Similar presentations:
Communication principles
1. Communication Principles
Managing Technical People2.
Topics and AgendaThe Importance of Interpersonal Communications
Communication Styles
Communicating Effectively
Nonverbal Communication
Questioning
Listening
Giving and Receiving Feedback
2
3.
Course ProgressModule 0: Factors Influencing Human Interaction
Module 01: Communication
Communication Principles
Module 02: Decision Making
Module 03: Negotiation
Module 04: Conflict Management
Module 05: Relationship Management
Module 06: Leadership
3
4.
Why is communication important?Factors in today’s workplace:
Technology
Time
Diversity
Liability
Organizational structure
4
5.
Why is communication important?Organizations today:
Flatter
Less formal
Matrixed
More fluid
5
6.
Why is communication important?Factors specific to software development:
Distributed development
Varying languages (Technical/Nontechnical)
Differing processes and methodologies
6
7.
Communication StylesPassive
Aggressive
Assertive
7
8.
Communication StylesPassive
Puts others first
Sends message of inferiority
Soft or apologetic tone of voice
Submissive nonverbal cues
Can lead to disrespect from others
8
9.
Communication StylesAggressive
Puts self first
Sends message of superiority
Loud and forceful tone of voice
Confrontational nonverbal cues
May anger coworkers
9
10.
Communication StylesAssertive
Stands up for personal opinions while respecting opinions of others
All parties are important and equal
Firm, confident tone of voice
Relaxed nonverbal cues
Projects high self-esteem
10
11.
Communication StylesWhat words would you use to describe the three styles?
How might each of these styles be perceived in the workplace?
11
12.
Communicating Effectively“There are two ways of exerting one's strength: one is pushing
down, the other is pulling up.”
Booker. T Washington
Educator, Author and Advisor to presidents of the United States
12
13.
Communicating EffectivelyConstructive communication helps build:
Employee morale
Teamwork
Relationships
Destructive communication creates:
Conflict
Resentment
Resistance/rebellion
13
14.
Communicating EffectivelyCommunication is more than just words
7%-38%-55% Principle
Words= 7%
Tone of Voice = 38%
Body Language = 55%
14
15.
Communicating EffectivelyUse words that show you are:
Knowledgeable
Credible
Trustworthy
Honest
Dependable
15
16.
Communicating EffectivelyAvoid words that are:
Demanding
Demeaning
Discriminatory
Offensive
Negative
Overused
16
17.
Communicating EffectivelyWhen might you communicate something other than a fact?
17
18.
Communicating EffectivelyFocus on the problem
Be specific
Be congruent
Take responsibility for statements and actions
Practice active listening
Show respect for other points of view
18
19.
Nonverbal Communication“What you do speaks so loud I cannot hear what you say…”
Ralph Waldo Emerson
American essayist, lecturer, and poet
19
20.
Nonverbal CommunicationInfluencing Factors
Context
Environment
People’s behaviors
20
21.
Nonverbal CommunicationVocal characteristics
Rate of speech
Pitch
Volume
Tone
21
22.
Nonverbal CommunicationWhat do you think of someone who talks too fast?
What do you think of someone who speaks too slowly?
What is a high pitch associated with?
What is a high volume (shouting) associated with?
What does it mean when someone says “Watch your tone”?
22
23.
Visual CuesFacial expressions
Eye contact
Gestures
Posture
Proxemics
23
24.
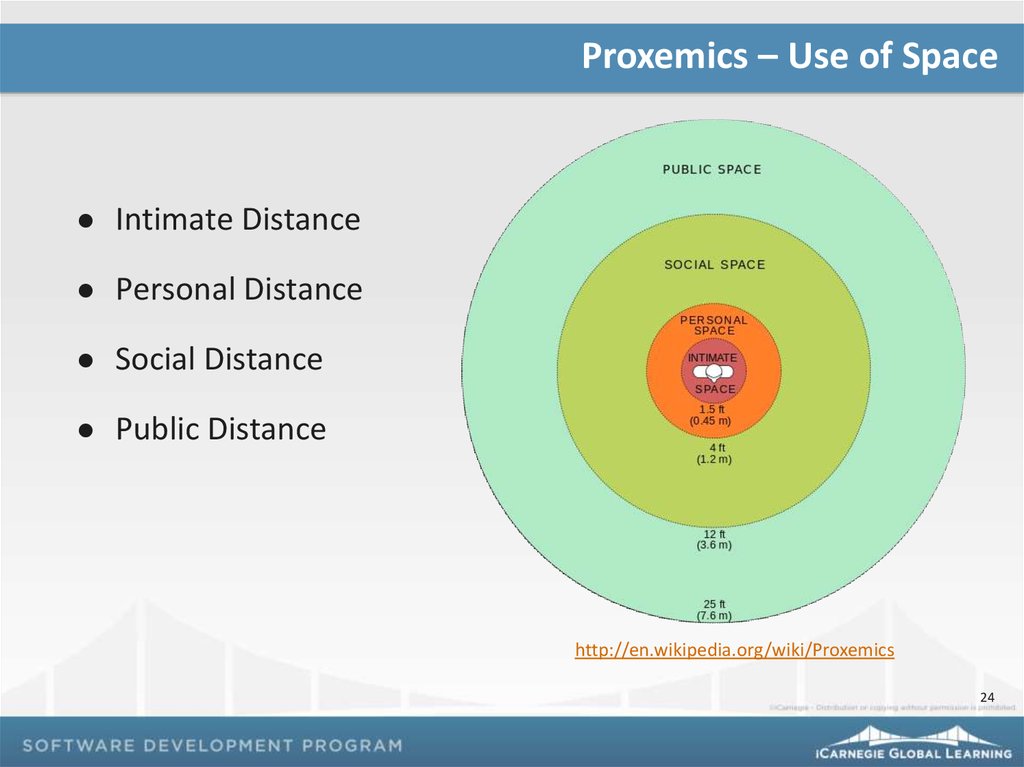
Proxemics – Use of SpaceIntimate Distance
Personal Distance
Social Distance
Public Distance
http://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Proxemics
24
25.
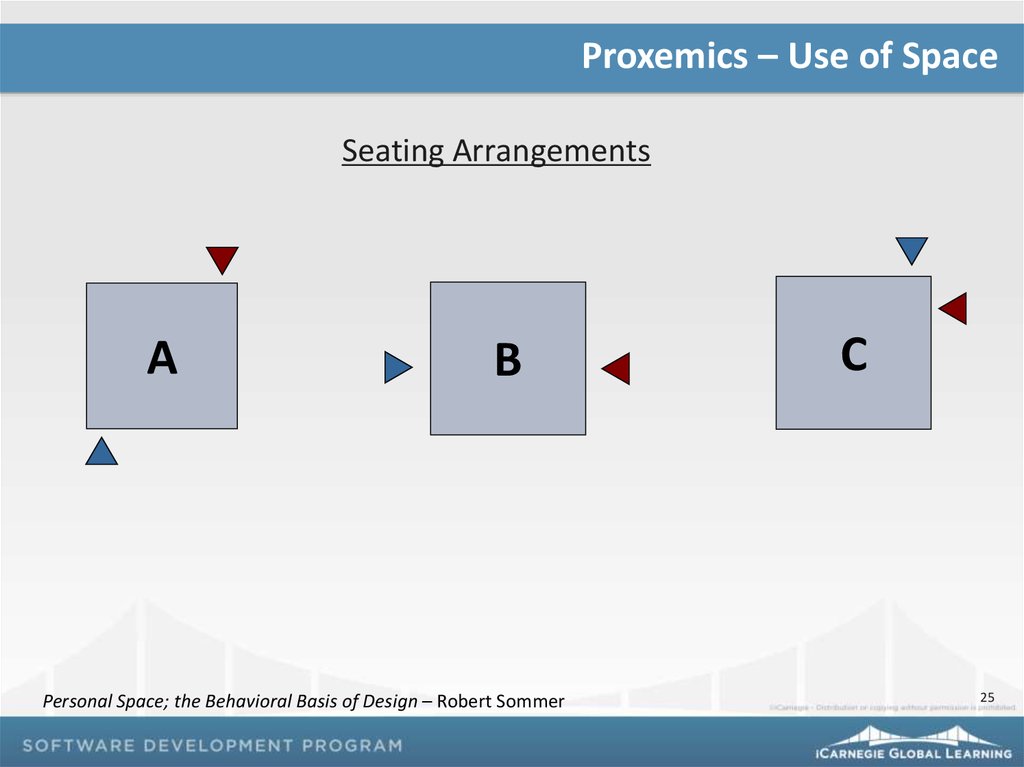
Proxemics – Use of SpaceSeating Arrangements
A
B
Personal Space; the Behavioral Basis of Design – Robert Sommer
C
25
26.
Chronemics – Use of TimeMonochronic People
Do one thing at a time
Concentrate on the job
Take time commitments seriously
Are committed to the job
Strictly adhere to plans
Emphasize promptness
Are accustomed to short-term
relationships
Polychronic People
Do many things at once
Are highly distractible and subject to
interruptions
Consider an objective to be achieved,
if possible
Are committed to people and human
relationships
Change plans often and easily
Base promptness on the relationship
Have strong tendency to build lifetime
relationships
http://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Chronemics
26
27.
QuestioningWhy do we ask questions?
Gain or provide information
Obtain participation
Check understanding or interest
Get people to think
Reach agreement
Discover differences
27
28.
QuestioningStrategies for asking “good” questions:
Ask open-ended questions
Show interest
Ask follow-up question
Ask what could be done better
Do not ask a question if you already know the answer
28
29.
ListeningTrue or False?
Effective listening is as important as effective speaking.
Most people are as good at listening as they are at talking.
College students listen to about 50% of what is said and
remember 25% of the content after 2 days.
29
30.
ListeningA conversation between a US Navy ship and Canadian authorities:
(Canadians) Please divert your course 15 degrees to the south to avoid a
collision.
(Americans) Recommend you divert your course 15 degrees to the north
to avoid a collision.
(Canadians) Negative! You will have to divert your course 15 degrees to
the south to avoid a collision.
(Americans) This is a captain of a US Navy ship. I say again, divert YOUR
course.
(Canadians) No, I say again, divert YOUR course.
30
31.
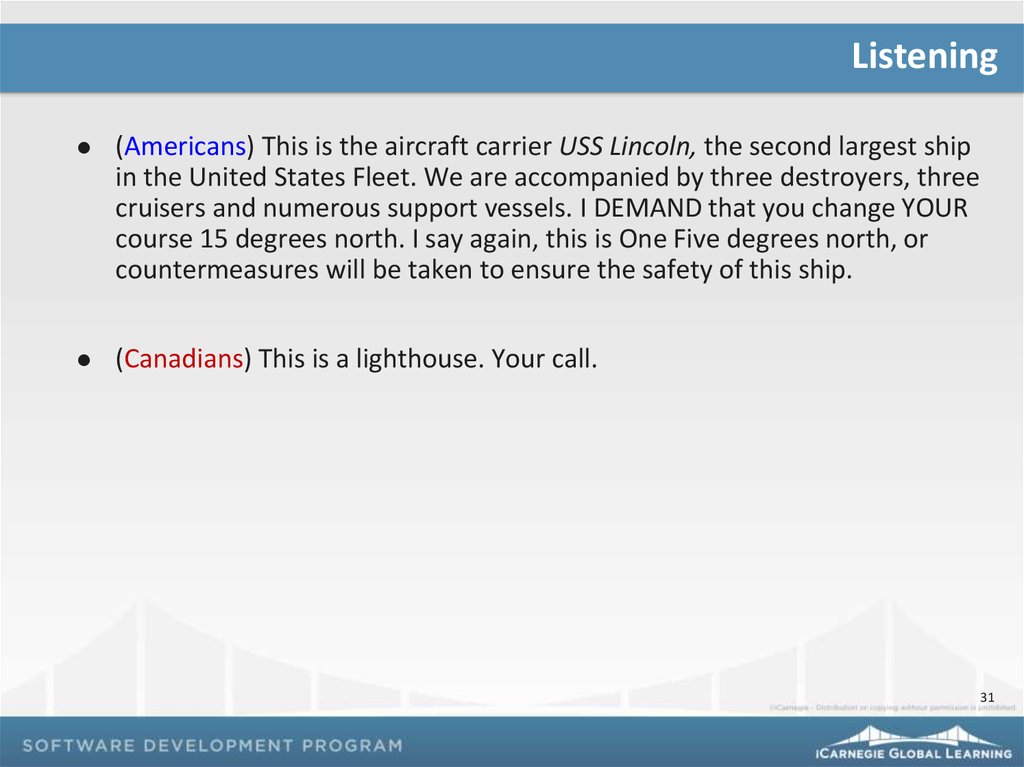
Listening(Americans) This is the aircraft carrier USS Lincoln, the second largest ship
in the United States Fleet. We are accompanied by three destroyers, three
cruisers and numerous support vessels. I DEMAND that you change YOUR
course 15 degrees north. I say again, this is One Five degrees north, or
countermeasures will be taken to ensure the safety of this ship.
(Canadians) This is a lighthouse. Your call.
31
32.
ListeningImportant management skill
Managers listen for up to 60% of workday
Benefits of listening:
Learning new things
Developing better understanding
Making better decisions
Saving time
32
33.
Active ListeningBarriers to listening:
Lack of interest
Distracting delivery
Noise or other distractions
Attitude
33
34.
Active ListeningTips for active listening:
Pay attention
Show you are listening
Show you understand
Allow the speaker to finish
Provide feedback
34
35.
Giving and Receiving FeedbackWhen providing feedback:
Balance positive and negative
Be specific and nonjudgmental
Provide suggestions and guidance
Be timely
35
36.
Giving and Receiving FeedbackWhen receiving feedback:
Ask for specific feedback
Listen and do not argue
Ask for advice on improvements
Summarize what you heard
Show your appreciation
36

































 management
management








