Similar presentations:
Neoclassical Theory of Production and Distribution of Income. Intermediate Macroeconomics
1.
EC 224Intermediate Macroeconomics
Neoclassical Theory of Production and
Distribution of Income
Gottfries, Chapters 2 and 6
2.
Neo-classical price-setting: IntroductionPerfect competition:
Firms produce identical goods and they can sell everything they produce at the
market price
Monopolistic competition:
Firms produce goods that are similar but not identical
A firm can set its own price and sales depend on the price A higher price will
reduce sales
In both cases: many firms – no ‘strategic’ interaction (no tacit collusion /
cartels /price wars)
2
3.
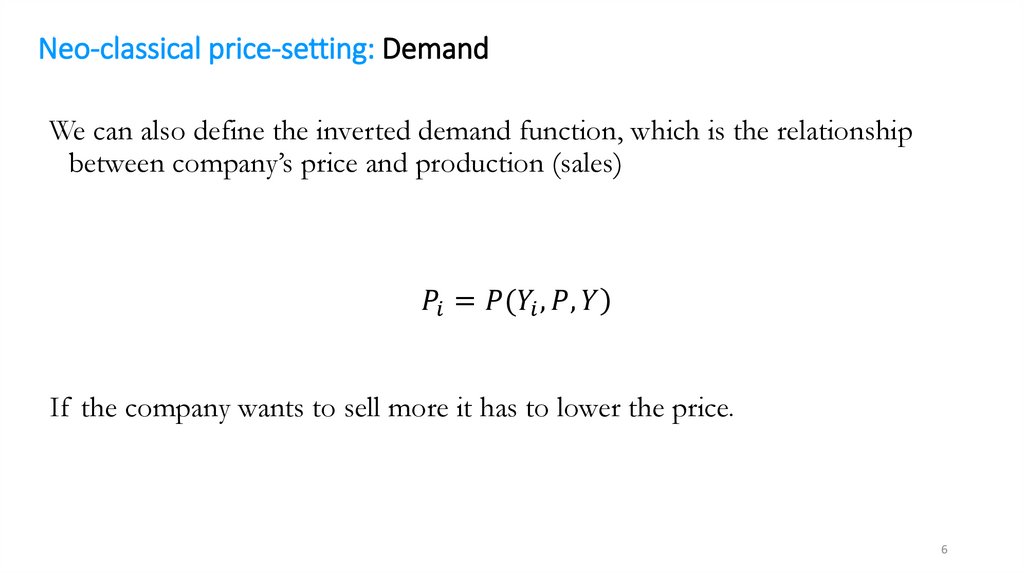
Neo-classical price-setting: DemandWe study a company named i – one of many companies in the
economy.
• How much will the company produce and sell?
• What price will the company set?
These two decisions are really just one because the company must choose
a point on the demand curve
3
4.
Neo-classical price-setting: DemandHigher price leads to lower demand for a company’s product, that is,
the company faces a downward sloping demand curve:






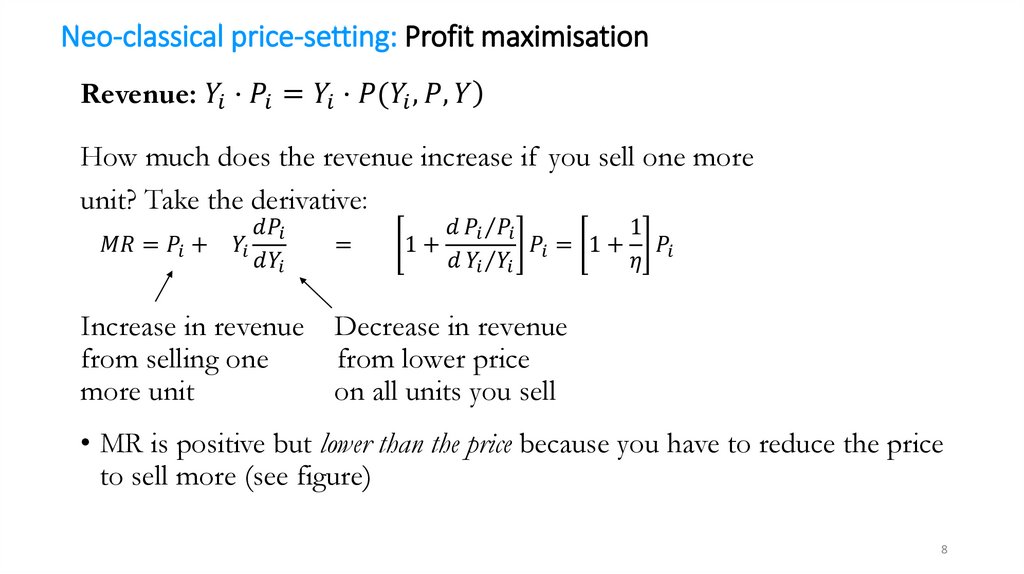
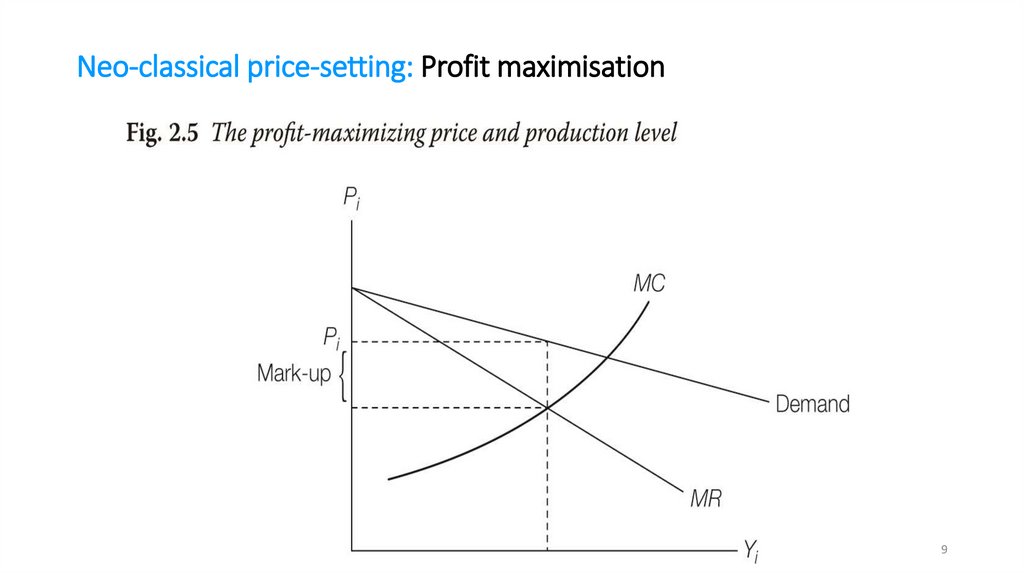
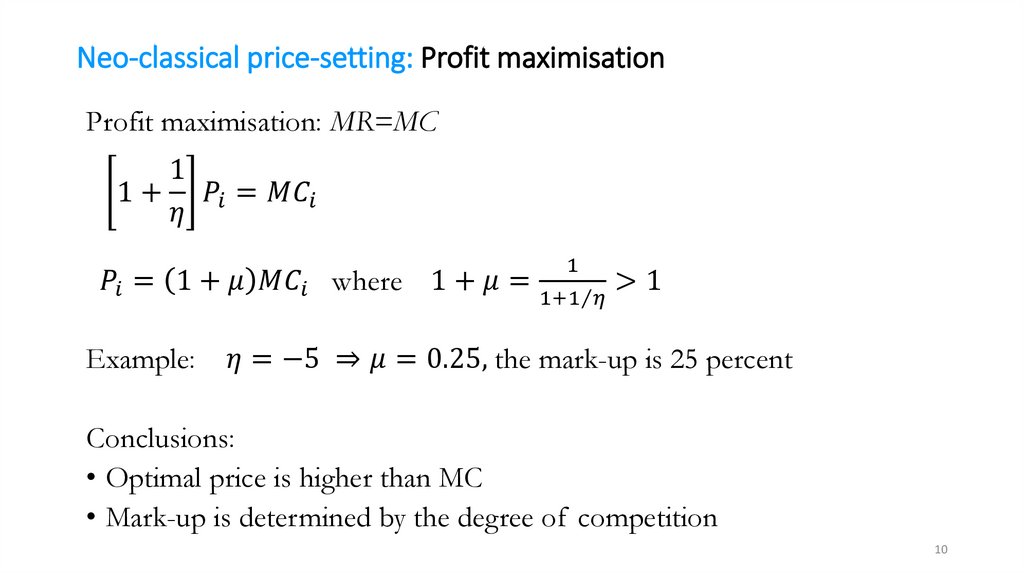

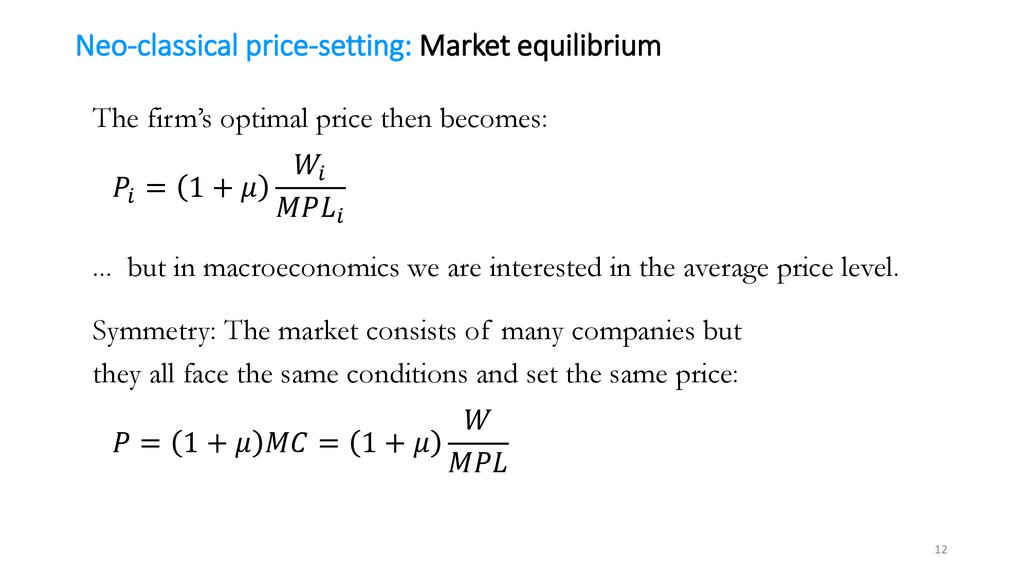
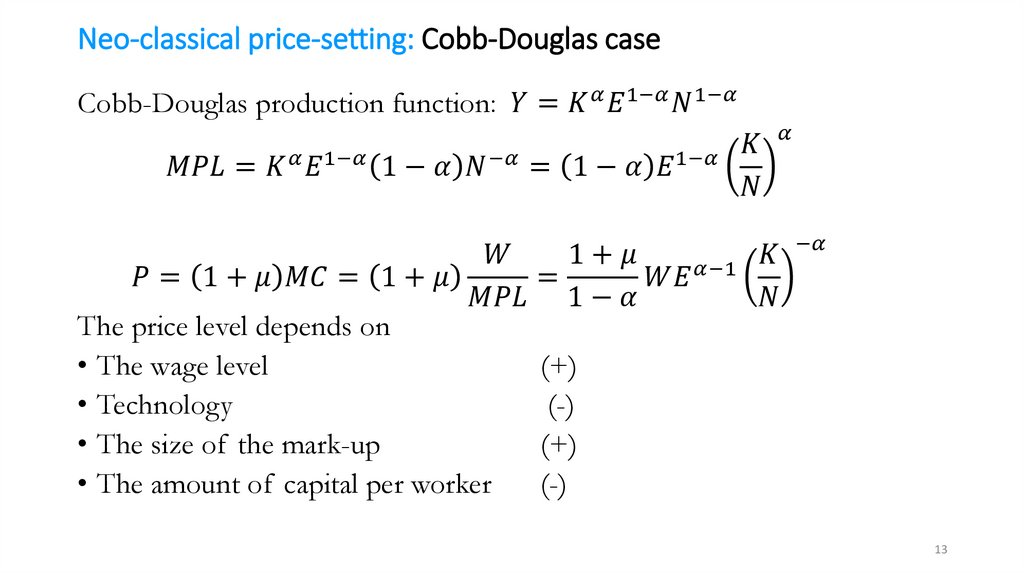


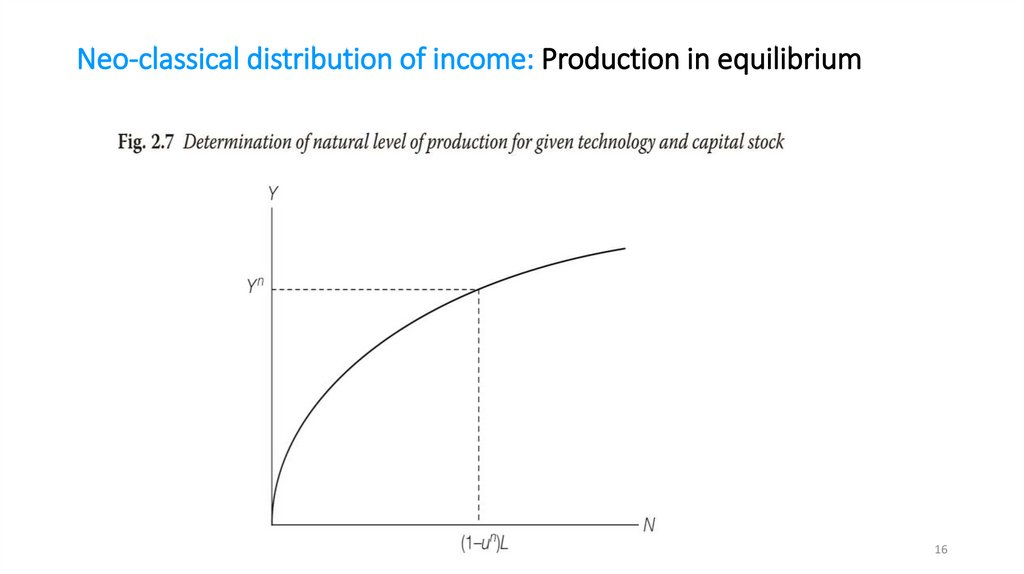




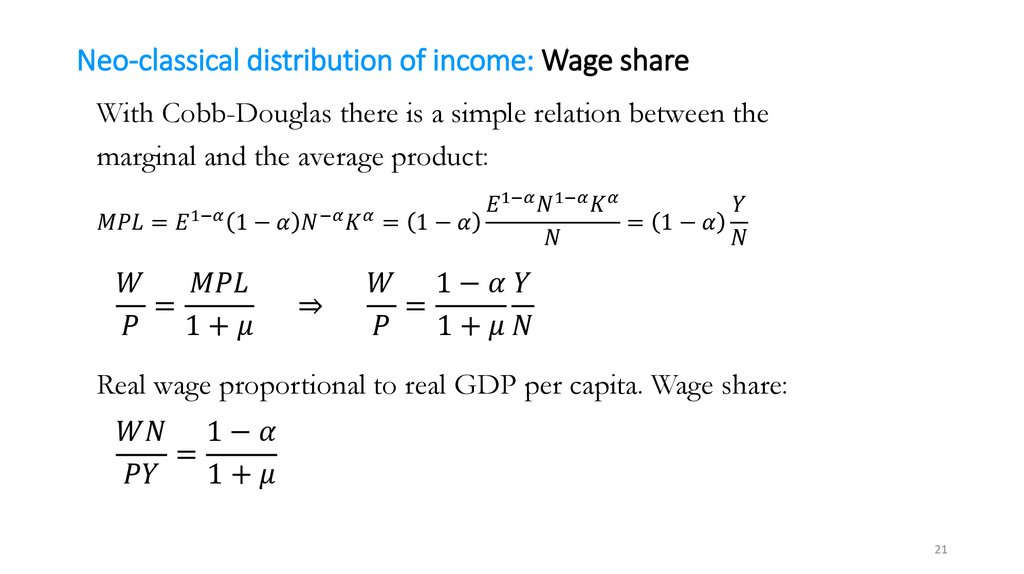












 mathematics
mathematics








