Similar presentations:
Surface plasma polaritons flow control using external fields
1. SURFACE PLASMA POLARITONS FLOW CONTROL USING EXTERNAL FIELDS
Skachkov SSCrimean Federal University named after V. I. Vernadsky
Institute of Physics and Technology
Department of Experimental Physics
2. Introduction
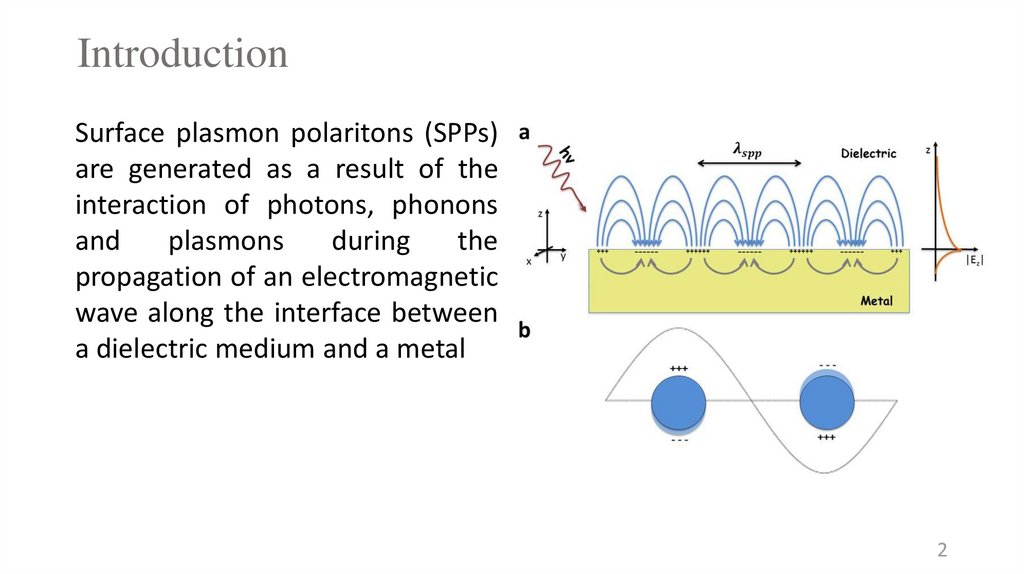
Surface plasmon polaritons (SPPs)are generated as a result of the
interaction of photons, phonons
and
plasmons
during
the
propagation of an electromagnetic
wave along the interface between
a dielectric medium and a metal
2
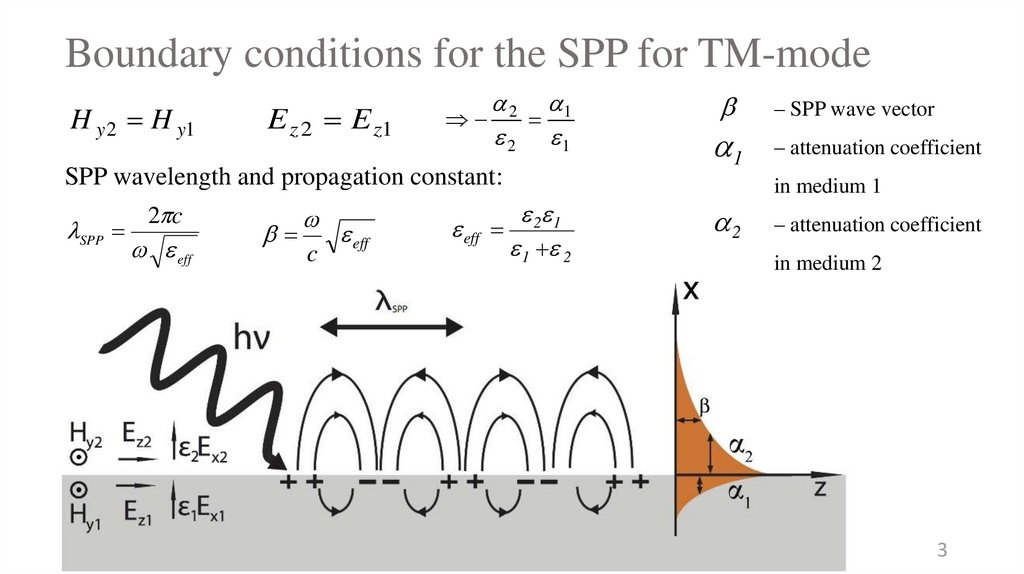
3. Boundary conditions for the SPP for TM-mode
H y 2 H y1E z 2 E z1
2 1
2 1
SPP wavelength and propagation constant:
SPP
2 c
eff
c
eff
eff
2 1
1 2
1
– SPP wave vector
– attenuation coefficient
in medium 1
2
– attenuation coefficient
in medium 2
3
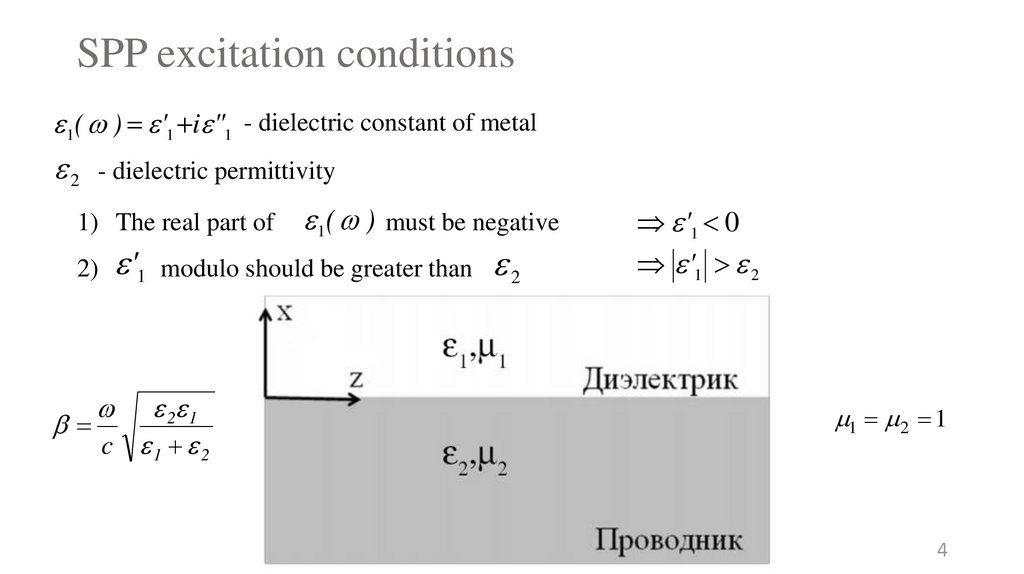
4. SPP excitation conditions
1( ) '1 i "1 - dielectric constant of metal2
- dielectric permittivity
1) The real part of
2)
'1
1( ) must be negative
modulo should be greater than
2 1
c 1 2
2
'1 0
'1 2
1 2 1
4
5.
Energy density flux distribution in a metal-insulatorsystem
The plasmon wave decays exponentially in
the metal and in the dielectric along the
normal axis to the interface
0 633nm
air 1
Re( Au ) 11.6
The propagation constant of the SPP on the
surface of the strip waveguide
Au Air
k0 Air
Au Air
1/ 2
5
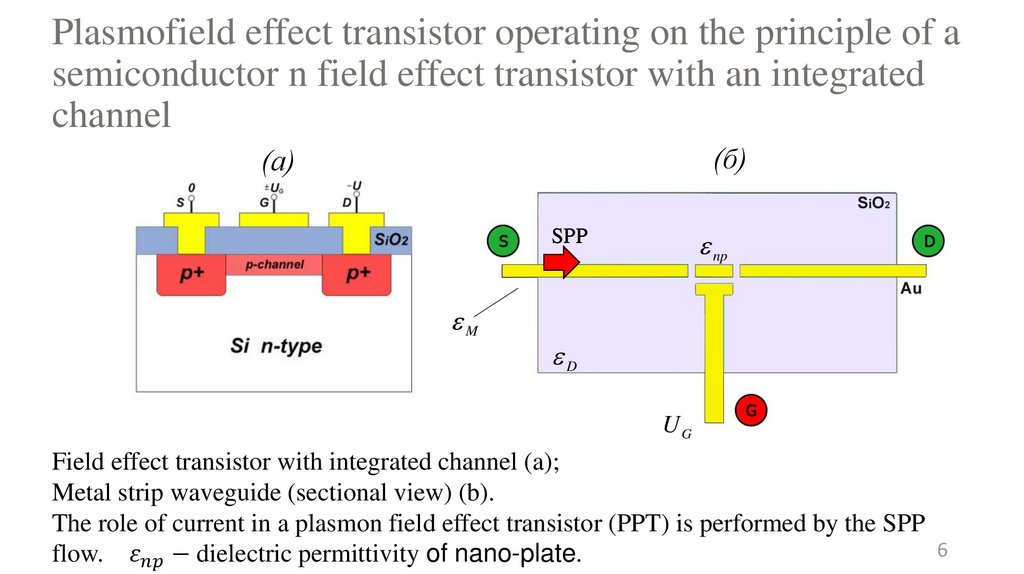
6. Plasmofield effect transistor operating on the principle of a semiconductor n field effect transistor with an integrated
channel(б)
(а)
np
SPP
M
D
UG
Field effect transistor with integrated channel (a);
Metal strip waveguide (sectional view) (b).
The role of current in a plasmon field effect transistor (PPT) is performed by the SPP
6
flow.


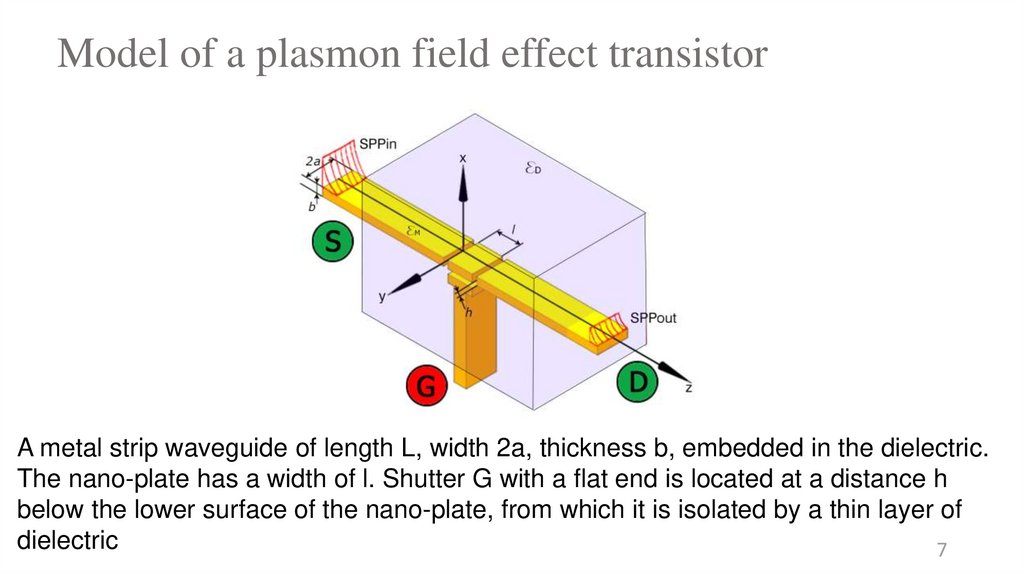
 physics
physics








