Similar presentations:
Protein structure at action: bind transform release
1.
PROTEIN PHYSICSLECTURE 24-25
PROTEIN STRUCTURE AT ACTION:
BIND TRANSFORM RELEASE
2.
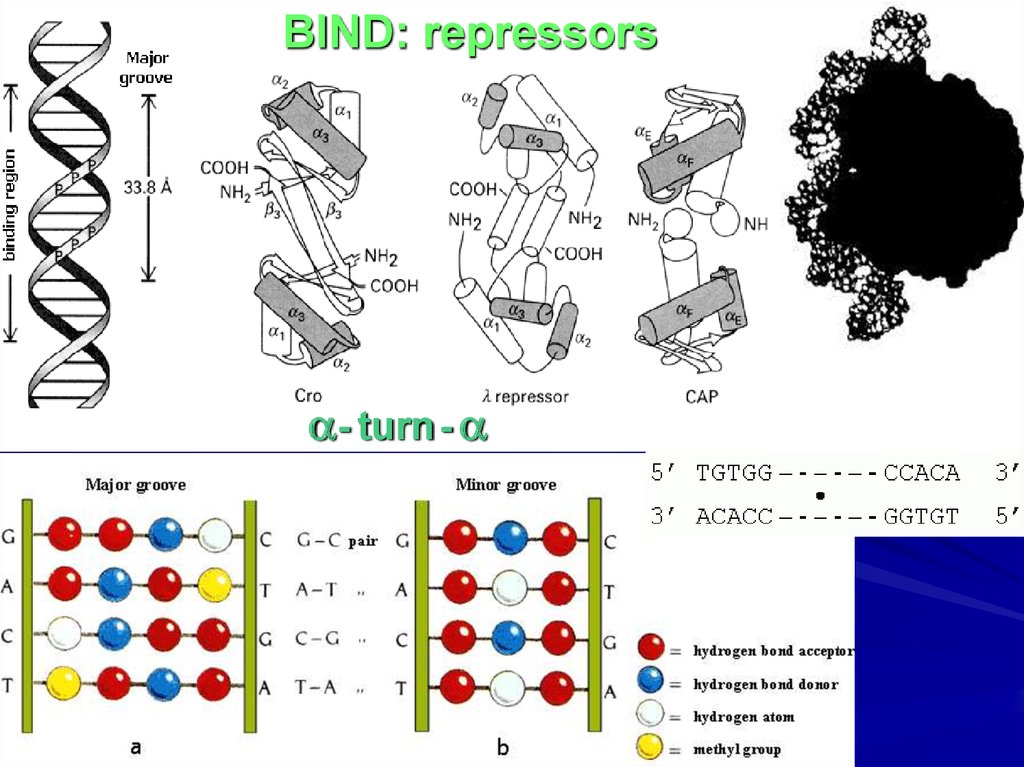
BIND: repressors- turn -
3.
ZnfingersDNA & RNA
BINDING
Leu-zipper
4.
BIND RELEASE: REPRESSOR-BINDING-INDUCED DEFORMATION
MAKES REPRESSOR ACTIVE, and IT BINDS TO DNA
5.
Immunoglobulin6.
Standard positions of active sitesin protein folds
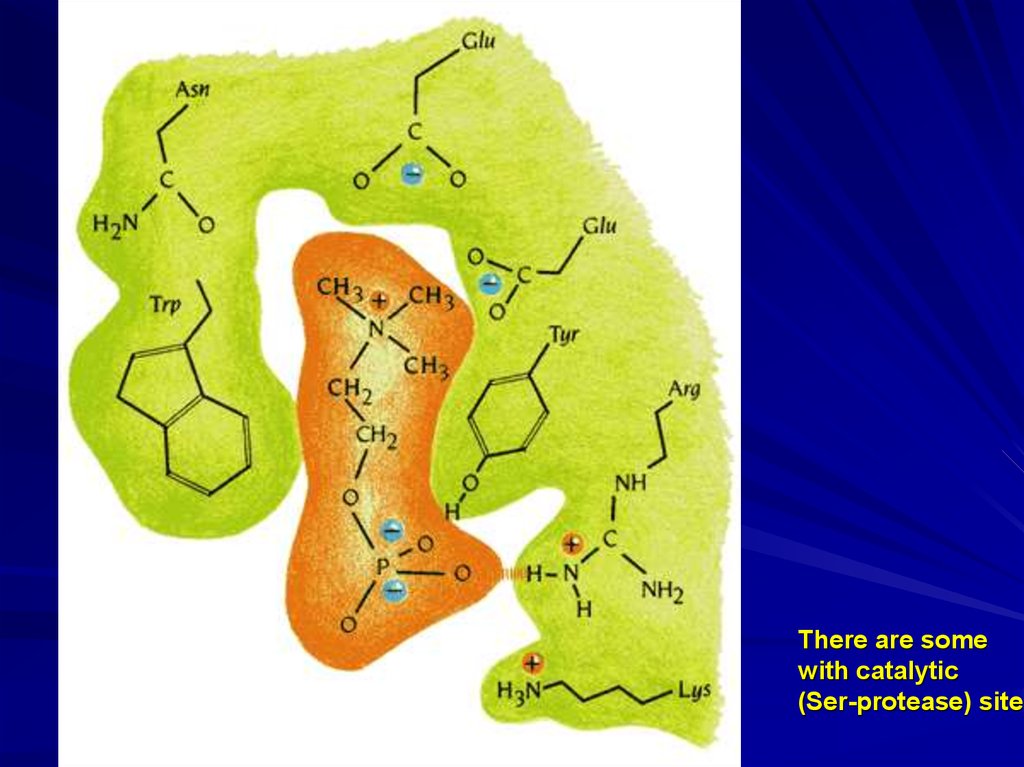
7.
There are somewith catalytic
(Ser-protease) site
8.
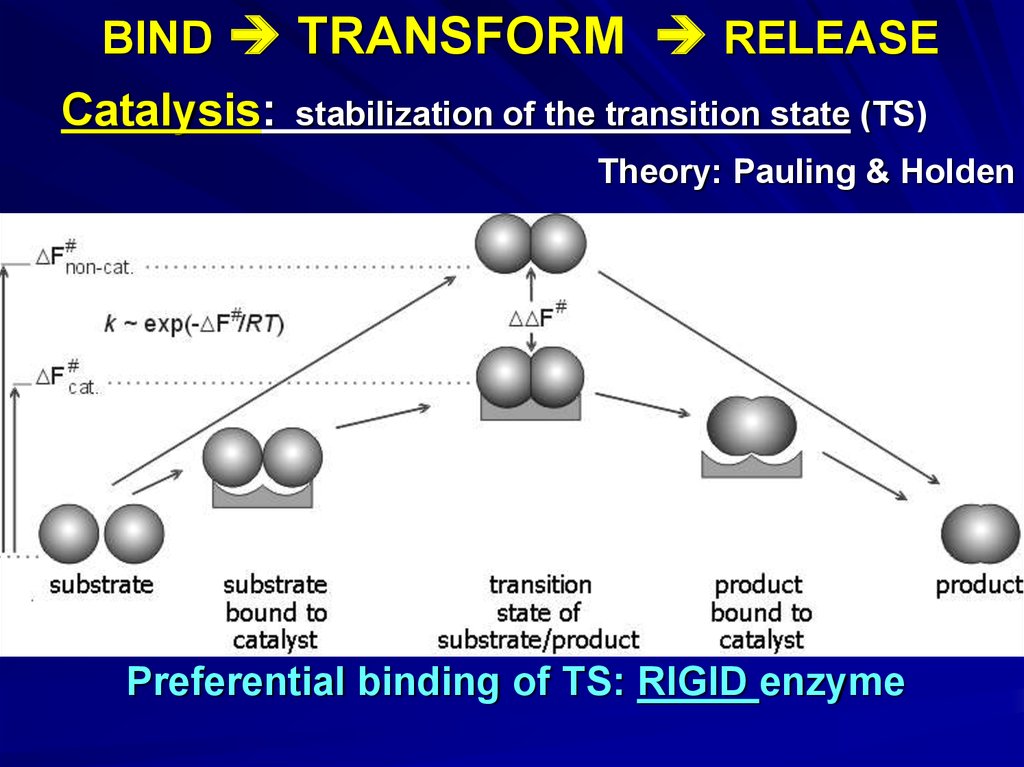
BIND TRANSFORM RELEASECatalysis:
stabilization of the transition state (TS)
Theory: Pauling & Holden
Preferential binding of TS: RIGID enzyme
9.
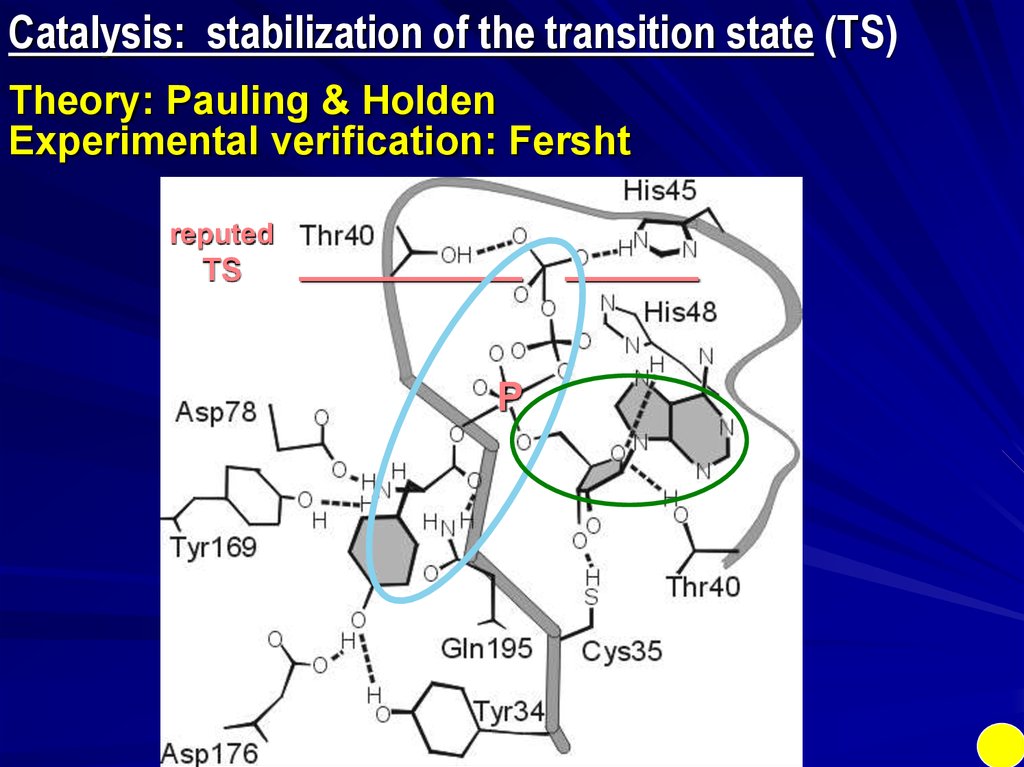
Catalysis: stabilization of the transition state (TS)Theory: Pauling & Holden
Experimental verification: Fersht
reputed
TS
__________
P
______
10.
Catalysis: stabilization of the transition state (TS)Theory: Pauling & Holden
Experimental verification: Fersht
reputed
TS
/
/
__________
P
/
/
______
This
protein
engineering
reduces
the rate
by 1000000
Preferential
binding
of TS:
RIGID
enzyme
11.
BIND TRANSFORM RELEASECatalytic antibodies
ABZYM = AntyBody enZYM
Suggested by Jencks in 1969
Done by Schultz and Lerner in 1994
Transition state (TS ‡)
Antibodies
are
selected
to TS-like
molecule
Preferential
binding
of TS:
RIGID
enzyme
12.
BIND TRANSFORM RELEASE: ENZYMEchymotrypsin
Note:
small
active
site
13.
Sometimes:Different folds with the same active site:
the same biochemical function
14.
POST-TRANSLATIONAL MODIFICATIONSometimes, only the CHAIN CUT-INDUCED DEFORMATION
MAKES THE ENZYME ACTIVE READY
non-active
“cat. site”
Chymotripsinogen
active
cat. site
Chymotripsin
CUT
15.
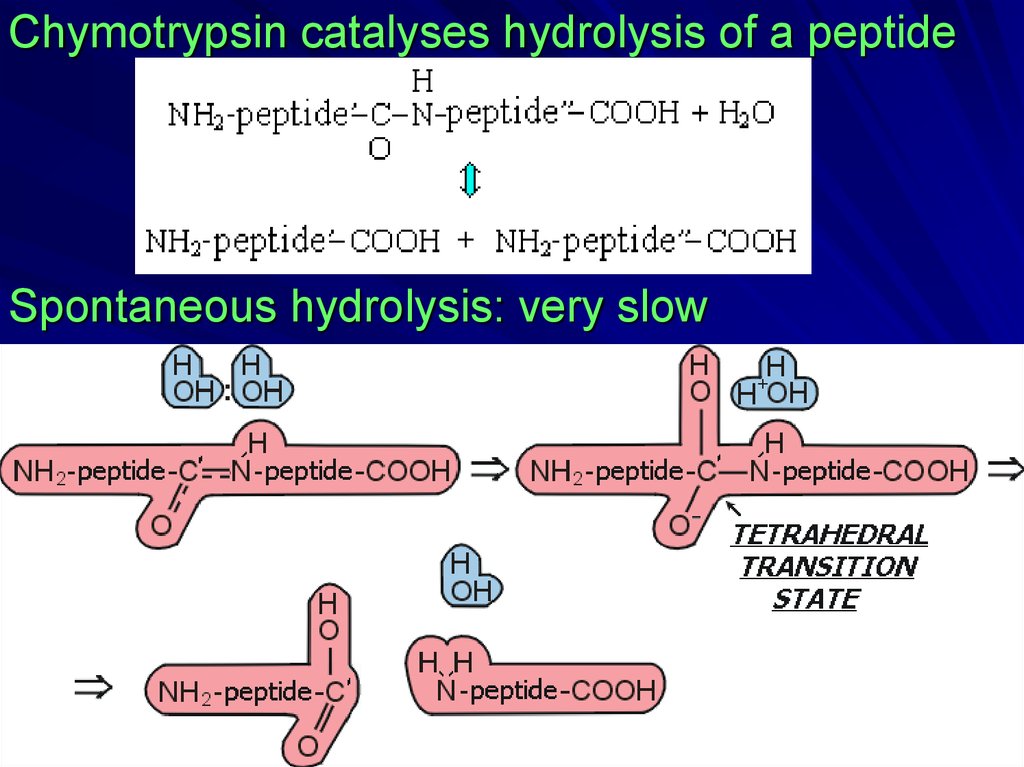
Chymotrypsin catalyses hydrolysis of a peptideSpontaneous hydrolysis: very slow
16.
SER-protease:catalysis
17.
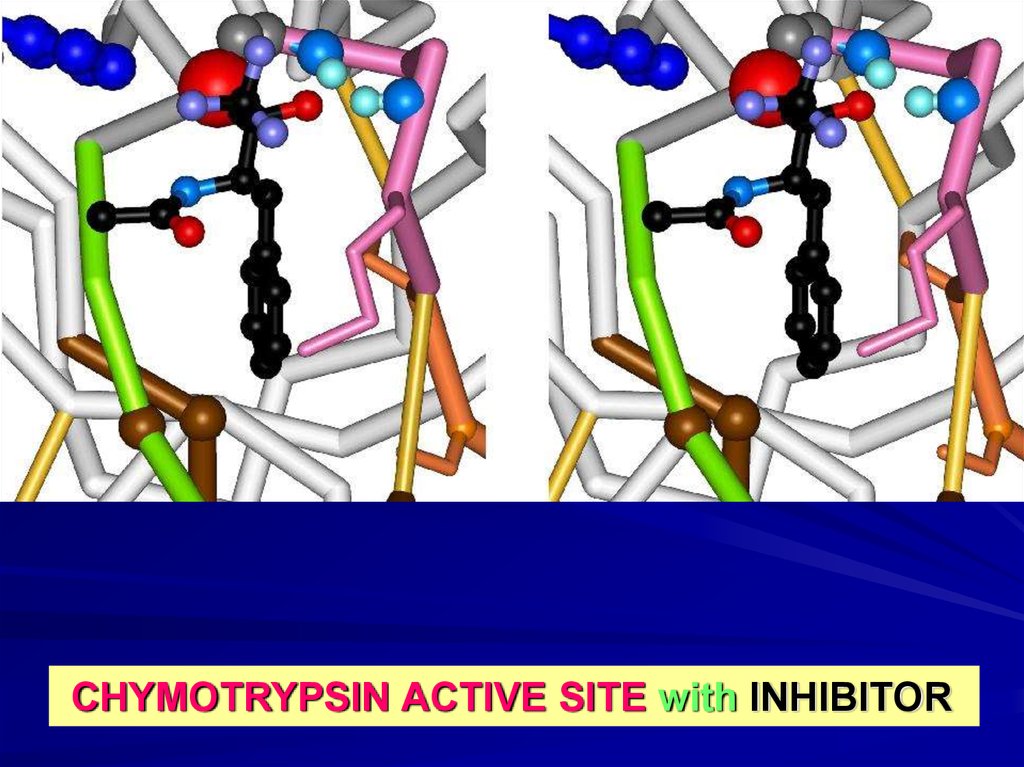
CHYMOTRYPSIN ACTIVE SITE with INHIBITOR18.
Preferential binding of TS: RIGID enzymeF = k1x1 = - k2x2
Hooke’s & 2-nd Newton’s
laws
Ei = (ki /2)(xi)2 = F2/(2ki )
Energy is concentrated
in the softer body.
Effective catalysis: when
substrate is softer than protein
Kinetic energy cannot be stored for catalysis
Friction stops a molecule within
picoseconds:
m(dv/dt) = -(3 D )v [Stokes law]
D – diameter; m ~ D3 – mass; – viscosity
tkinet 10-13 sec (D/nm)2
in water
19.
PROTEIN STRUCTURE AT ACTION:BIND TRANSFORM RELEASE
RIGID CATALITIC SITE
INDEPENDENT ON OVERALL CHAIN FOLD
20.
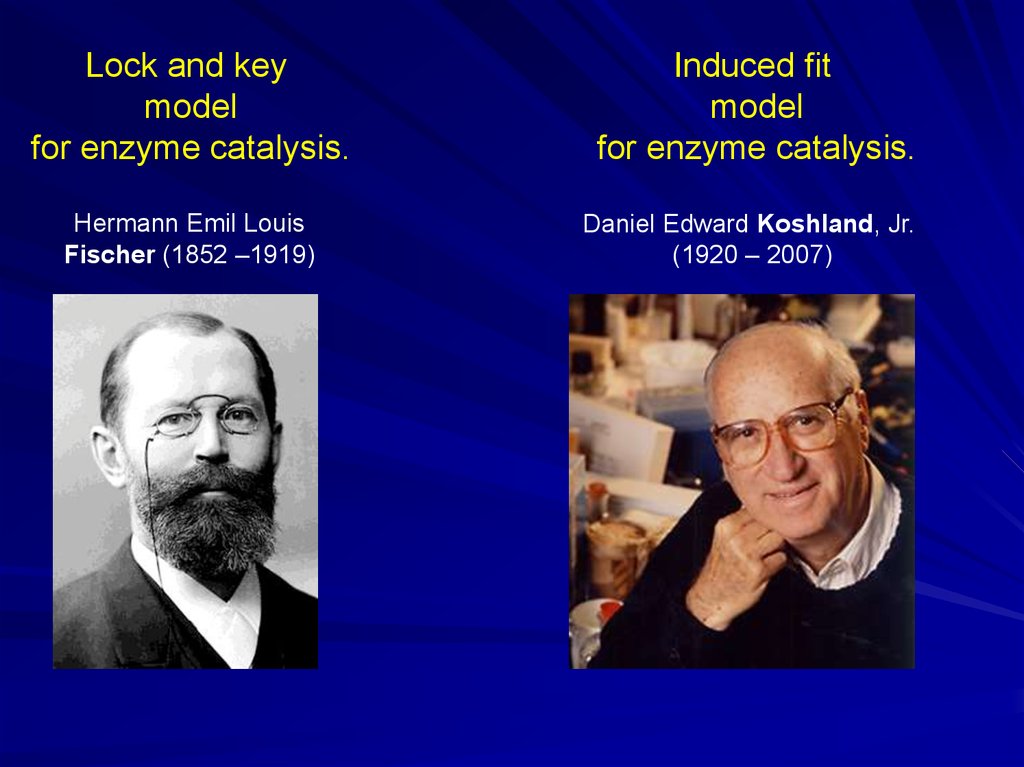
Lock and keymodel
for enzyme catalysis.
Hermann Emil Louis
Fischer (1852 –1919)
Induced fit
model
for enzyme catalysis.
Daniel Edward Koshland, Jr.
(1920 – 2007)
21. MOTIONS
22.
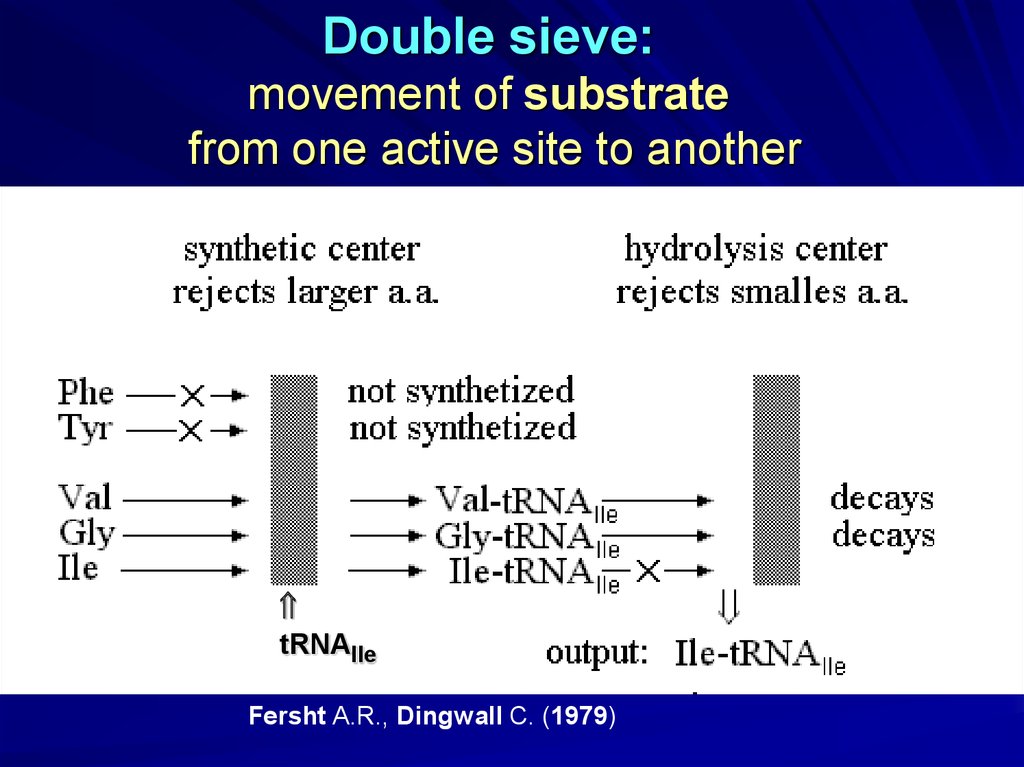
Double sieve:movement of substrate
from one active site to another
tRNAIle
Fersht A.R., Dingwall C. (1979)
23.
Movement in two-domain enzyme:One conformation for binding (and release),
another for catalysis
Induced fit
24.
Two-domain dehydrogenases:Universal NAD-binding domain;
Individual substrate-binding domain
25.
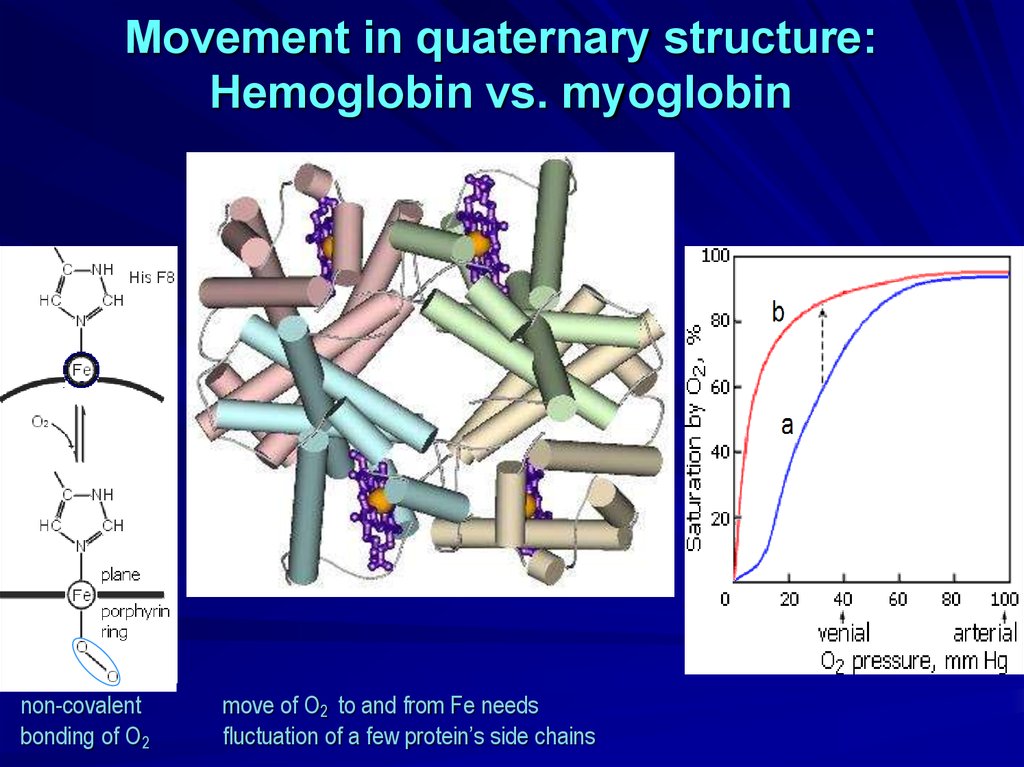
Movement in quaternary structure:Hemoglobin vs. myoglobin
non-covalent
bonding of O2
move of O2 to and from Fe needs
fluctuation of a few protein’s side chains
26.
Kinesin : Linear cyclic motorthe simplest one-direction walking machine with cyclic ligand-induced
conformational changes and bindings/unbindings to tubulin microtubule
Mandelkow & Mandelkow,
Trends Cell Biol. 12, 585 (2002)
The head “feels” its position, front or rear,
due to its interaction with the linker. Yildiz, Tomishige, Gennerich, Vale, Cell 134, 1030 (2008)
27.
Kinesin : Linear cyclic motorthe simplest one-direction walking machine with cyclic ligand-induced
conformational changes and bindings/unbindings to tubulin microtubule
28.
Sir Andrew Fielding Huxley(1917 – 2012)
Nobel Prize 1963
Myosin "cross-bridges"
29.
МиозинАктин
АТФ АДФ + Ф
15 ккал/моль
в клеточных
условиях
Механохимический цикл
30.
MyosinActin
Mechanochemical cycle
31.
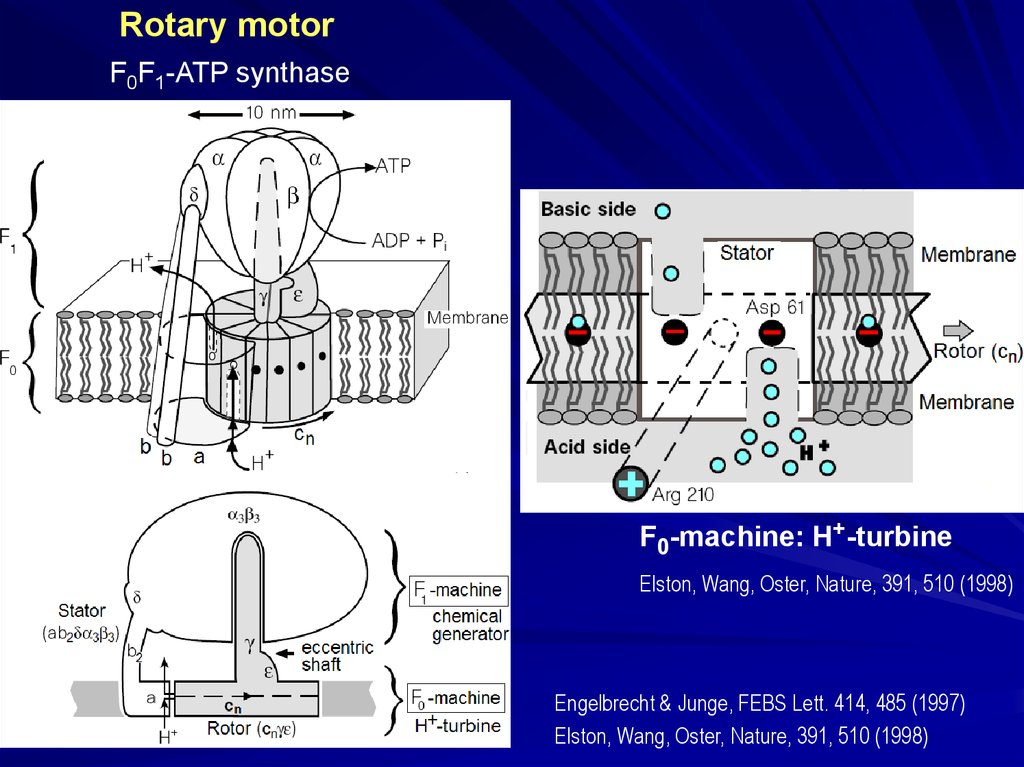
Rotary motorF0F1-ATP synthase
structure from the X-ray data: Junge, Sielaff, Engelbrecht, Nature, 459, 364 (2009)
32.
Rotary motorF0F1-ATP synthase
Basic side
Acid side
F0-machine: H+-turbine
Elston, Wang, Oster, Nature, 391, 510 (1998)
Engelbrecht & Junge, FEBS Lett. 414, 485 (1997)
Elston, Wang, Oster, Nature, 391, 510 (1998)
33.
Rotary motorF0F1-ATP synthase working cycle of the H+-turbine
34.
H+ binding in Spirulina platensisH3O+ binding in Bacillus pseudofirmus
Rotary motor
Ion binding
to the rotor ring of
F0F1-ATP synthase
Pogoryelov, Yildiz,
Faraldo-Gómez, Meier,
Nat. Struct. Mol. Biol.,
16, 1068 (2009)
Preiss, Yildiz, Hicks,
Krulwich, Meier,
PLoS Biol. 8,
e1000443 (2010)
35.
SUMMARYof the course
36.
PROTEIN PHYSICSInteractions
Structures
Selection
States &
transitions
37.
Intermediates& nuclei
Structure
prediction &
bioinformatics
Protein
engineering &
design
Functioning
38.
Благодарю за внимание…
товарищи офизевшие биологи!
39.
Благодарю за внимание…
товарищи офизевшие биологи!





























 biology
biology








