Similar presentations:
Loading, discharging and trim
1. Dia 1
Loading, discharging and trimmu
2. Dia 2
Making up a stowage planBefore the loading of the cargo
commences a stowage plan
must be made up to ensure the
safety of the vessel, the cargo
and the crew.
s
3. Dia 3
Making up a stowage planConsiderations regarding safety
of ship, cargo and crew
. the stowage factor of the cargo
. the trim of the vessel
. sweating and intermixing
(segregation of cargoes)
. order of destinations.
sound
4. Dia 4
The stowage factorThe stowage factor
indicates the volume
of the cargo hold
occupied by one ton
of cargo.
5. Dia 5
Bale spaceBy bale space is meant the volume of the cargo holds
that can be used for general cargo.
6. Dia 6
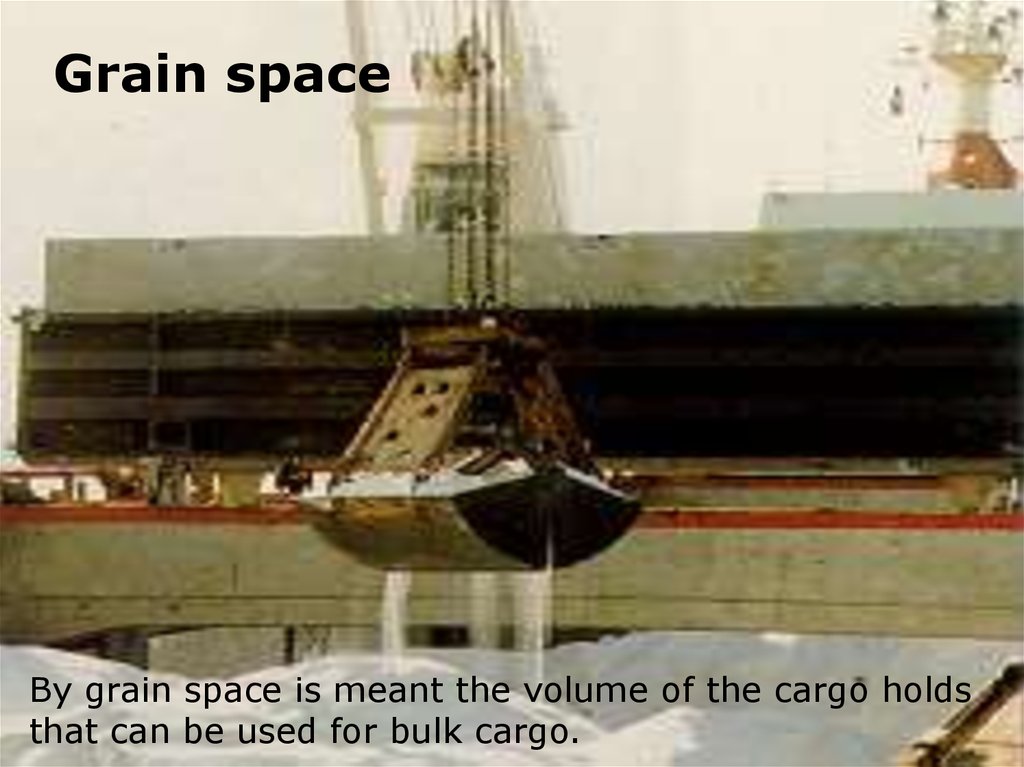
Grain spaceBy grain space is meant the volume of the cargo holds
that can be used for bulk cargo.
7. Dia 7
Oil spaceUllage – the free space above the liquid
in a tank, measured in metres or feet.
By Oil Space is understood 98% of the total
volume of the tank.
8. Dia 8
Types of cargoes9. Dia 9
General Cargo10. Dia 10
General CargoGeneral cargo is
cargo coming in
boxes, crates, bags
and pieces.
The stowage plan
will indicate where
the various
cargo-items
have been stowed.
11. Dia 11
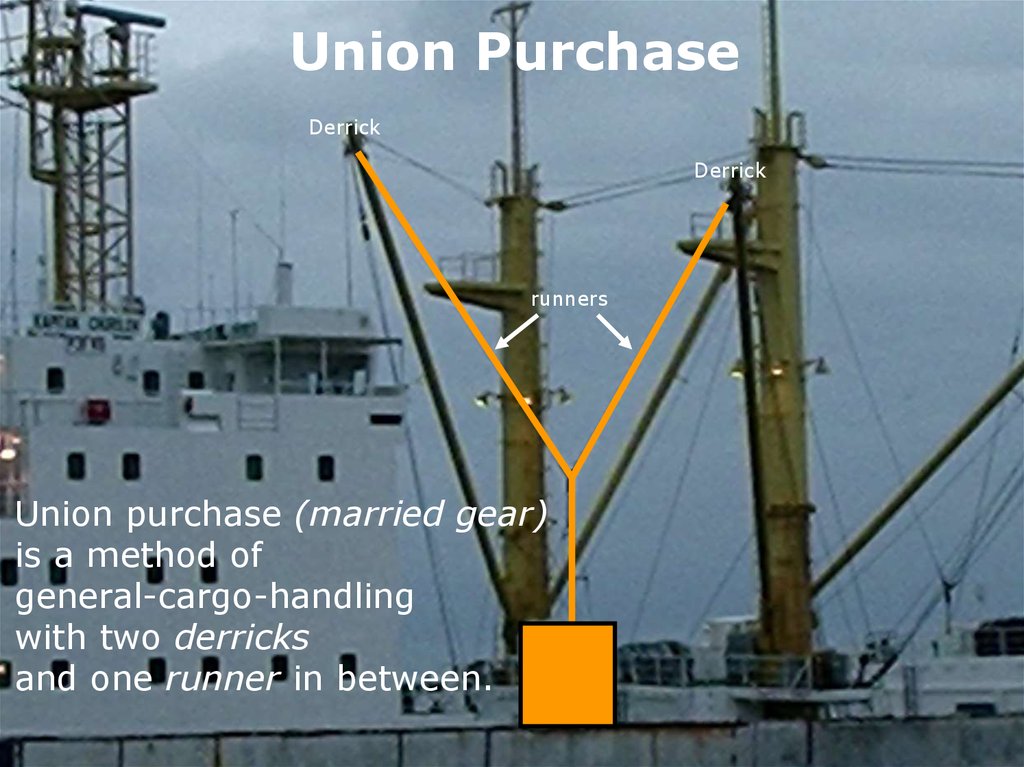
Union PurchaseDerrick
Derrick
runners
Union purchase (married gear)
is a method of
general-cargo-handling
with two derricks
and one runner in between.
12. THE HATCH
Hatch coverHatch coaming
A hatch gives access
to a hold.
13. Dia 13
Bulk cargo14. Dia 14
Bulk cargoBulk carrier carrying sugar.
Crude oil carriers.
Bulk cargo is unpacked cargo of one commodity.
There is dry bulk cargo (grain, ore)
and wet bulk cargo (oil).
15. Dia 15
sdWet bulk cargo
is loaded and discharged
by pumps.
Dry bulk cargo
is loaded and discharged
by cranes with grabs
or by pumps.
16. Dia 16
Containerized cargo17. Dia 17
When things have gone wrong ….18. Dia 18
Gantry CraneContainers are loaded by straddle carriers (or gantry
cranes) and stacked on the ship in Bays, Rows and Tiers.
19. Dia 19
The bays run abeam;the rows run fore to aft,
and the tiers are layers.
20. Dia 20
Trim and Drafts
21. Dia 21
LOAD LINESDeckline
TF
F
T
Plimsoll
mark
S
W
WNA
Lines that indicate
the greatest depth
to which the ship may
be loaded under
various circumstances
and in
different seasons.
22. Dia 22
PLIMSOLL MARKDeckline
Plimsoll line
The distance between deckline and Plimsoll line
indicates Summer Freeboard.
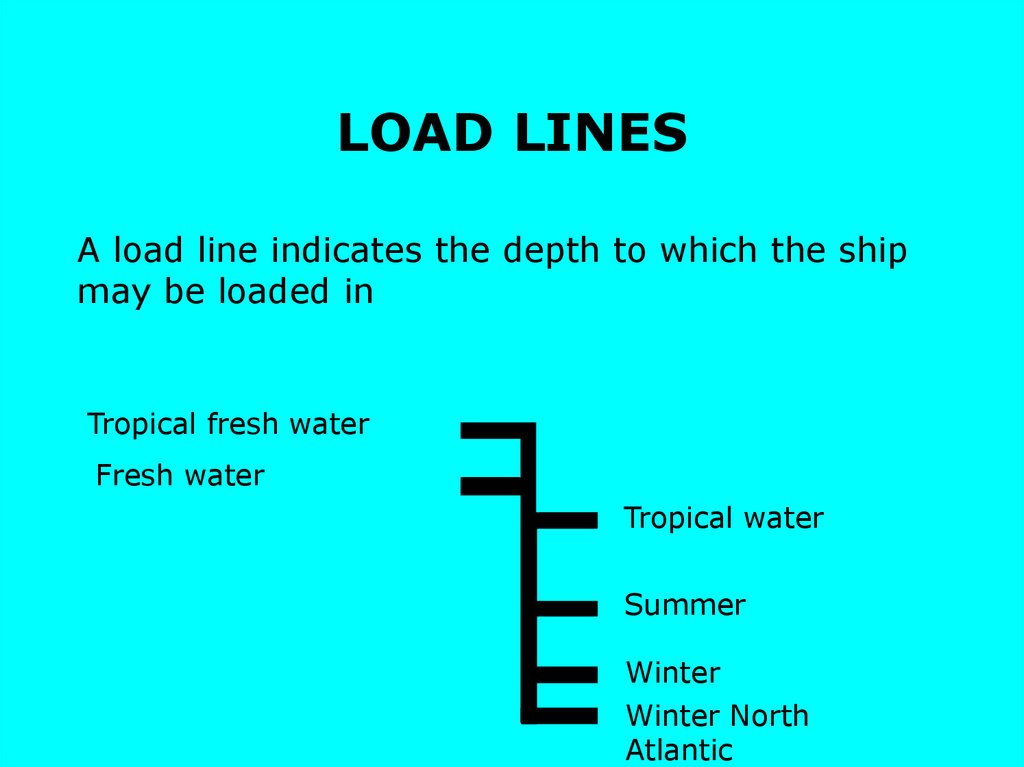
23. LOAD LINES
A load line indicates the depth to which the shipmay be loaded in
Tropical fresh water
Fresh water
Tropical water
Summer
Winter
Winter North
Atlantic
24. Dia 24
DRAFTDue to the salinity of
sea water
draft in sea water
is less than draft
in fresh water
Sea-water draft
Sea water has a higher
specific gravity than
fresh water.
Fresh-water draft
25. Dia 25
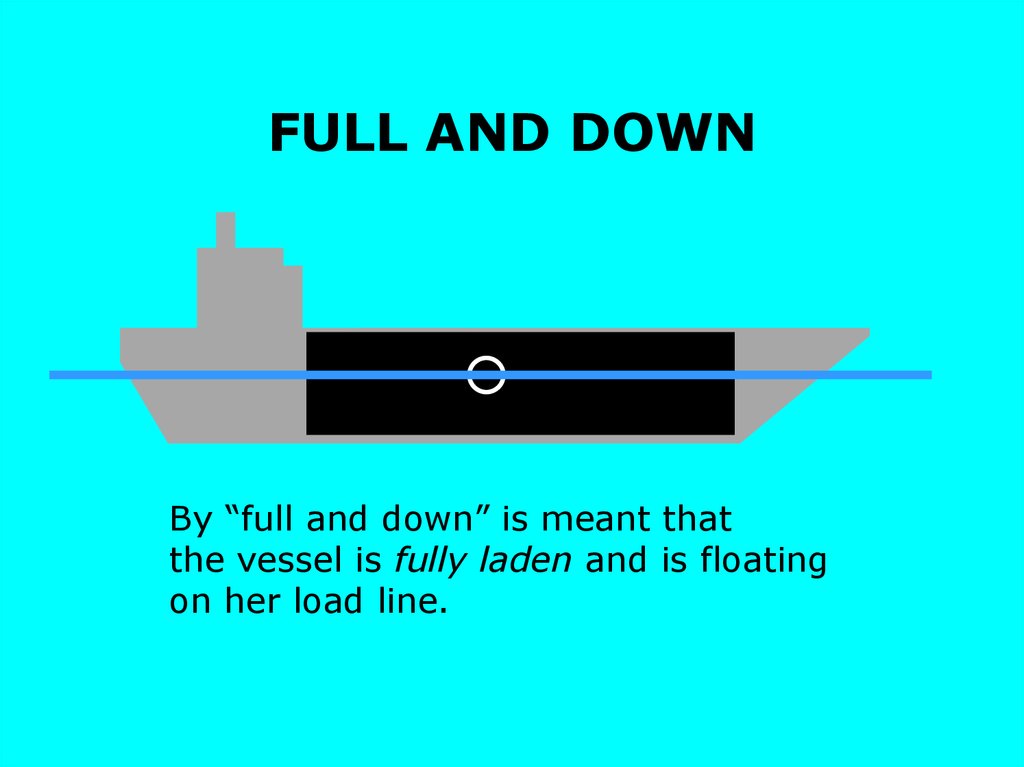
FULL AND DOWNBy “full and down” is meant that
the vessel is fully laden and is floating
on her load line.
26. Dia 26
EVEN KEELWhen a vessel is floating on even keel, there is no
difference between draft fore and draft aft
(“She is well trimmed”).
27. Dia 27
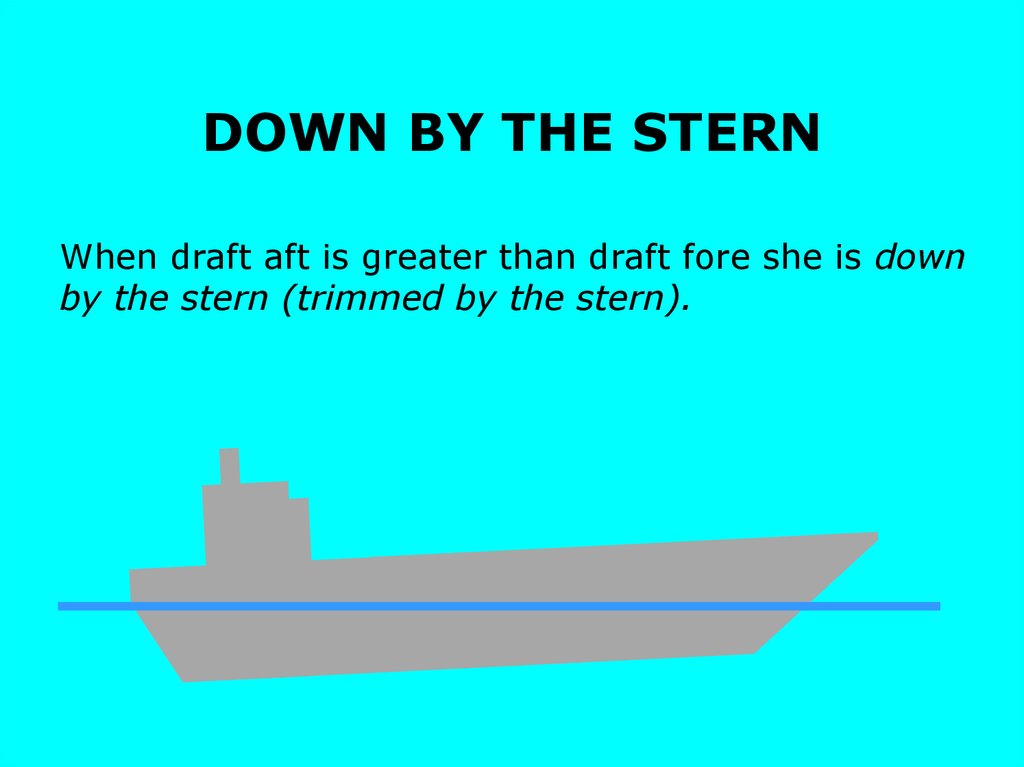
DOWN BY THE STERNWhen draft aft is greater than draft fore she is down
by the stern (trimmed by the stern).
S
28. Dia 28
DOWN BY THE HEADWhen draft fore is greater than draft aft she is down
by the head (trimmed by the head).
S
29. LIST (HEEL)
When starboard-draft is less than port-draft she hasa list to port.
S
30. Dia 30
SAGGINGWhen draft amidships is greater than draft fore and aft
the vessel is sagging.
S
31. Dia 31
HOGGINGWhen draft amidships is less than
draft fore and aft, the vessel is hogging.
S
32. Dia 32
TheInternational Maritime Language Programme – IMLP
C
The IMLP is an IMO-standard.
P.C. van Kluijven



























 industry
industry








