Similar presentations:
Geodesy. Modern geodetic technique
1. Geodesy
L14 Modern geodetic equipment2. TOTAL STATION
3.
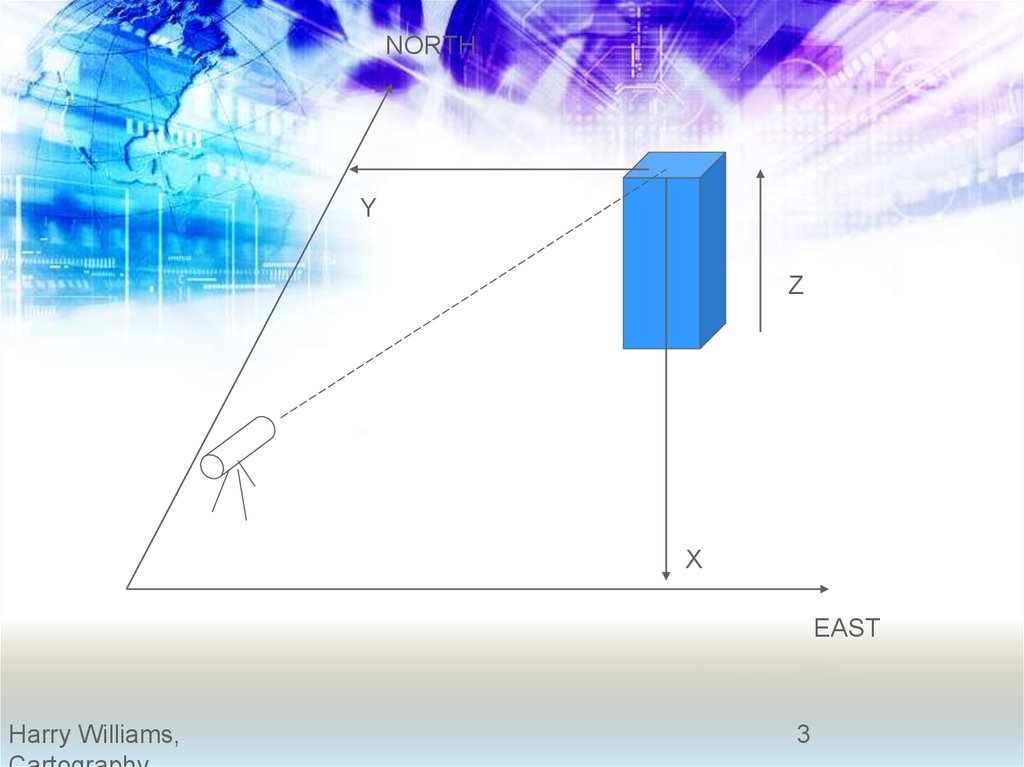
NORTHY
Z
X
EAST
Harry Williams,
3
4.
reflectorThe total station works by
firing an infrared laser beam
at a reflector mounted on a
stadia rod. The distance
between the total station
and the reflector is
calculated based on the
time taken for the beam to
reflect back to the total
station.
Total stations were originally developed for the construction industry – e.g.
surveying new roads, laying out building foundations, utility lines etc..
5.
NORTHANGLE
Example based on
UTM:
TOTAL STATION:
UTM = 3676595m N
672156m E
Y
Y=150m; X=70m
UNKNOWN POINT
UTM=3676595
-150
3676445m N
672156
+70
672226m E
X
5
6.
Most total stations have the ability to record survey data as adigital file, which can be imported to a PC-based GIS program.
MAP
6
7. Why use a total station?
1. Field work is carried out very fast.
2. Accuracy of measurement is high.
3. Manual errors involved in reading and
recording are eliminated.
4. Calculation of coordinates is very fast and
accurate. Even corrections for temperature
and pressure are automatically made.
5. Computers can be employed for map
making and plotting contour and crosssections. Contour intervals and scales can be
changed in no time.
8. When do you use a total station?
• For mapping small areas (the range of a total stationis around 2 miles or so – assuming you have good
lines of sight). A good example would be mapping
an archaeological dig site.
• There are many other applications in earth science
that require great accuracy e.g. monitoring cliff
erosion, glacier movement, changes in beach
profiles, sand dune movement.. and so on.
9.
10.
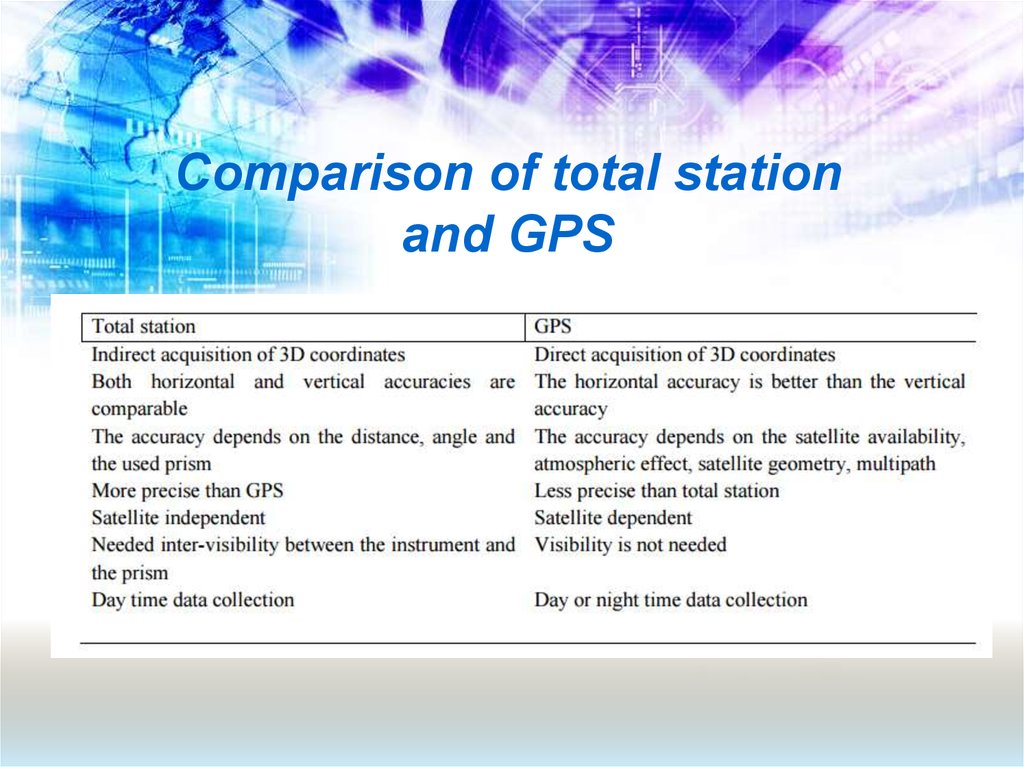
11. Comparison of total station and GPS
12. SMART STATION
Benefits of SmartStation:
■ Control points are not needed;
■ No awkward traversing required;
■ Consistent high accuracy;
■ Complete survey quicker;
■ Traversing skills not required;
13. Robotic total stations
• Allows the operator to controlthe instrument from a
distance via remote control
• This elliminates the need of
an assistant staf member, as
the operator holds the
reflector and controls the total
station from the observed
point











 physics
physics geography
geography








