Similar presentations:
Megaloblastic anemia
1.
2.
Objectives• Body stores and daily requirements of vitamin B12
and folate
• Absorption of vitamin B12 and folate from the gut
• Causes of vitamin B12 and folate deficiency
• Hematological consequences of vitamin B12 and
folate deficiency
• Neurological sequelae of vitamin B12 deficiency
• Diagnosis and management of megaloblastic
anemia
• Diagnosis and management of Pernicious Anemia
3.
Requirements for Red Blood CellProduction
Proteins, required for globin synthesis
Iron
Erythropoeitin
Vitamin B12 and folic acid
Vitamin B6
Vitamin C
Thyroid hormones, estrogens and androgens
4.
Vitamin B 12 and Folate5.
6.
7.
Macrocytic anemia with hypersegmented neutrophil8.
Macro-ovalocyte in megaloblastic anemia9.
Macro-ovalocyte in megaloblastic anemia10.
Megaloblastic Anemia – Bone Marrow11.
Bone marrow - megaloblasts12.
13.
14.
15.
Important for DNA synthesis,nervous tissue and fat metabolism
in the liver
an intermediate of the citric
acid cycle, porphyrin synthesis
(Heme synthesis)
16.
17.
18.
19.
20.
21.
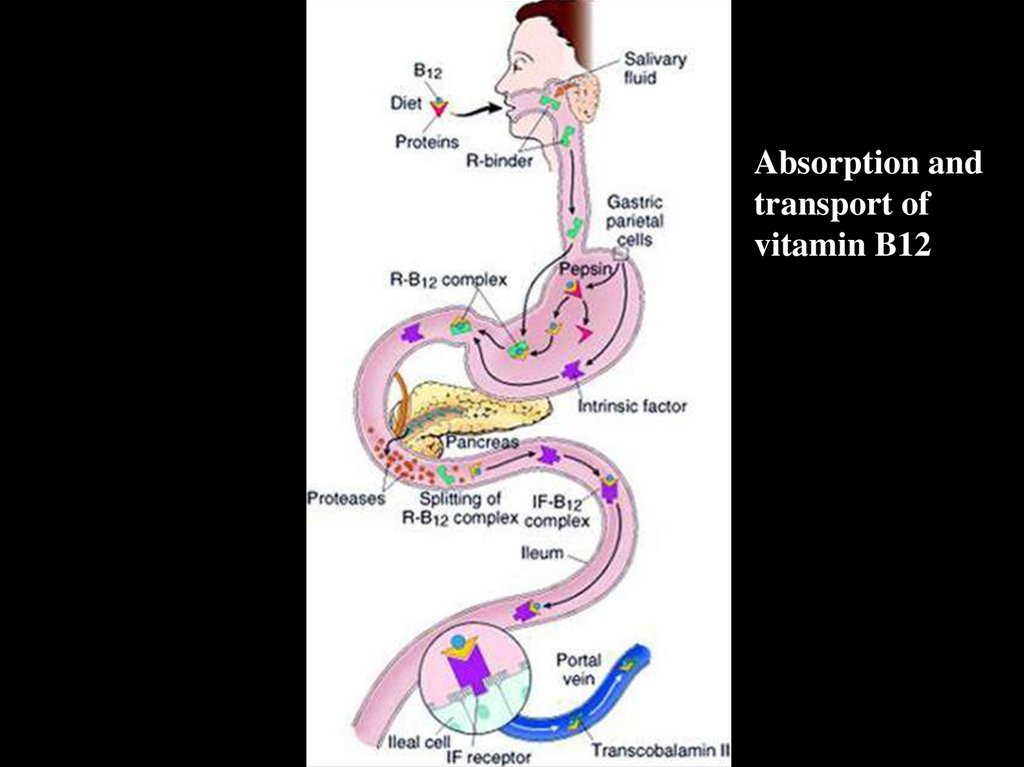
Absorption andtransport of
vitamin B12
22.
Absorption andtransport of
vitamin B12
23.
24.
B12 /25.
26.
27.
Pernicious Anemia (PA)Early graying of
hair
Blue eyes
28.
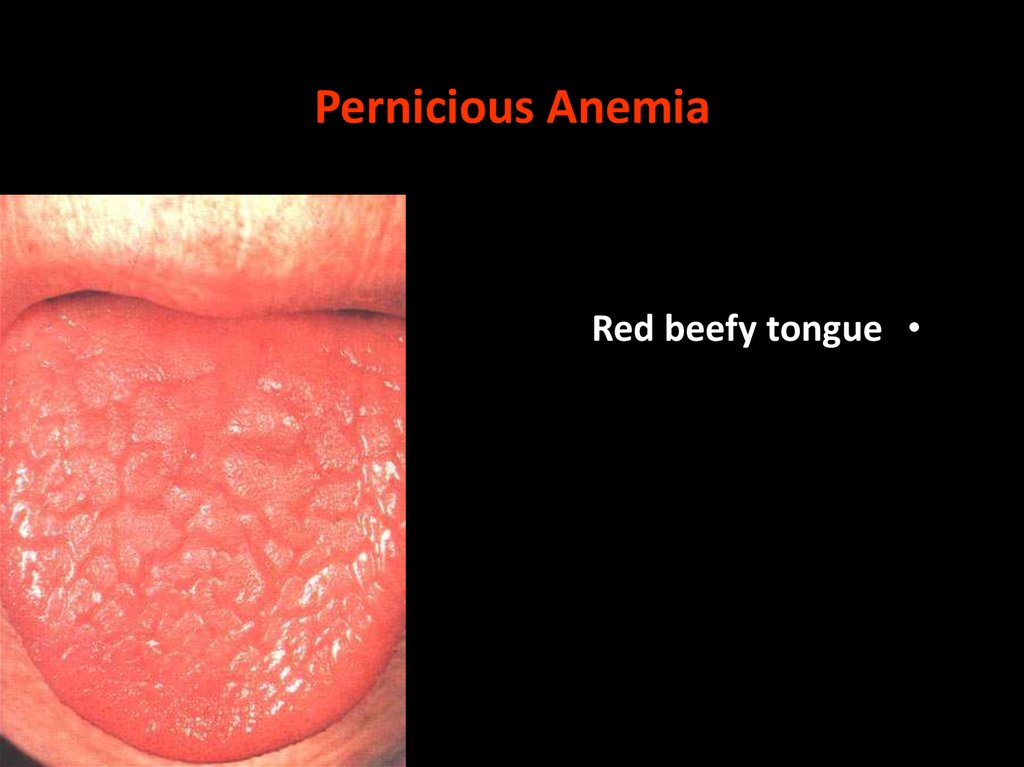
Pernicious AnemiaRed beefy tongue
29.
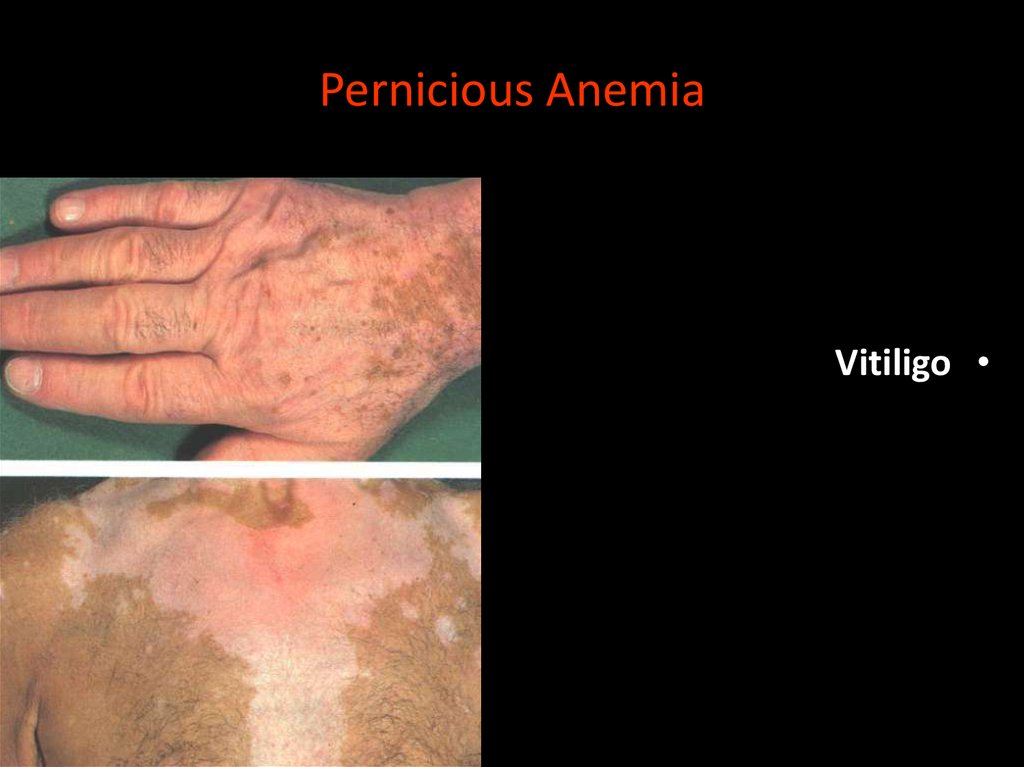
Pernicious AnemiaVitiligo
30.
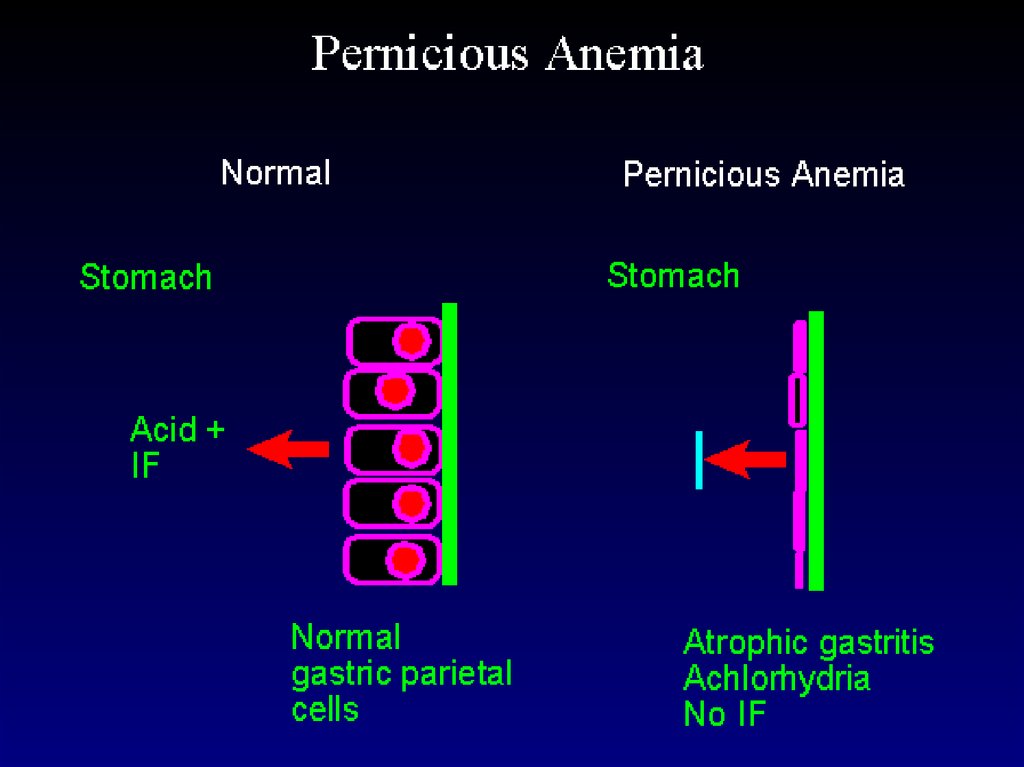
PANormal
Gastric atrophy
31.
Atrophic Gastritis32.
33.
34.
35.
Clinical Manifestations of Vitamin B12 DeficiencyHematologic
Megaloblastic anemia
Pancytopenia (leukopenia, thrombocytopenia)
Neurologic
Paresthesias
Peripheral neuropathy
Combined systems disease (demyelination of dorsal columns and corticospinal
tract)
Psychiatric
Irritability, personality change
Mild memory impairment, dementia
Depression
Psychosis
Cardiovascular
Possible increased risk of myocardial infarction and stroke
36.
37.
38.
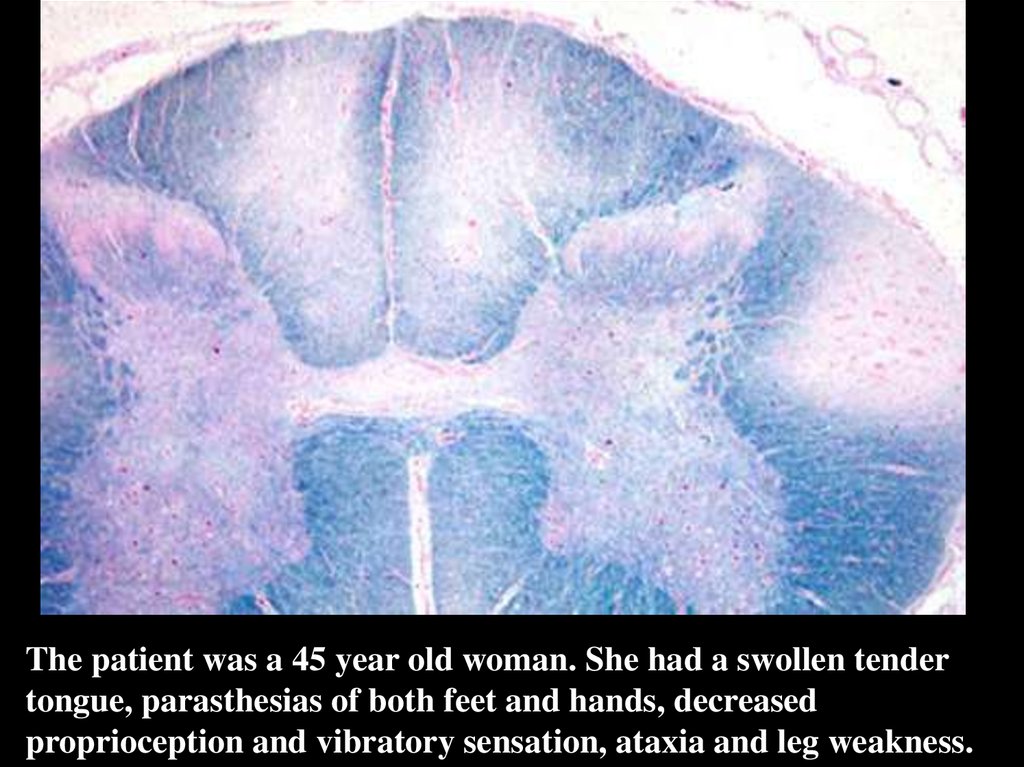
The patient was a 45 year old woman. She had a swollen tendertongue, parasthesias of both feet and hands, decreased
proprioception and vibratory sensation, ataxia and leg weakness.
39.
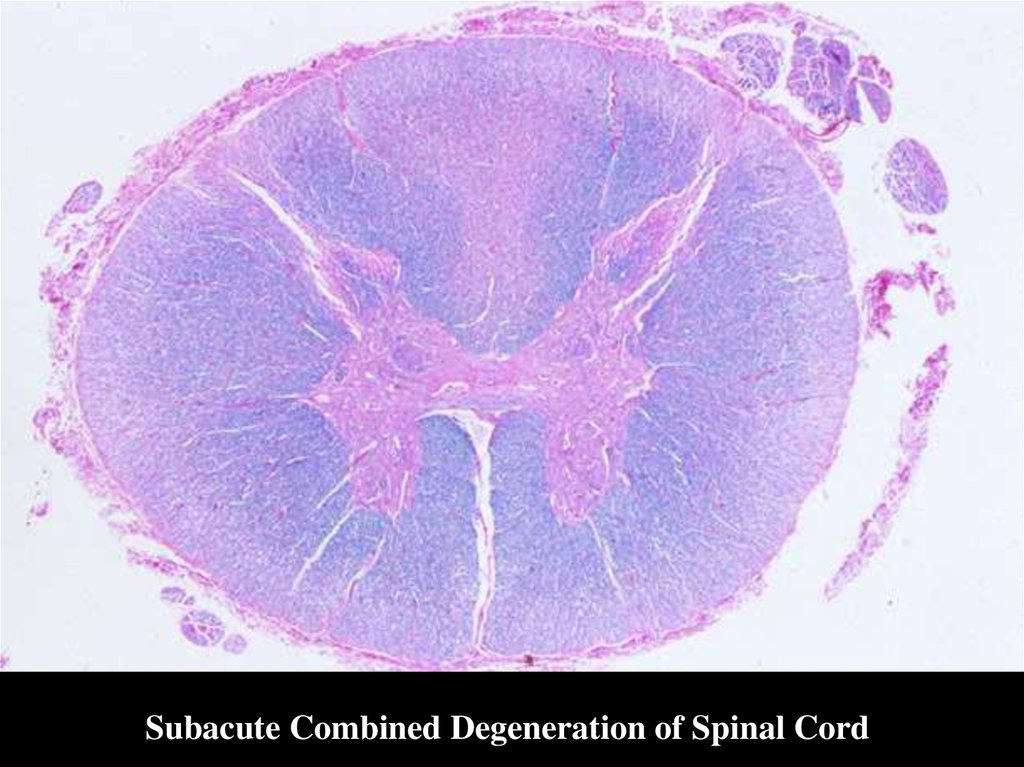
Subacute Combined Degeneration of Spinal Cord40.
41.
42.
43.
44.
45.
46.
47.
48.
49.
50.
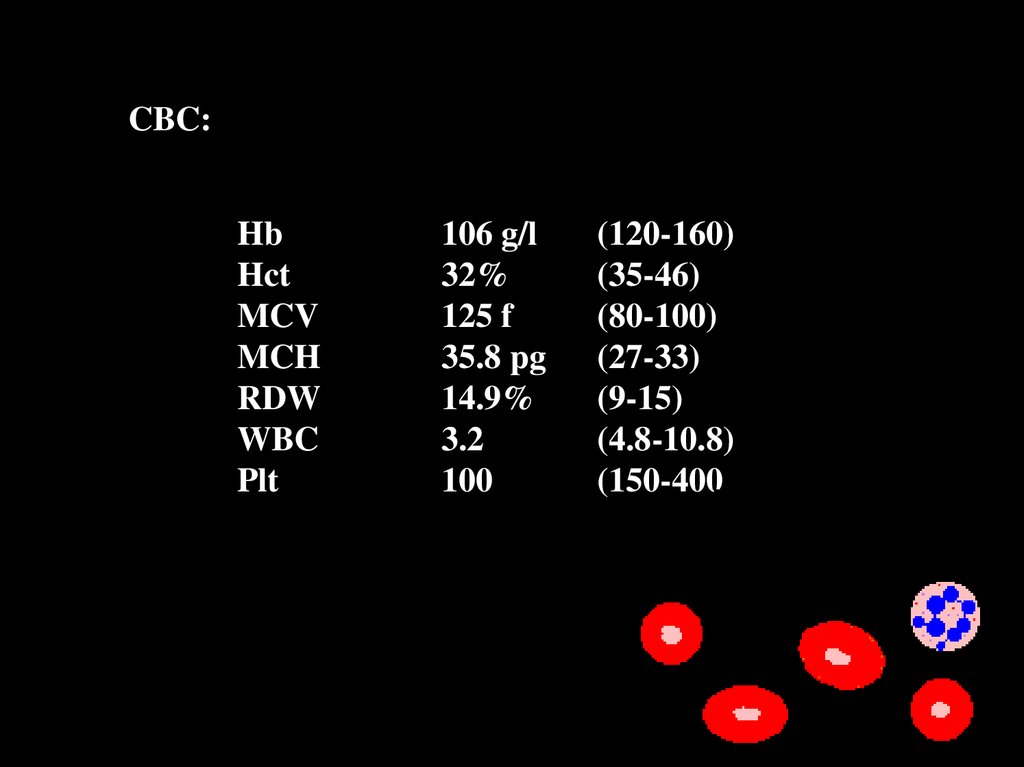
CBC:Hb
Hct
MCV
MCH
RDW
WBC
Plt
106 g/l
32%
125 f
35.8 pg
14.9%
3.2
100
(120-160)
(35-46)
(80-100)
(27-33)
(9-15)
(4.8-10.8)
(150-400
51.
52.
53.
54.
55.
56.
Reticcount


















































 medicine
medicine








