Similar presentations:
Tissues Epithelial tissue
1.
TissuesEpithelial tissue
2.
Structural and functional elements oftissues:
Cells
Extracellular matrix
Postcellular structures
Symplastos
Sincytium
3.
Laws of evolutionary development oftissues are extended in the theory of
divergent development of
tissues(N.G.Hlopin) and the theory of
collateral series, or parallel development
of tissues (A.A.Zavarzin)
4.
Similar structures in various branches ofphylogenetic tree arose parallel during
divergent development.
Tissues development (histogenesis)
occurs with processes of determination
and differentiation of their cells.
5.
Determination is the process of“programming” of the direction of their
development.
Differentiation is a process during which
of the definite tissue incomplement
potencies anchored with determination.
6.
- Is the complex of all cells of definiteline of differentiation from the least
differentiated (stem cell) up to the
most mature differentiated
7.
There are origin of other cellsdevelopment in all types of tissues.
Properties of SC :
form self-maintained population
divides seldom
stable for damage
pluripotetial in some tissues.
8.
Physiologic regenaration -is process ofrenovation during normal development of
tissue
Reparative regenaration - is process of
tissue reconstruction after injury
Levels of regenaration:
intracellular, cellular, tissue and organic.
9.
epithelialmuscle
connective
nervous
10.
Еpithelialtissue
is the whole complex of differons
of differentiated cells close as a layer
on a basal membrane on border with
external or internal environment, and
also forming a majority of body
glands.
11.
12.
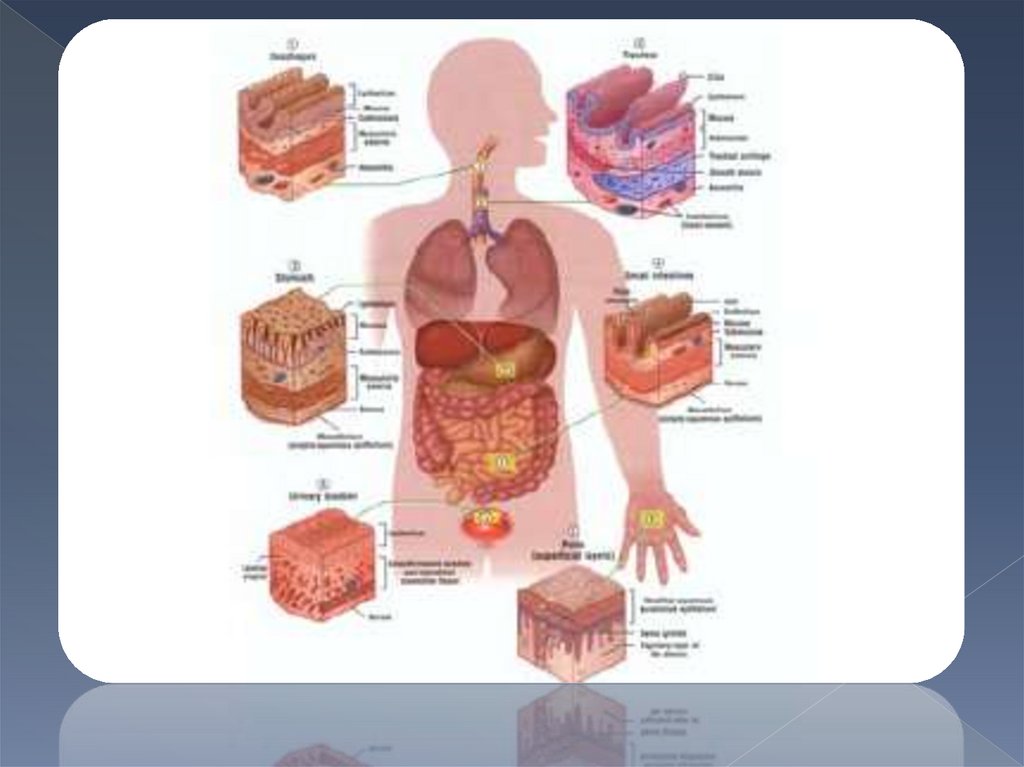
Еpithelialtissue
covers body surface and lines
mucous and serous layers of
internal organs (surface E).
Also it forms parenchyma of
numerous glands ( glandular E).
13.
14.
1. Form barriers and divide the bodyinto functional compartments.
2.Protection from mechanical, physical
and chemical influences.
3. Transport of substances through
epithelium.
4.Absorbtion of substances.
5.Secretory function.
6.Sensory function.
15.
I.Simple epithelium:1. Squamous
2. Cuboidal
3. Columnar
4. Pseudostratified columnar
16.
II. Stratified epithelium :1. Stratified squamous
а) keratinized
б) nonkeratinized
2. Stratified cuboidal
3. Stratified columnar
4. Transitional
17.
1. Epidermal type (from ectoderm)2. Endodermal type.
3. Coelonephrodermal (from
mesoderm)
4. Ependymoglial (from neural tube)
5. Angiodermal (from mesenchyme)
18.
Disposedon basement membrane
Form a layers
Minimum of extracellular matrix or
absence of it
Epithelial cells united with
junctional complexes
19.
Polarityof epithelial cells
Lack of blood and lymph vessels
High ability for regeneration
Maintenance of numerous
nervous receptors
20.
All cells are on a basal membraneAccording to a shape of cells it was
distinquished:
squamous, cuboidal and columnar
epithelium.
21.
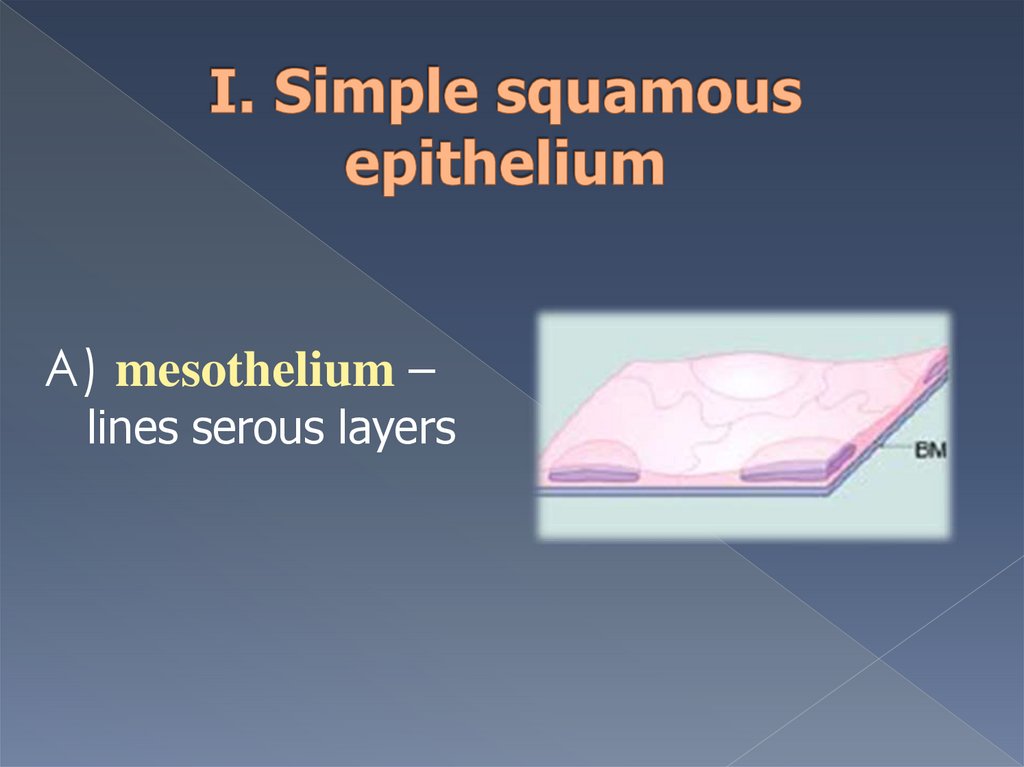
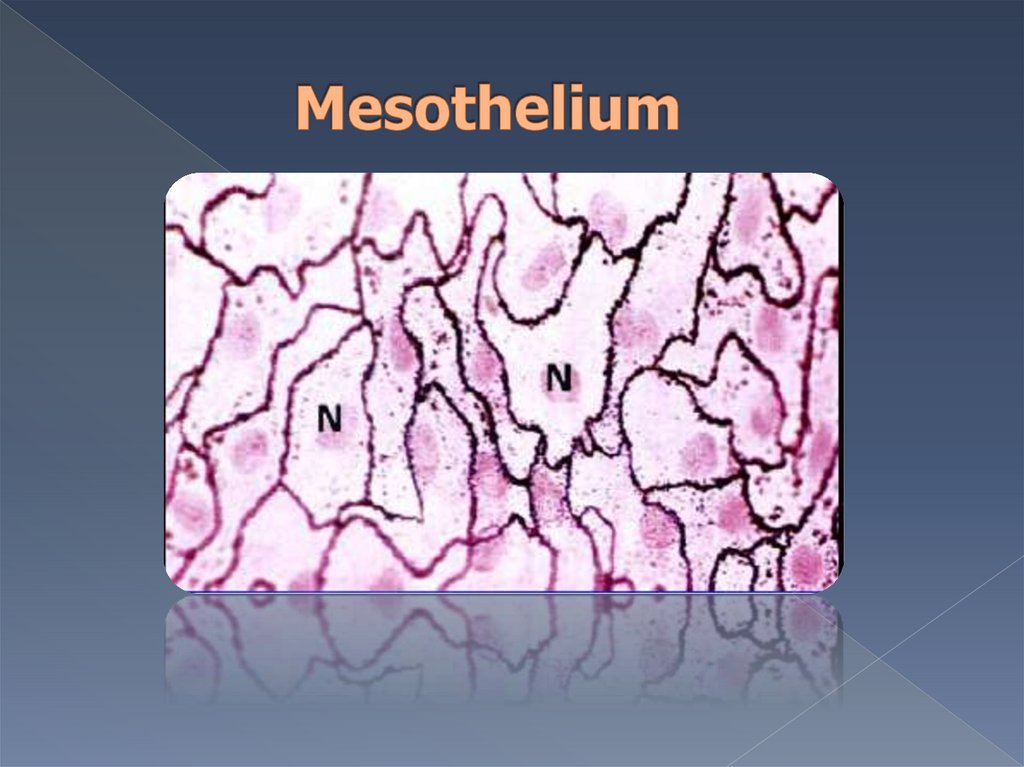
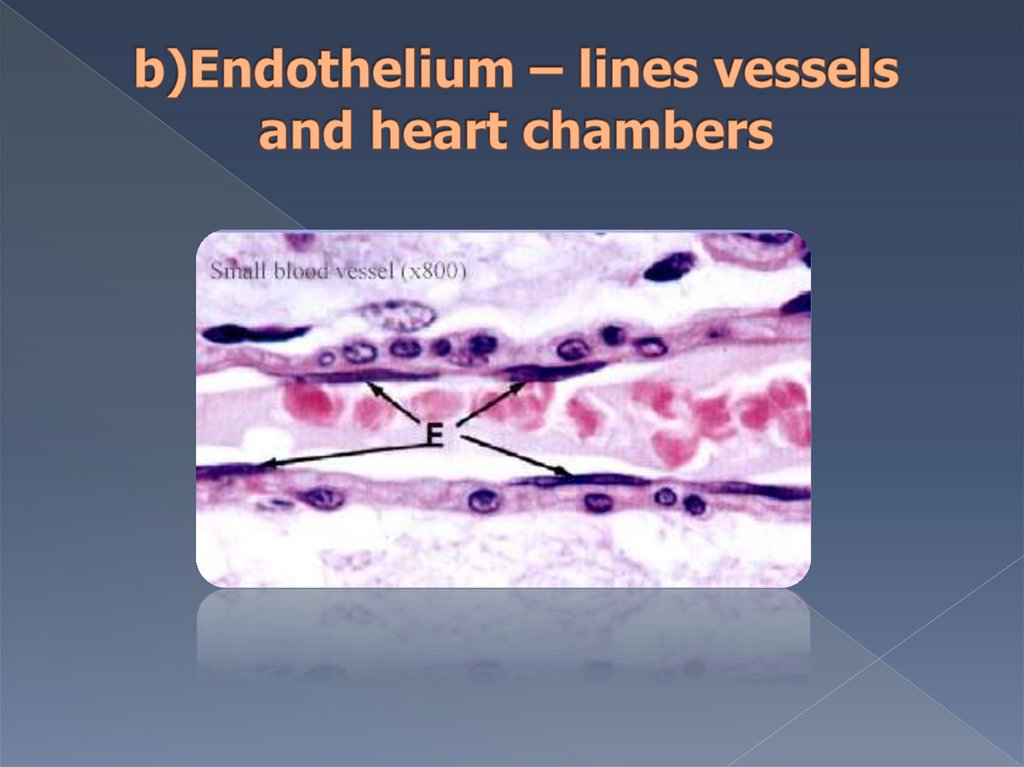
А) mesothelium –lines serous layers
22.
23.
24.
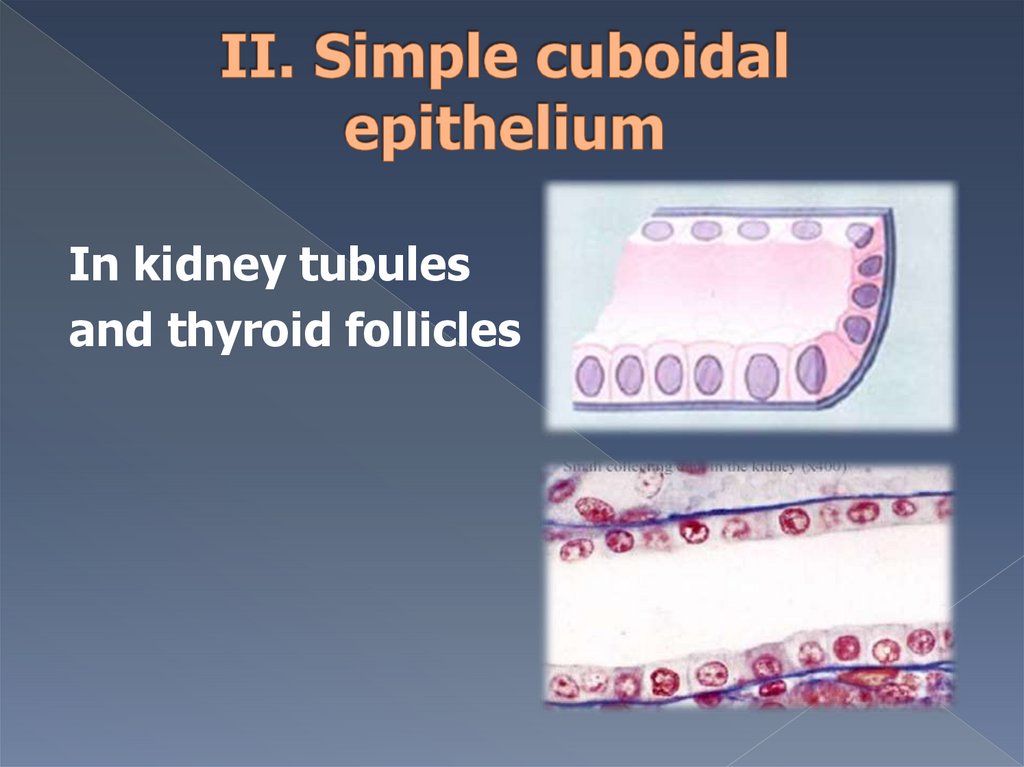
In kidney tubulesand thyroid follicles
25.
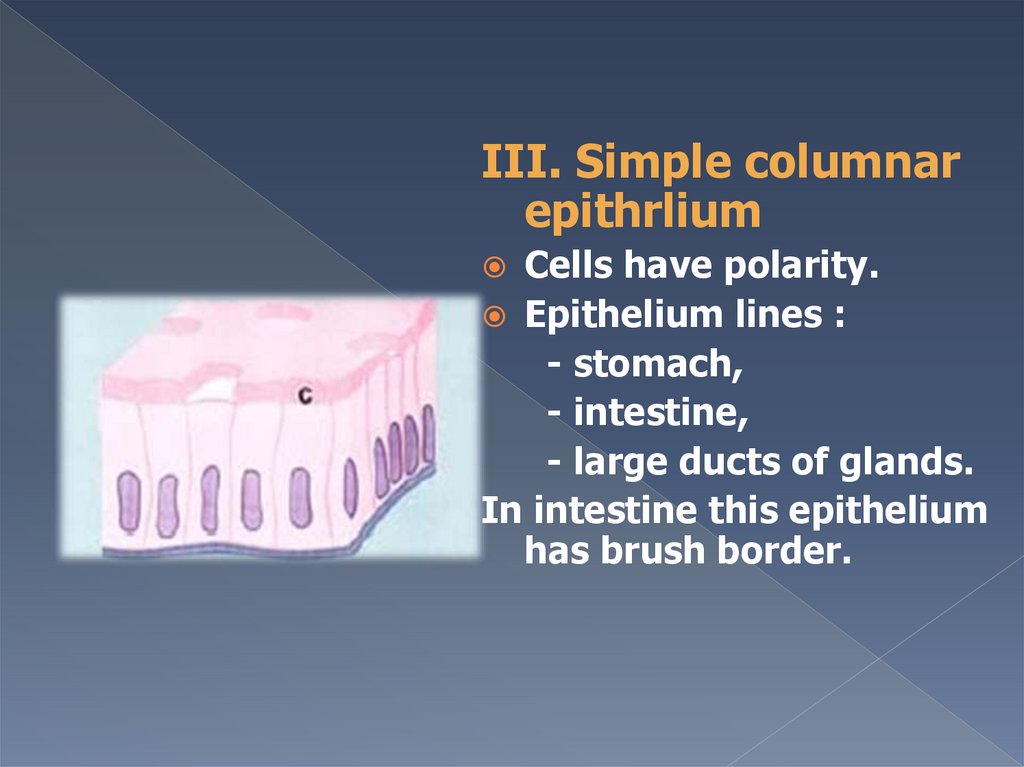
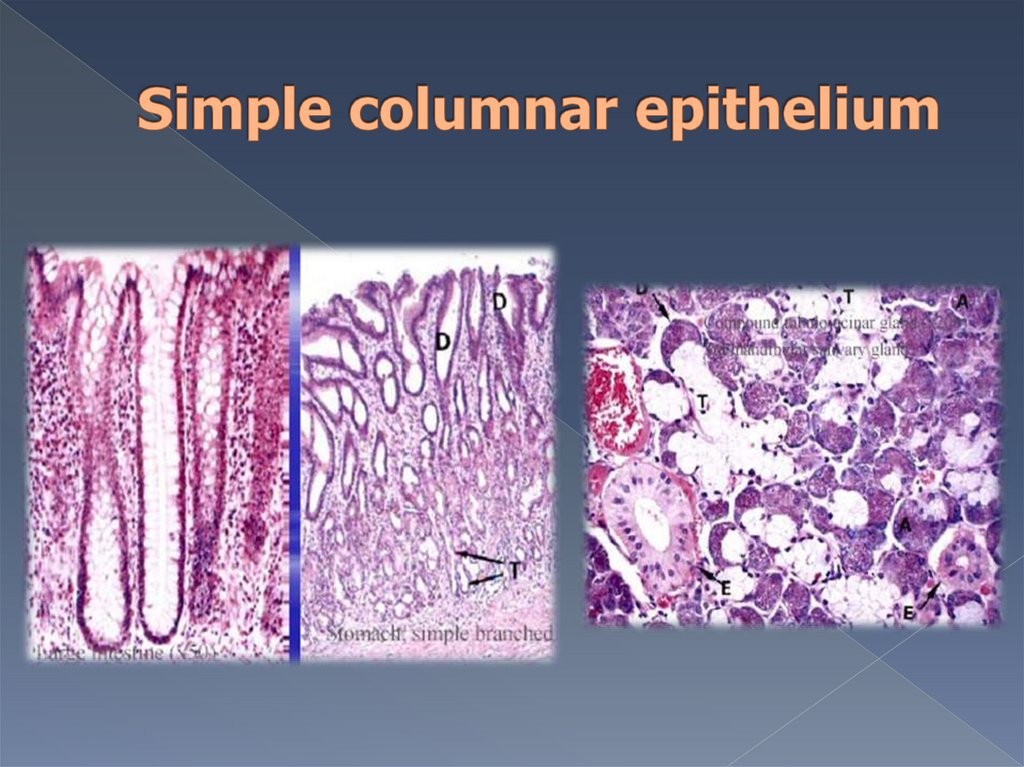
III. Simple columnarepithrlium
Cells have polarity.
Epithelium lines :
- stomach,
- intestine,
- large ducts of glands.
In intestine this epithelium
has brush border.
26.
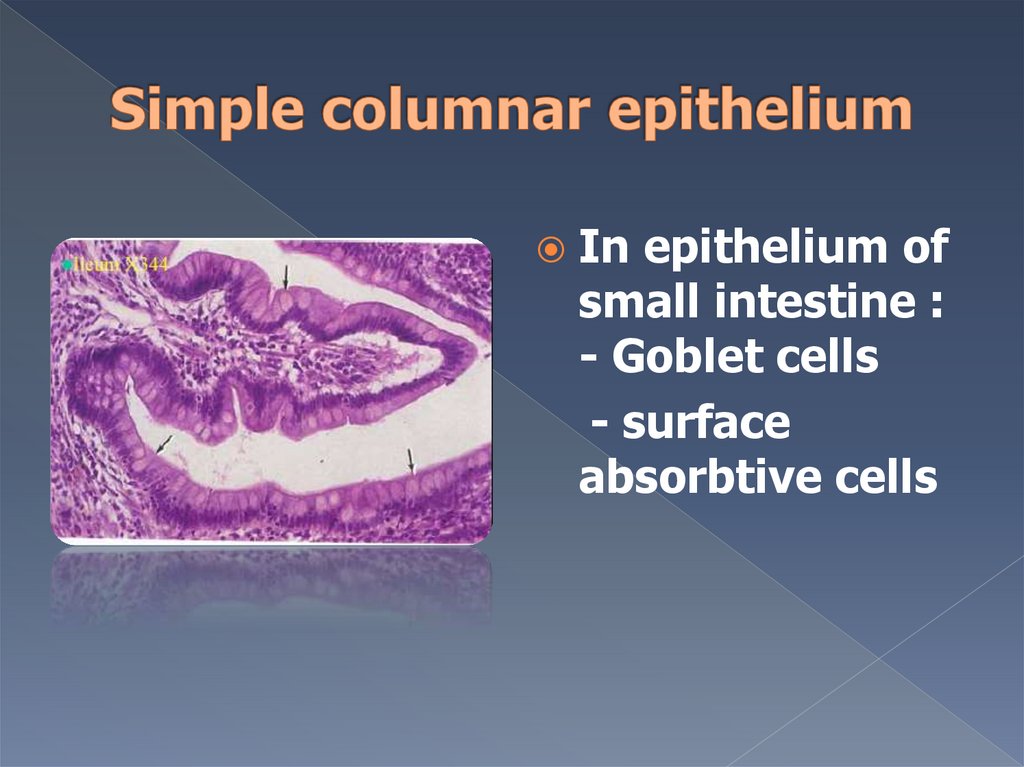
Inepithelium of
small intestine :
- Goblet cells
- surface
absorbtive cells
27.
28.
29.
30.
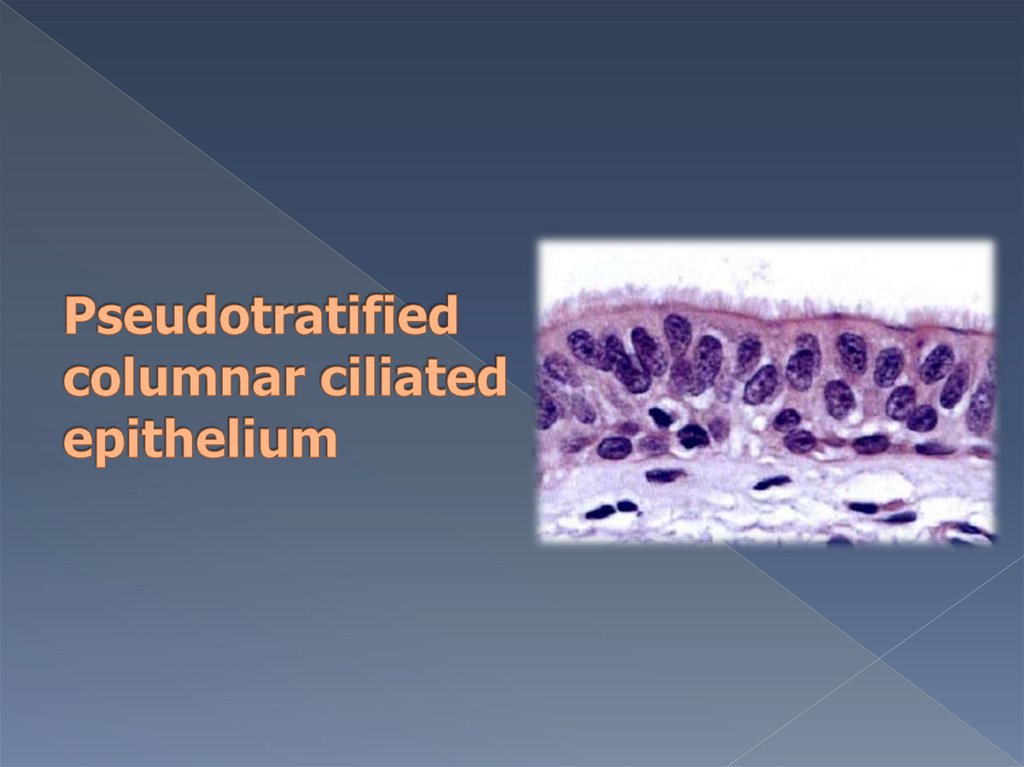
Pseudotratified columnar ciliatedepithelium lines mucosa of :
- respiratory tract
- some portions of male
reproductive tract
31.
Consists of several layers of epithelial cellsOnly proximal layer of cells is on a basal
lamina, others lose junctions with it
There are different shapes of cells in
distinctive layers
Type of epithelium estimated according
to shapes of a superficial cells layer
32.
Stratified epithelia subdivides into:I.
Keratinized
II.
Nonkeratinized
I. Stratified squamous keratinized
epithelium is found in the skin
epidermis, mucosa of gingiva, hard
palate, filiform papilla of tonque and
skin zone of anal canal
It forms a specialized barrier against
physical, chemical and antigens
influences.
33.
Forms outer layer of skin– epidermis.- Consists of 5 layers:
stratum basale
stratum spinosum
stratum granulosum
stratum lucidum
stratum corneum
-
34.
35.
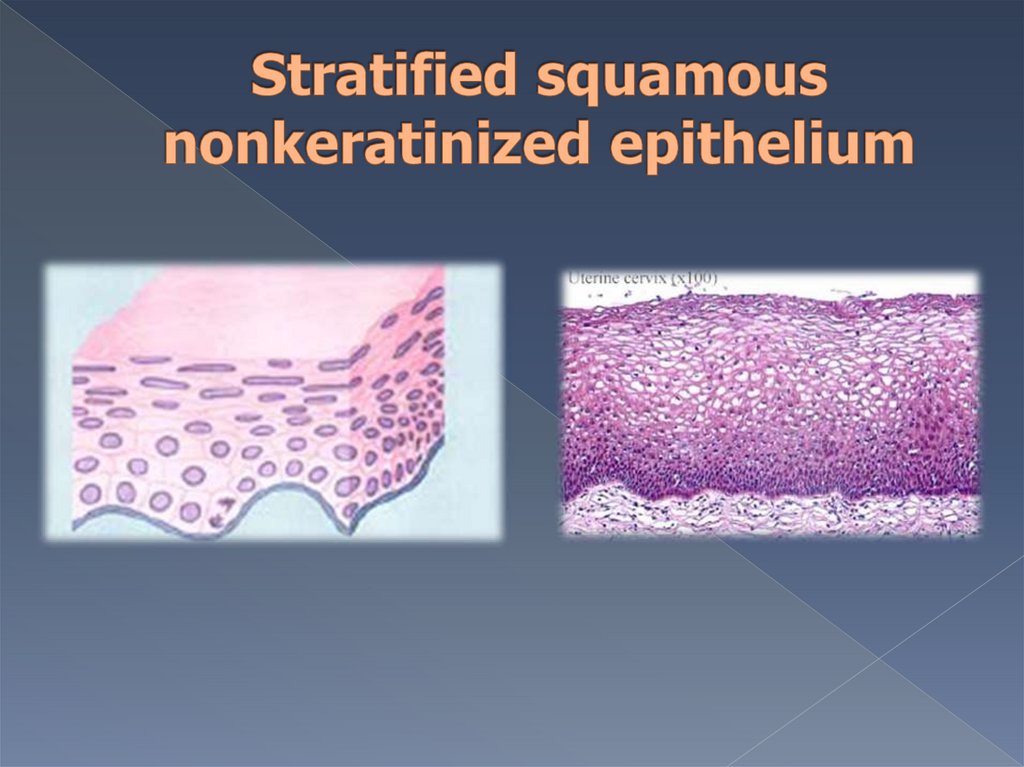
Covers cornea of eye, mucosaof oral cavity and pharynx,
esophagus, vagina, vaginal
portions of uterus.
36.
37.
Consists of 3 layers:stratum basale
stratum spinosum
superficial layer
-
38.
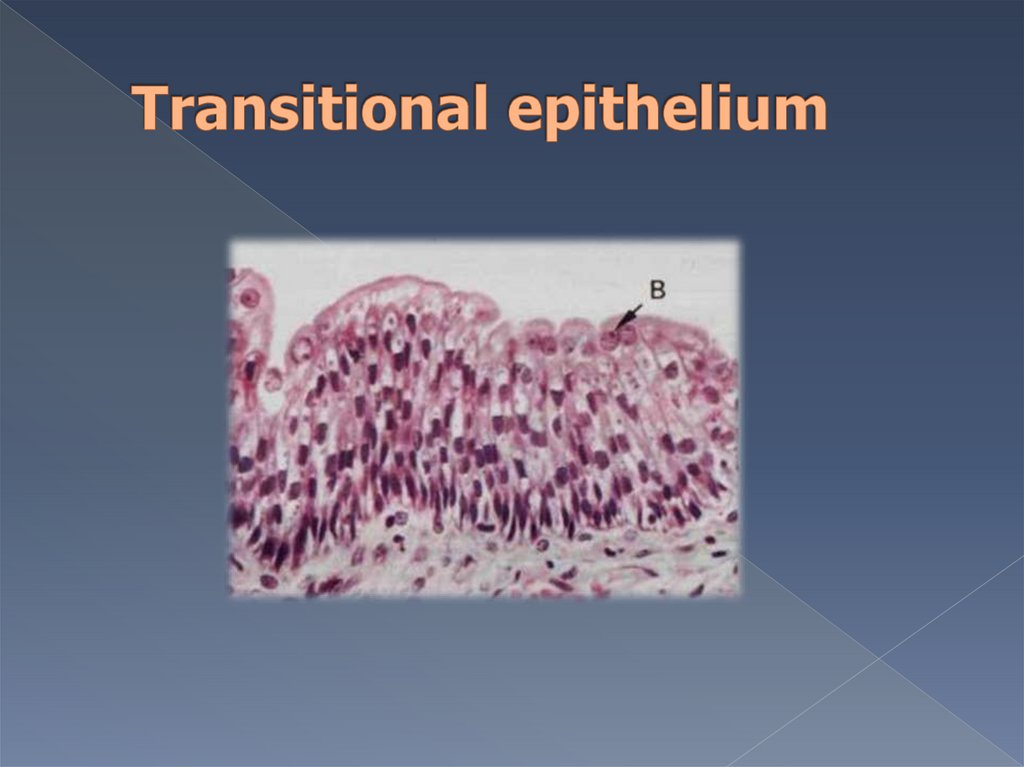
It is specialized type of epithelium,which lines urinary tracts.
Forms of cells and thickness of
epithelial layer dependents of
degree of tension of organ.
Layers of epithelium:
basal layer
intermediate
superficial layer
39.
40.
Accomplish secretory function:produce and release secretory
products, provided for
different functions of
organism.
41.
I.Endocrine glands
1) Produce hormones -high active
regulatory biologic substances,
circulated in blood
2) There are ductless
For example: thyroid, parathyroid,
suprarenal gland.
42.
Produce secretory products, whichrelease on a surface of body ( sweat gl.)
or into cavities of organism ( gastric gl.,
salivary gl., exocrine portion of pancreas).
43.
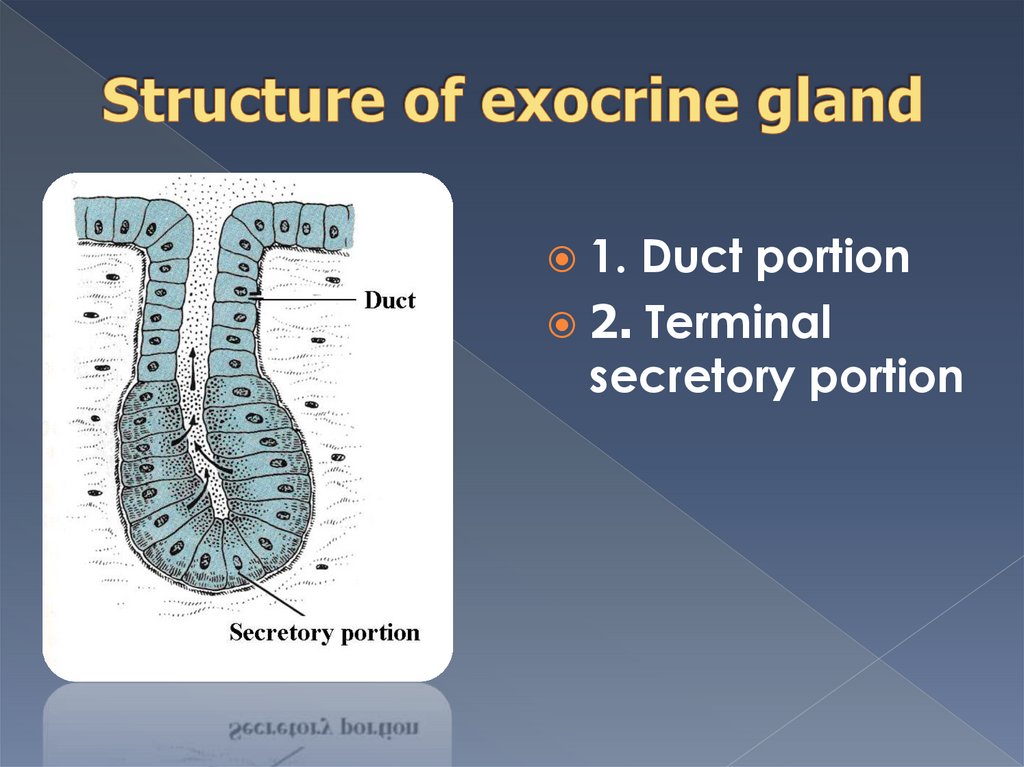
1.Duct portion
2. Terminal
secretory portion
44.
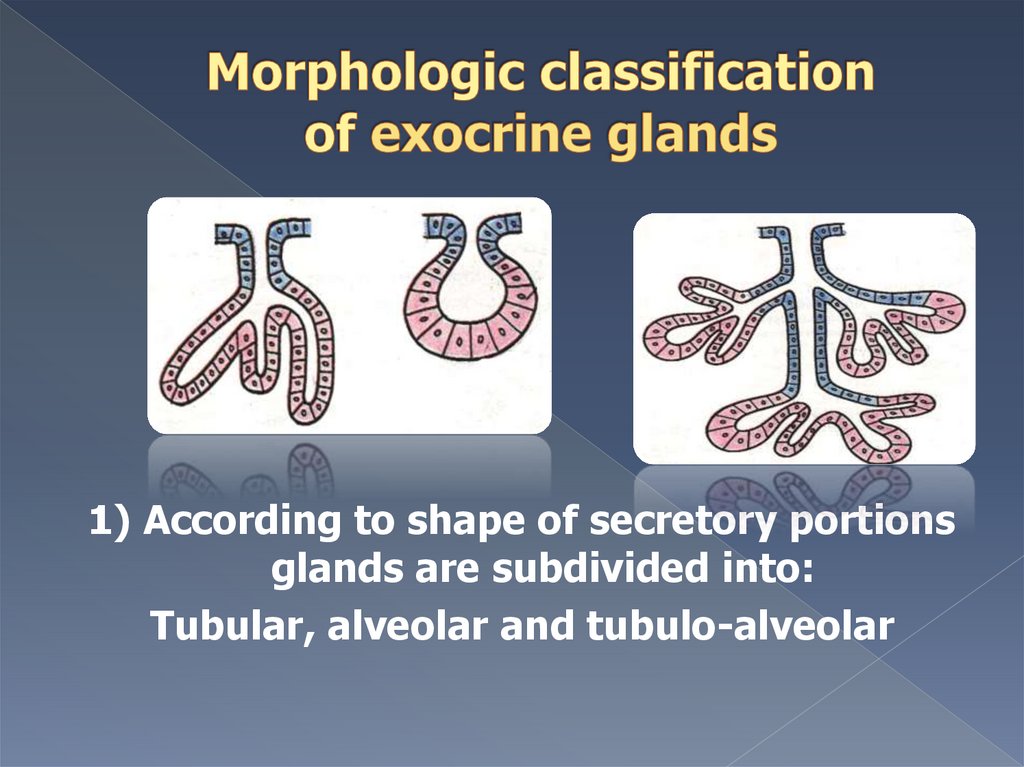
1) According to shape of secretory portionsglands are subdivided into:
Tubular, alveolar and tubulo-alveolar
45.
2) According to structure of secretoryportions :
1. branched
2. unbranched
3) According to structure of duct portions :
1. simple (with unbranched duct)
2. compound (with branched duct)
46.
Glands are subdivided into:1) merocrine (secretion by
exocytosis)
2) apocrine (secretion with
destruction of apical portion of cell)
3) holocrine (secretion with total
destruction of cell)
47.
1) Mucous2)Serous
3) Mixed
4) Sebaceous
5) Sweat
6) Mammary,
and others




































 biology
biology








