Similar presentations:
Cushing Syndrome
1. Cushing Syndrome
Dr. Nodelman Marina2. Cushing Syndrome
Cushing's syndrome is a collection of signs andsymptoms due to prolonged exposure to cortisol
In pituitary Cushing's, a benign pituitary adenoma
secretes ACTH. This is also known as Cushing's
disease and is responsible for 70% of endogenous
Cushing's syndrome.
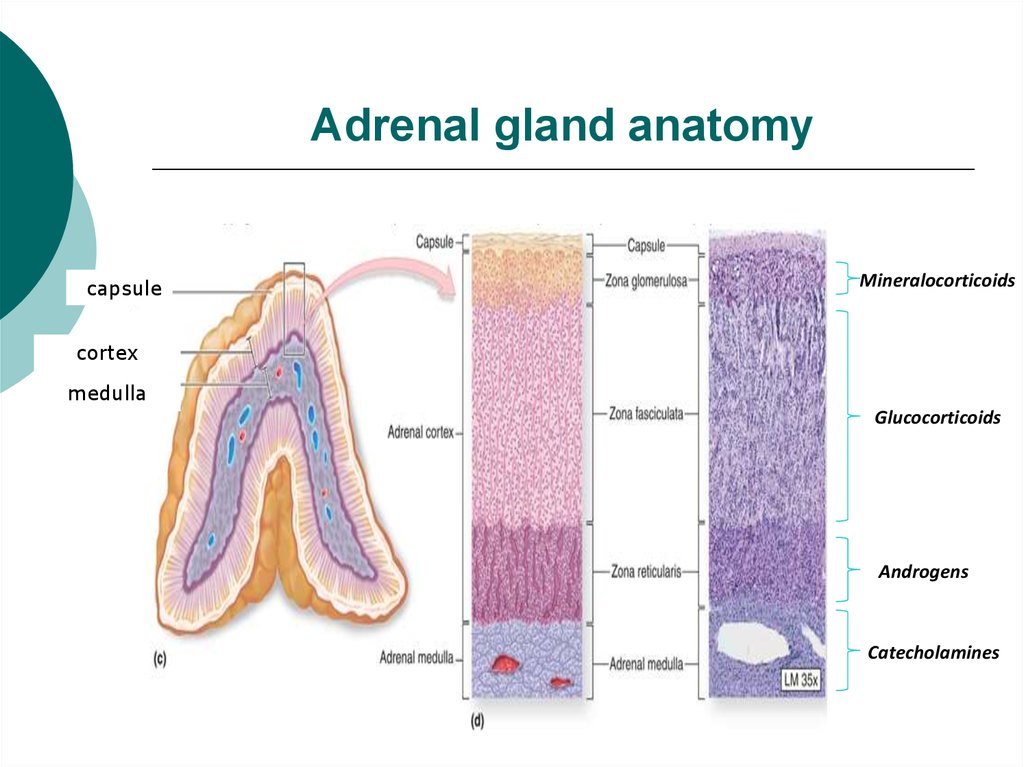
3. Adrenal gland anatomy
capsuleMineralocorticoids
cortex
medulla
Glucocorticoids
Androgens
Catecholamines
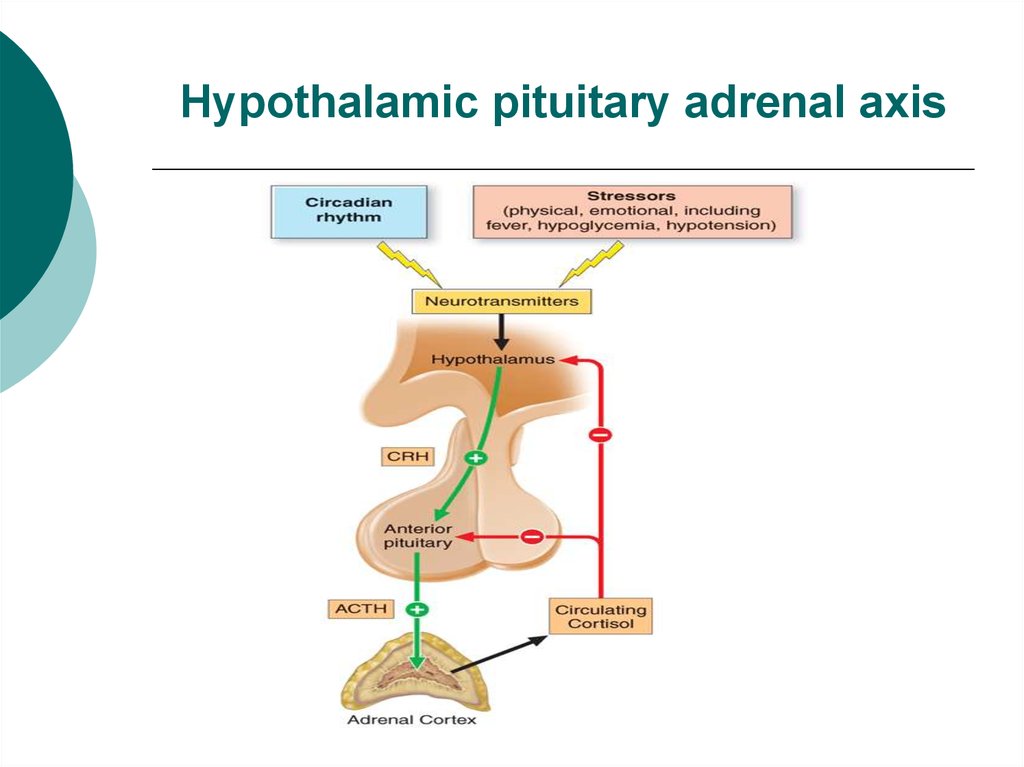
4. Hypothalamic pituitary adrenal axis
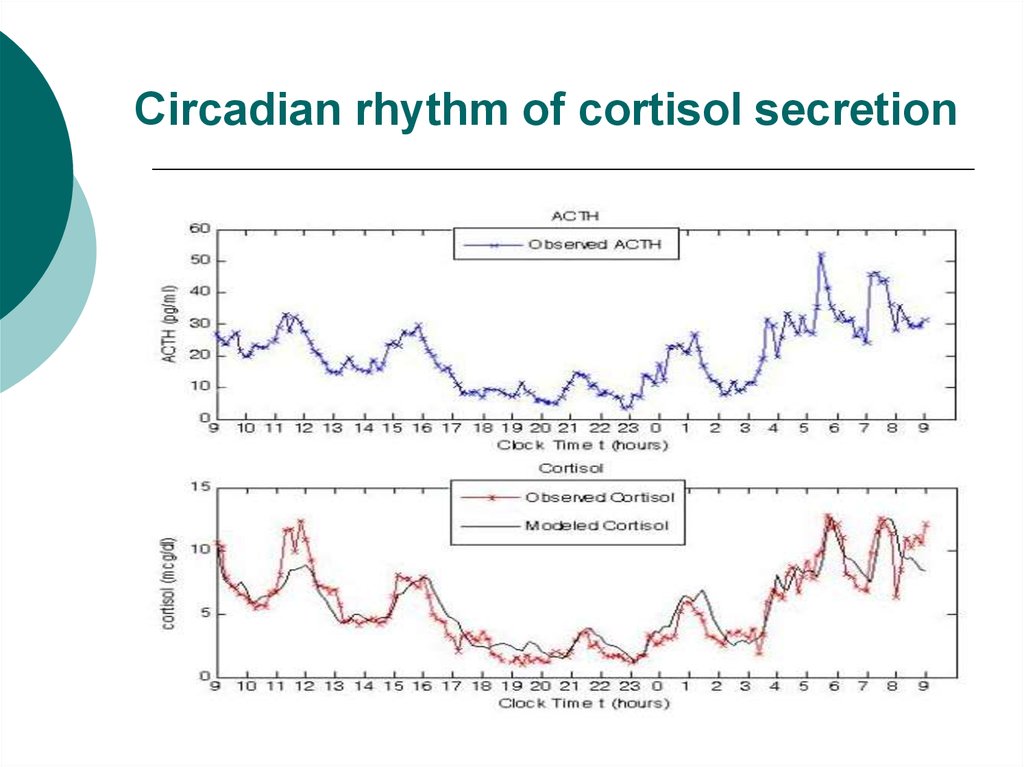
5. Circadian rhythm of cortisol secretion
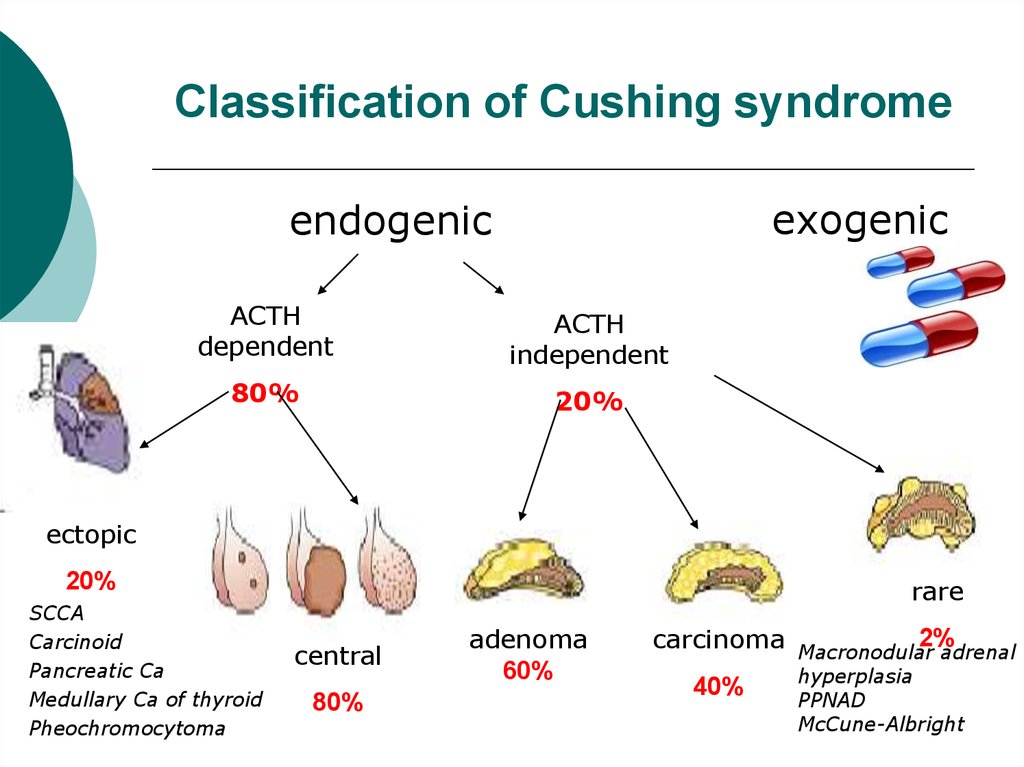
6. Classification of Cushing syndrome
exogenicendogenic
ACTH
dependent
ACTH
independent
80%
20%
ectopic
20%
SCCA
Carcinoid
Pancreatic Ca
Medullary Ca of thyroid
Pheochromocytoma
rare
central
80%
adenoma
60%
carcinoma
40%
2%
Macronodular adrenal
hyperplasia
PPNAD
McCune-Albright
7. Epidemiology
Rare endocrine disorder 2.3/1,000,000/yearCushings dis. 1.5/1,000,000/year, women>>men,
25-45
Adrenal adenoma 0.6/1,000,000/year,
women>>men
Adrenal carcinoma 0.2/1,000,000/year, 50%
Cushing syndr. in children
Ectopic Cushing, 1% SSCA, men>women, after 50
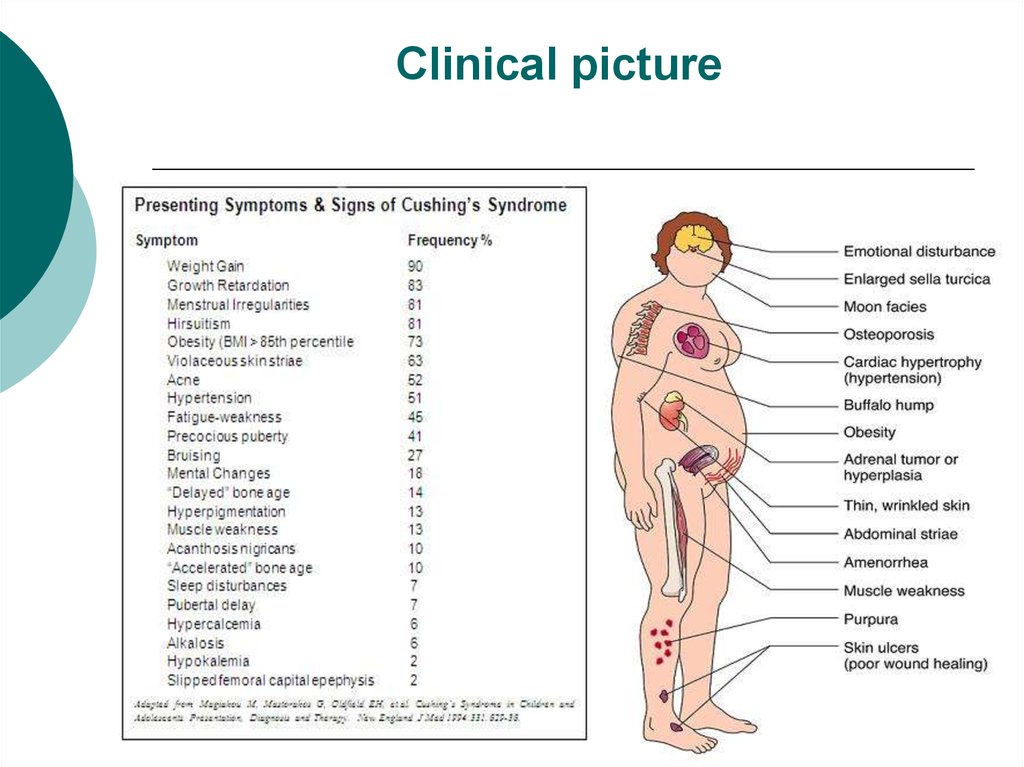
8. Clinical picture
9. Clinical picture
Central obesity10. Clinical picture
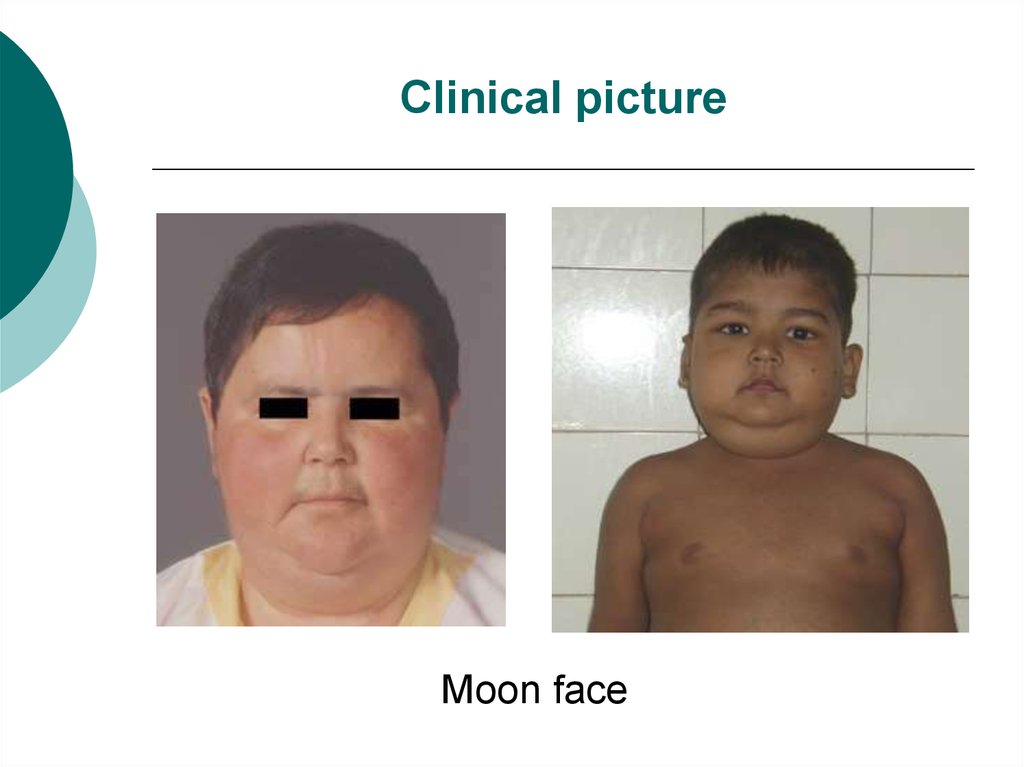
Moon face11. Clinical picture
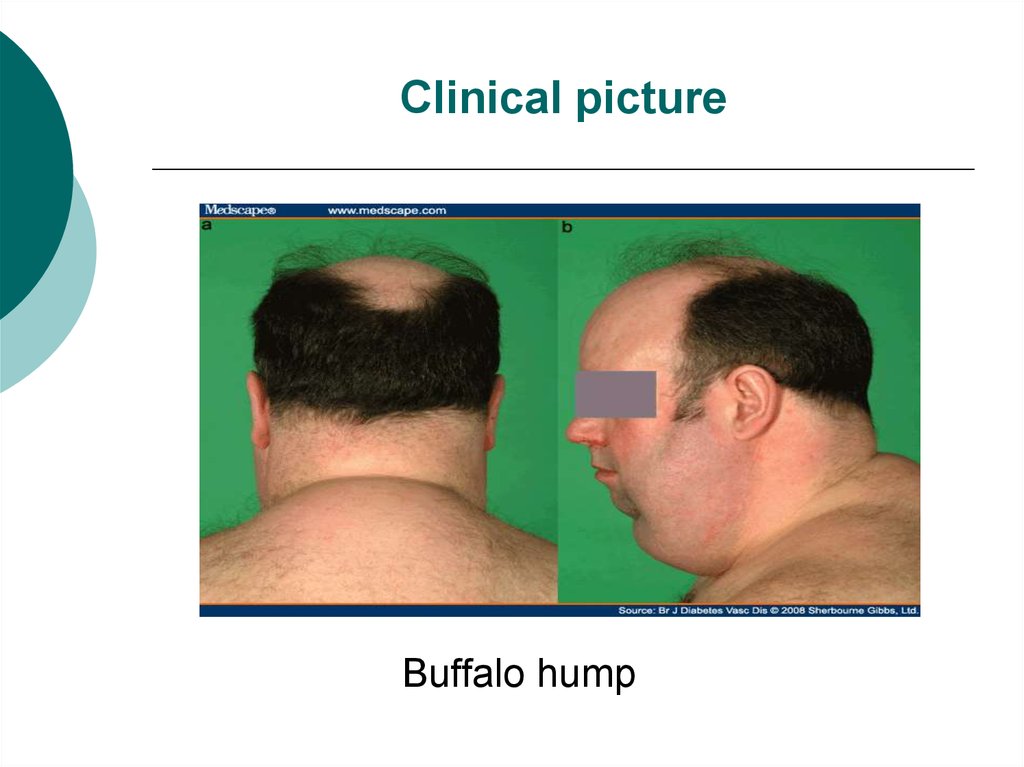
Buffalo hump12. Clinical picture
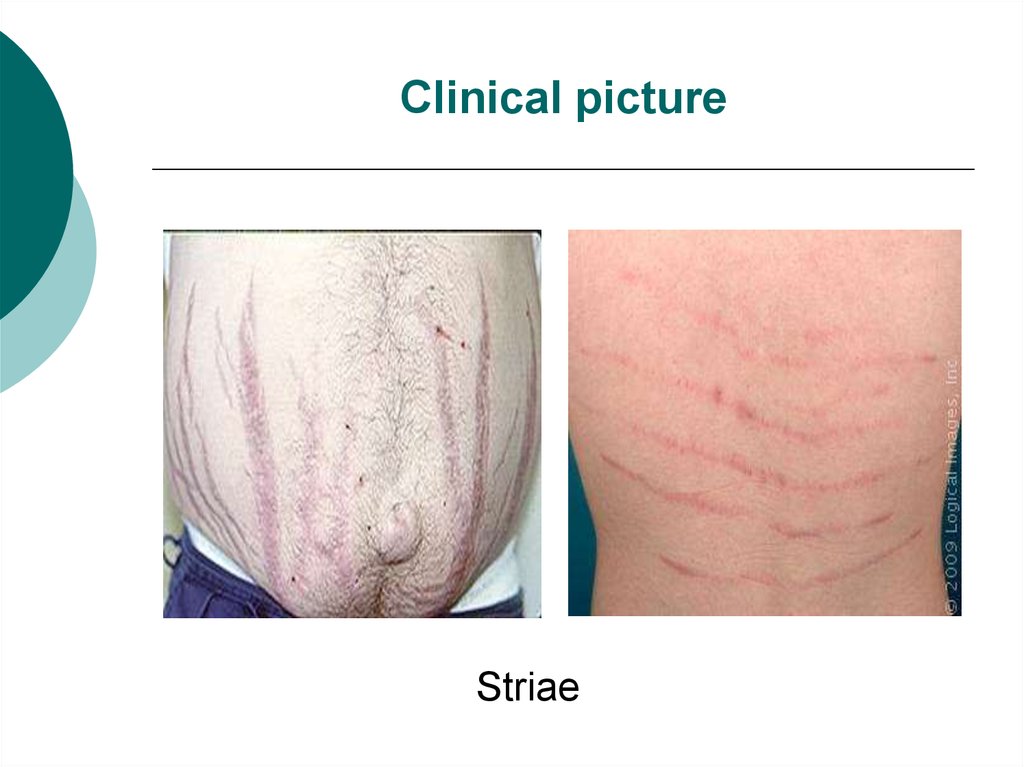
Striae13. Clinical picture
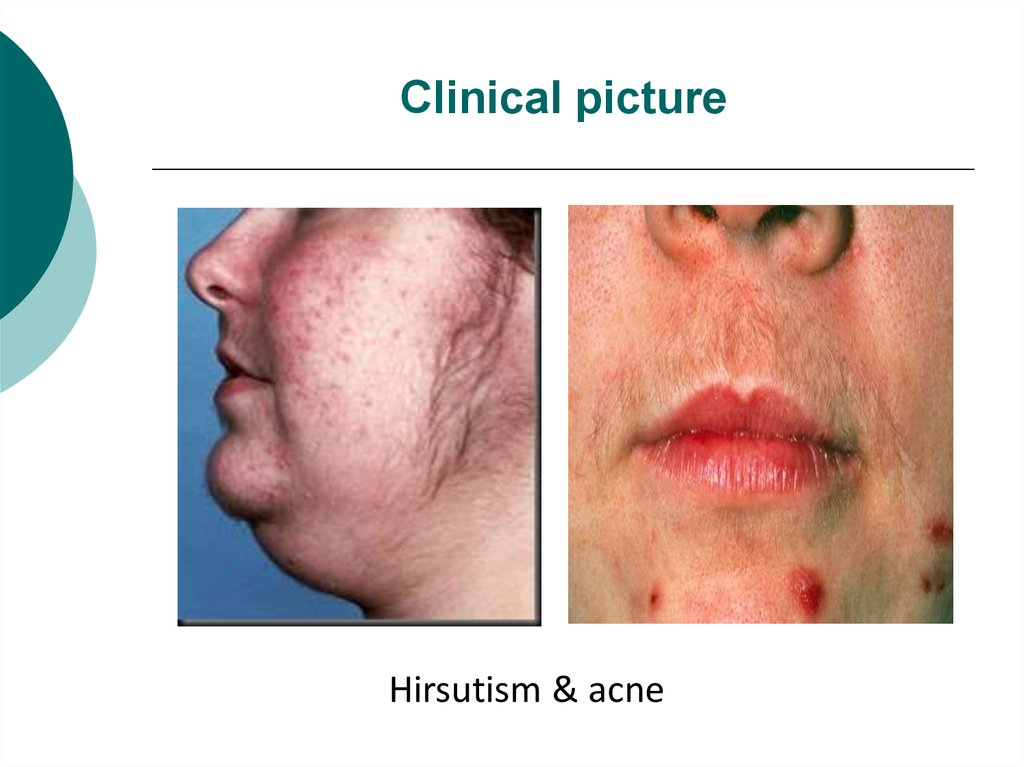
Hirsutism & acne14. Complications
Metabolic syndromeCVD
Hypercoagulability & thromboembolism
Bleeding
Immunosuppression & opportunistic infections
High mortality
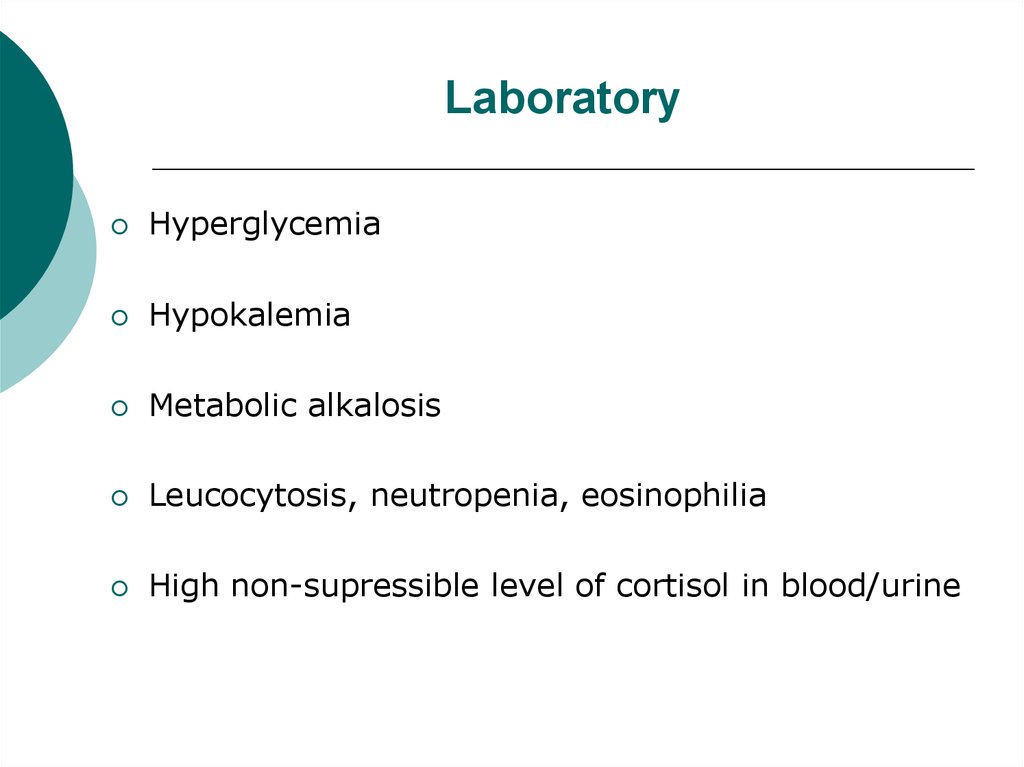
15. Laboratory
HyperglycemiaHypokalemia
Metabolic alkalosis
Leucocytosis, neutropenia, eosinophilia
High non-supressible level of cortisol in blood/urine
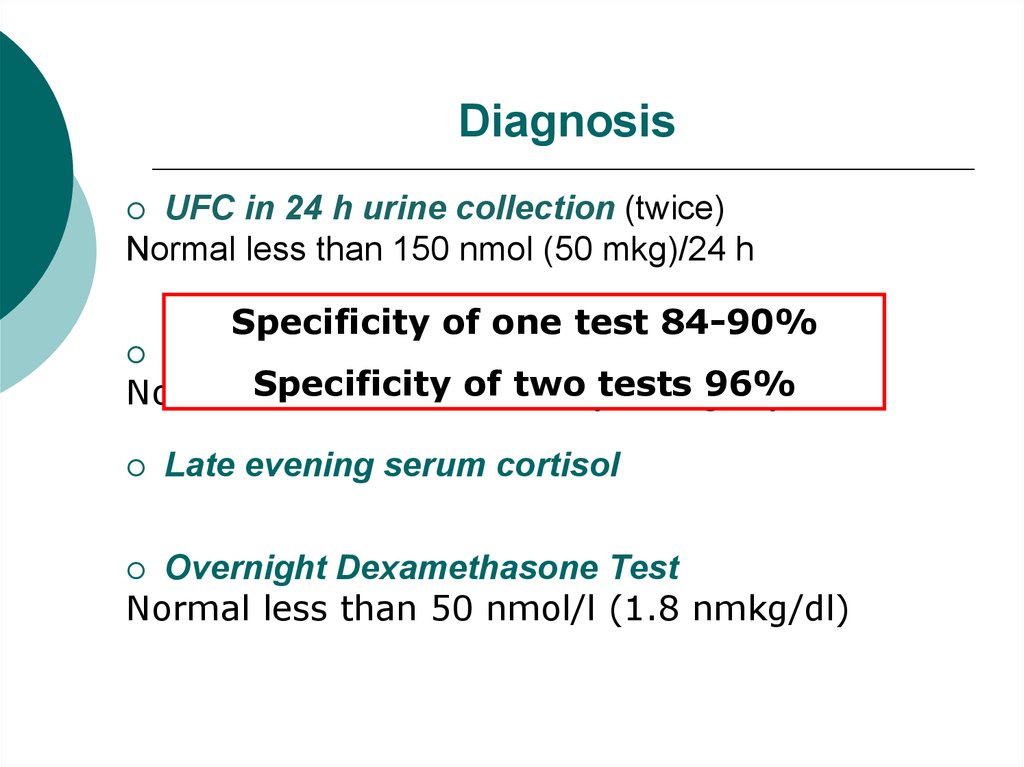
16. Diagnosis
UFC in 24 h urine collection (twice)Normal less than 150 nmol (50 mkg)/24 h
Specificity of one test 84-90%
Late evening salivary cortisol
two(150
testsng/dl)
96%
Normal Specificity
less than 4 of
nmol/l
Late evening serum cortisol
Overnight Dexamethasone Test
Normal less than 50 nmol/l (1.8 nmkg/dl)
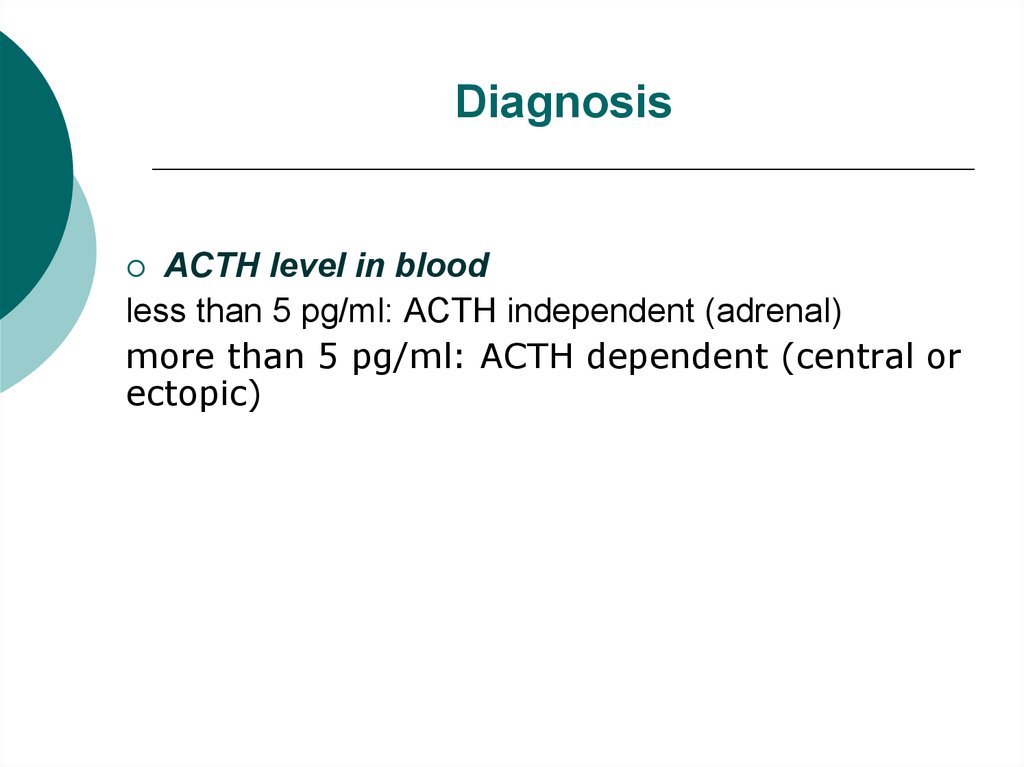
17. Diagnosis
ACTH level in bloodless than 5 pg/ml: ACTH independent (adrenal)
more than 5 pg/ml: ACTH dependent (central or
ectopic)
18. Cushing’s disease investigation
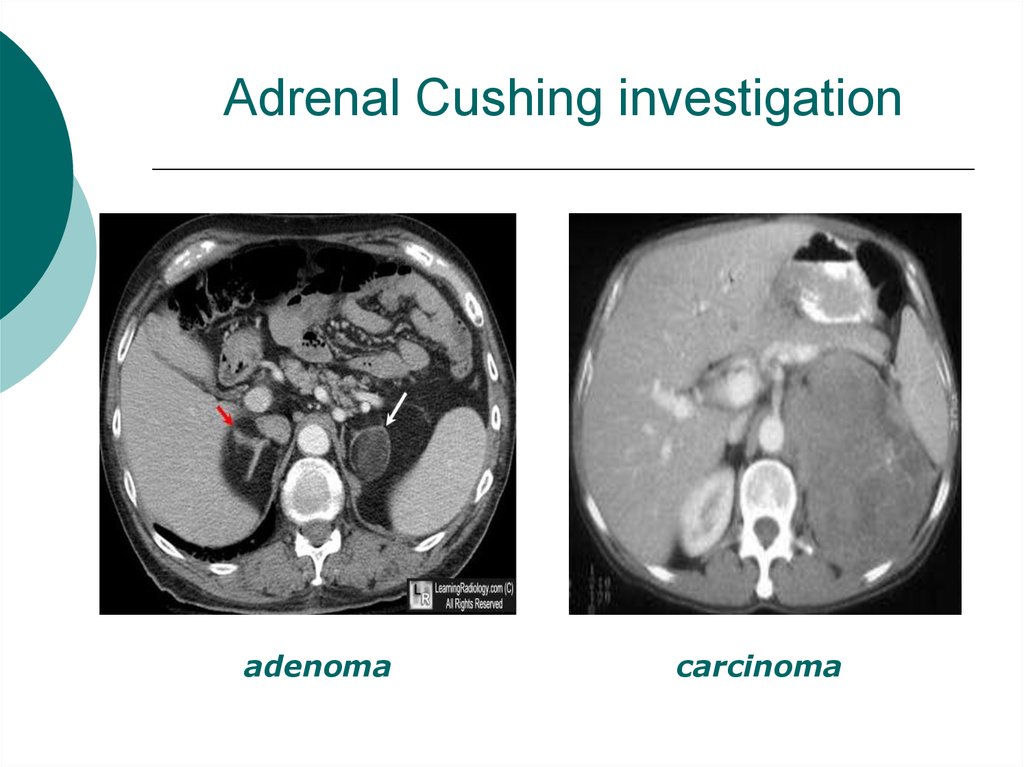
19. Adrenal Cushing investigation
adenomacarcinoma
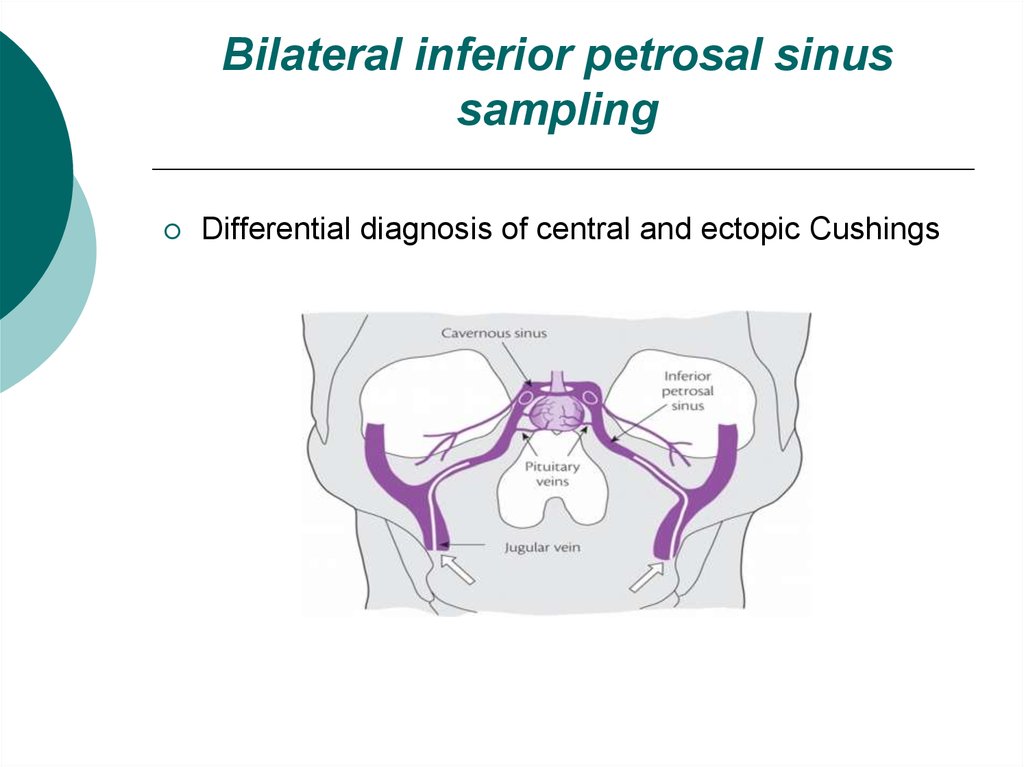
20. Bilateral inferior petrosal sinus sampling
Differential diagnosis of central and ectopic Cushings21. Treatment of Cushing’s disease
Transohenoidal surgeryCure after the operation 70-80%
10-years cure 60-70%
o
o Medical treatment
Dopamine-agonist Cabergoline
Somatostatine-analog Pasireotide
o Irradiation
o Adrenalectomy
Surgery
drugs
22. Treatment of Adrenal Cushing
AdrenalectomyMedical treatment (Ketoconazole, Metyrapone,
Mitotane)
GK supplemental treatment









 medicine
medicine








