Similar presentations:
Digestive organs
1.
4.3 Digestive organsNutrition
Yerbol Nurmaganbetov
2.
Oral cavityDigestion starts in the oral cavity.
There, teeth cut food into smaller pieces;
Tongue helps in tasting and mixing food.
3.
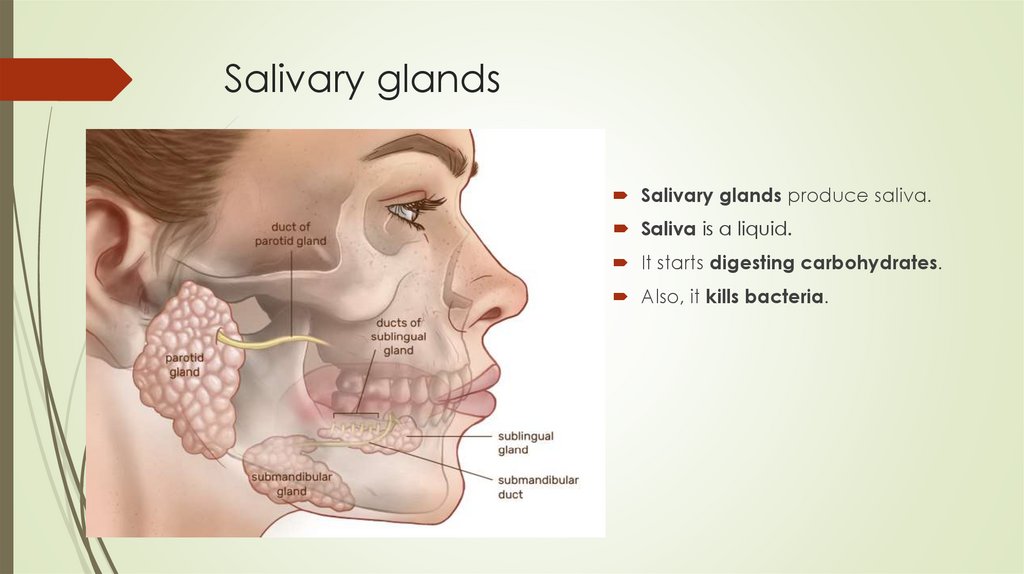
Salivary glandsSalivary glands produce saliva.
Saliva is a liquid.
It starts digesting carbohydrates.
Also, it kills bacteria.
4.
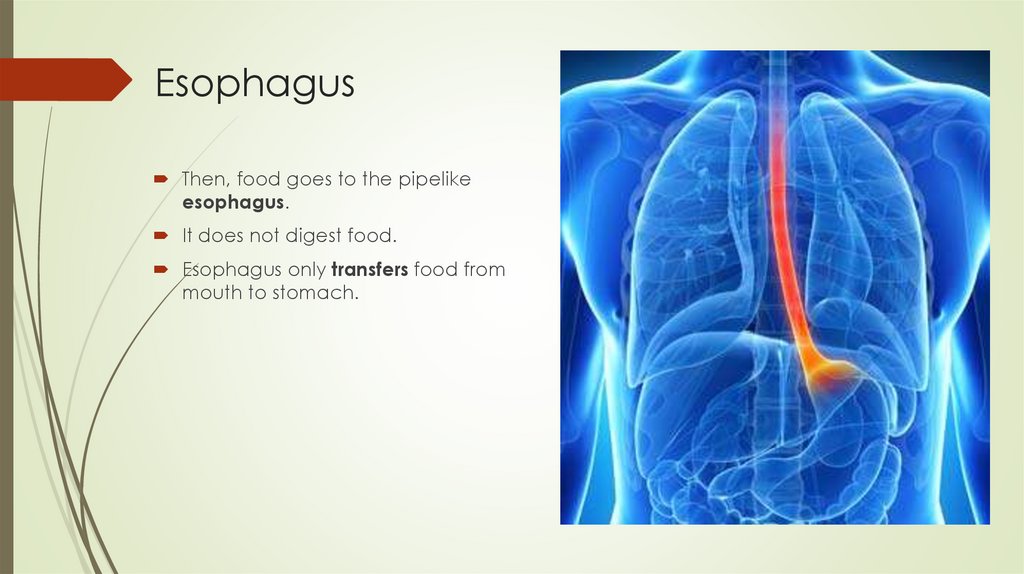
EsophagusThen, food goes to the pipelike
esophagus.
It does not digest food.
Esophagus only transfers food from
mouth to stomach.
5.
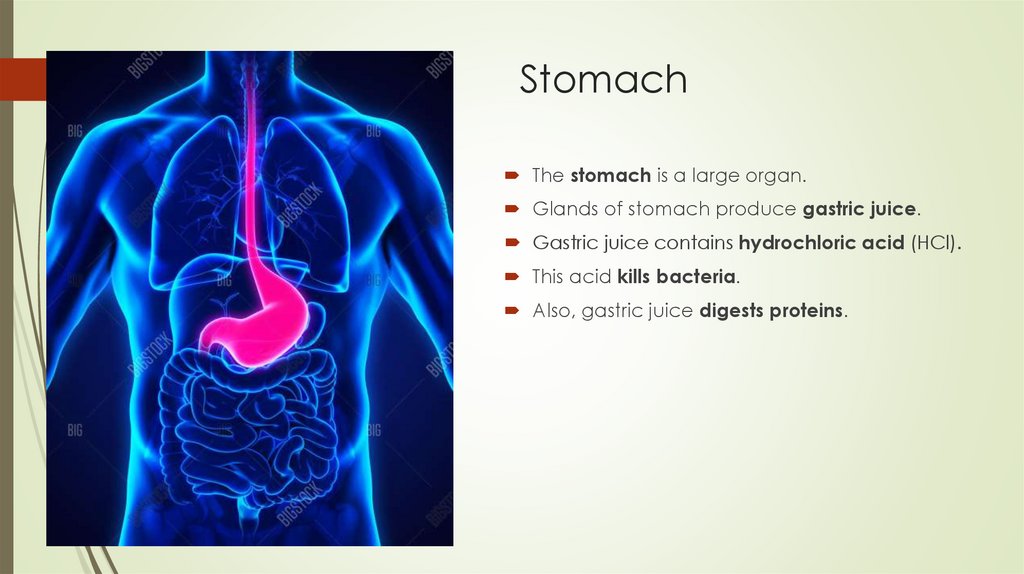
StomachThe stomach is a large organ.
Glands of stomach produce gastric juice.
Gastric juice contains hydrochloric acid (HCl).
This acid kills bacteria.
Also, gastric juice digests proteins.
6.
Small intestineFrom stomach, food goes to small intestine.
The small intestine is a long organ.
It digests proteins, carbohydrates, and lipids.
Also, it absorbs digested food.
7.
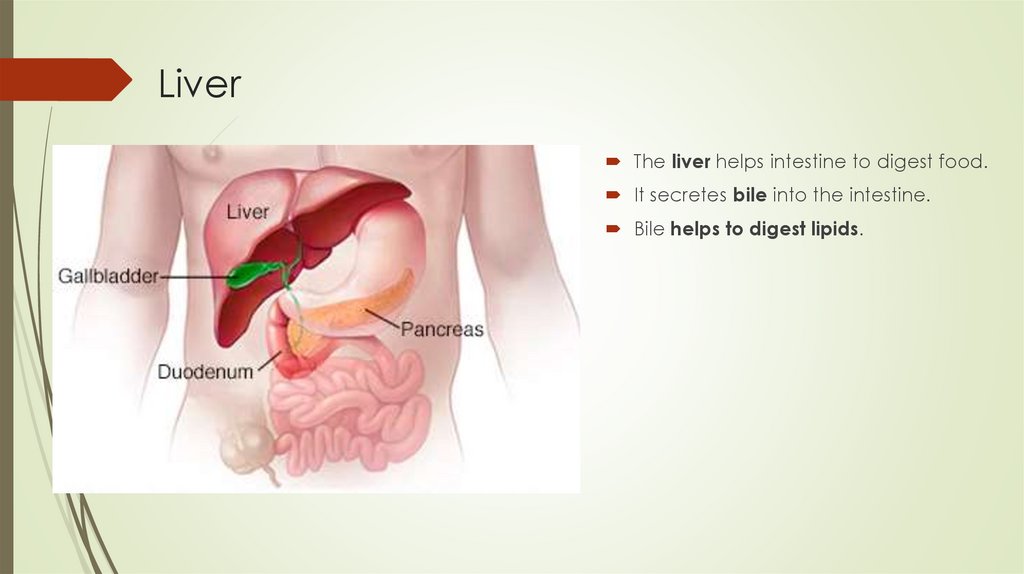
LiverThe liver helps intestine to digest food.
It secretes bile into the intestine.
Bile helps to digest lipids.
8.
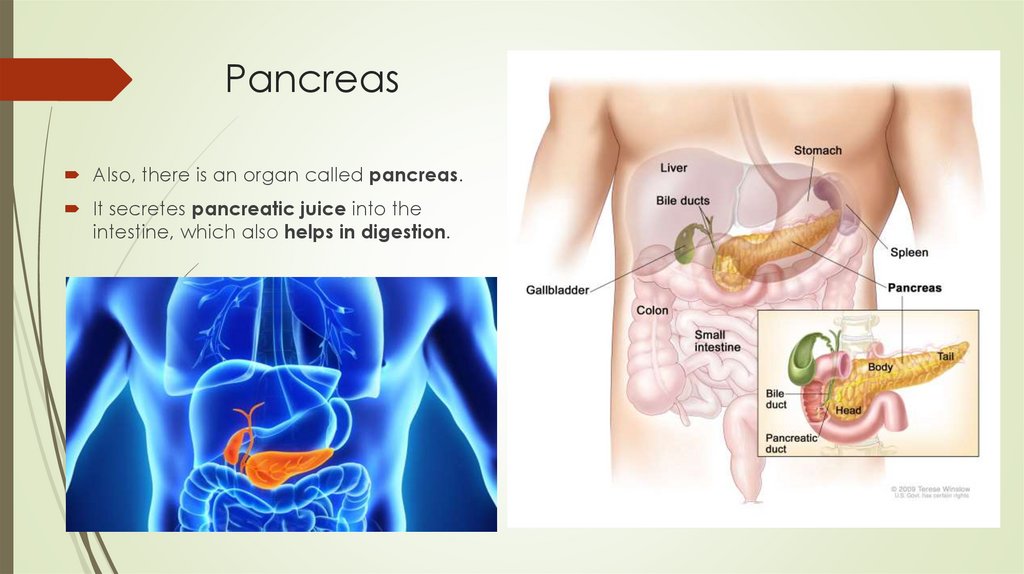
PancreasAlso, there is an organ called pancreas.
It secretes pancreatic juice into the
intestine, which also helps in digestion.
9.
Large intestineFrom small intestine, food
goes to large intestine.
It does not digest food but
absorbs water.
Undigested food is
temporarily stored in the
rectum and removed from
the organism.
10.
MicrovilliThe inner lining of the small intestine has fingerlike projections called microvilli.
11.
FactsIf we measure the area of small intestine it would be 0,6 m2. But the inner wall of
intestine is folded with fingerlike structures called villi. When these villi are unfolded,
actual area is 250 m2, which is same with a tennis court. These structures increase
the surface area of small intestine to absorb more food at one time.
12.
CareerDietitians are qualified health professionals that diagnose and treat dietary and
nutritional problems. Dietitians help both healthy and sick people to choose food and
meals suitable for their lifestyles.







 medicine
medicine biology
biology