Similar presentations:
Accounting
1.
Ho rn gren ’sAc co u ntin g
Lecture Eight
Lisa, Li
Accounting
1
2.
Learning Objectives – Chapter 31.
2.
3.
4.
5.
6.
Cash Basis vs Accrual Basis Accounting
Apply the time period concept, revenue recognition, and matching principles
Explain the purpose of and journalize and post adjusting entries
Prepare an adjusted trial balance
Identify the impact of adjusting entries on the financial statements
use a worksheet to prepare the adjusted trial balance
Accounting
Accounting
2
3.
Adjusting Journal EntriesAdjusting Journal Entries (AJE’s) can be divided into
two basic categories:
Prepaids
1.Prepaid Expenses
2.Unearned Revenues
Accruals
1.Accrued revenues
2.Accrued expenses
Accounting
3
4.
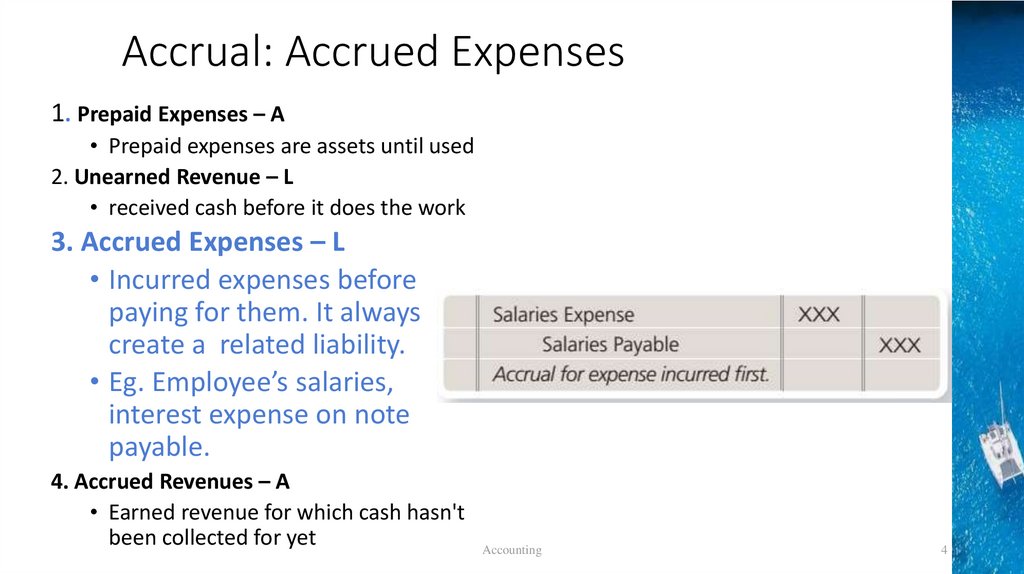
Accrual: Accrued Expenses1. Prepaid Expenses – A
• Prepaid expenses are assets until used
2. Unearned Revenue – L
• received cash before it does the work
3. Accrued Expenses – L
• Incurred expenses before
paying for them. It always
create a related liability.
• Eg. Employee’s salaries,
interest expense on note
payable.
4. Accrued Revenues – A
• Earned revenue for which cash hasn't
been collected for yet
Accounting
4
5.
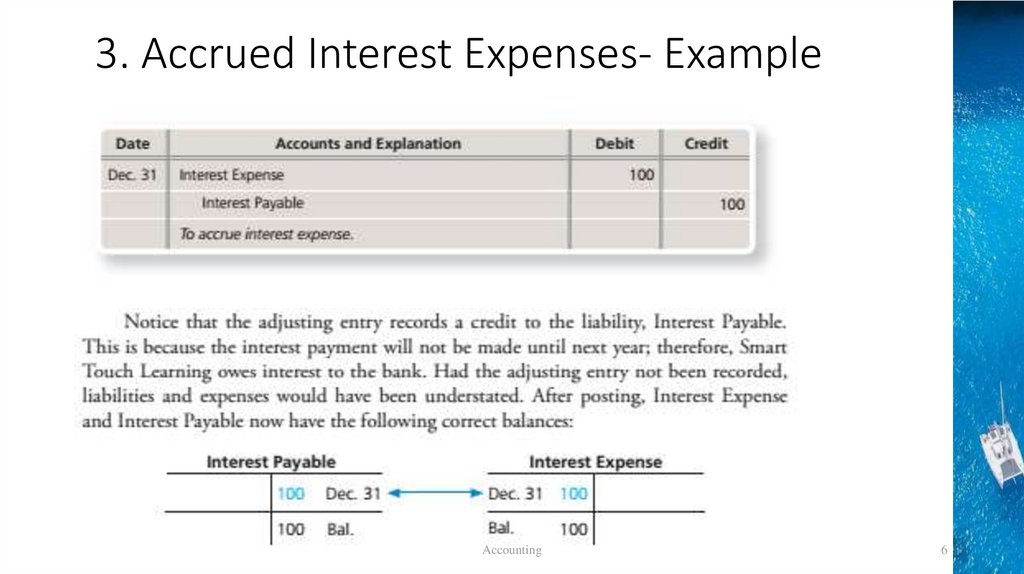
3. Accrued Interest Expenses- Example• On December 1, the company purchased of $60,000 building for a
note payable with the bank. In contract, interest on this note,$1200,
is payable one year later, on December 1,2020.
• The company must record the amount of interest expense that has
been incurred by December 31,2019.
Date
Dec. 1
Accounts and Explanation
Building
Note Payable
purchase of building with note
Date
Accounts and Explanation
Dec. 31 Interest Expense
Interest Payable
To accrue interest expense. Accounting
Debit
60,000
Credit
60,000
Debit
100
Credit
100
5
6.
3. Accrued Interest Expenses- ExampleAccounting
6
7.
3. Accrued ExpensesAccounting
7
8.
3. Accrued ExpensesAccounting
8
9.
Accrual: Accrued Revenue1. Prepaid Expenses – A
• Prepaid expenses are assets until used
2. Unearned Revenue – L
• received cash before it does the work
3. Accrued Expenses – L
• Incurred expenses before paying for
them. It always create a related
liability.
4. Accrued Revenues – A
• Earned revenue before we
receive the cash.
• Recognize R and A
Accounting
9
10.
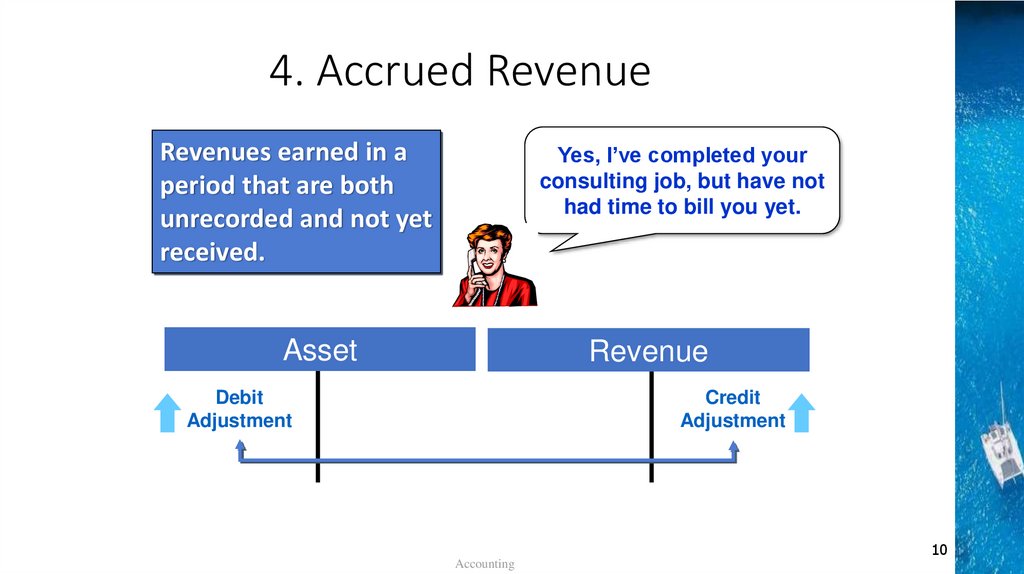
4. Accrued RevenueRevenues earned in a
period that are both
unrecorded and not yet
received.
Yes, I’ve completed your
consulting job, but have not
had time to bill you yet.
Asset
Revenue
Debit
Adjustment
Credit
Adjustment
10
Accounting
11.
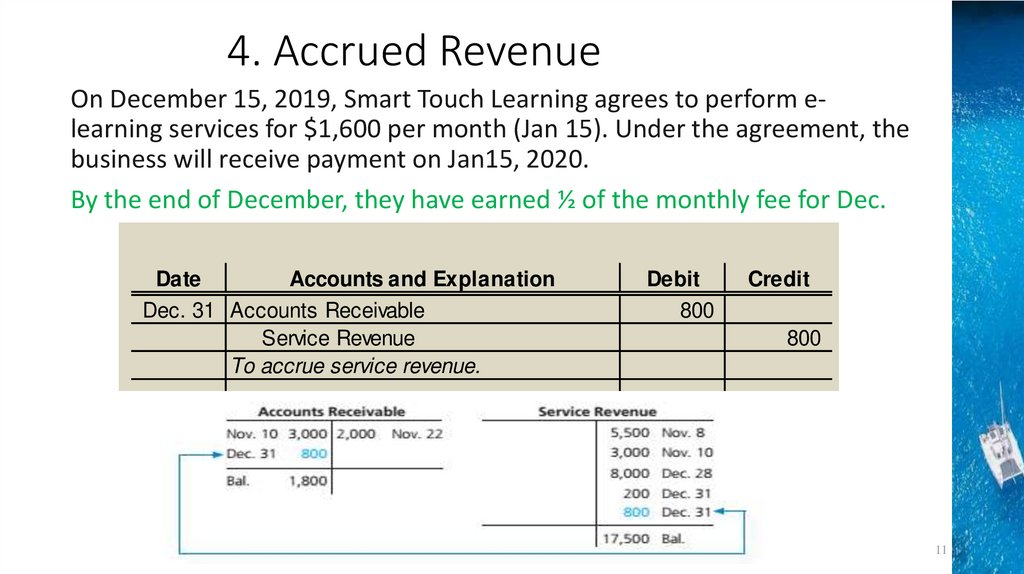
4. Accrued RevenueOn December 15, 2019, Smart Touch Learning agrees to perform elearning services for $1,600 per month (Jan 15). Under the agreement, the
business will receive payment on Jan15, 2020.
By the end of December, they have earned ½ of the monthly fee for Dec.
Date
Accounts and Explanation
Dec. 31 Accounts Receivable
Service Revenue
To accrue service revenue.
Accounting
Debit
800
Credit
800
11
12.
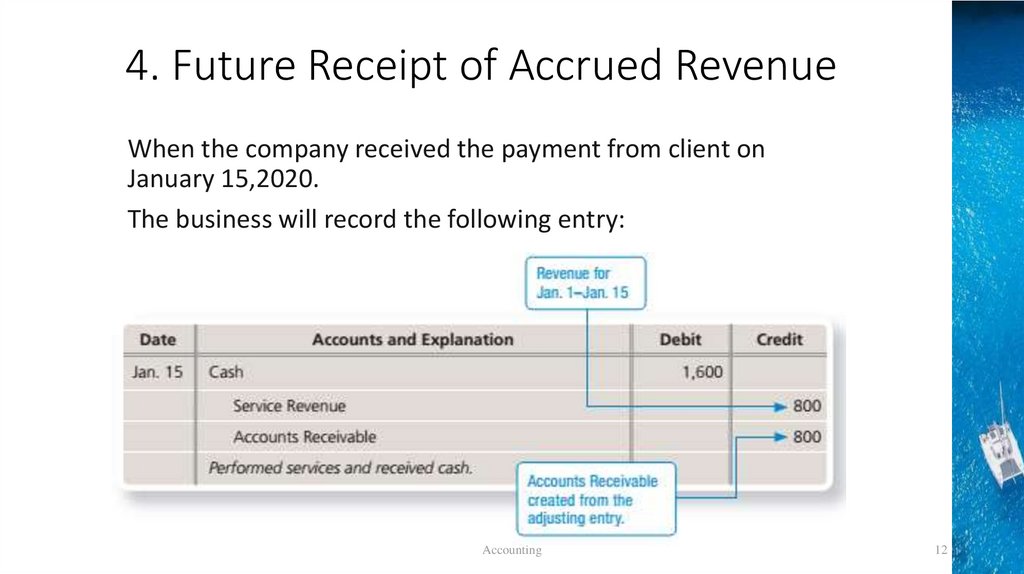
4. Future Receipt of Accrued RevenueWhen the company received the payment from client on
January 15,2020.
The business will record the following entry:
Accounting
12
13.
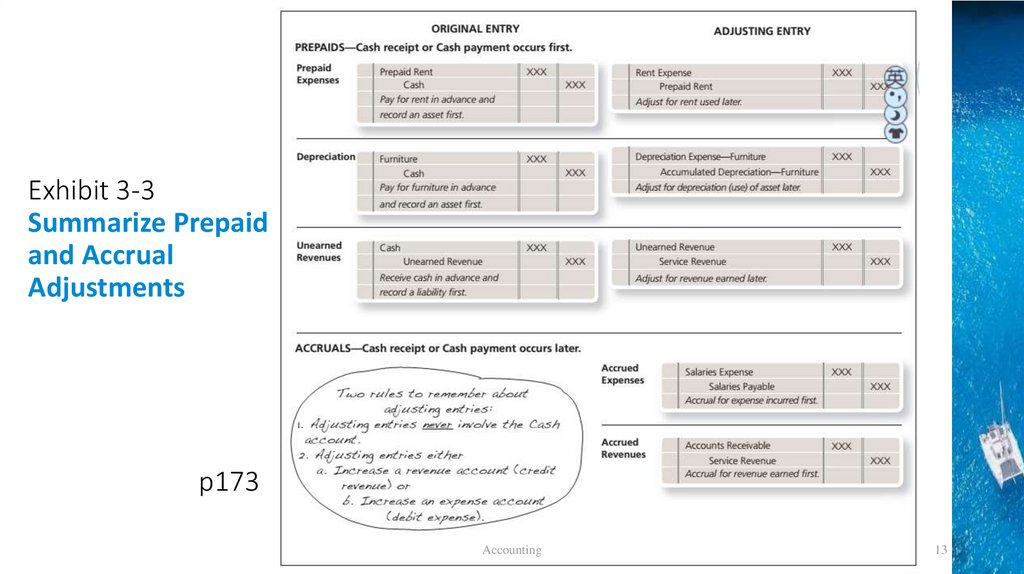
Exhibit 3-3Summarize Prepaid
and Accrual
Adjustments
p173
Accounting
13
14.
Try it Questionp176
SS Services had the following adjustments as of the end of the
year.
a.Equipment depreciation was $1,500.
b.$700 of advertising expense was incurred but not paid.( use advertising
payable)
c.Office supplies on hand at the end of the year totaled $250. the
beginning balance of office supplies was $600.
d.$1,200 of rent revenue was earned but not recorded or received.
e.Unearned revenue of $3,000 has been earned.
1. For each situation, indicate which category of adjustment is
described.
2. Journalize the adjustment entry needed.
Accounting
14
15.
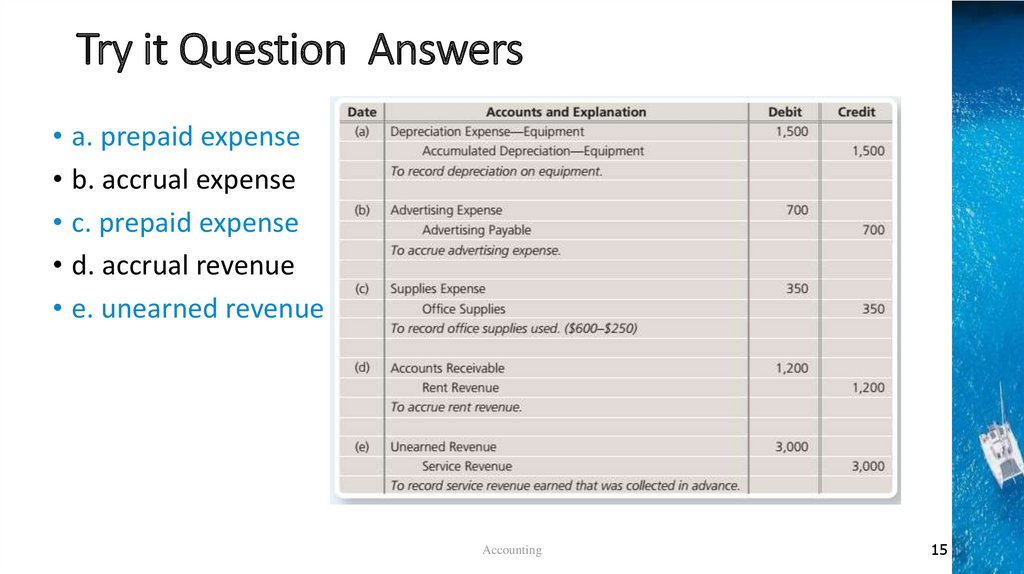
Try it Question Answers• a. prepaid expense
• b. accrual expense
• c. prepaid expense
• d. accrual revenue
• e. unearned revenue
Accounting
15
16.
Accounting16
17.
Accounting17
18.
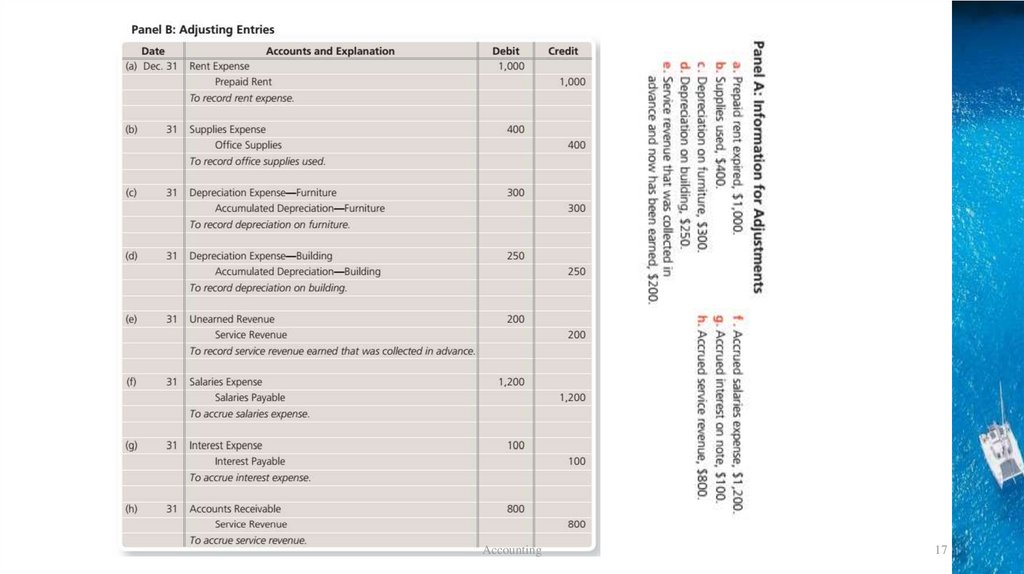
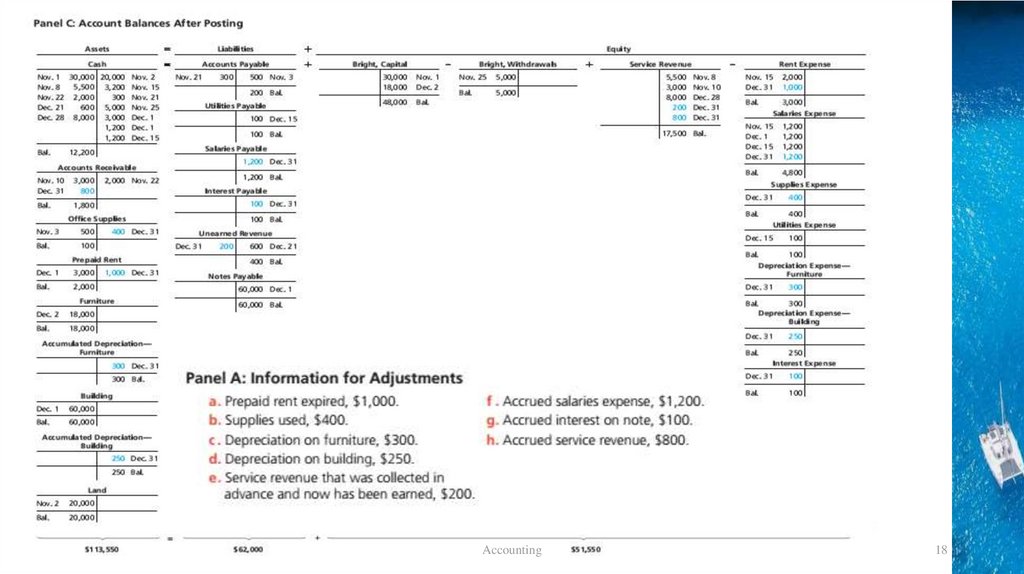
截图p175CAccounting
18
19.
Learning Objective 4Explain the purpose of and
prepare an adjusted trial
balance
Accounting
19
20.
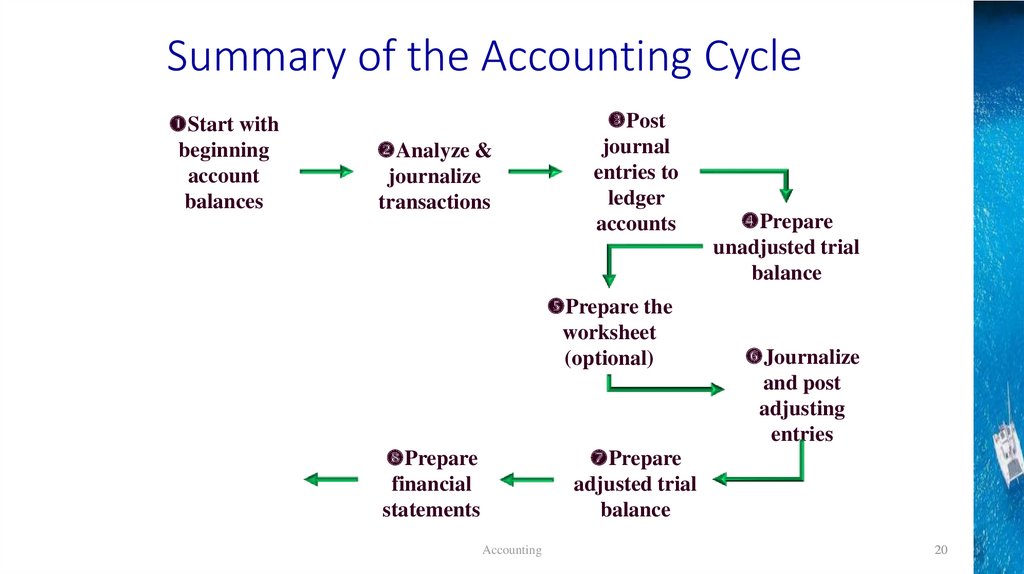
Summary of the Accounting CycleStart with
beginning
account
balances
Analyze &
journalize
transactions
Post
journal
entries to
ledger
accounts
Prepare the
worksheet
(optional)
Prepare
financial
statements
Prepare
unadjusted trial
balance
Journalize
and post
adjusting
entries
Prepare
adjusted trial
balance
Accounting
20
21.
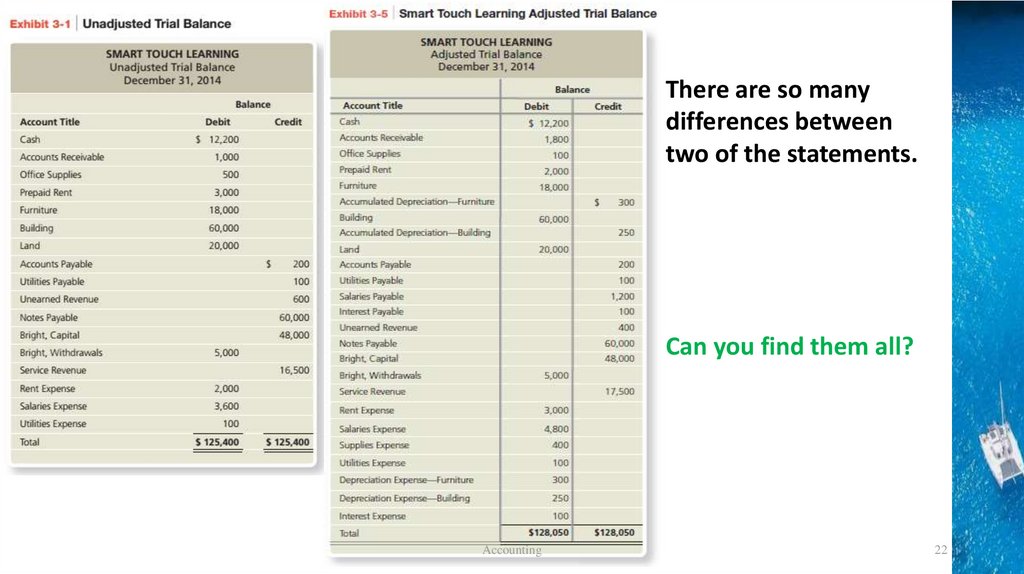
The Adjusted Trial Balance• After journalizing and posting all the adjusting journal
entries at the end of the fiscal period, a new adjusted
trial balance is prepared.
– List all accounts
– List debit balances in the debit column
– List credit balance in the credit column
• If it balances, financial statements can be prepared.
Accounting
21
22.
There are so manydifferences between
two of the statements.
Can you find them all?
Accounting
22
23.
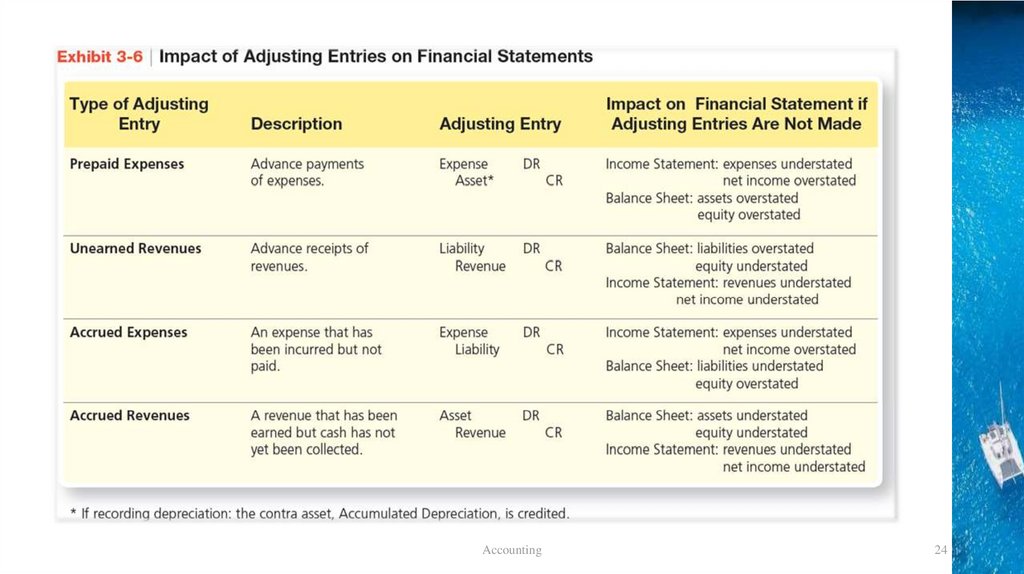
Learning Objective 5Identify the impact of
adjusting entries on the
financial statements
Accounting
23
24.
Accounting24
25.
Try it Questionp179
• Identify the impact on the income statement and balance
sheet if following adjusting entries were not recorded.
a.Office supplies used , $800.
b.Accrued service revenue,$4,000
c. Depreciation on building,$3,500.
d.Prepaid insurance expired,$650.
e.Accrued salaries expense,$2,750
f. Service revenue that was collected in advance has now been
earned,$130.
Accounting
25
26.
Try it Question AnswersAccounting
26
27.
Multiple Choices(more than one correct answers)
4 mins
$1200 of rent revenue was earned but not recorded or
received. Identify the impact on the financial
statement if adjusting entries for this situation were
not record.
A. Net income understated
B. Revenue overstated
C. Assets understated
D. Equity overstated
Accounting
27
28.
Learning Objective 6Explain the worksheet and
use it to prepare adjusting
entries and the adjusted
trial balance
P179-181
Accounting
28
29.
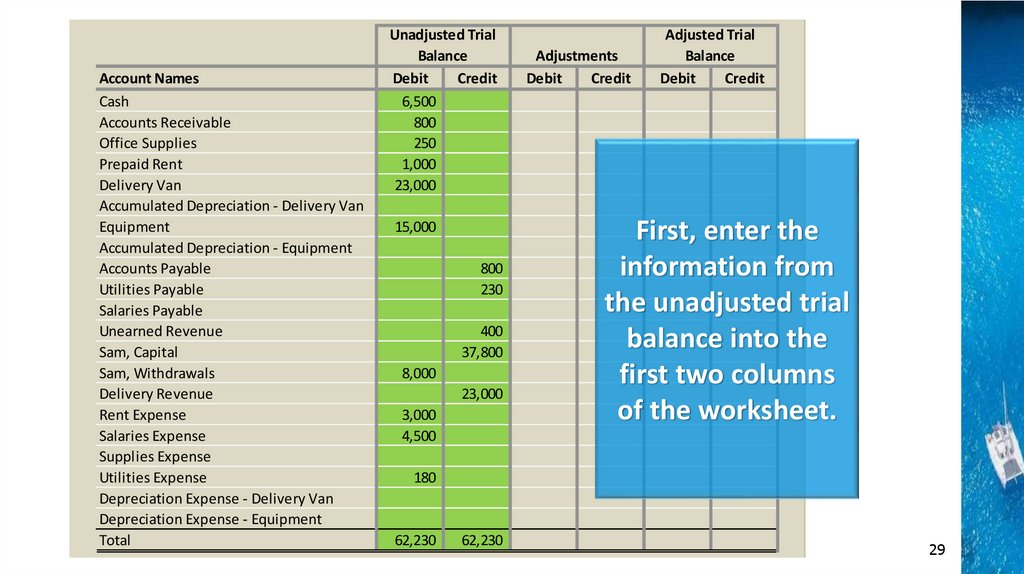
Account NamesCash
Accounts Receivable
Office Supplies
Prepaid Rent
Delivery Van
Accumulated Depreciation - Delivery Van
Equipment
Accumulated Depreciation - Equipment
Accounts Payable
Utilities Payable
Salaries Payable
Unearned Revenue
Sam, Capital
Sam, Withdrawals
Delivery Revenue
Rent Expense
Salaries Expense
Supplies Expense
Utilities Expense
Depreciation Expense - Delivery Van
Depreciation Expense - Equipment
Total
3-29
Unadjusted Trial
Balance
Debit
Credit
6,500
800
250
1,000
23,000
Adjustments
Debit
Credit
15,000
800
230
400
37,800
8,000
23,000
3,000
4,500
Adjusted Trial
Balance
Debit
Credit
First, enter the
information from
the unadjusted trial
balance into the
first two columns
of the worksheet.
180
62,230
62,230
Accounting
29
30.
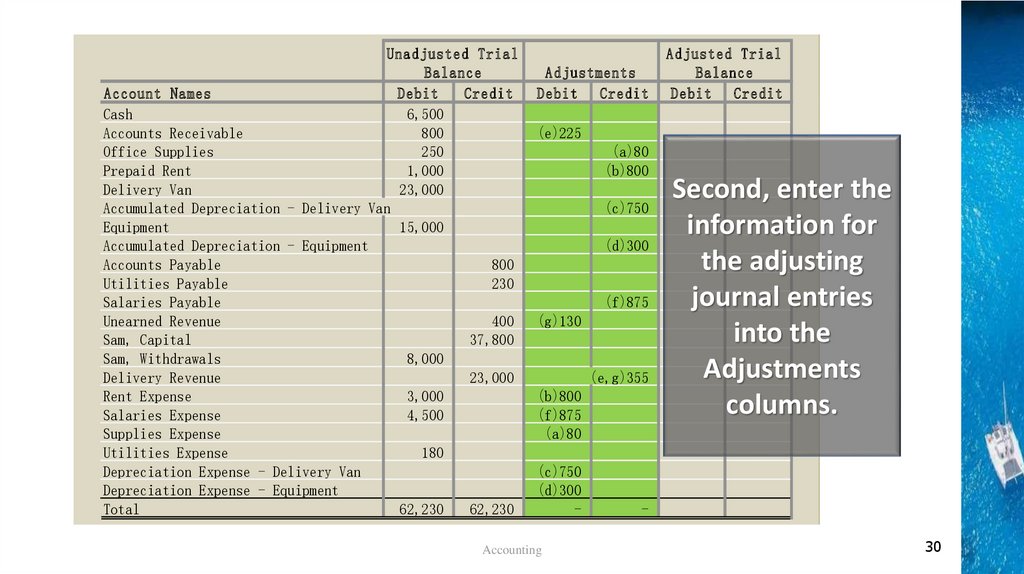
Unadjusted TrialBalance
Account Names
Debit
Credit
Cash
6,500
Accounts Receivable
800
Office Supplies
250
Prepaid Rent
1,000
Delivery Van
23,000
Accumulated Depreciation - Delivery Van
Equipment
15,000
Accumulated Depreciation - Equipment
Accounts Payable
800
Utilities Payable
230
Salaries Payable
Unearned Revenue
400
Sam, Capital
37,800
Sam, Withdrawals
8,000
Delivery Revenue
23,000
Rent Expense
3,000
Salaries Expense
4,500
Supplies Expense
Utilities Expense
180
Depreciation Expense - Delivery Van
Depreciation Expense - Equipment
Total
62,230
62,230
Adjustments
Debit Credit
Adjusted Trial
Balance
Debit Credit
(e)225
(a)80
(b)800
(c)750
(d)300
(f)875
(g)130
(e,g)355
(b)800
(f)875
(a)80
(c)750
(d)300
-
Accounting
Second, enter the
information for
the adjusting
journal entries
into the
Adjustments
columns.
30
31.
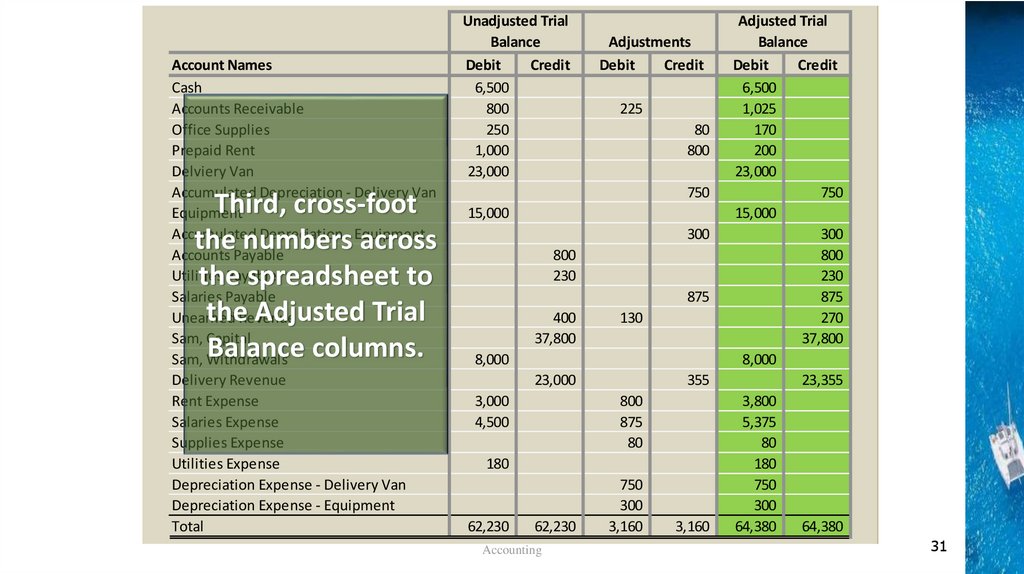
Account NamesCash
Accounts Receivable
Office Supplies
Prepaid Rent
Delviery Van
Accumulated Depreciation - Delivery Van
Equipment
Accumulated Depreciation - Equipment
Accounts Payable
Utilities Payable
Salaries Payable
Unearned Revenue
Sam, Capital
Sam, Withdrawals
Delivery Revenue
Rent Expense
Salaries Expense
Supplies Expense
Utilities Expense
Depreciation Expense - Delivery Van
Depreciation Expense - Equipment
Total
Third, cross-foot
the numbers across
the spreadsheet to
the Adjusted Trial
Balance columns.
Unadjusted Trial
Balance
Debit
Credit
6,500
800
250
1,000
23,000
Adjustments
Debit
Credit
225
80
800
750
15,000
300
800
230
875
400
37,800
130
8,000
23,000
3,000
4,500
355
800
875
80
180
62,230
62,230
Accounting
750
300
3,160
3,160
Adjusted Trial
Balance
Debit
Credit
6,500
1,025
170
200
23,000
750
15,000
300
800
230
875
270
37,800
8,000
23,355
3,800
5,375
80
180
750
300
64,380
64,380
31
32.
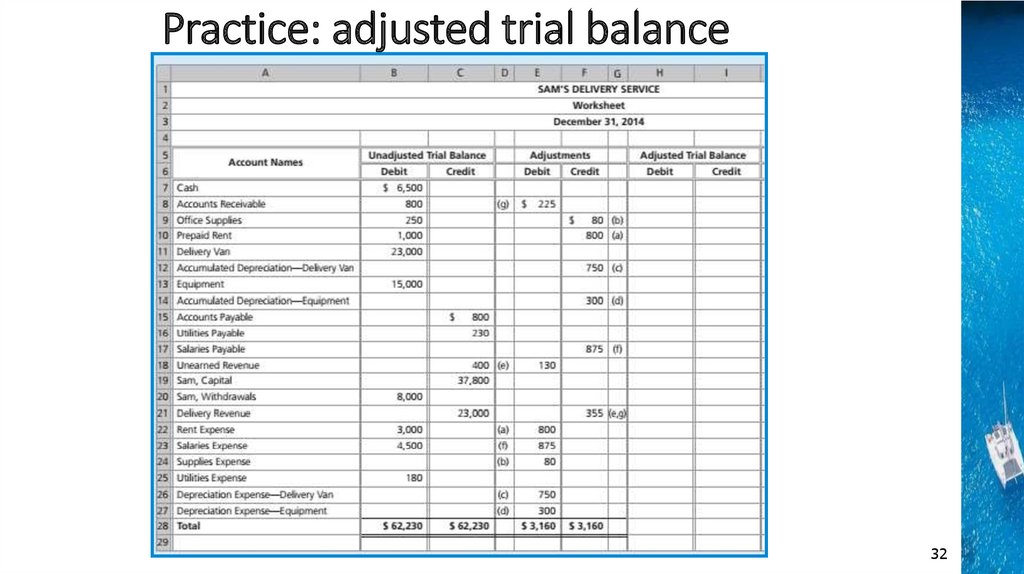
Practice: adjusted trial balanceAccounting
32
33.
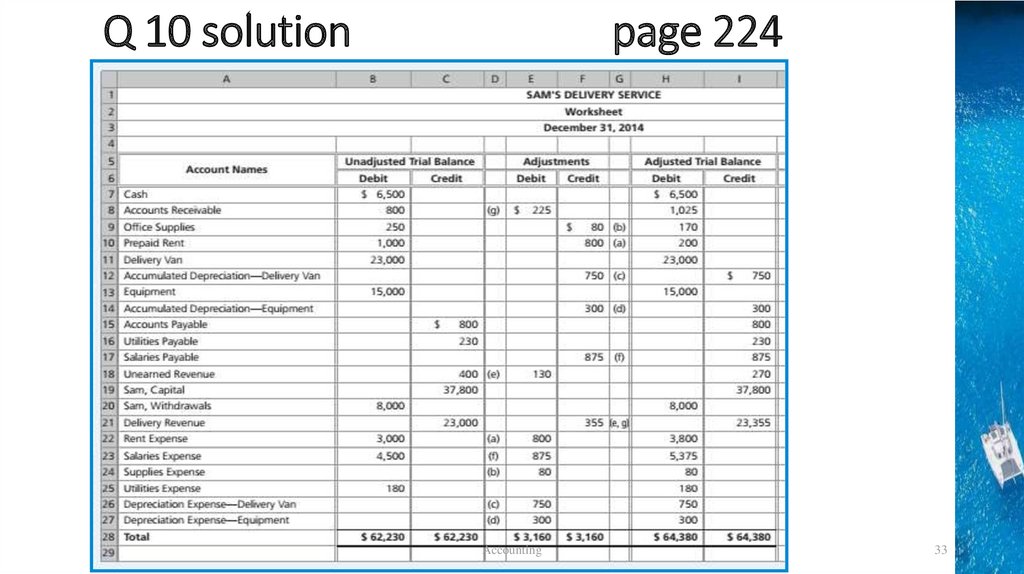
Q 10 solutionpage 224
Accounting
33
34.
Multiple Choices2mins
An internal document that helps summarize data for the
preparation of financial statements is called a:
A.
B.
C.
D.
ledger.
journal.
worksheet.
chart of accounts.
© 2015 Pearson Education, Limited.
34
35.
Multiple Choices2mins
An internal document that helps summarize data for the
preparation of financial statements is called a:
A.
B.
C.
D.
ledger.
journal.
worksheet.
chart of accounts.
© 2015 Pearson Education, Limited.
35
36.
Multiple Choices2mins
The adjusted trial balance shows:
A. amounts that are out of balance and ways to rectify
them.
B. amounts that are to be used to prepare the financial
statements.
C. amounts of assets and liabilities only.
D. amounts of revenues and expenses only.
© 2015 Pearson Education, Limited.
36
37.
Multiple Choices2mins
The adjusted trial balance shows:
A. amounts that are out of balance and ways to rectify
them.
B. amounts that are to be used to prepare the financial
statements.
C. amounts of assets and liabilities only.
D. amounts of revenues and expenses only.
© 2015 Pearson Education, Limited.
37
38.
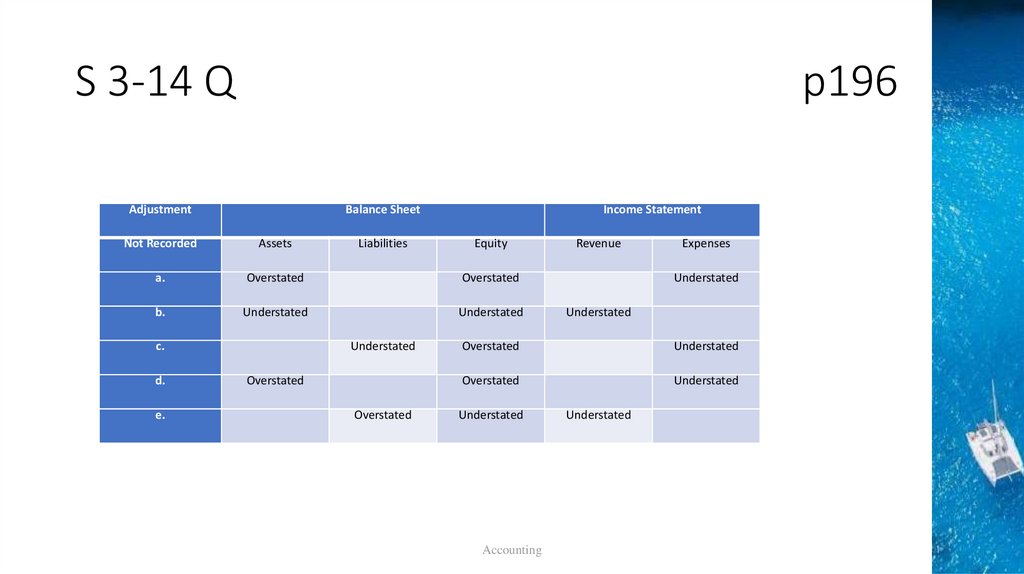
S 3-14 Qp196
Accounting
38
39.
S 3-14 Qp196
Adjustment
Balance Sheet
Not Recorded
Assets
a.
Overstated
Overstated
b.
Understated
Understated
c.
d.
e.
Liabilities
Income Statement
Understated
Overstated
Overstated
Equity
Revenue
Expenses
Understated
Understated
Overstated
Understated
Overstated
Understated
Understated
Accounting
Understated
39
40.
Unit Assessment Task• Homework
30%
- three times, each time account for 10%
• Final Individual Assignment
70%
- accounting cases
More than 60% of total marks will pass
Accounting
40
40
41.
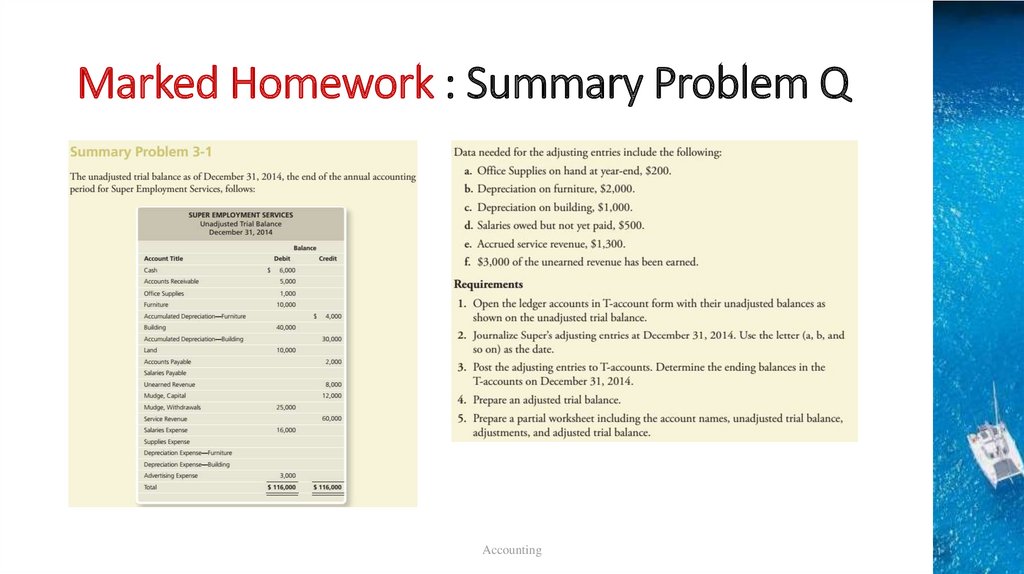
Marked Homework : Summary Problem QAccounting
41
42.
Enjoy yourSpring Break !
See you
th
on May 12 !
Accounting
42























 finance
finance








