Similar presentations:
WLS Definitions Training. Machine terminology, bucket sizing and selection
1. WLS Training
2. Machine terminology, bucket sizing and selection
Objective:to understand machine terminology
to understand how to match bucket and density to a required
payload, then relate this to a machine
3. Machine terminology, bucket sizing and selection
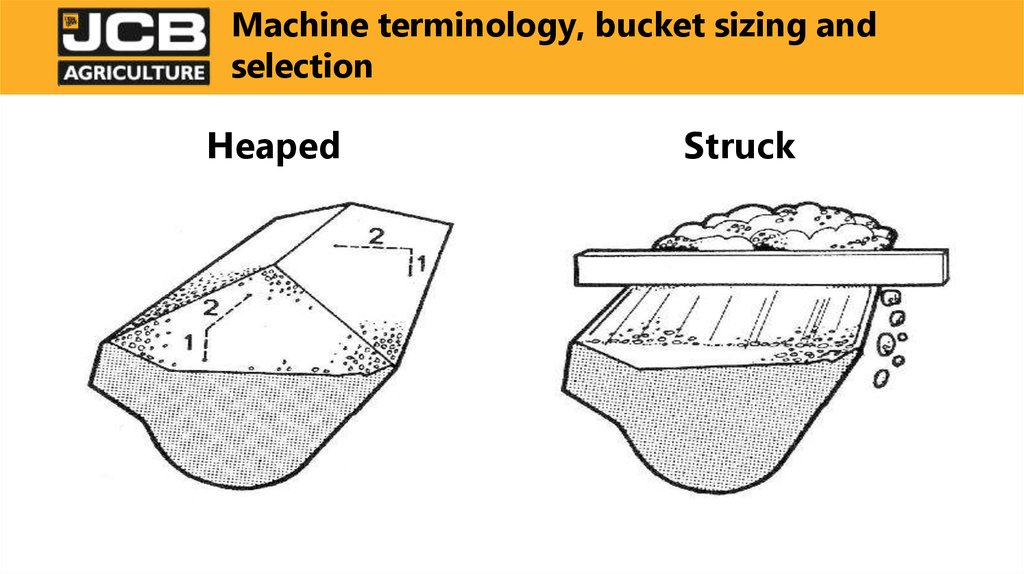
Bucket Capacities - Heaped vs. StruckHeaped Capacity - The volume of material held in a bucket with a 2 to
1 heap of material.
Struck Capacity - The volume of material held in a bucket when a
straight edge is slid across the top and bottom edge of a bucket, no
material outside dimension of bucket.
4. Machine terminology, bucket sizing and selection
HeapedStruck
5. Machine terminology, bucket sizing and selection
Tipping Loads - Straight vs. Full TurnStraight tipping load - The weight of material loaded into the
specified bucket which will raise the rear tires off of the ground
when the machine is not articulated.
Full Turn tipping load - The weight of material loaded into the
specified bucket which will raise any tire from the ground when
the machine is fully articulated. - This amount is always lower as
the counterweight moves nearer the pivot point. It is this
reason which makes articulated loaders harder to drive than
they at first appear.
6. Machine terminology, bucket sizing and selection
Straight tippingload
7. Machine terminology, bucket sizing and selection
Full Turn tipping load8. Machine terminology, bucket sizing and selection
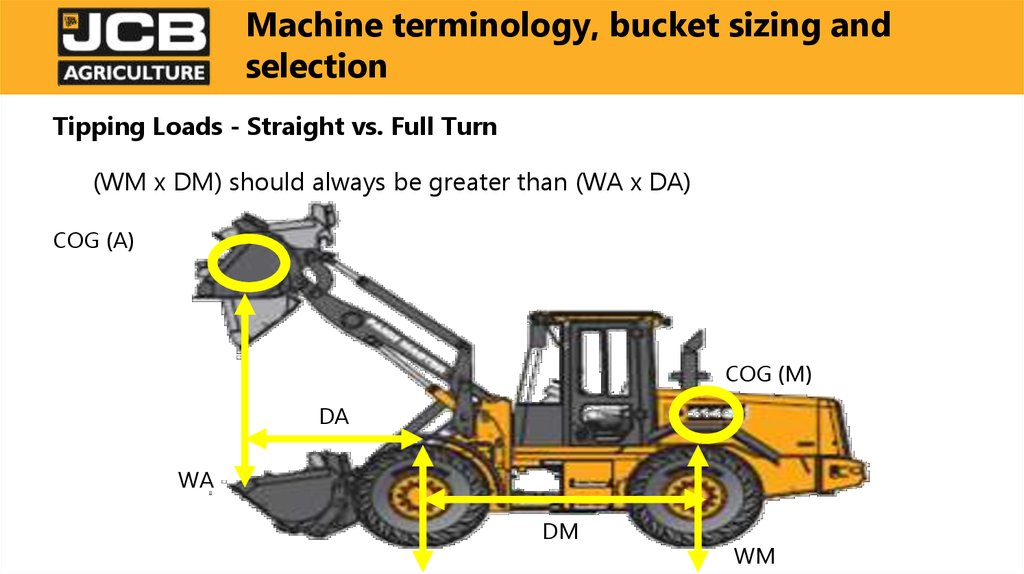
Tipping Loads - Straight vs. Full Turn(WM x DM) should always be greater than (WA x DA)
COG (A)
COG (M)
DA
WA
DM
WM
9. Machine terminology, bucket sizing and selection
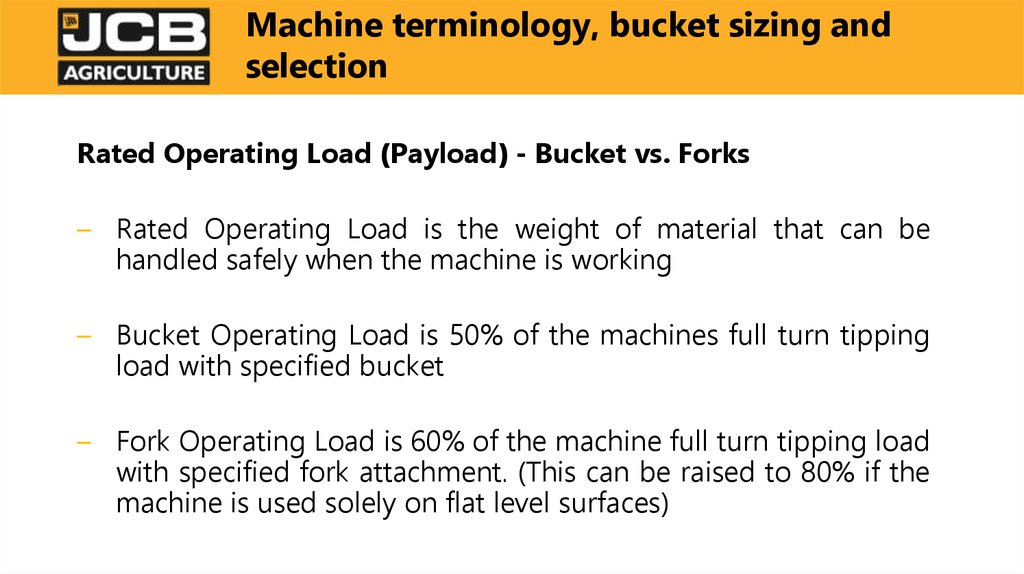
Rated Operating Load (Payload) - Bucket vs. Forks– Rated Operating Load is the weight of material that can be
handled safely when the machine is working
– Bucket Operating Load is 50% of the machines full turn tipping
load with specified bucket
– Fork Operating Load is 60% of the machine full turn tipping load
with specified fork attachment. (This can be raised to 80% if the
machine is used solely on flat level surfaces)
10. Machine terminology, bucket sizing and selection
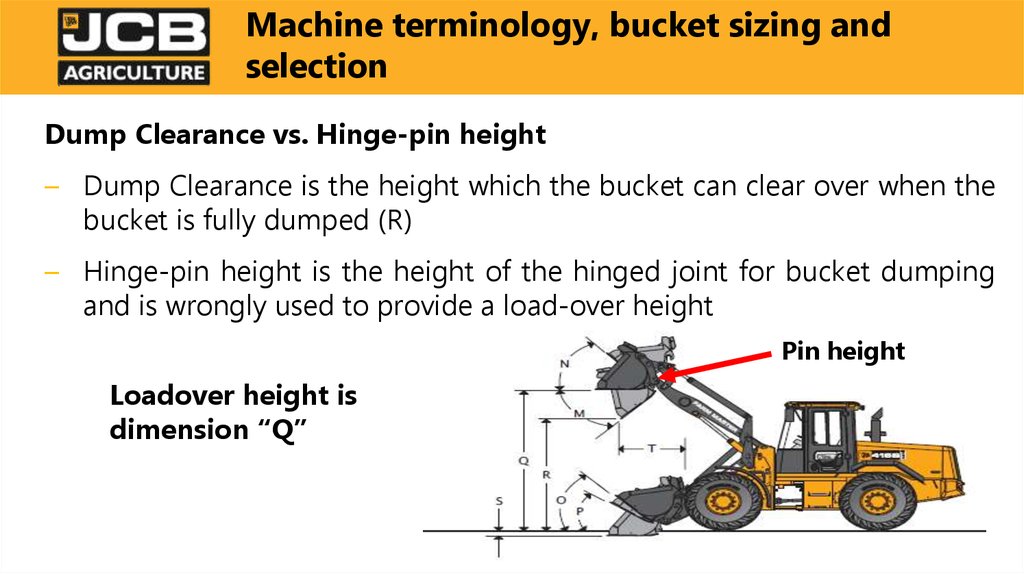
Dump Clearance vs. Hinge-pin height– Dump Clearance is the height which the bucket can clear over when the
bucket is fully dumped (R)
– Hinge-pin height is the height of the hinged joint for bucket dumping
and is wrongly used to provide a load-over height
Pin height
Loadover height is
dimension “Q”
11. Machine terminology, bucket sizing and selection
Basic RequirementsPrimarily we are interested in throughput, tonnage, m³ etc, whatever the
application
Variables to consider:
–
Site conditions
–
Material to be handled
–
Loadover height & reach
–
Required production rates and throughput
–
Truck/trailer loading rates and availability
12. Machine terminology, bucket sizing and selection
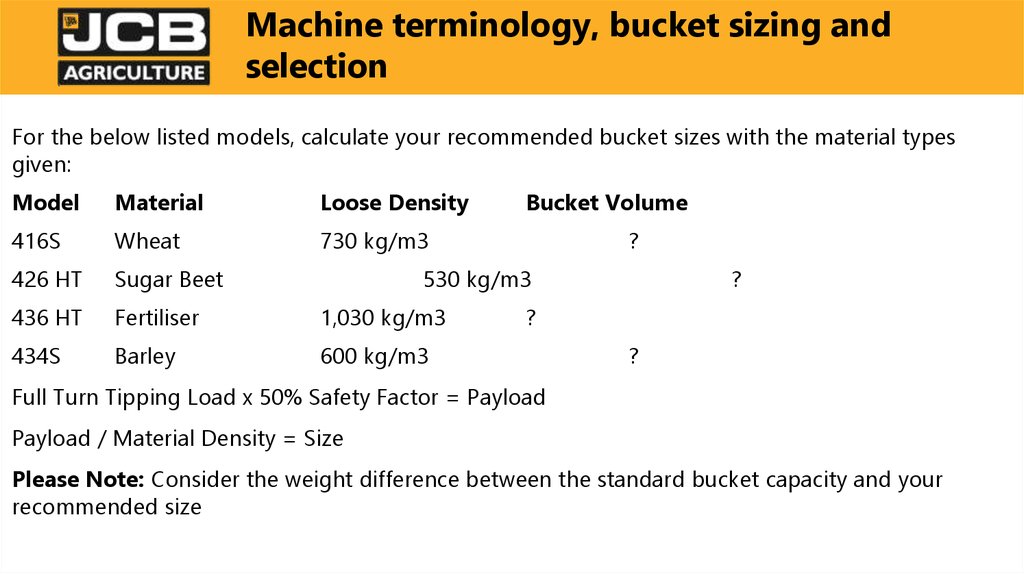
For the below listed models, calculate your recommended bucket sizes with the material typesgiven:
Model
Material
Loose Density
416S
Wheat
730 kg/m3
426 HT
Sugar Beet
436 HT
Fertiliser
1,030 kg/m3
434S
Barley
600 kg/m3
Bucket Volume
?
530 kg/m3
?
?
?
Full Turn Tipping Load x 50% Safety Factor = Payload
Payload / Material Density = Size
Please Note: Consider the weight difference between the standard bucket capacity and your
recommended size
13. Machine terminology, bucket sizing and selection
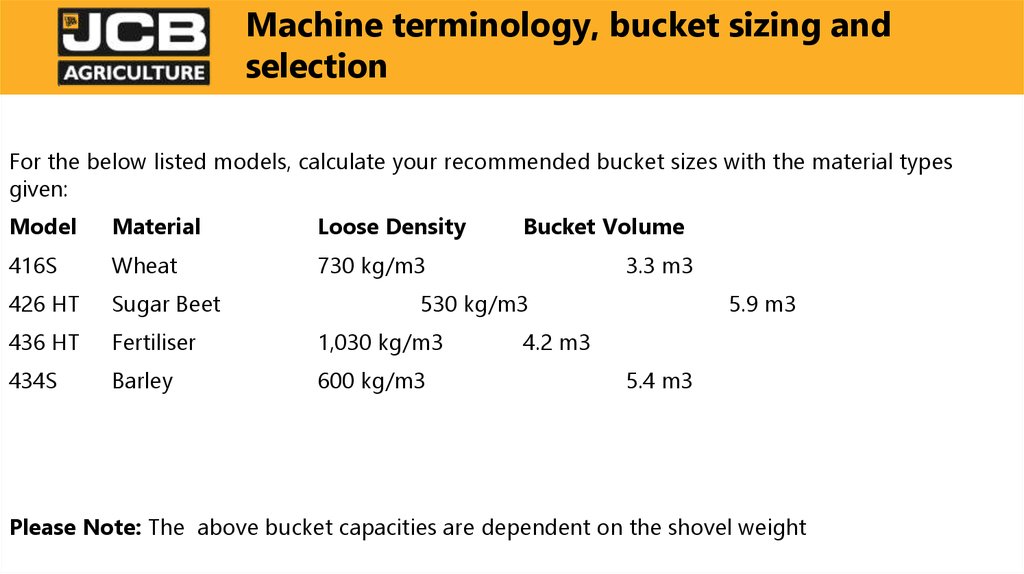
For the below listed models, calculate your recommended bucket sizes with the material typesgiven:
Model
Material
Loose Density
416S
Wheat
730 kg/m3
426 HT
Sugar Beet
436 HT
Fertiliser
1,030 kg/m3
434S
Barley
600 kg/m3
Bucket Volume
3.3 m3
530 kg/m3
5.9 m3
4.2 m3
5.4 m3
Please Note: The above bucket capacities are dependent on the shovel weight
14. Machine terminology, bucket sizing and selection
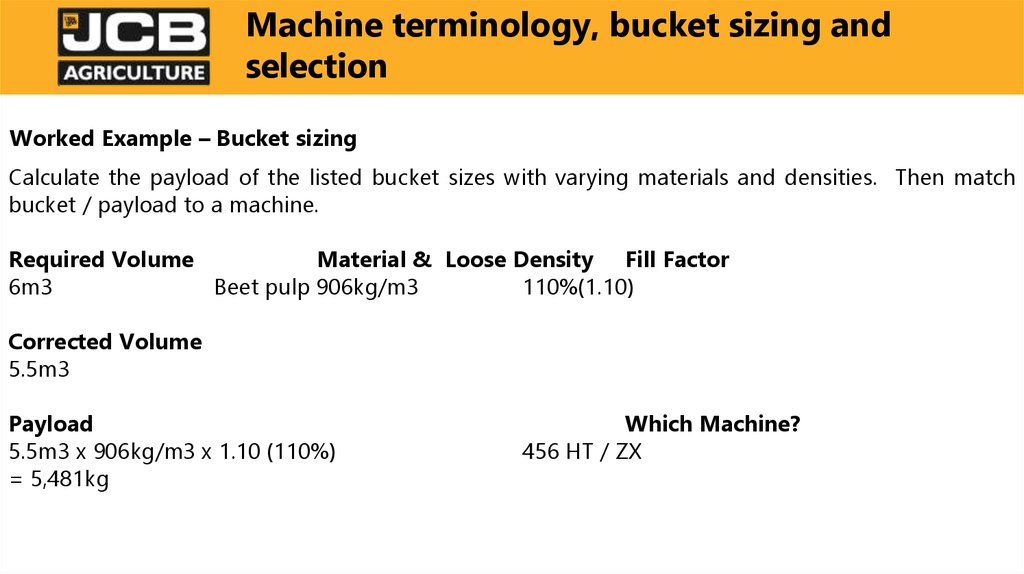
Worked Example – Bucket sizingCalculate the payload of the listed bucket sizes with varying materials and densities. Then match
bucket / payload to a machine.
Required Volume
Material & Loose Density Fill Factor
6m3
Beet pulp 906kg/m3
110%(1.10)
Corrected Volume
5.5m3
Payload
5.5m3 x 906kg/m3 x 1.10 (110%)
= 5,481kg
Which Machine?
456 HT / ZX



 industry
industry








