Similar presentations:
Fundamentals on grinding workshops
1. Fundamentals on Grinding Workshops
GRINDING I – Training Session2. Content
Fundamentals on Grinding WorkshopsContent
• Fundamentals on grinding
• Different types of ball mills
• Vertical mills
• Roller press
• Horomill
KUJ - July 2012 – Grinding I 2
3. Content
Fundamentals on Grinding WorkshopsContent
• Fundamentals on grinding
• Different types of ball mills
• Vertical mills
• Roller press
• Horomill
KUJ - July 2012 – Grinding I 3
4. Why do we grind in the cement business?
Fundamentals on Grinding WorkshopsWhy do we grind in the cement business?
• To create surface area for good chemical reactions
to occur
• Combination in the kiln (Raw grinding)
• Hydraulic reactions in the concrete (Cement grinding)
• Good combustion in the kiln flame (Coal grinding)
KUJ - July 2012 – Grinding I 4
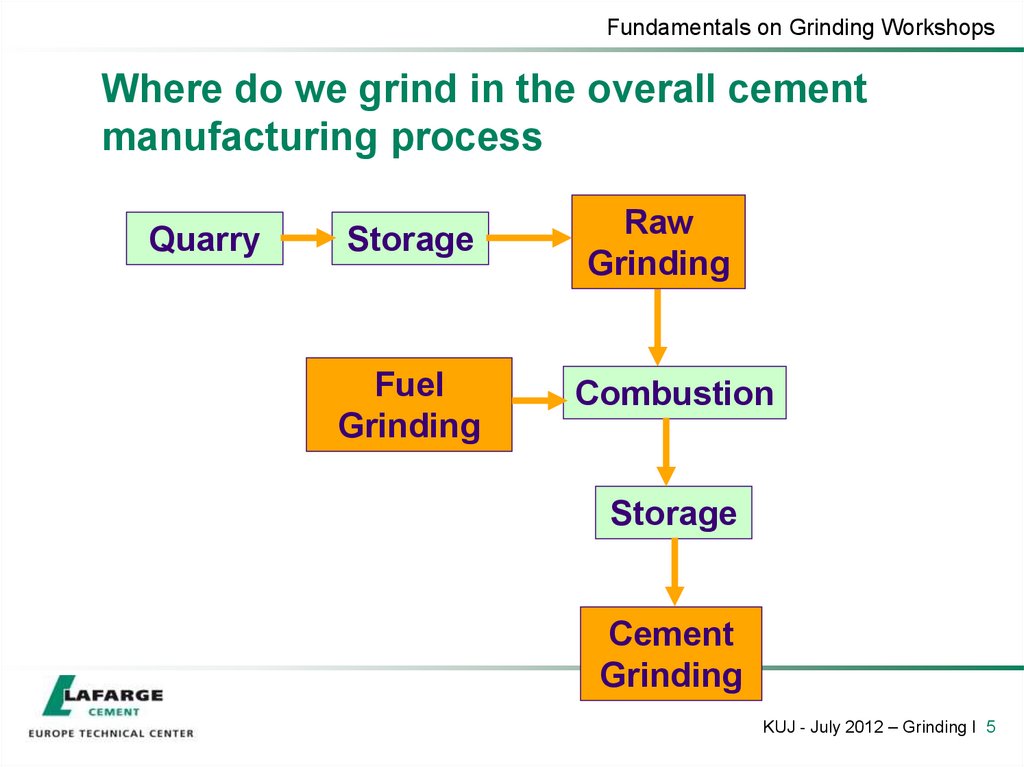
5. Where do we grind in the overall cement manufacturing process
Fundamentals on Grinding WorkshopsWhere do we grind in the overall cement
manufacturing process
Quarry
Storage
Fuel
Grinding
Raw
Grinding
Combustion
Storage
Cement
Grinding
KUJ - July 2012 – Grinding I 5
6. What are the main challenges for cement production
Fundamentals on Grinding WorkshopsWhat are the main challenges for cement
production
• Reduce power consumption
• Maximize production
• Optimize and improve product regularity
• Control maintenance costs
KUJ - July 2012 – Grinding I 6
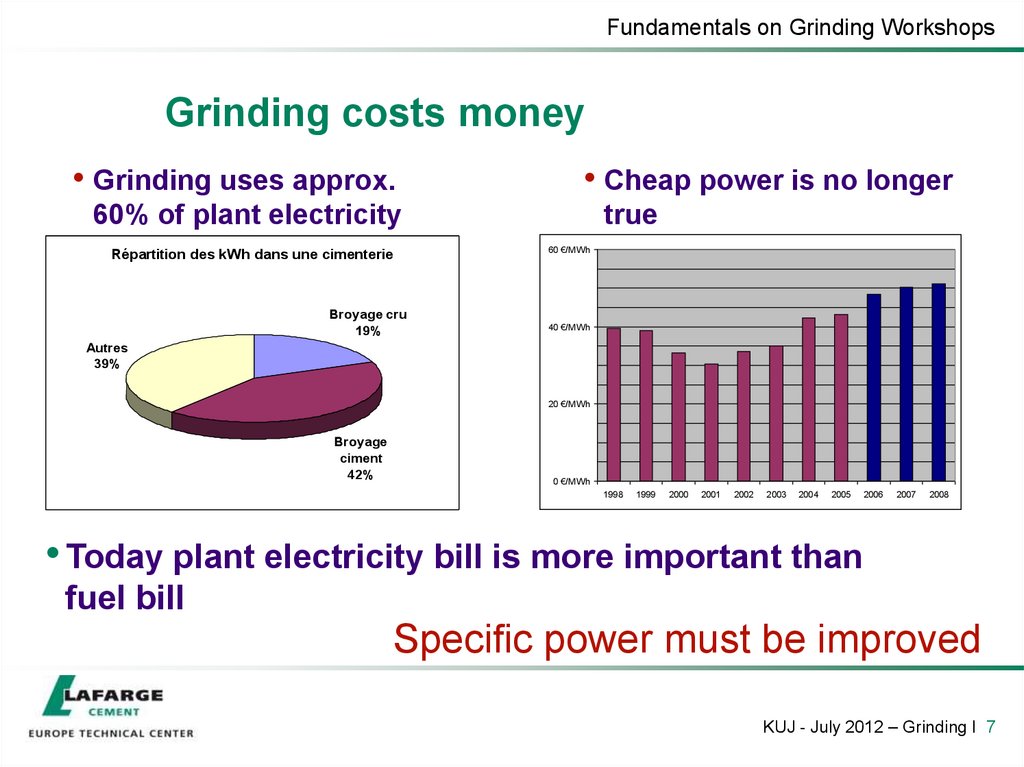
7. Grinding costs money
Fundamentals on Grinding WorkshopsGrinding costs money
• Grinding uses approx.
• Cheap power is no longer
60% of plant electricity
Répartition des kWh dans une cimenterie
Broyage cru
19%
true
60 €/MWh
40 €/MWh
Autres
39%
20 €/MWh
Broyage
ciment
42%
0 €/MWh
1998
1999
2000
2001
2002
2003
2004
2005
2006
2007
2008
• Today plant electricity bill is more important than
fuel bill
Specific power must be improved
KUJ - July 2012 – Grinding I 7
8.
Fundamentals on Grinding WorkshopsKUJ - July 2012 – Grinding I 8
9. Grinding costs money
Fundamentals on Grinding WorkshopsGrinding costs money
• Costs of wear parts increasing
• Joint visits between process and maintenance
departments upgrade the efficiency: wear takes place in
the process
PLN raw mill example:
• Change of iron source
• Wear before and after use
of this new raw material
• Material stays in the reject
TOTAL WEAR FROM 1998 TO 01-2004
TOTAL WEAR FROM 02-2004 TO 04-2004
KUJ - July 2012 – Grinding I 9
10. The different types of mill
Fundamentals on Grinding WorkshopsThe different types of mill
• Three different mill types with specific purposes
• Raw mills (for slag, shale, limestone…)
• Size reduction (targeted rejects at 90 and 200µm)
• Drying the materials
• Cement mills (pure or compound cements)
• Size reduction (objectives in SSB)
• Management of gypsum dehydration
• Fuel mills (coal and pet coke)
• Size reduction (targeted rejects at 90µm)
• Drying the materials
KUJ - July 2012 – Grinding I 10
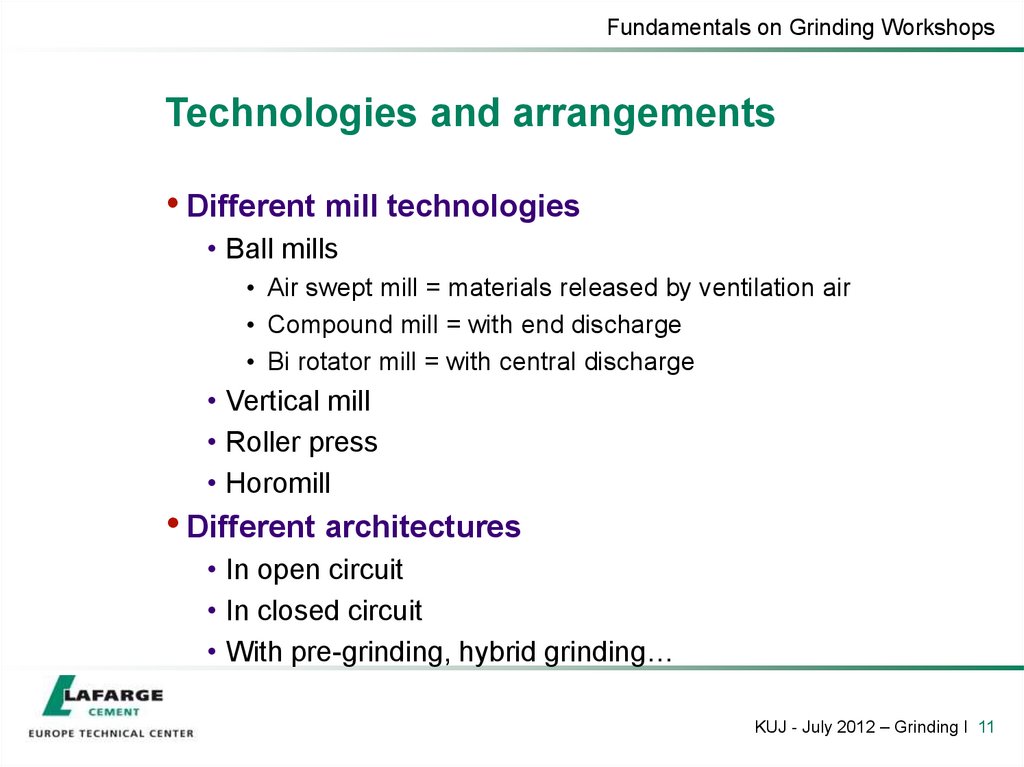
11. Technologies and arrangements
Fundamentals on Grinding WorkshopsTechnologies and arrangements
• Different mill technologies
• Ball mills
• Air swept mill = materials released by ventilation air
• Compound mill = with end discharge
• Bi rotator mill = with central discharge
• Vertical mill
• Roller press
• Horomill
• Different architectures
• In open circuit
• In closed circuit
• With pre-grinding, hybrid grinding…
KUJ - July 2012 – Grinding I 11
12. Origin of a current workshop
Fundamentals on Grinding WorkshopsOrigin of a current workshop
• Existing workshop design depends on
• Material feed specifications
• Feed size
• Moisture
• Outlet product specifications
• Flow rate
• Fineness target
• History of the plant and workshop
KUJ - July 2012 – Grinding I 12
13. Content
Fundamentals on Grinding WorkshopsContent
• Fundamentals on grinding
• Different types of ball mills
• Vertical mills
• Roller press
• Horomill
KUJ - July 2012 – Grinding I 13
14. The Ball Mill
Fundamentals on Grinding WorkshopsThe Ball Mill
KUJ - July 2012 – Grinding I 14
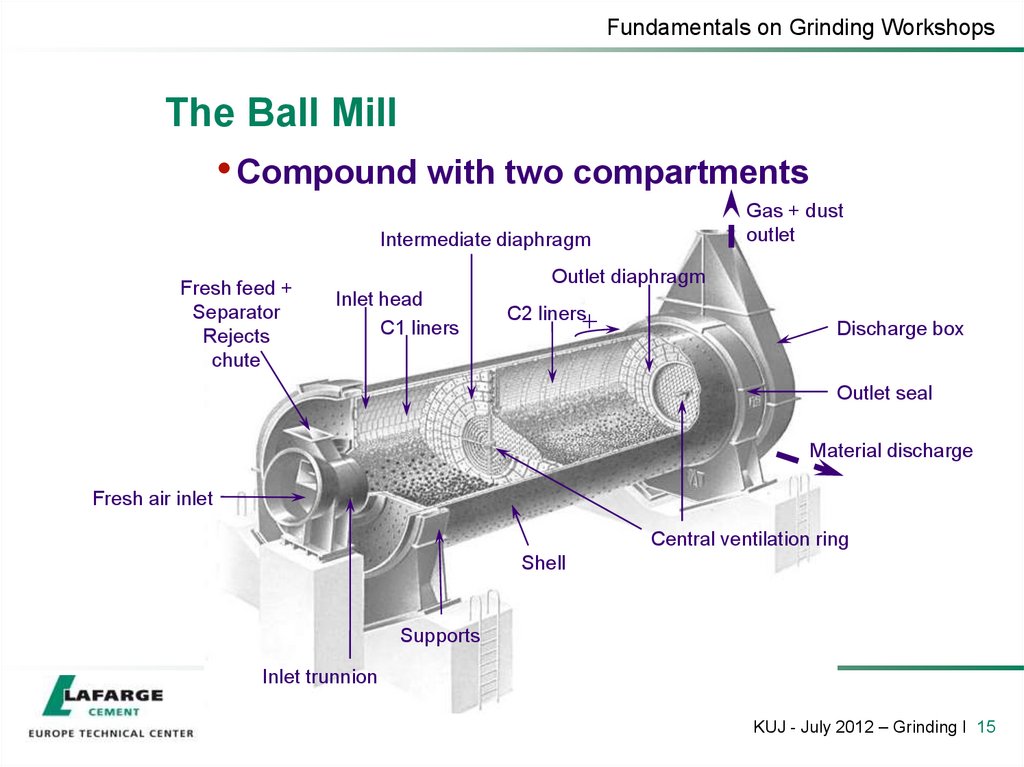
15. The Ball Mill
Fundamentals on Grinding WorkshopsThe Ball Mill
• Compound with two compartments
Gas + dust
outlet
Intermediate diaphragm
Fresh feed +
Separator
Rejects
chute
Outlet diaphragm
Inlet head
C1 liners
C2 liners
Discharge box
Outlet seal
Material discharge
Fresh air inlet
Central ventilation ring
Shell
Supports
Inlet trunnion
KUJ - July 2012 – Grinding I 15
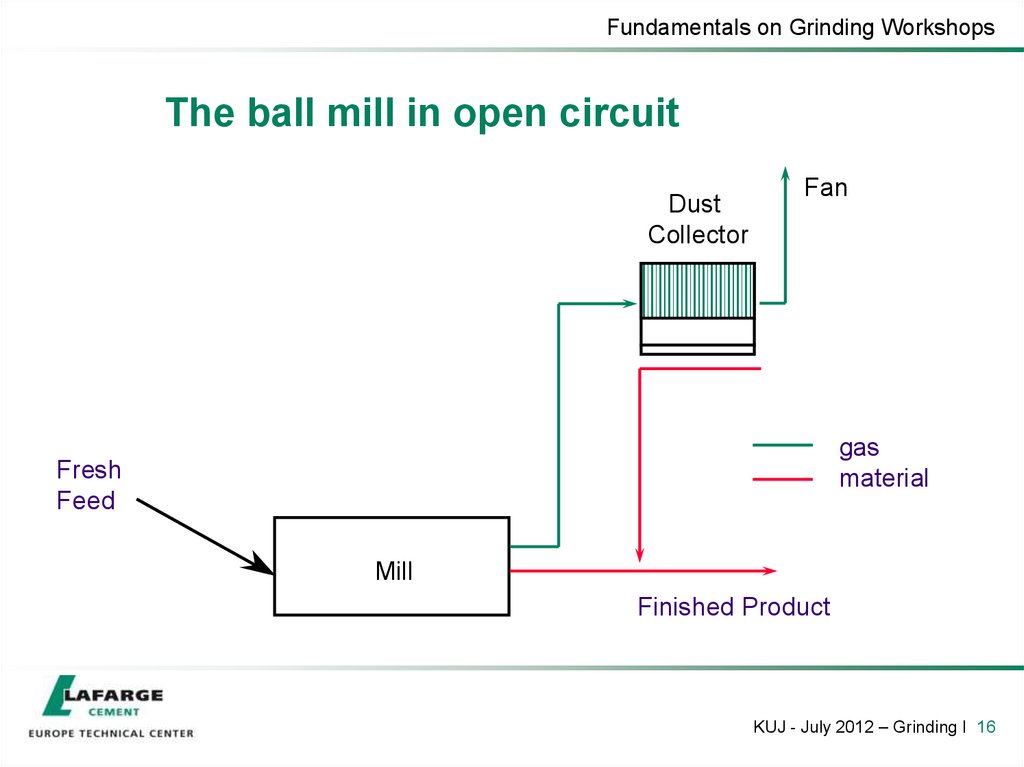
16. The ball mill in open circuit
Fundamentals on Grinding WorkshopsThe ball mill in open circuit
Dust
Collector
Fan
gas
material
Fresh
Feed
Mill
Finished Product
KUJ - July 2012 – Grinding I 16
17. The ball mill in open circuit
Fundamentals on Grinding WorkshopsThe ball mill in open circuit
• Advantages
Moderate investment costs
Simple operation
Simple maintenance
Highest reliability
• Disadvantages
little or no control of fineness
not adapted to high fineness (possibility of overgrinding)
broad particles size distribution
higher temperature of products
Limited drying capacity
KUJ - July 2012 – Grinding I 17
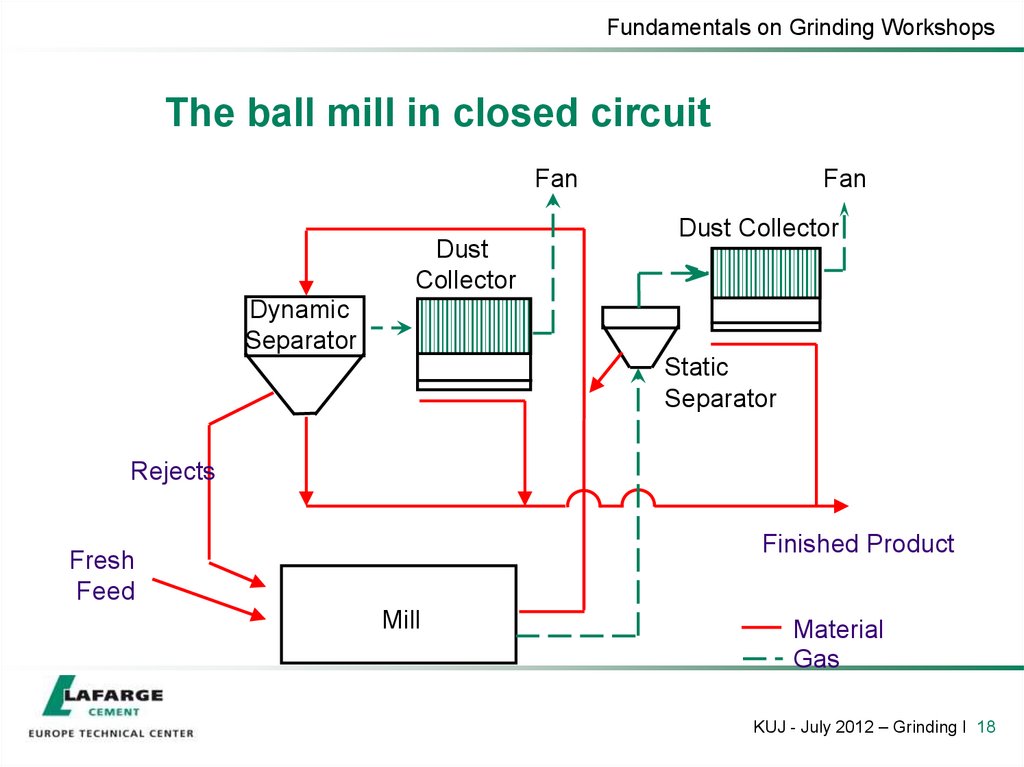
18. The ball mill in closed circuit
Fundamentals on Grinding WorkshopsThe ball mill in closed circuit
Fan
Dust
Collector
Fan
Dust Collector
Dynamic
Separator
Static
Separator
Rejects
Finished Product
Fresh
Feed
Mill
Material
Gas
KUJ - July 2012 – Grinding I 18
19. The ball mill in closed circuit
Fundamentals on Grinding WorkshopsThe ball mill in closed circuit
• General description
Better regularity thanks to a real control of the fineness
High fineness is possible
Higher flexibility and possibility of optimisation by product
Higher output, better efficiency
Possibility of higher mill ventilation
Better temperature control
• High mill ventilation
• Possibility to have a separated ventilation in the separator
• Narrow particle size distribution
• Higher investment costs
KUJ - July 2012 – Grinding I 19
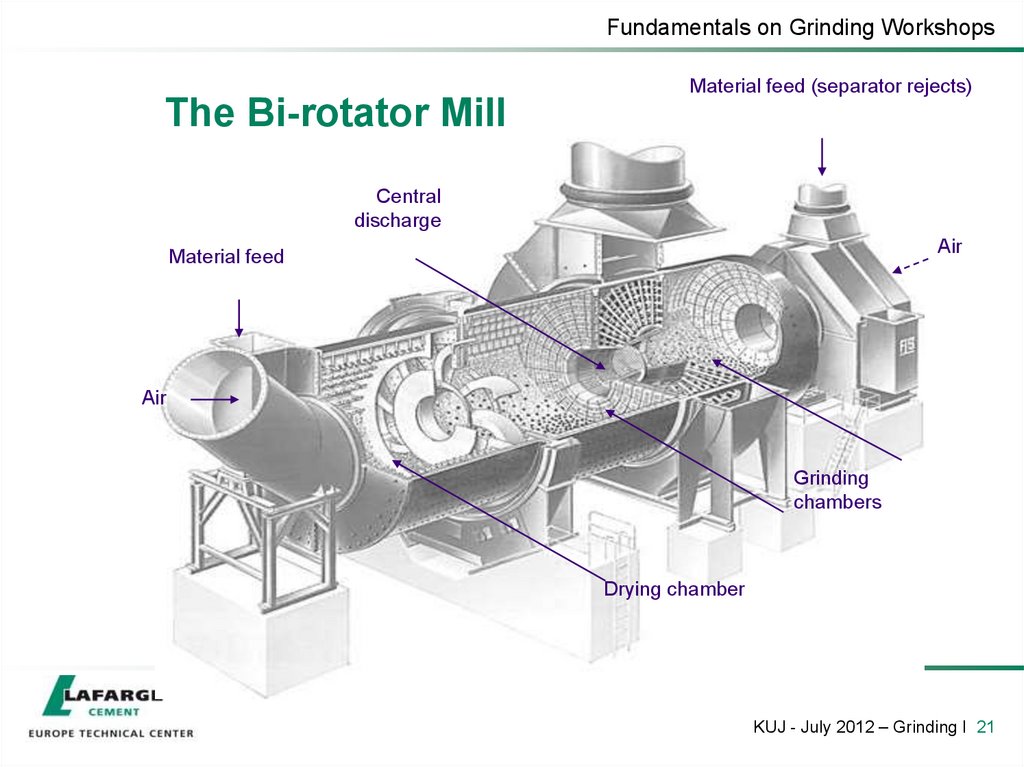
20. The Bi-rotator Mill
Fundamentals on Grinding WorkshopsThe Bi-rotator Mill
KUJ - July 2012 – Grinding I 20
21. The Bi-rotator Mill
Fundamentals on Grinding WorkshopsMaterial feed (separator rejects)
The Bi-rotator Mill
Central
discharge
Air
Material feed
Air
Grinding
chambers
Drying chamber
KUJ - July 2012 – Grinding I 21
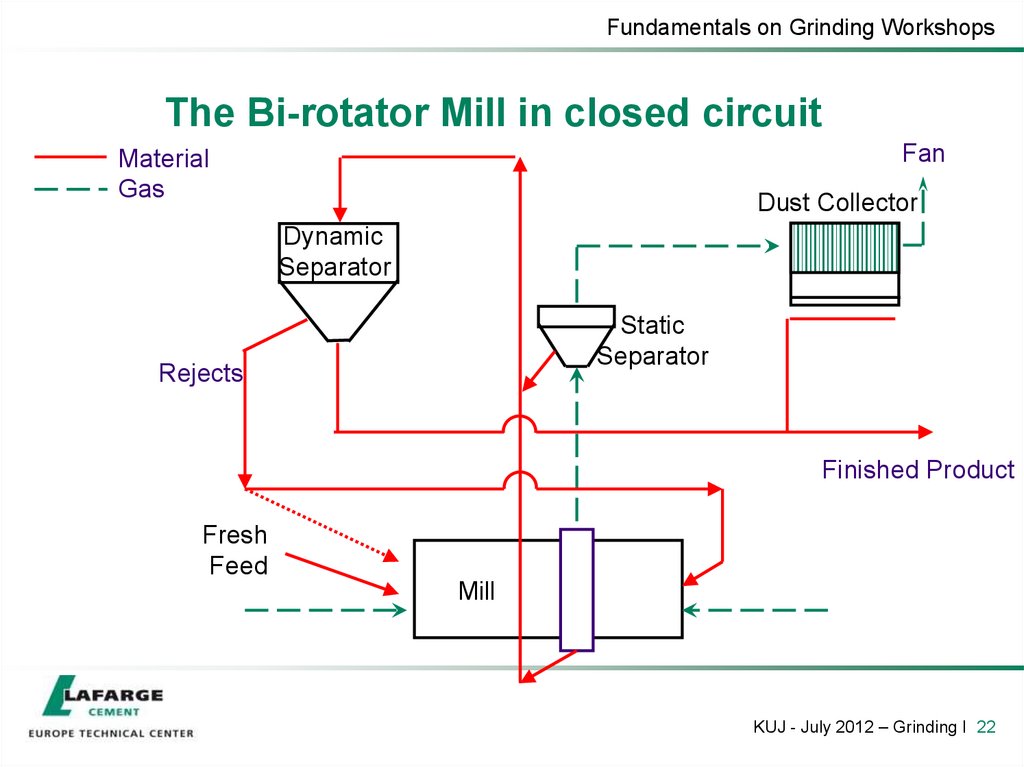
22. The Bi-rotator Mill in closed circuit
Fundamentals on Grinding WorkshopsThe Bi-rotator Mill in closed circuit
Fan
Material
Gas
Dust Collector
Dynamic
Separator
Static
Separator
Rejects
Finished Product
Fresh
Feed
Mill
KUJ - July 2012 – Grinding I 22
23. The Bi-rotator Mill
Fundamentals on Grinding WorkshopsThe Bi-rotator Mill
• Advantages
• High ventilation capacity for drying materials
• Disadvantages
• False air
KUJ - July 2012 – Grinding I 23
24. The Air-Swept Mill
Fundamentals on Grinding WorkshopsThe Air-Swept Mill
Material
Air + material
Intermediate
diaphragm
Air
Grinding
chamber
Drying
chamber
KUJ - July 2012 – Grinding I 24
25. The Air-Swept Mill in closed circuit
Fundamentals on Grinding WorkshopsThe Air-Swept Mill in closed circuit
Fan
Dust Collector
Material
Gas
Dynamic
Separator
Rejects
Finished Product
Fresh
Feed
Mill
KUJ - July 2012 – Grinding I 25
26. The Air-Swept Mill
Fundamentals on Grinding WorkshopsThe Air-Swept Mill
• Advantages
• High ventilation capacity to dry materials
• Disadvantages
• High specific power consumption due to swept solution
KUJ - July 2012 – Grinding I 26
27. Content
Fundamentals on Grinding WorkshopsContent
• Fundamentals on grinding
• Different types of ball mills
• Vertical mills
• Roller press
• Horomill
KUJ - July 2012 – Grinding I 27
28. The Vertical Mill
Fundamentals on Grinding WorkshopsThe Vertical Mill
Fine Product
Separator
Drive
Feed Material
HE Separator
Rejects Cone
Grinding Roller
Pressure
frame
Grinding Table
Port ring
Hydraulic
tensioning
cylinder
Air or Hot Gases
Mill Drive
KUJ - July 2012 – Grinding I 28
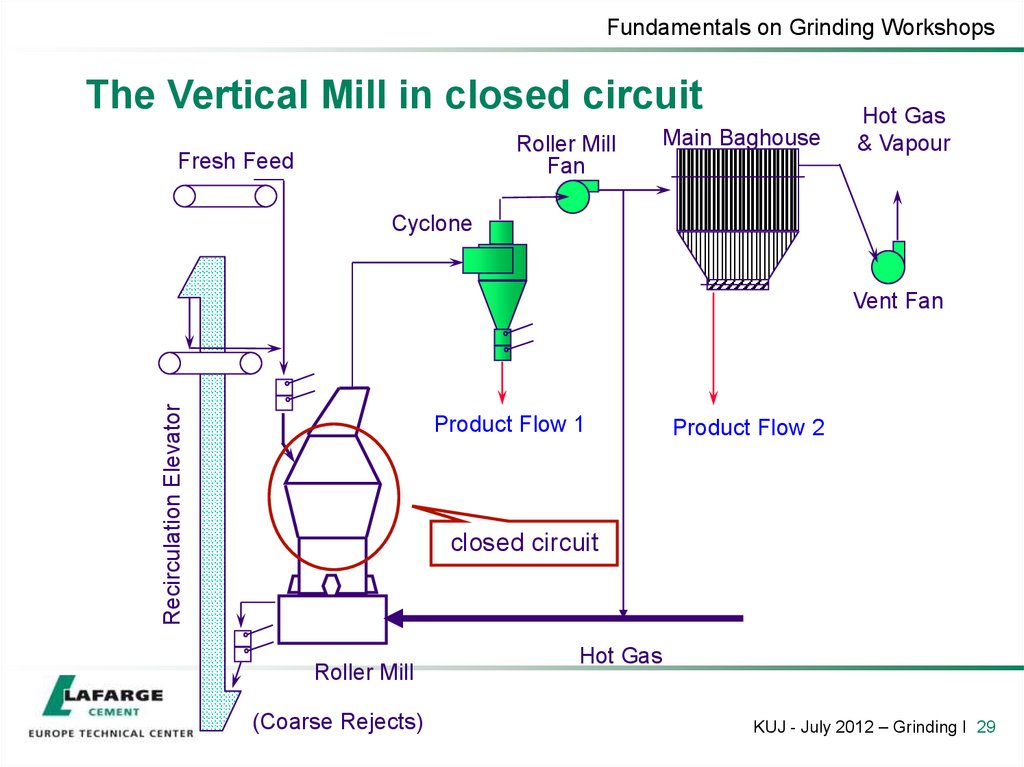
29. The Vertical Mill in closed circuit
Fundamentals on Grinding WorkshopsThe Vertical Mill in closed circuit
Roller Mill
Fan
Fresh Feed
Main Baghouse
Hot Gas
& Vapour
Cyclone
Recirculation Elevator
Vent Fan
Product Flow 1
Product Flow 2
closed circuit
Roller Mill
(Coarse Rejects)
Hot Gas
KUJ - July 2012 – Grinding I 29
30. The Vertical Mill
Fundamentals on Grinding WorkshopsThe Vertical Mill
• Advantages
Good efficiency factor
High drying capacity
Combined grinder, separator and dryer in one unit
Popular for coal and raw material grinding with high
moisture content
• Disadvantages
Complex operation
Reliability – maintenance costs
Vibrations
Management of gypsum dehydration in cement grinding
KUJ - July 2012 – Grinding I 30
31. Content
Fundamentals on Grinding WorkshopsContent
• Fundamentals on grinding
• Different types of ball mills
• Vertical mills
• Roller press
• Horomill
KUJ - July 2012 – Grinding I 31
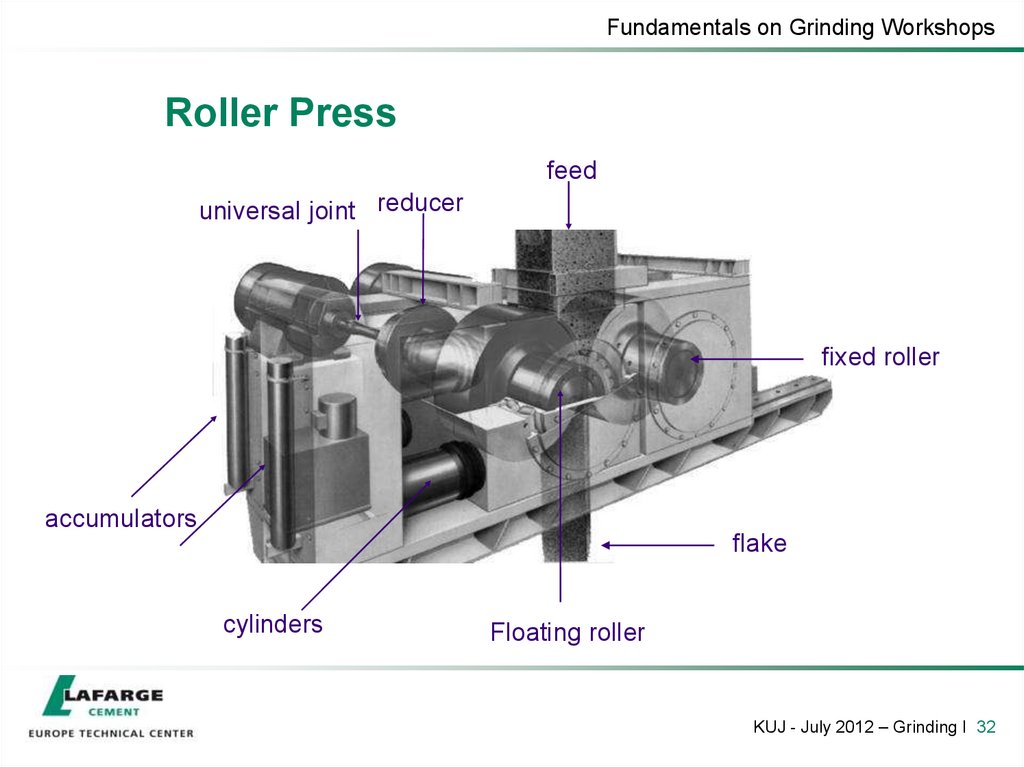
32. Roller Press
Fundamentals on Grinding WorkshopsRoller Press
feed
universal joint reducer
fixed roller
accumulators
flake
cylinders
Floating roller
KUJ - July 2012 – Grinding I 32
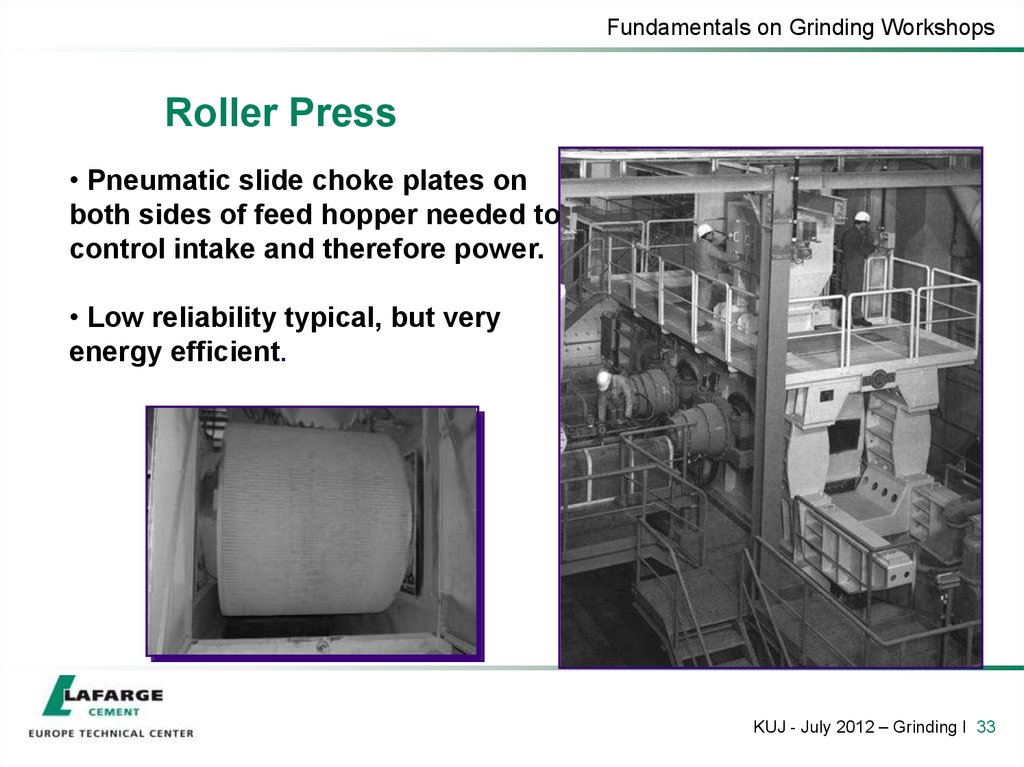
33. Roller Press
Fundamentals on Grinding WorkshopsRoller Press
• Pneumatic slide choke plates on
both sides of feed hopper needed to
control intake and therefore power.
• Low reliability typical, but very
energy efficient.
KUJ - July 2012 – Grinding I 33
34. Roller Press
Fundamentals on Grinding WorkshopsRoller Press
• Advantages
• High efficiency factor
• Compact installation
• High production increase when used as pregrinding
• Disadvantages
High investment costs
Complex operation
Reliabilty
Limited drying capacity
KUJ - July 2012 – Grinding I 34
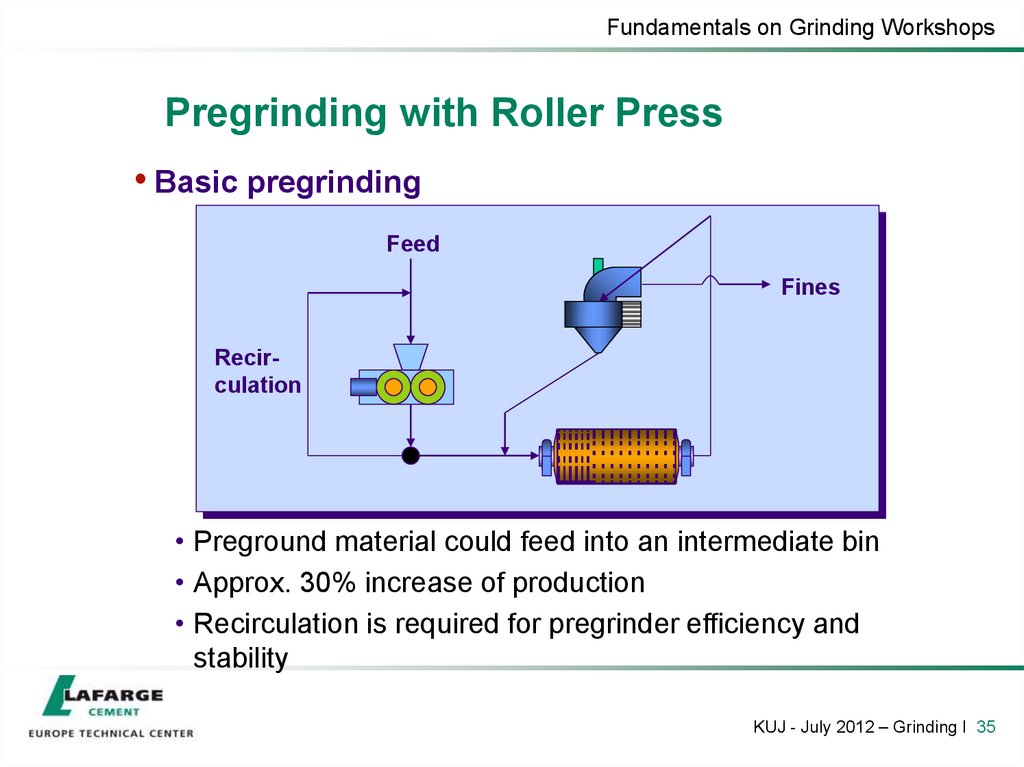
35. Pregrinding with Roller Press
Fundamentals on Grinding WorkshopsPregrinding with Roller Press
• Basic pregrinding
Feed
Fines
Recirculation
• Preground material could feed into an intermediate bin
• Approx. 30% increase of production
• Recirculation is required for pregrinder efficiency and
stability
KUJ - July 2012 – Grinding I 35
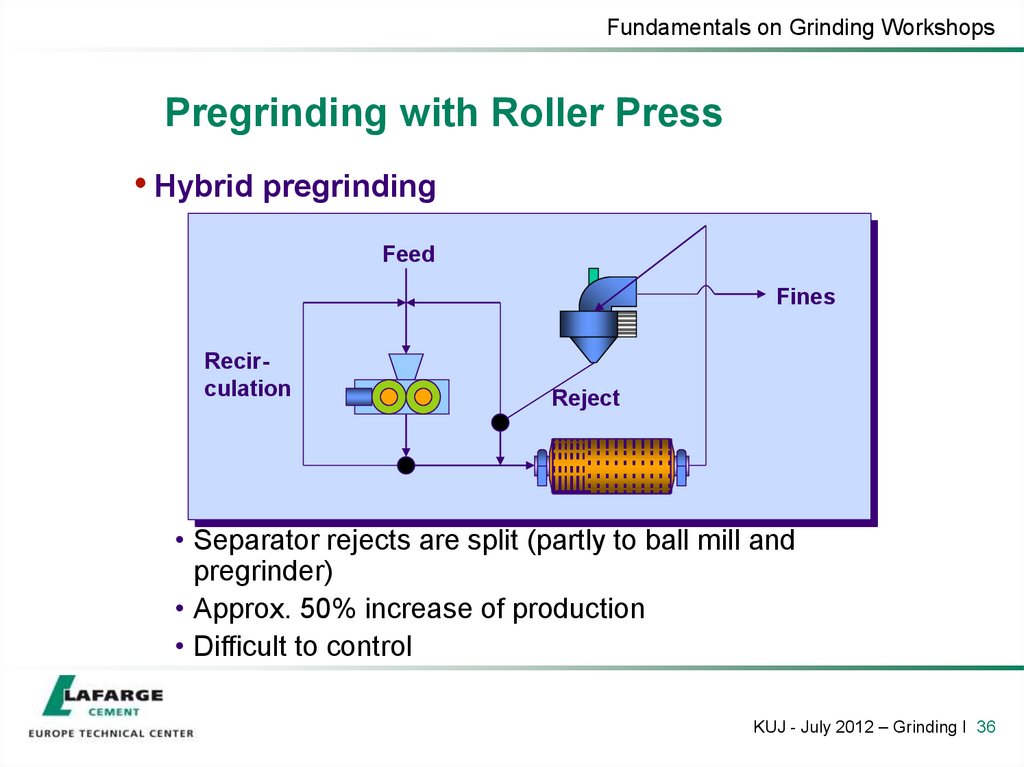
36. Pregrinding with Roller Press
Fundamentals on Grinding WorkshopsPregrinding with Roller Press
• Hybrid pregrinding
Feed
Fines
Recirculation
Reject
• Separator rejects are split (partly to ball mill and
pregrinder)
• Approx. 50% increase of production
• Difficult to control
KUJ - July 2012 – Grinding I 36
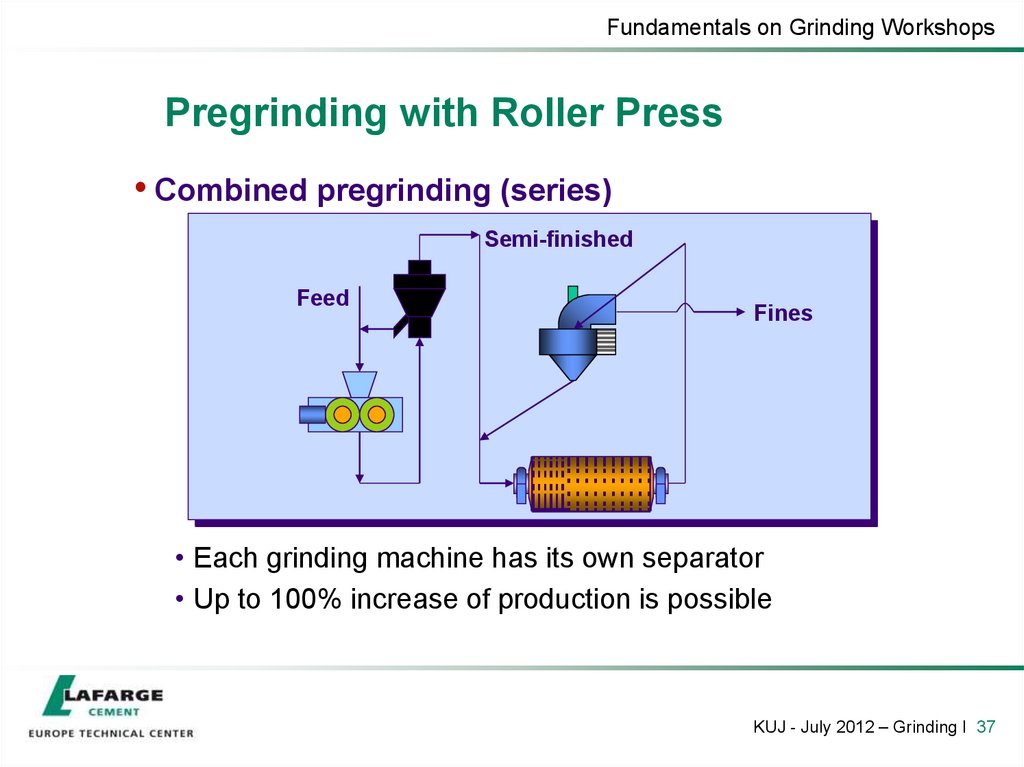
37. Pregrinding with Roller Press
Fundamentals on Grinding WorkshopsPregrinding with Roller Press
• Combined pregrinding (series)
Semi-finished
Feed
Fines
• Each grinding machine has its own separator
• Up to 100% increase of production is possible
KUJ - July 2012 – Grinding I 37
38. Content
Fundamentals on Grinding WorkshopsContent
• Fundamentals on grinding
• Different types of ball mills
• Vertical mills
• Roller press
• Horomill
KUJ - July 2012 – Grinding I 38
39. Horomill
Fundamentals on Grinding WorkshopsHoromill
• General description
Horizontal mill
Single roller inside a motorized tube shell
Slide shoe (thrust pad) bearings
Girth gear and pinion drive
Designed by FCB
KUJ - July 2012 – Grinding I 39
40. Horomill
Fundamentals on Grinding WorkshopsHoromill
Scraper and feed
forward plate
roller
pinion shaft
cylinder
KUJ - July 2012 – Grinding I 40
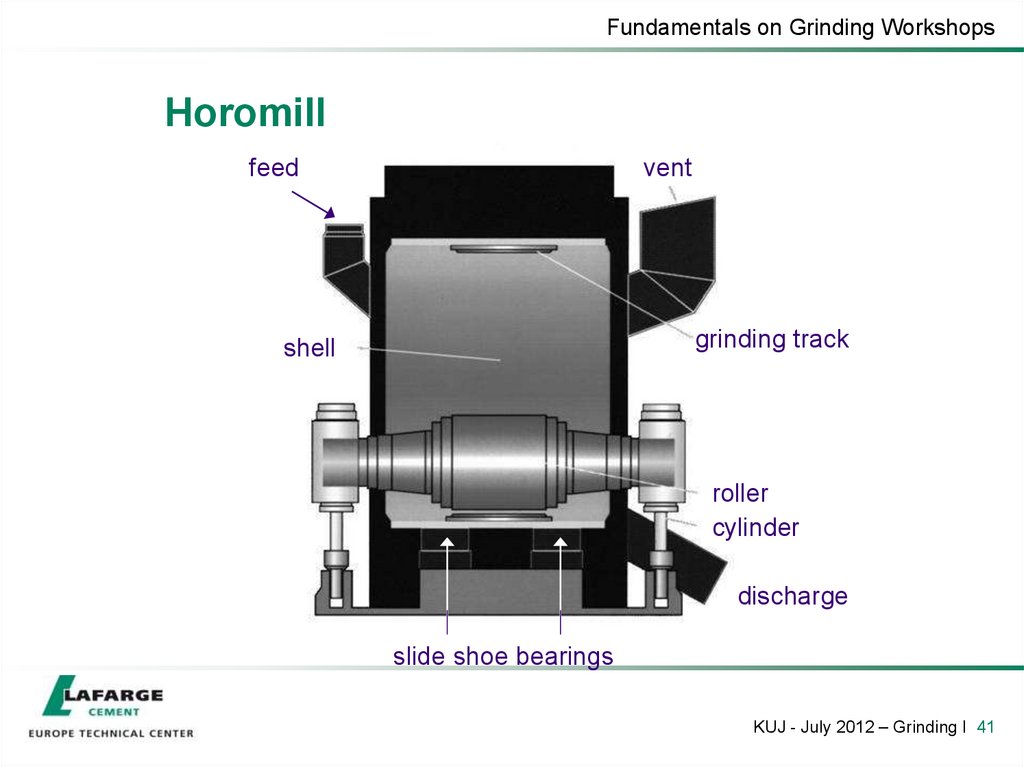
41. Horomill
Fundamentals on Grinding WorkshopsHoromill
feed
vent
grinding track
shell
roller
cylinder
discharge
slide shoe bearings
KUJ - July 2012 – Grinding I 41
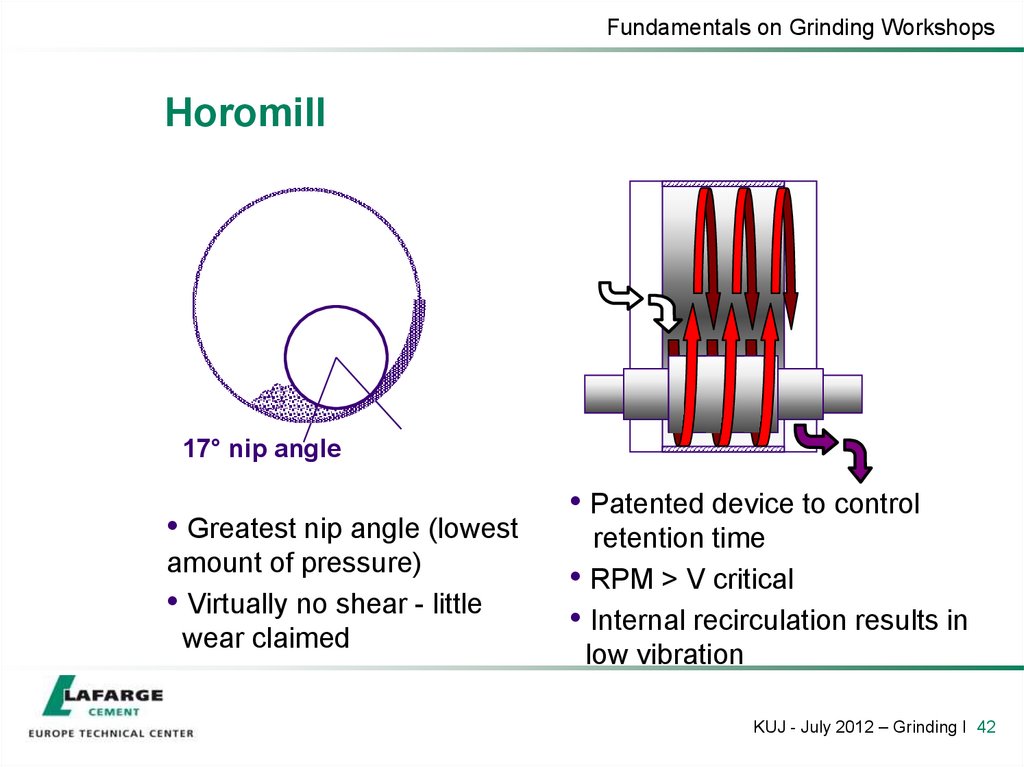
42. Horomill
Fundamentals on Grinding WorkshopsHoromill
17° nip angle
• Greatest nip angle (lowest
amount of pressure)
• Virtually no shear - little
wear claimed
• Patented device to control
retention time
• RPM > V critical
• Internal recirculation results in
low vibration
KUJ - July 2012 – Grinding I 42
43. Ways to upgrade a workshop
Fundamentals on Grinding WorkshopsWays to upgrade a workshop
• Optimisation of workshop operations
Ball charge design
Ventilation balance
Circulating load
Increase of the ball mill speed (target of 75% Vcrit)
• Replacement of the workshop separator with a third
generation one
KUJ - July 2012 – Grinding I 43
















 industry
industry







