Similar presentations:
Vitamins
1. Vitamins
2. Key terms
Vitamin – organic molecule essential forbody processes;
Avitaminosis – total deficiency of one or
more vitamins;
Hypovitaminosis – deficiency of one or
more vitamins;
Hypervitaminosis – excess amount of
intake of one or more vitamins.
3. Vitamins
Vitamins were firstdiscovered in 1890 when
the disease beriberi was
found to be due to a
lack of vitamin B
A small amount of
vitamins is ingested in
food and play important
roles in regulation of the
metabolism of the body.
The main source of
vitamins is plants
However, animal tissues,
especially liver, contain
a rich supply of vitamins
4. Vitamins
Overheating of food,therefore, may cause
destruction of vitamins
Functions of vitamins
--to give the body resistance
to infection
--to prevent against bleeding
and blood deficiency
--to assist in formation,
development and rigidity of
bone tissue
--to regulate growth,
development and
reproduction
--to provide a regular
program of nutrition
5.
Polish biochemist Casimir Funk discovered vitamin B1in 1912 in rice bran.
He proposed the complex be named "Vitamin" (vital
amines).
By the time it was shown that not all vitamins were
amines, the word was already ubiquitous.
6. Vitamin - definition
An organic compound required as a nutrient in tinyamounts by an organisms.
It cannot be synthesized in sufficient quantities by an
organism, and must be obtained from the diet.
Vitamins have diverse biological function:
hormone-like functions as regulators of mineral metabolism
(vit. D),
regulators of cell and tissue growth and differentiation
(some forms of vit. A)
antioxidants (vit. E, C)
enzyme cofactors (tightly bound to enzyme as a part of
prosthetic group, coenzymes)
7. Vitamin classification
Lipid-soluble vitamins (A, D, E and K)hydrophobic compounds, absorbed efficiently with
lipids,
transport in the blood in lipoproteins or attached to
specific binding proteins,
more likely to accumulate in the body,
more likely to lead to hypervitaminosis
8. Vitamin classification
Water-soluble vitamins - 8 B vitamins and vitamin CFunction: mainly as enzyme cofactors,
hydrophilic compounds dissolve easily in water,
not readily stored, excreted from the body,
their consistent daily intake is important.
Many types of water-soluble vitamins are synthesized
by bacteria.
9. Metabolic functions of vitamin A
VisionGene transcription
Immune function
Embryonic development and reproduction
Bone metabolism
Haematopoieis
Skin health
Antioxidant activity
10. Sources of vitamin A
cod liver oilmeat
egg
milk
dairy
products
carrot
broccoli
spinach
papaya
apricots
http://health.allrefer.com/health/nutrition.html
11. Vitamin D and imunity
It increases the activity of natural killer cells(cytotoxic lymphocytes).
Increases the phagocytic ability of macrophages .
Reduces the risk of virus diseases (colds, flu).
Reduces the risk of many cancers (colon, breast and
ovarian cancer).
Reduces the risk of cardiovascular disease → have a
positive impact on the composition of plasma lipids.
12. Sources of vitamin D
In addition to sunbathing:various fish species (salmon,
sardines and mackerel, tuna,
catfish, eel), fish oil, cod liver
eggs, beef liver, mushrooms
13. Vitamin C (Ascorbic acid )
Vitamin C is the most famous vitamin.sources: almost exclusively in foods from plant
sources (citrus fruits, broccoli, peppers, kiwi,
strawberries, potatoes, tomatoes), although
fresh milk and liver contain small amounts.
14. Major function in the body
helps form collagenhelps in growth and repair of body tissue and
blood vessels
prevents scurvy
a strong antioxidant
aids in absorption of iron
helps regulate the metabolism of cholesterol and
amino acids
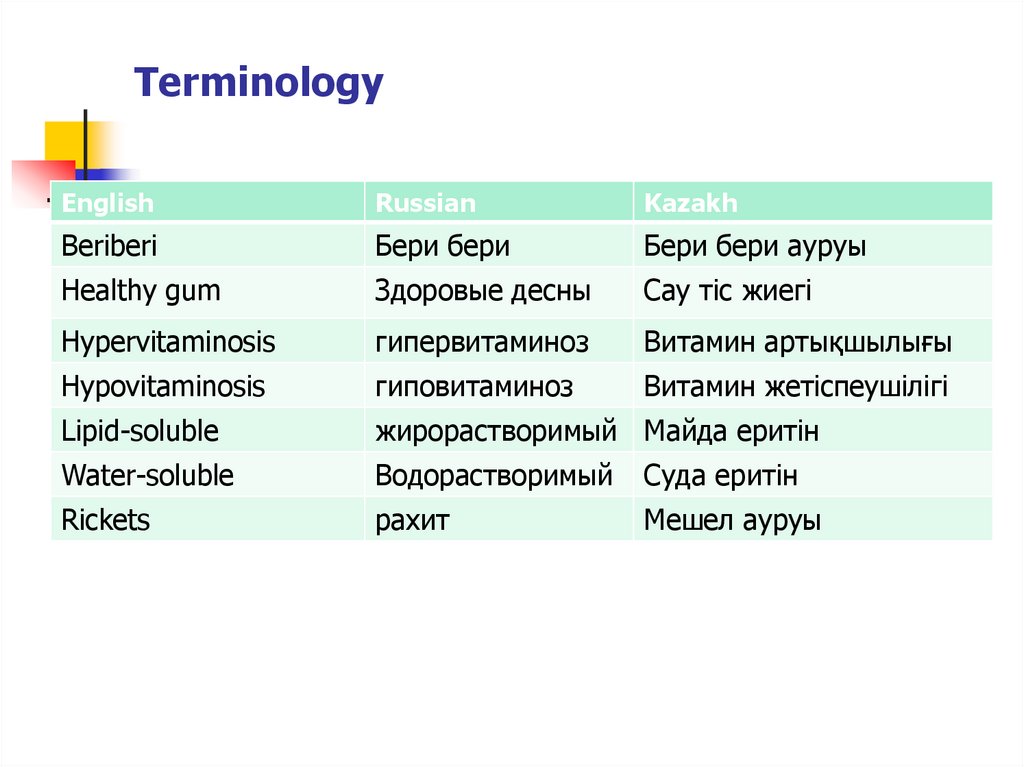
15. Terminology
EnglishRussian
Kazakh
Beriberi
Бери бери
Бери бери ауруы
Healthy gum
Здоровые десны
Сау тіс жиегі
Hypervitaminosis
гипервитаминоз
Витамин артықшылығы
Hypovitaminosis
гиповитаминоз
Витамин жетіспеушілігі
Lipid-soluble
жирорастворимый Майда еритін
Water-soluble
Водорастворимый
Суда еритін
Rickets
рахит
Мешел ауруы












 biology
biology








