Similar presentations:
Actual problems of science and Industry
1. actual Problems of Science and Production
Far Eastern Federal UniversitySchool of Engineering
Educational program
“Offshore and Coastal Engineering”
ACTUAL PROBLEMS
OF SCIENCE AND PRODUCTION
Professor Alexander Беккер
2018
2.
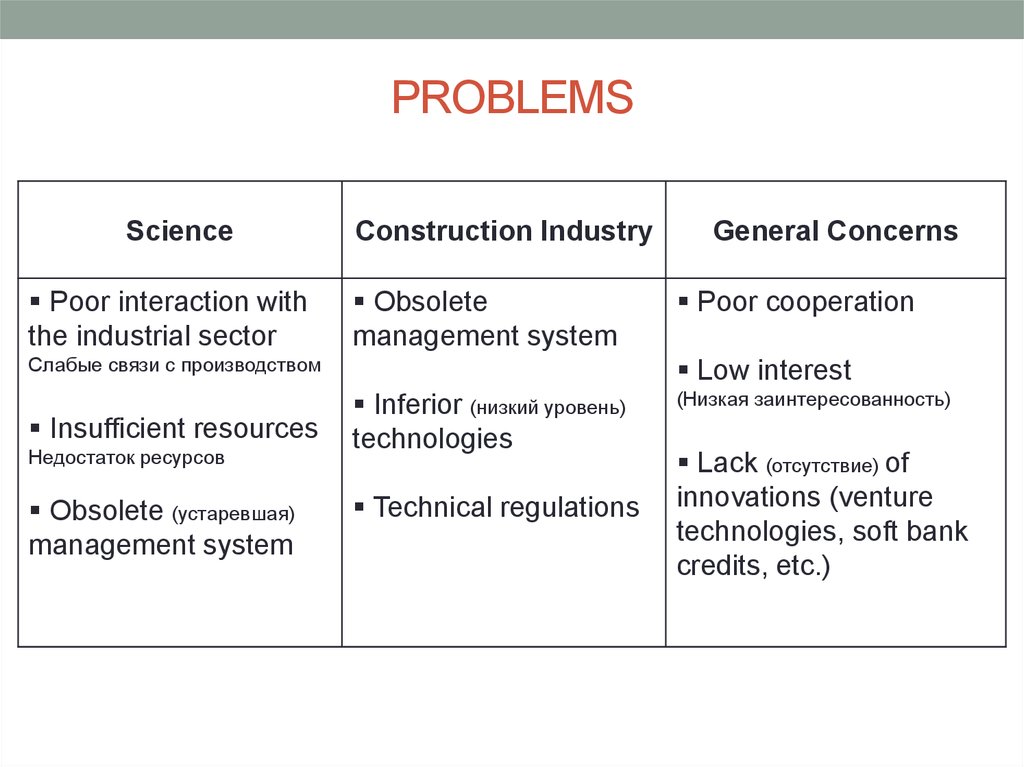
Problems of a general nature3. PROBLEMS
SciencePoor interaction with
the industrial sector
Construction Industry
Obsolete
management system
Слабые связи с производством
Insufficient resources
Недостаток ресурсов
Obsolete (устаревшая)
management system
General Concerns
Poor cooperation
Low interest
Inferior (низкий уровень)
technologies
Technical regulations
(Низкая заинтересованность)
Lack (отсутствие) of
innovations (venture
technologies, soft bank
credits, etc.)
4. Science: Poor interaction with the industrial sector
Consequences (последствия) of economic recession in1990th;
The traditional ties are lost;
Industrial enterprises show little interest in R&D (small
business merely cannot afford; large business already enjoys a variety of choice);
Government regulations (Resolution #218, Federal Target Programs,
intergovernmental agreements, etc.);
Poor administration (coming from the Ministry for Regional Development,
Ministry for Development of the Russian Far East, Ministry of Construction, Russian
Academy of Architecture and Construction Sciences, etc.)
5. Science Insufficient resources
Scarcity(нехватка)
Obsolete
of high-qualified personnel;
(устаревшая)
Insufficient
& worn-out laboratory facilities;
(недостаток) state
funding;
• Almost no private R&D funding (Почти нет частного финансирования
НИОКР);
No non-repayable state subsidies to scientific projects by
higher schools;
Poor protection of intellectual property
6. Science: Obsolete (устаревшая) management system
Ineffective structure of state management system;Few scientific institutions in higher schools;
Poor ties between state academies and higher schools;
Poor international cooperation;
Out-of-date system of top qualified personnel training
(Устаревшая система подготовки высококвалифицированных кадров);
No culture of intellectual property development and
protection.
7. Construction Industry Reorganization of the management system
• Elimination (ликвидация) of the current industry management system;Renewal (re-development) of the industry management system;
Establishment of the Central governmental agencies (such as the Ministry
for Regional Development, Ministry for Development of the Russian Far
East, Ministry of Construction, Russian Federal Agency for Construction,
Housing Maintenance and Utilities, etc.);
Rearrangement (перестройка) of State Academies management;
Further development of the competition-based resource distribution system
for scientific institutions;
Undeveloped system of state support for construction industry companies.
8. Construction Industry Inferior technologies
• Obsolete(устаревшая)
construction technologies;
• Poor construction industry basis;
• Technology gap in construction arrangement & management;
• Unsteady pricing principles;
• Poor progress in development of up-to-date construction
materials;
• Poor quality management.
9. Construction Industry Technical regulations
Unsettled (неустановившаяся) system of technical regulations inconstruction industry;
Obsolete system of regulatory documents;
Discrepancies (противоречие) between state supervision
agencies and regulatory / resource base in terms of construction
industry;
Inconsistencies (несовместимость) between construction orders
distribution system, requirements by regulatory documents and
resources available to Russian domestic companies.
10. The link between science, production (Связь науки производства)
Fundamental research → hypothesis → experiment →theory
Scientific research
(НИР)
→ prototype (Опытный образец) →
production
Time gap between science results and real production (It is
necessary to decrees this gap)
Inconsistencies (несовместимость) between construction
orders distribution system, requirements by regulatory
documents and resources available to Russian domestic
companies.
11. Science location
UniversitiesResearch Institutes of Academies
Research Institutes of Ministries
Research Institutes of big corporations
Research Companies
12. Supporting Science
State system(on competitive base):
- Government programs,
- Government Funds (different scales),
- others
Private:
- Big corporations
- Companies,
- Research business
13. Features of scientific research
Statement of the scientific problemDevelopment of research methods (theoretical,
experimental, computer modeling)
Modeling & analysis Comparison of theory and
experiment
Summary
14. Main characteristics of R & D
Main characteristics of R & DResearch topic
Purposes Tasks
Results
Scientific novelty
Practical significance
Implementation
15. Actual problems in Architecture
16. Architecture
• Development of environment friendly to biosphere and human society;• Fundamental basis for architectural and city-planning professional culture
and education;
• Development of architectural forming & composition theory based on liberal
arts and sciences using the up-to-date smart engineering structures, new
materials, technologies and equipment;
• Proper basis for healthy & fail-safe construction infrastructure;
• Development of theoretical background for reconstruction and renovation of
utility infrastructure of cities and smaller towns based on up-to-date and
perspective environmental-friendly technologies.
17. Architecture
• Provisions for energy and resource-efficient spatial development of citiesand smaller settlements given the continuous globalization trends;
• Information technologies and computer modeling in architecture, city
planning and construction science;
• Set up and development of comfortable biosphere-friendly environment in
terms of architecture and city planning;
• Apartment planning in line with demands and financial abilities of basic
social groups;
• Noise protection and acoustic improvements;
• Preservation and restoration of the disturbed soils, landscapes,
biodiversity and historical environment of settlements.
18. Architecture
• Development of scientific basis for state spatial and city planning policyconsidering the core principles of continuous and safe growth of cities and
smaller towns, and their integration with biosphere contributing to personal
development of humankind, and creation of healthy and favorable
conditions for labor, everyday life and recreation;
• Intensive study of scientific & social proposals for modernization of
engineering structures, units and construction materials production; as well
as for reconstruction and reorientation of industrial infrastructure and
facilities;
• Complex analysis of the current state of housing construction and
development of scientific recommendations for reconstruction of apartment
buildings to further improve the quality of living;
19. Architecture
• Development of methodology for complex examination of engineering,technological, ecological and economical state of industrial sites and
facilities, as well as scientific recommendations for their reconstruction,
renovation or demolition;
• Development of scientific recommendations for refurbishment of existing
and implementation of new utility systems which could significantly
improve energy and resource efficiency both in terms of large-scale city
planning and individual buildings design;
• Development and implementation of engineering solutions and methods
to secure protection of buildings and structures at certain level of
economic and social risks within new seismic areas, permafrost zones
affected by global warming and/or typhoon-exposed areas; as well as
disposal and dumping of industrial, anthropogenic and solid domestic
waste;
20. Architecture
• Development of experimental methods and up-to-date experimentalfacilities for determination of thermo-physical and acoustic properties of
structures, construction units and buildings;
• City-planning technologies for minimization of resources and energy
consumption; environmental-friendly spatial planning;
• Development of theoretical basis for safety and reliability of settlements;
• Implementation of effective architectural and construction systems;
• Calculation and substantiation of structural features for high rise
buildings;
• Mitigation of risks and consequences of natural and man-caused
disasters.
21. Architecture
• Development and optimization of space-planning and design solutions forbuildings and structural units with due consideration for internal
processes, natural climatic conditions, economical feasibility and
structural safety based on mathematical modeling;
• Formation of self-regulated system in terms of architectural and
construction regulations;
• Preservation and reconstruction of the historic environment of cities and
towns;
• Search for further city planning methods for small towns in today’s social
and ecological conditions;
• Architectural and city planning aspects of buildings fund reconstruction.
22. Actual problems in Structural mechanics
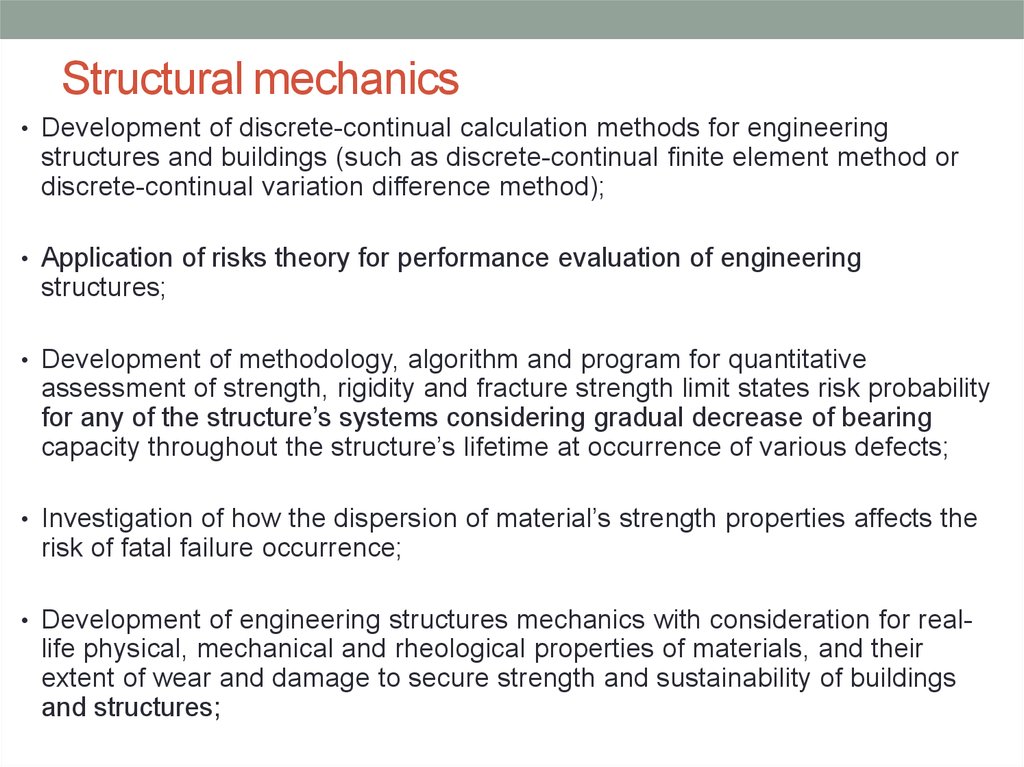
23. Structural mechanics
• Development of discrete-continual calculation methods for engineeringstructures and buildings (such as discrete-continual finite element method or
discrete-continual variation difference method);
• Application of risks theory for performance evaluation of engineering
structures;
• Development of methodology, algorithm and program for quantitative
assessment of strength, rigidity and fracture strength limit states risk probability
for any of the structure’s systems considering gradual decrease of bearing
capacity throughout the structure’s lifetime at occurrence of various defects;
• Investigation of how the dispersion of material’s strength properties affects the
risk of fatal failure occurrence;
• Development of engineering structures mechanics with consideration for real-
life physical, mechanical and rheological properties of materials, and their
extent of wear and damage to secure strength and sustainability of buildings
and structures;
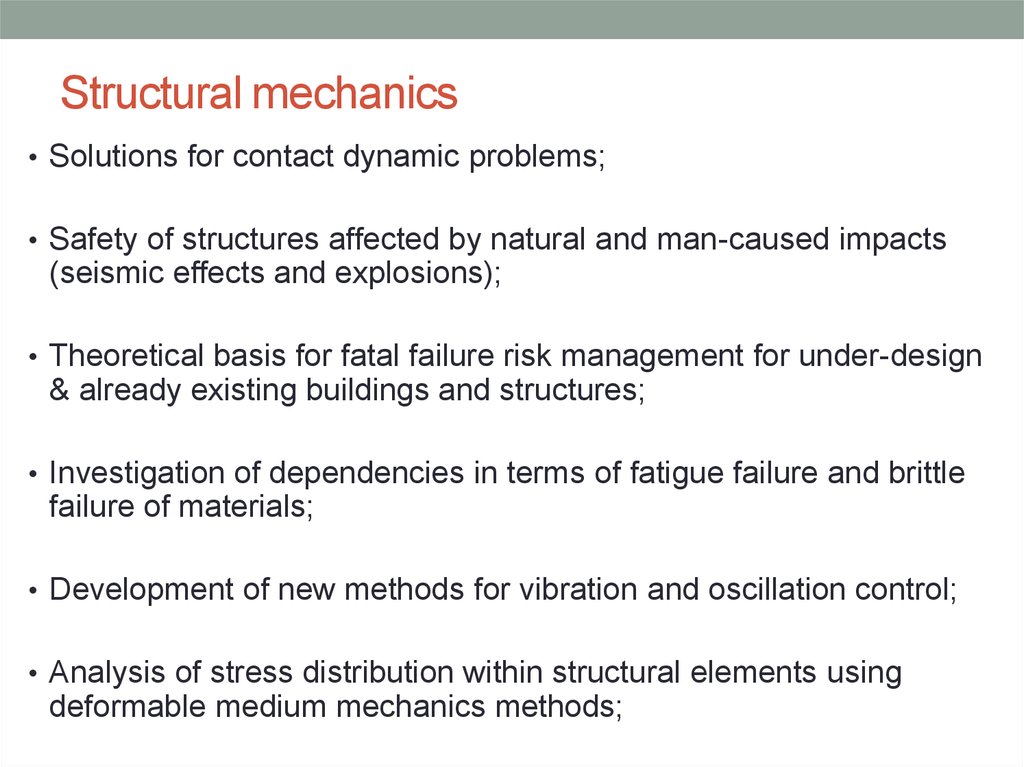
24. Structural mechanics
• Solutions for contact dynamic problems;• Safety of structures affected by natural and man-caused impacts
(seismic effects and explosions);
• Theoretical basis for fatal failure risk management for under-design
& already existing buildings and structures;
• Investigation of dependencies in terms of fatigue failure and brittle
failure of materials;
• Development of new methods for vibration and oscillation control;
• Analysis of stress distribution within structural elements using
deformable medium mechanics methods;
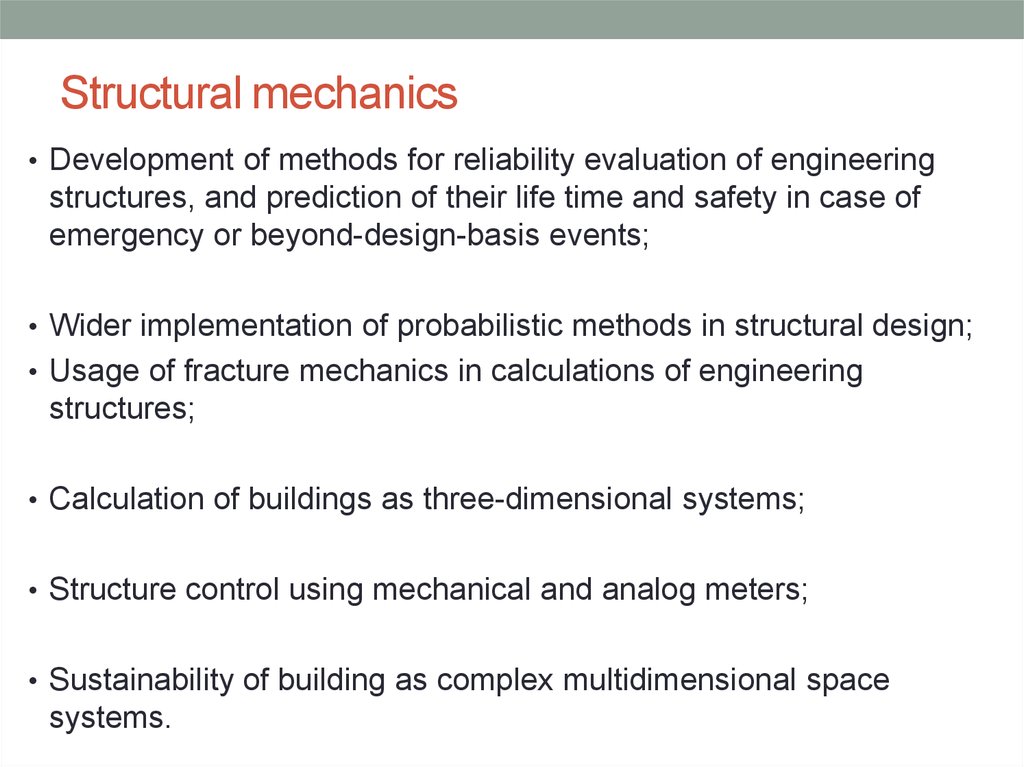
25. Structural mechanics
• Development of methods for reliability evaluation of engineeringstructures, and prediction of their life time and safety in case of
emergency or beyond-design-basis events;
• Wider implementation of probabilistic methods in structural design;
• Usage of fracture mechanics in calculations of engineering
structures;
• Calculation of buildings as three-dimensional systems;
• Structure control using mechanical and analog meters;
• Sustainability of building as complex multidimensional space
systems.
26. Actual problems in Engineering geology, soil mechanics
27. Engineering geology, soil mechanics
• Prediction of changing engineering-geologic & hydro-geologicconditions;
• Evaluation of spatial variability of physical &mechanical properties of
soil;
• Influence of oil, process solutions and hostile environments onto
strength and deformation properties of foundations;
• Development of instruments for analysis of physical & mechanical
properties of soil;
• Influence of dynamic impact parameters onto mechanical properties
of soil;
28. Engineering geology, soil mechanics
• Search for and feasibility study of raw materials;• Effective methods for determination of rheological properties of soil;
• Development of engineering and geological properties variability
theory;
• Investigation of correlation between the rate of loading and
mechanical properties of soil;
• Investigation of soil’s shear creep.
29.
Engineering geology, soil mechanics• Determination of ultimate shear deformation;
• Determination of creep rupture strength of soil;
• Investigation of soil torsion behavior;
• Investigation of soil behavior at combined compression & torsion
action;
• Influence of particular stress state type onto soil’s strength and
deformation properties;
30.
Engineering geology, soil mechanics• Investigation of critical creep rate of soils;
• Advanced methods for early prevention of negative processes in
soils;
• Development of engineering and geological maps of cities and
settlements with outlined future construction areas;
• Statistical models in geology.
31. Actual problems in Construction materials
32. Construction materials
• Decrease of energy and labor consumption for production ofmaterials, concrete and grout;
• Acceleration of concrete strength development, for example, due
to increased depth of cement hydration intensity, which can be
accomplished with thermal & vibratory treatment of cement
mixtures;
• Development of new types of chemical modifications and
regulators of concrete properties;
• Wide application of self-consolidating concrete;
33. Construction materials
• Wide application of light & cell (gas / foam) concrete of 400...600kg/m3 density to decrease thickness of enclosing elements while
maintaining the same heat insulation properties;
• Production and application of structured and heat-insulating cell
concrete types with D400...D700 density;
• Effective means of improving concrete waterproofing;
• Increase of durability and corrosion resistance of modified
concretes;
34. Construction materials
• Development and design of fibrous concretes;• Construction of plants for fiber production;
• Investigation of previous long-term loading effects onto the
mechanical properties of material;
• Investigation of specific features of non-linear deformation,
aftereffect and relaxation for tensions and long-term resistance of
construction materials, and change of their mechanical properties
over time.
35. Construction materials
• Advanced design methods for artificial conglomerates &compositions;
• Energy-saving modes of concretes heat treatment;
• Methods of concrete compositions design with active mineral
inclusions;
• Effective loamy compositions for bricks production;
• Nanomodified concrete mixtures;
• Fibrous concretes. Investigation of properties & arrangement of
production.
36. Construction materials
• Development of construction materials durability prediction subjectto operating loads and temperatures;
• Investigation of materials creeping dependencies;
• Development of new light, efficient, ecological, energy-efficient, non-
combustible, time-proof, technological concretes;
• Development of methodological basis for new regulatory and
recommendation materials in architecture, urban planning and
construction;
• Complex of investigations and design engineering in the field of
disposal and recycle of structural units, parts and construction materials
resulting out of demolition or reconstruction, as well as of other mineral
wastes;
37. Construction materials
• Investigation of modifying additives effect onto technologicalparameters of specific compositions and their strength in specific
operating conditions;
• Development and scientific substantiation of energy efficient concrete
mixing technology based on modified liquid oligodiens.
• Development of rational compositions of dispersive-reinforced polymer
mixtures;
• Advanced concepts and programs for further development of
construction materials industry;
• Development of scientific & methodological basis for synthesis and
design of construction mixture structures with pre-defined properties;
38. Construction materials
• Technical & economical efficiency of application of up-to-date constructionmaterials, products and structures in everyday housing construction;
• Significant increase of share of construction materials, products
and structures made of recycled waste;
• Influence of raw materials mixture’s composition onto physical and
mechanical properties of foam concrete;
• Significant increase of share of construction materials, products
and structures made of recycled waste;
• Influence of raw materials mixture’s composition onto physical and
mechanical properties of foam concrete;
• Application of destruction mechanics methods for evaluation of
strength, permeability and crack resistance of structures.
39. Construction materials
• Prediction of concrete durability subject to its destruction kinetics;• Increase of concrete and grout strength with application of
modifying additives;
• Prediction of strain deformations;
• Modification of structure and properties of concrete subject to
concrete aggregate;
• Strength and deformation of different types of concrete and
structures affected in humid environments;
40. Construction materials
• High-performance composition cementing agents with nano-modificators;
• Nano-technologies in construction materials science;
• High technologies and nano-technologies for construction
materials;
• Functional construction materials for extreme operating
environments;
• Computerized material engineering for construction composites;
41. Actual problems in Beddings and foundations
42. Beddings and foundations
• Multi-level management of structure-formation;• Problems of high-temperature process management in
construction industry;
• Innovations in the field of ceramic materials in construction;
• Effects of dispersive reinforcement onto structure formation
and strength properties of fibrous concrete;
• Observations of setting of civil and industrial buildings and
structures;
43. Beddings and foundations
• Investigation of stress-strain state of foundation beddingsubject to flat and spatial tasks;
• Development of new instruments and methods for strain-
stressed state measurement;
• Development of non-linear mechanics of soils;
• Design and development of soil bedding models;
44. Beddings and foundations
• Development of calculation methods for beddings and foundationsin two groups of limit states;
• Advanced calculation methods for displacement of foundations,
strain-stressed state of foundations and beddings over time;
• Development of calculation method for subsurface foundations;
• Implementation of "wall-in-soil" method;
• Design and implementation of efficient structures of foundations.
45. Beddings and foundations
• Investigation of effects by oils, deleterious substance and processsolutions onto mechanical properties of soil bedding;
• Improved calculation methods for flexible reinforced concrete
foundations;
• Classification of signs of near-failure state of bedding, foundations,
structures and buildings;
• Numerical modeling of all phases of construction, reconstruction
and further operations;
46. Beddings and foundations
• Geo-technical and geo-economic monitoring of construction works;• Safety issues during construction of high rise buildings of critical
importance in deep (20 m and more) construction pits;
• Prediction of geo-mechanical processes trends during construction of
underground and above-ground sections of large-area buildings;
• Advanced calculation methods for beddings on structurally unstable
soils;
• Development and implementation of methods for elimination of soil
settlement properties;
47. Beddings and foundations
• Advanced calculation and design methods for foundations onswelling soils;
• Development of construction techniques for buildings and
structures on filled-up soils;
• Development of construction techniques for buildings and
structures on alluvial soils;
• Development of construction techniques for buildings and
structures within karst areas;
48. Beddings and foundations
• Development of construction techniques for buildings and structureson saline and plaster soils;
• Development of construction techniques for buildings and structures
on weak water-saturated soils;
• Development of construction techniques for buildings and structures
on former waste landfill sites;
• Development of construction techniques for buildings and structures
on frozen and thawed soils;
• Development of construction techniques for buildings and structures
within undermined areas;
49. Beddings and foundations
• Development of calculation, design and constructionmethods considering the dynamic impacts on soil;
• Improved seismic resistance of beddings, foundations and
buildings;
• Update of regulatory basis for foundation construction
science and geo-technical construction;
• Development of efficient methods for design and construction
of underground structures and buildings;
• Evaluation of bearing capacity of beddings and foundations
in cases of complex force impacts;
50. Beddings and foundations
• Application of up-to-date numerical methods of deformablemedium mechanics with due consideration for actual properties of
materials and bedding soils;
• Solution of contact problems subject to construction technologies;
• Assessment of environment impact of construction;
• Investigation of contact tension distribution for different soils and
their states, rigidity of foundation and loading conditions;
• Solution of contact problems subject to various border conditions;
application of advanced foundation models;
51. Beddings and foundations
• Investigation of foundation scale influence onto bearing capacityand bedding displacement;
• Application of centrifugal units for analysis of foundation and
bedding behavior;
• Investigation of deformation of adjacent buildings resulting from
newly-constructed;
• Development of improved method for calculation of deformations
of neighbor buildings from the attached structures;
• Production of higher-effective instruments for determination of soil
compaction quality;
52. Beddings and foundations
• Development of mathematical and physical basis for monitoring ofsoils and underground structures;
• Prediction of soils mechanical properties change under the loaded
foundation bed;
53. Beddings and foundations
• Development and application of efficient methods for stabilization of settledsoils;
• Application of up-to-date methods for driven piles fabrication control;
• Arrangement of fabrication and implementation of pyramidal piles and
foundations in compacted pits;
• Application of up-to-date methods of quality control in construction &
installation operations;
• Evaluation of physical and mechanical properties of bedding soils;
• Investigation of anomalistic physical fields (temperature, vibration,
chemical, etc.) in soil columns;
54. Beddings and foundations
• Application of up-to-date methods of quality control in construction &installation operations;
• Evaluation of physical and mechanical properties of bedding soils;
• Investigation of anomalistic physical fields (temperature, vibration,
chemical, etc.) in soil columns;
• Change of physical and mechanical properties of soils within areas of
structures and buildings;
• Change of physical and mechanical properties of soils within areas of
structures and buildings;
• Solution of contact problems with due consideration for foundation
arrangement technologies;
55. Beddings and foundations
• Calculation of deformations of building beddings adjacent to deep pits;• Reliable evaluation of physical & mechanical properties of bedding soils;
• Means of improving the reliability and safety of building fund due to wear
and aging;
• Means of improving the reliability and safety of building fund due to wear
and aging;
• Improvement of bedding’s geomechanical model for description of its
inhomogeneity, isotropy or anisotropy, compaction level (normally
compacted, overcompacted), active area, well depth, and impact of
transferred loads;
56. Beddings and foundations
• Reliable assessment of engineering and geological conditions atconstruction site, soils properties with due consideration for specific
tensile state and its further transformations;
• Prediction of stability of loaded slopes serving as bedding for structures;
• Development and implementation of efficient methods for strengthening
of weak water saturated, swelling, loose soils, both natural and filled-up;
• Development of recommendations for application of efficient
foundations structures in case of various soil conditions;
• Arrangement and performance of investigations of physical and
mechanical properties of soils, inclusive of static loads tests.
57. Beddings and foundations
• Provision of design reliability in construction on settled, swelling,ever-frozen or poor water-saturated soils, in seismic and karst
areas;
• Development of efficient spatial planning solutions, technologies,
planning of populated areas with due provisions of safe labor, living
and recreation;
• Arrangement of continuous control over condition of power plants,
lifting and transport means, personal protective gear and fire-fighting
equipment;
• Development of mathematical and physical basis for monitoring of
soils and underground structures;
58. Beddings and foundations
• Observation of deformations of buildings adjacent to constructionarea;
• Development of measures to prevent damage to buildings due to
piles being driven or arrangement of utility lines nearby;
• Structural safety of construction Assessment of fire resistance of
structures used in high rise buildings;
• Assessment of risks and safety in construction;
• Prediction of soils mechanical properties change under the loaded
foundation bed;
59. Actual problems in Structural elements
60. Structural elements
• Accumulation, systematization and analysis of causes of building /structures failures;
Investigation of how work qualify affects the reliability of building,
structures and structural elements;
Development of theoretical basis for calculation of reinforcement of
structural elements and their joints;
Development of methods for reinforcement of structures and
structural joints;
Investigation of destruction pattern of structures, joints and
buildings;
Investigation of cycle loading effects onto strain-stressed state of
structural elements against specific parameters of such cycle
loading;
Development of calculation methodology for structural elements
with various types of defects and damage.
61. Structural elements
• Increased resistance to progressive failure for buildings, structuresand structural elements;
Search and substantiation of most efficient structure forms;
Improvement of materials, structures, construction and overall quality
of installation works.
Substantiation of technology and work sequence with appropriate
calculations;
Clarification of calculation diagrams of structures, elements &
mounting units;
Prediction of alteration of mechanical properties of materials
throughout their lifetime;
Investigation of one structure’s failure effects onto neighboring
structures;
Investigation of tension concentrators effects;
62. Structural elements
• Investigation and implementation of simple and efficient instrumentsfor weld joints quality control;
Implementation of scientific & technical achievements into
production routine;
Assessment of operational suitability and risk of failure of
engineering structure;
Evaluation and selection of efficient parameters of basic bearing
elements of the building’s structural system;
Advanced calculation methodology for bearing elements of
structure based on calculating models of next generation;
Determination of strain-stressed state parameters of cross-sections
of structural elements throughout all phases of load application.
Compilation of database for specific engineering structure for
proper determination of standard and actual failure risks of its
bearing frame;
63. Structural elements
• Building failure risk management at design stage;• Calculation methods for determination of structural life;
• Forecasting failure risks;
• Experimental research and practical development of various
surfacing materials for large buildings and structures;
Optimization of forms, sizes and reinforcement of concrete
structures;
Development of calculation methods for reinforced concrete
structures depending on temperature effects;
Development of complex waterproofing problem as applicable to
underground and embedded buildings and structures;
Development of spacial non-linear calculation method for slab
systems using slab-bar structural design made with finite elements
method.
Assessment of failure resistance of buildings and structures;
64. Structural elements
• Development of system survivability theory specifying the system’sability to perform the required functions under designed regimes and
conditions;
Arrangement of risk management in construction;
Development of structures reliability calculation methods;
Effects of fabrication, installation and operation quality of structures
onto their bearing capacity;
Failure-preventive measures for structures and buildings;
Analysis of buildings failure causes;
Development of verifying calculations of structures with due
consideration to their possible defects;
Effective up-to-date methods of evaluation of structure’s protective
coating’s state;
65. Structural elements
• Investigation of structures deformation, fracture and crackformation details;
Establishment and development of efficient calculation methods
and experimental studies for new, reconstructed or strengthened
structural elements with detailed consideration of effects, structural
solutions and properties of materials used.
Assessment of failure resistance of buildings and structures;
Long-term geodetic observations of buildings and structures;
Implementation of thin-walled cold-formed profiles structures with
bolt connections;
Development of combined holding structures on earthfall slopes;
Development of frost destruction safety methods for reinforced
concrete structures;
66. Structural elements
• Implementation of measures against salt appearance on structuressurface, especially on external brick walls;
Protection of structural elements against fungi;
Wide application of reinforcing steel with optimal mechanical
properties, good weldability and rational form of profile, for example,
A500SP;
Advanced structure durability calculations;
Development of vibration control system against wind and seismic
impacts;
Effective means of evaluation of early concealed aging of concrete,
bricks, anchor parts of reinforcement and metal structures.
Technical analysis of failures against their possible reasons;
Increased number of floors for concrete panels buildings providing
the required stability, rigidity and durability;
Investigation of buildings - foundations cross-effects;
67. Structural elements
• Effect of building’s or structure’s rigidity onto displacement ofbedding and foundation;
Methods of seismic and vibration protection of buildings, structures
and construction elements;
Problems of dynamic stability of beddings, structures, buildings and
elements;
Mathematical modeling of construction elements and buildings
behavior;
Fulfillment of basic principles of correct operation of buildings and
structures;
Implementation of preliminary tension during the skeleton-type
building mounting;
External reinforcement of concrete structures using composite
materials;
Stability, strength and deformation of reinforced structures;
68. Structural elements
• Development of scientific basis for prevention of defects;• Tensile-stressed state of reinforced bending pre-stressed beams;
• Strength of bending reinforced and steel structures in case of
corrosion damage;
Optimization of structural elements subject to force and thermal
effects;
Development of the end-element model for monolithic-type frames
with flat slabs and undetected longitudinal girders;
Tensile-deformation state of steel-concrete beams and slabs
affected by force impacts and temperature;
Decrease of metal consumption for metal structures;
Up-to-date construction materials and technologies;
Accidents on main pipes and the respective preventive measures;
Determination of accidental state principals for various structures,
tensile units, buildings and structures.
69. Actual problems in Buildings and structures
70. Buildings and structures
• Development of scientific basis for prevention of defects;• Tensile-stressed state of reinforced bending pre-stressed beams;
• Classification of reasons for failure and damage or
buildings/structures;
Reasons for uneven deformation of bedding;
Stability of "building-bedding" system;
Variation of "Building-bedding" system quality parameters;
Prediction of structure’s interaction with uneven bedding
deformations;
Selection of bedding, structure and rigidity properties calculation
models;
Calculation methods for large concrete panels buildings;
Calculation methods for brick buildings;
Calculation methods for skeleton-type buildings;
71. Buildings and structures
• Calculation method for skeleton-type buildings using complex models of"building-bedding" system;
Development and improvement of spatial calculation methods for
buildings and structures on homogeneous and non-homogeneous
beddings.
Calculation of relative rigidity of "building-bedding" system;
Effect by physical nonlinearity of materials onto relative bending rigidity of
"building-bedding" system under bending and curving deformation;
Calculation of brick, concrete panel and skeleton-type buildings on
swelling soils;
Complex evaluation of residual resources of structure related to "buildingbedding" system;
Effects by defects and damaged structures and units onto relative rigidity
and stability of buildings and structures;
Development of measures against progressive failure of buildings and
structures;
72. Buildings and structures
• Development and implementation of buildings and structures rigidity andbearing capacity recovery;
Evaluation of "building-bedding" system reliability subject to change of soil
state due to watering or dynamic effects;
Construction and preservation of buildings within karst areas;
Methods of stability and efficiency evaluation of "building-bedding" system
with complicated soil conditions;
Up-to-date calculation schemes for "building-bedding" system with
complicated soil conditions;
Experimental investigation of buildings and structures interaction with
bedding;
Development of measures for design of buildings and structures on
swelling soils;
Calculation of complex systems with due consideration to actual
properties of soil beddings.
73. Actual problems in Technology and arrangement of construction
74. Technology and arrangement of construction
• Wider application of areal dredging, especially in bottomland;• Increased works efficiency and reliability in winter period;
• Stimulation of concrete works by mixture’s pre-activation (preliminary
heating of mixture and its components; magnetization, ionization and
ultrasonic treatment of water, vibration mixing, etc.);
Development and implementation of measures for elimination of
early concrete damage;
Implementation of programs for automatic process management for
thermal treatment of reinforced concrete products;
Implementation of methods and instrumentation for measurement of
density, porosity, humidity, temperature, permeability, strain, tension,
cracks parameters, defects, deformations, moving, pressure,
vibration, energy, etc.;
Development and improvement of methods and systems of buildings
and structures quality control during construction, strengthening and
reconstruction;
75. Technology and arrangement of construction
• Arrangement of geo-monitoring (system of observation for soil,underground structures, foundations, soil waters);
Improving, development and implementation of efficient methods of
engineering treatment of area, arrangement of natural and artificial
beddings, construction of buildings.
Development, improvement and implementation of effective
technologies for stone and concrete works in winter conditions;
Improvement of calculation, design & arrangement methods for
temporary reinforcement of the construction pit walls;
Arrangement of buildings / structures demolition and disposal of
dismantled parts;
Technologies for preservation of beddings, construction elements,
buildings and structures;
Effects of construction & assembly work sequence on sustainability of
buildings and structures;
76. Technology and arrangement of construction
• Arrangement of construction in immediate vicinity of existing buildingsand structures;
Development and implementation of automation system for the
technological process of ceramic bricks fabrication;
Control over adherence of construction technology to the designed
requirements;
Improved rates and quality of construction with cast reinforced
concrete;
Implementation of cost-saving technologies in construction and
operations;
New design solutions, materials and technologies in today’s
construction industry;
Proper equipment and technology for reconstruction / renovation of
buildings and structures.
77. Actual problems in Environment protection
78. Environment protection
• Development of reliable methods, means and technologies forenvironment protection against toxic waste, disposal and recycle of
industrial and domestic waste to generate addition energy and raw
material resources that could be used in construction and operating
of buildings and structures;
• Development and implementation of efficient methods of
constructing buildings and structures of various purpose in
conditions as follows:
- tight urban built-up areas;
- areas adjacent to natural or man-made water bodies;
- waste landfills, filled-up gullies or marshland, floodplains or other
types of difficult terrain.
79. Environment protection
• Provision of landslide slope stability & reinforcement of slopes;• Usage of detailed designs upon environmental impact assessment
only;
• Usage of technologies that ensure no pollution of soils, ground
waters and underground springs;
• Development and implementation of programs for recycle and reuse of industrial waste for fabrication of construction materials and
for other economic purposes;
• Arrangement of parks, mini-parks and recreation areas on territories
which are not suitable for construction.
80. Actual problems in Provision of overall and fire safety
81. Provision of overall and fire safety
• Proper regulatory documents as applicable to provision of complexsafety & fire safety;
Up-to-date utilities and equipment to secure complex & fire safety;
Active and passive means for protection of structural elements
against fire loads (development, implementation, continuous
improvement);
Up-to-date classification of fire loads;
Development and further improvement of calculation methodologies
for structural elements affected by high temperatures;
Experimental & engineering investigation of fracture resistance,
rigidity and strength of structural elements under high temperatures;
Experimental investigation of physical & technical properties of
construction materials under high temperatures;
82. Provision of overall and fire safety
• Provision of design fire resistance of bearing frameworks andenclosing structures of high rise buildings;
Total exclusion of progressive failure cases.
Provision of design reliability in construction on settled, swelling,
ever-frozen or poor water-saturated soils, in seismic and karst
areas;
Development of efficient spatial planning solutions, technologies,
planning of populated areas with due provisions of safe labor, living
and recreation;
Arrangement of continuous control over condition of power plants,
lifting and transport means, personal protective gear and firefighting equipment;
83. Provision of overall and fire safety
• Observation of deformations of buildings adjacent to constructionarea;
Development of measures to prevent damage to buildings due to
piles being driven or arrangement of utility lines nearby;
Structural safety of construction elements and buildings.
Assessment of fire resistance of structures used in high rise
buildings
Assessment of risks and safety in construction;
Provision of reliability of engineering systems of building and
structures;
Means of improving the reliability and safety of building fund due to
wear and aging.



































































 education
education industry
industry








