Similar presentations:
Macroeconomic equilibrium
1. Theme 11. Macroeconomic equilibrium
2. 1.Macroeconomic equilibrium and its characteristics
3. Aggregate demand (AD) - represented as a curve that shows the amount of goods and services that consumers, businesses, the
pricesupport
height
AD
Р1
Р2
Q1
Q2
PPR
4.
Factors determine acurve AD
The
effectiveness
The
The
of the
effective
effectiveness
interest rate of foreign
wealth
(solvency of
method
purchases
buyers)
5.
Non-price factors affecting thechange in demand (AD schedule
shifts to the left or to the right)
Change in
consumer
spending
The change The change The change
in
in
in the cost
investment government
of net
costs
expenditure
exports
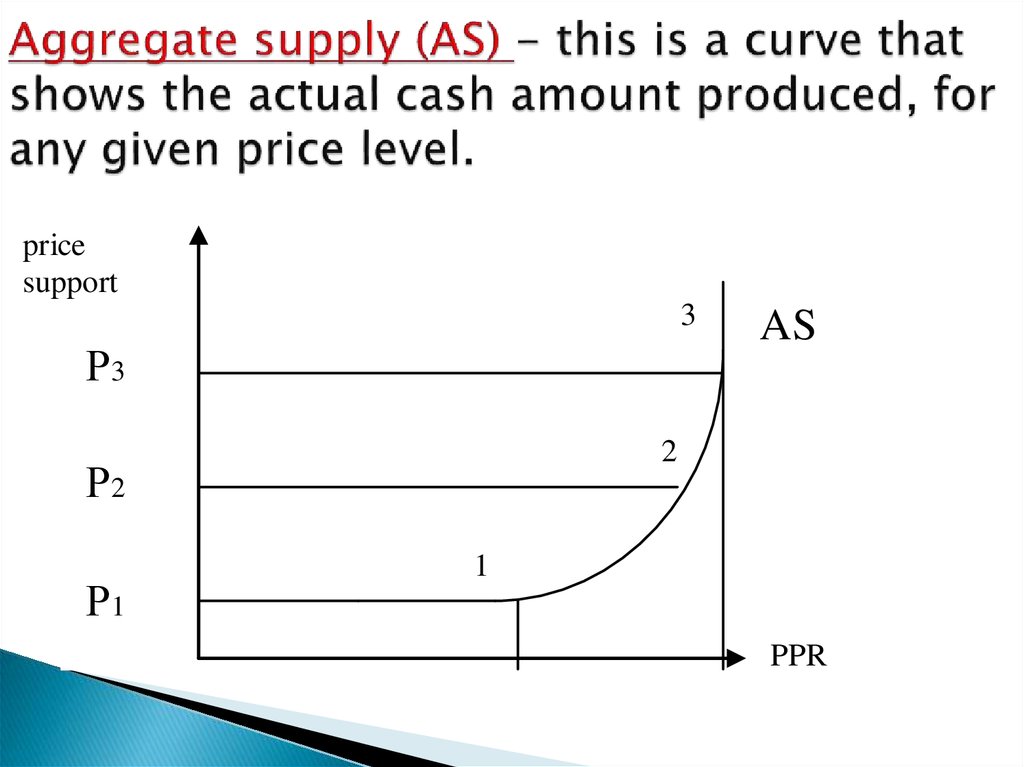
6. Aggregate supply (AS) - this is a curve that shows the actual cash amount produced, for any given price level.
pricesupport
3
Р3
2
Р2
Р1
AS
1
PPR
7.
Non-price factors affecting thechange in supply
change in
change in
the prices of
performance
resources
Taxes
government
regulation
8. The equilibrium price level and equilibrium PPR, ie Q = Q AS AD.
АД1price
support
АД2
АД3 АS
Р3
Р2
Е
Е
Е
Р1
Q1
Q2
Q3
PPR
9. 2. Models of employment resources
10. The essence of the classical theory of employment
Full employment of resources isthe norm
Qs (supply) varies adequate
changes in the price level
The capitalist economy is
self-regulating.
11. The essence of Keynesian theory
The economy may be poised for a significant levelof unemployment and significant inflation.
Full employment is casual.
In the short term prices, wages are inelastic, so the
total supply represented by the horizontal line.
On the contrary, the equilibrium can be achieved
with the availability of resources, ie unemployment
and inflation. .










 economics
economics








