Similar presentations:
The Skeleton
1.
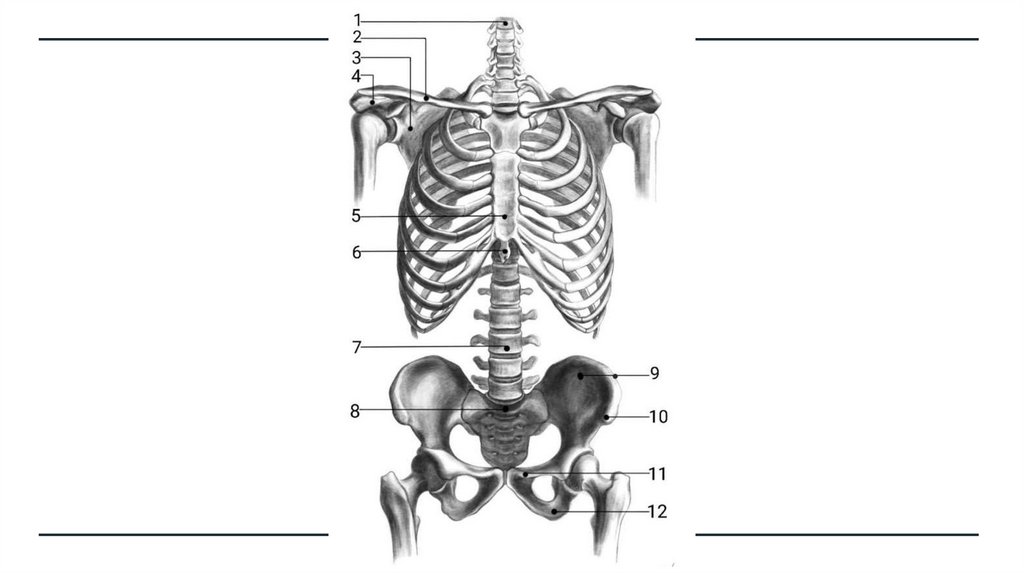
The Skeleton2
2.
Human Skeleton Quiz• How many bones are there in an adult human skeleton?
A) 206
B) 210
C) 215
D) 200
• Which is the largest bone in the human body?
A) Humerus
B) Femur
C) Tibia
D) Vertebrae
• Which part of the skeleton protects the brain?
A) Thoracic cage
B) Skull
C) Pelvis
D) Spine
• What is the name of the bone that forms the upper jaw?
A) Maxilla
B) Mandible
C) Zygomatic
D) Nasal
3.
Human Skeleton Quiz• How many vertebrae are in the adult human spine?
A) 24
B) 26
• The patella is commonly known as the wrist bone.
True
C) 30
False
D) 32
• The femur is located in the arm.
• True/False Questions
• The human skeleton is made up of both bones and cartilage.
True
True
False
False
• Bones can regenerate and heal after injuries.
• The rib cage consists of 12 pairs of ribs.
True
True
False
False
4.
5.
6.
7.
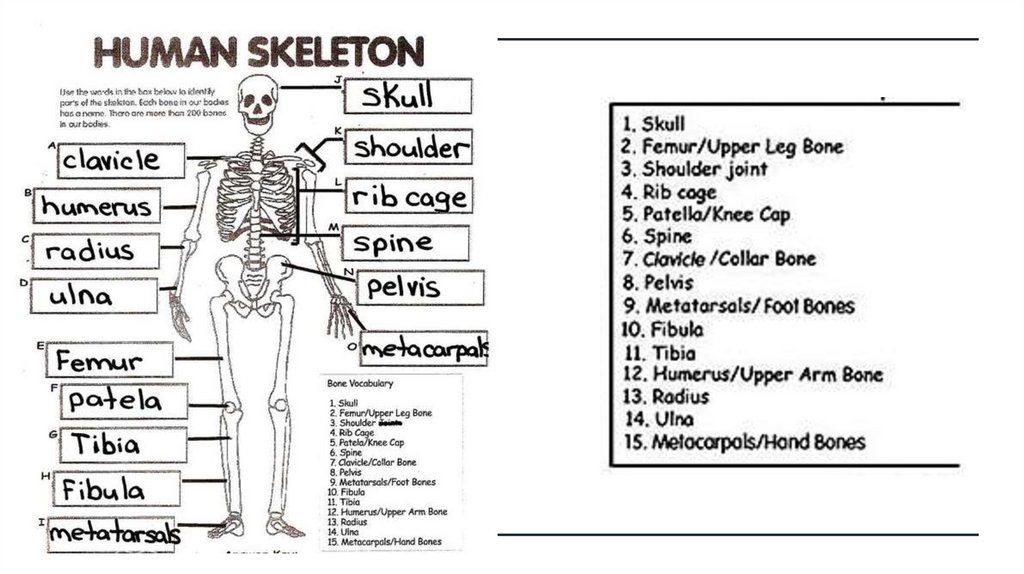
Task 1: Bone Identificationand Function Study
Objective: To develop familiarity with the major bones of the human skeleton as well as their structural and
functional attributes.
Task 2: Case Study Analysis
Objective: To analyze a clinical case involving skeletal injuries.
Instructions:
Instructions:
Use a skeleton model or anatomical software to identify the following bones:
Read the following fictional case study:
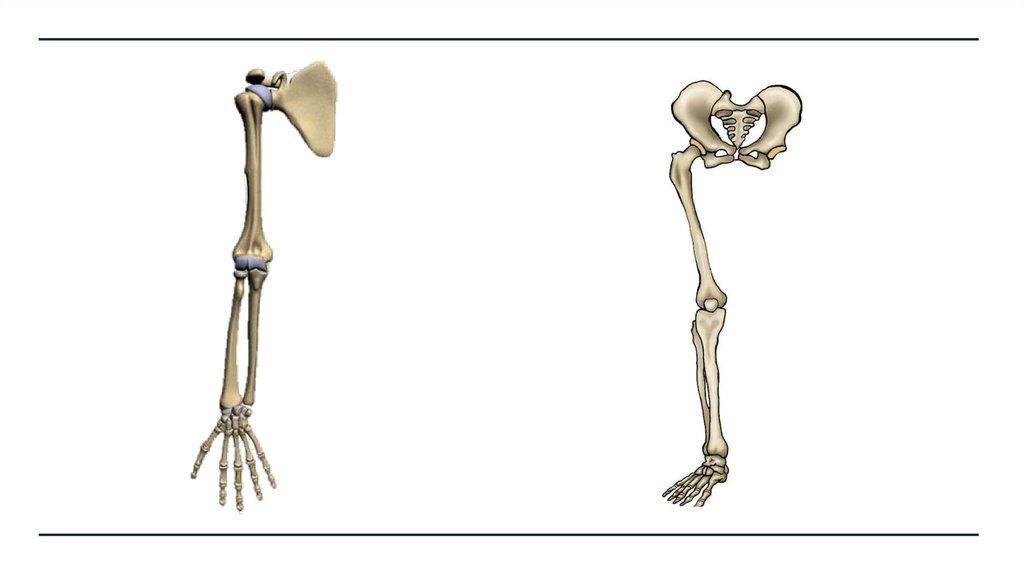
Scapula
A 35-year-old male presents with severe pain in the right wrist after a fall. Imaging reveals a scaphoid fracture.
Clavicle
Answer the following questions:
Vertebrae (Cervical, Thoracic, Lumbar)
What is the significance of the scaphoid bone in the wrist?
Pelvis
Discuss the potential complications of a scaphoid fracture.
Humerus
Propose a treatment plan, including any necessary imaging, surgery, or rehabilitation.
Femur
Reflect on the importance of recognizing complex fractures in the skeletal system.
For each bone identified, write a brief report that includes:
Location in the body
Primary functions (e.g., movement, support, protection)
Common pathologies associated with each bone (e.g., fractures, arthritis).
8.
Task 3:Comparative
Anatomy
Objective: To compare and contrast the human skeleton with that of another mammal.
Instructions:
Select a mammal (e.g., dog, cat, or primate) and research its skeletal structure.
Create a presentation that includes:
Key similarities and differences in the bone structure and function between the selected mammal and humans.
Discussion on evolutionary adaptations in skeletal structures that allow for different modes of locomotion or habitat use.
Visual aids, such as diagrams or comparative charts, to illustrate your points.





 biology
biology