Signal-to-noise ratio
1. Signal-to-noise ratio
2. Raw siesmic data is usually affected by various kinds of noises that is considered as unwanted data.
3. Types of Seismic noises :-
•Types of Seismic noises :1. Coherent Noise.2. Incoherent Noise.
4. Coherent Noise: undesirable seismic energy that shows consistent phase from trace to trace.
1.Coherent Noise: undesirable seismic energy
that shows consistent phase from trace to
trace.
a. Interference from other seismic surveys.
b. Interference from other vessels.
c. Reflections/Diffractions from rigs or other
objects.
d. Cable noise.
e. Mud roll.
f. Multiples
g. Ground roll.
5. 2. Incoherent Noise: undesirable seismic energy that lack the phase relationship between adjacent traces and cannot be
correlated tothe seismic energy source.
a. Ambient noise.
b. Swell noise.
c. Electronic noise (spikes).
6. Noise Attenuation
•Noise Attenuation1. Trace editing and
muting.
2. Gain recovery.
3. Filtering.
4. Static correction.
5. NMO correction.
6. Deconvolution.
7. CMP gather (stacking).
8. Velocity analysis.
9. Multiple attenuation.
10 . Migration.
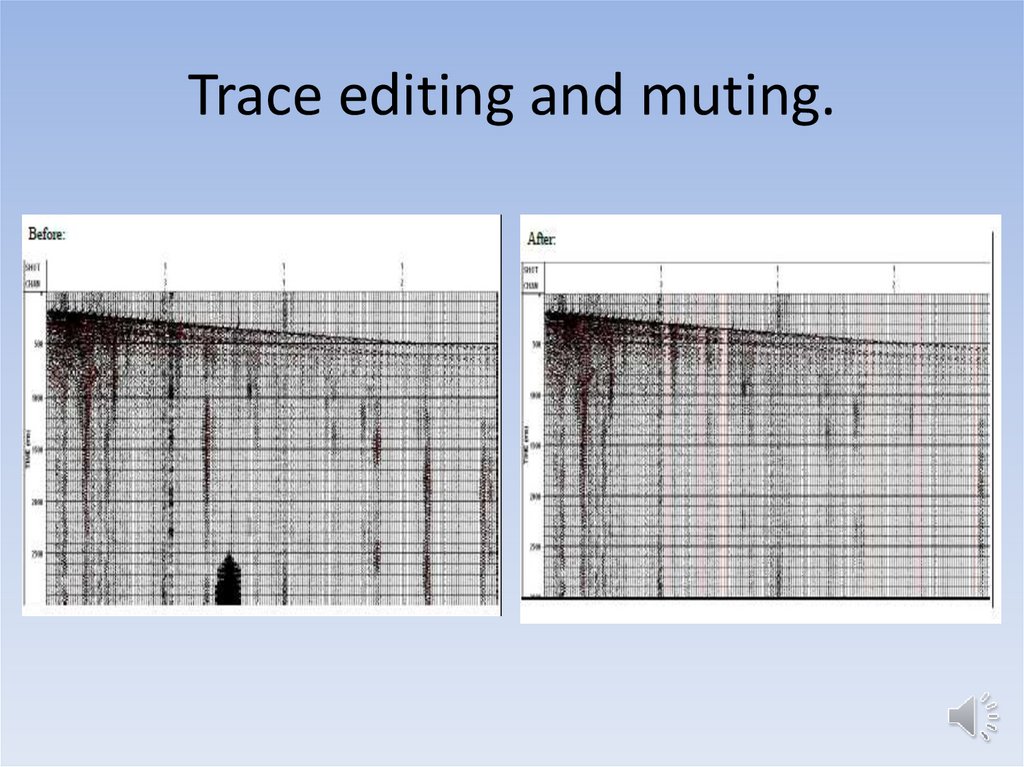
7. 1. Trace editing and muting
• Remove dead traces.• Remove noisy traces.
• Switch polarity on reversed traces.
8. Trace editing and muting.
9.
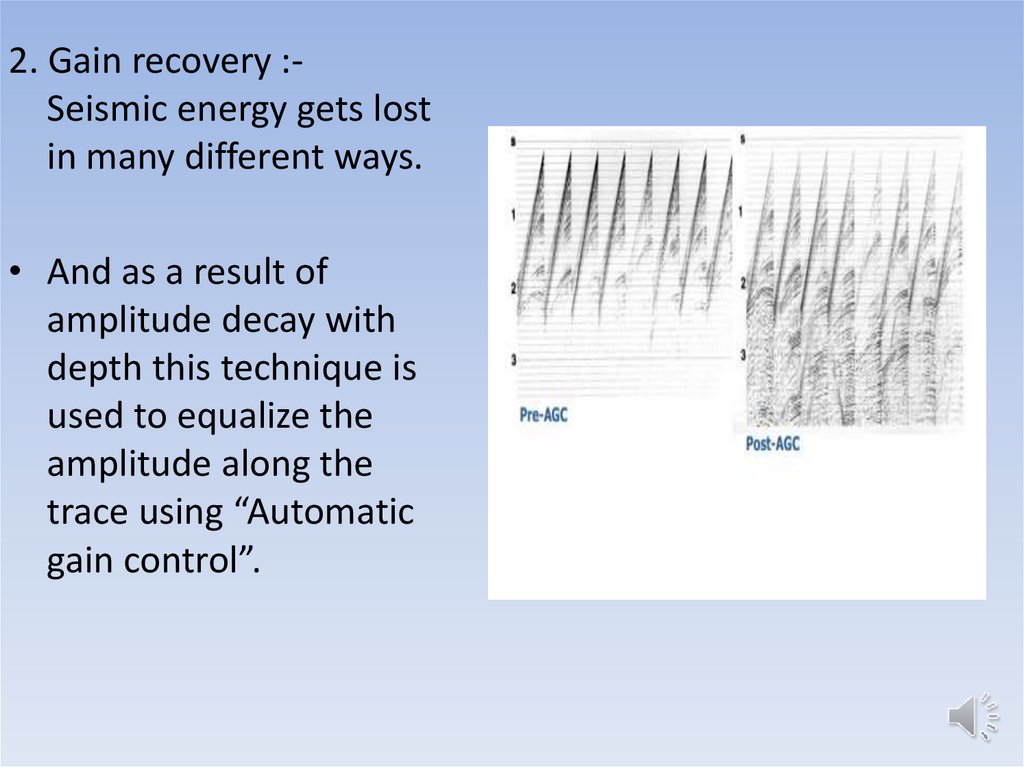
2. Gain recovery :Seismic energy gets lostin many different ways.
• And as a result of
amplitude decay with
depth this technique is
used to equalize the
amplitude along the
trace using “Automatic
gain control”.
10.
3. Filtering :• This technique is usedto remove the
unwanted parts of the
frequency spectrum.
• Low pass (high cut),
high pass (low cut),
band pass and notch
filter.
11. Fk filter :- This technique is used to remove the linear noise.
•Fk filter :This technique is used to remove thelinear noise.
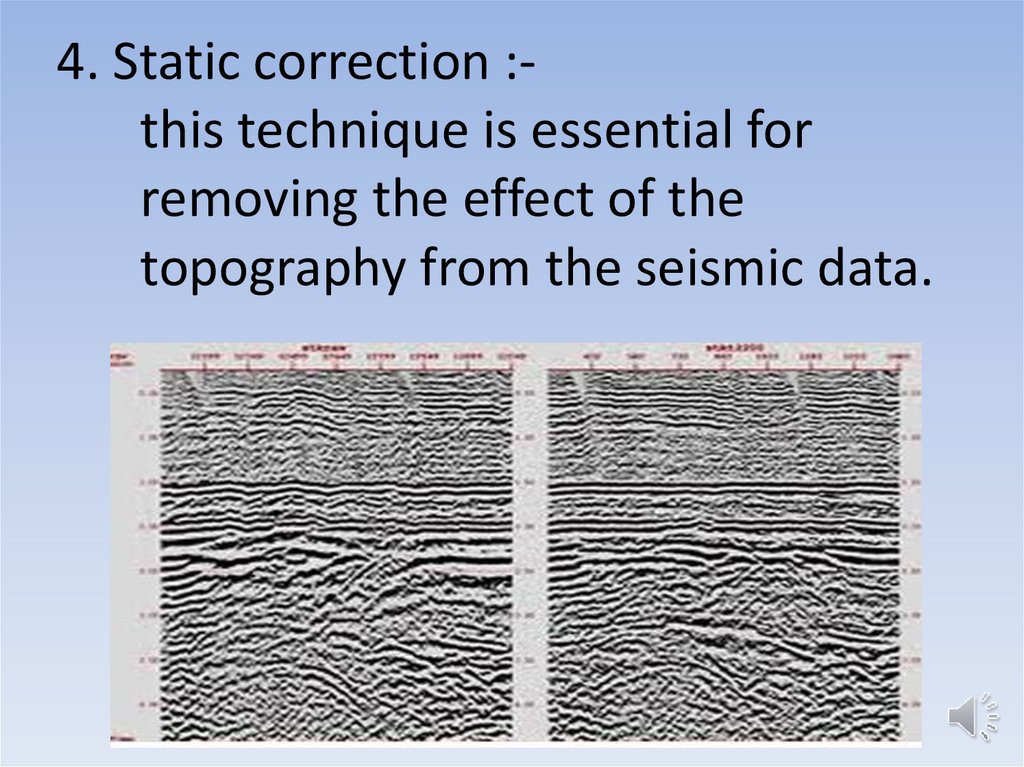
12. 4. Static correction :- this technique is essential for removing the effect of the topography from the seismic data.
4. Static correction :this technique is essential forremoving the effect of the
topography from the seismic data.
13.
5. NMO correction :• This refers to the increaseof travel time with
increasing offset distance.
• This increase make the
reflectors look dipping, and
make the dipping reflectors
even more dipping.
• The amount of correction
needed decreases with
depth , so the shallower
ones get more streched
than the deeper ones do.
14. 6. Deconvolution : This technique make the reflectors look better by increasing the temporal resolution and remove echoes
15.
7. CMP Gathers :• To enhance signal tonoise ratio we use more
than one shot.
• Reflections from the
same point are recorded
by different source
station pairs.
• The purpose of the CMP
gather is to enhance
where the seismic
reflected energy was
weak.
16.
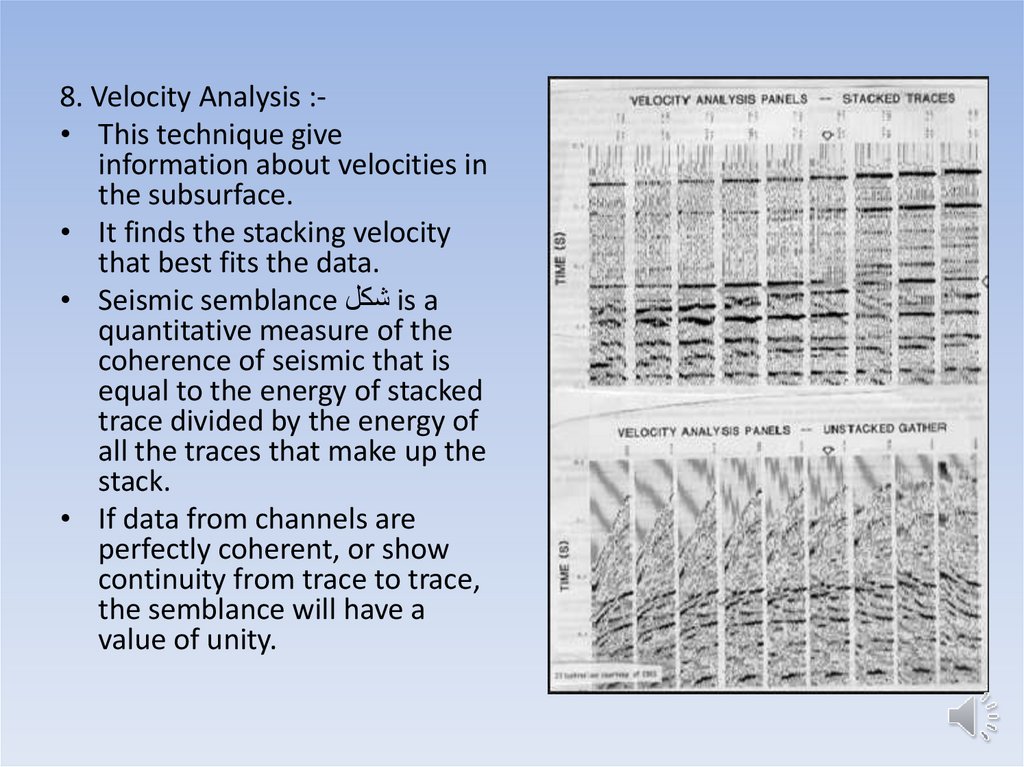
8. Velocity Analysis :• This technique giveinformation about velocities in
the subsurface.
• It finds the stacking velocity
that best fits the data.
• Seismic semblance شكلis a
quantitative measure of the
coherence of seismic that is
equal to the energy of stacked
trace divided by the energy of
all the traces that make up the
stack.
• If data from channels are
perfectly coherent, or show
continuity from trace to trace,
the semblance will have a
value of unity.
17. 9.Multiple attenuation :- Multiples are an event on the seismic record that has incurred more than one reflection, it can be
9.Multiple attenuation :Multiples are an event on the seismic record that hasincurred more than one reflection, it can be either
short-path or longer path depending upon whether
they interfere with primary reflections or not, so this
technique is used mainly to remove it
Before Demultiple
After Demultiple
18.
10. Migration :• This process moves thereflectors into their
right subsurface
locations.
• It improves the lateral
resolution and collapses
diffractions into
identifiable points in
the seismic section.














 geography
geography