Similar presentations:
Value chain analysis
1. Value chain analysis
WIUU Business Policy, 2017. J. Bentz2. VALUE
THE VALUE IS THE TOTAL AMOUNT (i.e. TOTALREVENUE) THAT BUYERS ARE WILLING TO PAY FOR A
FIRM’S PRODUCTS.
THE DIFFERENCE BETWEEN THE TOTAL VALUE (OR
REVENUE) AND THE TOTAL COST OF PERFORMING ALL
OF THE FIRM’S ACTIVITIES PROVIDES THE MARGIN .
THE VALUE CHAIN IS A TOOL DEVELOPED BY DR.
MICHAEL PORTER(HARVARD BUSINESS SCHOOL)
2
WIUU Business Policy, 2017. J. Bentz
3. WHAT IS THE VALLUE CHAIN?
Porter’s definition includes all activities to design,produce, market, deliver, and support the
product/service.
The value chain is concentrating on the activities
starting with raw materials till the conversion into final
goods or services.
Two categories:
Primary Activities (operations, distribution, sales)
Support Activities (R&D, Human Resources)
3
WIUU Business Policy, 2017. J. Bentz
4. TYPES OF VALUE CHAIN
Value Chain is categorized into types based on thetype of organizations.
Manufacturing based.
Service based.
Both manufacturing and service based.
4
WIUU Business Policy, 2017. J. Bentz
5. WHAT IS VALUE CHAIN ANALYSIS?
Used to identify sources of competitive advantageSpecifically:
Opportunities to secure cost advantages
Opportunities to create product/service
differentiation
Includes the value-creating activities of all industry
participants
5
WIUU Business Policy, 2017. J. Bentz
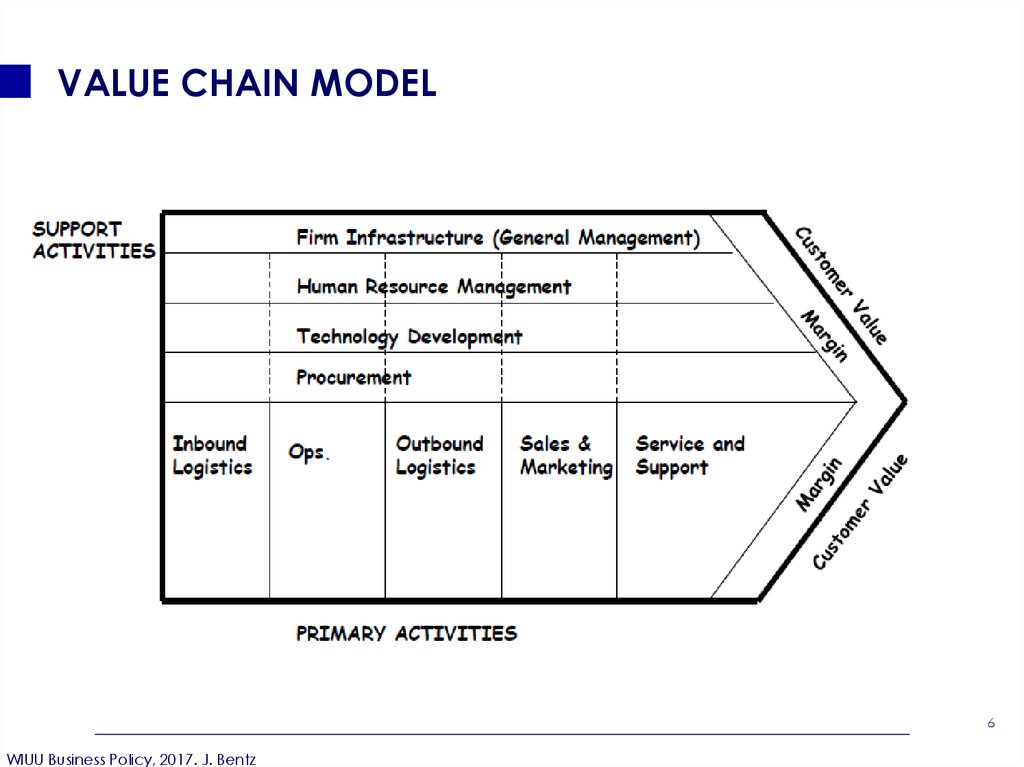
6. VALUE CHAIN MODEL
6WIUU Business Policy, 2017. J. Bentz
7. TYPES OF FIRM ACTIVITIES
Primary activities:Support Activities:
Those that are involved in the
creation, sale and transfer of
products (including after-sales
service)
Those that merely support the
primary activities
Inbound logistics
Operations
Outbound logistics
Human resources
(general and admin.)
Tech. development/ IT
Procurement
Sales and marketing
Service and support
7
WIUU Business Policy, 2017. J. Bentz
8. VALUE CHAIN MODEL
8WIUU Business Policy, 2017. J. Bentz
9. PRIMARY ACTIVITIES
INBOUND LOGISTICSCONCERNED WITH RECEIVING, STORING, DISTRIBUTING
INPUTS (e.g. HANDLING OF RAW MATERIALS, WAREHOUSING,
INVENTORY CONTROL)
OPERATIONS
COMPRISE THE TRANSFORMATION OF THE INPUTS INTO THE
FINAL PRODUCT FORM (E.G. PRODUCTION, ASSEMBLY, AND
PACKAGING)
OUTBOUND LOGISTICS
INVOLVE THE COLLECTING, STORING, AND DISTRIBUTING THE
PRODUCT TO THE BUYERS (e.g. PROCESSING OF ORDERS,
WAREHOUSING OF FINISHED GOODS, AND DELIVERY)
9
WIUU Business Policy, 2017. J. Bentz
10. PRIMARY ACTIVITIES
MARKETING AND SALESIdentification of customer needs and generation of sales.
(e.g. ADVERTISING, PROMOTION, DISTRIBUTION)
SERVICE -INVOLVES HOW TO MAINTAIN THE VALUE OF THE
PRODUCT AFTER IT IS PURCHASED (e.g. INSTALLATION, REPAIR,
MAINTENANCE, AND TRAINING)
10
WIUU Business Policy, 2017. J. Bentz
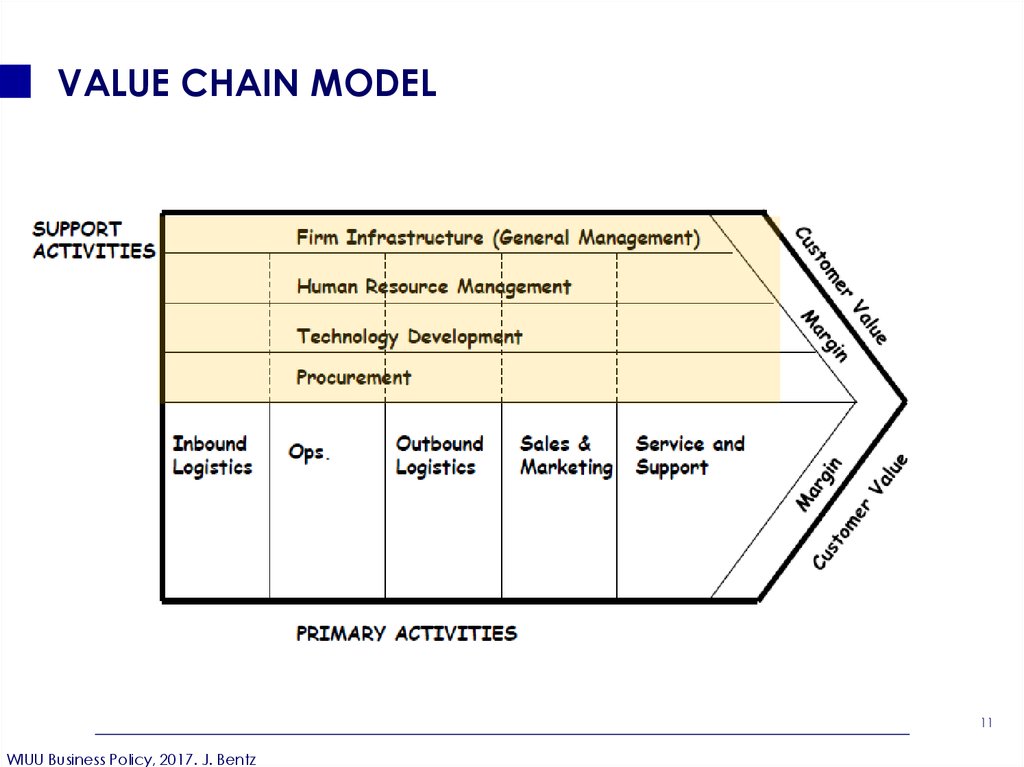
11. VALUE CHAIN MODEL
11WIUU Business Policy, 2017. J. Bentz
12. SUPPORT ACTIVITIES
FIRM INFRASTRUCTUREThe activities such as Organization structure, control system,
company culture are categorized under firm infrastructure.
HUMAN RESOURCE MANAGEMENT
Involved in recruiting, hiring, training, development and
compensation.
TECHNOLOGY DEVELOPMENT
These activities are intended to improve the product and
the process, can occur in many parts of the firm.
PROCUREMENT
Concerned with the tasks of purchasing inputs such as raw
materials, equipment, and even labor.
12
WIUU Business Policy, 2017. J. Bentz
13. USES OF THE VALUECHAIN
The sources of the competitive advantage of a firm can beseen from its discrete activities and how they interact with one
and another.
The value chain is a tool for systematically examining the
activities of a firm and how they interact with one another and
affect each other’s cost and performance.
A firm gains a competitive advantage by performing these
activities better or at lower cost than competitors.
Helps you to stay out of the “No Profit Zone”
Presents opportunities for integration
Aligns spending with value processes
13
WIUU Business Policy, 2017. J. Bentz
14. VERTICAL LINKAGE
LINKAGES CAN ALSO EXIST OUTSIDE THE FIRM; FOR INSTANCETHERE IS A LINKAGE BETWEEN A FIRM’S CHAIN AND THE VALUE
CHAIN OF ITS SUPPLIERS AND CHANNELS.
e.g. THE ACTIVITIES OF THE RAW MATERIALS SUPPLIERS AFFECT THE
ACTIVITIES OF THE FIRM. SIMILARLY, THE ACTIVITIES OF THE
DISTRIBUTOR ALSO AFFECT THE FIRM.
14
WIUU Business Policy, 2017. J. Bentz
15. APPLYING THE VALUE CHAIN TO AN INDUSTRY
THE VALUE CHAINS OF THE DIFFERENT FIRMS WITHIN AN INDUSTRYVARY FROM ONE ANOTHER.
IN FACT, THE DIFFERENCES IN THE VALUE CHAINS AMONG THE
DIFFERENT INDUSTRY PLAYERS PROVIDE THE SOURCE OF
COMPETITIVE ADVANTAGES BETWEEN THESE PLAYERS.
15
WIUU Business Policy, 2017. J. Bentz













 finance
finance








