Similar presentations:
The Digestive System
1.
THEDIGESTIVE
SYSTEM
2.
3.
OUTLINE• Embryogenesis, structure and functions.
• The digestive tract, its layers and
characteristics of its layers.
• Innervation and blood supply.
• Glands of the digestive tract, structure and
localization.
• Oral cavity.
4.
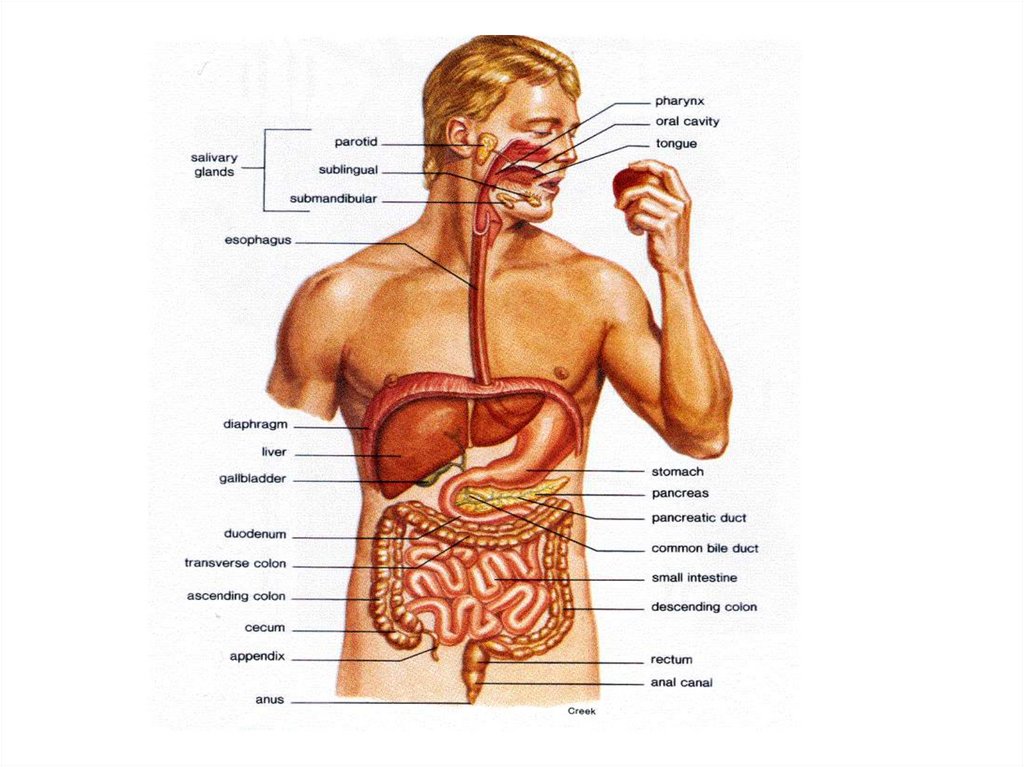
The digestive system is made upof a long tube extending from the
mouth to the anus, and associated
glands such as salivary glands,
pancreas and liver.
5.
Digestion involves first, thebreakdown of food into small
particles. This action is carried out
by the teeth and HCL and digestive
enzymes.
6.
Embryogenesis• The gut is an endoderm-derived
structure. At approximately the
sixteenth day of human development,
the embryo begins to fold ventrally
(with the embryo's ventral surface
becoming concave) in two directions:
the sides of the embryo fold in on each
other and the head and tail fold toward
one another.
7.
The result is that a piece of theyolk sac, an endoderm-lined
structure in contact with the
ventral aspect of the embryo,
begins to be pinched off to
become the primitive gut.
8.
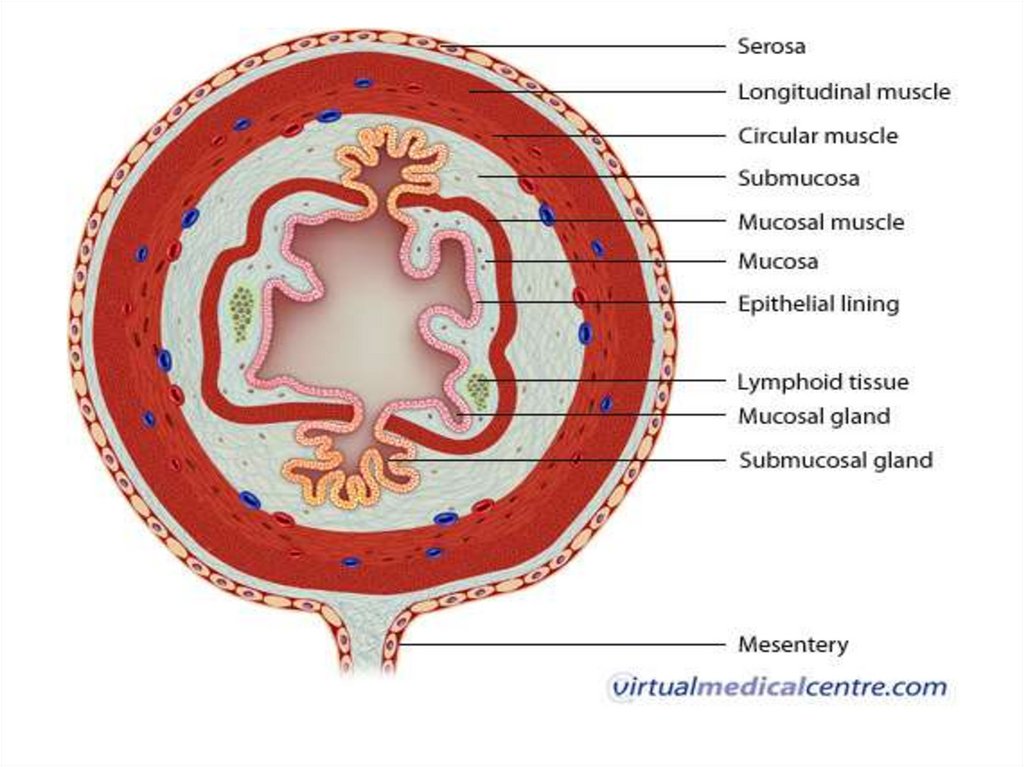
Layers of the digestivetract
• The mucosa;
• The submucosa;
• The muscular;
• The serous (adventitia).
9.
10.
The mucosa:Made up of stratified squamous
epithelium,it is lubricated by
mucous and rests on a basal
lamina. The epithelium is derived
from the endoderm.
11.
• The submucosa:this layer lies between the mucous
and the muscular layers. It consists
of loose connective tissue. It also
contains plexuses of blood vessels
and nerves.
12.
• The muscular layer:The muscle fibres here are
arranged as inner circular an outer
longitudinal. This layer helps in
peristalsis and churning
movements. This layer also helps in
forming sphincters.
13.
• The serous layer (adventitia)It is the outermost layer and is
made up of dense and elastic
connective tissue. In many regions
it is covered by peritoneum. Blood
and lymphatic vessels are also
present here.
14.
15.
Blood supply andinnervation
• The main source of blood supply is from
the abdominal aorta for the part in
abdominal cavity. The various digestive
organs have their own blood supply.
• Parasympathetic innervation is from the
vagus nerve and sympathetic
innervation from the sympathetic trunk.
16.
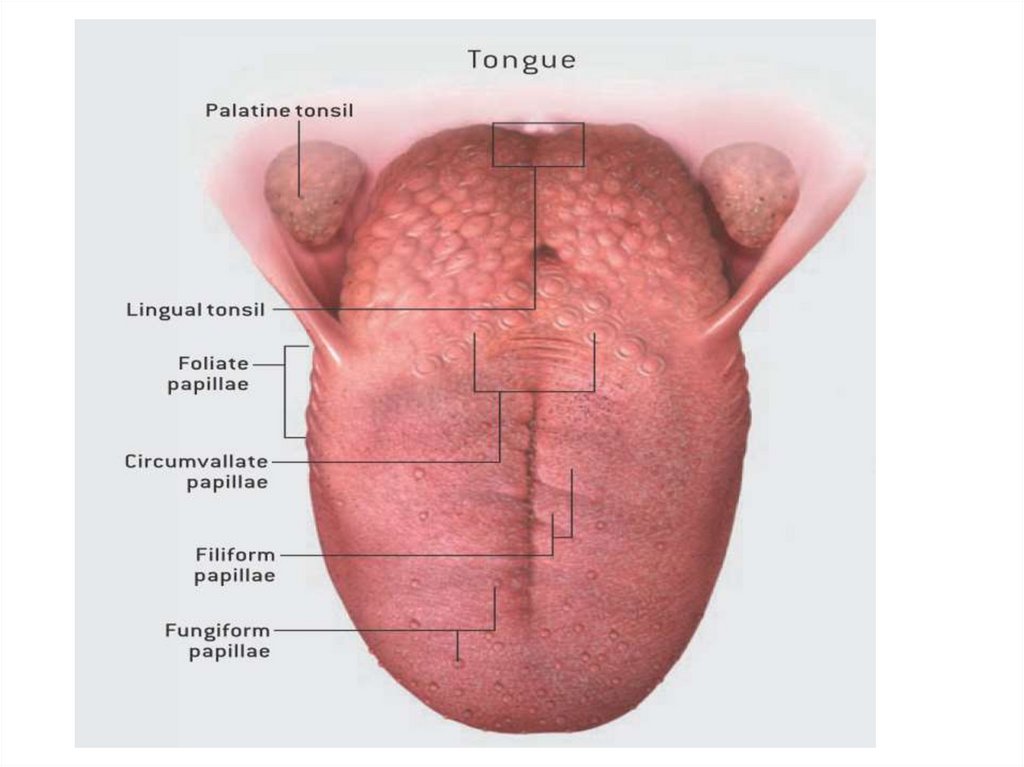
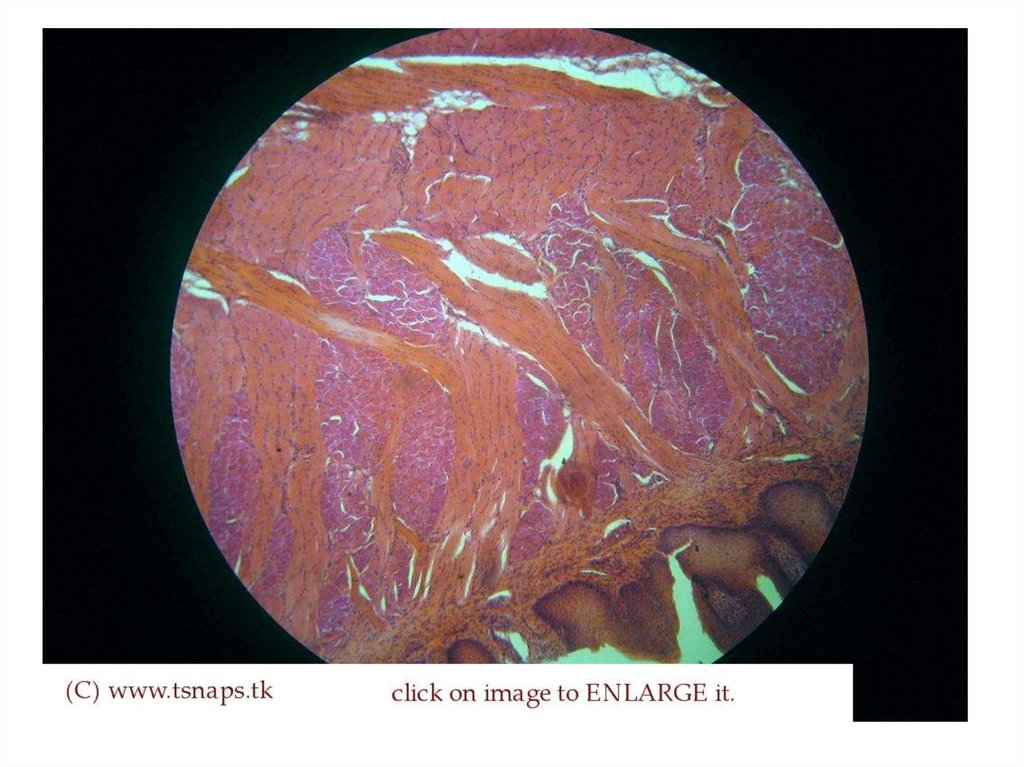
tongue• The tongue is the organ of taste, it
consists of a freely moveable
portion(body) and a base, or root
attached to the floor and forming
part of the anterior wall of the
pharynx. The tongue consists of
striated muscle fibers and glands
covered by mucous membrane.
17.
• The tongue also features variouspapillae namely: filiform,
fungiform, circumvallate and
foliate.
• Only 4 fundamental taste
sensations can be detected. They
are: sweet, sour, bitter and salty.
18.
19.
20.
21.
22.
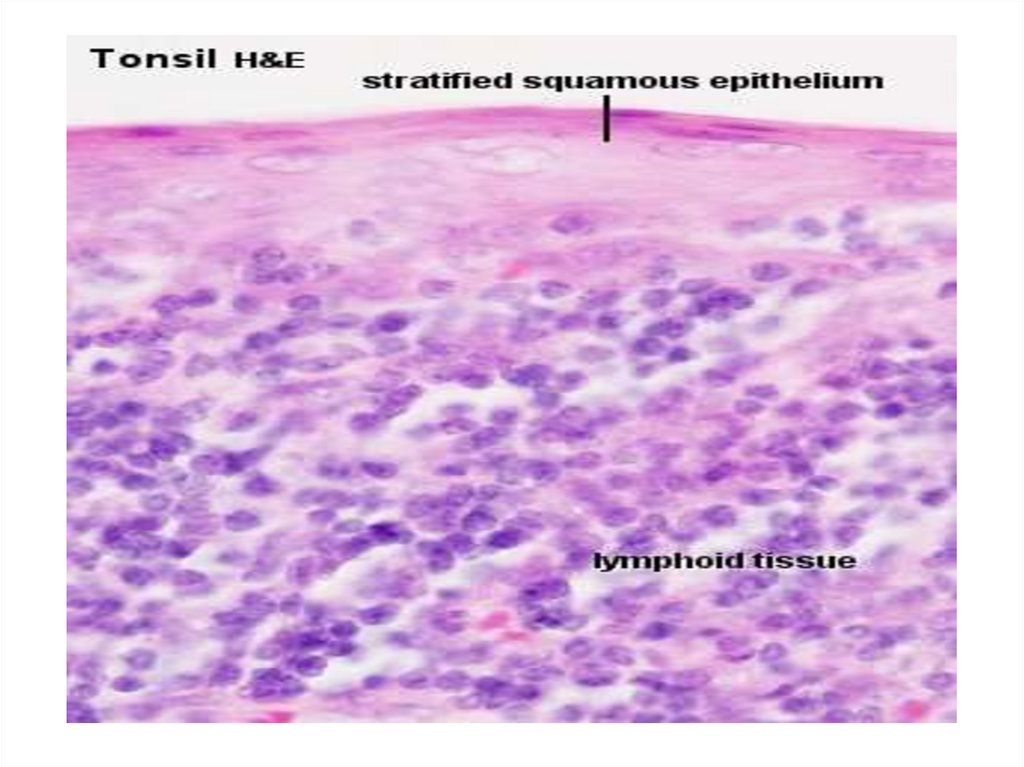
The tonsils• They are aggregates of unencapsulated
lymphoid tissue that lie in close
association with a wet epithelial
membrane. It has immune function. The
tonsils sometimes get infected and are
enlarged leading to tonsilitis. The tonsils
are stratified squamous non-keratinized
epithelium.
23.
24.
25.
• The tonsils are of 3 groups:a) the palatine tonsils (paired);
b) the lingual tonsil;
c) the pharyngeal tonsil(adenoid).
26.
The salivary glandsTo moisten the mucosa of oral
cavity, vestible and lips, saliva is
needed. Saliva is secreted by
numerous small glands associated
with the oral cavity. The saliva is
passed out through ducts. The
glands are of ectodermal and
mesenchymal origin.
27.
28.
• The salivary glands are :• the parotid;
• submandibular and
• sublingual glands.
29.
The acinus is the secretory unit ofthe salivary glands.
Other cells of the glands are:
Serous cells, mucous cells,
myoepithelial cells.
Salivary glands have merocrine
type of secretion.

























 biology
biology