Similar presentations:
Connective tissue
1.
Presentation prepared byPhD Inna A. Demyanenko
(Histology department, MA CFU, Simferopol)
CONNECTIVE TISSUE
2.
Connective tissue (CT) participates in junction of allothers tissues in organs
CT differs from others tissues besides of presence of cells,
the availability of much quantity of extracellular matrix .
CT comprises more than 50% of body mass.
3.
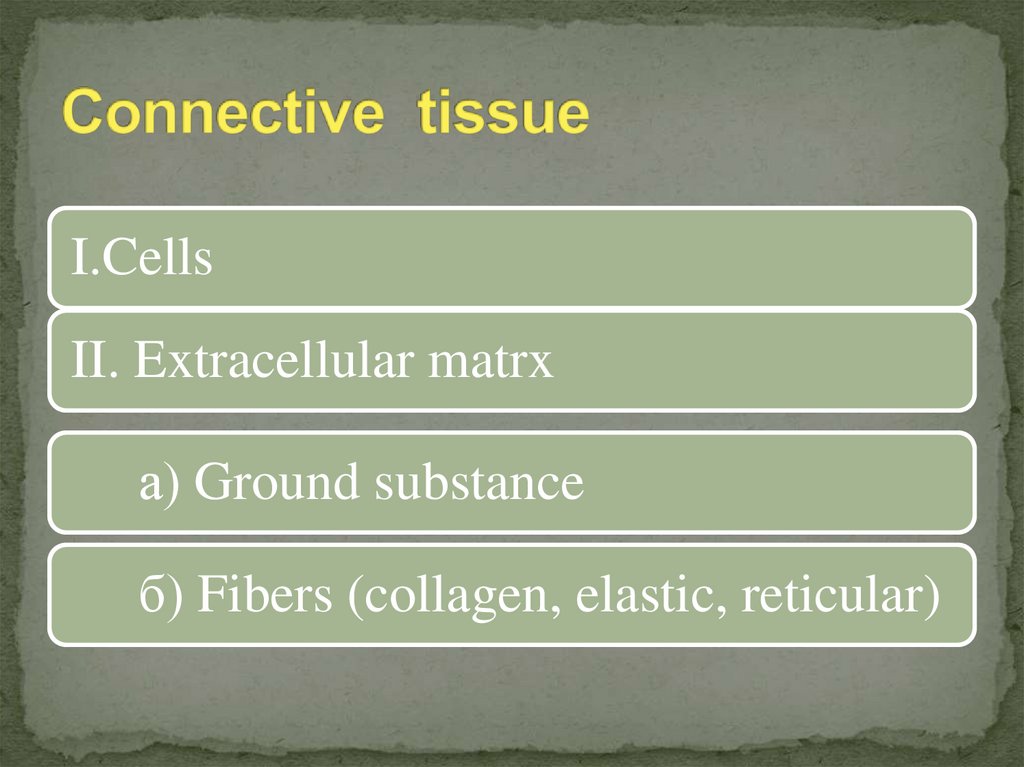
I.CellsII. Extracellular matrx
а) Ground substance
б) Fibers (collagen, elastic, reticular)
4.
2. Main functions:support, specific and nonspecific defense,
transport, repair, storage, homeostasis and
thermoregulation.
3. Histogenesis.
All types of connective tissues develop from
mesenchyme.
5.
6.
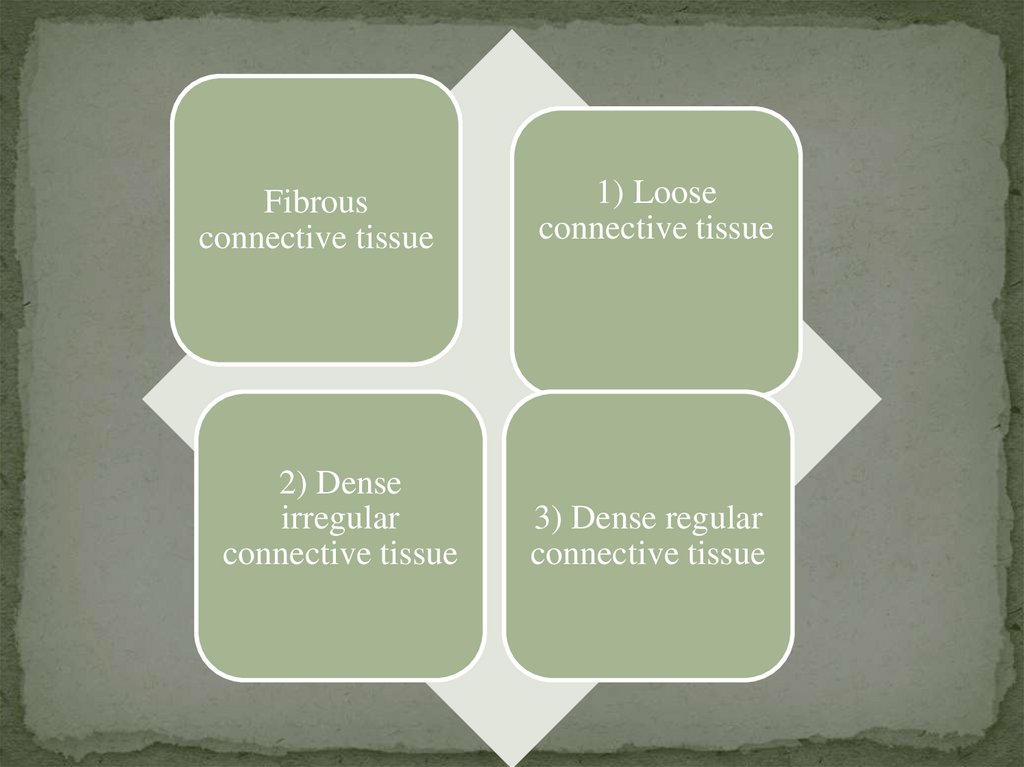
Connective tissues subdivides into:I. Connective tissue proper
1. Fibrous connective tissue
2.Connective tissues with special properties
II. Skeletal connective tissues (cartilage, bone, dentin and
cementum of tooth)
7.
Fibrousconnective tissue
2) Dense
irregular
connective tissue
1) Loose
connective tissue
3) Dense regular
connective tissue
8.
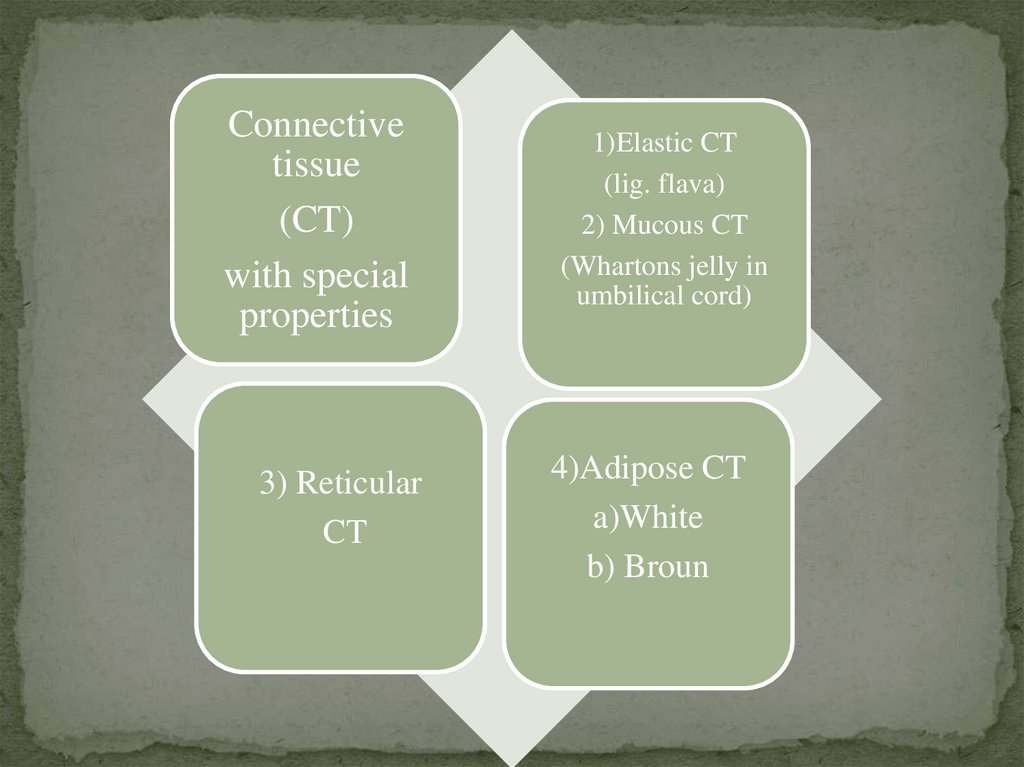
Connectivetissue
(CT)
with special
properties
3) Reticular
CT
1)Elastic CT
(lig. flava)
2) Mucous CT
(Whartons jelly in
umbilical cord)
4)Adipose CT
a)White
b) Broun
9.
10.
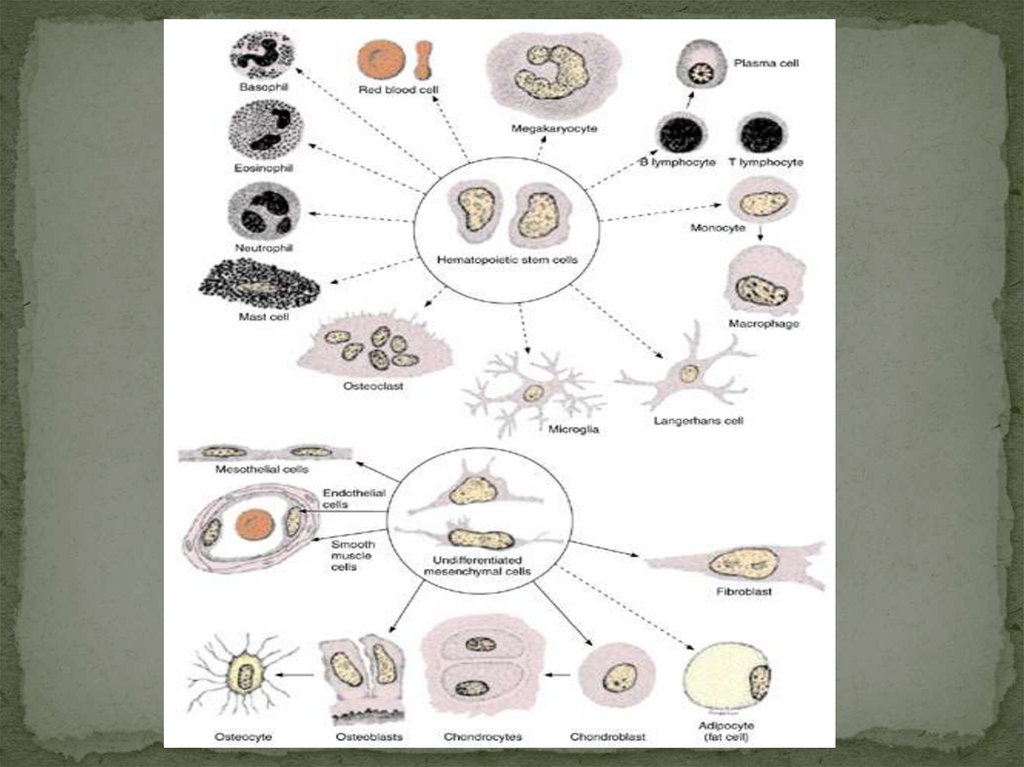
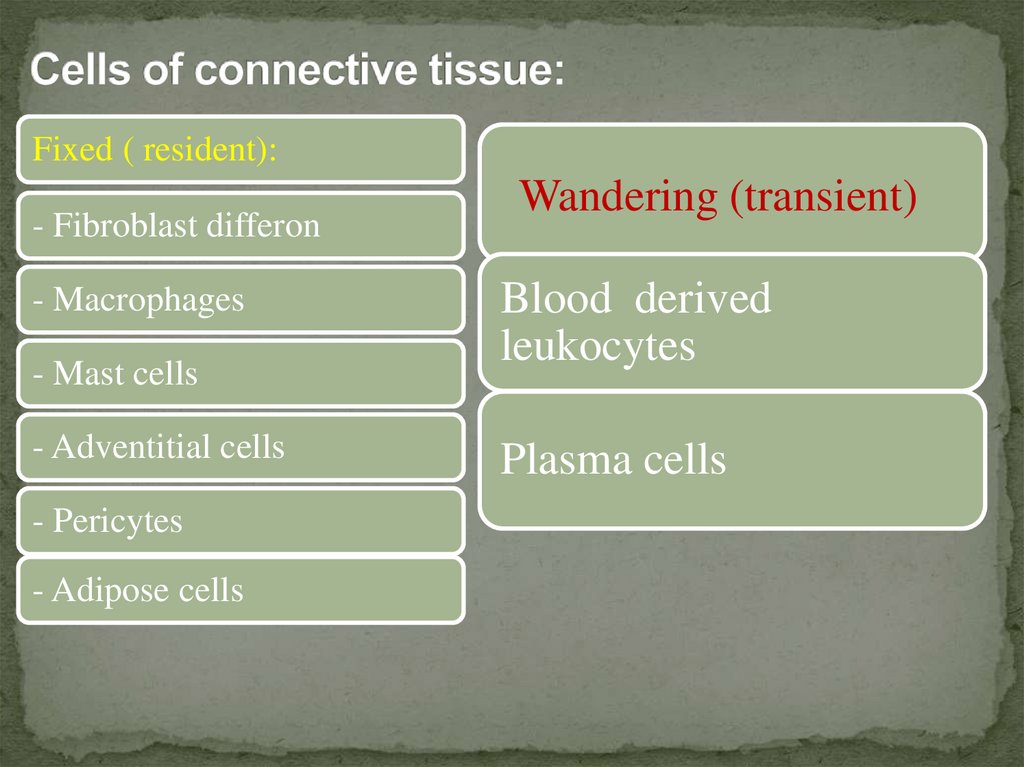
Fixed ( resident):- Fibroblast differon
- Macrophages
- Mast cells
- Adventitial cells
- Pericytes
- Adipose cells
Wandering (transient)
Blood derived
leukocytes
Plasma cells
11.
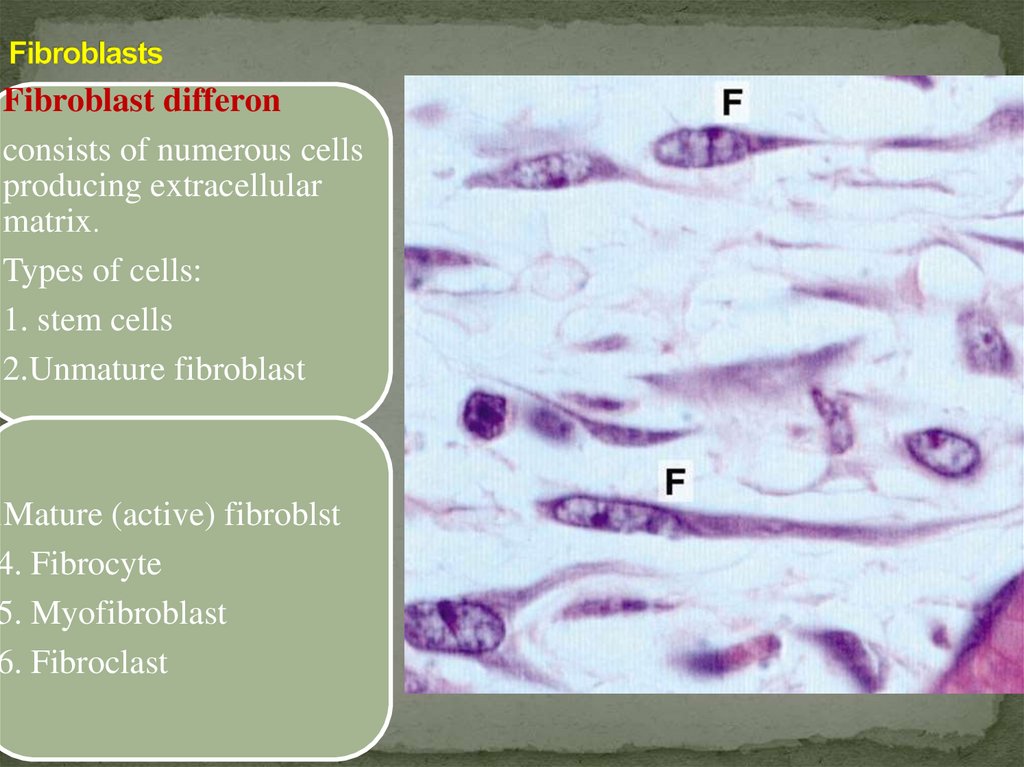
Fibroblast differonconsists of numerous cells
producing extracellular
matrix.
Types of cells:
1. stem cells
2.Unmature fibroblast
Mature (active) fibroblst
4. Fibrocyte
5. Myofibroblast
6. Fibroclast
3.
12.
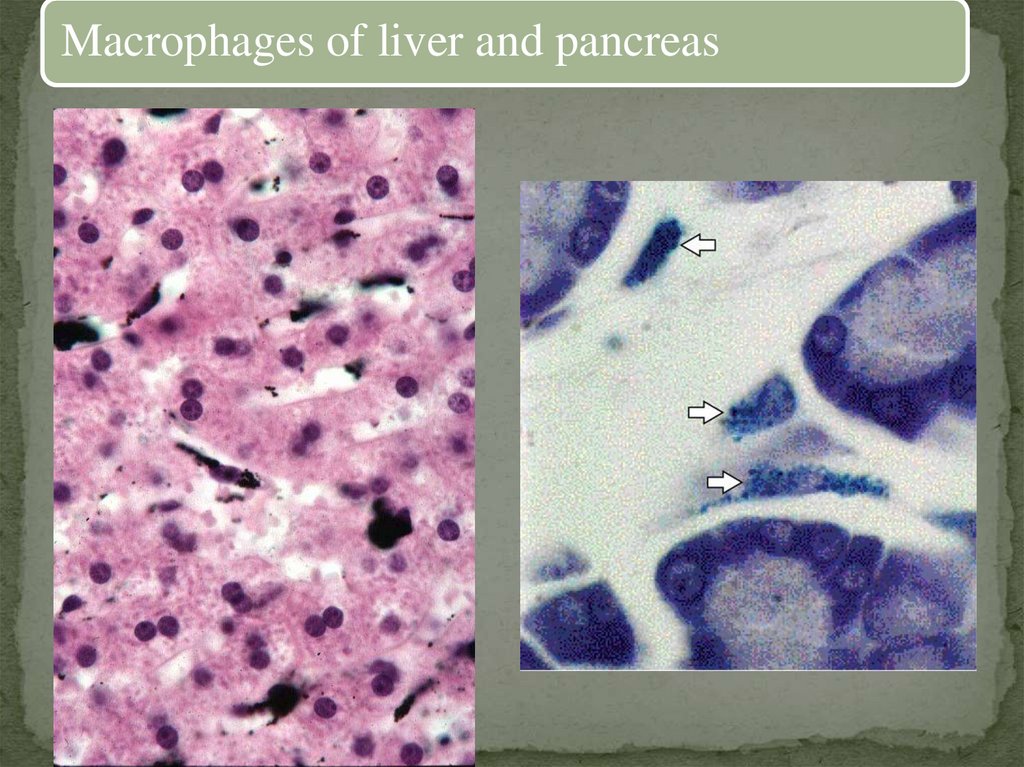
Macrophages of liver and pancreas13.
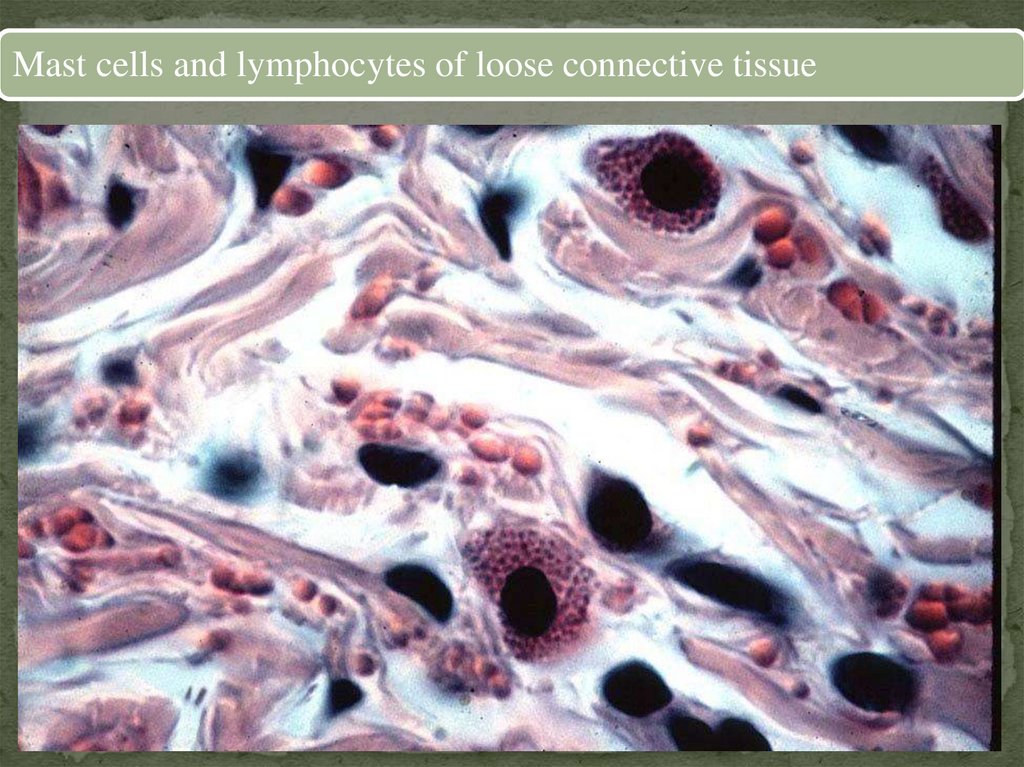
Mast cells and lymphocytes of loose connective tissue14.
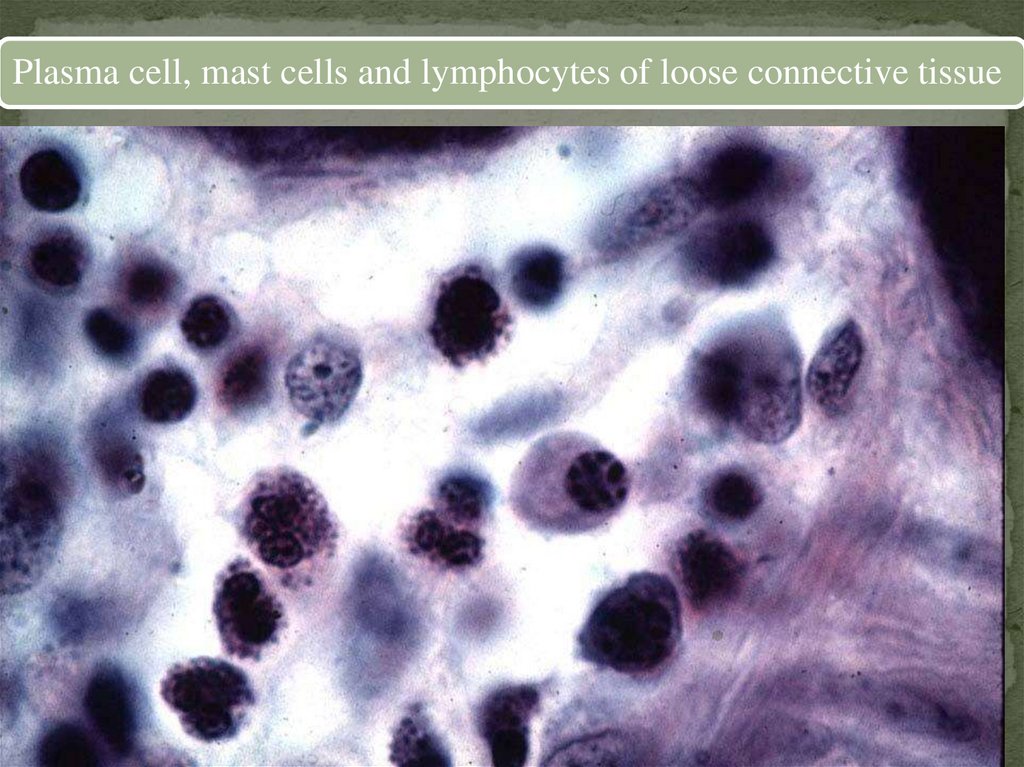
Plasma cell, mast cells and lymphocytes of loose connective tissue15.
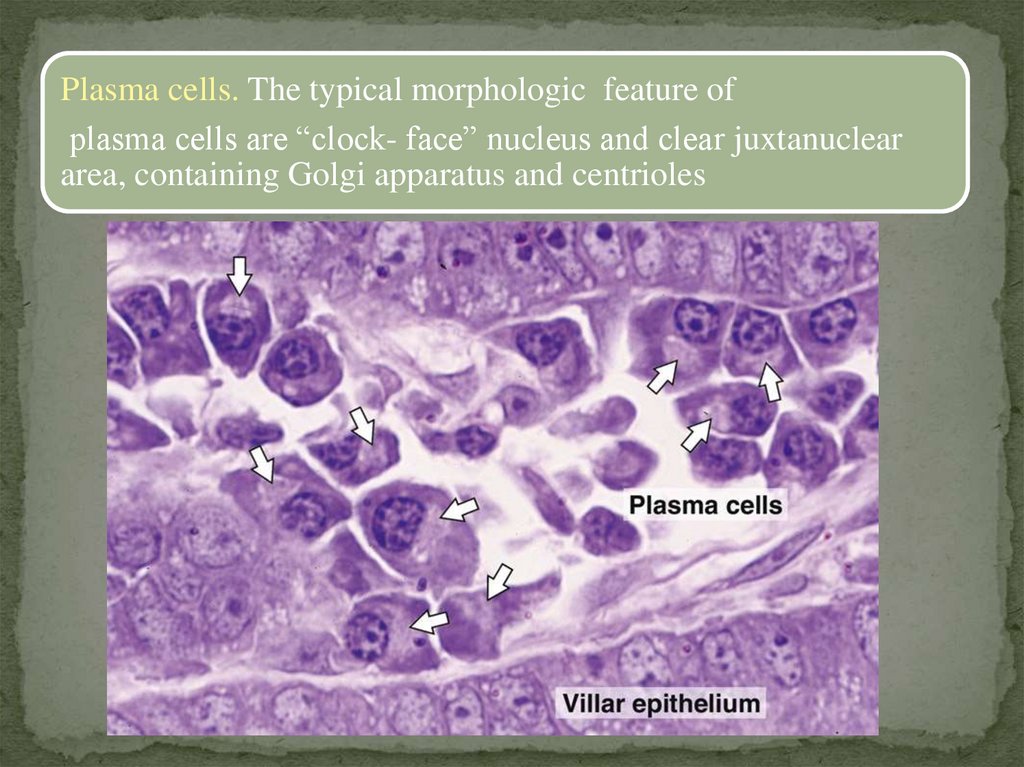
Plasma cells. The typical morphologic feature ofplasma cells are “clock- face” nucleus and clear juxtanuclear
area, containing Golgi apparatus and centrioles
16.
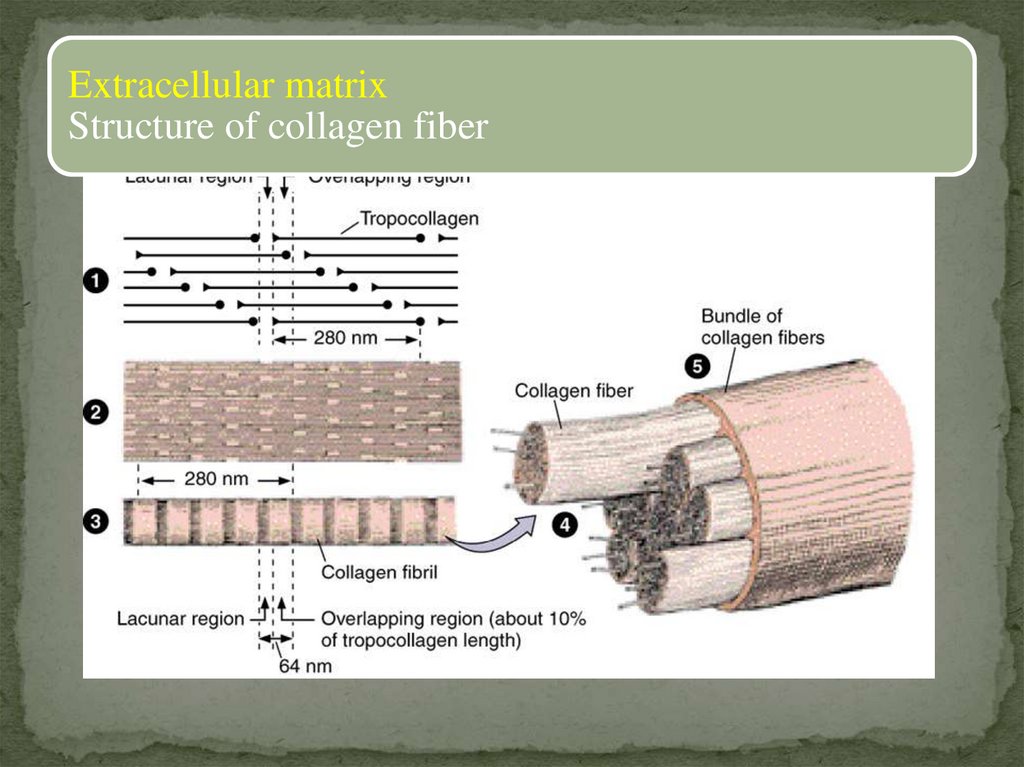
Extracellular matrixStructure of collagen fiber
17.
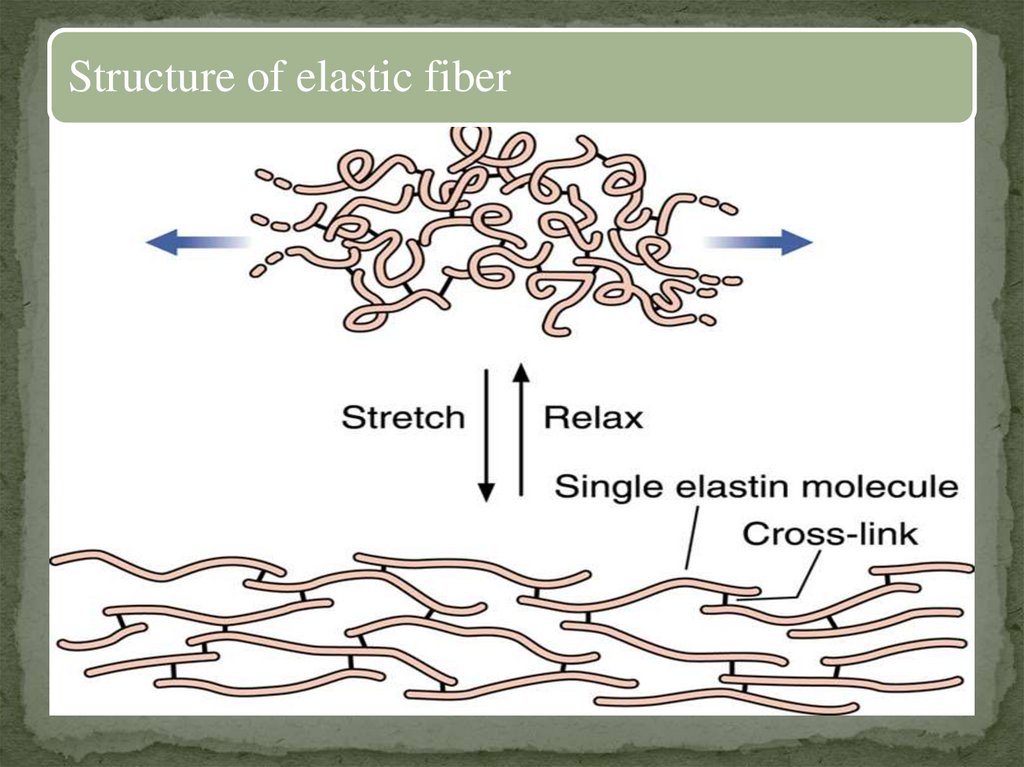
Structure of elastic fiber18.
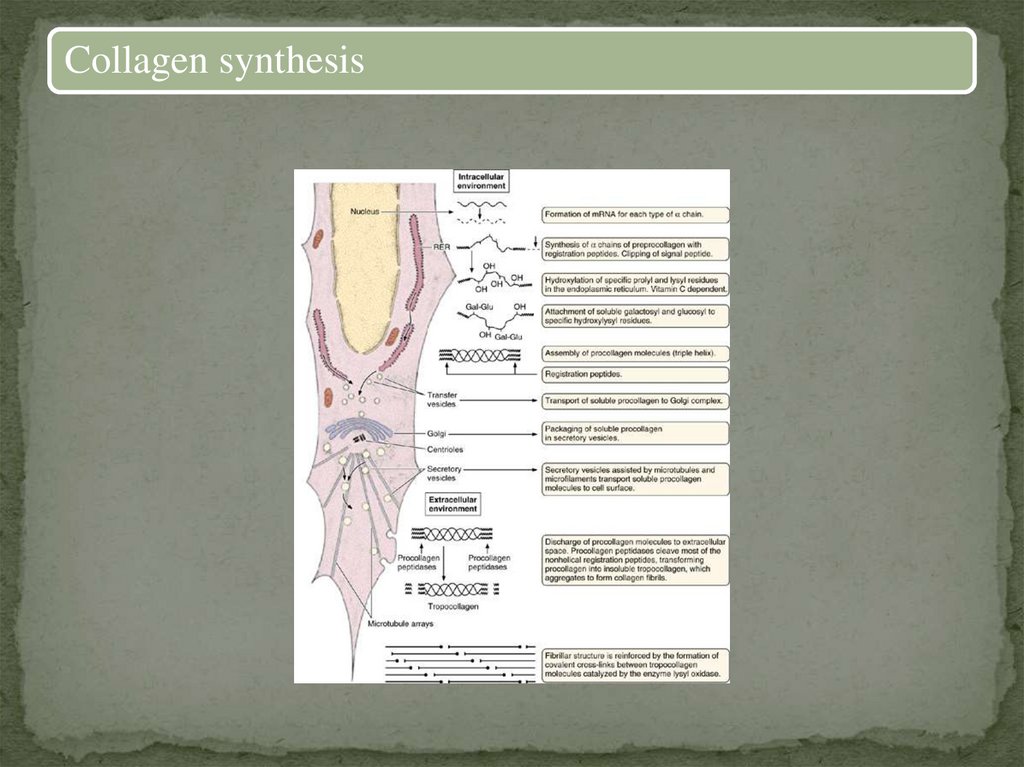
Collagen synthesis19.
Ground substancemainly formed by the fibroblasts.
It consists of :
glycosaminoglicans (GAG), hyaluronic acid,
chondroitine sulfate, dermatan sulfate, keratan sulfate,
proteoglycans, glycoproteins, and also proteins,
carbohydrates, lipids and others
20.
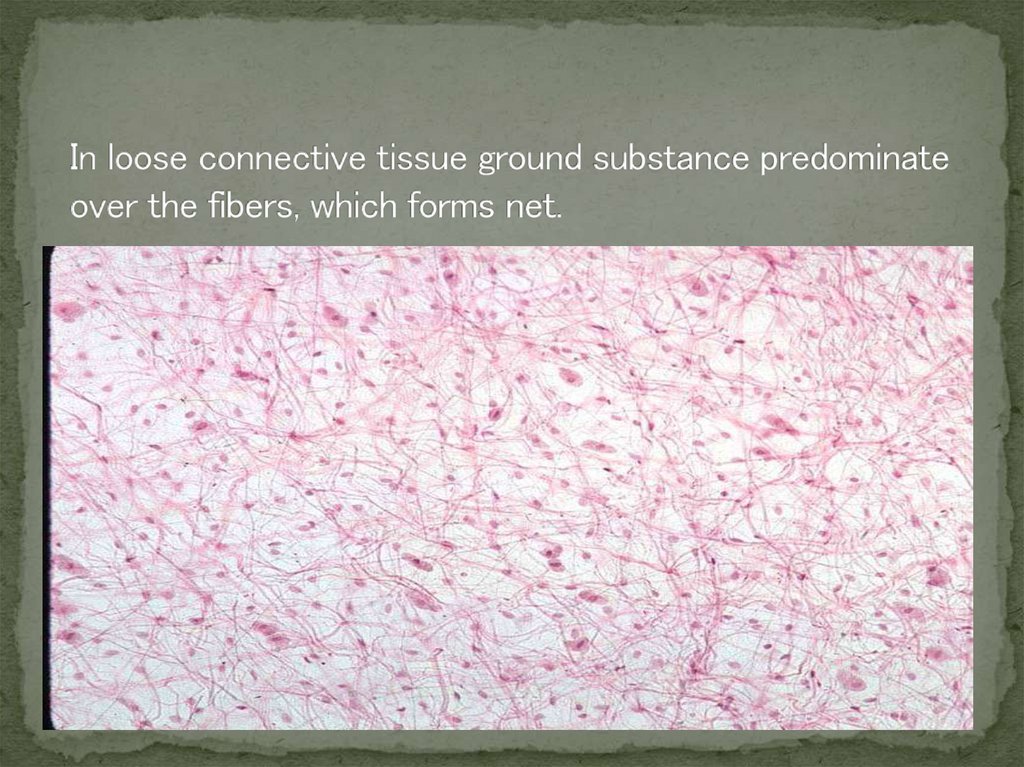
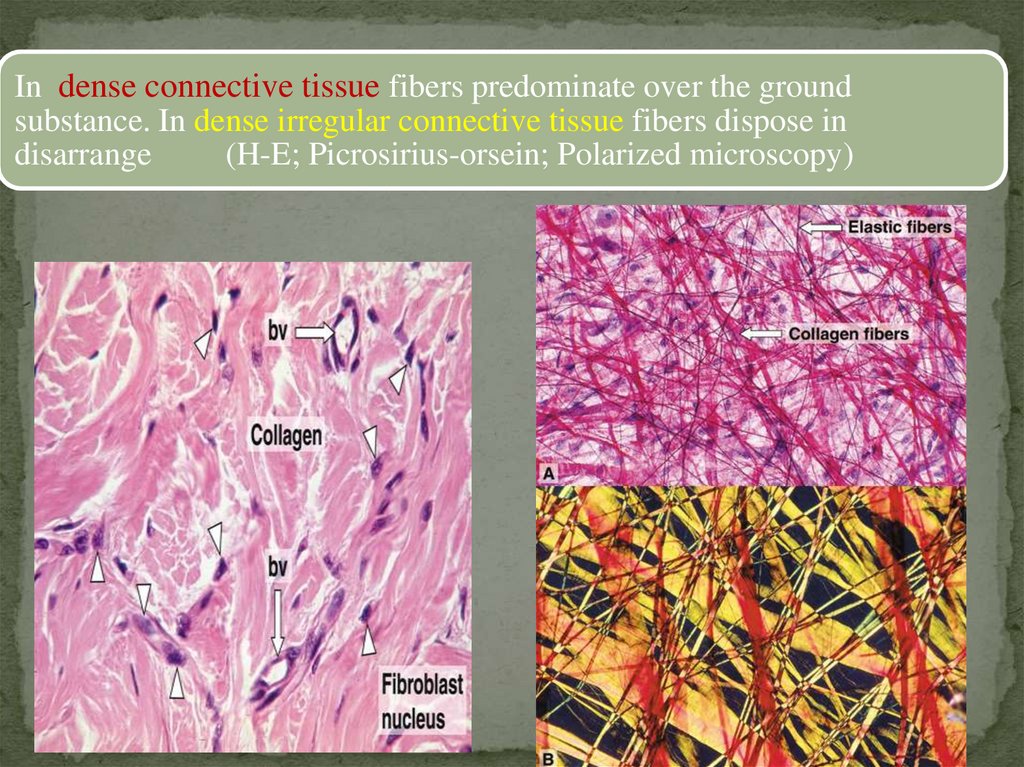
In dense connective tissue fibers predominate over the groundsubstance. In dense irregular connective tissue fibers dispose in
disarrange
(H-E; Picrosirius-orsein; Polarized microscopy)
21.
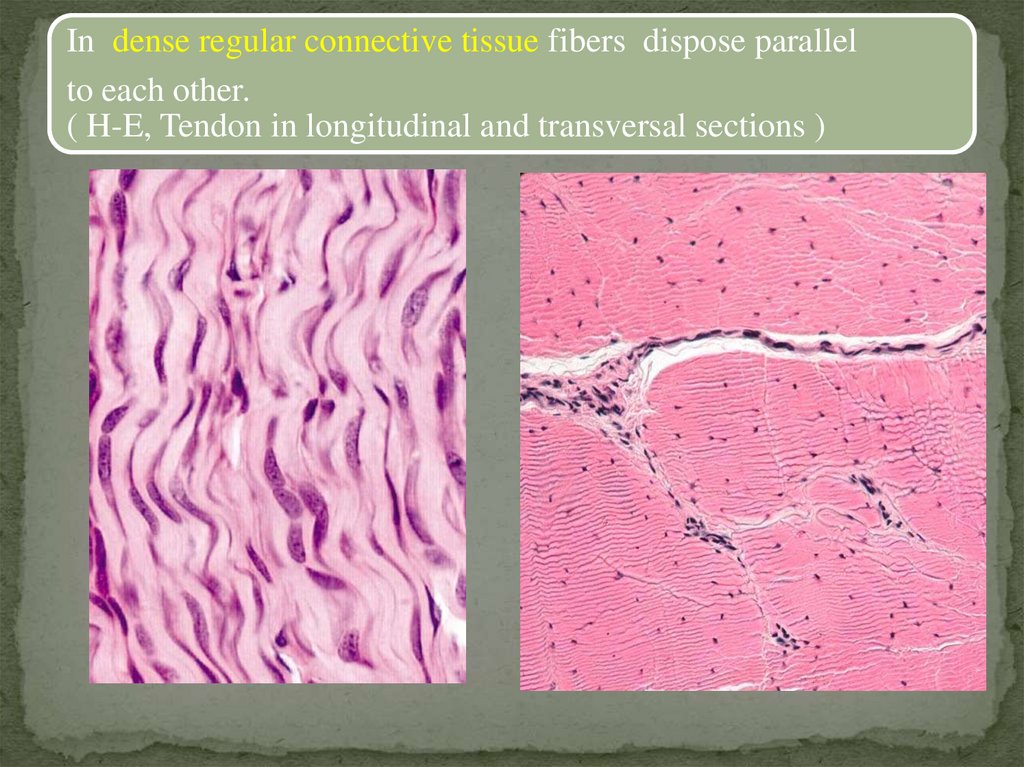
In dense regular connective tissue fibers dispose parallelto each other.
( H-E, Tendon in longitudinal and transversal sections )
22.
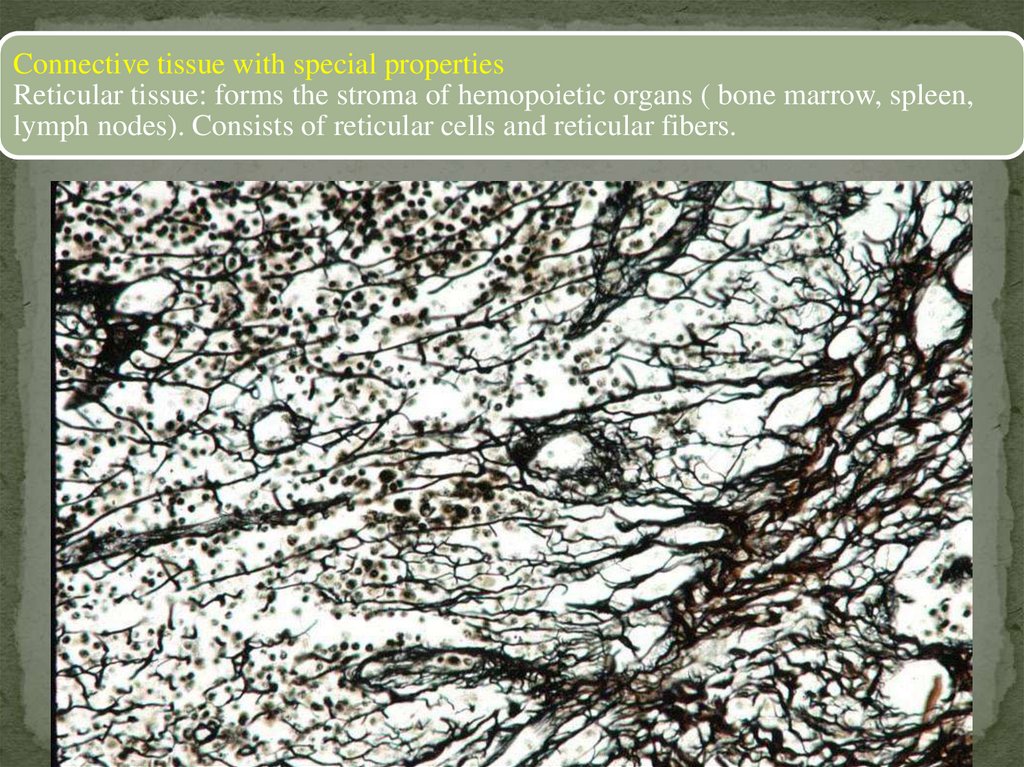
Connective tissue with special propertiesReticular tissue: forms the stroma of hemopoietic organs ( bone marrow, spleen,
lymph nodes). Consists of reticular cells and reticular fibers.
23.
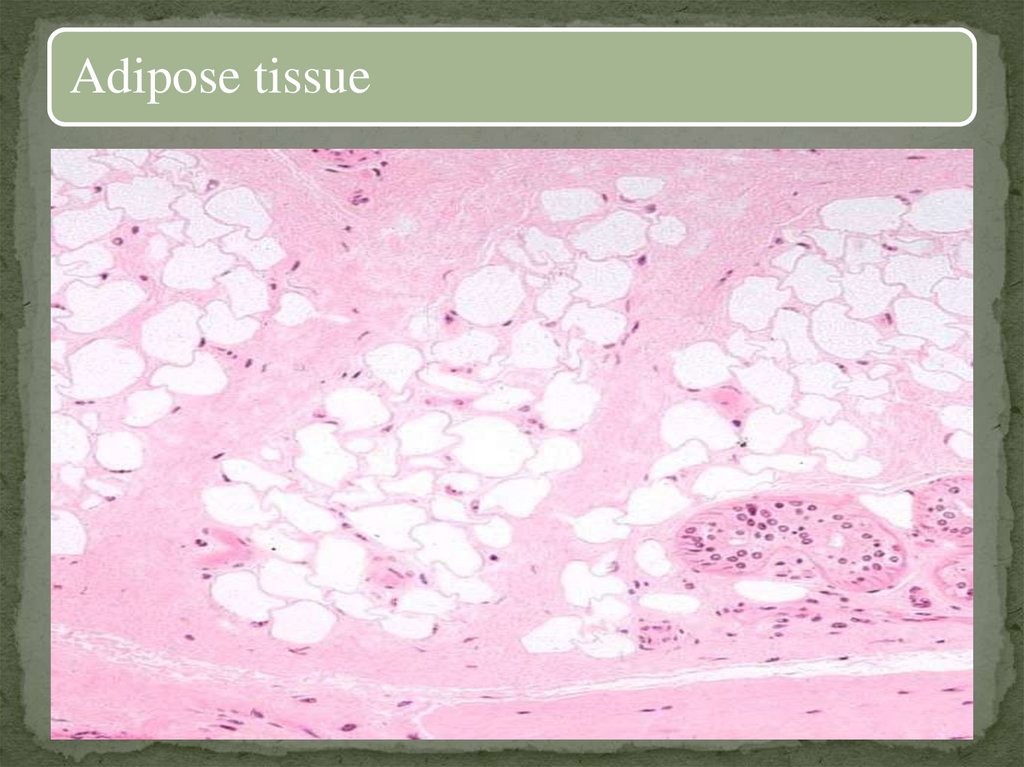
Adipose tissue24.
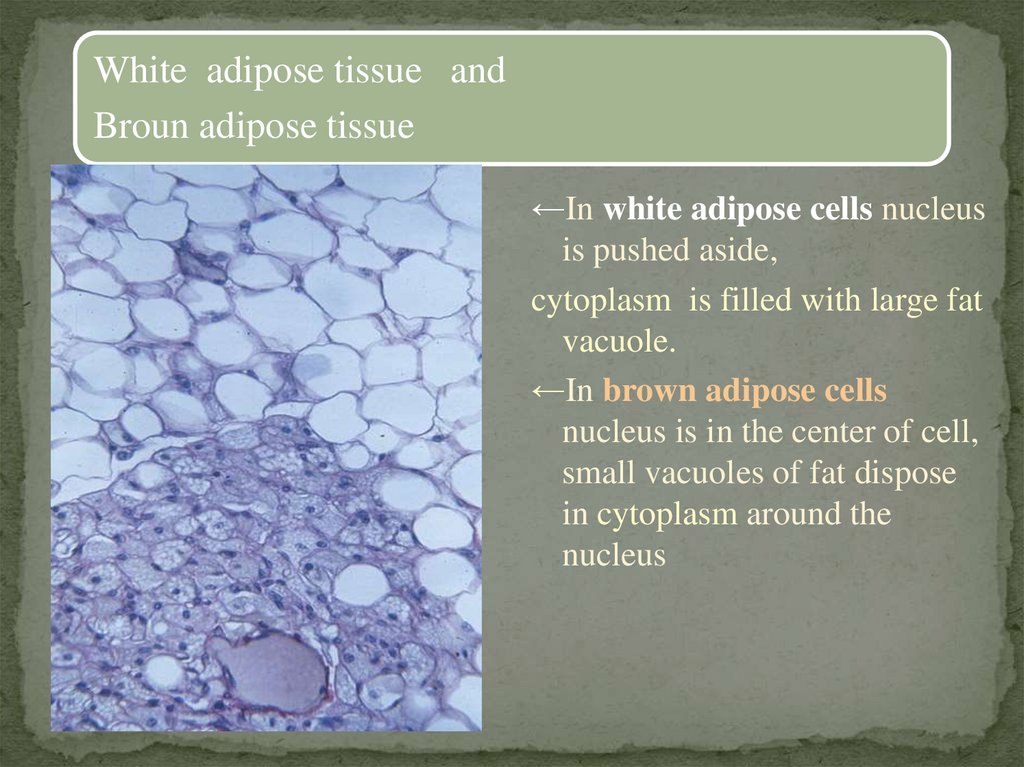
White adipose tissue andBroun adipose tissue
←In white adipose cells nucleus
is pushed aside,
cytoplasm is filled with large fat
vacuole.
←In brown adipose cells
nucleus is in the center of cell,
small vacuoles of fat dispose
in cytoplasm around the
nucleus
25.
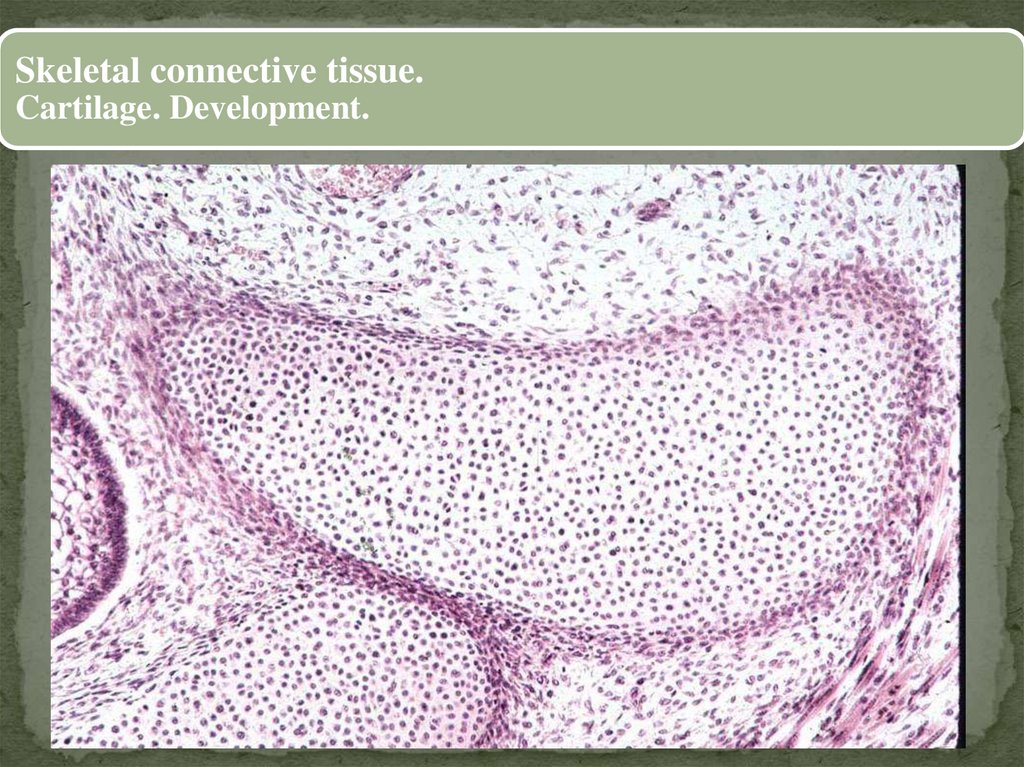
Skeletal connective tissue.Cartilage. Development.
26.
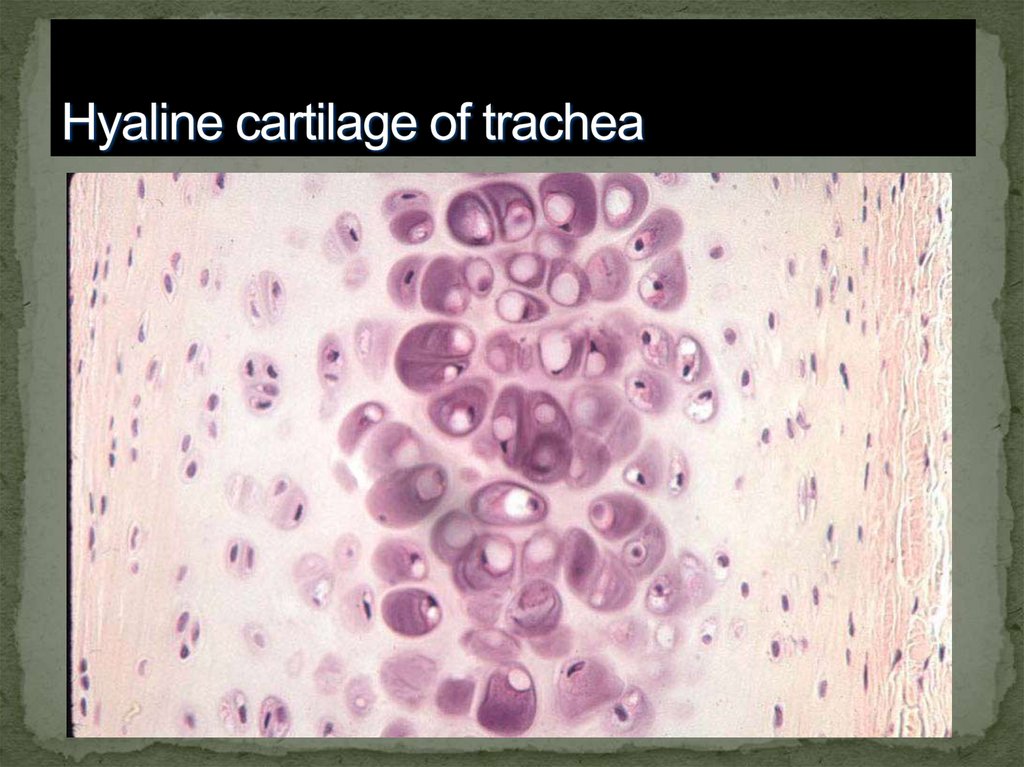
27.
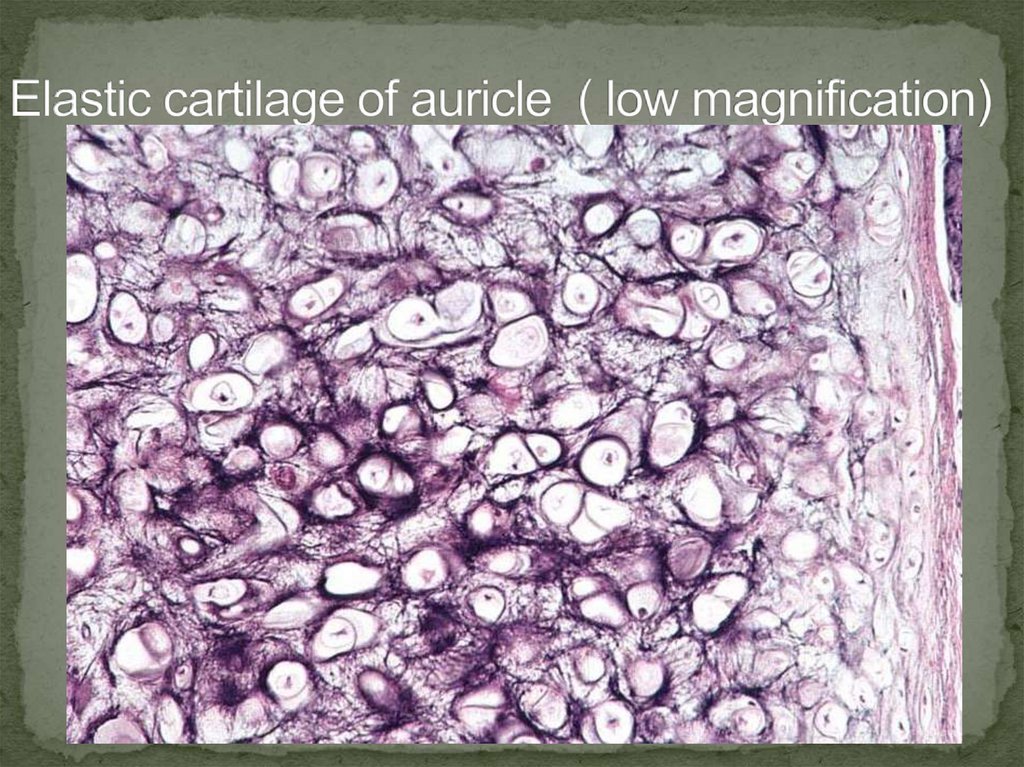
28.
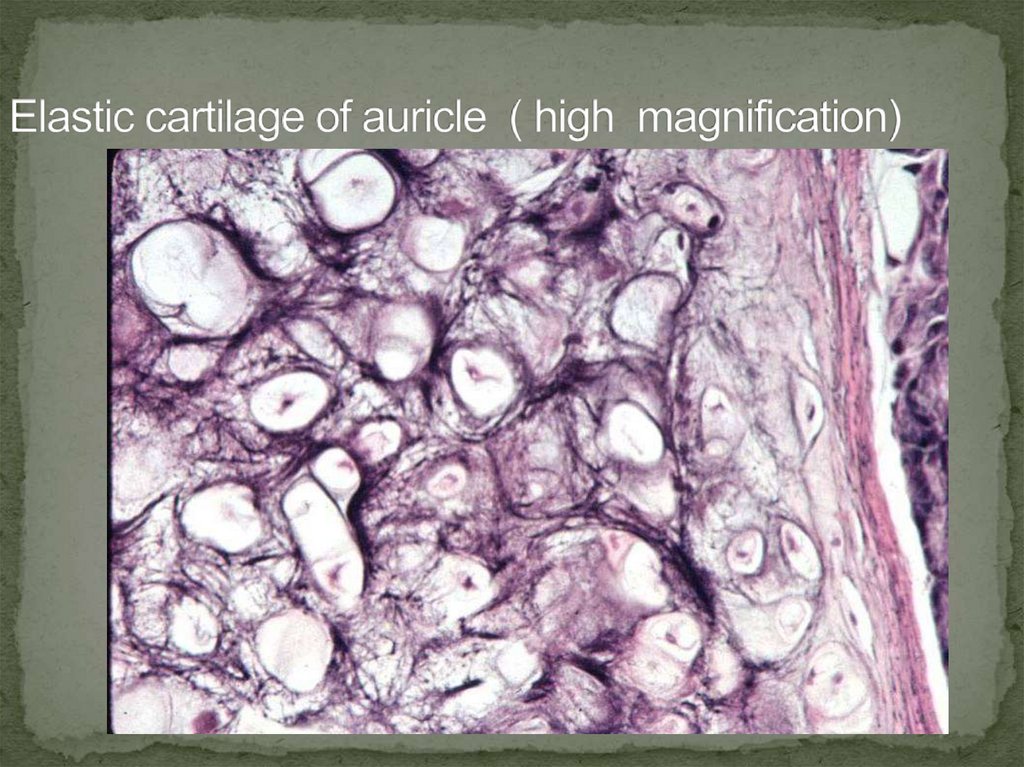
29.
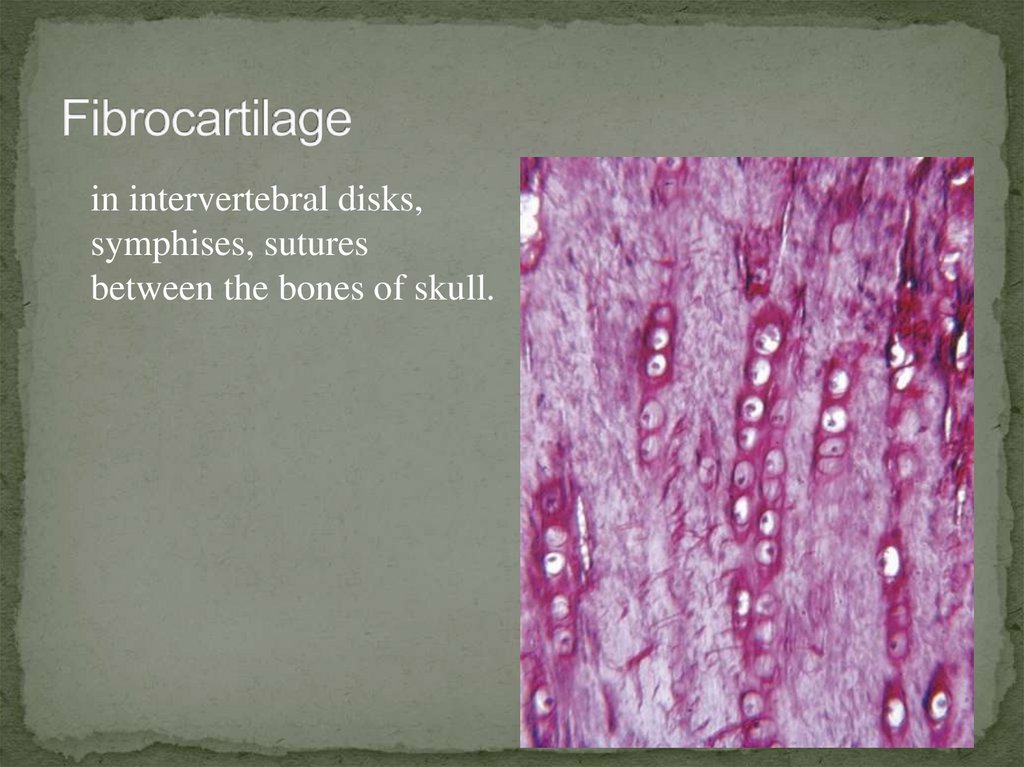
in intervertebral disks,symphises, sutures
between the bones of skull.






 biology
biology