Similar presentations:
Material Formats
1. Material Formats
2. Raw materials for processing
Generally, raw materials are materials which need to be processed beforethey are used- for example, melted and cast in a mould. Common formats of
raw material are:
• powder: quantities of very fine (small) particles, such as cement powder
• pellets: larger, standard-sized pieces of material, typically pea-sized to eggsized, intended to be melted for forming in moulds - for instance, plastic
pellets
• fibres: very fine, hair-like lengths, such as glass fibres.
When steel and other metals are produced, they are made into blocks called
ingots, which can subsequently be melted and cast. Very large steel ingots are
called blooms. One standard size for steel blooms is 630 mm x 400 mm x 6 m.
Steel can also be supplied in smaller blocks, of various sizes, called billets.
3. Decide whether the sentences below are true or false, and correct the false sentences.
1 Raw materials are often intended to be melted or mixed.2 Powder particles are smaller than pellets.
3 Pellets do not reg uire further processing.
4 A steel bloom is a type of ingot.
5 Steel billets can be cut into smaller sized pieces called
blooms.
4. Formats of processed materials
Materials are frequently supplied ready for use in the formats described below.• Bars are long lengths of solid metal with a relatively small cross-sectional area.
These can be round bars (or rods) which have a circular section. They may also be
square bars, with a square section, and flat bars, with a flat, rectangular section. A
bar is generally made of metal, but a rod can be made of any material.
• Sheets are flat, wide and thin - for steel, thinner than about 3 mm. Other
materials supplied in sheets include plastic, glass and wood. However, sheets of
wood are often called boards. When sheets of metal (or metal sheets) are
delivered in large quantities, they can be supplied in rolls called coils.
• Plates are flat pieces of metal that are wide, but thicker than sheets (for steel,
thicker than 3mm). Non-metals, such as glass, plastic or wood, are not usually
called plates; even ifthese materials are thicker than 3 mm, they are usually called
sheets.
5.
• Structural steel sections are made from rolled or extruded steel, andproduced in a variety of section shapes. I-sections, with profiles in the shape
of the letter i, are common examples. (See Appendix V on page 106 for types
of structural section.)
• Tubes are hollow, not solid. The most common types are round tubes, but
square tubes and rectangular tubes are also produced. Pipes are specifically
for carrying liquid or gas. A pipe is therefore just one type of tube.
• Wires are thin lengths of metal with circular sections, consisting of one
strand - that is, a long, thin, single piece of material. They are usually supplied
in coils. Several wires can be combined to form a cable. An electrical wire is a
single conductor covered with insulation. The conductor can be a single wire
(called a solid wire) or several strands of wire grouped together (called a
stranded wire). An electrical cable has several conductors, separately covered
with insulation, grouped within a second outer layer of insulation.
6.
7.
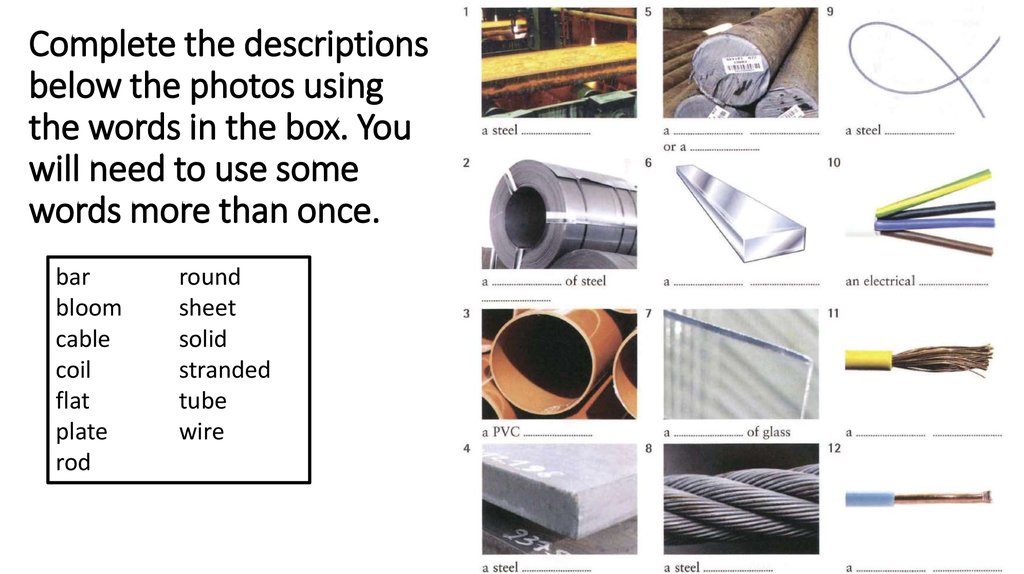
8. Complete the descriptions below the photos using the words in the box. You will need to use some words more than once.
barbloom
cable
coil
flat
plate
rod
round
sheet
solid
stranded
tube
wire






 industry
industry








