Similar presentations:
Modelling, shading and simulation in animation
1.
Modelling, shadingand simulation in
animation
Welcome to this presentation on modelling, shading, and simulation in
animation! This presentation will guide you through the essential
techniques and concepts used in creating stunning and realistic
animations. We will explore how these techniques are used to bring
characters, environments, and effects to life in both traditional and
computer-generated animation.
SS
2.
Presentation contents1
Importance of modelling in animation
2
Techniques for character modelling
3
Principles of lighting and shading
4
Realistic material simulation
5
Dynamics and physics-based animation
6
Simulation in animation
7
Integrating simulation with keyframing
8
Conclusion and future trends
3.
Importance of modelling in animationFoundation of animation
Defining character
Creating environments
Modelling is the cornerstone of 3D
In character animation, modelling plays a
Modelling is equally essential for creating
animation. It involves creating the shapes,
crucial role in defining the personality,
believable and immersive environments.
forms, and structures of all the objects
emotions, and physical features of your
Whether you are creating a fantastical
that appear in your animation. A strong
characters. A well-crafted model can
landscape, a bustling city, or a cozy
model forms the basis for realistic
convey a character's age, gender, weight,
interior, accurate modelling brings your
movement, texture, and lighting. It's like
and even their mood through subtle
world to life and immerses your viewers in
building the skeleton of your animated
details.
the story.
world.
4.
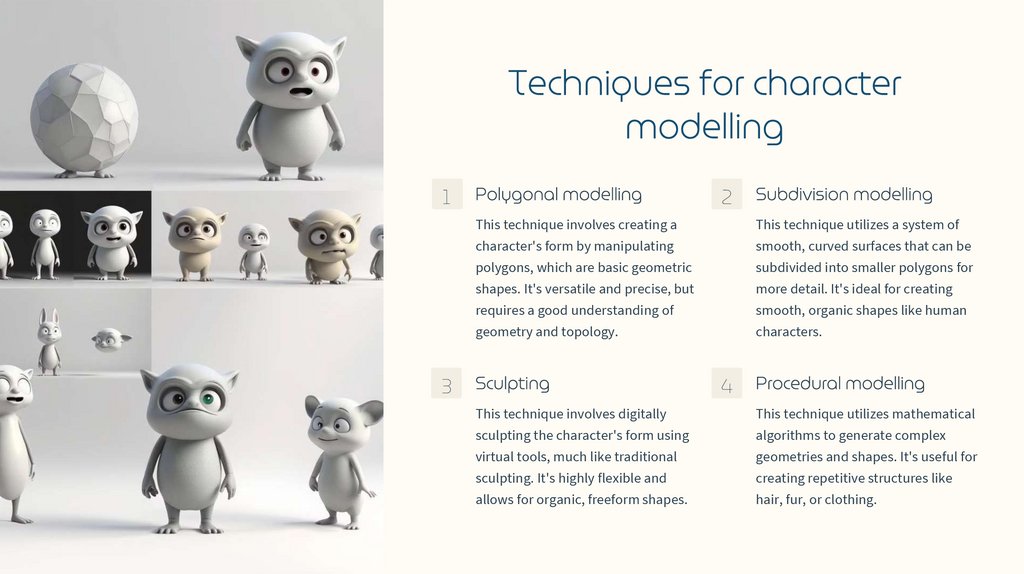
Techniques for charactermodelling
1
3
Polygonal modelling
2
Subdivision modelling
This technique involves creating a
This technique utilizes a system of
character's form by manipulating
smooth, curved surfaces that can be
polygons, which are basic geometric
subdivided into smaller polygons for
shapes. It's versatile and precise, but
more detail. It's ideal for creating
requires a good understanding of
smooth, organic shapes like human
geometry and topology.
characters.
Sculpting
4
Procedural modelling
This technique involves digitally
This technique utilizes mathematical
sculpting the character's form using
algorithms to generate complex
virtual tools, much like traditional
geometries and shapes. It's useful for
sculpting. It's highly flexible and
creating repetitive structures like
allows for organic, freeform shapes.
hair, fur, or clothing.
5.
Principles of lighting andshading
Light sources
Light sources play a crucial role in establishing mood, atmosphere, and
realism in animation. Different light sources, such as ambient, directional,
and point lights, create distinct effects on objects and characters.
Shading models
Shading models define how light interacts with surfaces, creating the
illusion of texture, form, and depth. Common shading models include
Phong, Blinn-Phong, and Lambert, each with its unique characteristics.
Material properties
Materials influence how light interacts with objects. By defining properties
like colour, reflectivity, and roughness, you can create convincing materials,
such as wood, metal, or skin.
6.
Realistic material simulationMaterial
Simulation techniques
Fabric
Cloth simulation, using physics-based
methods to calculate how fabric drapes
and interacts with other objects.
Water
Fluid simulation, using numerical
methods to simulate the movement
and behaviour of water, including
waves, splashes, and ripples.
Hair and fur
Particle systems and hair simulation,
using individual particles to represent
hair strands and simulating their
movement and interaction.
7.
Dynamics and physics-based animationRigid body dynamics
Fluid dynamics
This technique simulates the movement and interaction of rigid
bodies, like balls, boxes, and cars, under the influence of gravity and
other forces. It creates realistic collisions, bounces, and rotations.
1
This technique simulates the movement and interaction of fluids, like
water, smoke, and fire, using computational fluid dynamics methods
to create realistic flow patterns, turbulence, and buoyancy effects.
2
Soft body dynamics
This technique simulates the behaviour of deformable objects, like
cloth, ropes, and muscles, using physics-based calculations to
capture realistic deformation and elasticity.
3
8.
Simulation in animationExplosions and fire
Smoke and dust
Simulations can create realistic
explosions and fires, adding dramatic
impact and visual spectacle to
Simulations can create realistic smoke
and dust effects, adding visual
complexity and atmosphere to
animated scenes.
animated scenes.
Water effects
Destruction and
deformation
Simulations can create realistic water
effects, such as waves, splashes, and
currents, adding depth and dynamism
to animated scenes.
Simulations can create realistic
destruction and deformation effects,
showcasing the impact of collisions,
explosions, and other forces.
9.
Integrating simulation withkeyframing
Enhanced realism
Time savings
Combining keyframing with
simulation allows animators to
achieve more realistic and
believable movement. Keyframing
provides control over the overall
animation flow, while simulation
handles the fine details and physics.
Simulations can automate
repetitive or complex movements,
saving animators time and effort.
They can also handle interactions
between objects more efficiently
than manual keyframing.
Creative flexibility
Simulations offer creative flexibility by allowing animators to experiment with
different physical parameters and explore unique movement possibilities.
10.
Conclusion and futuretrends
Modelling, shading, and simulation are essential techniques in
animation, enabling the creation of stunning and realistic visuals. With
the continuous advancements in technology, these techniques are
evolving rapidly. The future of animation holds exciting possibilities,
including more realistic and complex simulations, advanced rendering
techniques, and immersive virtual reality experiences.








 software
software








