Similar presentations:
Compare the domains of living organisms
1.
2.
Compare the domains of living organismsAssessment criteria:
1. Discuss the domains of living organisms
2. Describes the domains of living organisms
3.
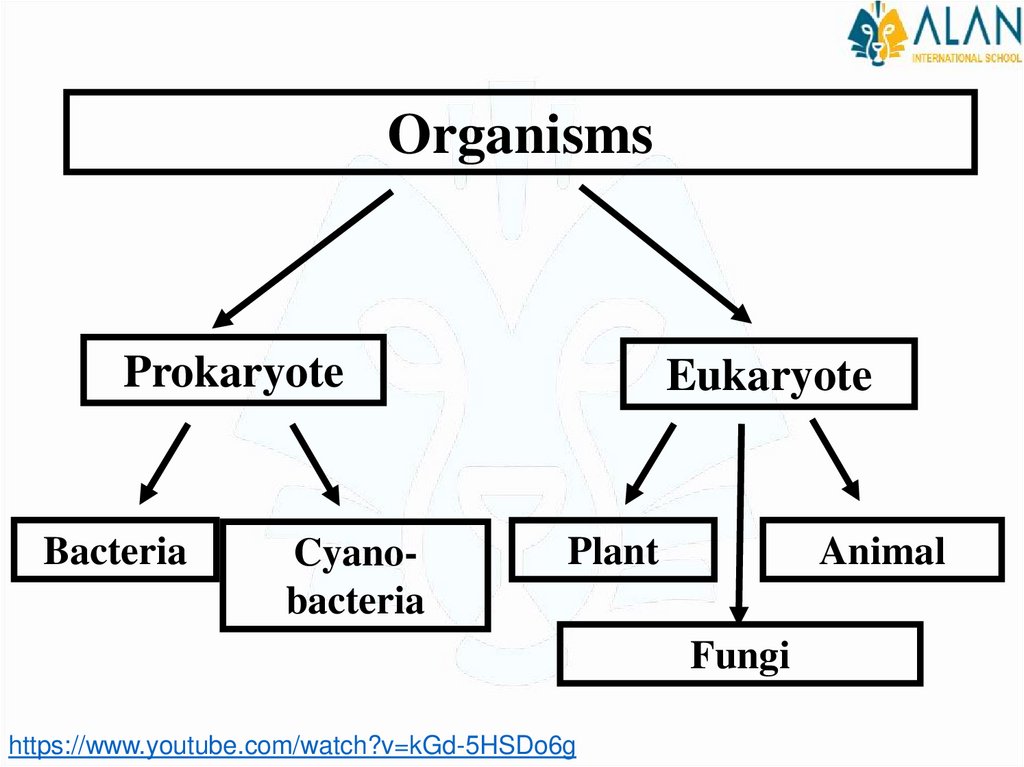
OrganismsProkaryote
Bacteria
Cyanobacteria
Eukaryote
Animal
Plant
Fungi
https://www.youtube.com/watch?v=kGd-5HSDo6g
4.
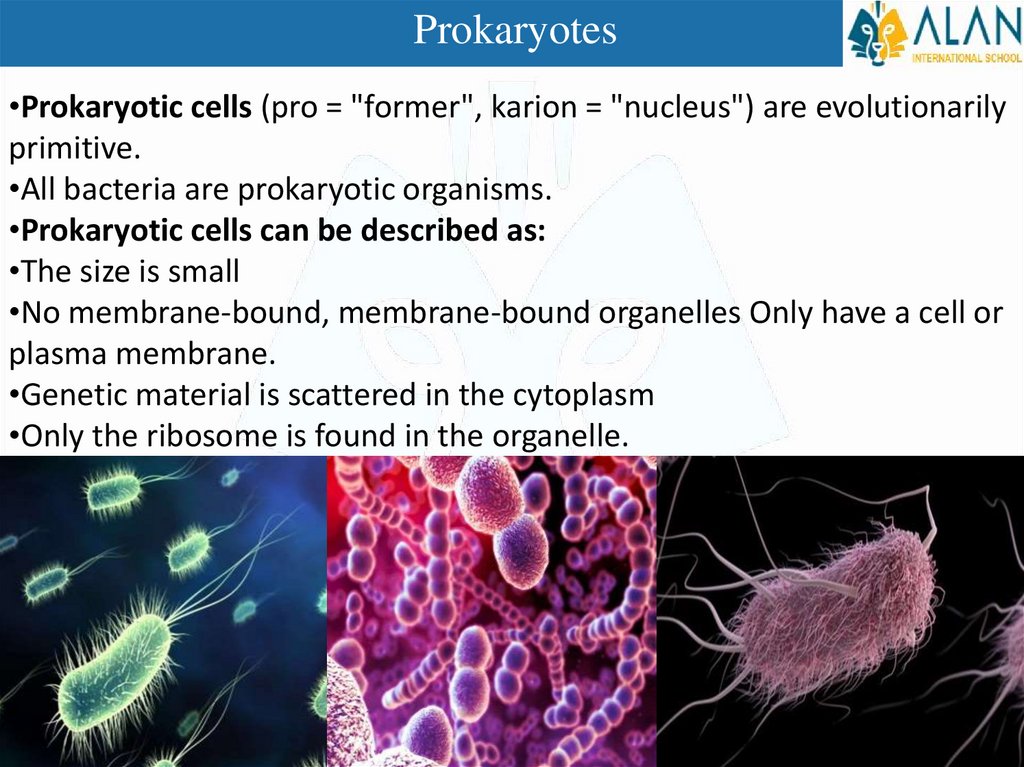
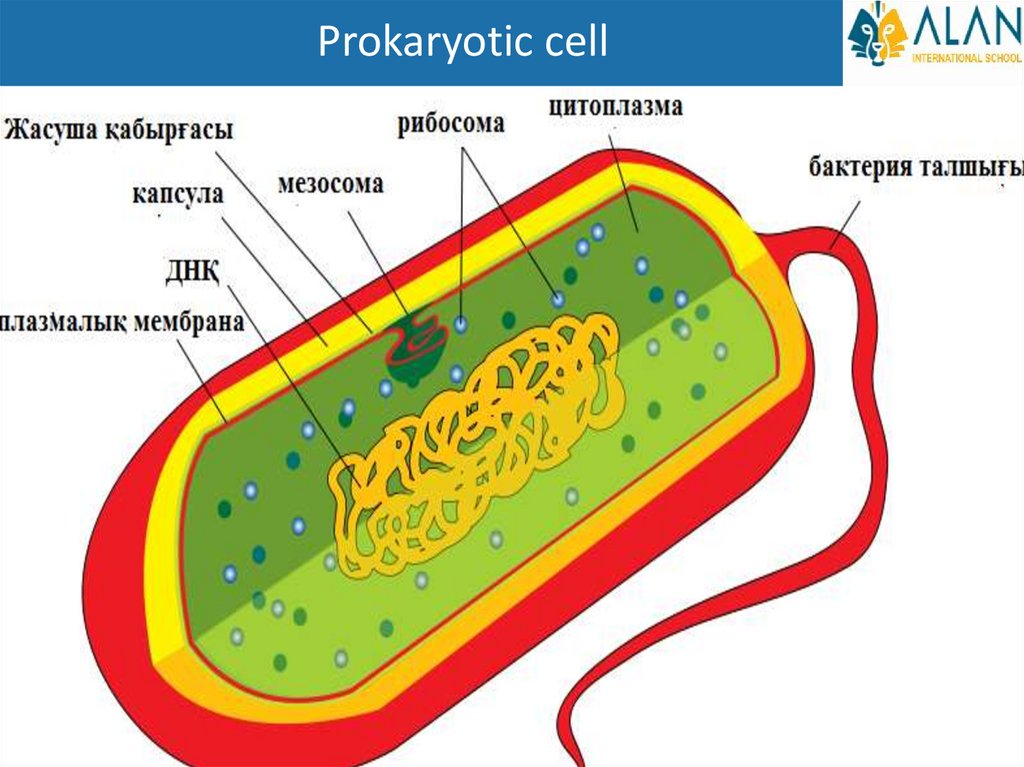
Prokaryotes•Prokaryotic cells (pro = "former", karion = "nucleus") are evolutionarily
primitive.
•All bacteria are prokaryotic organisms.
•Prokaryotic cells can be described as:
•The size is small
•No membrane-bound, membrane-bound organelles Only have a cell or
plasma membrane.
•Genetic material is scattered in the cytoplasm
•Only the ribosome is found in the organelle.
5.
Prokaryotic cell6.
EukaryotesEukaryotes (Eu = "true", karyon = "nucleus") are unicellular and multicellular
organisms. Eukaryotic cells evolved from prokaryotic cells.
A eukaryotic cell can be described as:
• the genetic material of the cell is located in the nucleus surrounded by a double
membrane
• endomembrane systems such as membranous organelles, smooth and granular
endoplasmic reticulum, Golgi complex, and vesicles.
• Organelles that produce energy and take part in metabolism: mitochondria and
chloroplasts are found. Since the eukaryotic cell has many organelles, its size is also large.
• The reason for the large number of organelles in it is due to the complexity of eukaryotes'
life activities
• Organelles in eukaryotic cells are adapted to perform various functions.
7.
Eukaryotic cell8.
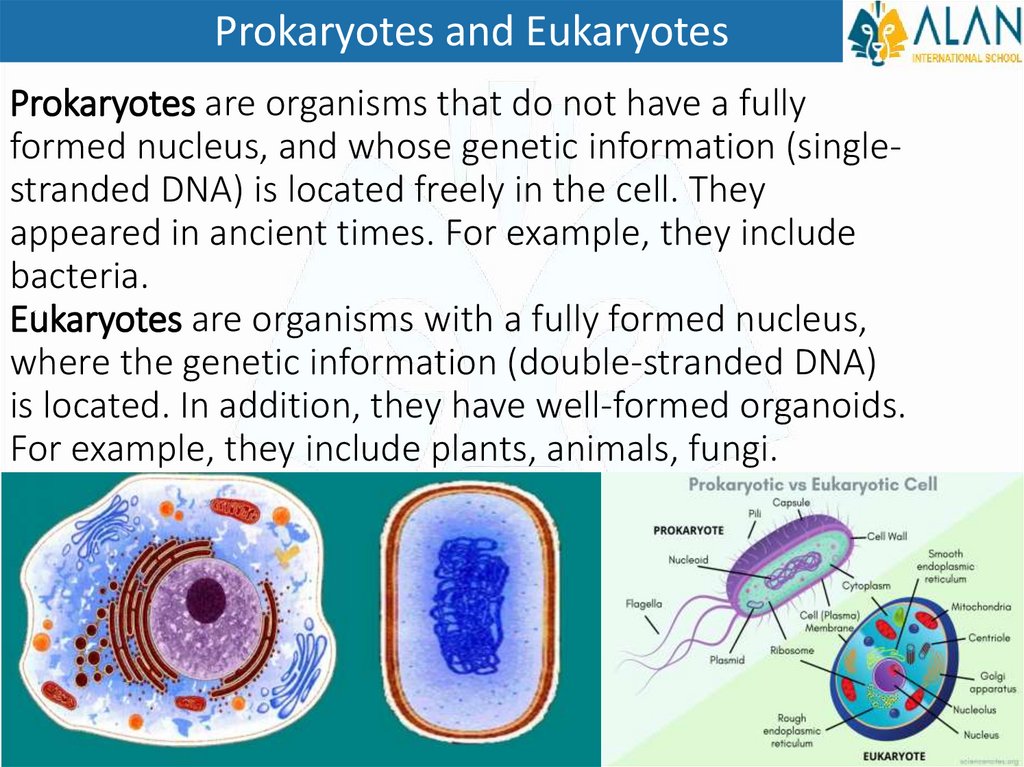
Prokaryotes and EukaryotesProkaryotes are organisms that do not have a fully
formed nucleus, and whose genetic information (singlestranded DNA) is located freely in the cell. They
appeared in ancient times. For example, they include
bacteria.
Eukaryotes are organisms with a fully formed nucleus,
where the genetic information (double-stranded DNA)
is located. In addition, they have well-formed organoids.
For example, they include plants, animals, fungi.
9.
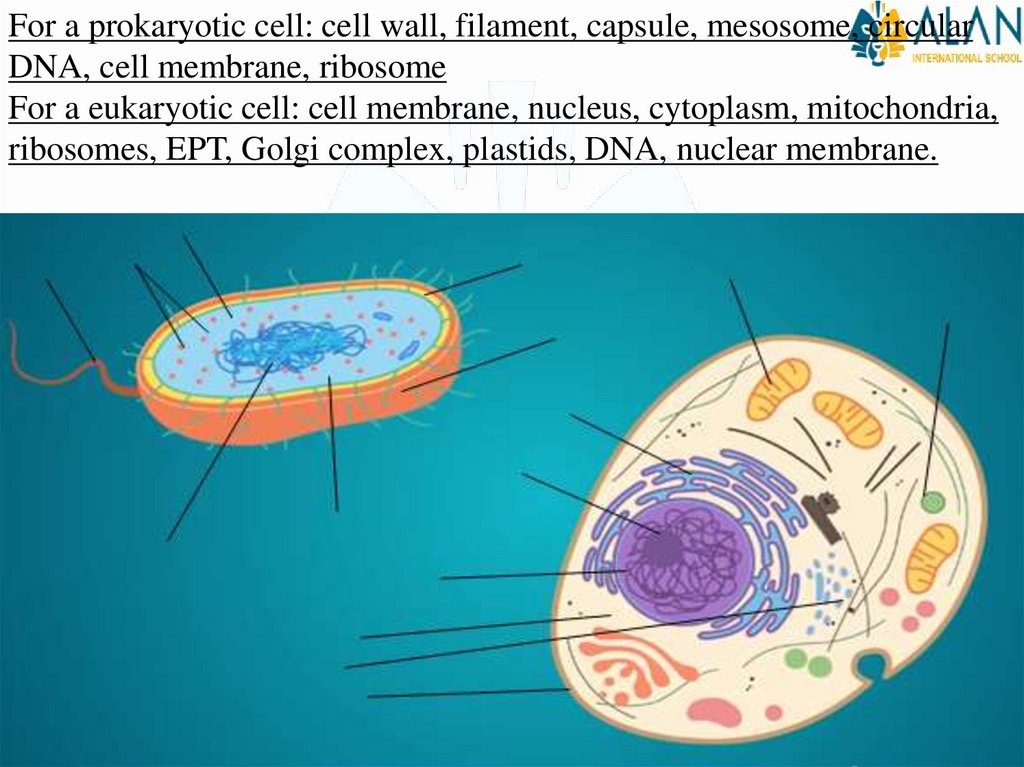
For a prokaryotic cell: cell wall, filament, capsule, mesosome, circularDNA, cell membrane, ribosome
For a eukaryotic cell: cell membrane, nucleus, cytoplasm, mitochondria,
ribosomes, EPT, Golgi complex, plastids, DNA, nuclear membrane.
10.
11.
12.
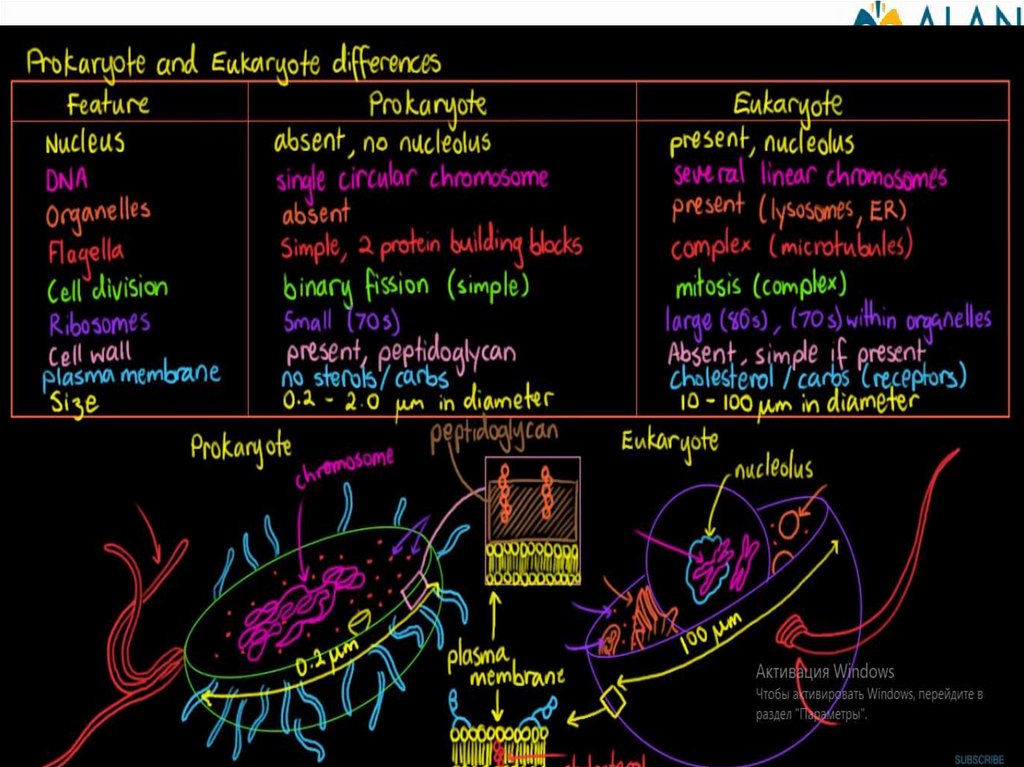
The difference between prokaryotic and eukaryotic cellsCell organelles
Cell membrane
Cytoplasm
Ribosome
Mitochondria
Endoplasmic reticulum
Golgi complex
Plastids
Nuclear membrane
Membrane organelles
Scattered DNA
Capsule
Circular DNA
Mesosoma
Eukaryotic cell
+
+
+
+
+
+
+
+
+
+
-
Prokaryotic cell
+
+
+
+
+
+






 biology
biology