Similar presentations:
Decision-making principles
1. Decision-Making Principles
Managing Technical People2.
Topics and AgendaWhy is Decision Making Important?
How Do We Make Decisions?
Exercise 09: Decision Making
Decision-Making Techniques and Styles
Group Decision Making
Factors Influencing Decision Making
2
3.
Course ProgressModule 0: Factors Influencing Human Interaction
Module 01: Communication
Module 02: Decision Making
Class 09: Decision-Making Principles
Module 03: Negotiation
Module 04: Conflict Management
Module 05: Relationship Management
Module 06: Leadership
3
4.
Why is Decision Making Important?Decision making is an
integral part of the job
• For you as a
manager
• For the technical
people you
manage
http://www.flickr.com/photos/theilr/345056969/
4
5.
Thought Experiment #1• Two coins are in front of you.
They are both skewed
• Coin 1 has 55% chance
of landing on heads
• Coin 2 has 45% chance
of landing on heads
• If you call a coin and it lands on
heads you get $10,000. If it lands
on tails you win $0
• Which coin do you choose?
5
6.
Thought Experiment #2• You are the CEO of a company and you have the option of
promoting one of two products
• Product 1 has 55% chance of being a success
• Product 2 has 45% chance of being a success
• If you choose a product and it is successful, your company
will get a $10,000 pre=tax benefit. If it is unsuccessful you
get $0
• Which product do you promote?
6
7.
How Do You Make Decisions?• Are you following a general process?
• Are you using intuition?
• Are you consistent?
7
8.
What Types of Decisions Will You Need to Make?• Operational
• Everyday decisions, often made with little thought or structure
• Tactical
• Normally support strategic decisions and direction
• Strategic
• Relate to general direction, long term goals, philosophies and
values
8
9.
How Do We Make Decisions?Identify
Decision
Frame
Decision
Impacts &
Valuation
Define the
Problem
Identify
Alternatives
Devise a
Plan
Expected
Value for
Alternatives
Develop
Decision
Model
Carry Out
the Plan
Rethink the
Problem
Implement
Alternatives
Quantify
Uncertainty
Reflect
Opportunities
Lessons
Learned; PostMortem
Risk and Decision
Adapted
from HowAnalysis
to SolveinIt:Projects:
A New Aspect
Cases in
ofProject
Mathematical
and Program
Method:
Management
George Polya
Series: John R. Schuyler
9
10.
How Do We Make Decisions?Frame the Decision
• What is the unknown?
• What are the data?
• What are the conditions?
• Root cause or symptom?
10
11.
How Do We Make Decisions?Devise a Plan
• Draw a picture
• Look for similar decisions/problems
• Break up the decision/problem
• Work backwards
11
12.
How Do We Make Decisions?Carry Out the Plan
• Check each step
• Can you derive the solution another way?
12
13.
How Do We Make Decisions?Reflect
• Was your solution successful?
• If not, how can you modify it?
• If so, can it be used on other decisions or problems?
13
14.
Who Should Make Decisions?• Employees in the Marketing and Product Development groups at an auto
manufacturer were asked “Who is responsible for decisions?”
Marketing
17%
Who decides standard features?
Product Development
We Do
83%
Who decides colors?
Other
Product Development
We Do
61%
We Do
64%
Other
Marketing
39%
36%
Other
23%
We Do
77%
Other
Who Has the D? How Clear Decision Roles Enhance Organizational Performance: Paul Rogers and Marcia Blenko
14
15.
Who Should Make Decisions?• RAPID Decision Making Roles
• Recommend: This role gathers the input and information
necessary to make a proposal. Individuals in this role must be
analytical and organized.
• Agree: An individual in the “agree” role has the ability to say
yes or no to a recommendation.
• Perform: This is the individual or group responsible for
implementing a decision.
• Input: These individuals provide input and advice on the
decision.
• Decide: This is the individual responsible for making the
final decision.
Who Has the D? How Clear Decision Roles Enhance Organizational Performance: Paul Rogers and Marcia Blenko
15
16.
Decision-Making Techniques• T-Charts
• SWOT
• Pareto Analysis
• Pairwise Comparison
• Cost/Benefit Analysis
16
17.
Decision-Making Techniques: T-ChartsShould I go to Carol’s party tonight?
Pros
Cons
1. She makes the most
delicious canapes
1. I have to get up early
tomorrow
2. I might see Susie
2. I might run into Lester
3. Etc.
3. Etc.
17
18.
ExternalInternal
Decision-Making Techniques: SWOT Analysis
Helpful
Harmful
Strengths
• People/knowledge/
experience
• Strong standards
• Interdepartmental cooperation
• Datacenter
• State-of-the-art wireless network
Weaknesses
• Funding
• Lack of training and
documentation
• Outdated equipment
• Lack of support
• Employee skills and qualifications
• Space constraints
Opportunities
• Data Center
• Equipment upgrades
• Implementing new technologies
• New funding
• Administrative support
• New leadership
• Improved reliability of services
Threats
• Funding
• Turnover and employee retention
• Disaster recovery
• Lack of redundant systems
• Aging facilities
• Aging equipment
18
19.
Decision-Making Techniques: Pareto Analysis• 80/20 Rule:
• 80% of sales come from 20% of customers
• 80% of employees take 20% of sick time
• Microsoft discovered that they could eliminate 80% of the errors
and crashes by fixing the top 20% most reported bugs
19
20.
Decision-Making Techniques: Pairwise ComparisonProduct 1
Product 2
Product 3
Product 4
Total
Product 1
-
1
1
1
3
Product 2
0
-
1
1
2
Product 3
0
0
-
0
0
Product 4
0
0
1
-
1
20
21.
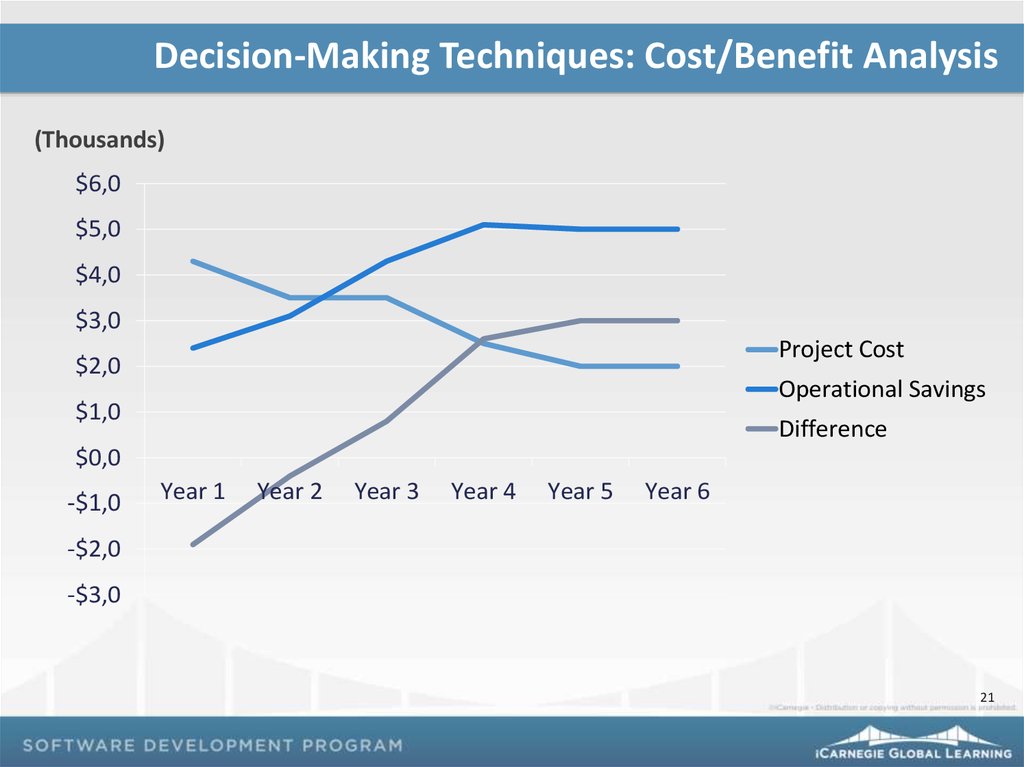
Decision-Making Techniques: Cost/Benefit Analysis(Thousands)
$6,0
$5,0
$4,0
$3,0
Project Cost
$2,0
Operational Savings
$1,0
Difference
$0,0
-$1,0
Year 1
Year 2
Year 3
Year 4
Year 5
Year 6
-$2,0
-$3,0
21
22.
What Is Intuitive Decision Making?• Developed from research by Gary Klein
• Fire Fighters
• Police forces
• Other First Responders
• A “translation of experience into action”
• Making decisions without a comprehensive formal analysis
• Intuition can be built, applied and safeguarded
The Power of Intuition: How to Use Your Gut Feelings to Make Better Decisions at Work: Gary Klein
22
23.
Thin-SlicingRapid decisions made with minimal information:
• John Gottman’s Love Lab
• Morse Code/British Interceptors
• Doctors and Malpractice
Blink: The Power of Thinking without Thinking: Malcolm Gladwell
23
24.
What Is Intuitive Decision Making?Situation
Observe
Cues
Choose
Course of
Action
Recognize
Patterns
The Power of Intuition: How to Use Your Gut Feelings to Make Better Decisions at Work: Gary Klein
24
25.
Influencing Factors: Decision-Making StylesDecides on Multiple Options
Decides on One Option
Uses Less Information
Uses More Information
Decisive
Task oriented
Direct
Efficient
Likes to stick to decision
Hierarchic
Flexible
Social and responsive
Decides quickly
Can change direction of
decision
Intellectual
Analytical
Focused
Expect others to contribute
to decisions
Decisions are final
Integrative
Participative
Use inputs from multiple
sources
May change decision over
time
Adapted from The Seasoned Executive’s Decision-Making Style: Kenneth R. Brousseau, Michael J. Driver, Gary Hourihan, and Rikard Larsson
25
26.
Influencing Factors: Decision-Making StylesAverage Leadership Style Scores
Supervisor
Manager
Director
VP
Senior
Executive
Average Thinking Style Scores
Supervisor
Manager
Director
VP
Senior
Executive
Flexible
Integrative
Hierarchic
Decisive
The Seasoned Executive’s Decision-Making Style: Kenneth R. Brousseau, Michael J. Driver, Gary Hourihan, and Rikard Larsson
26
27.
Influencing Factors: Group Decision Making• What typically happens in a group, committee, board?
• No decision
• Self-Appointed Decision Maker
• Minority Rule
• Majority Rule
• Consensus
Decision-Making Styles and Techniques: Marlene K. Rebori
27
28.
Influencing Factors: Group Decision Making• When making decisions in a group, consider:
• Timeliness
• Appropriateness
• Relationships
Decision-Making Styles and Techniques: Marlene K. Rebori
28
29.
Influencing Factors: TimeHow do time pressures
affect decision making?
Blink: The Power of Thinking without Thinking: Malcolm Gladwell
29
30.
Influencing Factors: Personality TypesRelater
Thinker
Socializer
Director
30
31.
Remember…Case Study 01: Due by Next Class
Video Analysis 02: Due by Class 11
Due by 8 p.m.
Due by 8 p.m.
Role Play 02 Scenario Planning Questionnaire: Due by Class 12
Due by 8 p.m.
31






























 management
management








