Similar presentations:
ACS large drive family
1. ACS large drive family
ACS6000cAC/AC
•direct AC to AC converter(cyclo), no DClink
•SCR Thyristor
•synchronous motor(AC motor with DC
excitation)
•high power and low speed, example
roughing mills and ship main propulsion
AC/AC
SM
AC/AC
ACS6000sd
© Copyright 2003 ABB - 1 -
•AC/DC/AC drive with DC-link
•IGCT semiconductor which is gate
commutated
•synchronous motor(AC motor with DC
excitation)
•best possible performance with DTC
•cold rolling mills and mine hoists
ACS6000ad / ACS1000
•AC/DC/AC drive with DC-link
•IGCT semiconductor
•induction motor(no excitation)
•6000ad for marine application
•1000 for pumps and fans
AC/DC
DC/AC
SM
AC/DC
DC/AC
IM
2. ACS6000c cycloconverter drive
Main components of cycloconverter drive:• Main circuit breaker
• Transformers to connect the drive to high
voltage network 6..36kV.
• Cycloconverter
• High speed circuit breakers
© Copyright 2003 ABB - 2 -
• 3 or 2*3 phase Synchronous motor(ACmotor) with DC-excitation
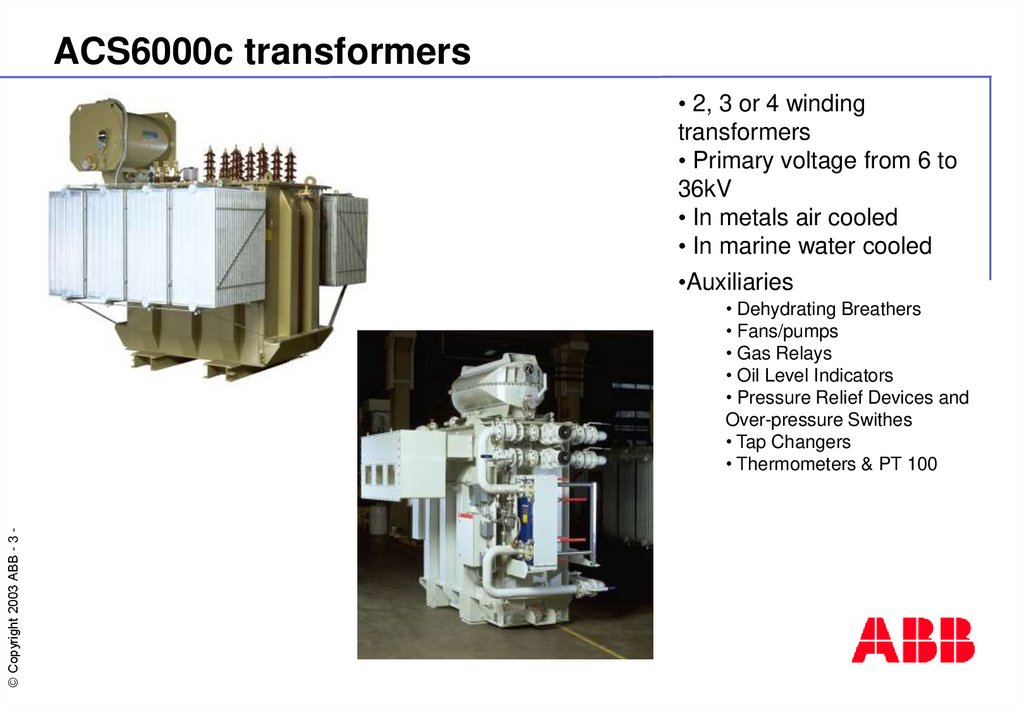
3. ACS6000c transformers
• 2, 3 or 4 windingtransformers
• Primary voltage from 6 to
36kV
• In metals air cooled
• In marine water cooled
•Auxiliaries
© Copyright 2003 ABB - 3 -
• Dehydrating Breathers
• Fans/pumps
• Gas Relays
• Oil Level Indicators
• Pressure Relief Devices and
Over-pressure Swithes
• Tap Changers
• Thermometers & PT 100
4. ACS6000c system description
© Copyright 2003 ABB - 4 -Basic 3-phase cycloconverter
three phase units
one water or air cooling unit
two control units
one excitation unit
5. ACS6000c system description
2 ) 6-pulse, 3-phase motor, separatedphase windings
1 ) 6-pulse, 3-phase motor
6p 6p
6p 6p
6p 6p
SM
6p 6p
6p 6p
6p 6p
3 ) 6-pulse, 2*3-phase motor, separated
stators
4 ) 12-pulse, 3-phase motor
6p 6p
6p 6p
6p 6p
6p 6p
6p 6p
6p 6p
SM
© Copyright 2003 ABB - 5 -
SM
6p 6p
6p 6p
6p 6p
6p 6p
6p 6p
6p 6p
SM
6. ACS6000c cycloconverter drive
Phase© Copyright 2003 ABB - 6 -
current
Excitation current
(DC current)
Positive bridge
Negative bridge
7. ACS6000c Phase unit main parts
3 phase supply(1000..1200VAC)3 overvoltage suppressors
PAI
12 (24 if parallel) fuses
GDR
12 thyristor’s
12 RC circuits
12 pulse transformers
2 Gate DRiver boards
1 Pulse Amplifier Interface board
1 Thyristor STAtus measurement
board
1 voltage tranducer
1 shunt and current tranducer
To CCB
STA
© Copyright 2003 ABB - 7 -
U
Neutral point of
cycloconveter
I
HSCB/motor
8. ACS6000c thyristor
Thyristorthyristor
module
type
© Copyright 2003 ABB - 8 -
W1-49-10
W2-73-10
W2-84-10
W3-96-10
A2-49-10
A2-73-10
A3-73-10
A3-84-10
A3-96-10
max.
overload 60 s [A]
continuous (preload 1/2 * I60s )
current [A]
1600
2850
4150
5200
1420
2300
2700
3750
4500
Micro switch
Fuse
overload
preload
1850
3400
5250
6700
1760
3050
3200
4500
5600
925
1700
2625
3350
880
1525
1600
2250
2800
Thyristor type
5STP1242F0000
5STP1842F0001
5STP2842F0017
5STP3842F0007
5STP1242F0000
5STP1242F0000
5STP1842F0001
5STP2842F0017
5STP3842F0007
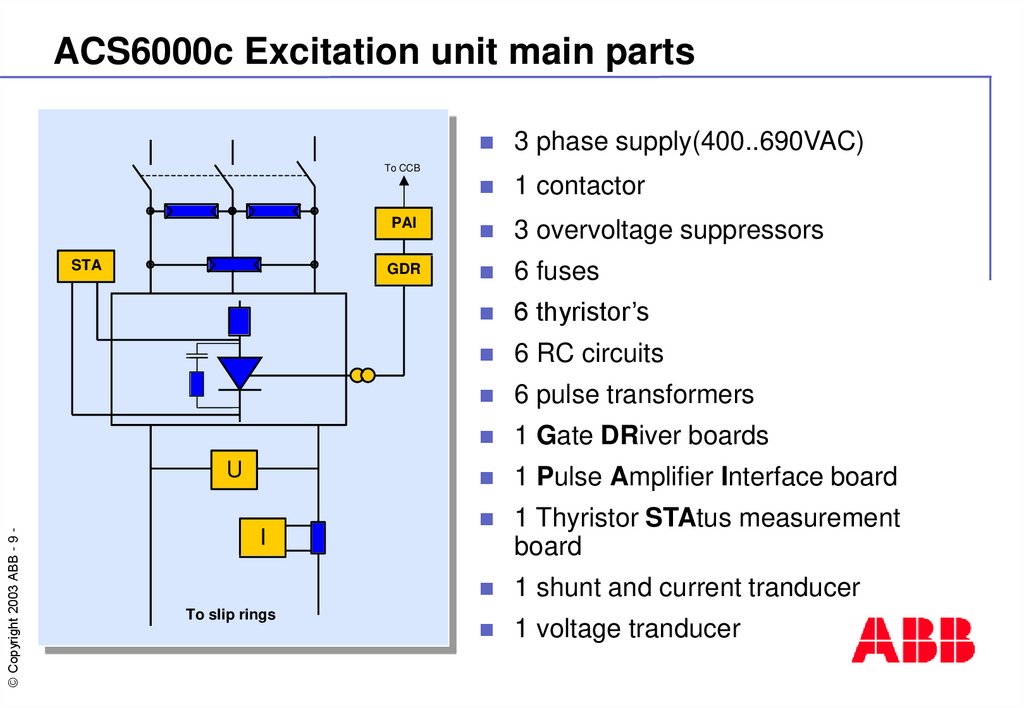
9. ACS6000c Excitation unit main parts
3 phase supply(400..690VAC)1 contactor
PAI
3 overvoltage suppressors
GDR
6 fuses
6 thyristor’s
6 RC circuits
6 pulse transformers
1 Gate DRiver boards
1 Pulse Amplifier Interface board
1 Thyristor STAtus measurement
board
1 shunt and current tranducer
1 voltage tranducer
To CCB
STA
© Copyright 2003 ABB - 9 -
U
I
To slip rings
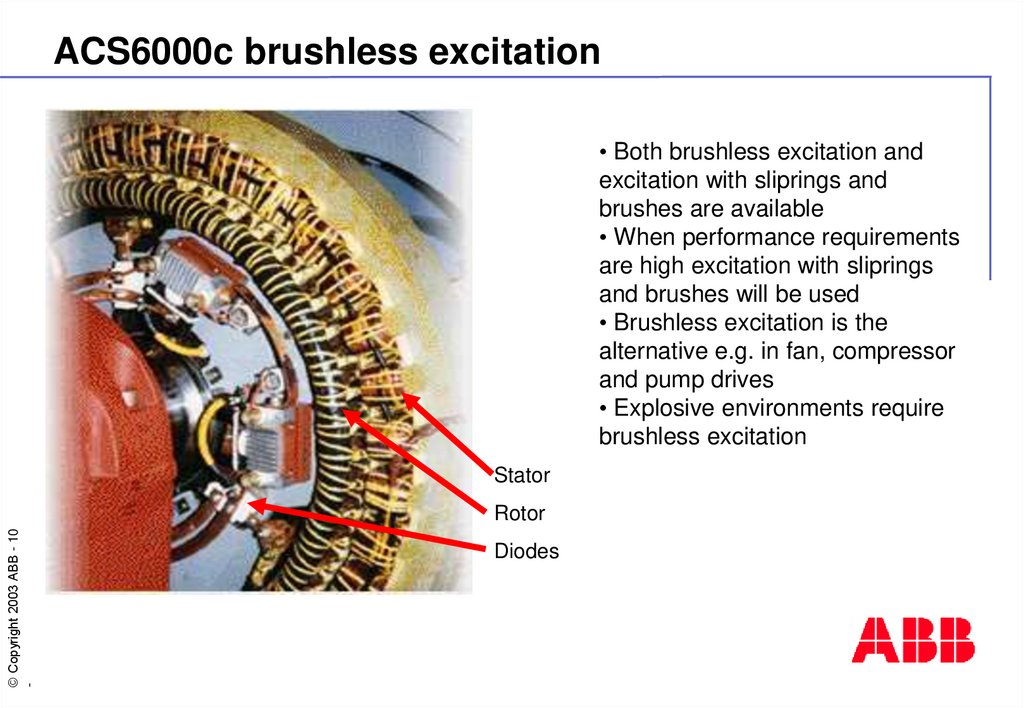
10. ACS6000c brushless excitation
• Both brushless excitation andexcitation with sliprings and
brushes are available
• When performance requirements
are high excitation with sliprings
and brushes will be used
• Brushless excitation is the
alternative e.g. in fan, compressor
and pump drives
• Explosive environments require
brushless excitation
Stator
© Copyright 2003 ABB - 10
-
Rotor
Diodes
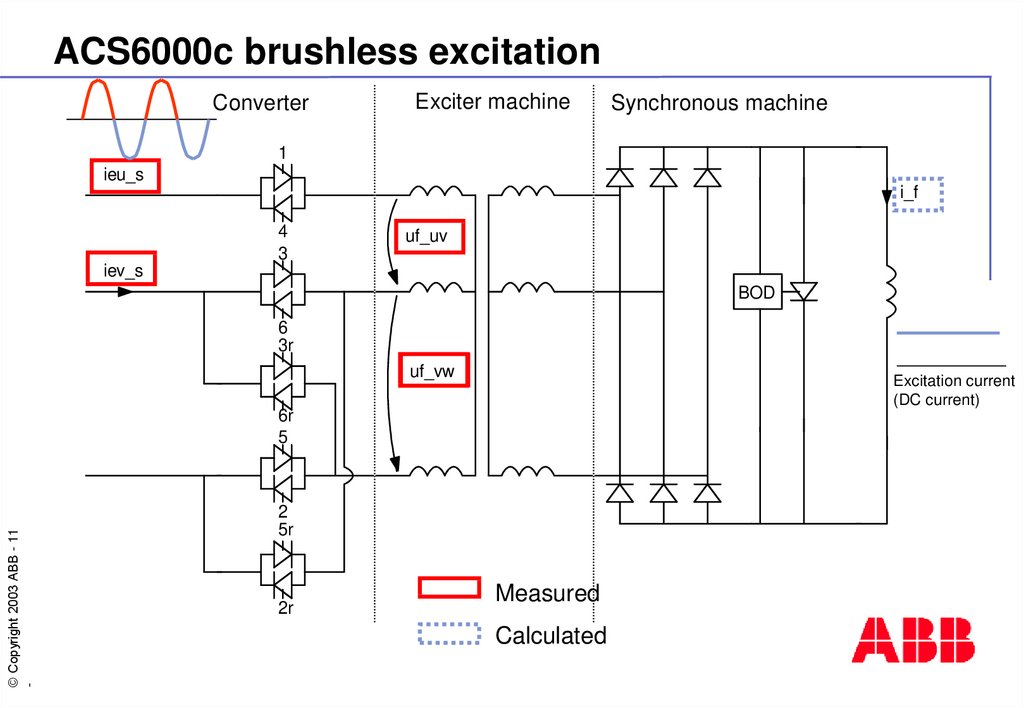
11. ACS6000c brushless excitation
ConverterExciter machine
Synchronous machine
1
ieu_s
i_f
4
3
uf_uv
iev_s
BOD
6
3r
uf_vw
Excitation current
(DC current)
© Copyright 2003 ABB - 11
-
6r
5
2
5r
2r
Measured
Calculated
12. ACS6000c brushless excitation
ThyristorsPulse transformers
Supply fuses
© Copyright 2003 ABB - 12
-
Supply cables
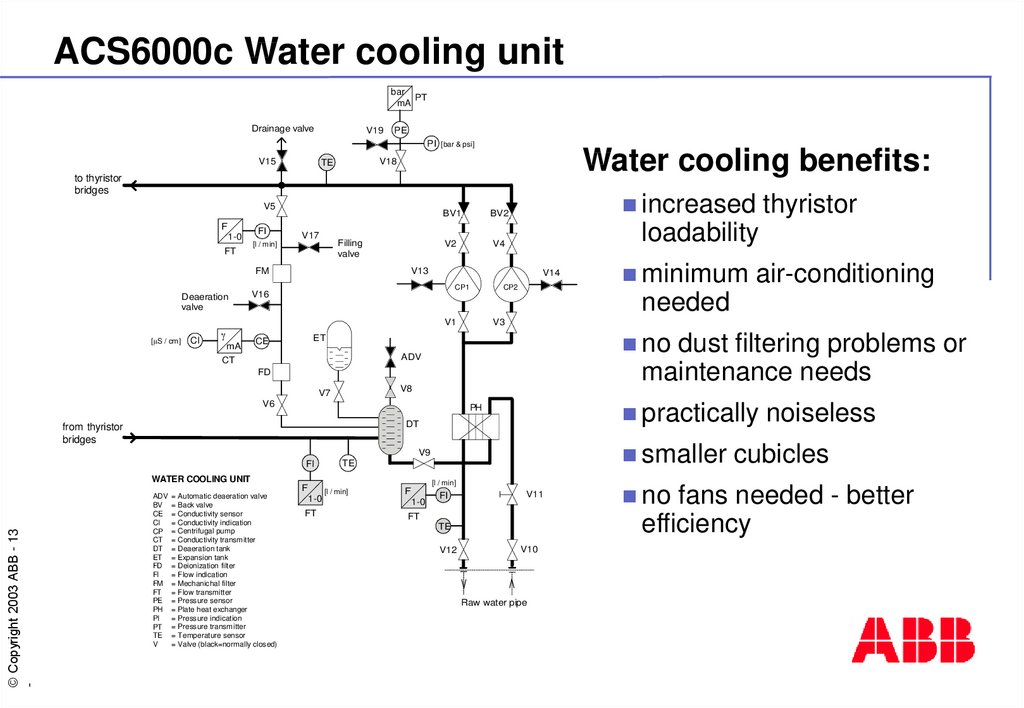
13. ACS6000c Water cooling unit
barPT
mA
Drainage valve
V19
PE
PI [bar & psi]
V15
Water cooling benefits:
V18
TE
to thyristor
bridges
V5
F
1-0
FT
FI
V17
[l / min]
Filling
valve
BV2
V2
V4
V16
CI
mA
CE
CP2
no
dust filtering problems or
maintenance needs
ET
FD
V8
V7
V6
practically
PH
DT
from thyristor
bridges
smaller
V9
FI
TE
WATER COOLING UNIT
© Copyright 2003 ABB - 13
-
air-conditioning
V3
ADV
= Automatic deaeration valve
= Back valve
= Conductivity sensor
= Conductivity indication
= Centrifugal pump
= Conductivity transmitter
= Deaeration tank
= Expansion tank
= Deionization filter
= Flow indication
= Mechanichal filter
= Flow transmitter
= Pressure sensor
= Plate heat exchanger
= Pressure indication
= Pressure transmitter
= Temperature sensor
= Valve (black=normally closed)
minimum
needed
CT
ADV
BV
CE
CI
CP
CT
DT
ET
FD
FI
FM
FT
PE
PH
PI
PT
TE
V
thyristor
loadability
V14
CP1
V1
[ S / cm]
increased
V13
FM
Deaeration
valve
BV1
F
[l / min]
1-0
FT
[l / min]
F
1-0
FI
V11
FT
TE
V12
V10
Raw water pipe
no
noiseless
cubicles
fans needed - better
efficiency
14. ACS6000c Water cooling unit
Expansion vesselTwo pumps
Ion-compound
ion-compound water flow
meter
Pressure sensors
© Copyright 2003 ABB - 14
-
External water cooling
connection
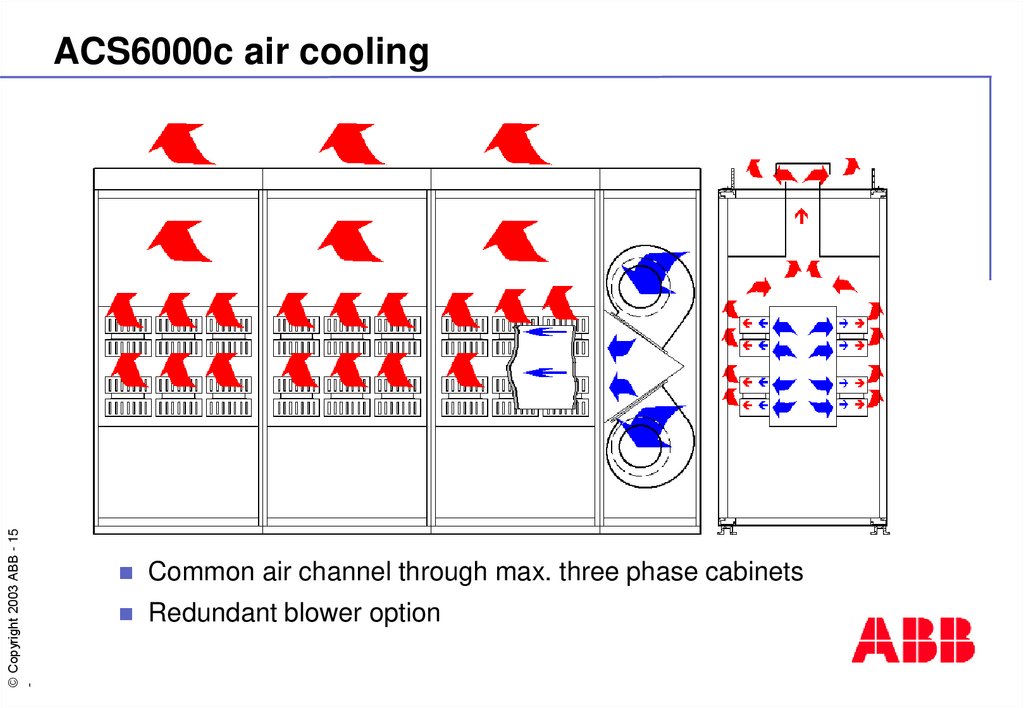
15. ACS6000c air cooling
© Copyright 2003 ABB - 15-
ACS6000c air cooling
Common air channel through max. three phase cabinets
Redundant blower option
16. ACS6000c high speed circuit breakers(HSCB)
© Copyright 2003 ABB - 16-
ACS6000c high speed circuit breakers(HSCB)
Made by Secheron,
Geneva, Switzerland
Nominal voltages up to
4000V
Maximum rated currents
up to 6000A
More selective protection
in case of short circuit in
motor or commutation
failure during
regenerating(loss of supply
voltage)
Voltage level of the fuses
lower. 1.25kV instead of
2.0kV without HSCB
17. ACS6000c HSCB operation
ARC CHUTE© Copyright 2003 ABB - 17
-
MOVING CONTACT
COIL
Fork
TRIPPING DEVICE
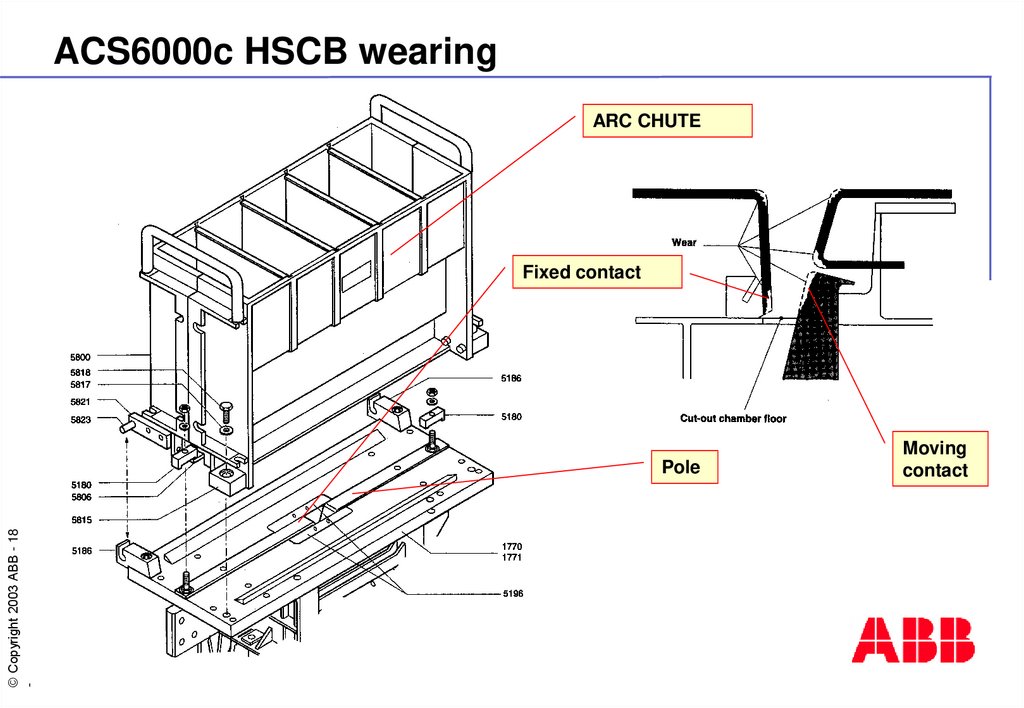
18. ACS6000c HSCB wearing
ARC CHUTEFixed contact
© Copyright 2003 ABB - 18
-
Pole
Moving
contact
19. ACS6000c HSCB setting
© Copyright 2003 ABB - 19-
ACS6000c HSCB setting
Trip limit=
1.41 × maximum motor current ×1.3
1.41 × 2100A × 1.3=3850A
Phase current
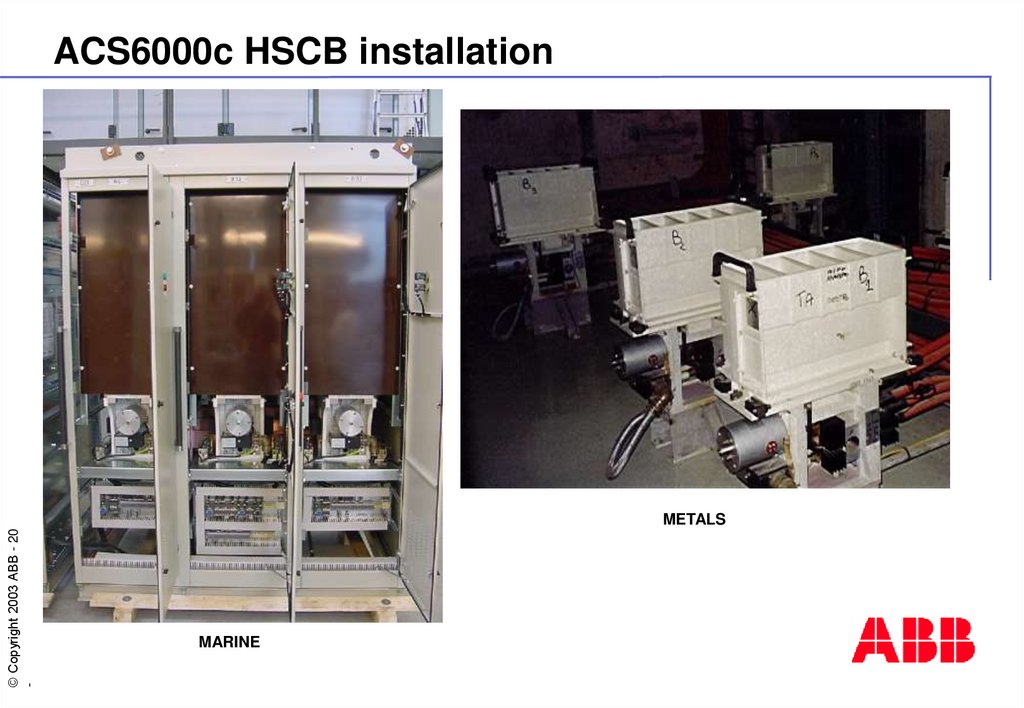
20. ACS6000c HSCB installation
© Copyright 2003 ABB - 20-
METALS
MARINE
21. ACS6000c, Synchronous motor compared to DC
© Copyright 2003 ABB - 21-
Smaller mechanical size
No commutation problems
Lower losses
Full overload up to max speed
Less maintenance
Moment of inertia can be kept low: long
rotor, small diameter
AC-Synchronous motor is thermally less
critical
Stator monitored with Pt-100
elements
Rotor construction is not thermally
critical
Gearless solutions: noise - losses
22. ACS6000c, SM rotor design
Salient pole motor with highoverloadability and easy cooling of
rotor
means smaller inertia and lower weight
means lower losses in the rotor
means higher margins to the pole angle
limit (90 degrees)
direct cooling of the excitation windings
© Copyright 2003 ABB - 22
-
Salient pole rotor with removable
poles
means only a pole as a spare part, not
the whole rotor
means that the rotor can be repaired at
site
23. ACS6000c control
AMC3 with DDCS -Optic LinksFieldbus Adapter
to other systems
or link to the
Advant Controller
RS485
Application and Motor
Controller, AMC3
Control panel
PC Link
CONVERTER
CONTROL
BOARDS
(CCB)
S800 I/O Station
© Copyright 2003 ABB - 23
-
Temperature measurement
Gray encoder interface
Pulse encoder interface
Position feedback
Speed feedback
PT100
PAI
Converter PAI
PAI
Unit 1
Converter
Excitation
Unit
N
Unit
24. ACS6000c control
PROCESS AND USER I/OCOMMON ELECTRONICS
S800 I/O STATION
TO ADVANT
CONTROLLER
TB820
FIELDBUS
ADAPTER
TACHOM.
BOARD
NTAC-02
PROCESS I/O
GRAY ENC. BASIC I/O
BOARD
UNITS
(GRB)
(BIO1...3)
CDP
312
DRIVE CONTROL
D
D
C
S
D
D
C
S
R
S4
85
D
D
C
S
CONVERTER UNIT 1
LOCAL
I/O
D
D
C
S
CONVERTER
CONTROL
BOARD (CCB)
MUB MUB
CONVERTER UNIT 3
STA
STA
STA
APPLICATION AND MOTOR
CONTROL BOARD (AMC3)
MUB MUB
CONVERTER UNIT 2
CONVERTER
CONTROL
BOARD (CCB)
POWER
SUPPLY
PULSE AMPL. GDR
INTERFACE
GDR
(PAI)
LOCAL
I/O
POWER
SUPPLY
PULSE AMPL. GDR
INTERFACE
GDR
(PAI)
LOCAL
I/O
POWER
SUPPLY
PULSE AMPL. GDR
INTERFACE
GDR
(PAI)
EXCITATION UNIT
STA
LOCAL
I/O
POWER
SUPPLY
PULSE AMPL. GDR
INTERFACE
(PAI)
DDCS
DDCS
DDCS
DDCS
© Copyright 2003 ABB - 24
-
MEAS.UNIT
INTERF.(MUI)
MTR
MEAS.UNIT
INTERF.(MUI)
1...8
1...8
1...8
1...8
MTR
MTR
MTR
25. ACS6000c speed and current control loops
AMC3Speed controller and
current reference
calculation
CCB
Phase unit
Current
controller
Synchronization
and firing logic
Speed
reference
Current
measurement
Motor
SM
© Copyright 2003 ABB - 25
-
Rotor position
measurement
SE
Speed
measurement
PG
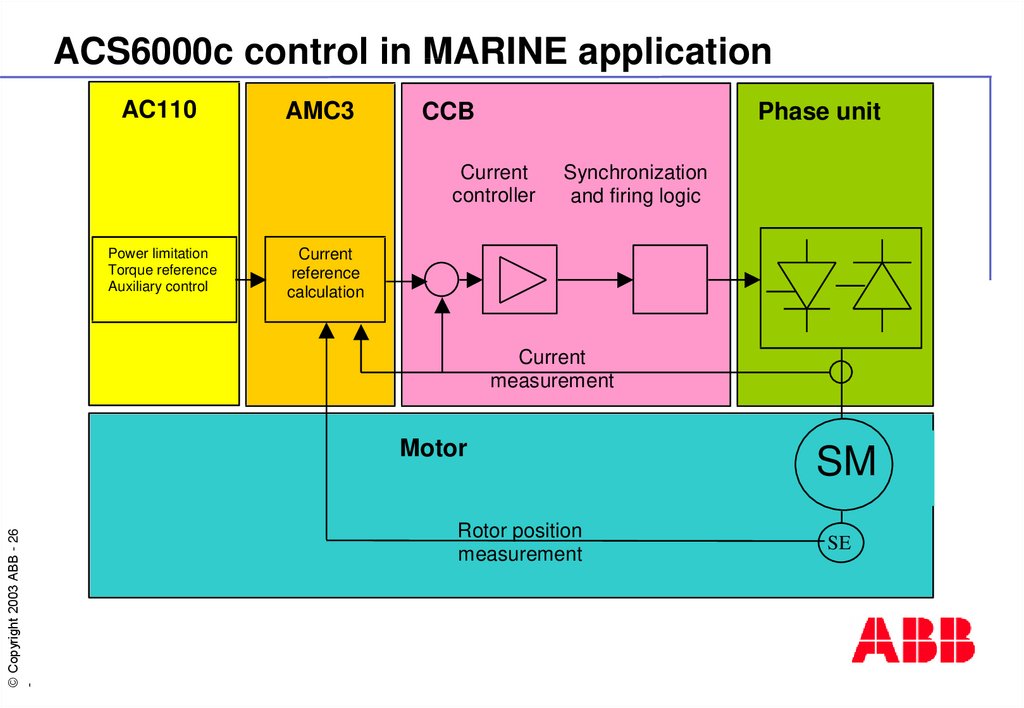
26. ACS6000c control in MARINE application
AC110AMC3
CCB
Phase unit
Current
controller
Power limitation
Torque reference
Auxiliary control
Synchronization
and firing logic
Current
reference
calculation
Current
measurement
© Copyright 2003 ABB - 26
-
Motor
Rotor position
measurement
SM
SE
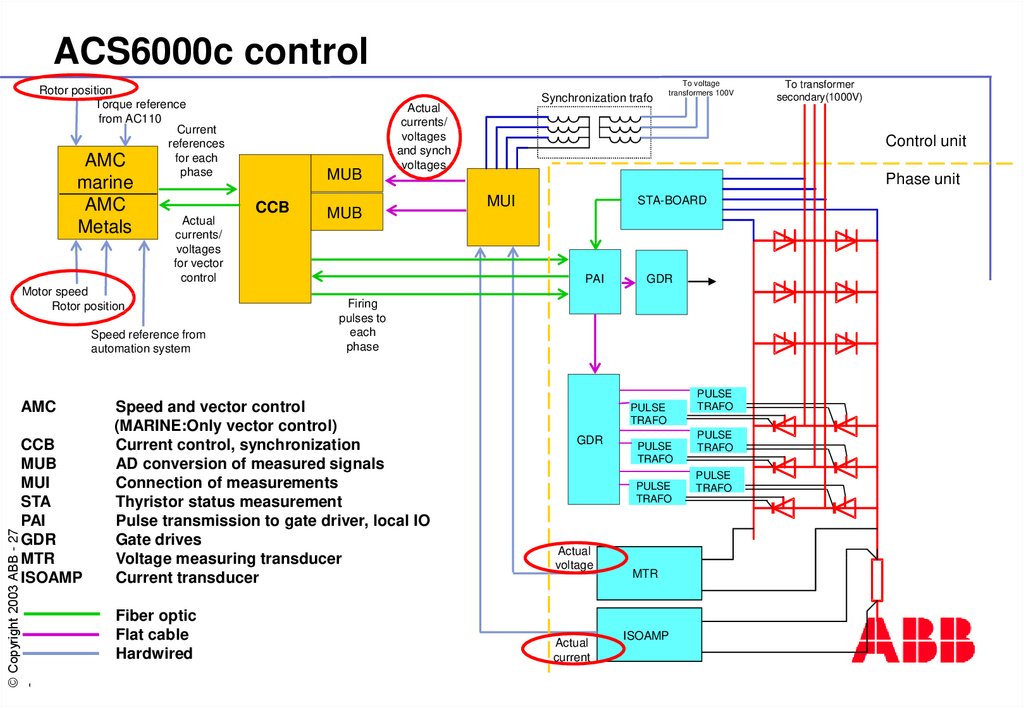
27. ACS6000c control
Rotor positionTorque reference
from AC110
Current
references
for each
AMC
phase
marine
AMC
Metals
CCB
Actual
currents/
voltages
for vector
control
Motor speed
Rotor position
Speed reference from
automation system
AMC
© Copyright 2003 ABB - 27
-
CCB
MUB
MUI
STA
PAI
GDR
MTR
ISOAMP
MUB
Actual
currents/
voltages
and synch
voltages
MUB
To voltage
transformers 100V
To transformer
secondary(1000V)
Control unit
Phase unit
MUI
STA-BOARD
PAI
GDR
Firing
pulses to
each
phase
Speed and vector control
(MARINE:Only vector control)
Current control, synchronization
AD conversion of measured signals
Connection of measurements
Thyristor status measurement
Pulse transmission to gate driver, local IO
Gate drives
Voltage measuring transducer
Current transducer
Fiber optic
Flat cable
Hardwired
Synchronization trafo
PULSE
TRAFO
GDR
PULSE
TRAFO
PULSE
TRAFO
Actual
voltage
Actual
current
MTR
ISOAMP
PULSE
TRAFO
PULSE
TRAFO
PULSE
TRAFO

















 industry
industry








