Similar presentations:
Vascular anastomoses
1. Vascular anastomoses
Dashdamirova Nargiz 304 AHamitov Firat 403 Б
2.
• An anastomosis is theconnection of two
normally divergent
structures. It refers
especially to
connections
between blood vessels
3.
4. Types of vascular anastomoses
«End-to-End»«Side to end»
«Side to side»
5. «End-to-End»
6.
1 — Carrel's suture with three fixing threads2— Morozova's suture with two fixing threads
3 — Suture of Blalock and Polyantsev
7.
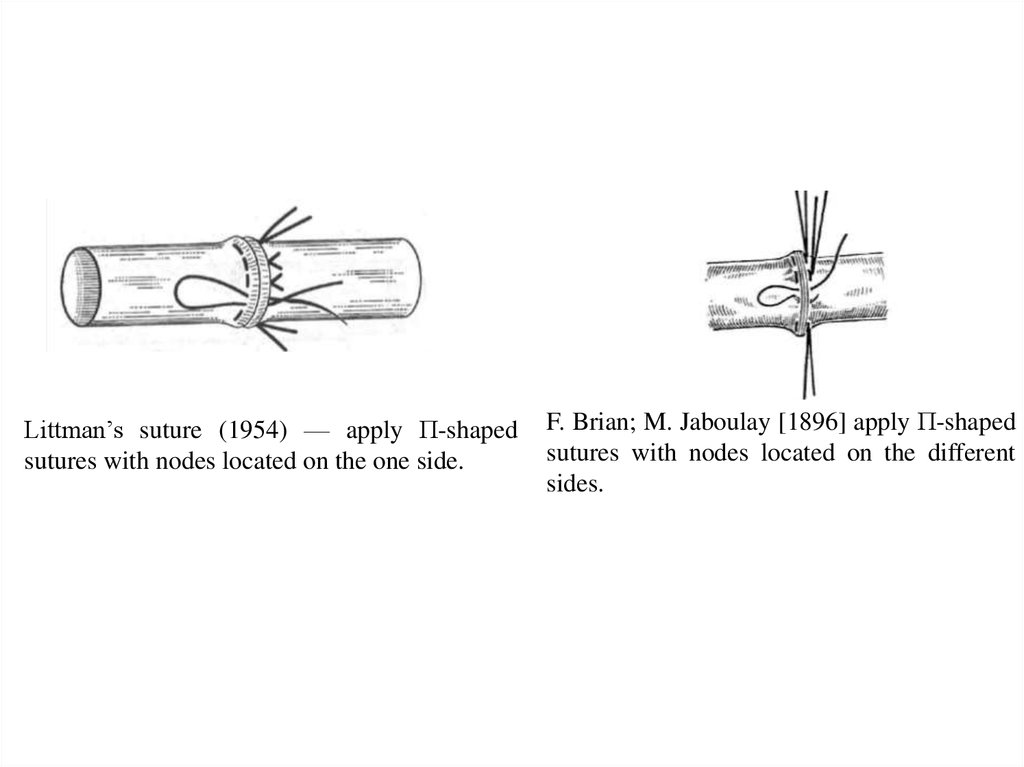
Littman’s suture (1954) — apply П-shapedsutures with nodes located on the one side.
F. Brian; M. Jaboulay [1896] apply П-shaped
sutures with nodes located on the different
sides.
8.
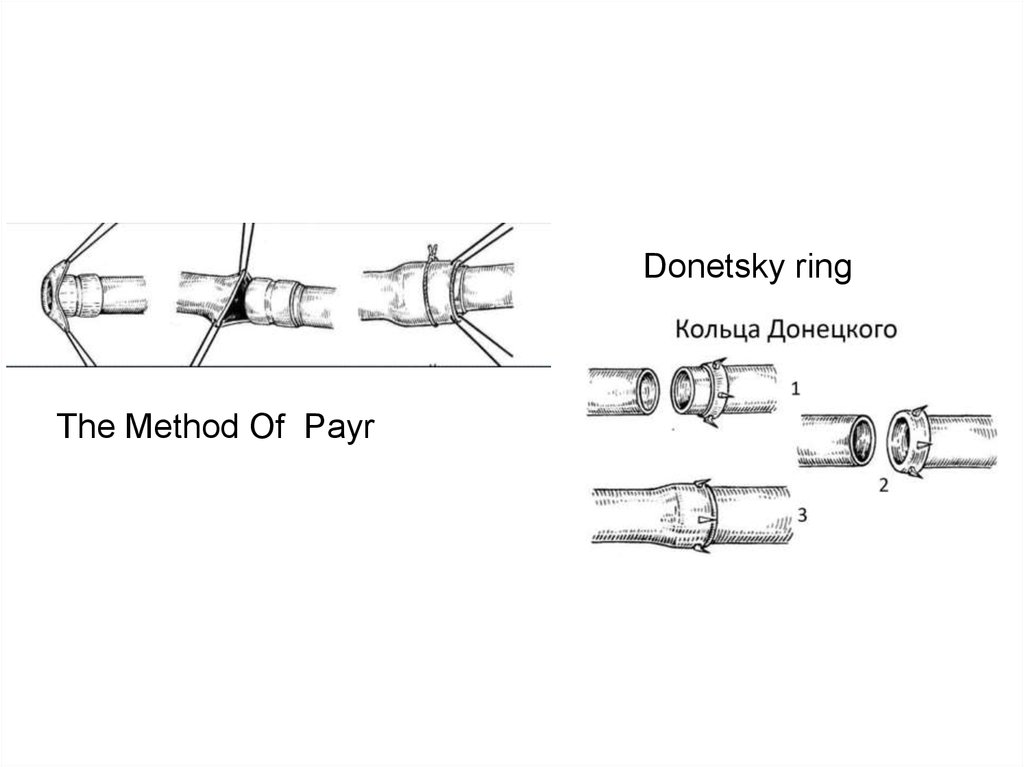
Donetsky ringThe Method Of Payr
9.
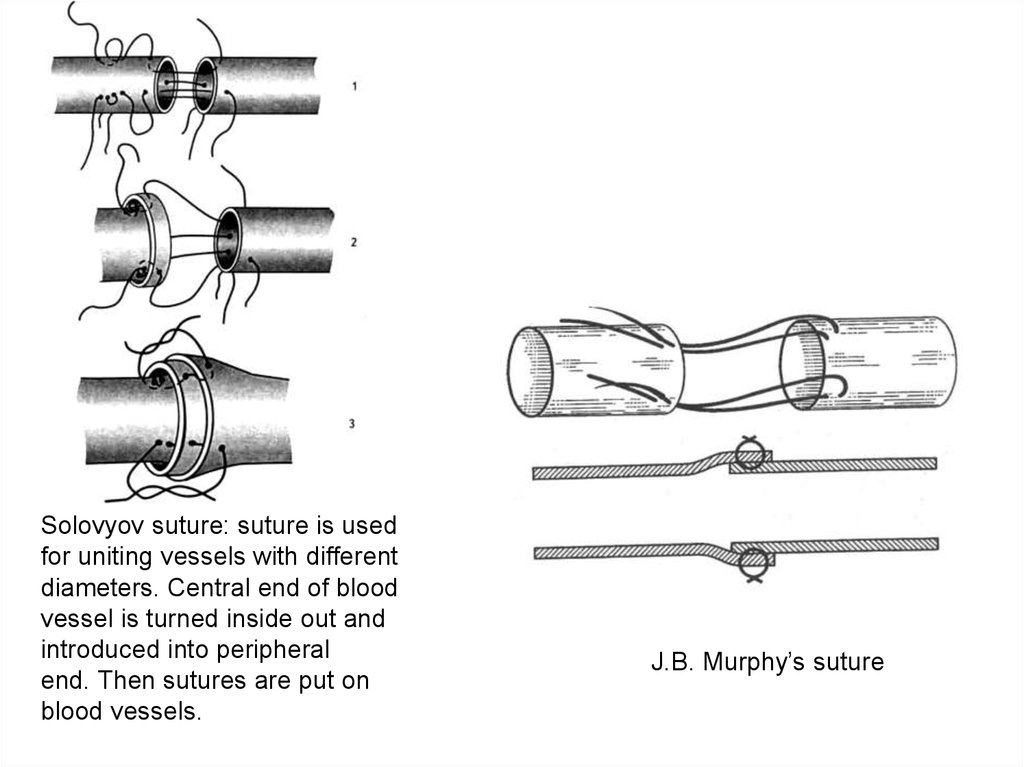
Solovyov suture: suture is usedfor uniting vessels with different
diameters. Central end of blood
vessel is turned inside out and
introduced into peripheral
end. Then sutures are put on
blood vessels.
J.В. Murphy’s suture
10.
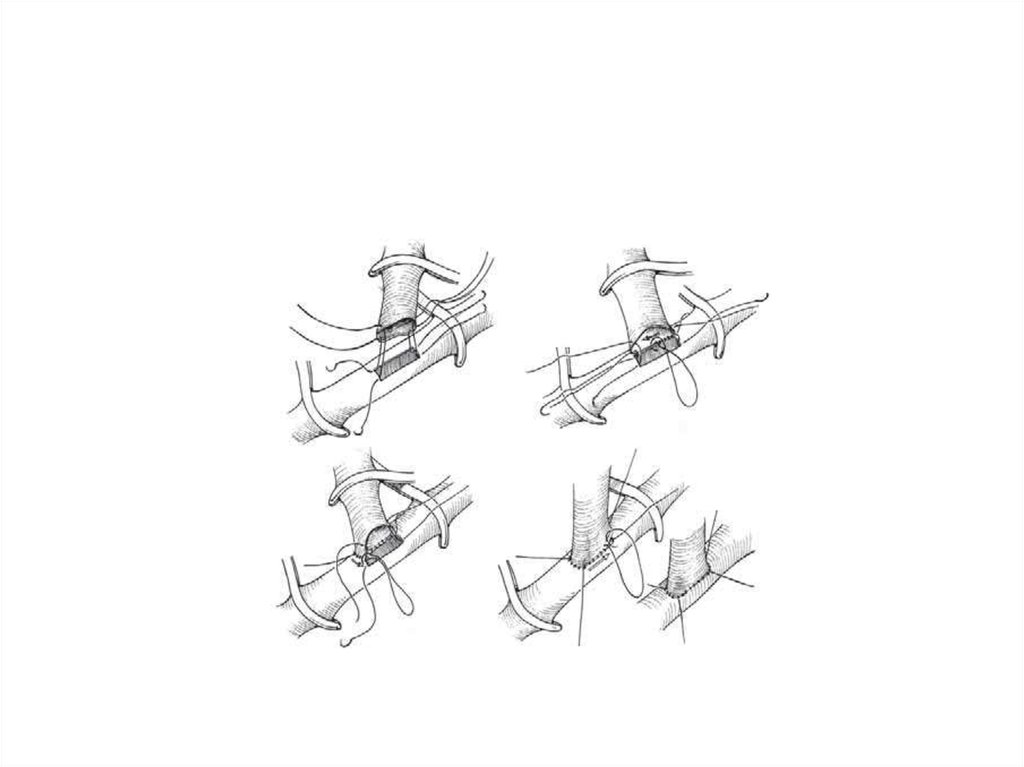
11. End to side
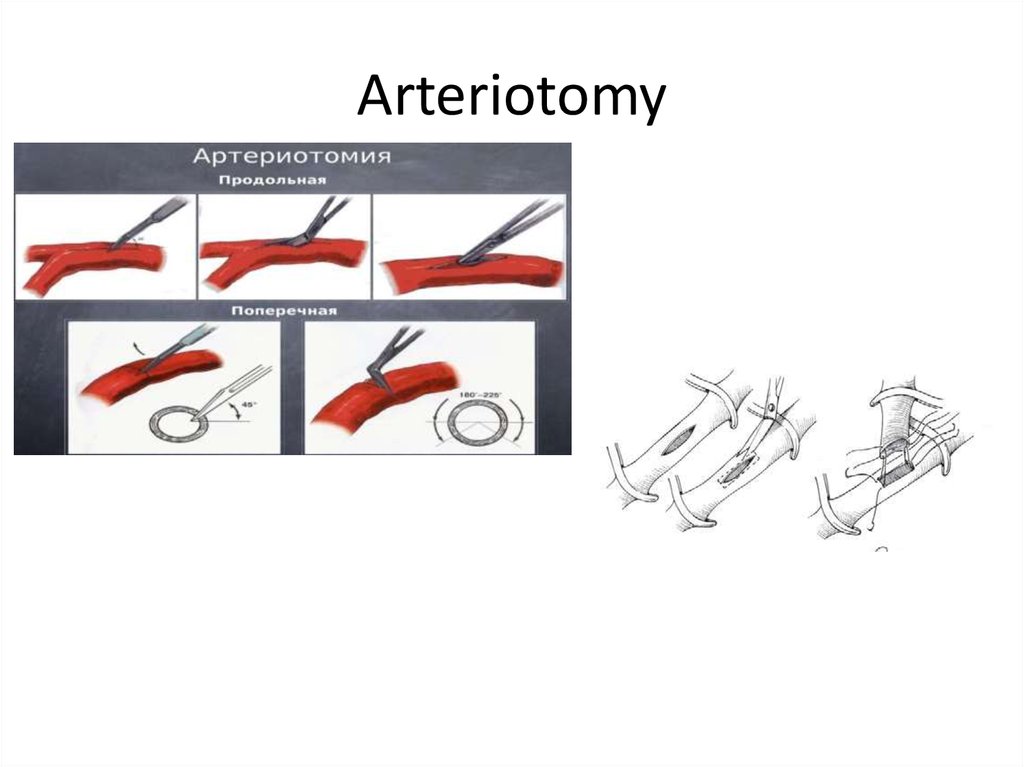
12. Arteriotomy
13.
heel-and-toe14.
15.
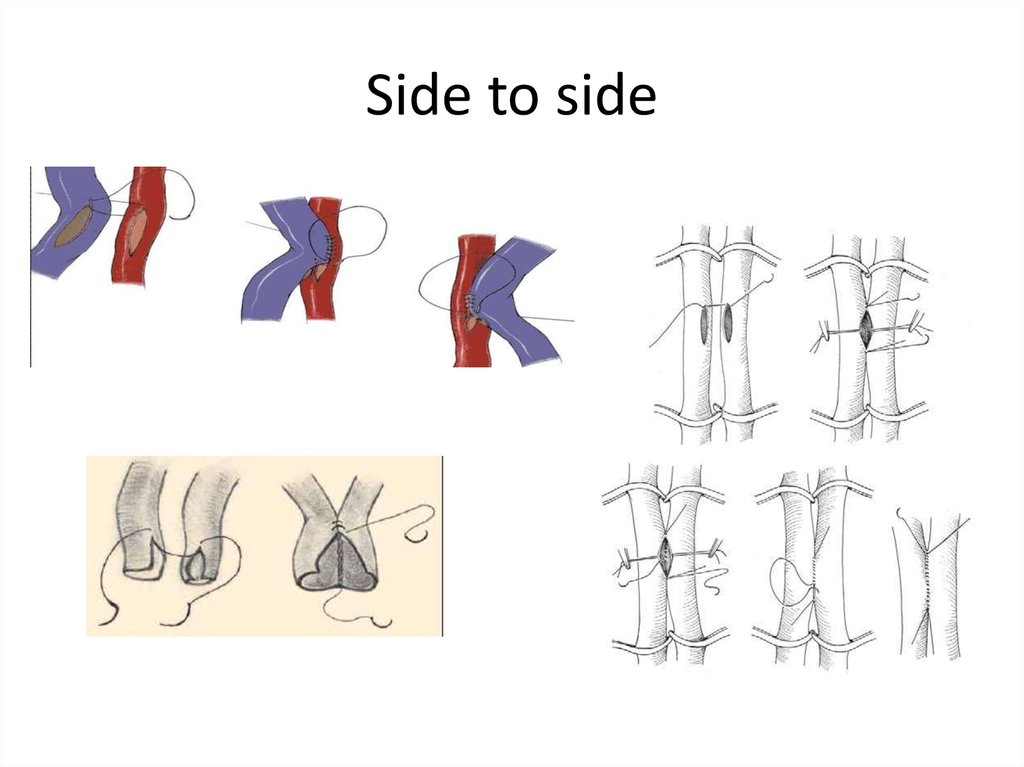
16. Side to side
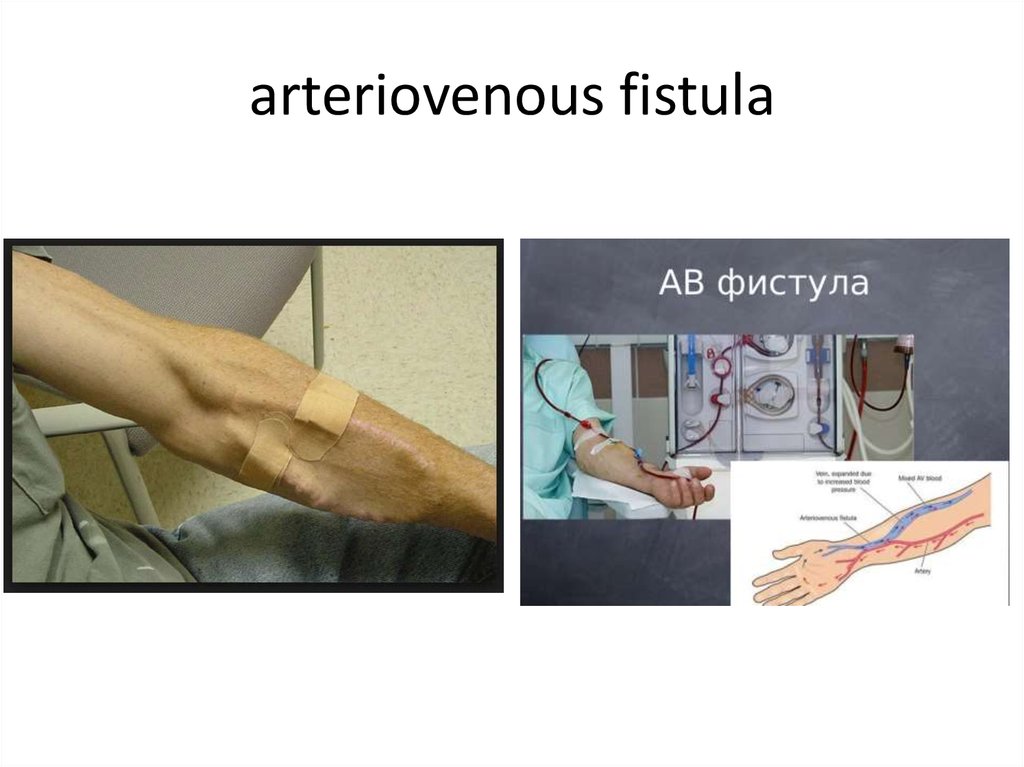
17. arteriovenous fistula
18. Cardiac Artery Bypass Graft
Cardiac Artery Bypass Graft19.
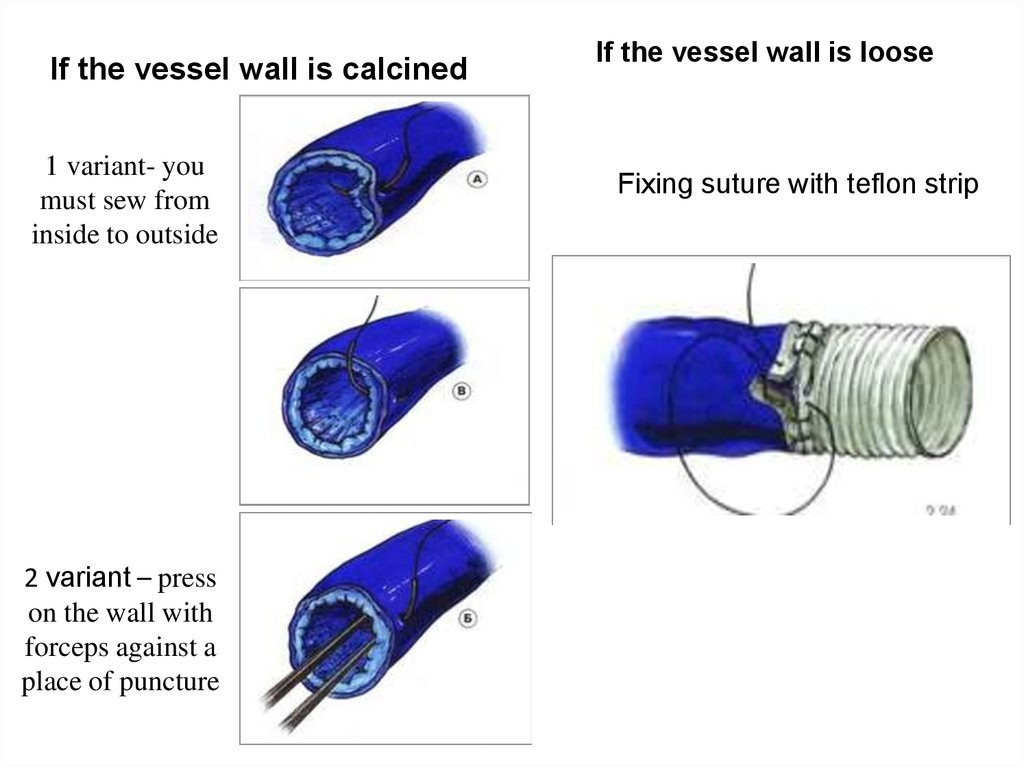
If the vessel wall is calcined1 variant- you
must sew from
inside to outside
2 variant – press
on the wall with
forceps against a
place of puncture
If the vessel wall is loose
Fixing suture with teflon strip
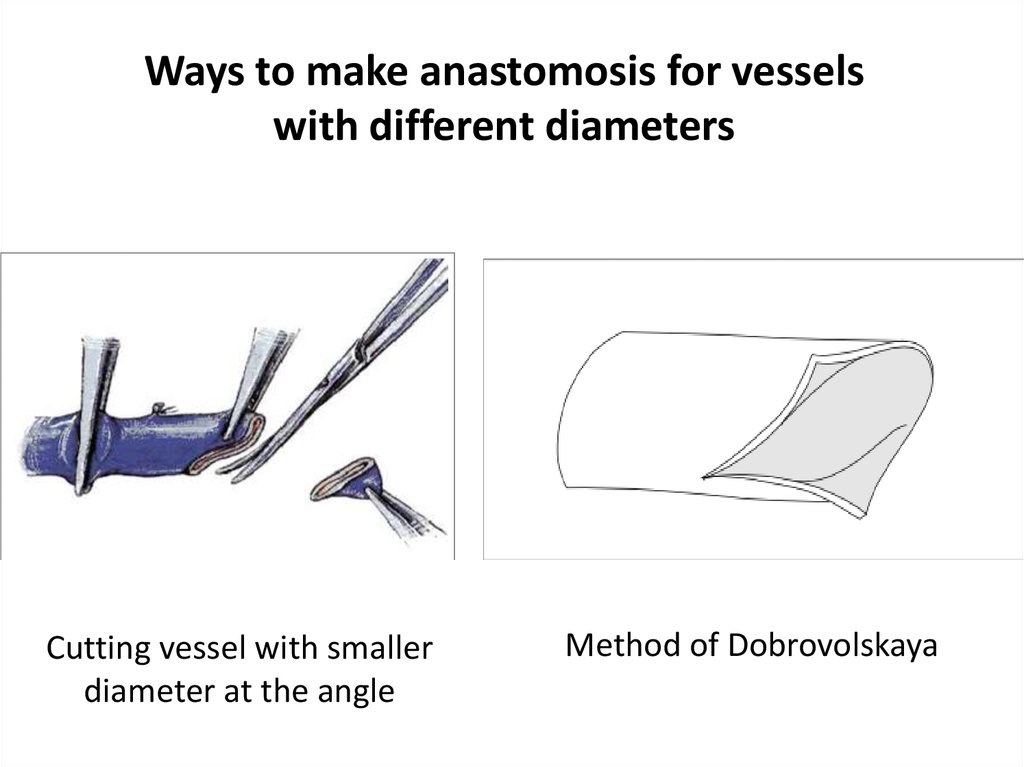
20. Ways to make anastomosis for vessels with different diameters
Cutting vessel with smallerdiameter at the angle
Method of Dobrovolskaya
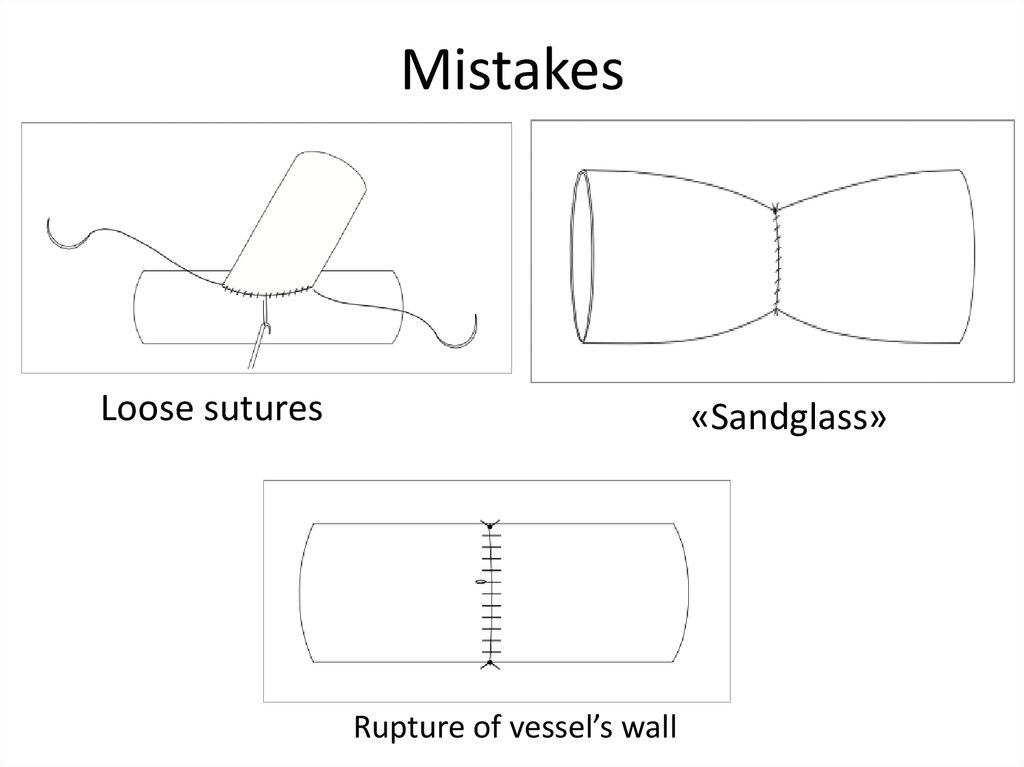
21. Mistakes
Loose sutures«Sandglass»
Rupture of vessel’s wall
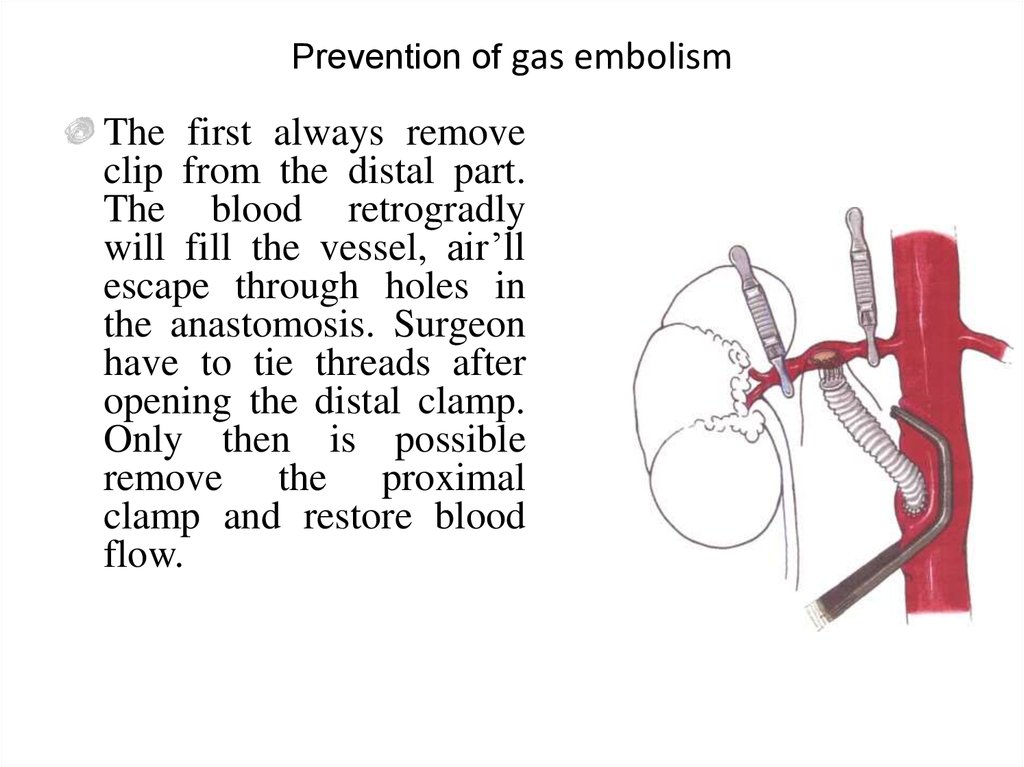
22. Prevention of gas embolism
The first always removeclip from the distal part.
The blood retrogradly
will fill the vessel, air’ll
escape through holes in
the anastomosis. Surgeon
have to tie threads after
opening the distal clamp.
Only then is possible
remove the proximal
clamp and restore blood
flow.
23. Requirements for suture material and instruments
1. Minimal harm for tissuesNeedles only atraumatic
Wide working parts to reduce the specific
pressure on the fabric;
Г-the shaped form of the transition of the
handle into the working part, which does not
complicate the overview of the bottom of the
operating wound;
the possibility of using elastic sleeves on the
working parts to prevent excessive
compression of the vascular wall
2. Minimal bleeding through the hole made
by the needle
3. No thrombosis on the suture material
4. Non-absorbable filament: polypropylene,
polytetrafluoroethylene
5. The vessels of different diameters are
suturing with different suture material:
aorta 2/0-3/0, coronary arteries 7/0-8/0
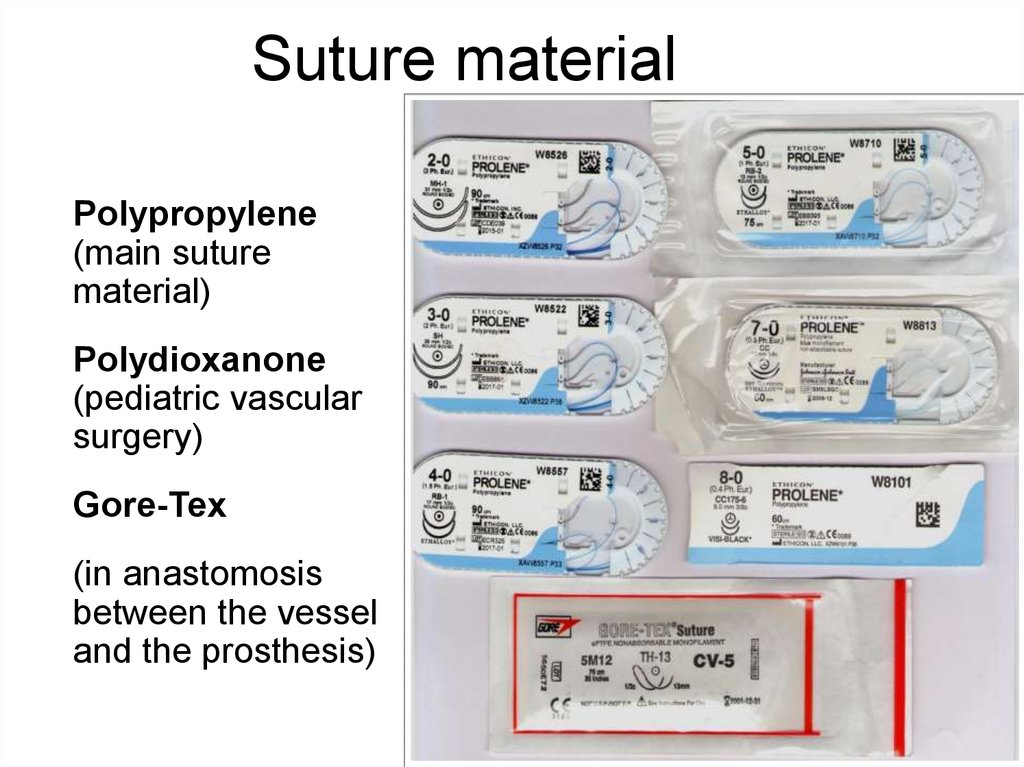
24. Suture material
• Polypropylene(main suture
material)
• Polydioxanone
(pediatric vascular
surgery)
• Gore-Tex
• (in anastomosis
between the vessel
and the prosthesis)













 medicine
medicine








