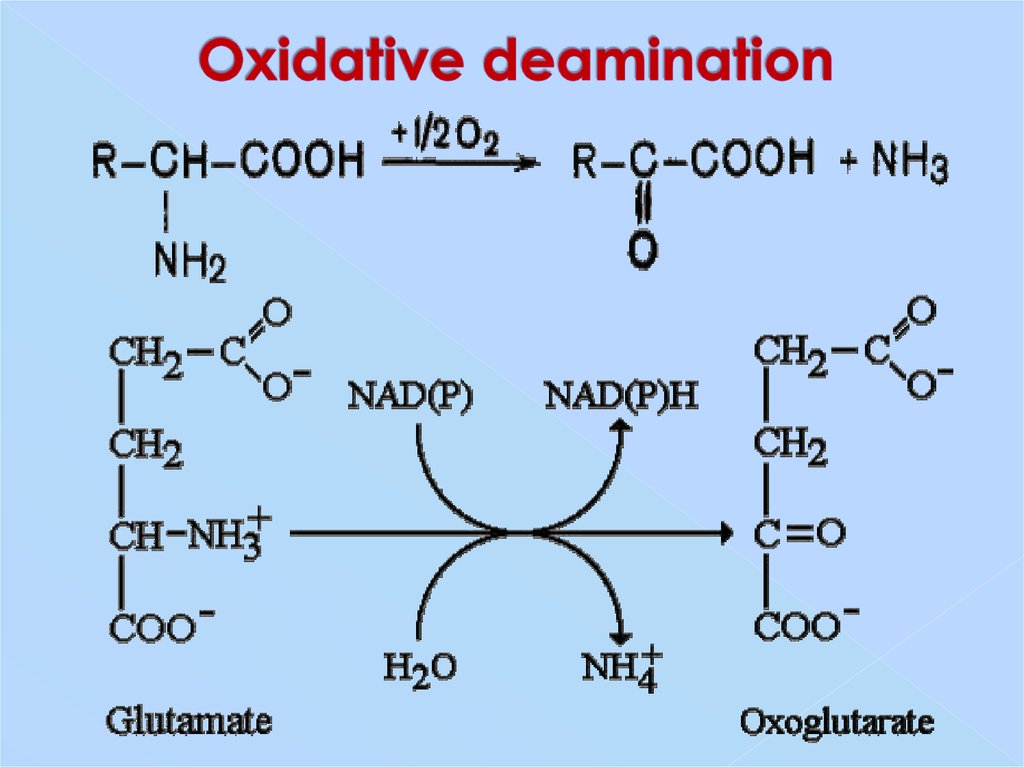
18. Oxidative deamination
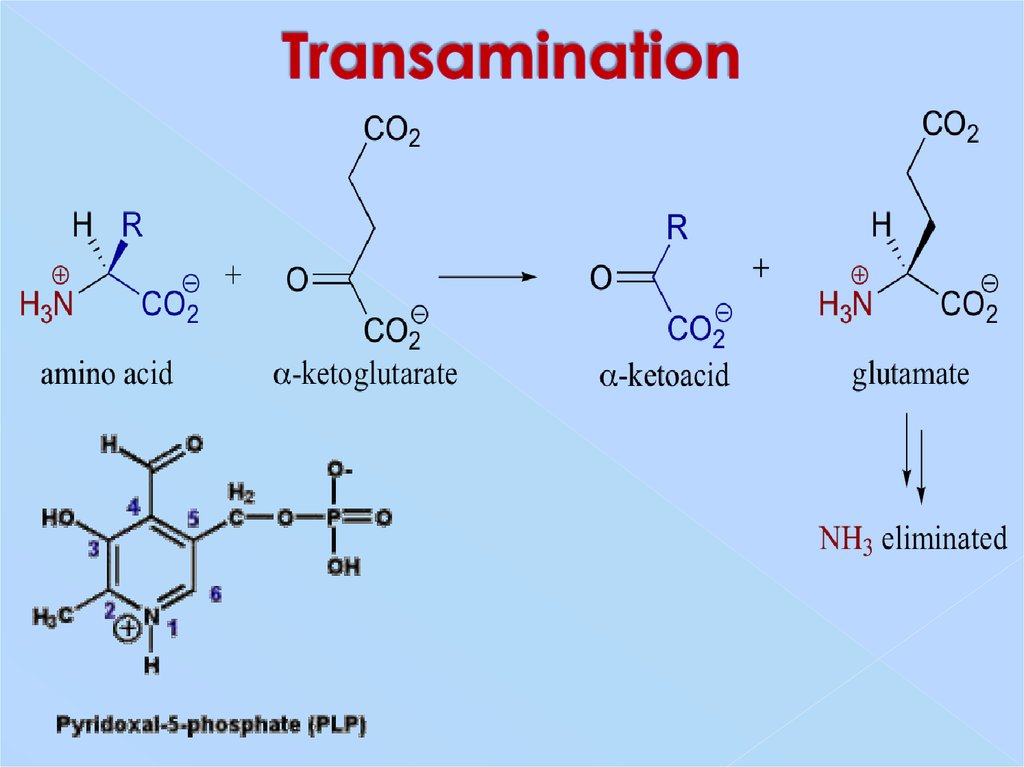
19. Transamination
20. Evaluation of transaminase activity
ASTALT
Alanine + α-ketoglutarate
pyruvate + glutamate
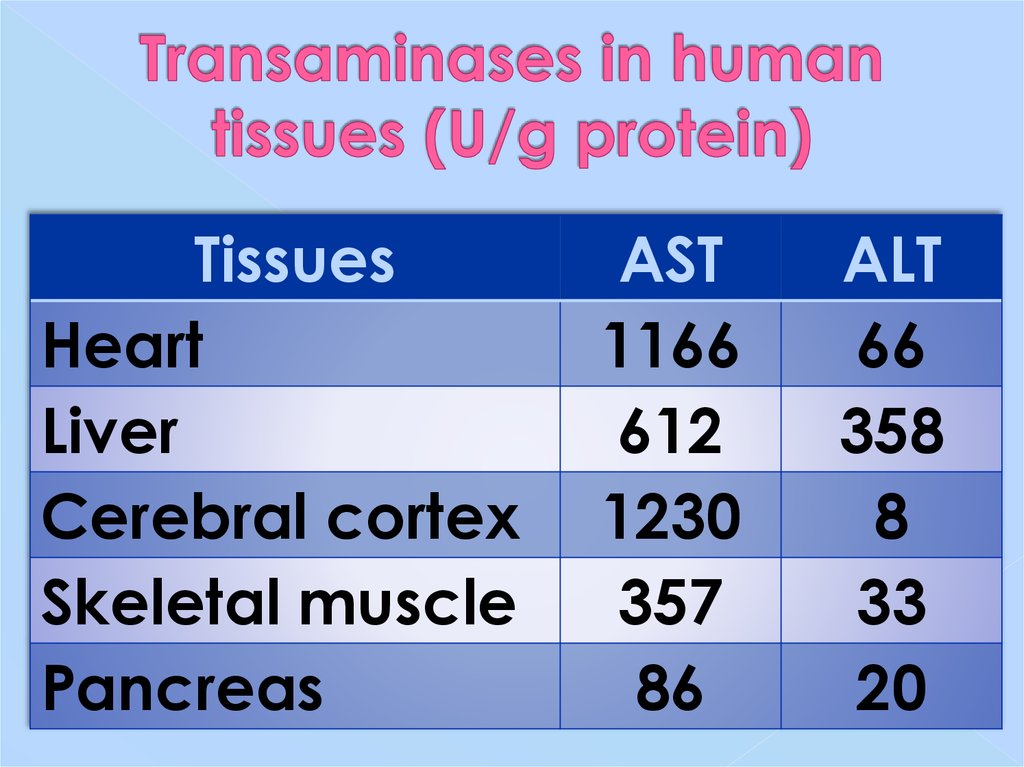
21. Transaminases in human tissues (U/g protein)
TissuesHeart
Liver
Cerebral cortex
Skeletal muscle
Pancreas
AST
1166
612
1230
357
86
ALT
66
358
8
33
20
22.
АSТde Ritis ratio =
АLТ
Myocardial infarction DRr 1,3
Viral hepatitis DRr 1
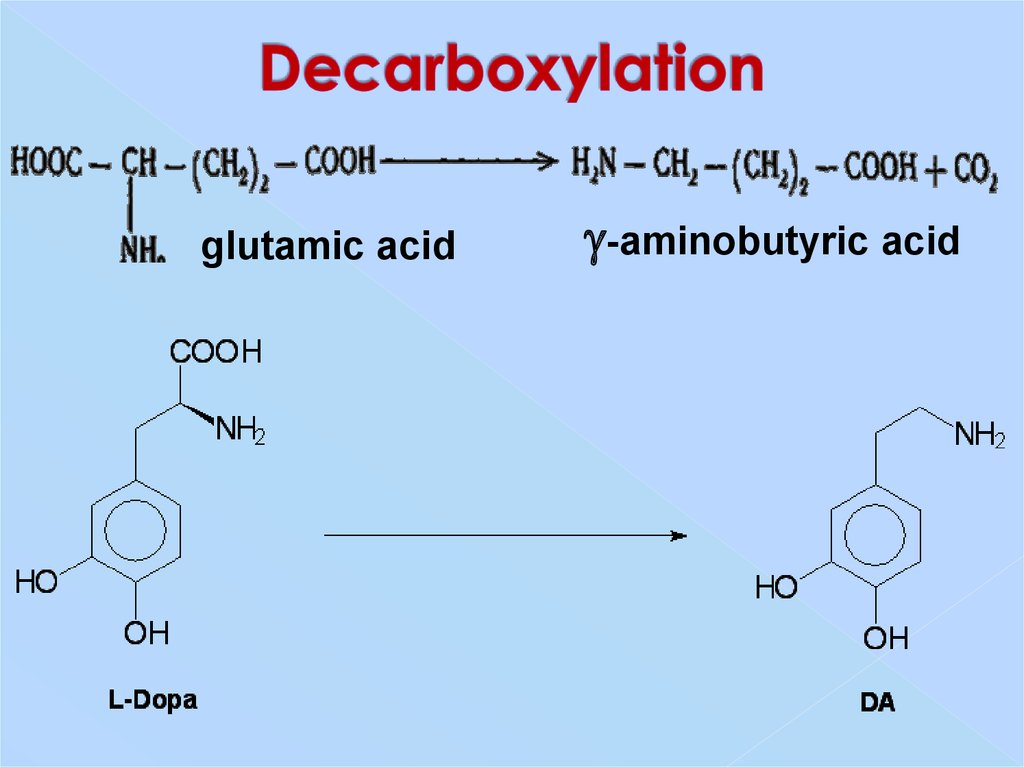
23. Decarboxylation
24.
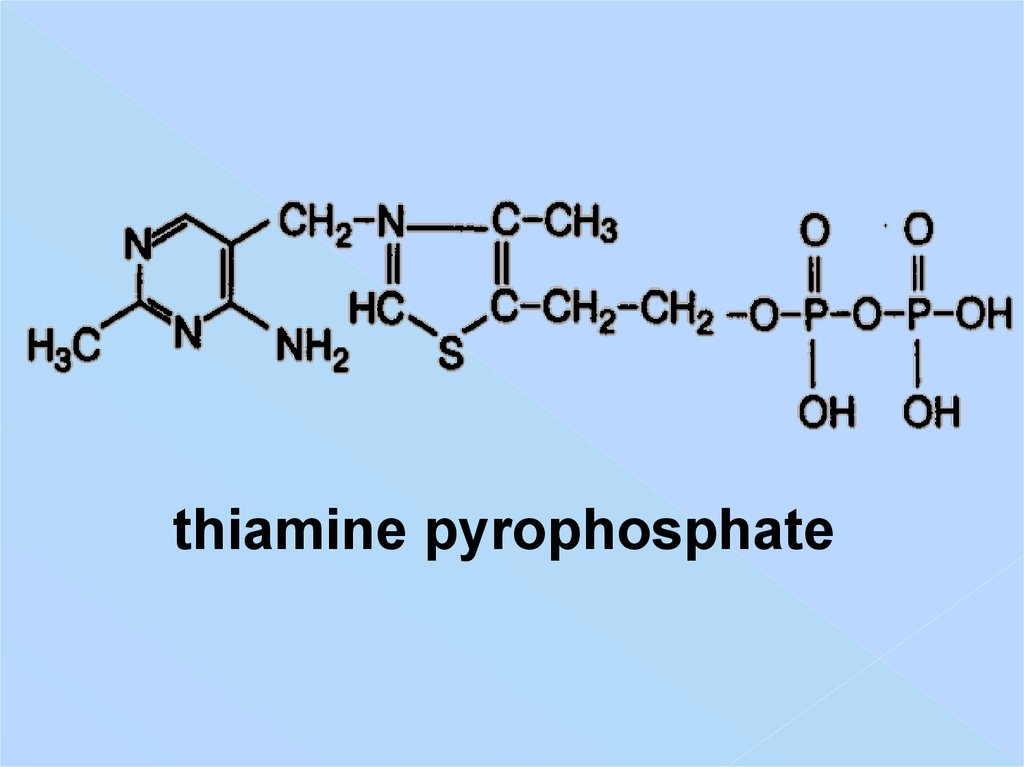
thiamine pyrophosphate25. Decarboxylation
glutamic acid-aminobutyric acid
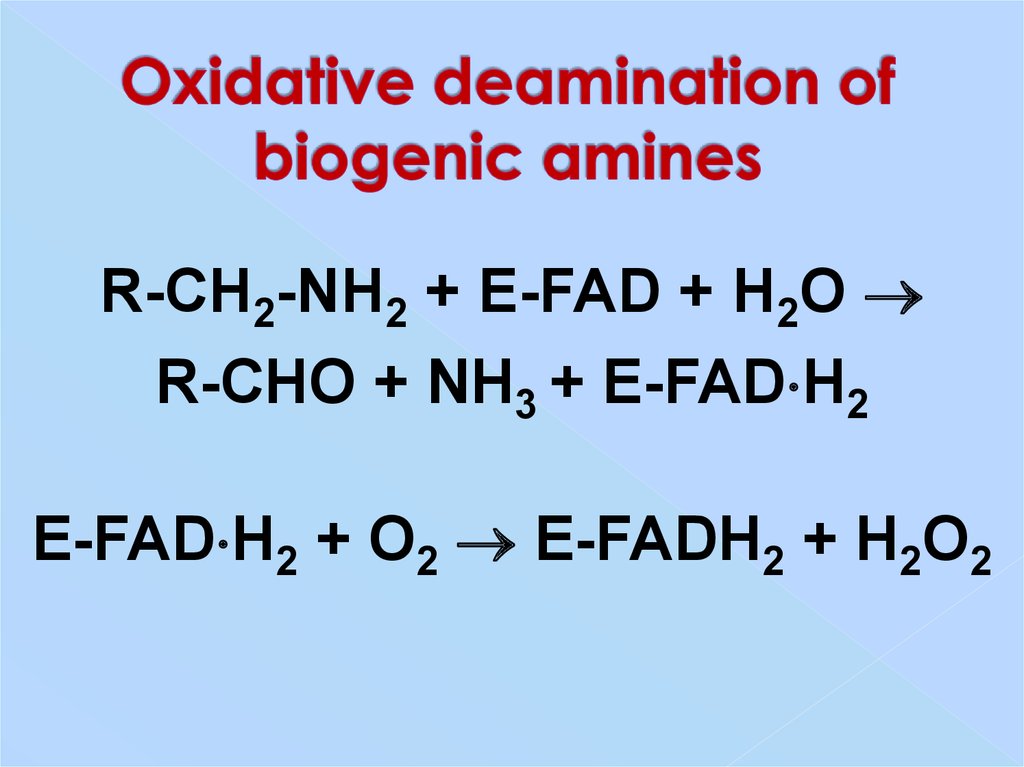
26. Oxidative deamination of biogenic amines
R-CH2-NH2 + E-FAD + H2OR-CHO + NH3 + E-FAD H2
E-FAD H2 + O2 E-FADH2 + H2O2
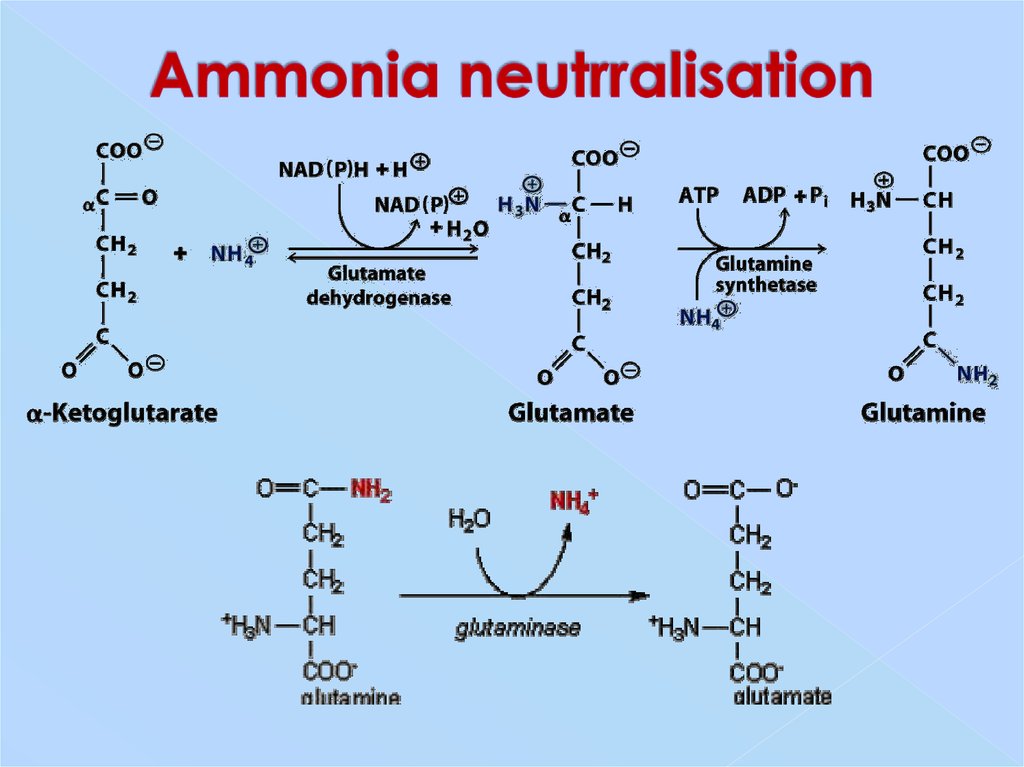
27. Ammonia neutrralisation
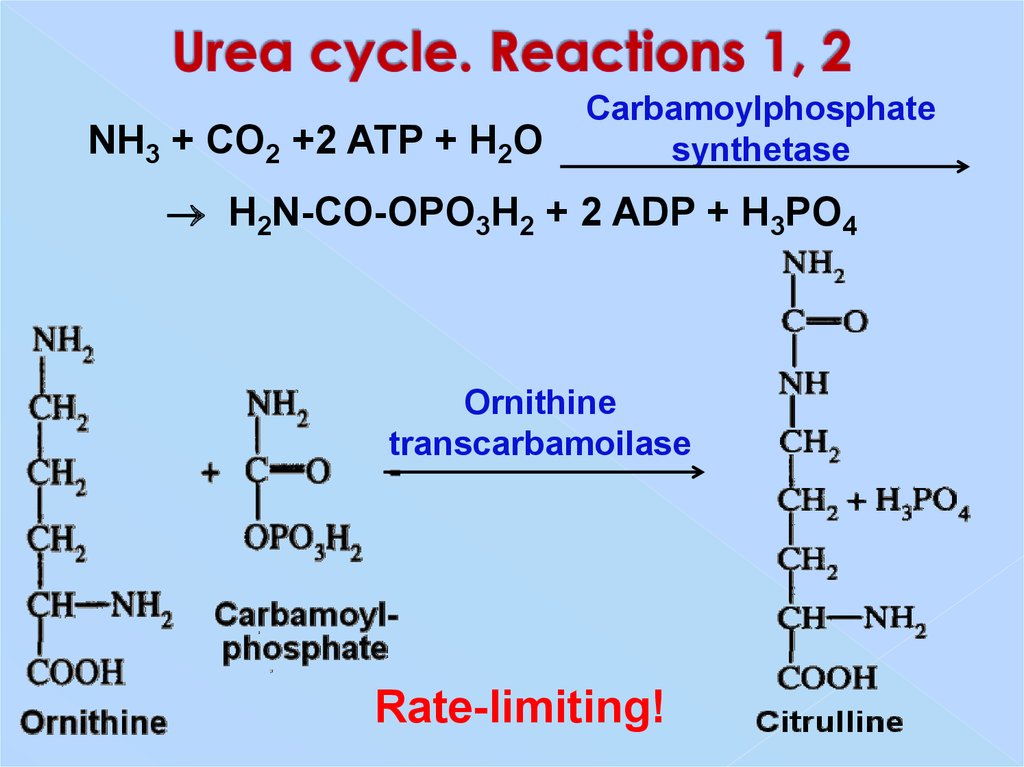
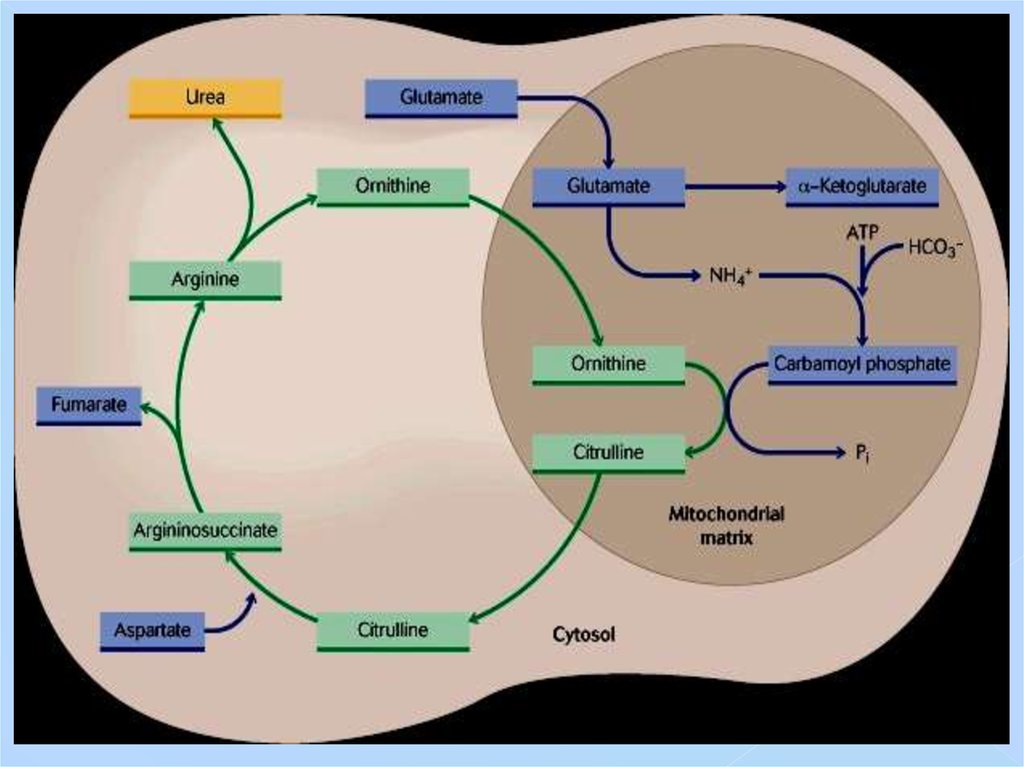
28. Urea cycle. Reactions 1, 2
NH3 + CO2 +2 ATP + H2OCarbamoylphosphate
synthetase
H2N-CO-OPO3H2 + 2 ADP + H3PO4
Ornithine
transcarbamoilase
Rate-limiting!
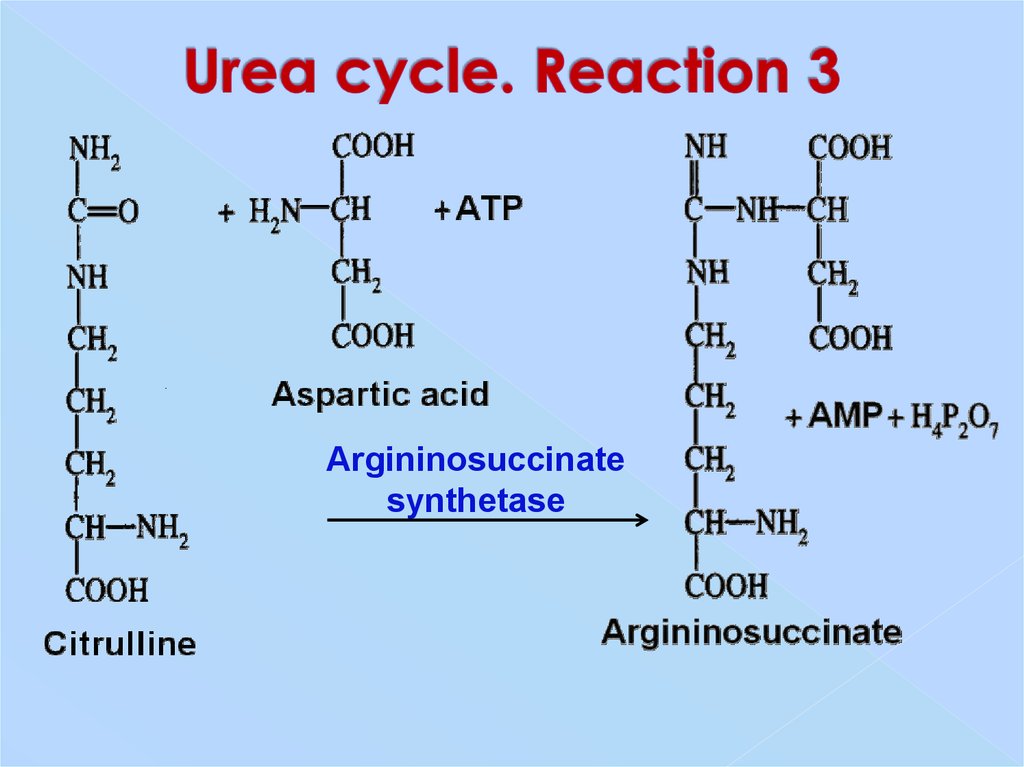
29. Urea cycle. Reaction 3
Argininosuccinatesynthetase
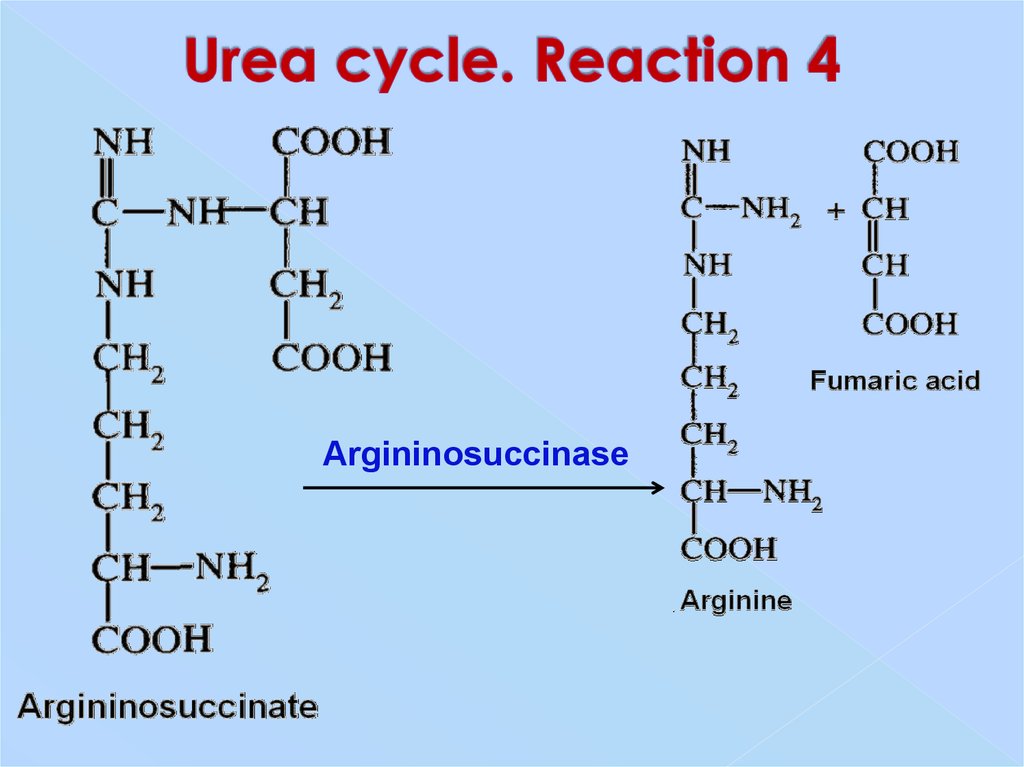
30. Urea cycle. Reaction 4
Argininosuccinase31. Urea cycle. Reaction 5
Rate-limiting!32.
33. Kwashiorkor
34.
35.
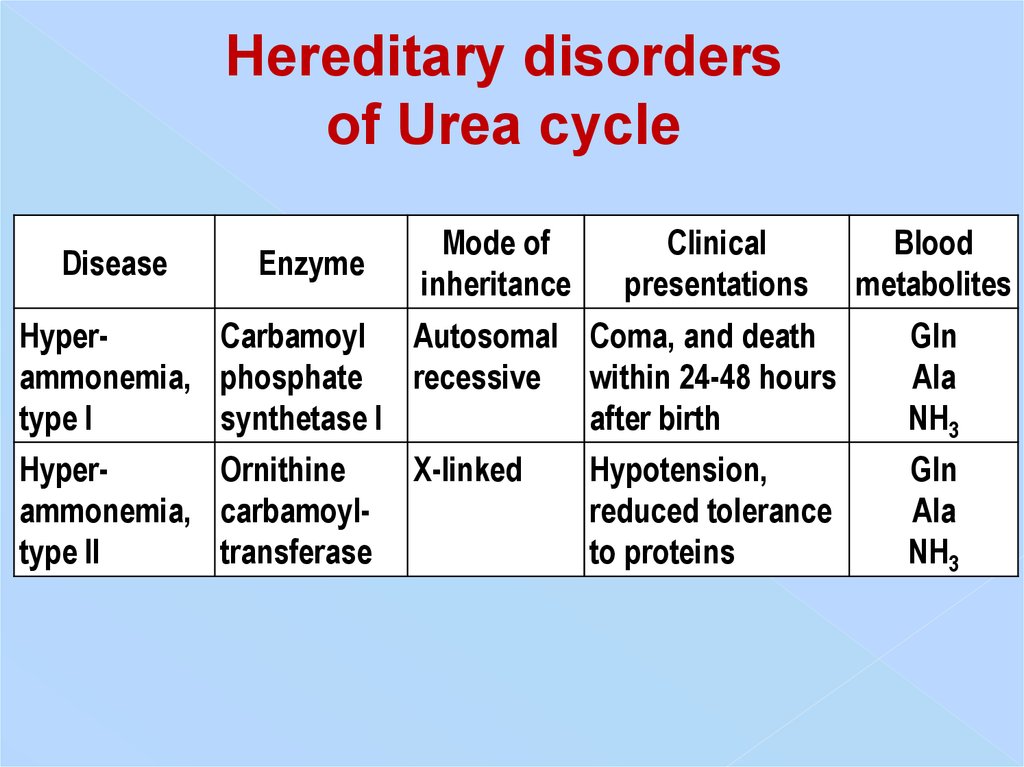
Hereditary disordersof Urea cycle
Disease
Enzyme
Mode of
inheritance
Clinical
presentations
Blood
metabolites
HyperCarbamoyl Autosomal Coma, and death
ammonemia, phosphate recessive within 24-48 hours
type I
synthetase I
after birth
Gln
Аlа
NH3
HyperOrnithine
ammonemia, carbamoyltype II
transferase
Gln
Аlа
NH3
X-linked
Hypotension,
reduced tolerance
to proteins











 chemistry
chemistry








