Similar presentations:
Inter-VLAN Routing
1.
Inter-VLAN Routing1
2. Inter-VLAN Routing
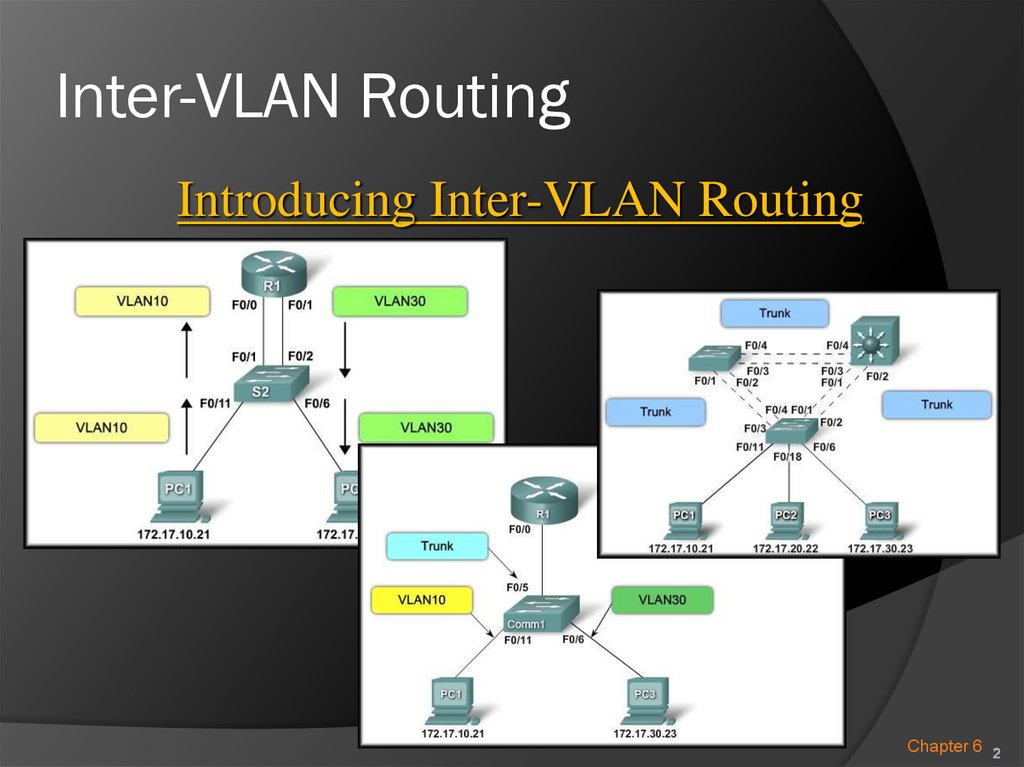
Introducing Inter-VLAN RoutingChapter 6 2
3. Introducing Inter-VLAN Routing
What is Inter-VLAN Routing?Each VLAN is a unique broadcast domain.
○ Computers on separate VLANs are, by default, not able
to communicate.
Each VLAN is a unique IP subnetwork.
To allow VLANs to communicate, we need a router to
communicate among separate broadcast domains
and unique IP subnetworks.
Inter-VLAN routing, then, is a process of
forwarding traffic from one VLAN to another
VLAN using a router.
Chapter 6 3
4. Introducing Inter-VLAN Routing
Methods:Traditional Inter-VLAN Routing.
Router-on-a-stick Inter-VLAN Routing.
Switch Based Inter-VLAN Routing.
Chapter 6 4
5. Introducing Inter-VLAN Routing
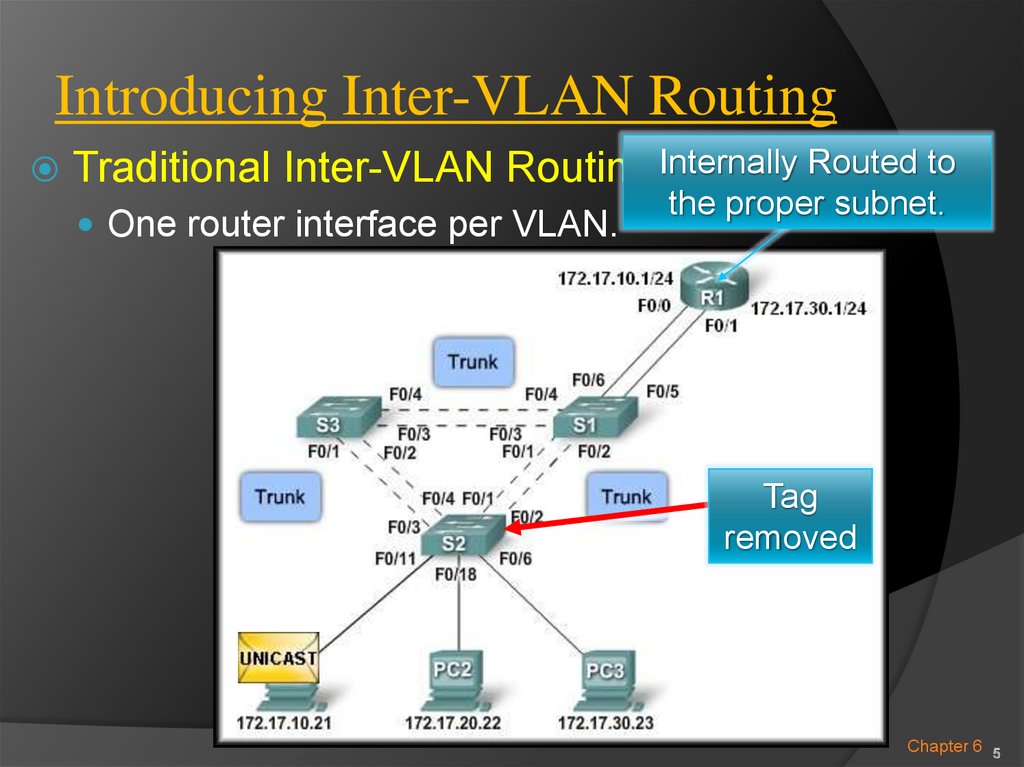
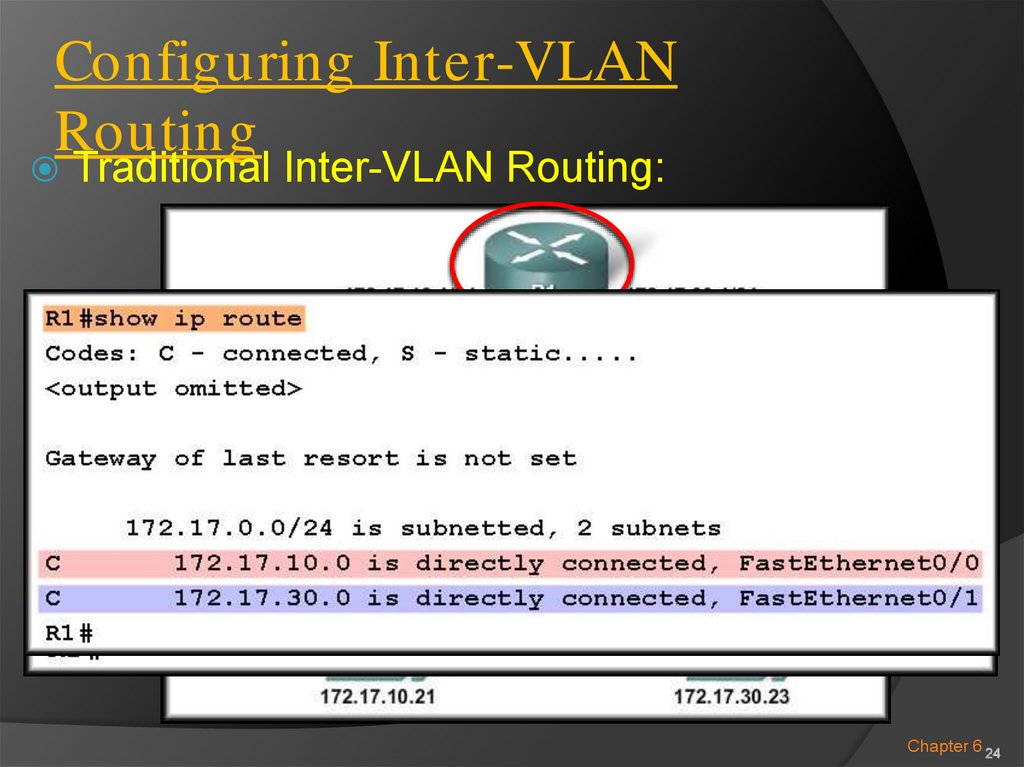
Traditional Inter-VLAN Routing:Internally Routed tothe proper subnet.
One router interface per VLAN.
VLAN
Tag
removed
Tagged
Chapter 6 5
6. Introducing Inter-VLAN Routing
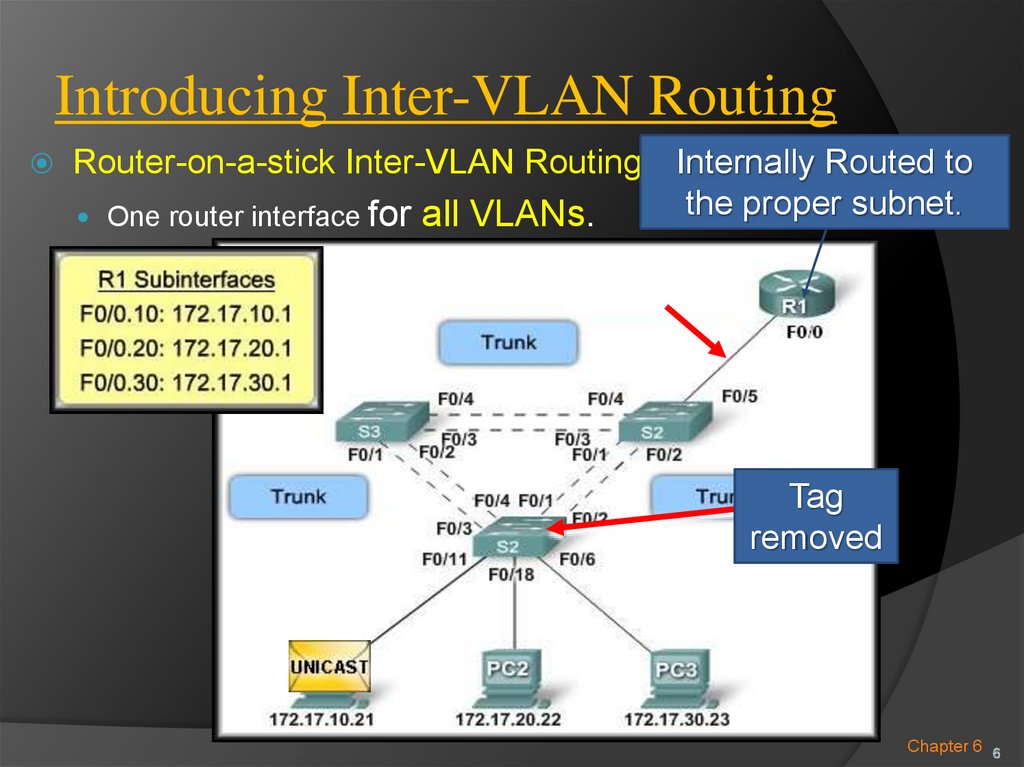
Router-on-a-stick Inter-VLAN Routing:One router interface for all VLANs.
Internally Routed to
the proper subnet.
VLAN
Tag
removed
Tagged
Chapter 6 6
7. Introducing Inter-VLAN Routing
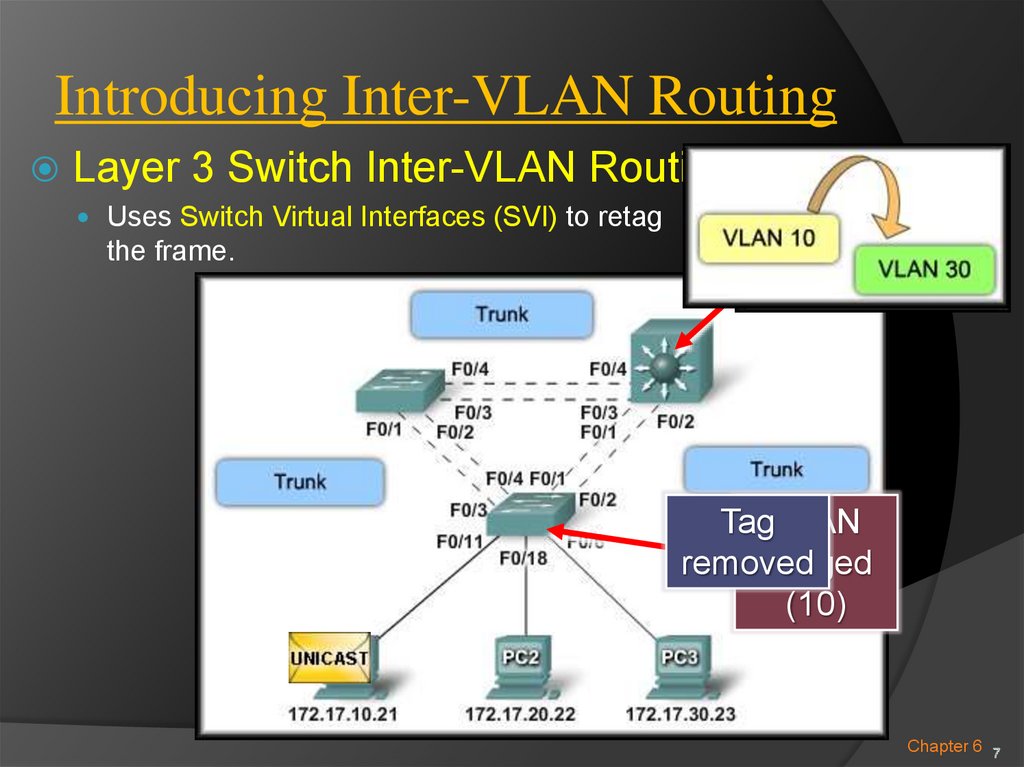
Layer 3 Switch Inter-VLAN Routing:Uses Switch Virtual Interfaces (SVI) to retag
the frame.
TagVLAN
removed
Tagged
(10)
Chapter 6 7
8. Interfaces and Subinterfaces
Traditional Inter-VLAN Routing:Traditional routing requires routers to have multiple
physical interfaces to facilitate inter-VLAN routing.
Each interface is also configured with an IP address
for the subnet associated with the particular VLAN
that it is connected to.
In this configuration, network devices can use the
router as a gateway to access the devices connected
to the other VLANs.
Chapter 6 8
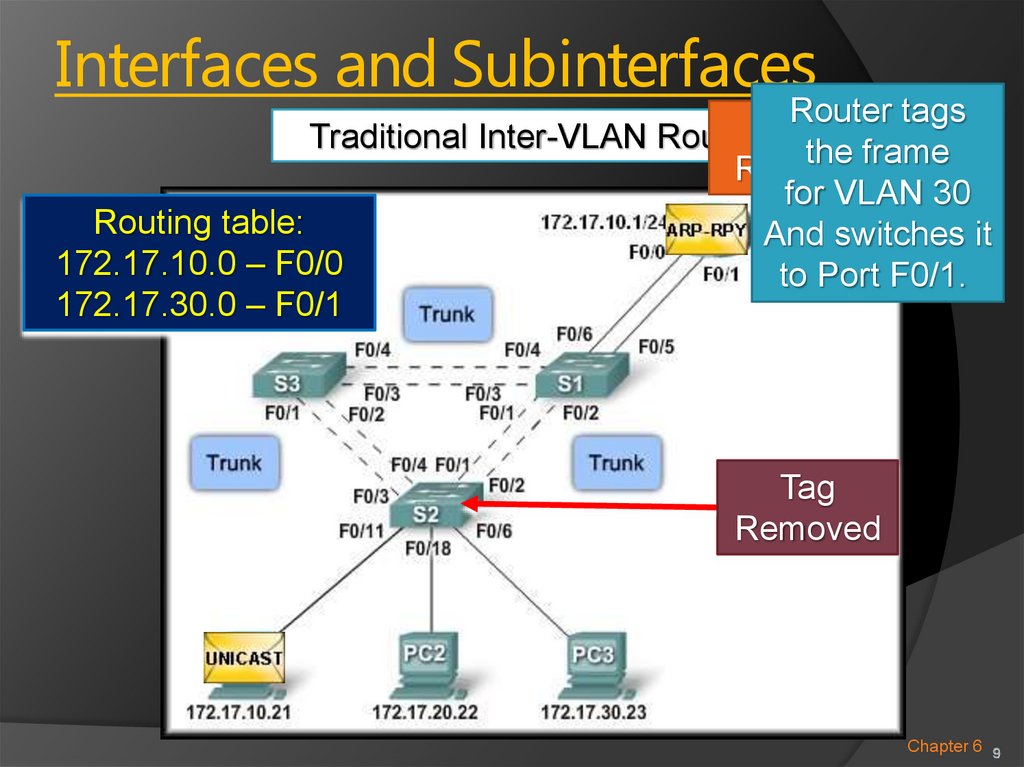
9. Interfaces and Subinterfaces
Router tagsRouter
Traditional Inter-VLAN Routing the frame
Responds
for VLAN 30
Routing table:
And switches it
172.17.10.0 – F0/0
to Port F0/1.
172.17.30.0 – F0/1
Tagged
Tag
Removed
VLAN 10
Chapter 6 9
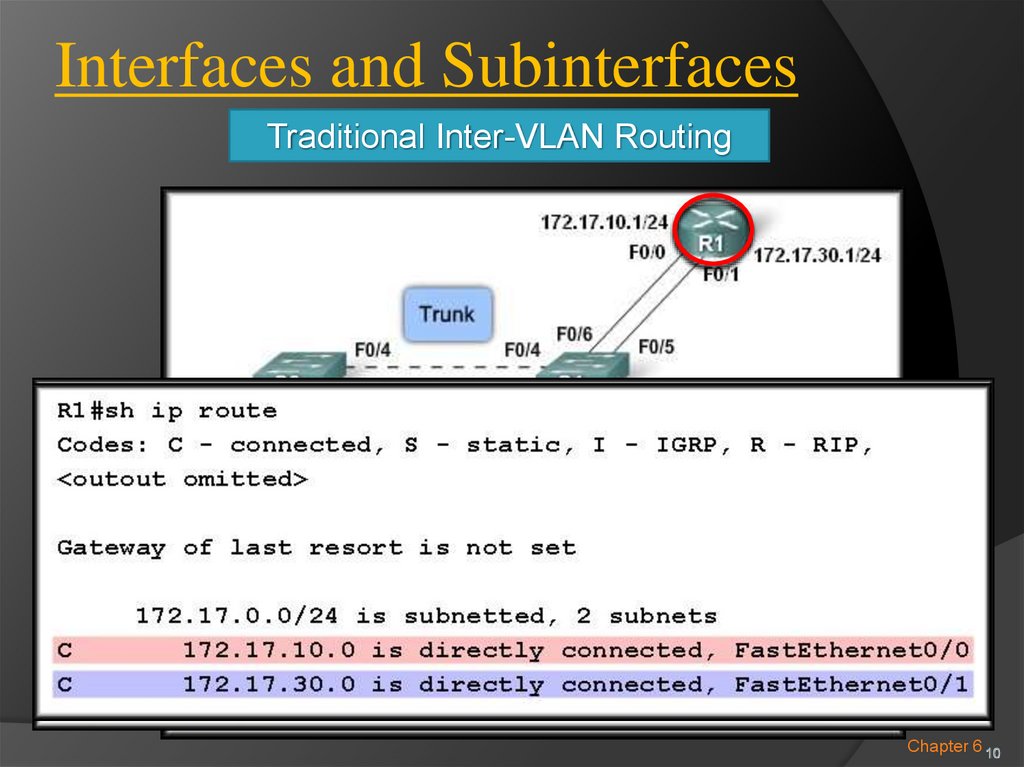
10.
Interfaces and SubinterfacesTraditional Inter-VLAN Routing
Chapter 6 10
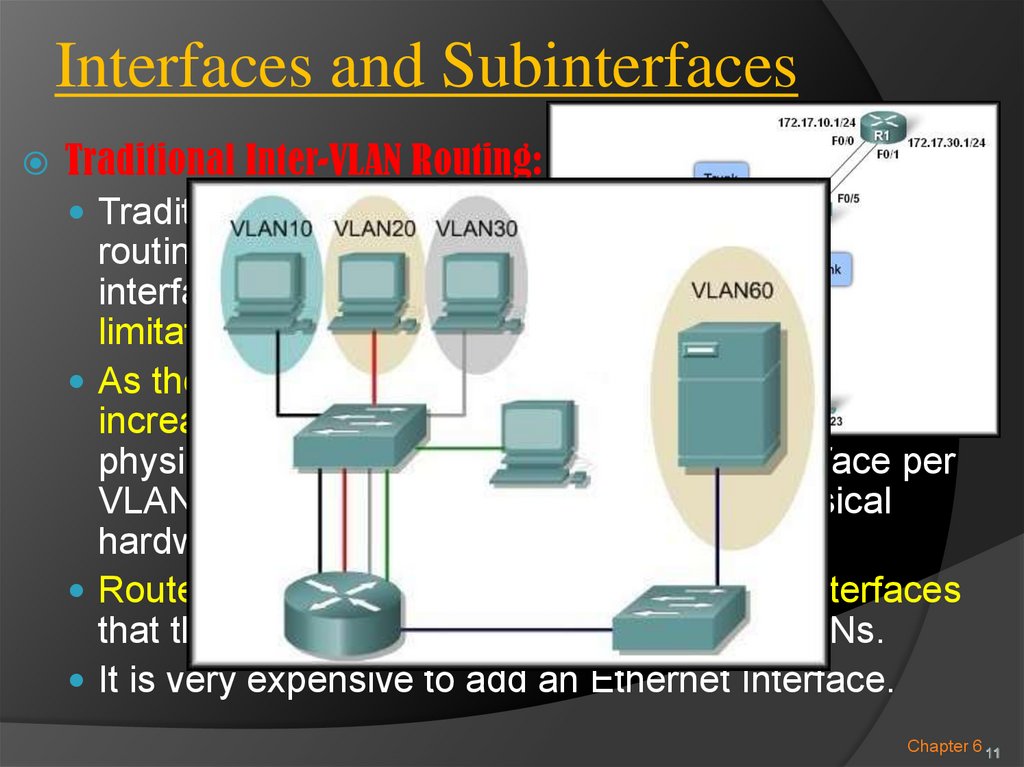
11.
Interfaces and SubinterfacesTraditional Inter-VLAN Routing:
Traditional inter-VLAN
routing using physical
interfaces does have a
limitation.
As the number of VLANs
increases on a network, the
physical approach of having one router interface per
VLAN quickly becomes hindered by the physical
hardware limitations of a router.
Routers have a limited number of physical interfaces
that they can use to connect to different VLANs.
It is very expensive to add an Ethernet Interface.
Chapter 6 11
12. Interfaces and Subinterfaces
Router-on-a-stick Inter-VLAN Routing:Subinterfaces:
○ Overcomes the hardware limitation of a router.
○ Subinterfaces are software-based virtual interfaces that
are assigned to physical interfaces.
○ Each subinterface is configured with its own IP address,
subnet mask, and unique VLAN assignment.
○ Connected to a switch trunk link.
○ Functionally the same as using the traditional routing
model.
Chapter 6 12
13. Interfaces and Subinterfaces
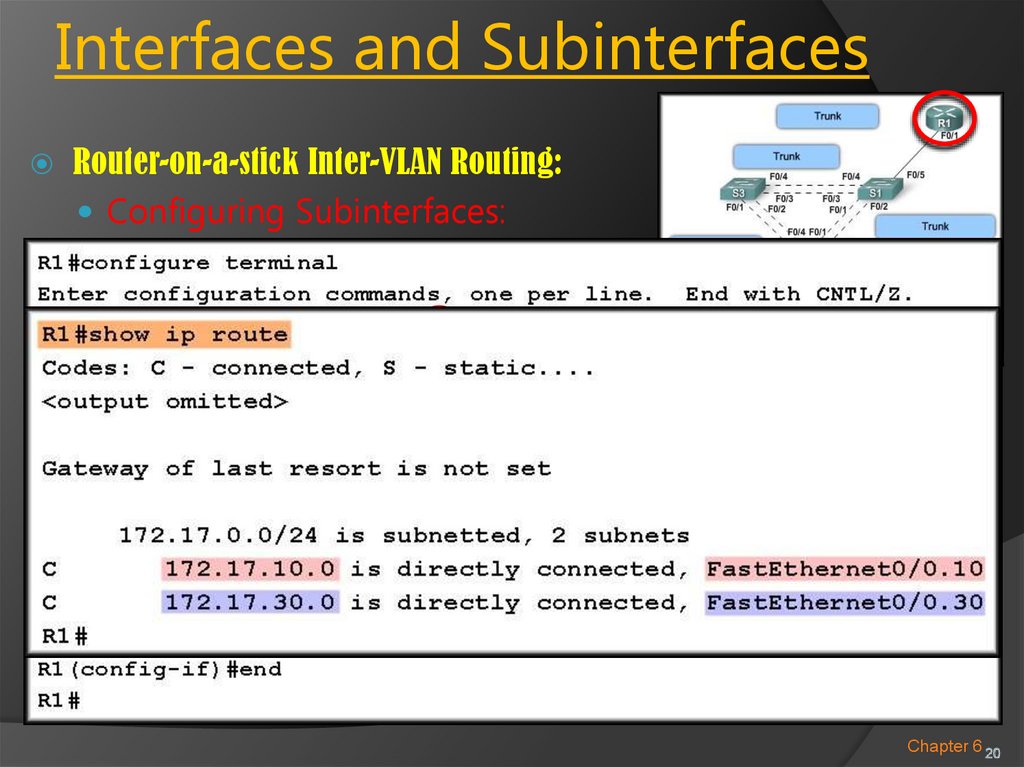
Router-on-a-stick Inter-VLAN RoutingRouting table:
172.17.10.0 – F0/0.10
172.17.30.0 – F0/0.30
Tagged
VLAN 30
Tagged
Tag
Tag
Removed
Removed
VLAN 30
10
Chapter 6 13
14. Interfaces and Subinterfaces
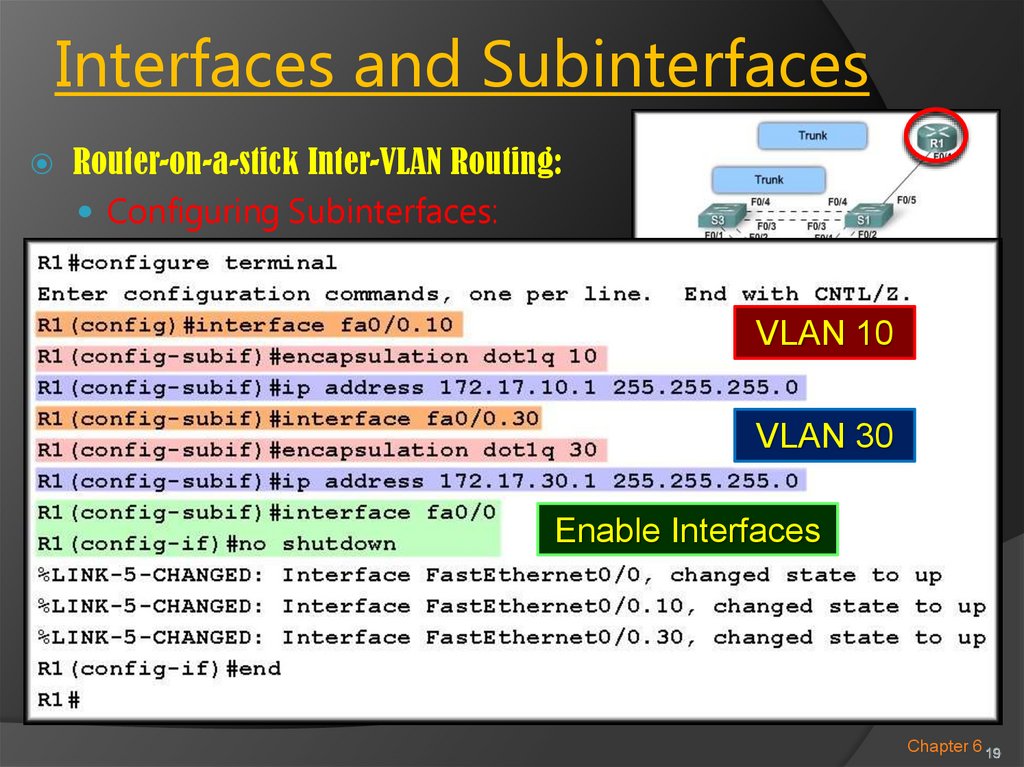
Router-on-a-stick Inter-VLAN Routing:Configuring Subinterfaces:
○ Similar to configuring physical interfaces.
Create the subinterface.
Assign it to a VLAN.
Assign an IP Address.
Enable the interface.
Chapter 6 14
15. Interfaces and Subinterfaces
Router-on-a-stick Inter-VLAN Routing:Create the subinterface:
○ The syntax for the subinterface is always the physical
interface, followed by a period and a subinterface
number.
○ The subinterface number is configurable, but it is
typically associated to reflect the VLAN number.
R1(config)#interface [interface].nn
NOTE:
Chapter 6 15
16. Interfaces and Subinterfaces
Router-on-a-stick Inter-VLAN Routing:Assign it to a VLAN:
○ Before assigning an IP Address, the interface must to
be configured to operate on a specific VLAN using the
proper encapsulation.
R1(config-subif)#encapsulation
dot1q vlan-id
Chapter 6 16
17. Interfaces and Subinterfaces
Router-on-a-stick Inter-VLAN Routing:Assign an IP Address:
○ The IP Address assigned here will become the default
gateway for that VLAN.
R1(config-subif)#ip address
[address] [mask]
Chapter 6 17
18. Interfaces and Subinterfaces
Router-on-a-stick Inter-VLAN Routing:Enable the interface:
○ Subinterfaces are not enabled individually.
○ When the physical interface is enabled, all associated
subinterfaces are enabled.
R1(config-if)#no shutdown
Chapter 6 18
19. Interfaces and Subinterfaces
Router-on-a-stick Inter-VLAN Routing:Configuring Subinterfaces:
VLAN 10
VLAN 10
VLAN 30
Enable Interfaces
Chapter 6 19
20. Interfaces and Subinterfaces
Router-on-a-stick Inter-VLAN Routing:Configuring Subinterfaces:
Planning!
Chapter 6 20
21. Interfaces and Subinterfaces
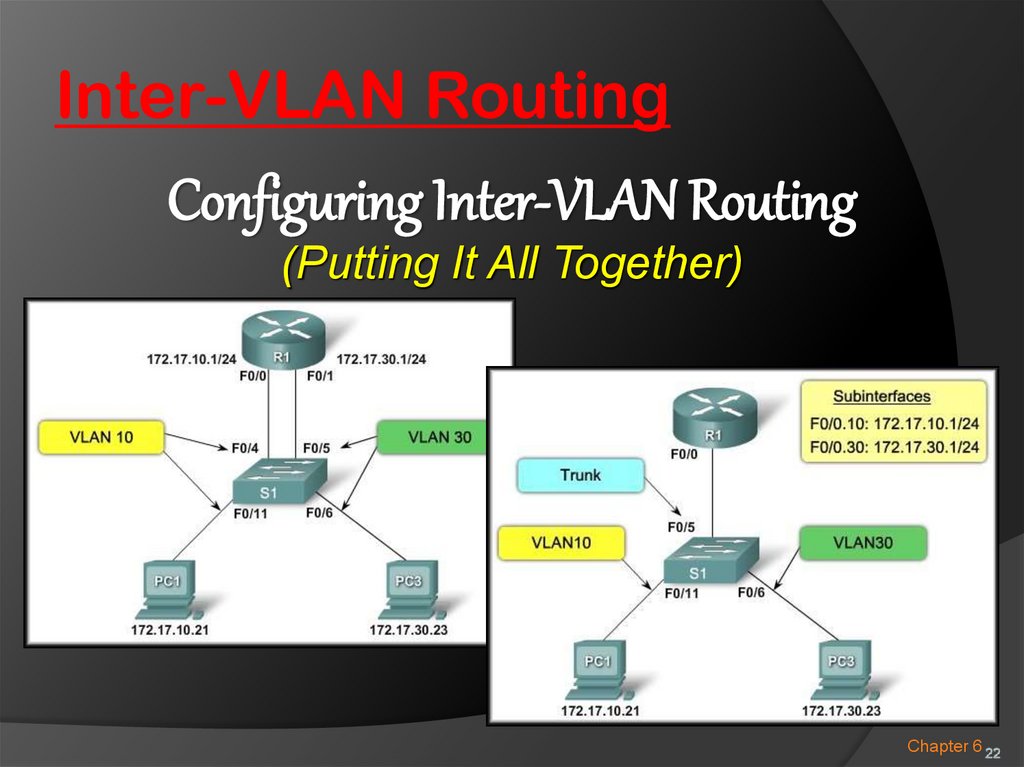
Inter-VLAN RoutingConfiguring Inter-VLAN Routing
(Putting It All Together)
Chapter 6 22
22. Inter-VLAN Routing
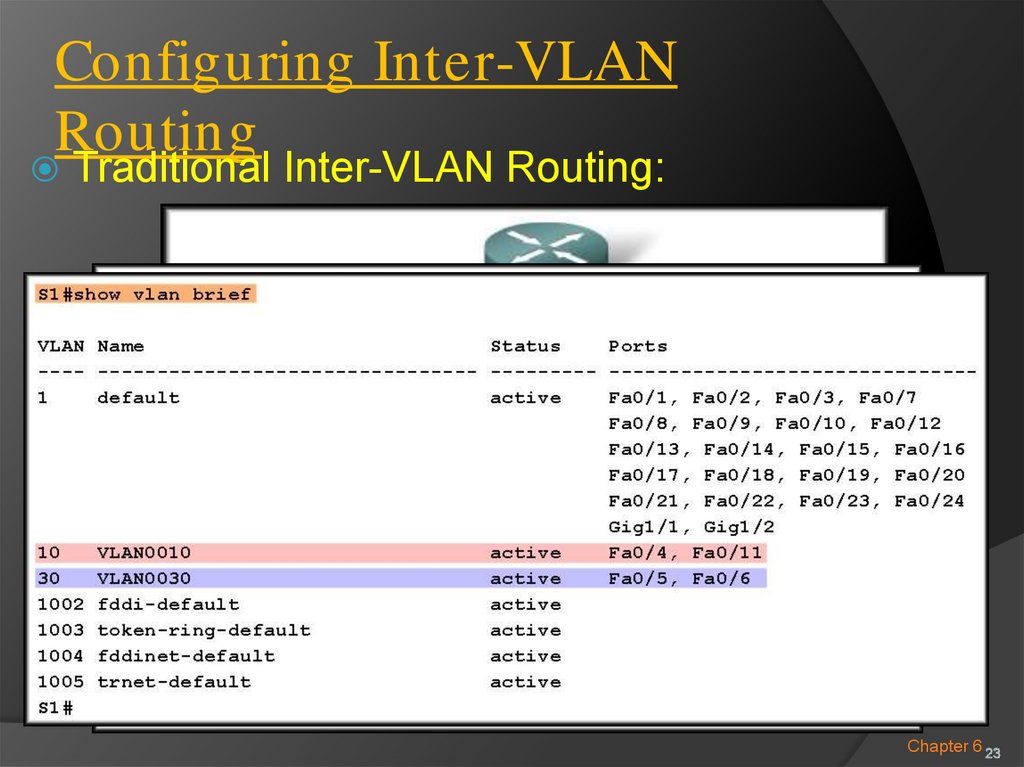
Configuring Inter-VLANRouting
Traditional Inter-VLAN Routing:
Chapter 6 23
23. Configuring Inter-VLAN Routing
Traditional Inter-VLAN Routing:Chapter 6 24
24. Configuring Inter-VLAN Routing
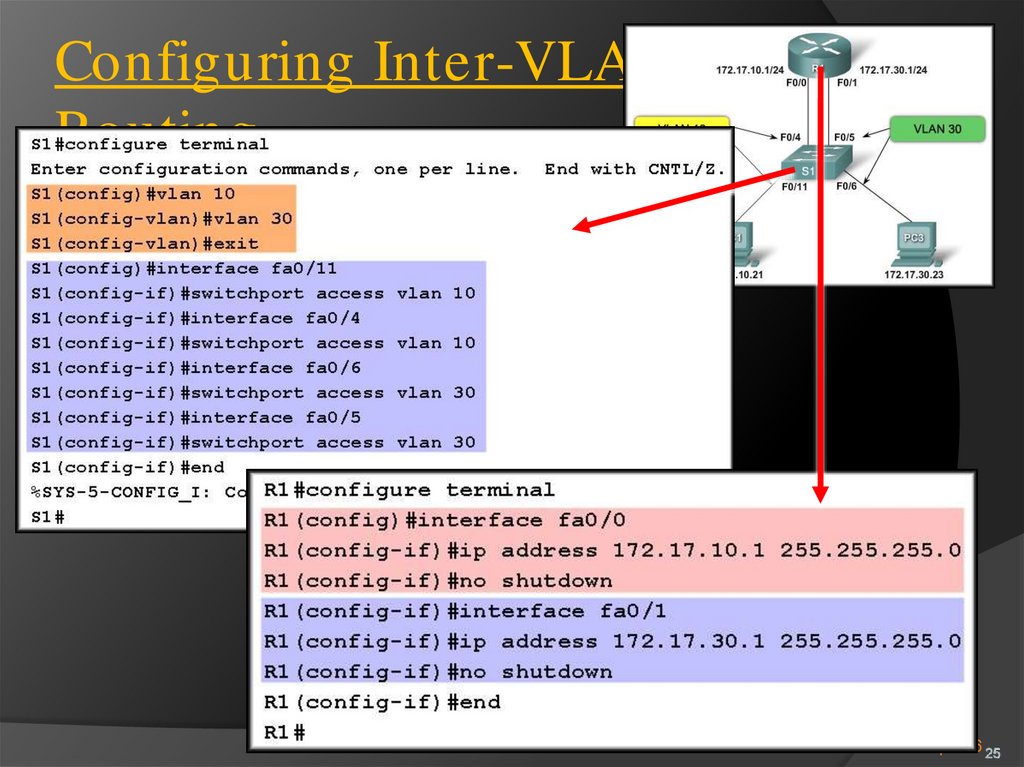
Traditional Inter-VLAN Routing:Chapter 6 25
25. Configuring Inter-VLAN Routing
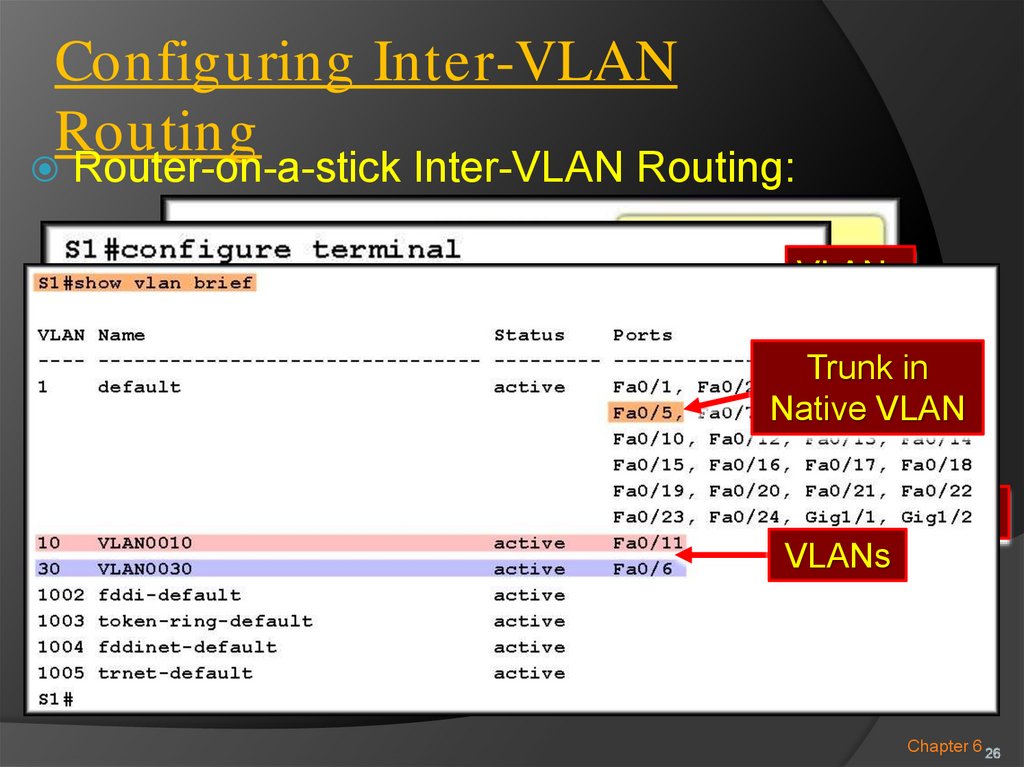
Router-on-a-stick Inter-VLAN Routing:VLANs
Trunk in
Trunk
Native
VLAN
Interfaces
VLANs
Chapter 6 26
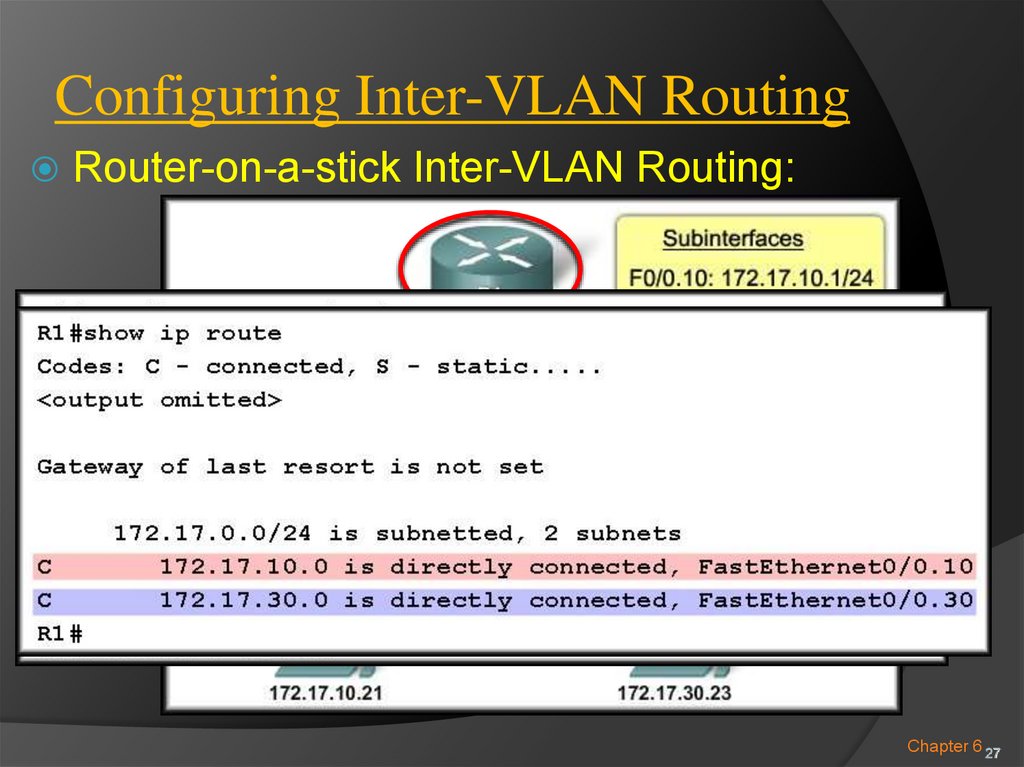
26. Configuring Inter-VLAN Routing
Router-on-a-stick Inter-VLAN Routing:VLAN 10
VLAN 30
Enable All
Subinterfaces
Chapter 6 27
27. Configuring Inter-VLAN Routing
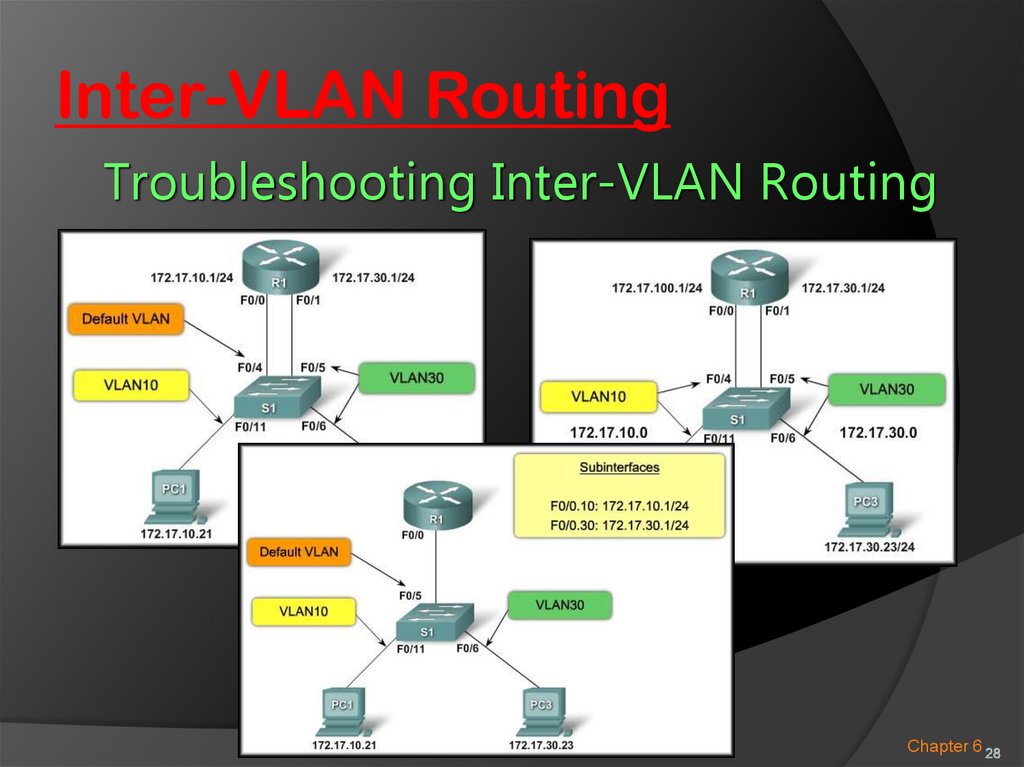
Inter-VLAN RoutingTroubleshooting Inter-VLAN Routing
Chapter 6 28
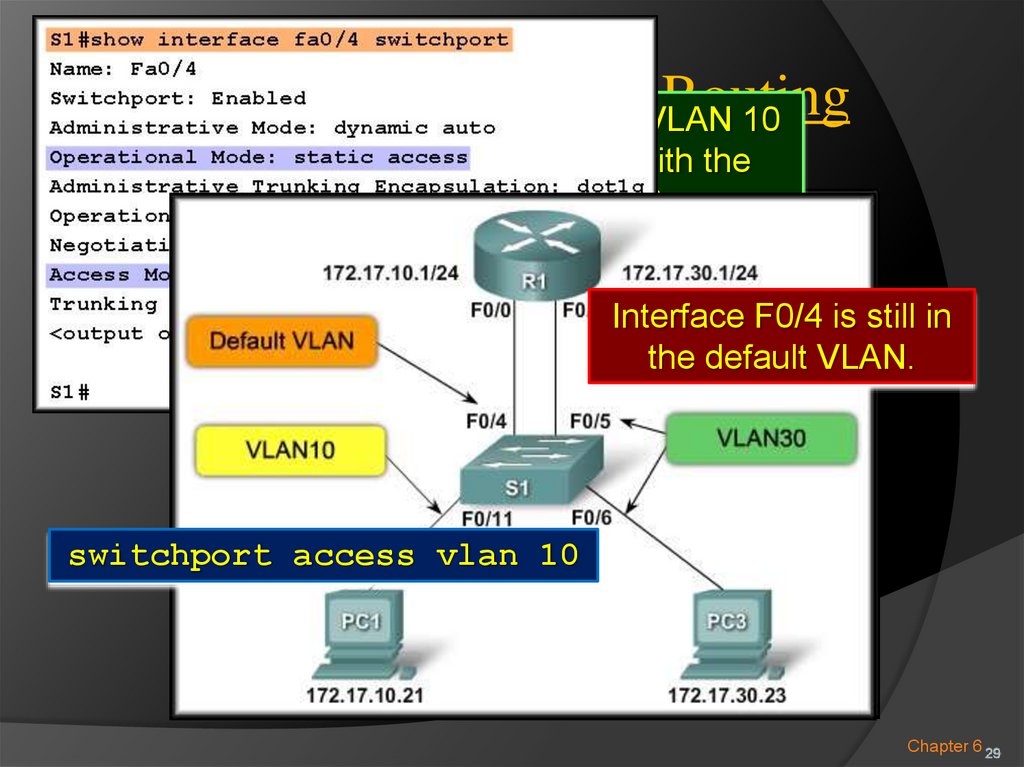
28. Inter-VLAN Routing
ConfiguringRouting
VLANInter-VLAN
30 is working but VLAN
10
cannot communicate
Switch Configuration
Issues: with the
router or VLAN 30.
Interface F0/4 is still in
the default VLAN.
switchport access vlan 10
Chapter 6 29
29. Configuring Inter-VLAN Routing
Each of the configuredSwitch Configuration
Issues:
subinterfaces
is unable to
send or receive VLAN traffic.
Interface F0/5 is still in
the default VLAN.
switchport mode trunk
Chapter 6 30
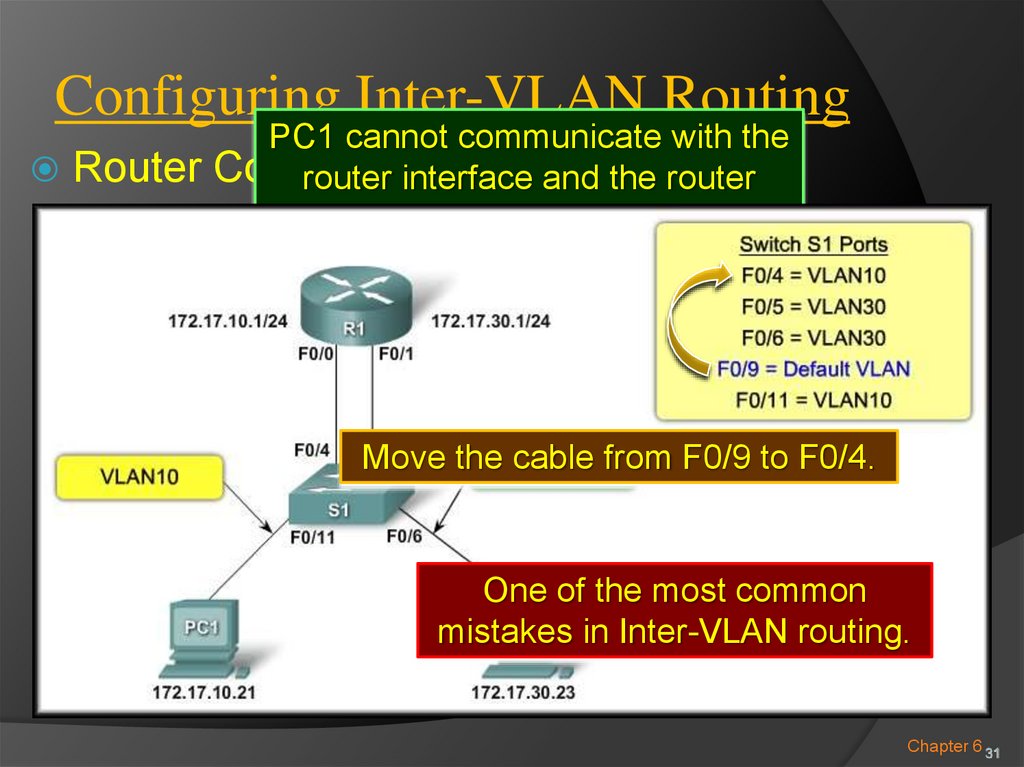
30. Configuring Inter-VLAN Routing
PC1 cannot communicate with theRouter Configuration
Issues:
router interface
and the router
cannot route to VLAN 30.
Switch port F0/4 is
for VLAN 10.
Switch port F0/9 is
Move the cable from F0/9 to F0/4.
assigned to the
default VLAN.
One of the most common
mistakes in Inter-VLAN routing.
Chapter 6 31
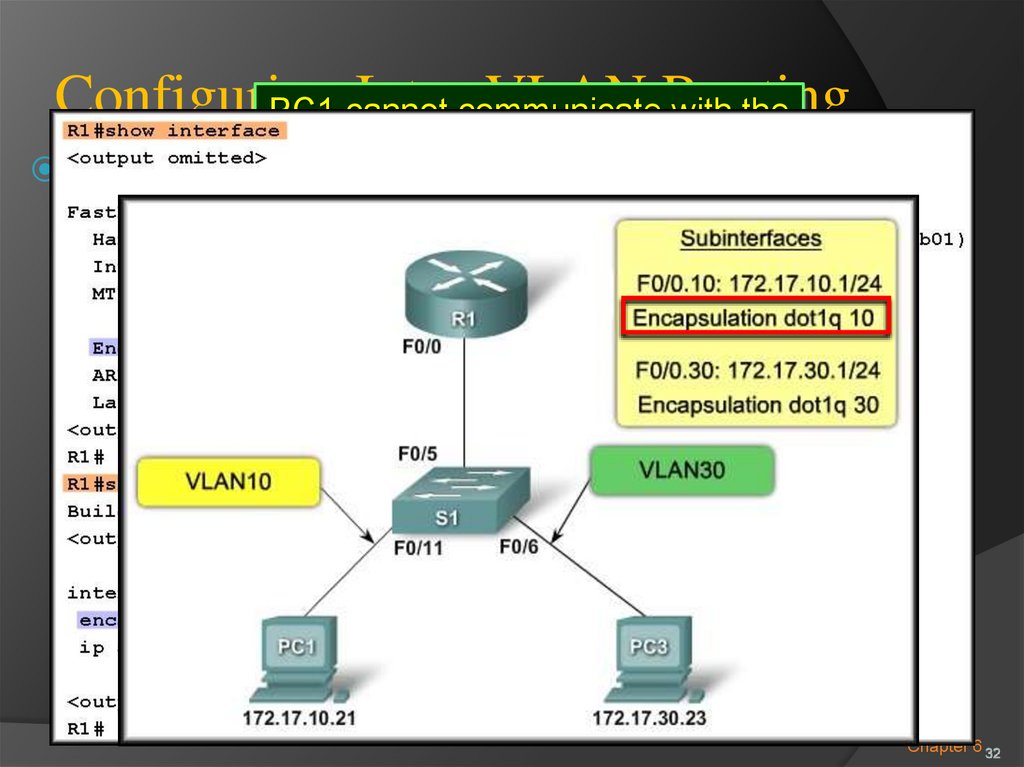
31. Configuring Inter-VLAN Routing
ConfiguringInter-VLAN
PC1 cannot
communicateRouting
with the
router interface and the router
Router Configuration Issues:
cannot route to VLAN 30.
Chapter 6 32
32. Configuring Inter-VLAN Routing
IP Addressing Issues:PC1 cannot communicate.
Incorrect IP address for
subnet 172.16.10.0/24.
Incorrect
Incorrect IP
subnet
address
mask
forfor
subnet
subnet172.16.10.0/24.
172.16.10.0/24.
Chapter 6 33









 internet
internet








