Similar presentations:
Human skeleton
1.
Made by: Nazar Kostiuk2.
The biggest bone in the body is the femur in the thigh andthe smallest is the stapes bone in the middle ear. Several
factors contribute to the bone density and average mass of
the human skeleton including; gender, race, hormonal
factors, nutrition, physical activity and lifestyle behaviors.
Because of these and other factors affecting an individual's
weight the human skeleton may comprise between 12 and
20 percent of a person's total body weight with the average
being 15 percent.
Fused bones include those of the pelvis and the cranium.
Not all bones are interconnected directly: there are three
bones in each middle ear called the ossicles that articulate
only with each other. The hyoid bone, which is located in the
neck and serves as the point of attachment for the tongue,
does not articulate with any other bones in the body, being
supported by muscles and ligaments.
3.
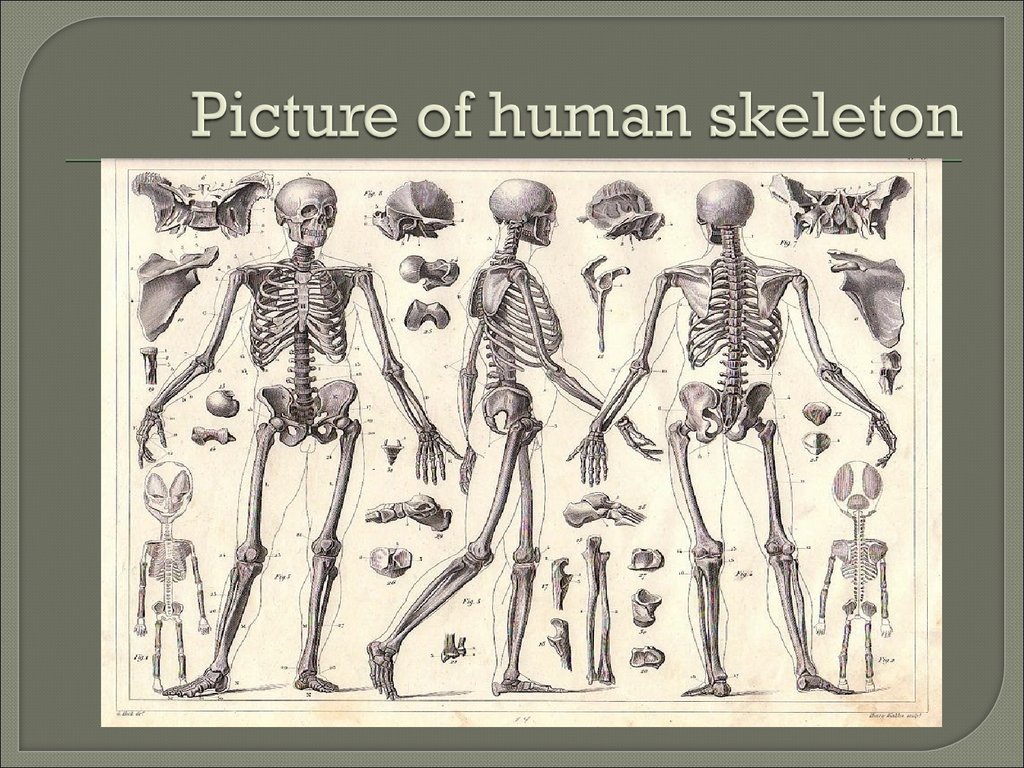
There are over 206 bones in the adulthuman skeleton, a number which
varies between individuals and with
age – newborn babies have over 270
bones some of which fuse together
into a longitudinal axis, the axial
skeleton, to which the appendicular
skeleton is attached.
4.
It has six functions:Support
Movement
Protection
Blood cell production
Storage
Endocrine regulation
5.
There are many differences between themale and female human skeletons. Most
prominent is the difference in the pelvis,
owing to characteristics required for the
processes of childbirth. The shape of a
female pelvis is flatter, more rounded
and proportionally larger to allow the
head of a fetus to pass. A male's pelvis
is about 90 degrees or less of angle,
whereas a woman's is 100 degrees or
more.
6.
Components: (neurocranium)Occipital bone
Two temporal bones
Two parietal bones
Sphenoid bone
Ethmoid bone
Frontal bone
7.
Components: (viscerocranium)Vomer
Two conchae
Two nasal bones
Maxilla
Mandible
Palatine bone
2 zygomatic bones
2 lacrimal bones
8.
9.
Appendicular – АппендикулярныйLongitudinal – Продольний
Pelvis - Таз
Prominent – Видний
Fetus – Плід
Occipital bone – Потилична кістка
Temporal bone – Скронева кістка
Parietal bone – Тімяна кістка
Sphenoid bone – Клиноподібна кістка
Ethmoid bone – Решітчата кістка
Vomer – Сошник
Conchae – Раковина
Maxilla – Верхня щелепа
Mandible – Нижня щелепа
Palatine bone – Піднебінна кістка
Zygomatic bone – Вилична кістка
Lacrimal bone – Слізна кістка









 biology
biology english
english