Similar presentations:
Accounting Cycle
1.
Ho rn gren ’sAc co u ntin g
Lecture Ten
Lisa, Li
Accounting
1
2.
Learning Objectives – Chapter 41. Prepare the financial statements including the
classified balance sheet
2. Use the worksheet to prepare financial
statements
3. Explain the purpose of, journalize, and postclosing entries
Accounting
2
3.
Learning Objectives – Chapter 44. Prepare the post-closing trial balance
5. Describe the accounting cycle
6. Use the current ratio to evaluate business
performance
Accounting
3
4.
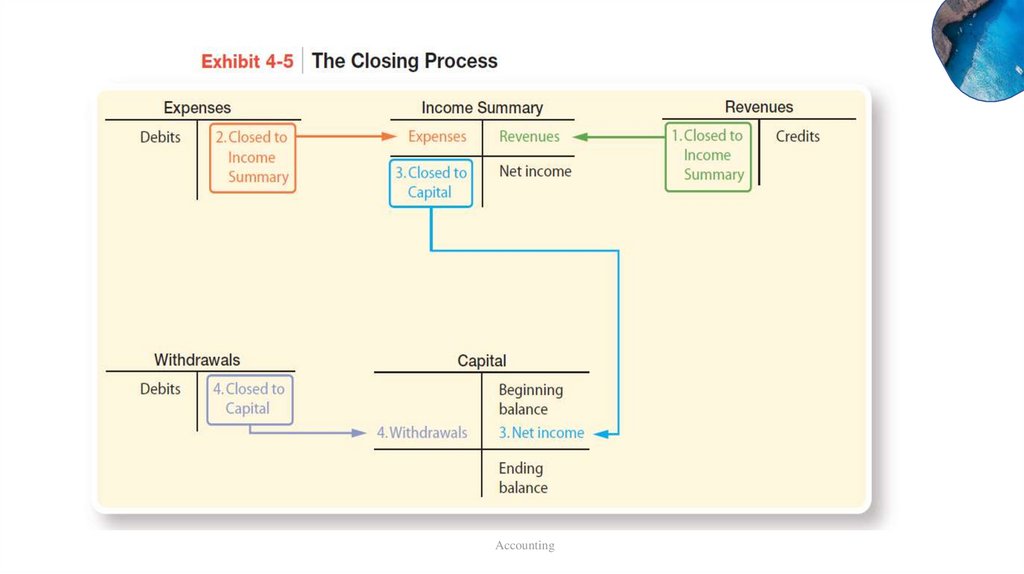
Review: Closing Process• Resets revenue, expense and
withdrawal account balances to
zero at the end of the period.
Identify accounts
for closing.
• Helps summarize a period’s
revenues and expenses in the
Income Summary account.
Record and post
closing entries.
• the process of closing the books
and getting ready for the next
accounting period.
Prepare post-closing
trial balance.
Accounting
5.
Accounting6.
Review: HomeworkAccounting
7.
Homework SolutionsMEL’S BOWLING ALLEY
Post-Closing Trial Balance
December 31, 2014
Date
Dec. 31
Accounts and Explanation
Service Revenue
Income Summary
To close revenue.
Debit
94,000
Credit
94,000
Account Title
Debit
Cash
31
Income Summary
Insurance Expense
Salaries Expense
Supplies Expense
Utilities Expense
Depreciation Expense—Equipment
Depreciated Expense—Building
To close expenses.
Balance
70,525
Accounts Receivable
20,000
36,000
800
12,000
1,500
225
Office Supplies
Prepaid Insurance
Equipment
$ 15,400
2,310
450
2,300
40,000
Accumulated Depreciation—Equipment
Building
$ 12,000
75,000
Accumulated Depreciation—Building
31
31
Income Summary
Turner, Capital
To close Income Summary.
Turner, Capital
Turner, Withdrawals
To close withdrawals.
23,475
Land
23,475
28,000
28,000
4,500
15,000
Accounts Payable
3,400
Utilities Payable
620
Salaries Payable
2,840
Unearned Revenue
1,300
Turner, Capital
Current Ratio = Total current assets / Total current liabilities
Total
= ($15,400 + $2,310 + $450 + $2,300) / ($3,400 + $620 + $2,840 + $1,300)
= $20,460 / $8,160 = 2.51
Accounting
Credit
125,800
$ 150,460
$ 150,460
7
8.
Review: Current Ratio•The most commonly used ratio is the Current Ratio.
•It is a measure of the company’s ability to quickly pay its debts.
•A company prefers to have a high current ratio because that means
it has plenty of current assets to pay its current liabilities.
A rule of thumb: A strong current ratio is 1.50,
A current ratio of 1.00 is considered low and somewhat risky.
Accounting
8
9.
Learning Objective 1Prepare the financial
statements including the
classified balance sheet
Accounting
9
10.
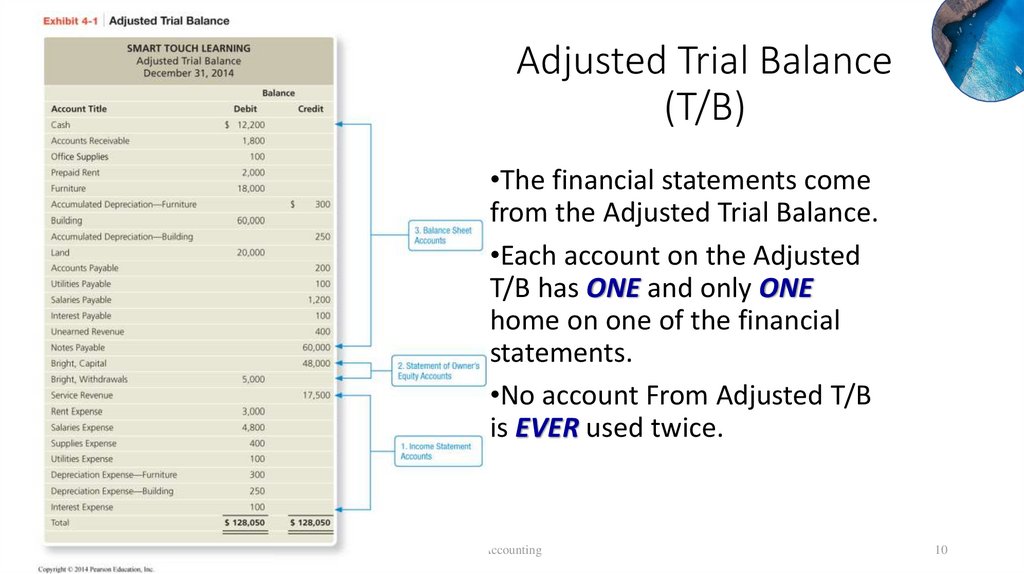
Adjusted Trial Balance(T/B)
•The financial statements come
from the Adjusted Trial Balance.
•Each account on the Adjusted
T/B has ONE and only ONE
home on one of the financial
statements.
•No account From Adjusted T/B
is EVER used twice.
Accounting
10
11.
How do we prepare Financial Statements?The financial statements should be prepared in the
following order:
1.Income statement —reports revenues and expenses
and calculates net income or net loss for the time
period.
2.Statement of owner’s equity —shows how capital
changed during the period due to owner contributions,
net income (or net loss), and owner withdrawals.
3.Balance sheet —reports assets, liabilities, and owner’s
equity as of the last day of the period.
Accounting
11
12.
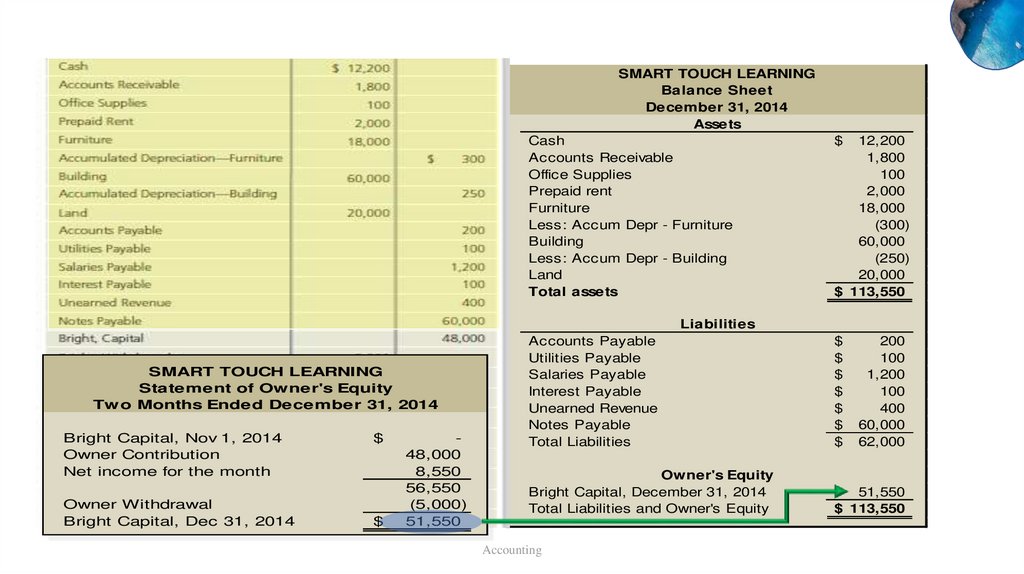
SMART TOUCH LEARNINGIncome Statement
Two Months Ended December 31, 2014
Revenues
Service Revenue
$ 17,500
Expenses
Rent Expense
$ 3,000
Salaries Expense
4,800
Supplies Expense
400
Utilities Expense
100
Depr Exp - Furniture
300
Depr Exp - Building
250
Interest Expense
100
Total expenses
8,950
Net income
$ 8,550
Income Statement Amounts
Accounting
12
13.
SMART TOUCH LEARNINGIncome Statement
Two Months Ended December 31, 2014
Revenues
Service Revenue
$ 17,500
Expenses
Rent Expense
$ 3,000
Salaries Expense
4,800
Supplies Expense
400
Utilities Expense
100
Depr Exp - Furniture
300
Depr Exp - Building
250
Interest Expense
100
Total expenses
8,950
Net income
$ 8,550
SMART TOUCH LEARNING
Statement of Owner's Equity
Two Months Ended December 31, 2014
Bright Capital, Nov 1, 2014
Owner Contribution
Net income for the month
Owner Withdrawal
Bright Capital, Dec 31, 2014
Accounting
$
$
48,000
8,550
56,550
(5,000)
51,550
13
14.
SMART TOUCH LEARNINGBalance Sheet
December 31, 2014
Assets
Cash
Accounts Receivable
Office Supplies
Prepaid rent
Furniture
Less: Accum Depr - Furniture
Building
Less: Accum Depr - Building
Land
Total assets
$
12,200
1,800
100
2,000
18,000
(300)
60,000
(250)
20,000
$ 113,550
Liabilities
SMART TOUCH LEARNING
Statement of Owner's Equity
Two Months Ended December 31, 2014
Bright Capital, Nov 1, 2014
Owner Contribution
Net income for the month
Owner Withdrawal
Bright Capital, Dec 31, 2014
$
$
48,000
8,550
56,550
(5,000)
51,550
Accounts Payable
Utilities Payable
Salaries Payable
Interest Payable
Unearned Revenue
Notes Payable
Total Liabilities
$
$
$
$
$
$
$
Owner's Equity
Bright Capital, December 31, 2014
Total Liabilities and Owner's Equity
51,550
$ 113,550
Accounting
200
100
1,200
100
400
60,000
62,000
15.
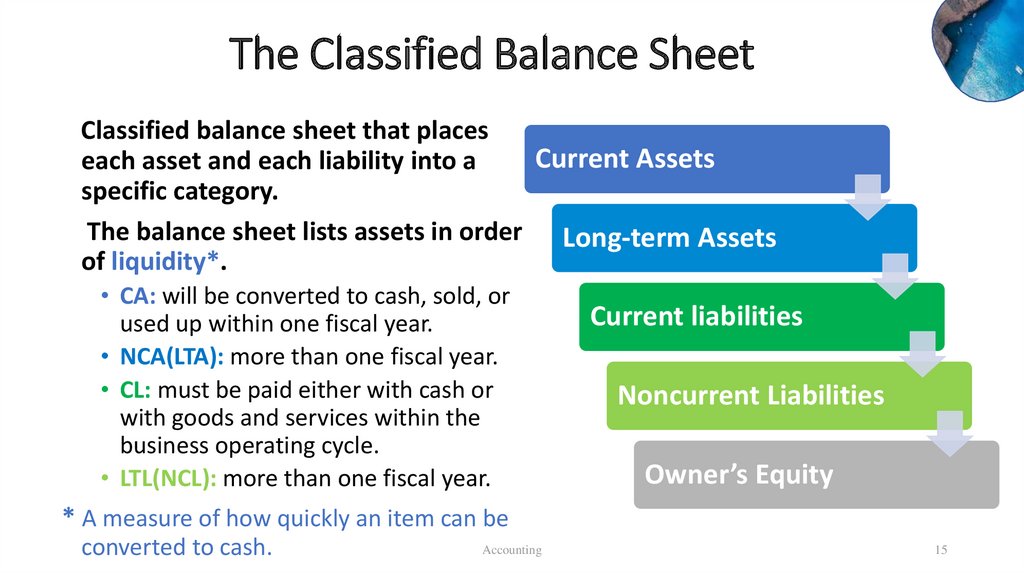
The Classified Balance SheetClassified balance sheet that places
Current Assets
each asset and each liability into a
specific category.
The balance sheet lists assets in order Long-term Assets
of liquidity*.
• CA: will be converted to cash, sold, or
used up within one fiscal year.
• NCA(LTA): more than one fiscal year.
• CL: must be paid either with cash or
with goods and services within the
business operating cycle.
• LTL(NCL): more than one fiscal year.
Current liabilities
Noncurrent Liabilities
Owner’s Equity
* A measure of how quickly an item can be
converted to cash.
Accounting
15
16.
SMART TOUCH LEARNINGBalance Sheet
December 31, 2014
Assets
Current Assets:
Cash
Accounts Receivable
Office Supplies
Prepaid rent
Total Current Assets
Plant Assets:
Furniture
Less: Accum Depr - Furniture
Building
Less: Accum Depr - Building
Land
Total Plant Assets
Total assets
The Classified
Balance Sheet
$
12,200
1,800
100
2,000
16,100
18,000
(300)
60,000
(250)
20,000
97,450
$ 113,550
Liabilities
Current Liabilities:
Accounts Payable
Utilities Payable
Salaries Payable
Interest Payable
Unearned Revenue
Total Current Assets
Long-term Liabilities
Notes Payable
Total Liabilities
Owner's Equity
Bright, Capital, Dec. 31, 2014
Total Liabilities & Owner's Equity
Accounting
$
200
100
1,200
100
400
2,000
60,000
62,000
51,550
$ 113,550
16
17.
SMART TOUCH LEARNINGBalance Sheet
December 31, 2014
Assets
Current Assets:
Cash
Accounts Receivable
Office Supplies
Prepaid rent
Total Current Assets
Plant Assets:
Furniture
Less: Accum Depr - Furniture
Building
Less: Accum Depr - Building
Land
Total Plant Assets
Total assets
$
12,200
1,800
100
2,000
16,100
18,000
(300)
60,000
(250)
20,000
97,450
$ 113,550
• The Asset section is sub-divided
into current and long-term groups.
• Sometimes, there is also a subgrouping for plant assets
intangible assets and long-term
investments.
Liabilities
Current Liabilities:
Accounts Payable
Utilities Payable
Salaries Payable
Interest Payable
Unearned Revenue
Total Current Assets
Long-term Liabilities
Notes Payable
Total Liabilities
Owner's Equity
Bright, Capital, Dec. 31, 2014
Total Liabilities & Owner's Equity
Accounting
$
200
100
1,200
100
400
2,000
60,000
62,000
51,550
$ 113,550
17
18.
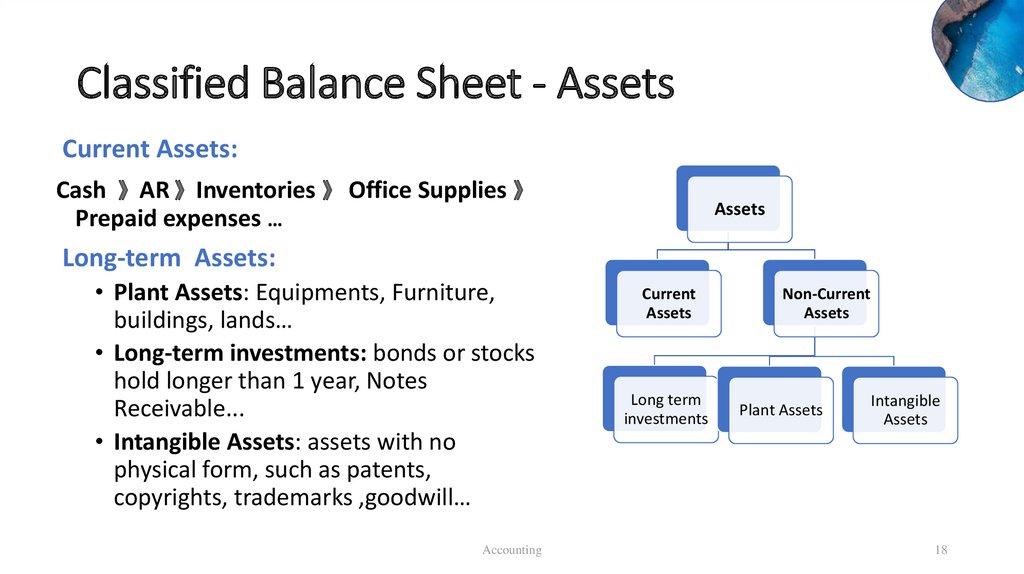
Classified Balance Sheet - AssetsCurrent Assets:
Cash 》AR 》Inventories 》 Office Supplies 》
Prepaid expenses …
Assets
Long-term Assets:
• Plant Assets: Equipments, Furniture,
buildings, lands…
• Long-term investments: bonds or stocks
hold longer than 1 year, Notes
Receivable...
• Intangible Assets: assets with no
physical form, such as patents,
copyrights, trademarks ,goodwill…
Accounting
Current
Assets
Long term
investments
Non-Current
Assets
Plant Assets
Intangible
Assets
18
19.
SMART TOUCH LEARNINGBalance Sheet
December 31, 2014
Assets
Current Assets:
Cash
Accounts Receivable
Office Supplies
Prepaid rent
Total Current Assets
Plant Assets:
Furniture
Less: Accum Depr - Furniture
Building
Less: Accum Depr - Building
Land
Total Plant Assets
Total assets
$
12,200
1,800
100
2,000
16,100
18,000
(300)
60,000
(250)
20,000
97,450
$ 113,550
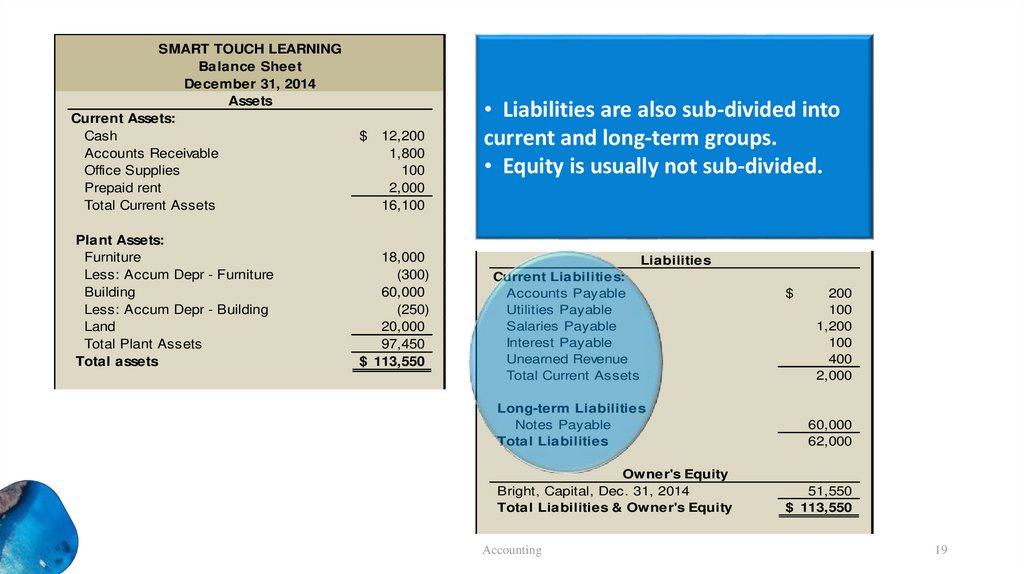
• Liabilities are also sub-divided into
current and long-term groups.
• Equity is usually not sub-divided.
Liabilities
Current Liabilities:
Accounts Payable
Utilities Payable
Salaries Payable
Interest Payable
Unearned Revenue
Total Current Assets
Long-term Liabilities
Notes Payable
Total Liabilities
Owner's Equity
Bright, Capital, Dec. 31, 2014
Total Liabilities & Owner's Equity
Accounting
$
200
100
1,200
100
400
2,000
60,000
62,000
51,550
$ 113,550
19
20.
Accounting20
21.
Accounting21
22.
Learning Objective 2Use the worksheet to prepare
financial statements
Accounting
22
23.
Accounting23
24.
Accounting24
25.
4-25Accounting
26.
Accounting26
27.
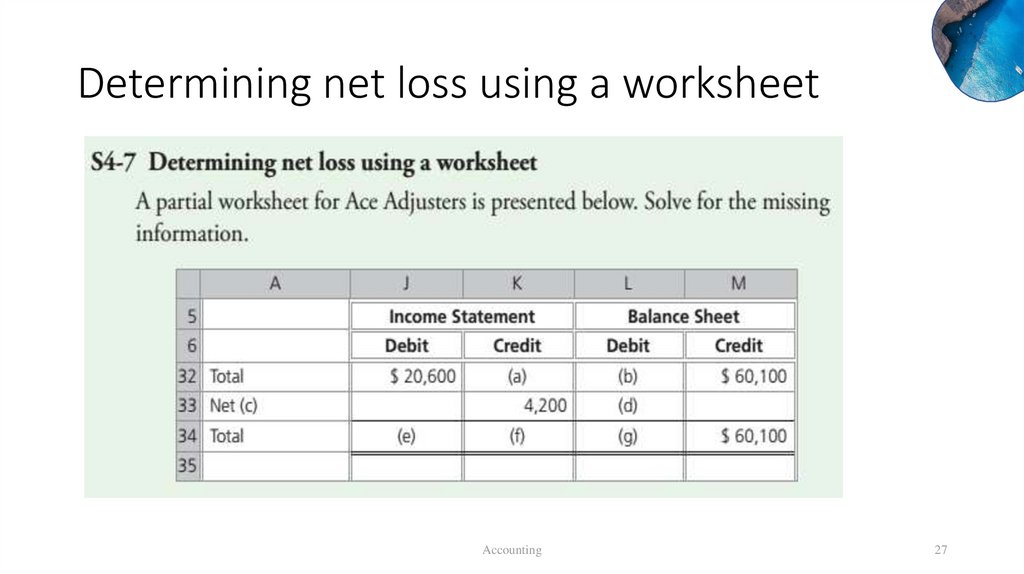
Determining net loss using a worksheetAccounting
27
28.
Determining net loss using a worksheeta. $16,400 ($20,600 – $4,200)
c. Loss
d. $4,200
f. $20,600 ($16,400 + $4,200)
b. $55,900 ($60,100 – $4,200)
e. $20,600
g. $60,100 ($55,900 + $4,200)
Accounting
28
29.
Learning Objective 5Describe the
accounting cycle
Accounting
30.
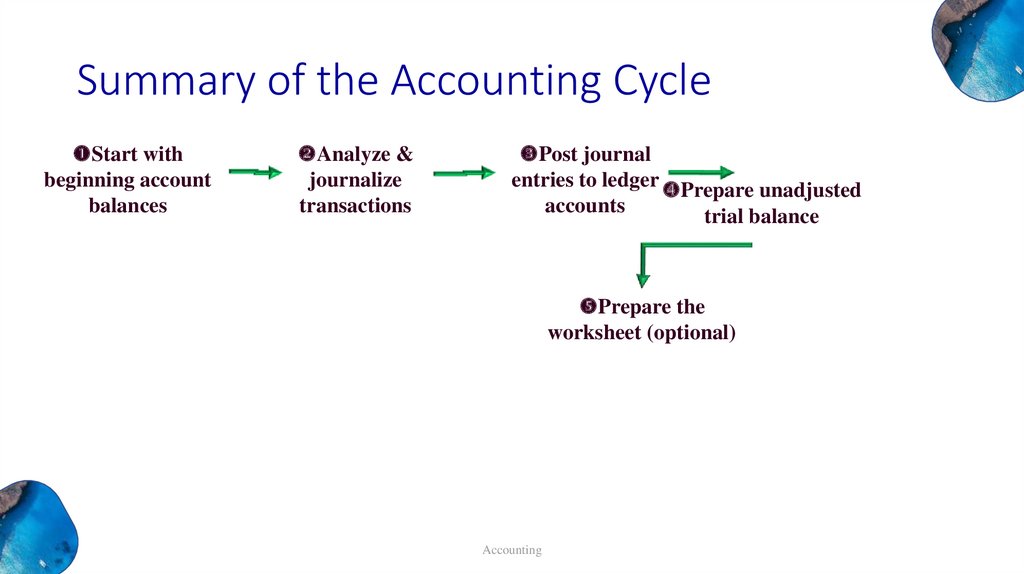
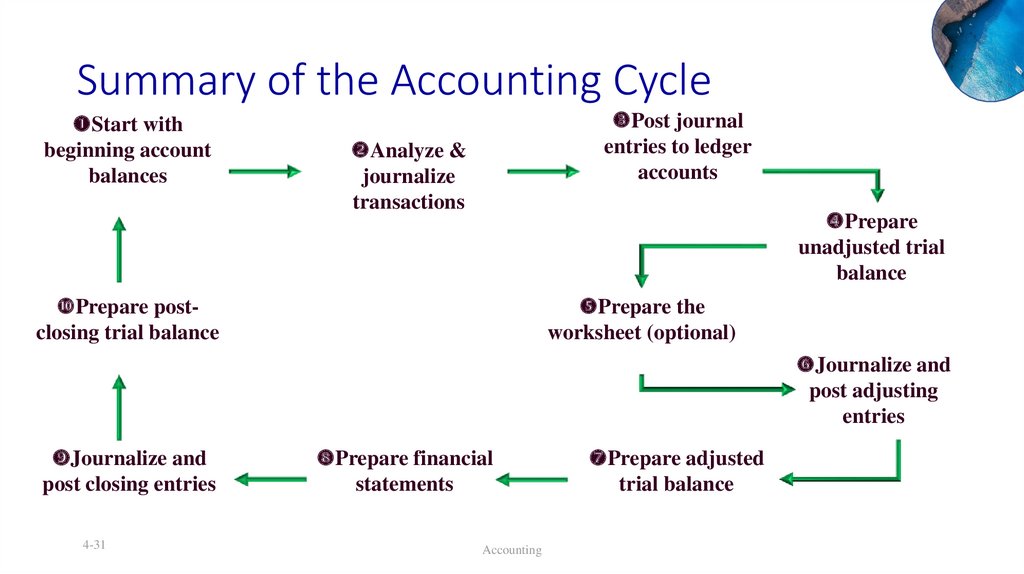
Summary of the Accounting CycleStart with
beginning account
balances
Analyze &
journalize
transactions
Post journal
entries to ledger Prepare unadjusted
accounts
trial balance
Prepare the
worksheet (optional)
Accounting
31.
Summary of the Accounting CycleStart with
beginning account
balances
Post journal
entries to ledger
accounts
Analyze &
journalize
transactions
Prepare
unadjusted trial
balance
Prepare postclosing trial balance
Prepare the
worksheet (optional)
Journalize and
post adjusting
entries
Journalize and
post closing entries
4-31
Prepare financial
statements
Accounting
Prepare adjusted
trial balance
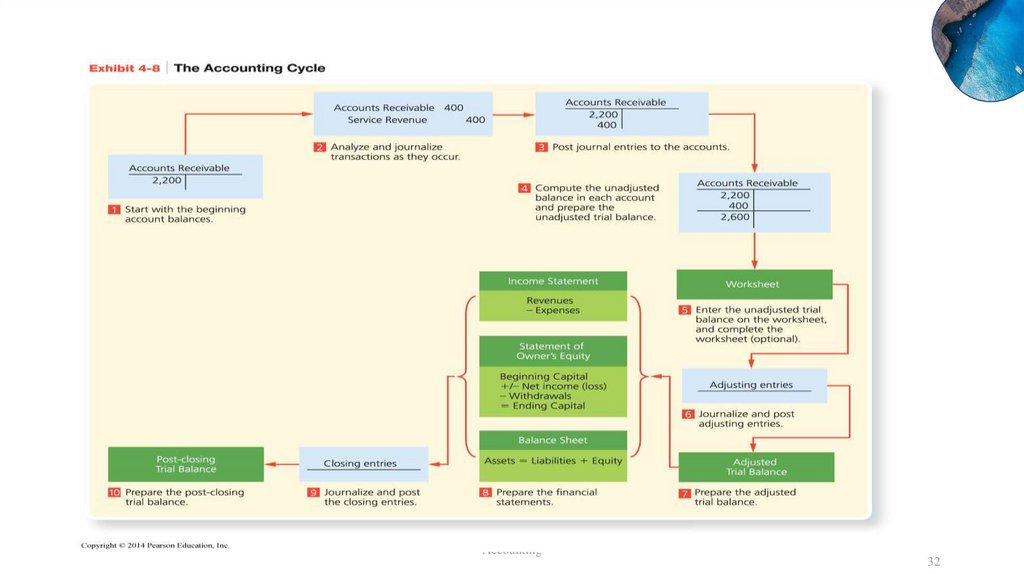
32.
Accounting32
33.
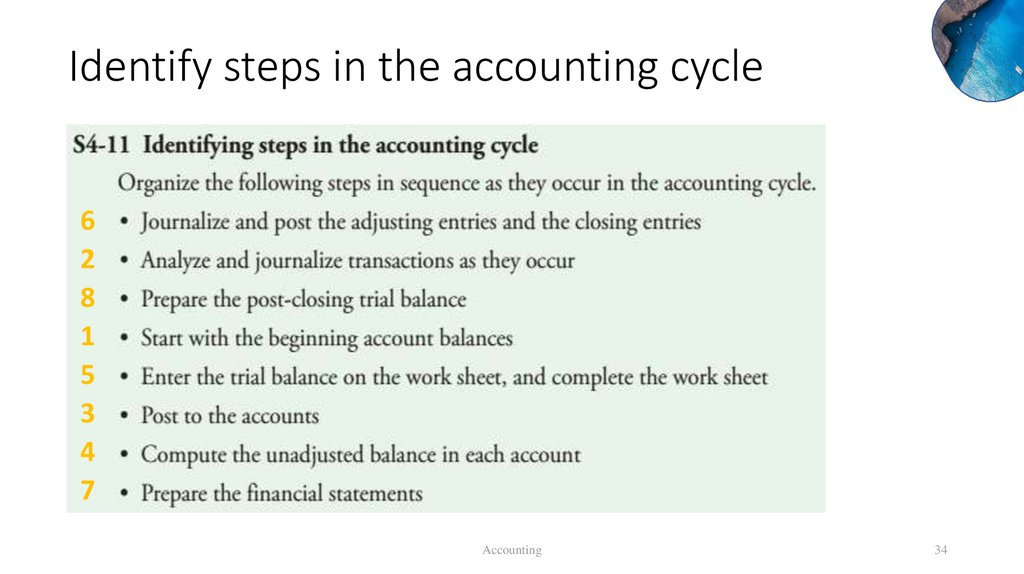
Identify steps in the accounting cycleAccounting
33
34.
Identify steps in the accounting cycle6
2
8
1
5
3
4
7
Accounting
34
35.
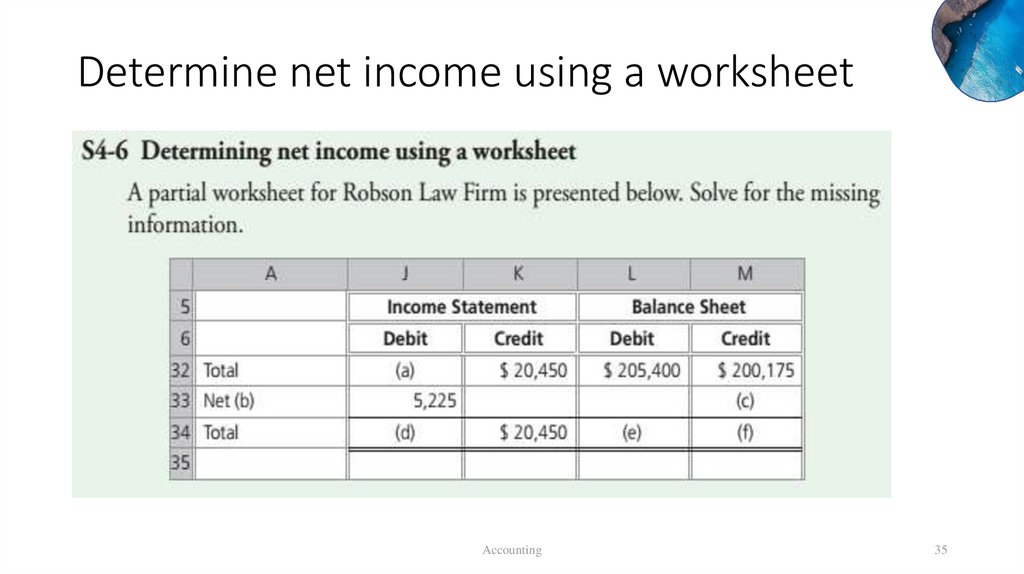
Determine net income using a worksheetAccounting
35
36.
Determine net income using a worksheeta. $15,225 ($20,450 – $5,225)
d. $20,450 ($15,225 + $5,225)
f. $205,400 ($200,175 + $5,225)
b. Income
e. $205,400
Accounting
c. $5,225
36
37.
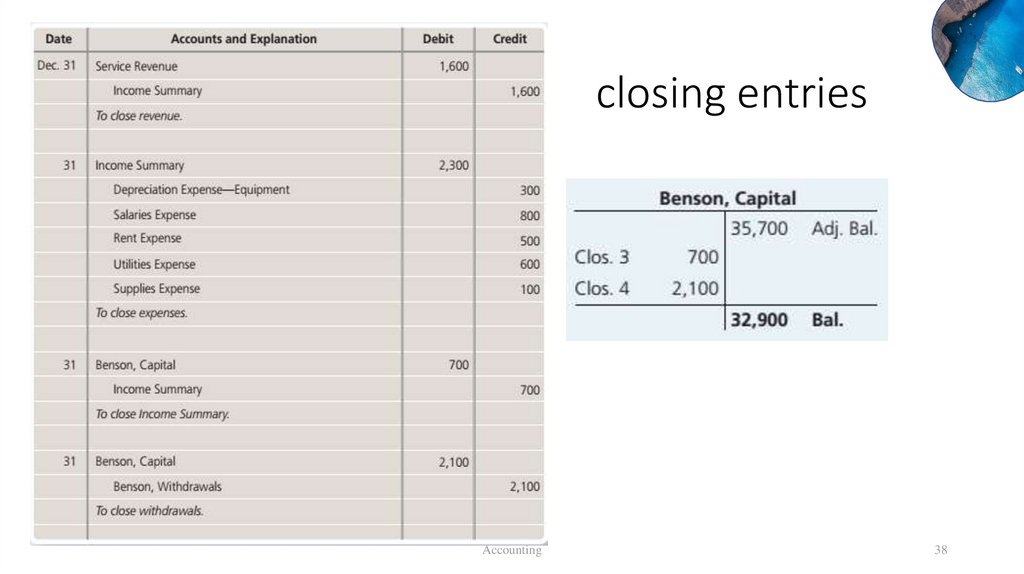
Practice closing entriesAccounting
37
38.
closing entriesAccounting
38
39.
Practice: Current RatioAccounting
39
40.
Current RatioAccounting
40
41.
Summary problemAccounting
41
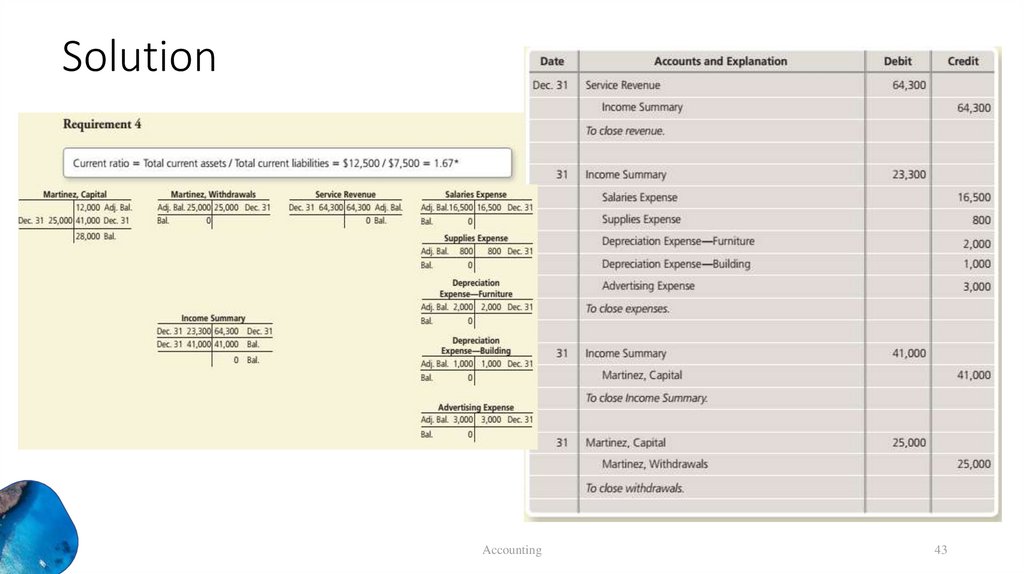
42.
SolutionAccounting
42
43.
SolutionAccounting
43






























 finance
finance








