Similar presentations:
Eukarya Kingdom: Animalia ٍSubkigdom : Metazoa Triploblastic Animal
1. Domain : Eukarya Kingdom: Animalia ٍSubkigdom : Metazoa Triploblastic Animals- I- Acoelomate Animals Flate worms))- Phylum:
Domain : EukaryaKingdom: Animalia
Subkigdom : Metazoaٍ
- Triploblastic Animals
I- Acoelomate Animals
- Phylum: Platyhelminthes )Flate worms)
1
30 April 2019
2. Characteristics
1. They are soft bodied, unsegmented worms.2. They show bilateral symmetry and
dorsiventrally flat worms
3. Triploplastic.
4. Exo or Endo skeleton is completely absent.
5. The parasite shows suckers or hooks or both for attachment to the
host body.
6. They are the first animals to illustrate the development of organ
system.
7. A true body cavity or coelome is absent, and the space between
the body organs is filled with loose parenchyma.
2
30 April 2019
3. Characteristics cont.
8. Circulatory and respiratory systems are absent.9. Nervous system and sense organs are poorly
developed.
10. Usually hermaphrodite animals.
11. May be free living (Turbellaria), ectoparasitic or
endoparasitic. A few may be commensals.
12. The alimentary canal is either absent or highly
branched. Anus is absent.(incomplete digestive
system)
3
30 April 2019
4. Phylum Platyhelminthes is divided into three classes:
Class I:- TURBELLARIAEx. Planaria sp.
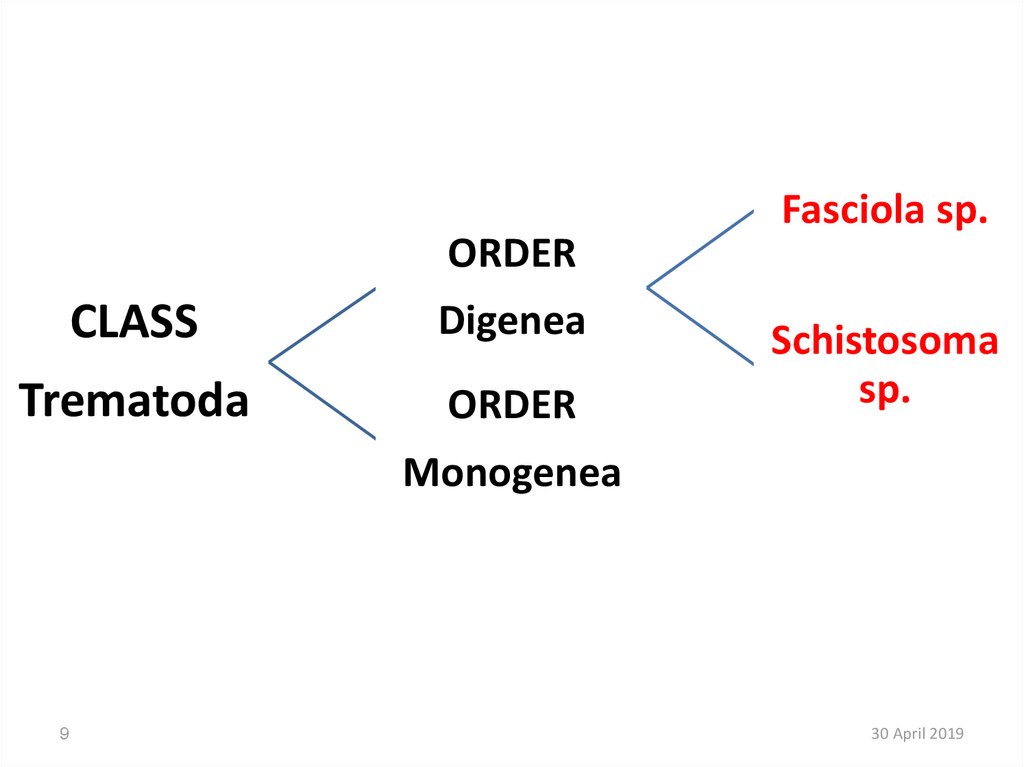
Class II:- TERMATODA
Order: Diginea
Ex1- Fasciola sp.
Ex2- Schistosoma sp.
Class III:- CESTODA
Ex. Taenia sp.
4
30 April 2019
5. CLASS I: TURBELLARIA :
1. Mostly free - living forms found in fresh or seawaters or on land.
2. Body is unsegmented and dorsoventrally
flattened.
3. Epidermis is cellular or syncytial.
4 Intestine is either absent (Acoela) or simple
and sac like (Rhabdocoela) or branched.
5
30 April 2019
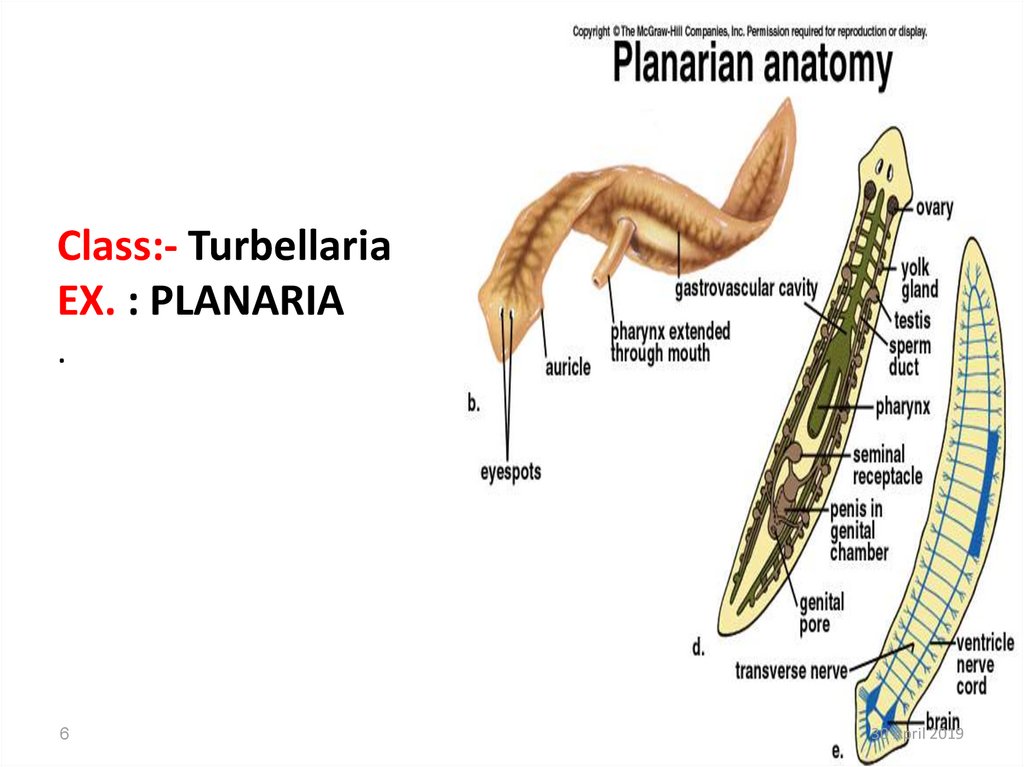
6. Class:- Turbellaria EX. : PLANARIA .
630 April 2019
7.
730 April 2019
8. CLASS II : TERMATODA :
CLASS II : TERMATODA :I. These are commonly known as flukes.
II. These are ectoparasitic or endoparasitic
forms.
III. Body is unsegmented and enlongated.
IV. Adhesive organs are, one or two suckers
without hooks and spines.
V. Digestive tract is bifurcated and highly
diverticulated. Anus is absent.
8
30 April 2019
9.
ORDERCLASS
Digenea
Trematoda
ORDER
Fasciola sp.
Schistosoma
sp.
Monogenea
9
30 April 2019
10. Ex 1: Fasciola Hepatica (liver flukes)
An endoparasite
Has 2 hosts(digenea)
Primary host : sheep
Secondary host : snail
Infective stage to
snail:miracidium
• Infective stage to
sheep:metacercariae
10
30 April 2019
11.
1130 April 2019
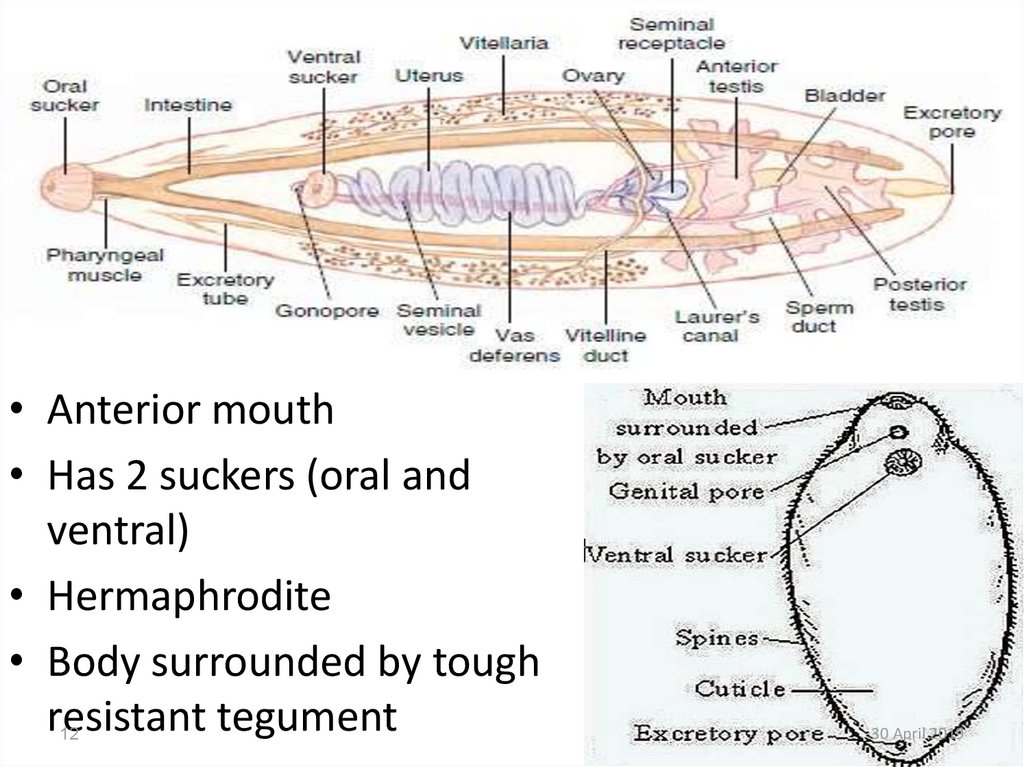
12.
• Anterior mouth• Has 2 suckers (oral and
ventral)
• Hermaphrodite
• Body surrounded by tough
resistant tegument
12
30 April 2019
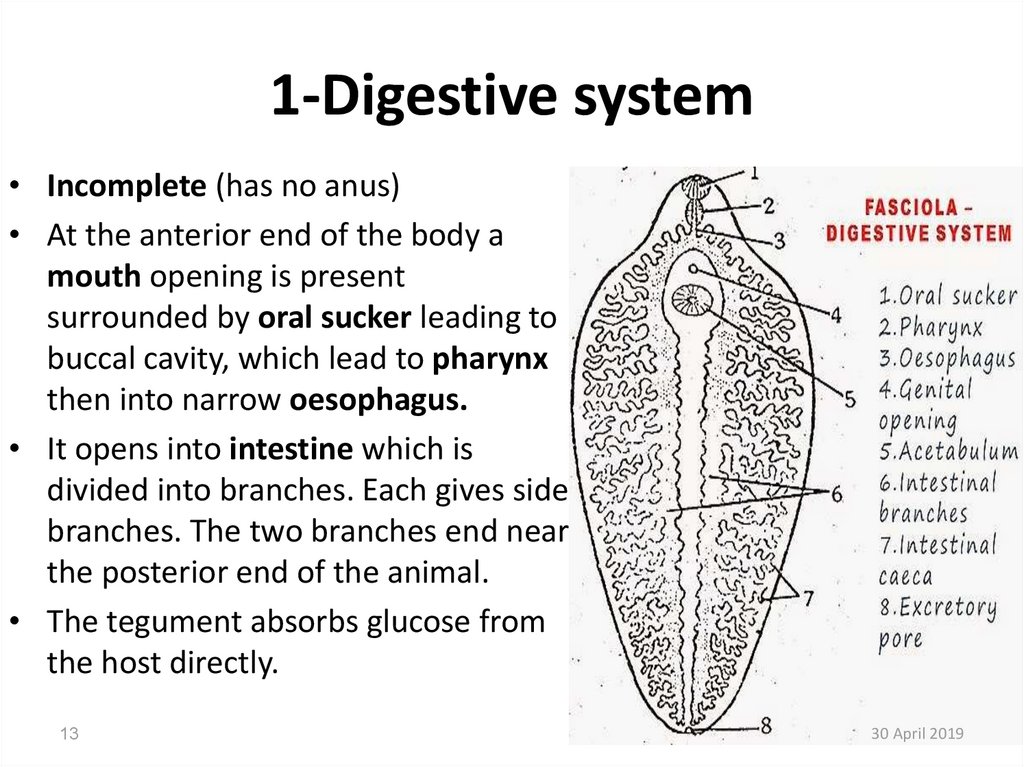
13. 1-Digestive system
• Incomplete (has no anus)• At the anterior end of the body a
mouth opening is present
surrounded by oral sucker leading to
buccal cavity, which lead to pharynx
then into narrow oesophagus.
• It opens into intestine which is
divided into branches. Each gives side
branches. The two branches end near
the posterior end of the animal.
• The tegument absorbs glucose from
the host directly.
13
30 April 2019
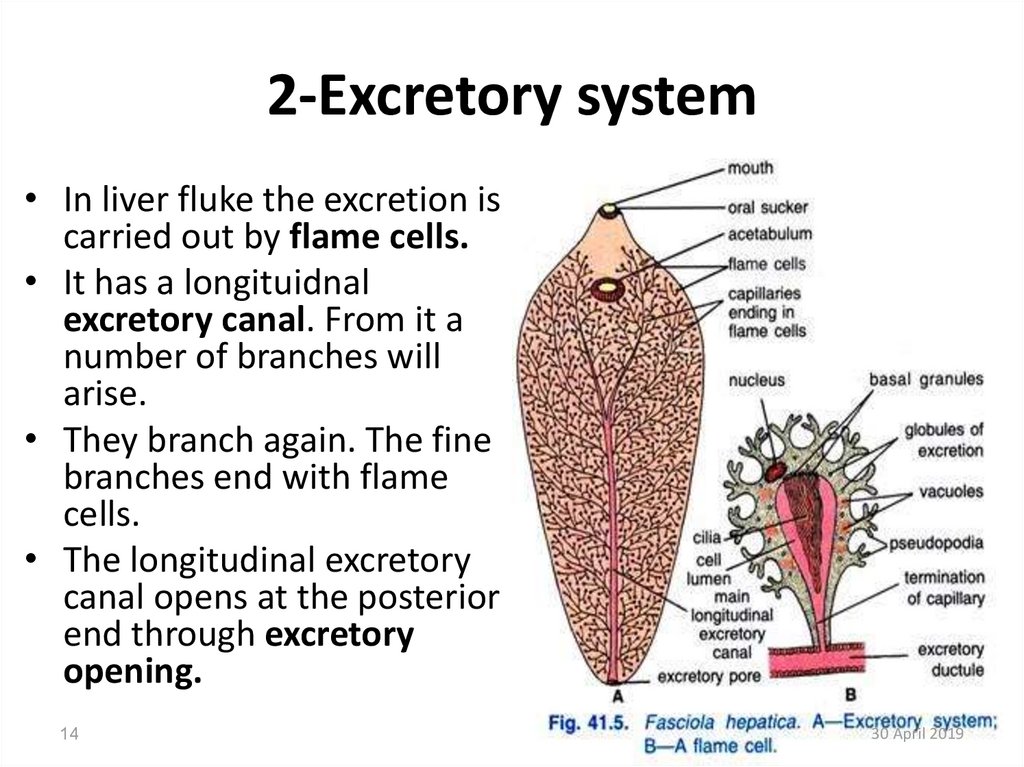
14. 2-Excretory system
• In liver fluke the excretion iscarried out by flame cells.
• It has a longituidnal
excretory canal. From it a
number of branches will
arise.
• They branch again. The fine
branches end with flame
cells.
• The longitudinal excretory
canal opens at the posterior
end through excretory
opening.
14
30 April 2019
15. 3-Reproductive system
1530 April 2019
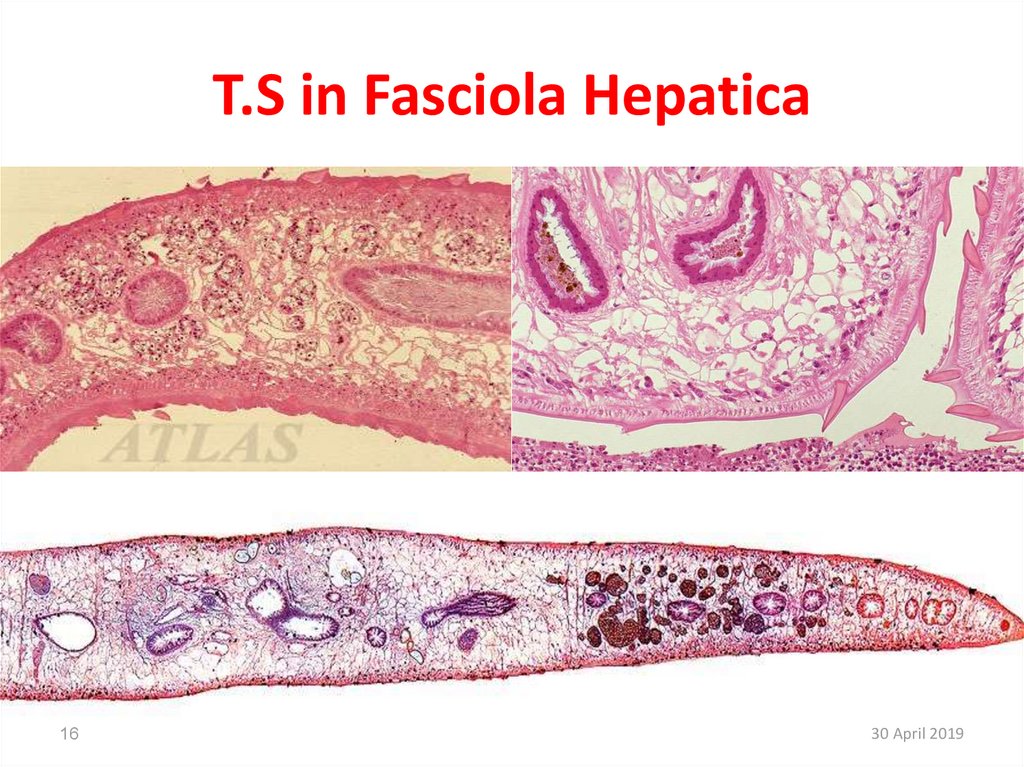
16. T.S in Fasciola Hepatica
1630 April 2019
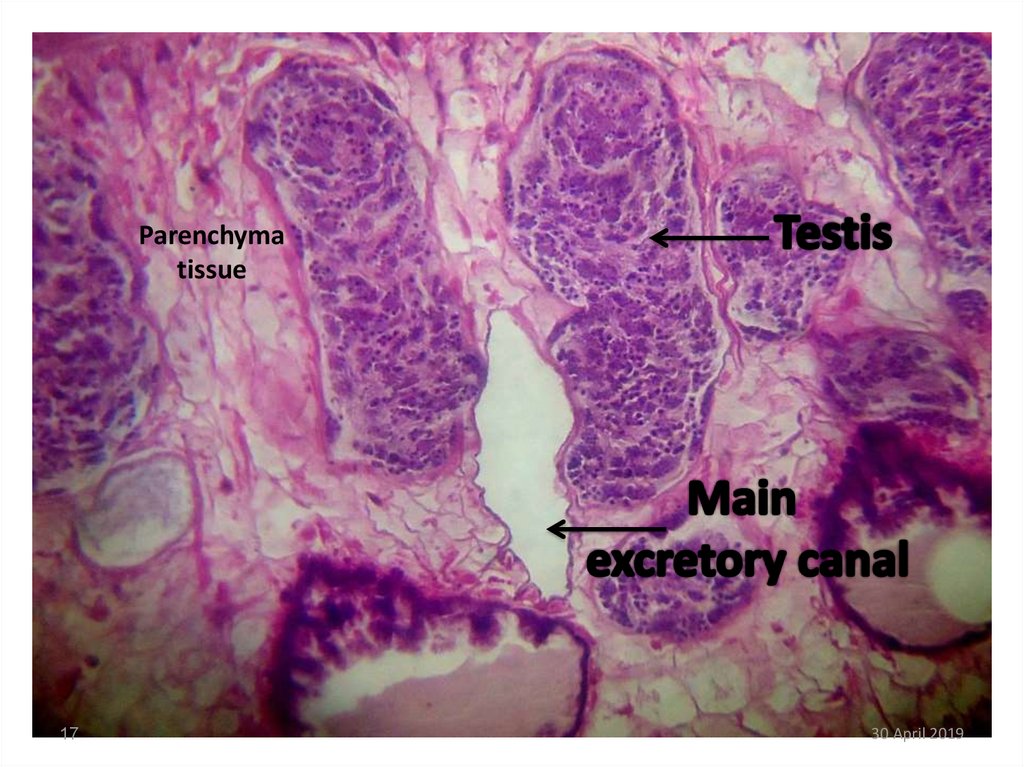
17.
Parenchymatissue
17
30 April 2019
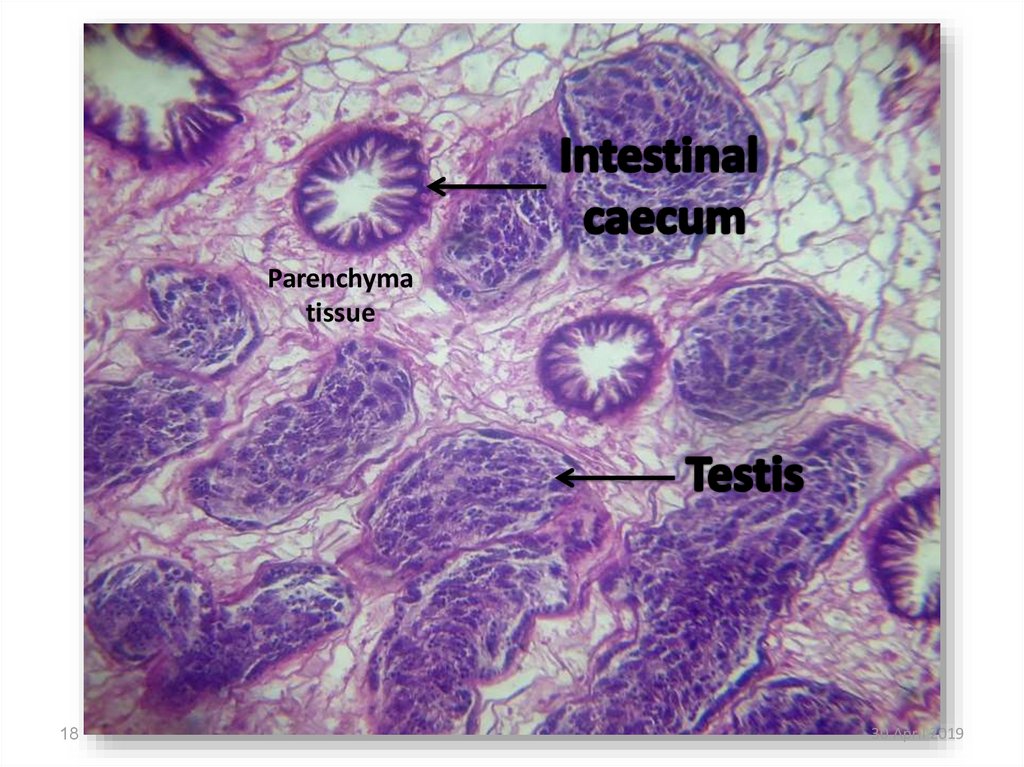
18.
Parenchymatissue
18
30 April 2019
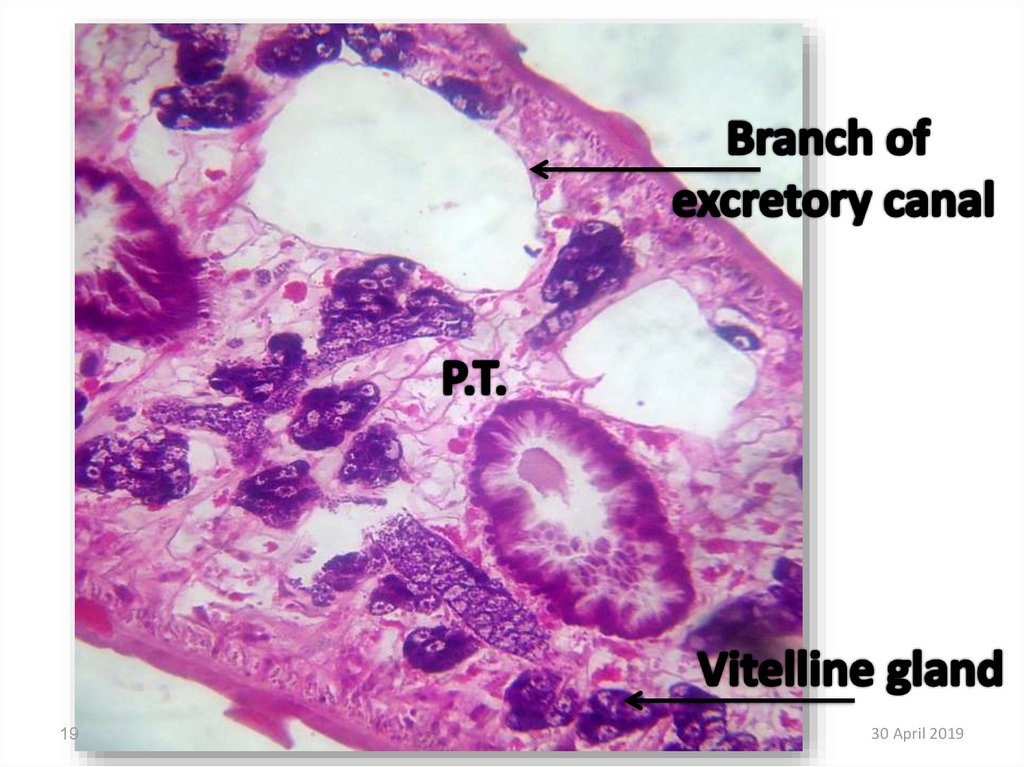
19.
1930 April 2019
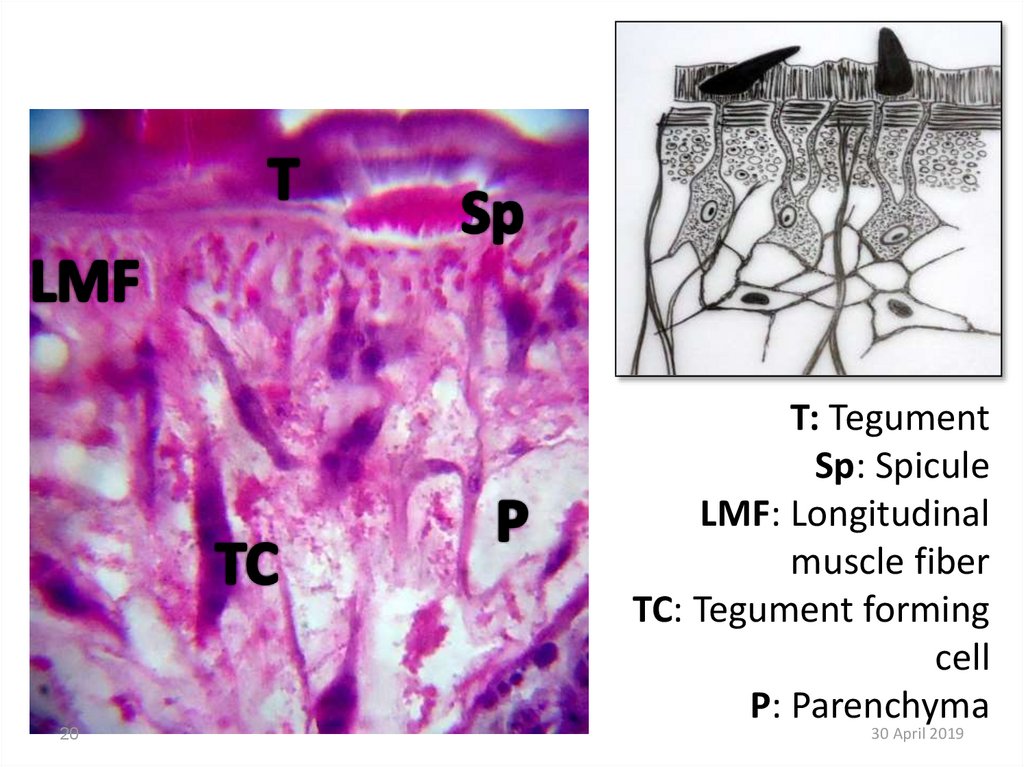
20.
20T: Tegument
Sp: Spicule
LMF: Longitudinal
muscle fiber
TC: Tegument forming
cell
P: Parenchyma
30 April 2019
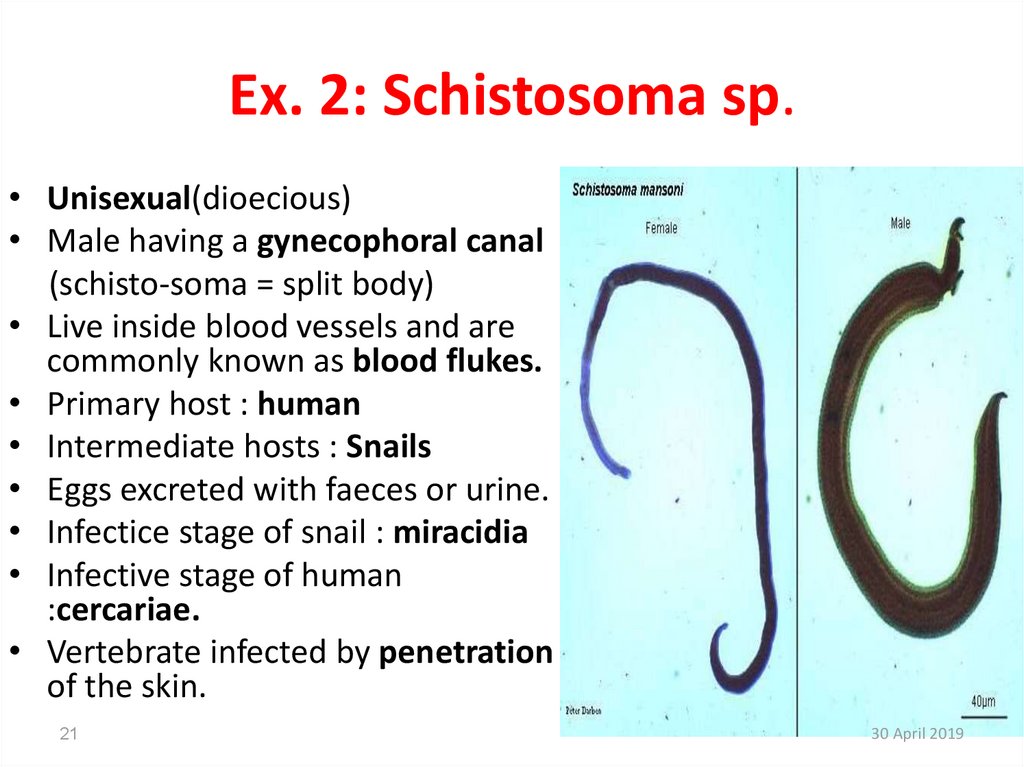
21. Ex. 2: Schistosoma sp.
• Unisexual(dioecious)• Male having a gynecophoral canal
(schisto-soma = split body)
• Live inside blood vessels and are
commonly known as blood flukes.
• Primary host : human
• Intermediate hosts : Snails
• Eggs excreted with faeces or urine.
• Infectice stage of snail : miracidia
• Infective stage of human
:cercariae.
• Vertebrate infected by penetration
of the skin.
21
30 April 2019
22.
2230 April 2019
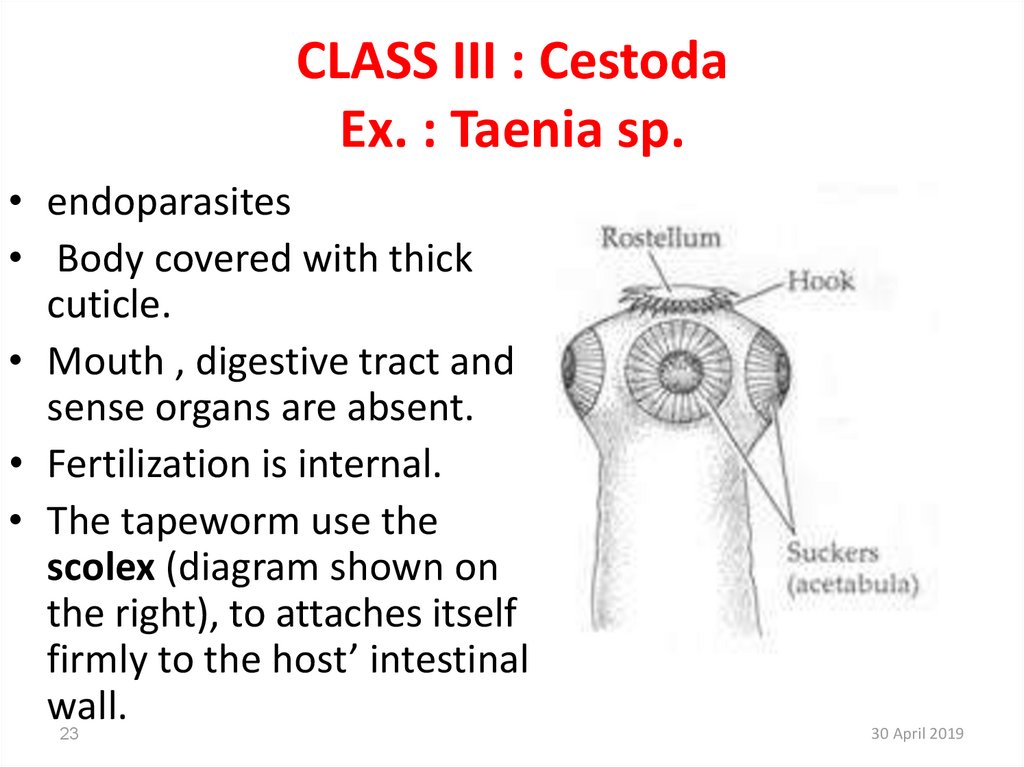
23. CLASS III : Cestoda Ex. : Taenia sp.
• endoparasites• Body covered with thick
cuticle.
• Mouth , digestive tract and
sense organs are absent.
• Fertilization is internal.
• The tapeworm use the
scolex (diagram shown on
the right), to attaches itself
firmly to the host’ intestinal
wall.
23
30 April 2019
24.
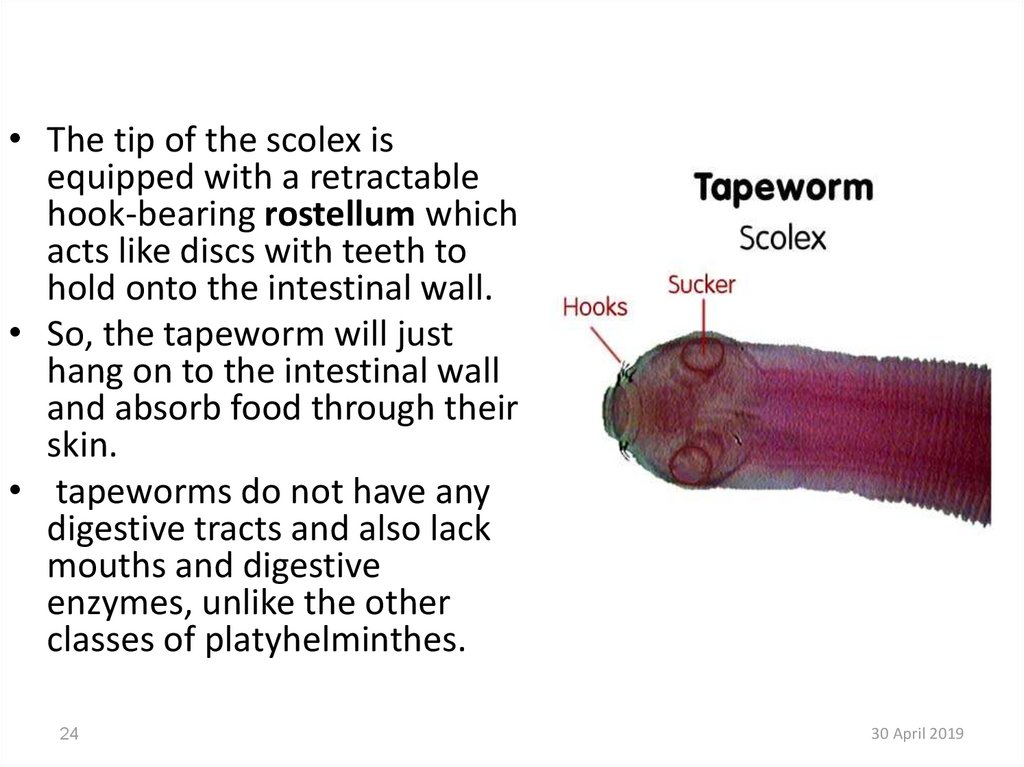
• The tip of the scolex isequipped with a retractable
hook-bearing rostellum which
acts like discs with teeth to
hold onto the intestinal wall.
• So, the tapeworm will just
hang on to the intestinal wall
and absorb food through their
skin.
• tapeworms do not have any
digestive tracts and also lack
mouths and digestive
enzymes, unlike the other
classes of platyhelminthes.
24
30 April 2019
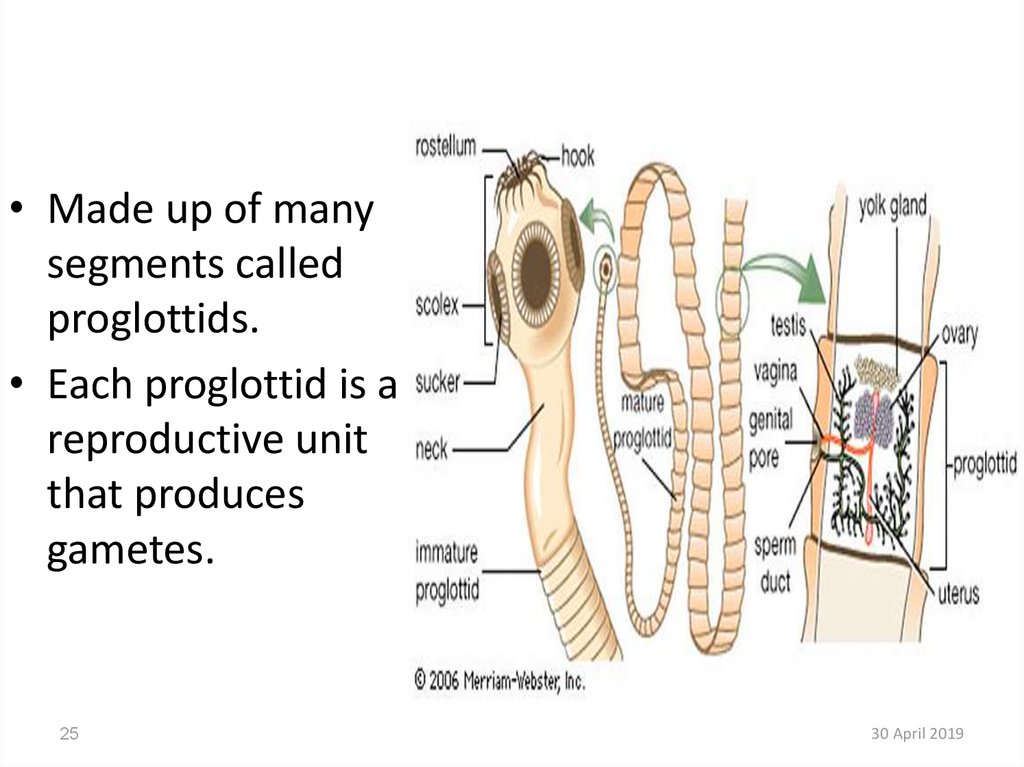
25.
• Made up of manysegments called
proglottids.
• Each proglottid is a
reproductive unit
that produces
gametes.
25
30 April 2019
26.
• The neck produces segments calledproglottids which make up the body
and tail.
• Each segment has both male and
female reproductive organs.
• Segments can produce eggs on their
own but sometimes mate with other
segments or even other tapeworms.
• Segments absorb nutrients through
their skin and have the ability to
produce eggs.
• Over time the segments fill with eggs
and detach from the tail. They are
then carried out of the body in the
feces.
26
30 April 2019
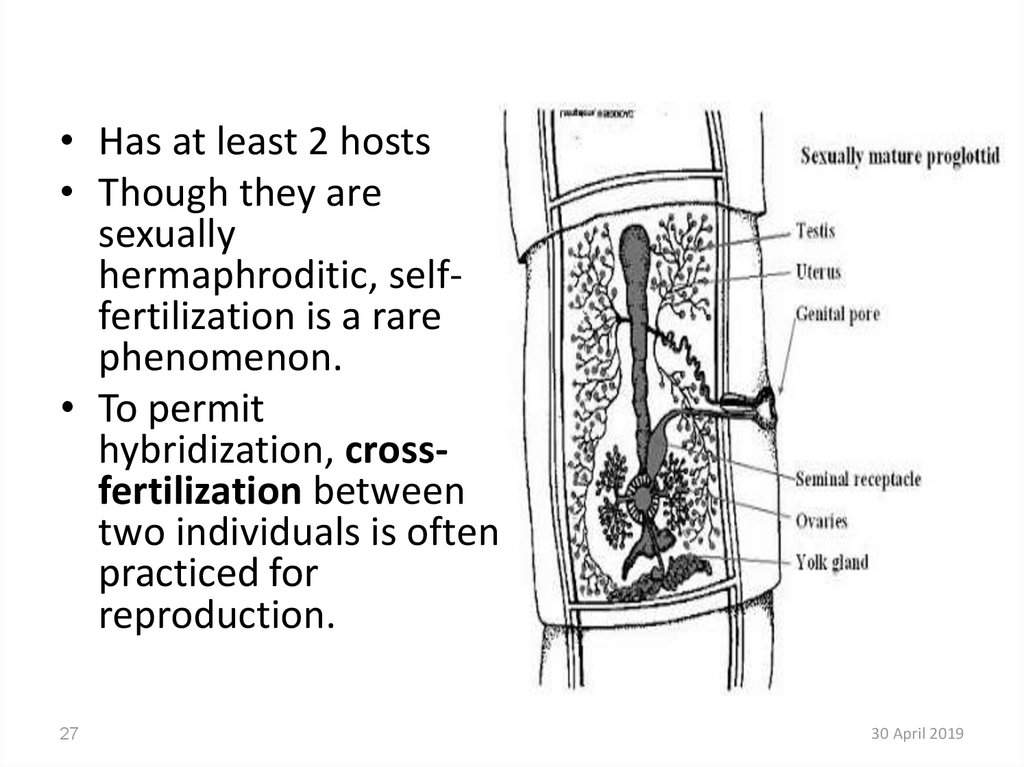
27.
• Has at least 2 hosts• Though they are
sexually
hermaphroditic, selffertilization is a rare
phenomenon.
• To permit
hybridization, crossfertilization between
two individuals is often
practiced for
reproduction.
27
30 April 2019
28.
• Endoparasitic• Primary host :
human
• Secondary host:
pigs or cattle
• Infective stage to
human :
cysticercus
• Infective stage to
pigs:
eggs or proglottid
28
30 April 2019
29.
Thank you!29
30 April 2019












 biology
biology