Similar presentations:
Surface Plasmon Resonance. General Introduction
1. Surface Plasmon Resonance
General IntroductionSteffen Jockusch
07/15/07
Plasmons:
- collective oscillations of the “free electron gas” density,
often at optical frequencies.
2. Surface Plasmon Resonance
General IntroductionSteffen Jockusch
07/15/07
Plasmons:
- collective oscillations of the “free electron gas” density,
often at optical frequencies.
Surface Plasmons:
- plasmons confined to surface (interface) and interact
with light resulting in polaritons.
- propagating electron density waves occurring at the
interface between metal and dielectric.
3. Surface Plasmon Resonance
General IntroductionSteffen Jockusch
07/15/07
Plasmons:
- collective oscillations of the “free electron gas” density,
often at optical frequencies.
Surface Plasmons:
- plasmons confined to surface (interface) and interact
with light resulting in polaritons.
- propagating electron density waves occurring at the
interface between metal and dielectric.
Surface Plasmon Resonance:
- light ( ) in resonance with surface plasmon oscillation
4. Requirements:
2Requirements:
- Material with free electrons:
Metals
Pb, In, Hg, Sn, Cd
Cu, Ag, Au
plasma frequency
UV
VIS
5. Requirements:
2Requirements:
- Material with free electrons:
Metals
Pb, In, Hg, Sn, Cd
Cu, Ag, Au
plasma frequency
UV
VIS
- Surface (interface):
flat surfaces
Au
50 nm
nanoparticles
6. Requirements:
2Requirements:
- Material with free electrons:
Metals
Pb, In, Hg, Sn, Cd
Cu, Ag, Au
plasma frequency
UV
VIS
- Surface (interface):
flat surfaces
Au
nanoparticles
50 nm
- Light: How to couple the photons to the surface?
7.
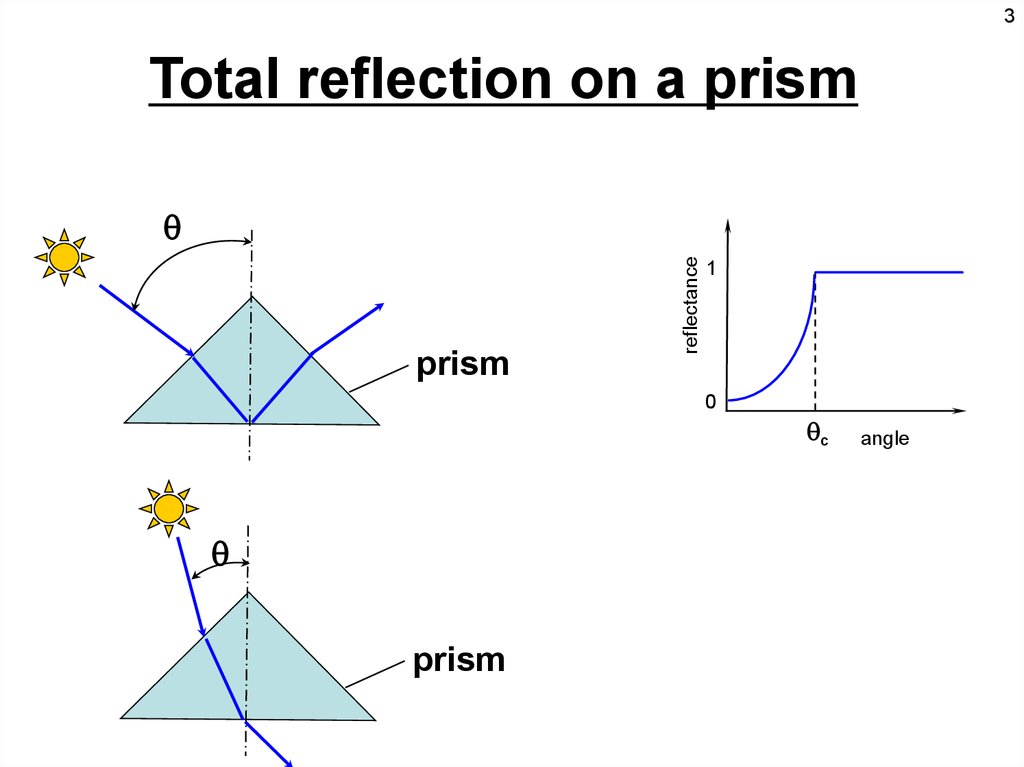
3Total reflection on a prism
prism
reflectance
1
0
c
prism
angle
8.
4Evanescent Wave
prism
reflectance
1
0
c
angle
evanescent field
evanescent wave: - nearfield standing wave,
- extends about 1/2 ,
- decays exponentially with the distance
9.
5Surface Plasmon Resonance
detector
Au
50 nm
(Kretschmann)
reflectance
1
0
c
o
angle
10.
6Surface Plasmon Resonance
Spectroscopy
detector
reflectance
Au
analyte
To measure:
- thickness changes,
- density fluctuation,
- molecular adsorption
1
0
c
o 1
angle
11.
Surface Plasmon Resonance Spectroscopy in SensorsKnoll, et.al. Biosensors & Bioelectronics, 1995, 10, 903
7
12.
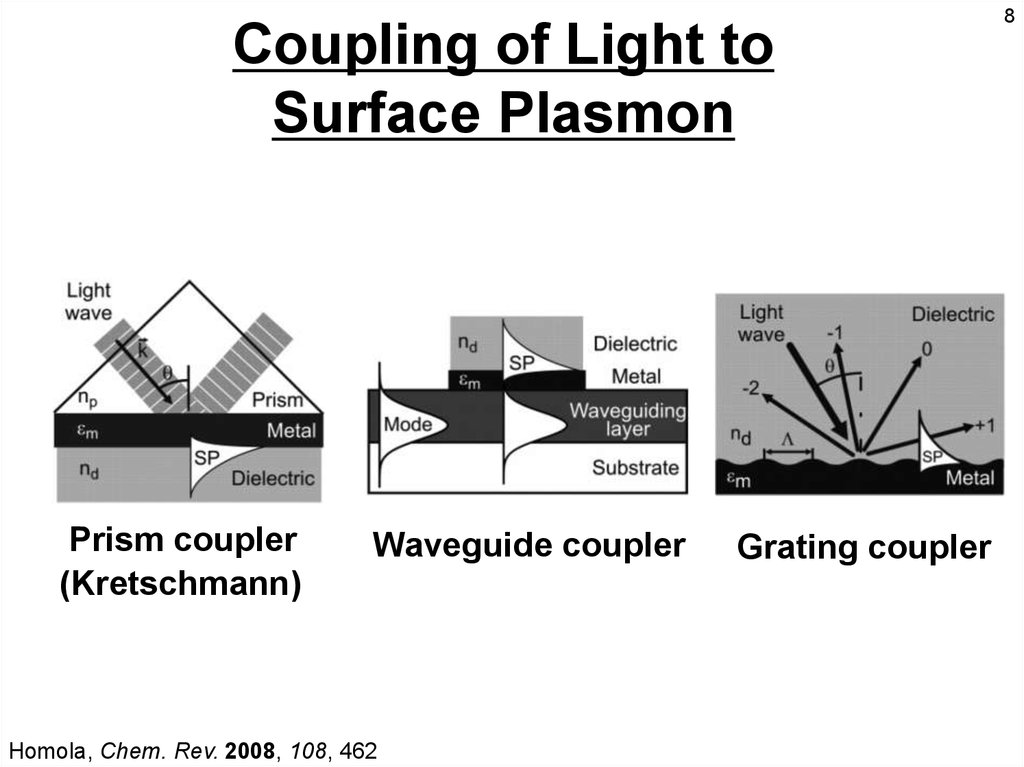
Coupling of Light toSurface Plasmon
Prism coupler
(Kretschmann)
Waveguide coupler
Homola, Chem. Rev. 2008, 108, 462
Grating coupler
8
13.
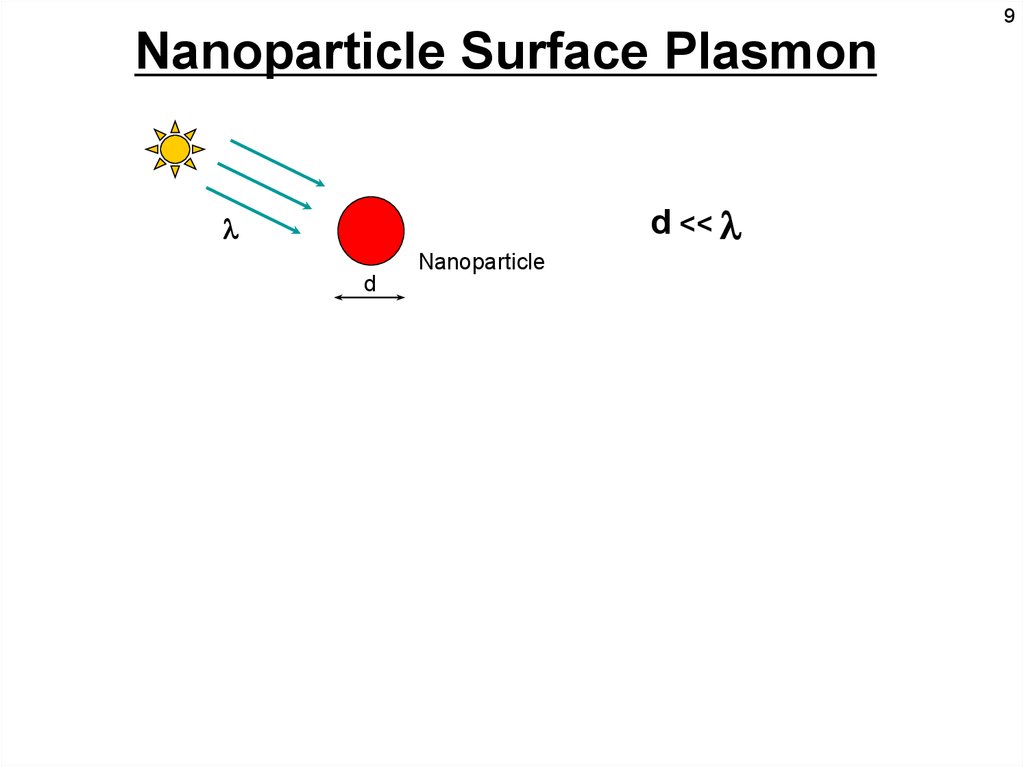
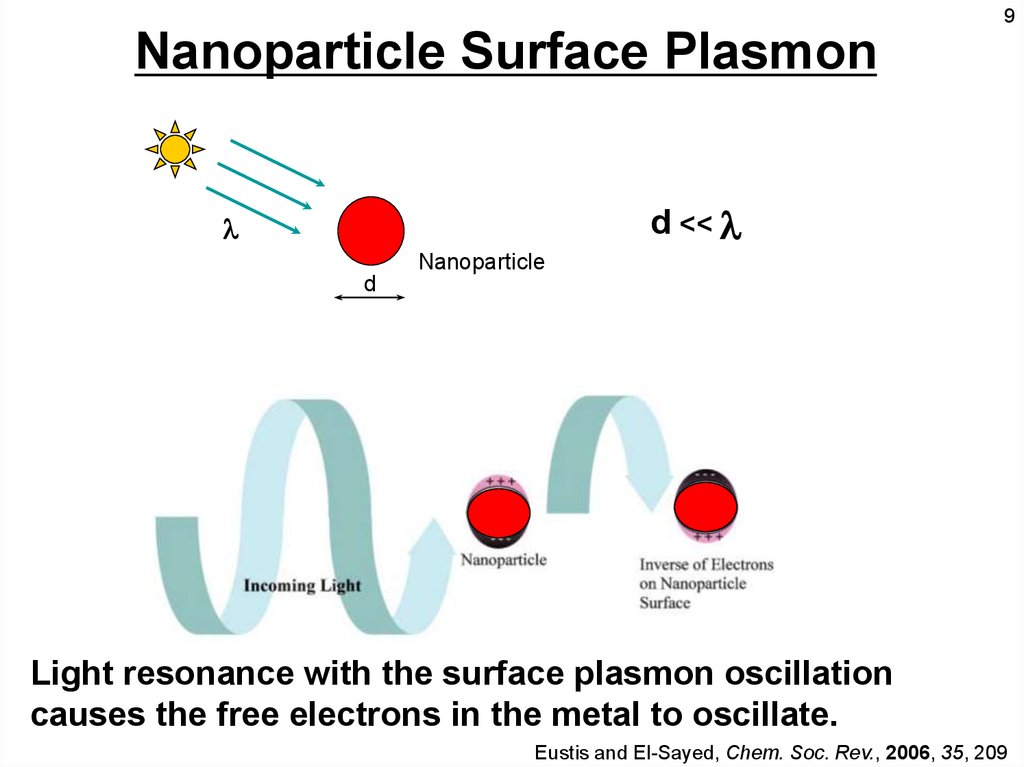
9Nanoparticle Surface Plasmon
d <<
Nanoparticle
d
14.
9Nanoparticle Surface Plasmon
d <<
Nanoparticle
d
Light resonance with the surface plasmon oscillation
causes the free electrons in the metal to oscillate.
Eustis and El-Sayed, Chem. Soc. Rev., 2006, 35, 209
15.
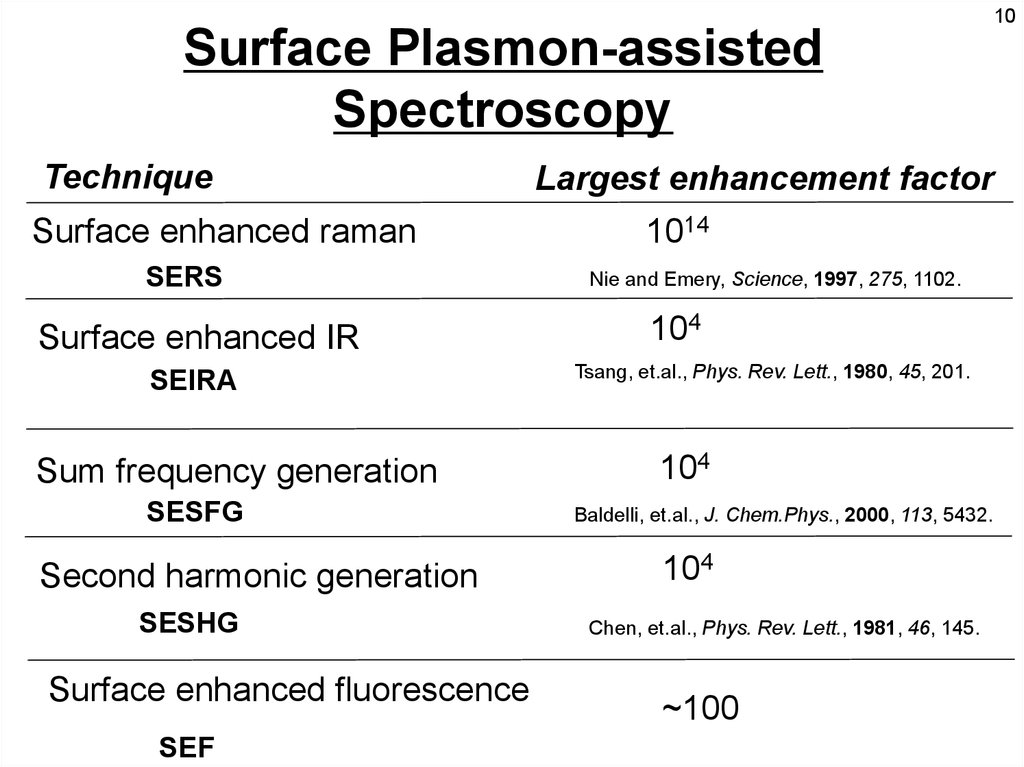
10Surface Plasmon-assisted
Spectroscopy
Technique
Surface enhanced raman
SERS
Surface enhanced IR
SEIRA
Sum frequency generation
SESFG
Second harmonic generation
SESHG
Surface enhanced fluorescence
SEF
Largest enhancement factor
1014
Nie and Emery, Science, 1997, 275, 1102.
104
Tsang, et.al., Phys. Rev. Lett., 1980, 45, 201.
104
Baldelli, et.al., J. Chem.Phys., 2000, 113, 5432.
104
Chen, et.al., Phys. Rev. Lett., 1981, 46, 145.
~100










 physics
physics