Similar presentations:
Cell structure and types 8th grade
1.
1.1 Cell structure and types8th grade
Yerbol Nurmaganbetov
2.
3.
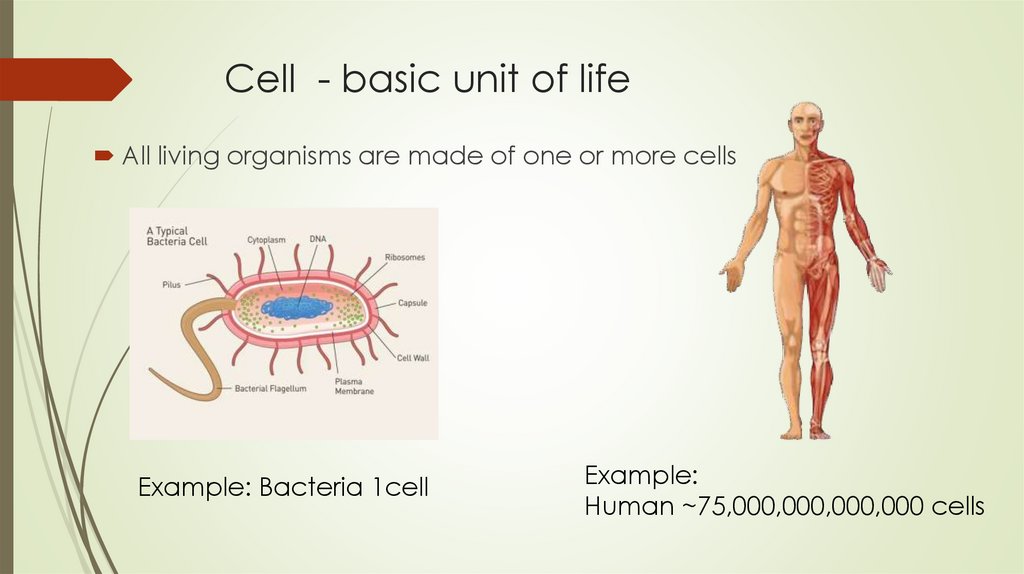
Cell - basic unit of lifeAll living organisms are made of one or more cells
Example: Bacteria 1cell
Example:
Human ~75,000,000,000,000 cells
4.
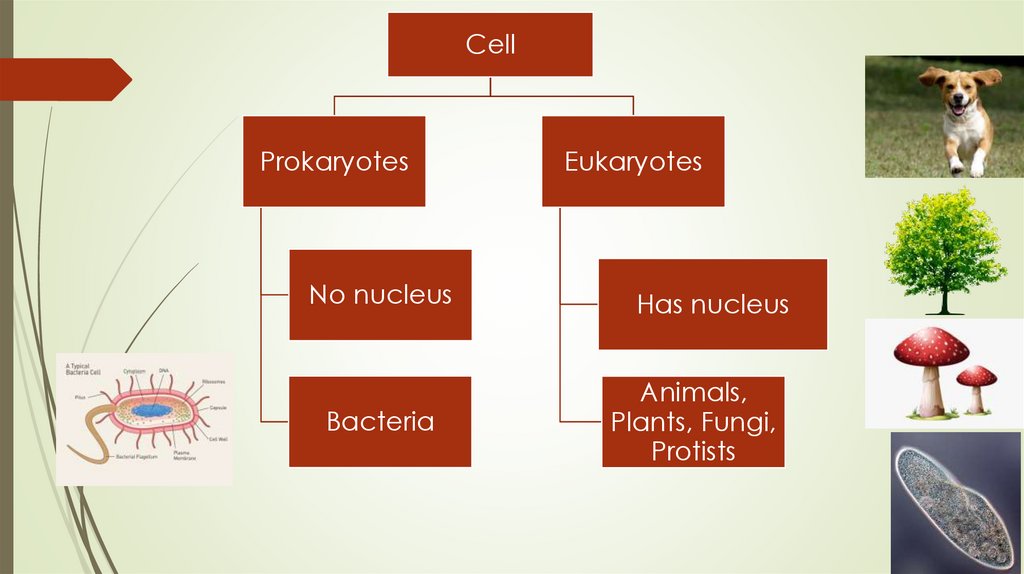
CellProkaryotes
Eukaryotes
No nucleus
Has nucleus
Bacteria
Animals,
Plants, Fungi,
Protists
5.
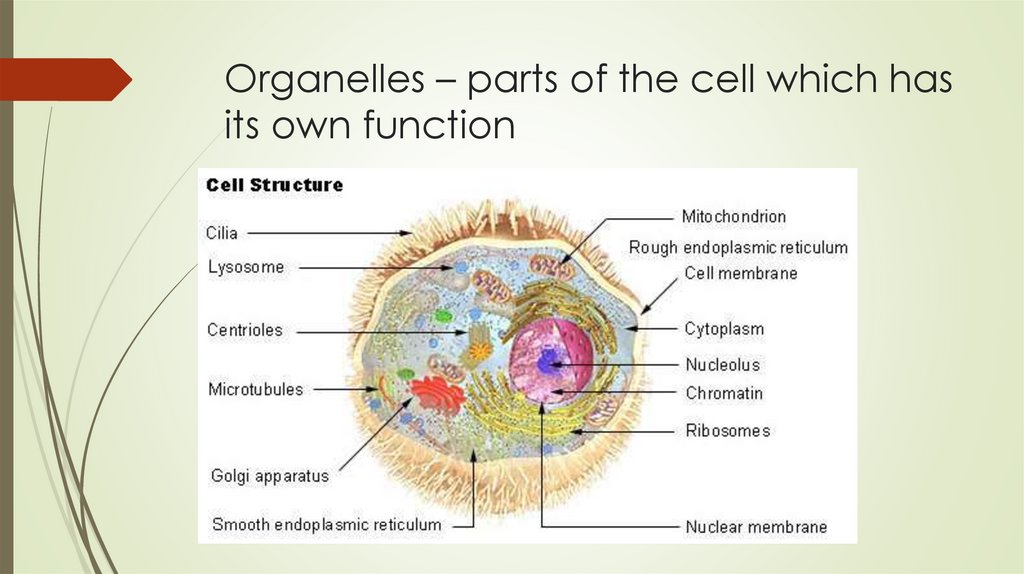
Organelles – parts of the cell which hasits own function
6.
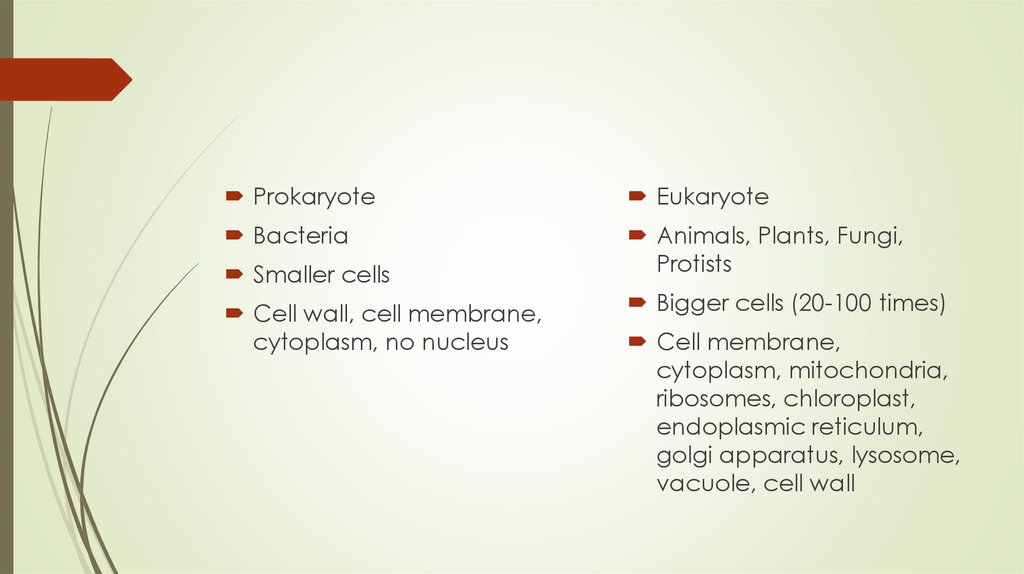
ProkaryoteEukaryote
Bacteria
Animals, Plants, Fungi,
Protists
Smaller cells
Cell wall, cell membrane,
cytoplasm, no nucleus
Bigger cells (20-100 times)
Cell membrane,
cytoplasm, mitochondria,
ribosomes, chloroplast,
endoplasmic reticulum,
golgi apparatus, lysosome,
vacuole, cell wall
7.
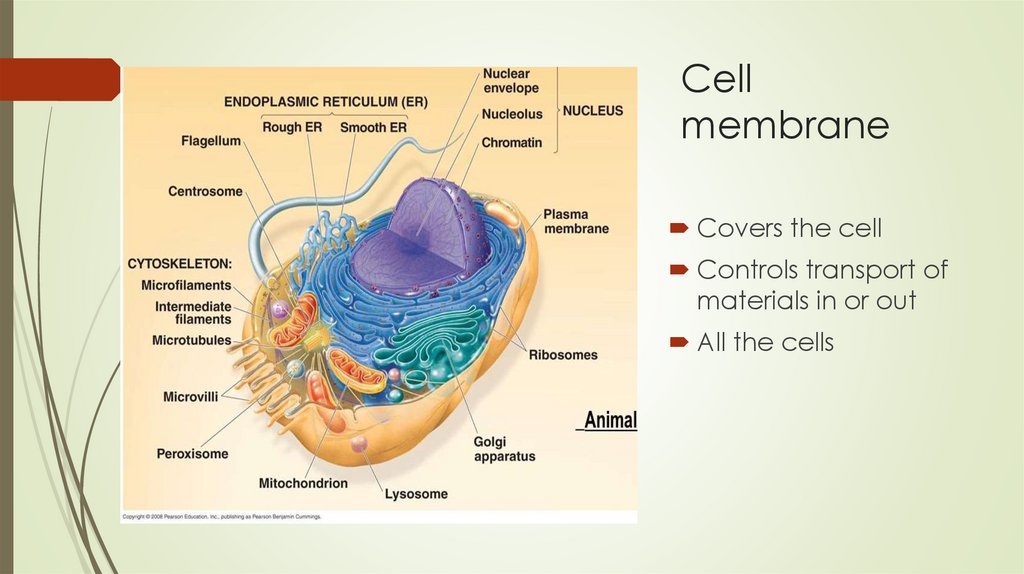
Cellmembrane
Covers the cell
Controls transport of
materials in or out
All the cells
8.
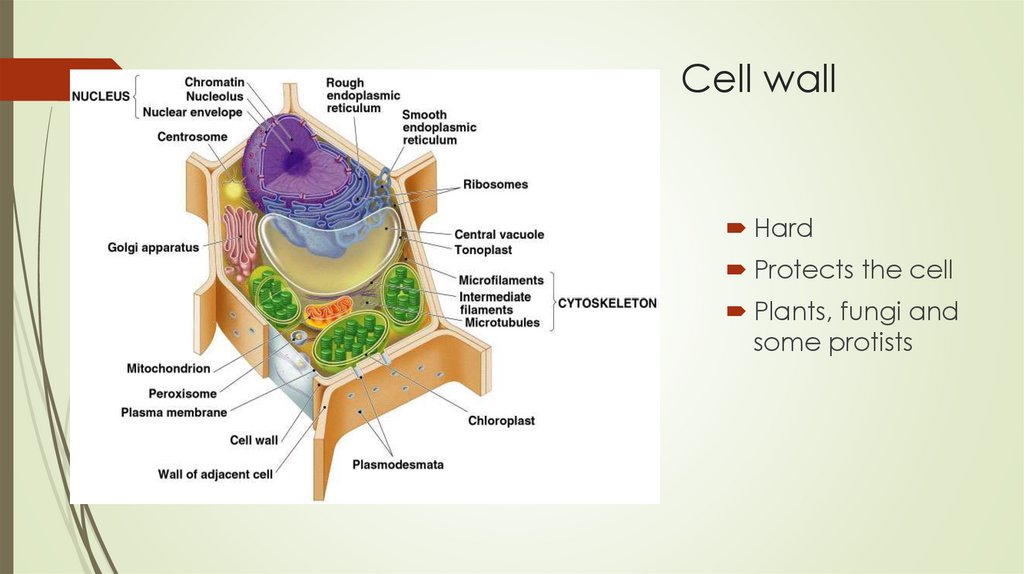
Cell wallHard
Protects the cell
Plants, fungi and
some protists
9.
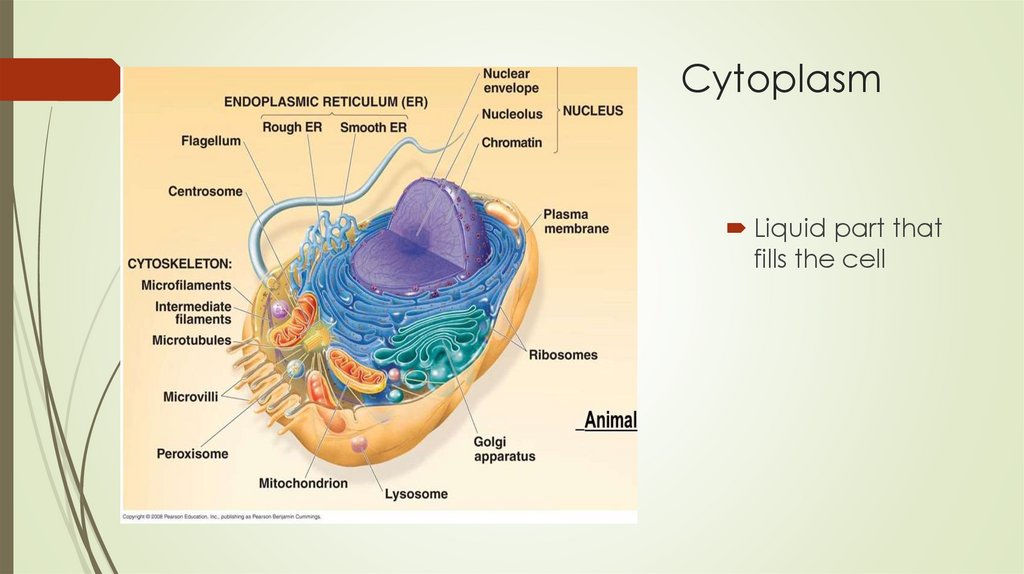
CytoplasmLiquid part that
fills the cell
10.
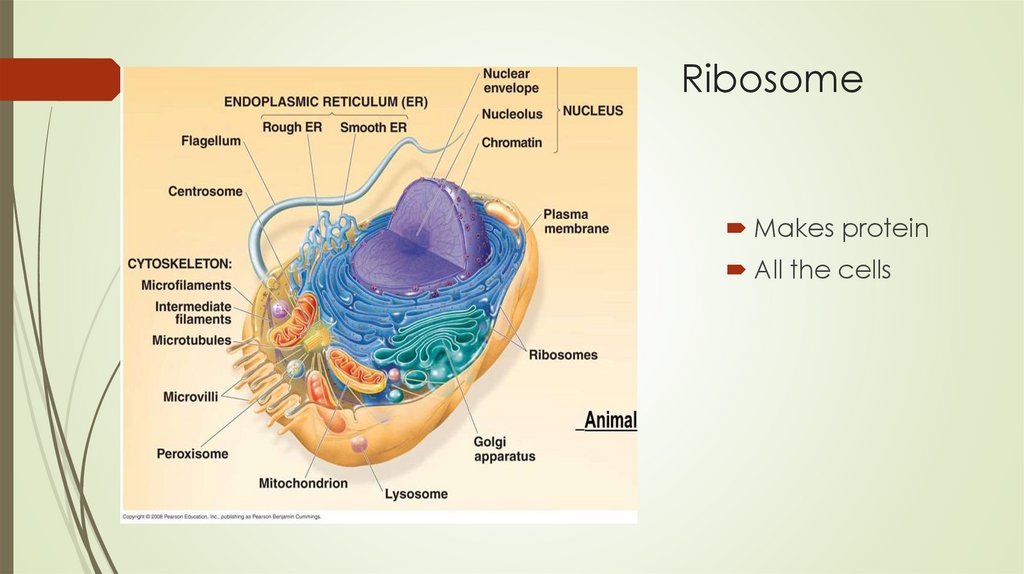
RibosomeMakes protein
All the cells
11.
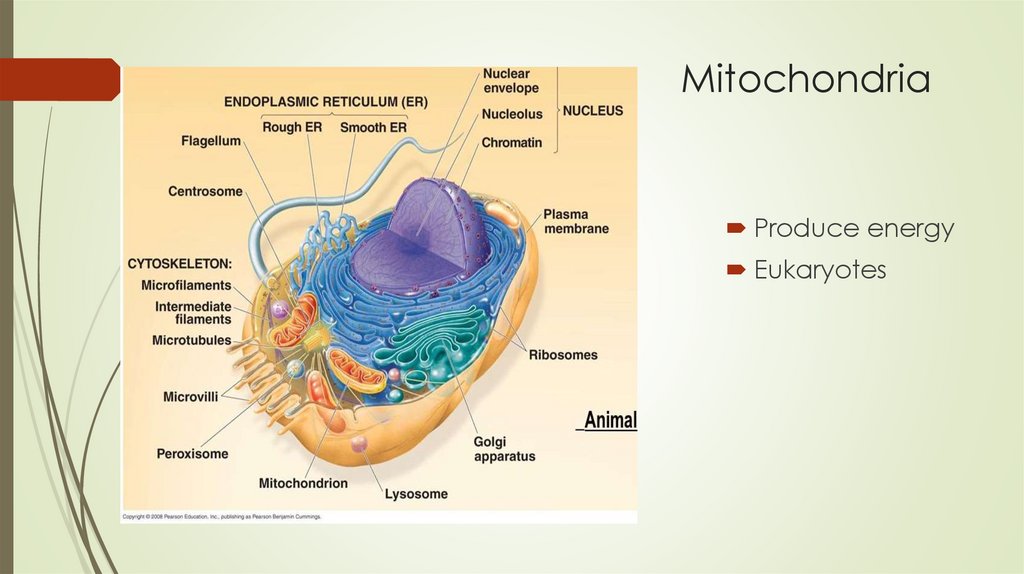
MitochondriaProduce energy
Eukaryotes
12.
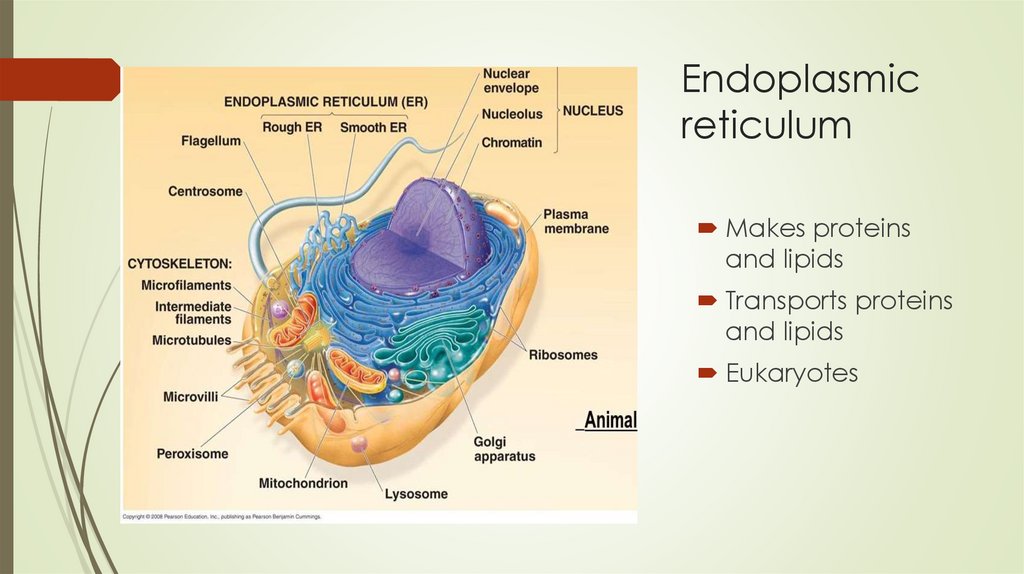
Endoplasmicreticulum
Makes proteins
and lipids
Transports proteins
and lipids
Eukaryotes
13.
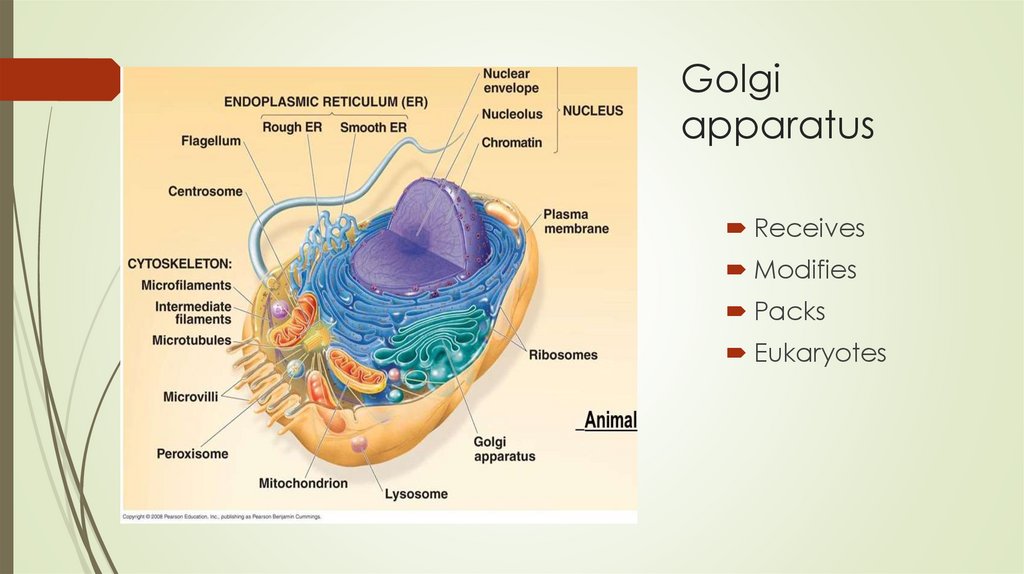
Golgiapparatus
Receives
Modifies
Packs
Eukaryotes
14.
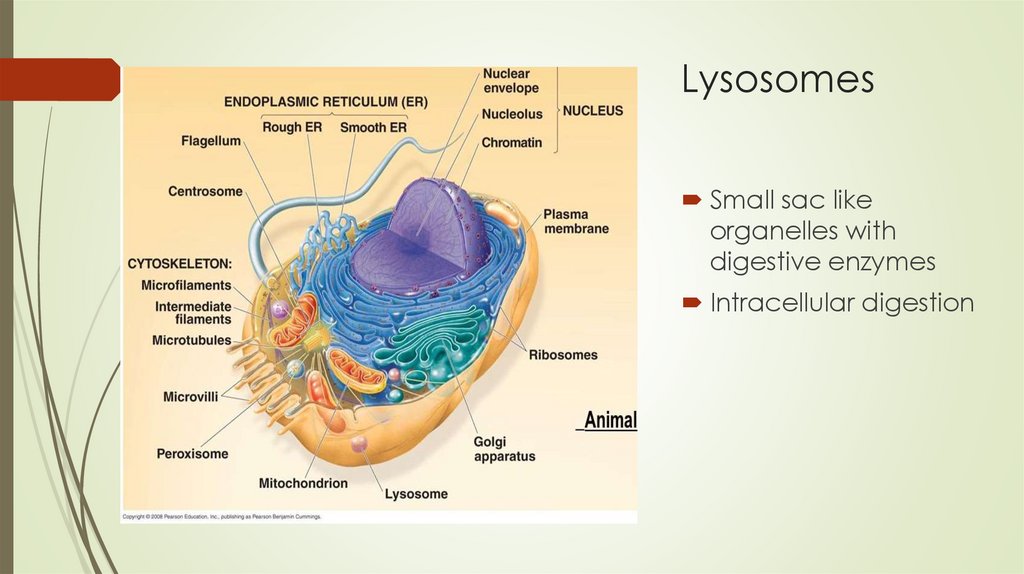
LysosomesSmall sac like
organelles with
digestive enzymes
Intracellular digestion
15.
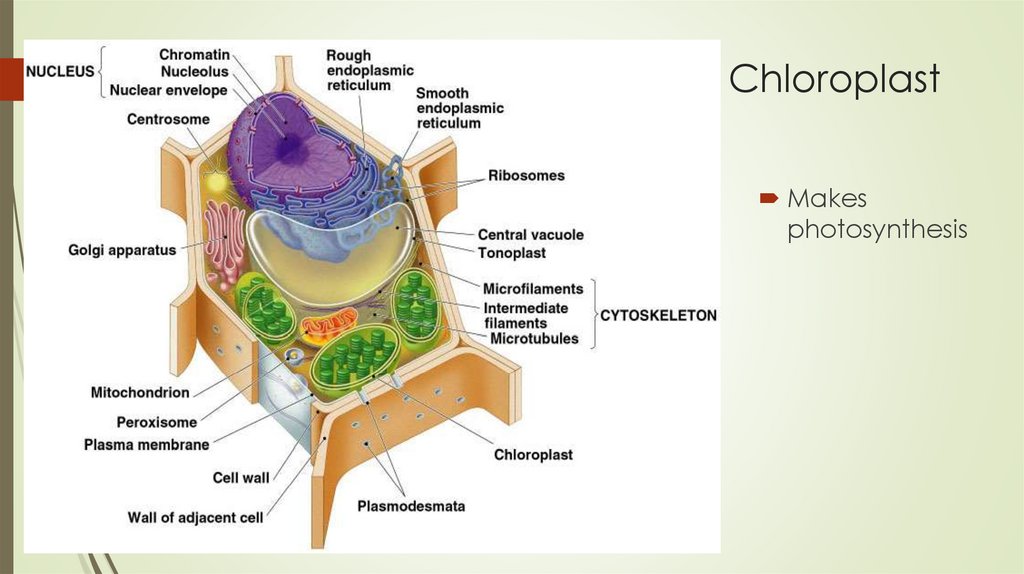
ChloroplastMakes
photosynthesis
16.
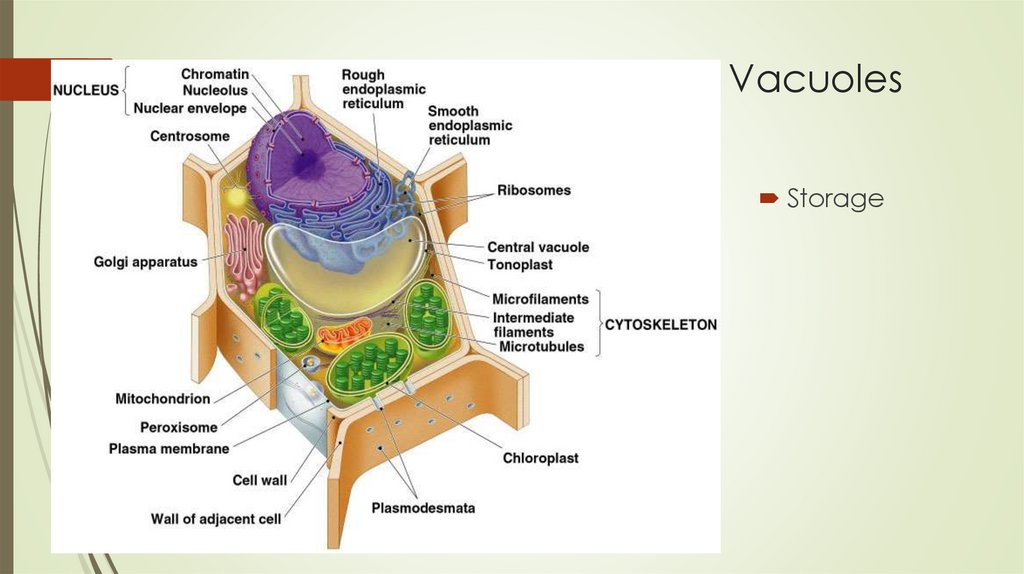
VacuolesStorage
17.
MicrobiologistBacteria can be useful and harmful.
Microbiologists study these bacteria.
They use good things from bacteria;
they can make food or
pharmaceuticals.
Some bacteria can cause illnesses.
Microbiologists study them and help
people not to be ill.
18.
Record-breaker cellsThe smallest bacteria – Mycoplasma – diameter – 0.2-0.4micrometer
The longest cell – Blue whale’s nerve cell – 10-30 meter long
“Sociable” cell – nerve cell – can connect up to 10,000 cells



 biology
biology