Similar presentations:
Histology and research methods used in it
1.
TASHKENT MEDICAL ACADEMYDepartment of Histology and Medical Biology
Topic: Histology and
research methods used
in it
Tashkent-2023
2.
HistologyHistology is the study of the tissues of the
body and how these tissues are arranged to
constitute organs. The Greek root histo can
be translated as either “tissue” or “web,”
both of which are appropriate because
tissues are usually webs of interwoven fi
laments and fi bers, both cellular and
noncellular, with membranous linings.
Histology involves all aspects of tissue
biology, with the focus on how cells’
structure
and
arrangement
optimize
functions specifi c to each organ.
2
3.
MicroscopyMicroscopes are scientific
instruments
designed
to
produce magnified visual or
photographic images of small
objects which are not visible
by naked eye. Micro - Small
Scope - Look Microscopy
Some type of microscope
* Light microscope
* Electron microscope
A- Transmission electron microscope
B- Scanning electron microscope
* Darkground microscope
* Phase-contrast microscope
*Interference microscope
* Fluorescence microscope
* Confocal microscope
3
4.
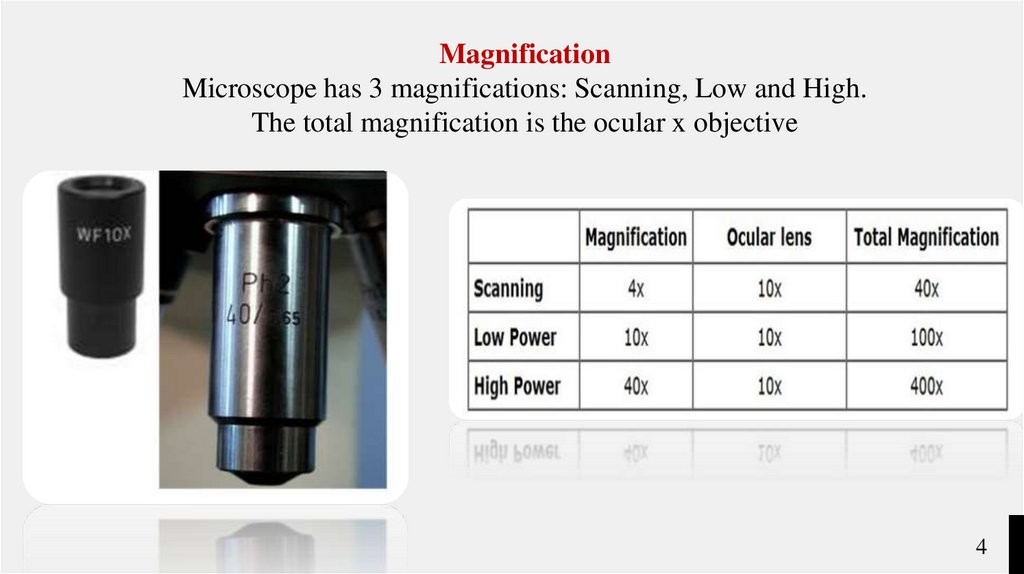
MagnificationMicroscope has 3 magnifications: Scanning, Low and High.
The total magnification is the ocular x objective
4
5.
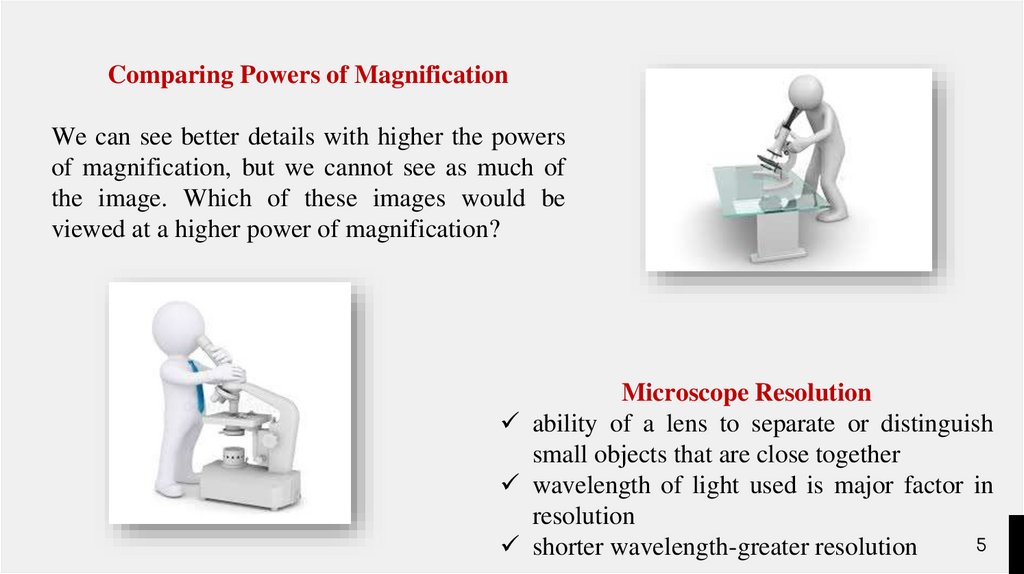
Comparing Powers of MagnificationWe can see better details with higher the powers
of magnification, but we cannot see as much of
the image. Which of these images would be
viewed at a higher power of magnification?
Microscope Resolution
ability of a lens to separate or distinguish
small objects that are close together
wavelength of light used is major factor in
resolution
5
shorter wavelength-greater resolution
6.
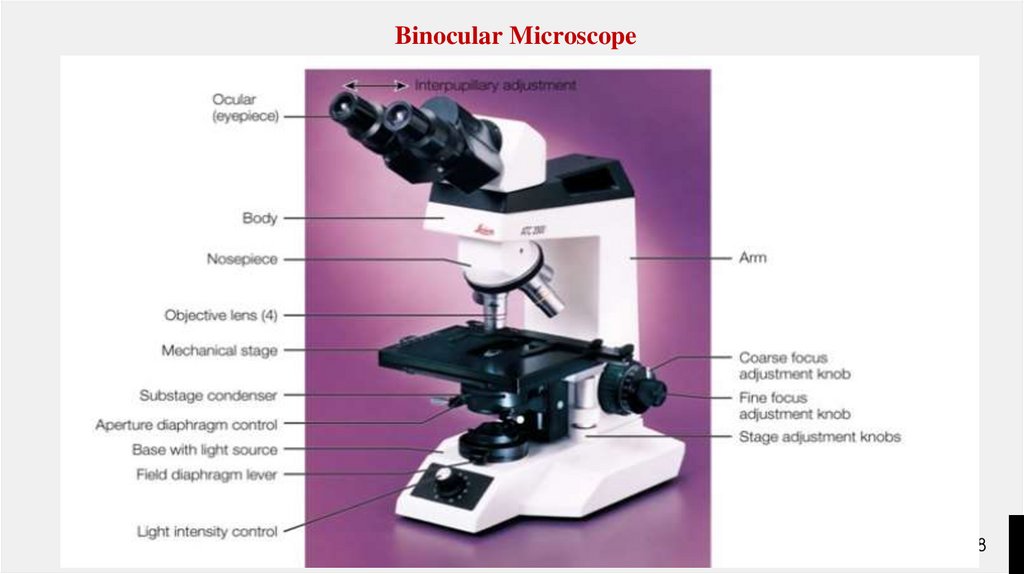
Parts of the MicroscopeThree main parts:
Optical
Illuminating
Mechanical
Optical Parts Used for the Magnification of an
image
Ocular or Eye Piece
Objectives
Illuminating Parts
Mirror: Used for reflecting the light rays to the
condenser.
Diaphragm: regulates the amount of light
reflected
6
7.
Mechanical PartsMovement and support
Base
Pillar
Stage
Arm
Revolving Nose Piece
Draw Tube
Coarse and Fine Adj knobs
Inclination Points
Mirror Rack
Stage Clips
7
8.
Binocular Microscope8
9.
910.
1011.
1112.
1213.
Sectioning fixed and embedded tissue13
14.
Preparations of sections for histopathology1- paraffin embedding method ( the routine &
widely used procedure).
2- frozen section (intra-operative).
3- cytological diagnosis (exfoliative & fine needle
aspiration cytology.
4- digital pathology & telepathology.
14
15.
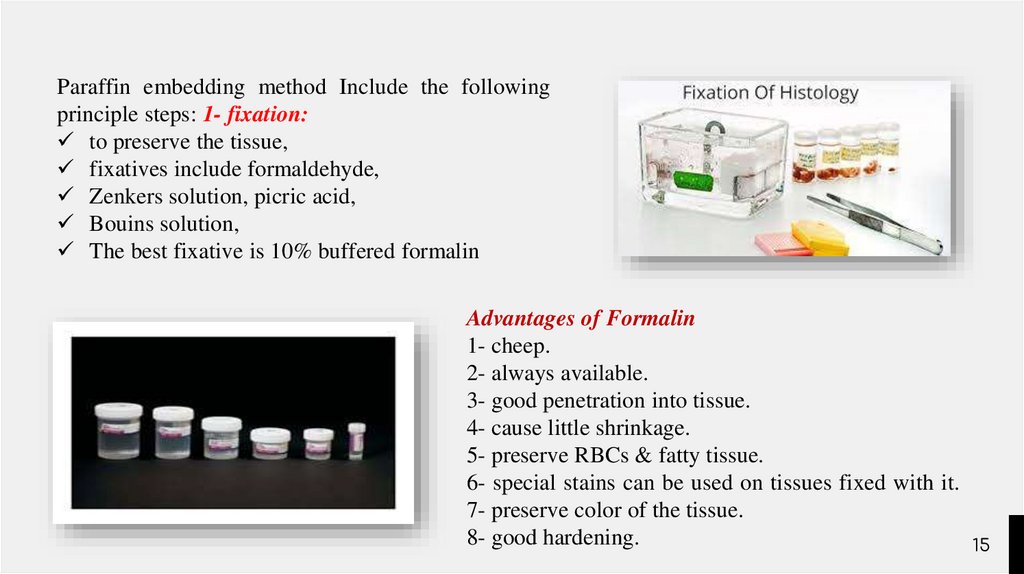
Paraffin embedding method Include the followingprinciple steps: 1- fixation:
to preserve the tissue,
fixatives include formaldehyde,
Zenkers solution, picric acid,
Bouins solution,
The best fixative is 10% buffered formalin
Advantages of Formalin
1- cheep.
2- always available.
3- good penetration into tissue.
4- cause little shrinkage.
5- preserve RBCs & fatty tissue.
6- special stains can be used on tissues fixed with it.
7- preserve color of the tissue.
8- good hardening.
15
16.
Disadvantages of Formalin1- if tissue preserved in formalin for long time,
formic acid will be formed which affect
stainability of tissue with different stains, so it
should be changed every 3-6 months.
2- when formalin solution is stored for long
period a white precipitate of para formaldehyde
which will not affect the efficiency of formalin as
a fixative & can be removed by alcohol.
3- cannot preserve glycogen.
2- Dehydration:- by using different concentrations of
alcohol.
3- Clearing:- by using xyline.
4- Paraffin impregnation.
16
17.
5- Embedding:- to make the tissue as a block of hardparaffin
6- Sectioning:- by using a microtome, the tissue is
sliced into very thin sections ranging from 4-6
micrometer in thickness.
7- Attaching sections to the slides.
8- Deparaffinization:- by using xylol & alcohol until
the paraffin is dissolved.
9- Staining:- the standard staining method is H & E
which stain the nucleus blue (basophilic) & the
cytoplasm pink-red (acidophilic).
10- Mounting:- by using DPX &cover slip.
17













 medicine
medicine biology
biology








