Similar presentations:
Topic: Flatworms
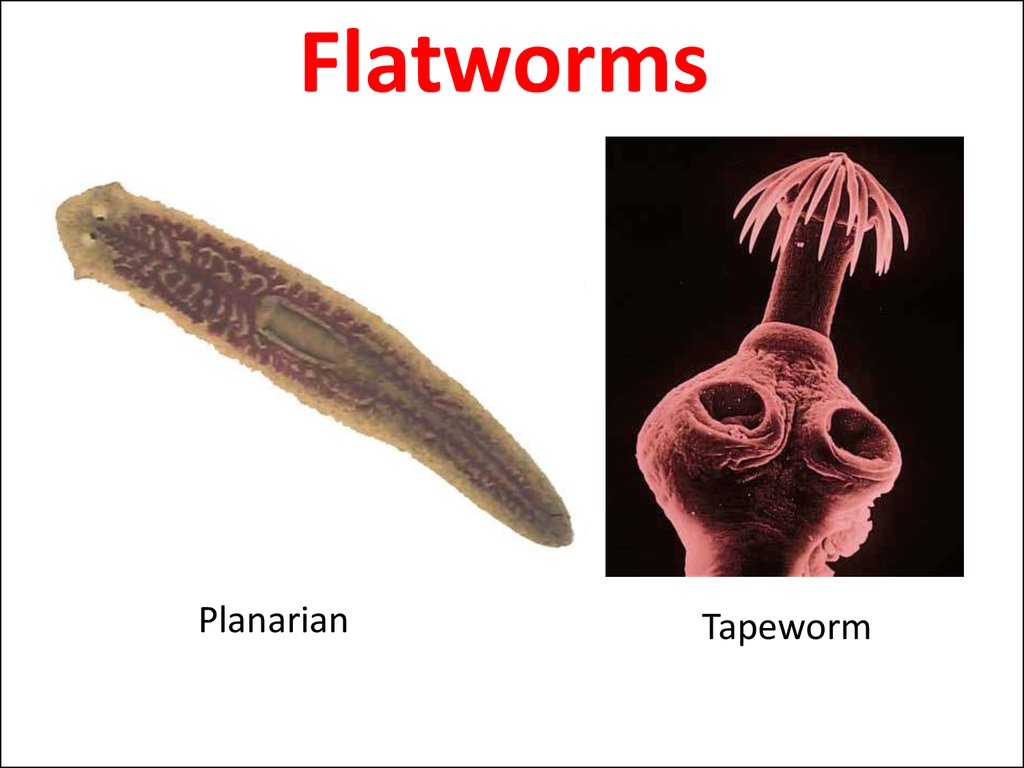
1. Flatworms
PlanarianTapeworm
2. Platyhelminthes (Flat Worms)
They have soft and flat bodies.They show bilateral symmetry.
They have three tissue layers;
Ectoderm
Mesoderm
Endoderm
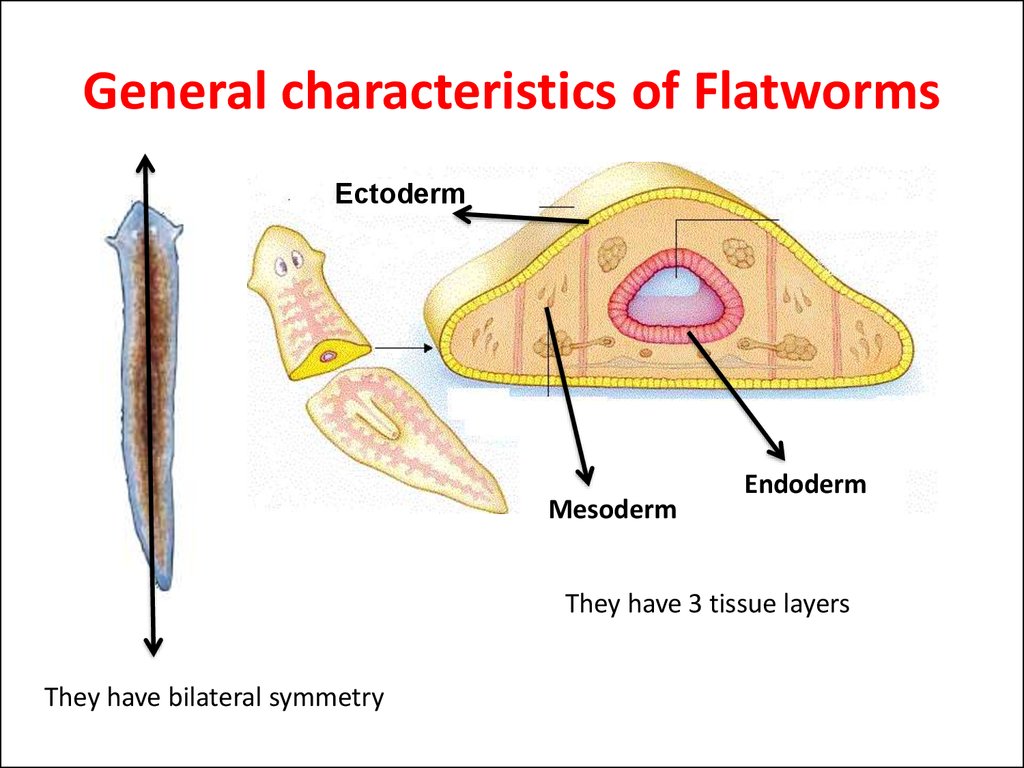
3. General characteristics of Flatworms
EctodermMesoderm
Endoderm
They have 3 tissue layers
They have bilateral symmetry
4.
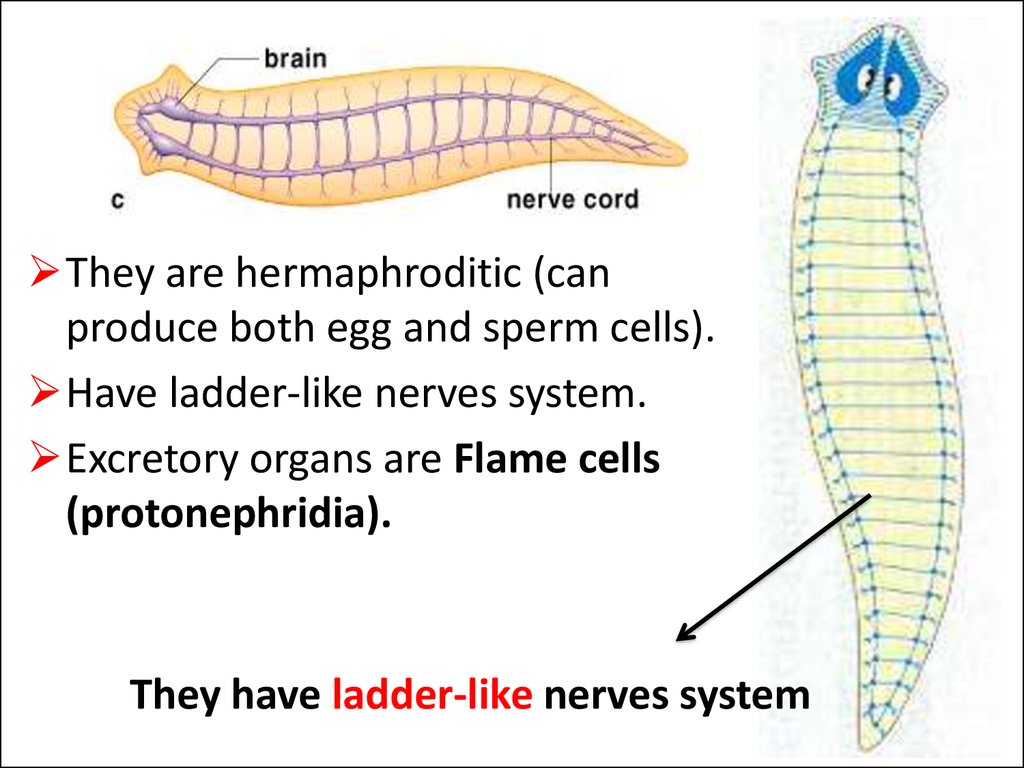
They are hermaphroditic (canproduce both egg and sperm cells).
Have ladder-like nerves system.
Excretory organs are Flame cells
(protonephridia).
They have ladder-like nerves system
5.
Excretory organsare Flame cells
(protonephridia)
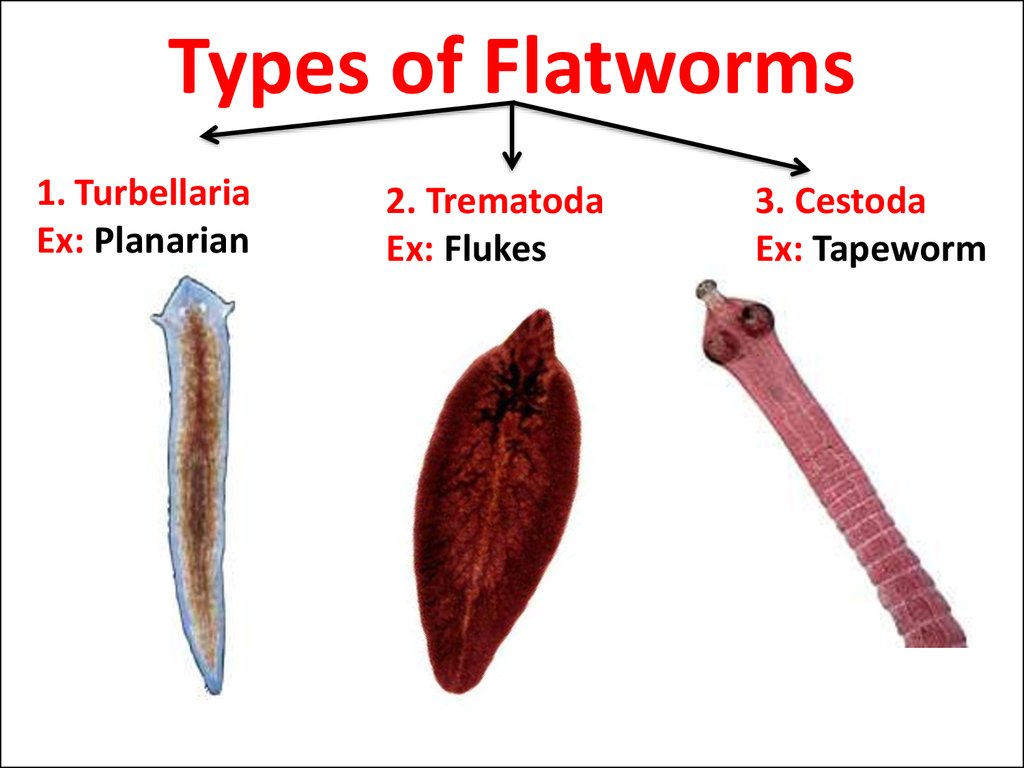
6. Types of Flatworms
1. TurbellariaEx: Planarian
2. Trematoda
Ex: Flukes
3. Cestoda
Ex: Tapeworm
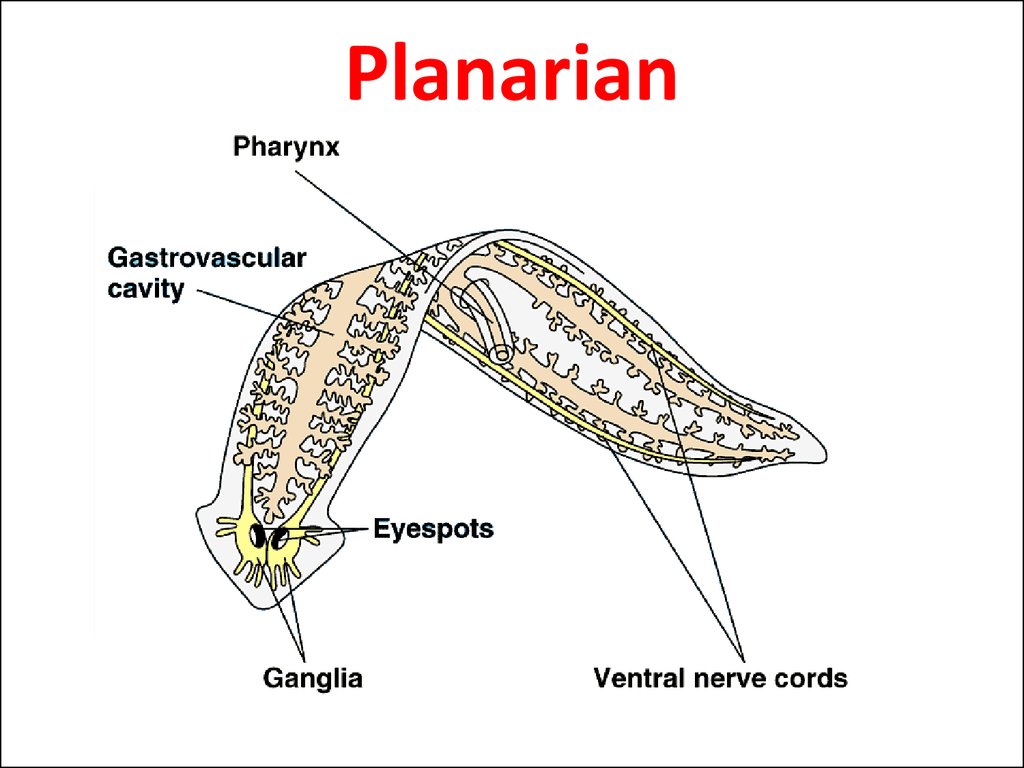
7. 1. Turbellaria: Characteristics of Planarian
Planaria is the most important example.Mostly live in fresh water.
Have two eye spots.
Have only one opening at the centre serve as
mouth and anus.
The ability of regeneration is high.
8. Planarian
9. Regeneration of Planaria
The ability of an organism to regrow lost parts is calledregeneration.
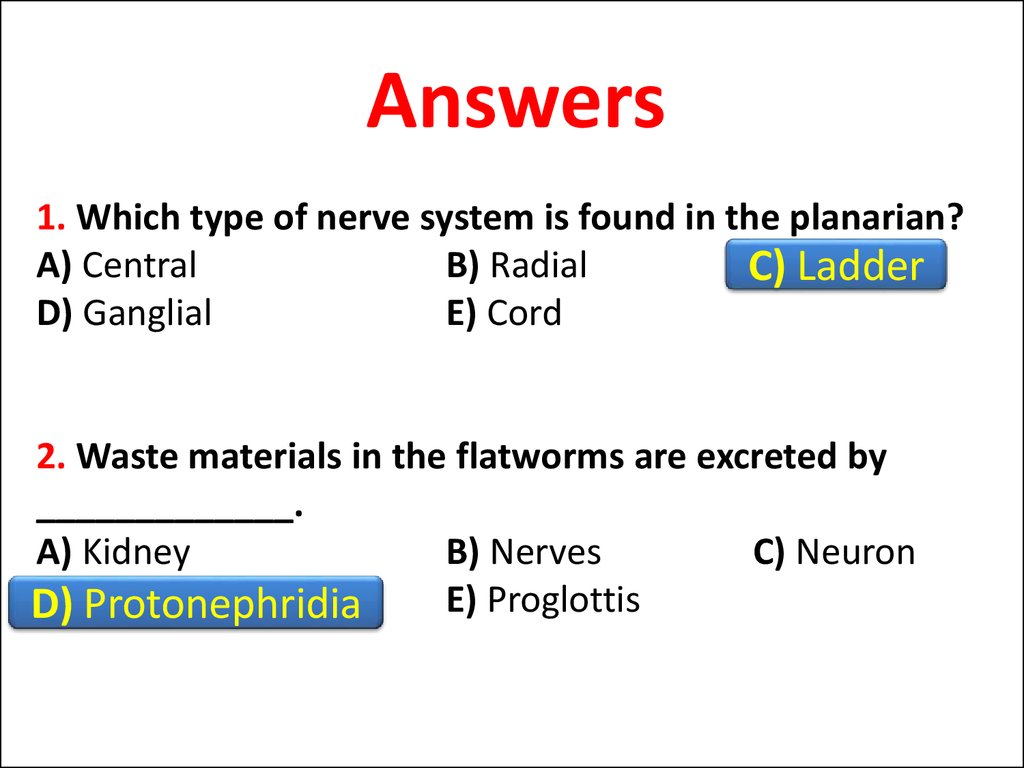
10. Question
1. Which type of nerve system is found in the planarian?A) Central
B) Radial
C) Ladder
D) Ganglial
E) Cord
2. Waste materials in the flatworms are excreted by
_____________.
A) Kidney
B) Nerves
C) Neuron
D) Protonephridia
E) Proglottis
11. Answers
1. Which type of nerve system is found in the planarian?A) Central
B) Radial
C) Ladder
C)
Ladder
D) Ganglial
E) Cord
2. Waste materials in the flatworms are excreted by
_____________.
A) Kidney
B) Nerves
C) Neuron
D) Protonephridia
E) Proglottis
D)
Protonephridia
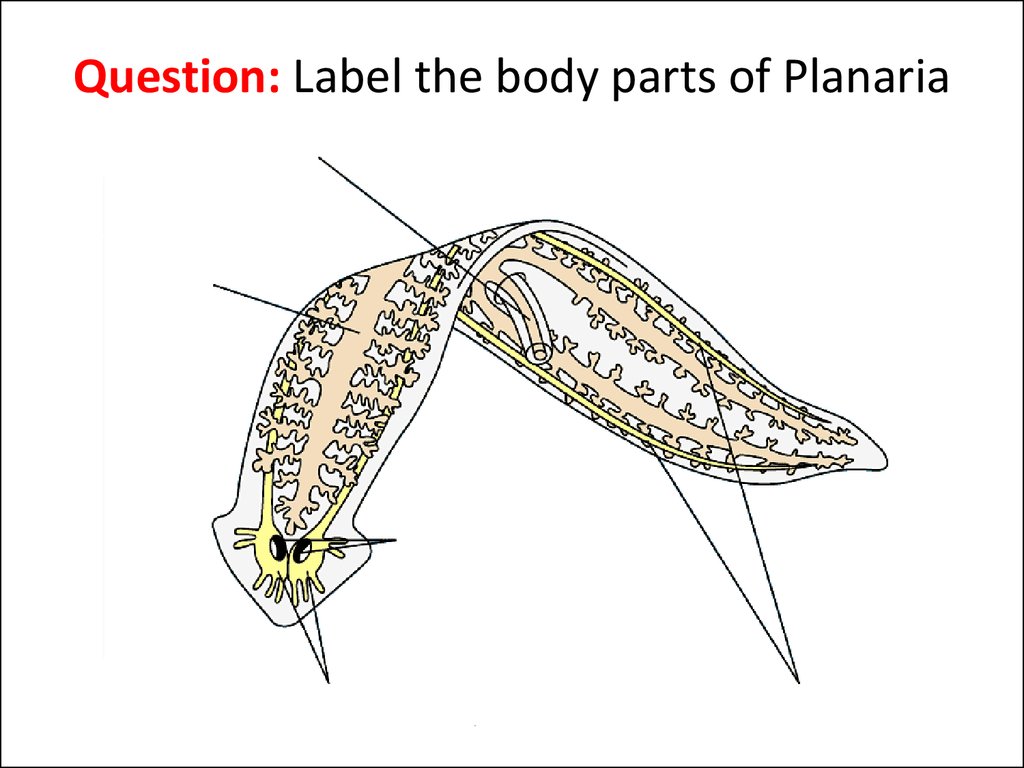
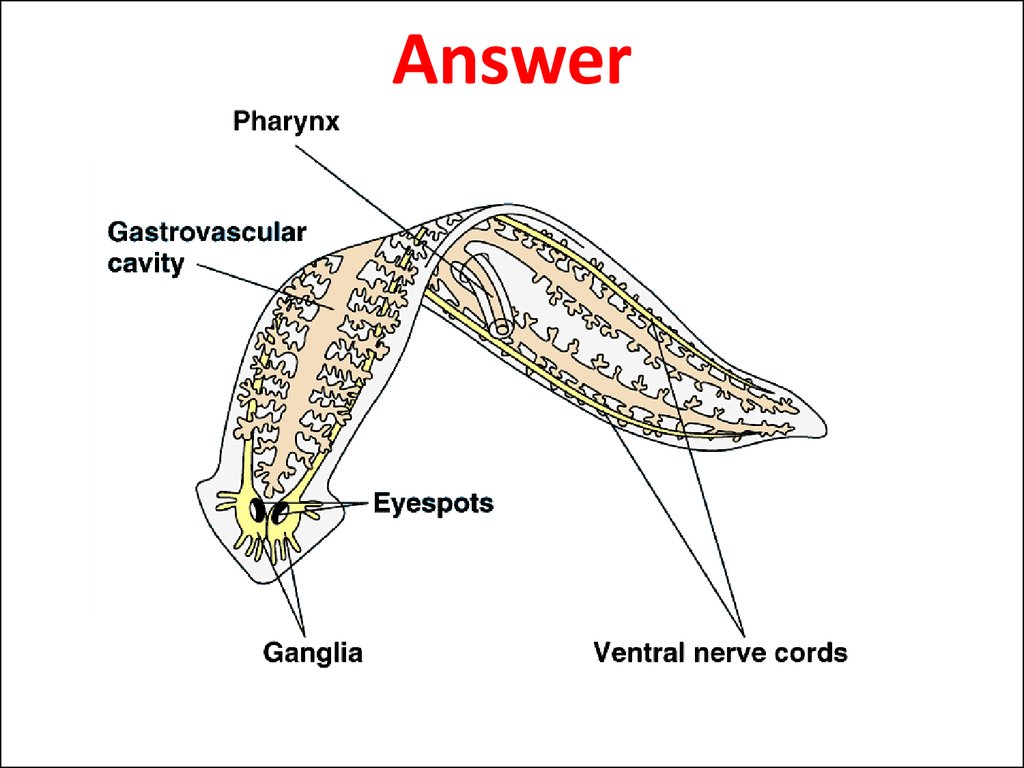
12. Question: Label the body parts of Planaria
13. Answer
14. 2) Trematoda
Example: FlukesFlukes are the most important example.
They are parasite on vertebrates and human.
They use human and snail as a Host.
Ex: Blood flukes and Liver flukes.
15.
Life cycle of flukes16.
Flukes in the liver17. 3. Cestoda: Tapeworms
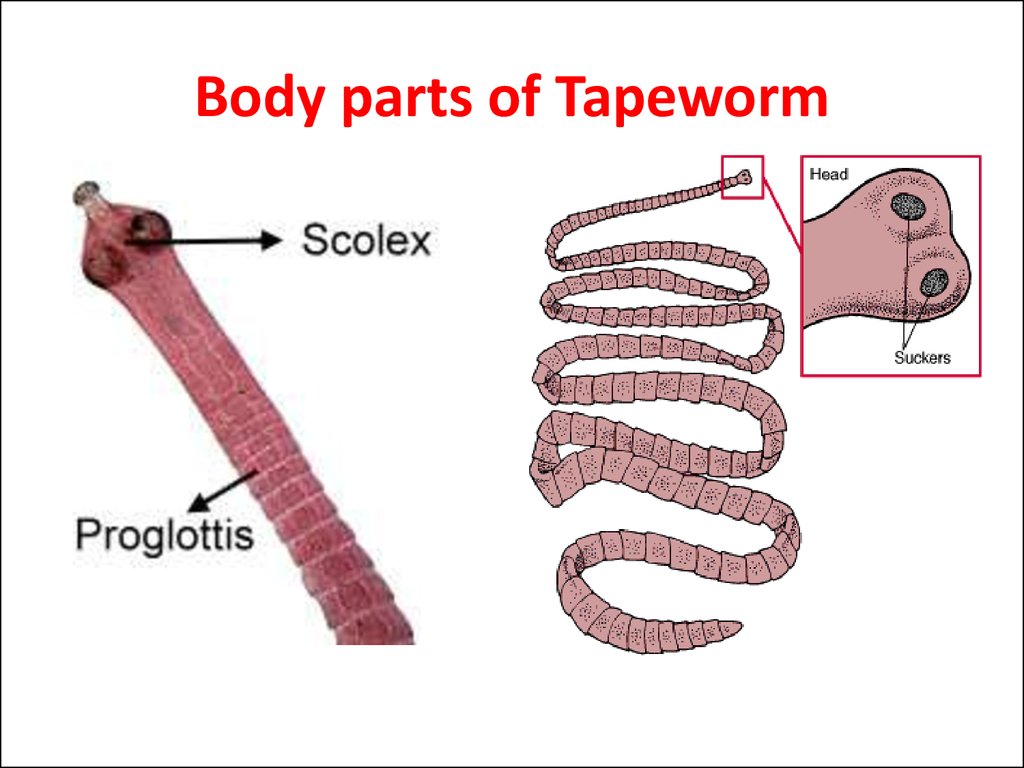
Tapeworms are the most important example.They are parasite on vertebrates and human.
Have 2 body part Scolex (head) and
Proglottis (all body segments).
Have hooks and suckers on their scolex to
attach the host.
18. Body parts of Tapeworm
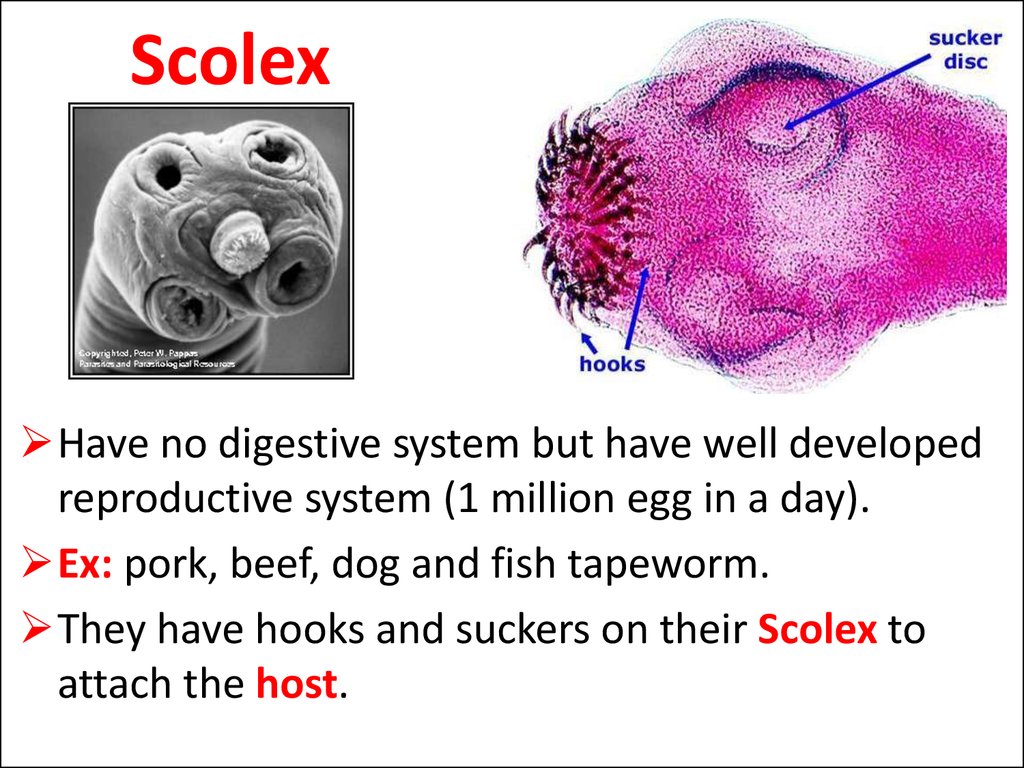
19. Scolex
Have no digestive system but have well developedreproductive system (1 million egg in a day).
Ex: pork, beef, dog and fish tapeworm.
They have hooks and suckers on their Scolex to
attach the host.
20. Proglottis
ProglottisThey have no digestive system but have well
developed reproductive system
(1 million egg in a day)
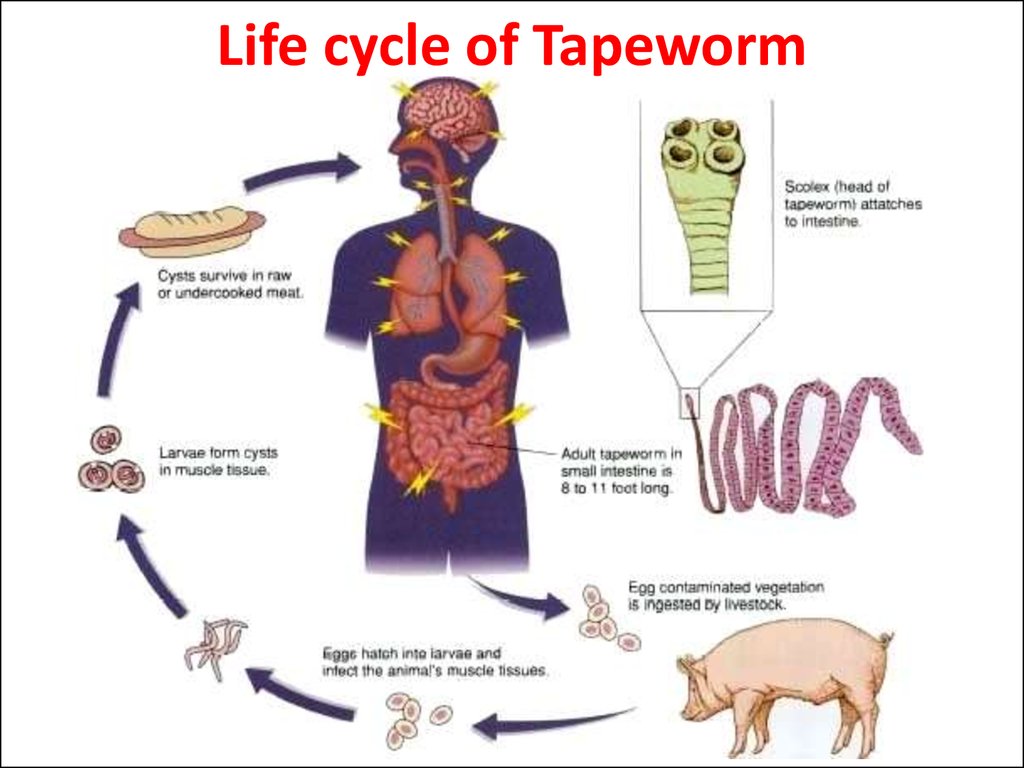
21. Life cycle of Tapeworm
22. Questions
1. Which of the following lives in human liver asparasite?
A) Flukes
B) Tapeworm
C) Earthworm
D) Ascarida
E) Trichina
2. Which structure produces egg and sperm cells in the
tapeworms?
A) Scolex
B) Sucker
C) Head
D) Hooks
E) Proglottids
23. Answers
1. Which of the following lives in human liver asparasite?
A)
B) Tapeworm
A)Flukes
Flukes
C) Earthworm
D) Ascarida
E) Trichina
2. Which structure produces egg and sperm cells in the
tapeworms?
A) Scolex
B) Sucker
C) Head
D) Hooks
E)
E) Proglottids
Proglottids











 biology
biology








