Similar presentations:
Vitamins. About vitamins
1.
VitaminsSubbotin Pavel
3722B1BL10
2.
About vitamins• Vitamins are a group of chemical compounds united by one common
feature – the need for their presence in the body for existence
• Vitamins are found in food in very small quantities and are therefore
classified as micronutrients along with trace elements. Vitamins do
not include not only microelements, but also essential amino acids
and essential fats.
• Due to the lack of an exact definition, different amounts of
substances were classified as vitamins at different times. As of mid2018, 13 vitamins are known
3.
Thiamine• Thiamine vitamin B1 is an organic
heterocyclic compound, a water-soluble
vitamin corresponding to the formula
C12H17N4OS
• More commonly known as vitamin B1,
thiamine plays an important role in the
metabolism of carbohydrates, fats and
proteins. The human body can store up to
30 mg of thiamine in tissues. Thiamine is
mainly concentrated in skeletal muscles.
Other organs where it is found are the
brain, heart, liver and kidneys. The
substance is necessary for normal growth
and development and helps maintain
proper functioning of the heart, nervous
and digestive systems.
4.
Riboflavin• Riboflavin (lactoflavin, vitamin B2) is one of the
most important water-soluble vitamins, a
coenzyme of many biochemical processes.
• Vitamin B2 is necessary for the formation of red
blood cells, antibodies, and for regulating
growth and reproductive functions in the body.
It is also essential for healthy skin, nails, hair
growth and overall health of the entire body,
including thyroid function.
5.
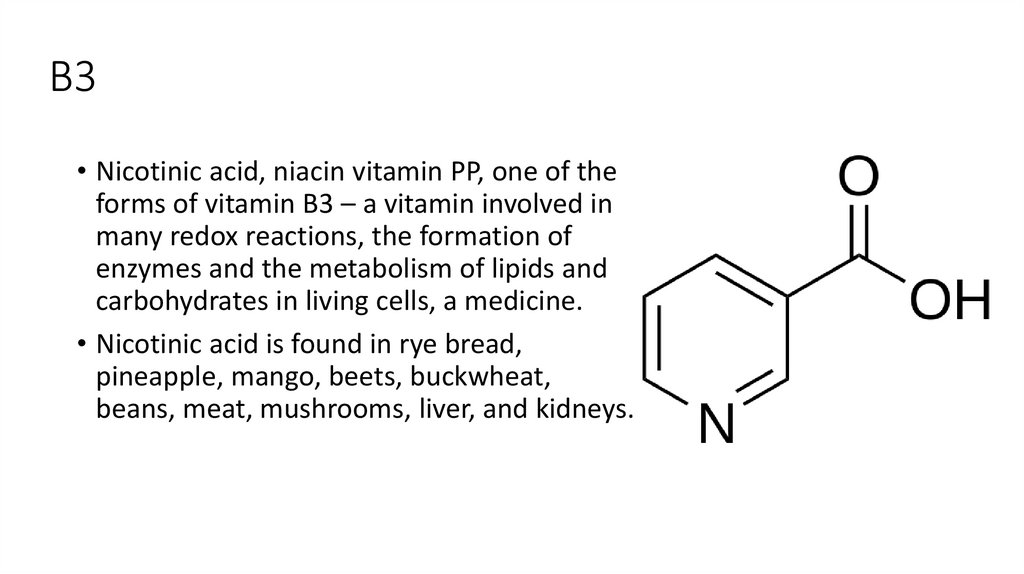
В3• Nicotinic acid, niacin vitamin PP, one of the
forms of vitamin B3 – a vitamin involved in
many redox reactions, the formation of
enzymes and the metabolism of lipids and
carbohydrates in living cells, a medicine.
• Nicotinic acid is found in rye bread,
pineapple, mango, beets, buckwheat,
beans, meat, mushrooms, liver, and kidneys.
6.
В5• Pantothenic acid (vitamin B5) is a
water-soluble B vitamin, an amide
of the amino acid β-alanine and
pantoic acid.
• In animal and plant cells,
pantothenic acid is part of
coenzyme A (KoA), which takes part
in the most important metabolic
reactions; the main function is the
transfer of carboxylic acid residues
in biochemical processes.
7.
В7• Biotin (coenzyme R, vitamin B7) is a watersoluble B vitamin.
• It is part of enzymes that regulate protein and
fat balance and is highly active. Participates in
the synthesis of glucokinase, an enzyme that
regulates carbohydrate metabolism. It is a
coenzyme of various enzymes, including
transcarboxylases. Participates in the synthesis
of purine nucleotides. It is a source of sulfur,
which takes part in collagen synthesis.
Activation and transfer reactions of CO2 occur
with the participation of biotin






 biology
biology








