Similar presentations:
Tuberculosis. Clinical forms
1. tuberculosis
Зеленюк Ирина М3/9-22.
Tuberculosis is chronica bacterial infection that
how does another cause the greatest
the number of deaths around the
world. Transferred
by airborne droplets
3.
The causative agents oftuberculosis are
mycobacteria - acidresistant bacteria (Koch
bacillus, Koch bacillus) of
the genus
Mycobacteriaceae. A total
of 74 species of
mycobacteria are known.
They are widespread in soil,
water, among people and
animals.
4.
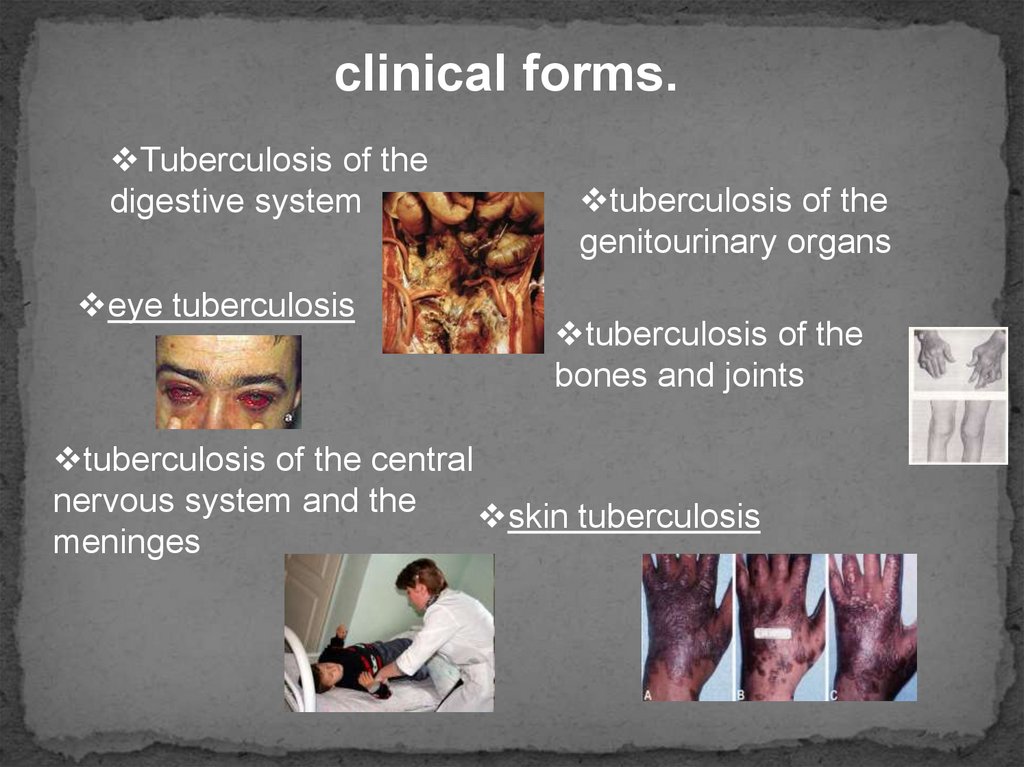
clinical forms.Tuberculosis of the
digestive system
eye tuberculosis
tuberculosis of the
genitourinary organs
tuberculosis of the
bones and joints
tuberculosis of the central
nervous system and the
skin tuberculosis
meninges
5.
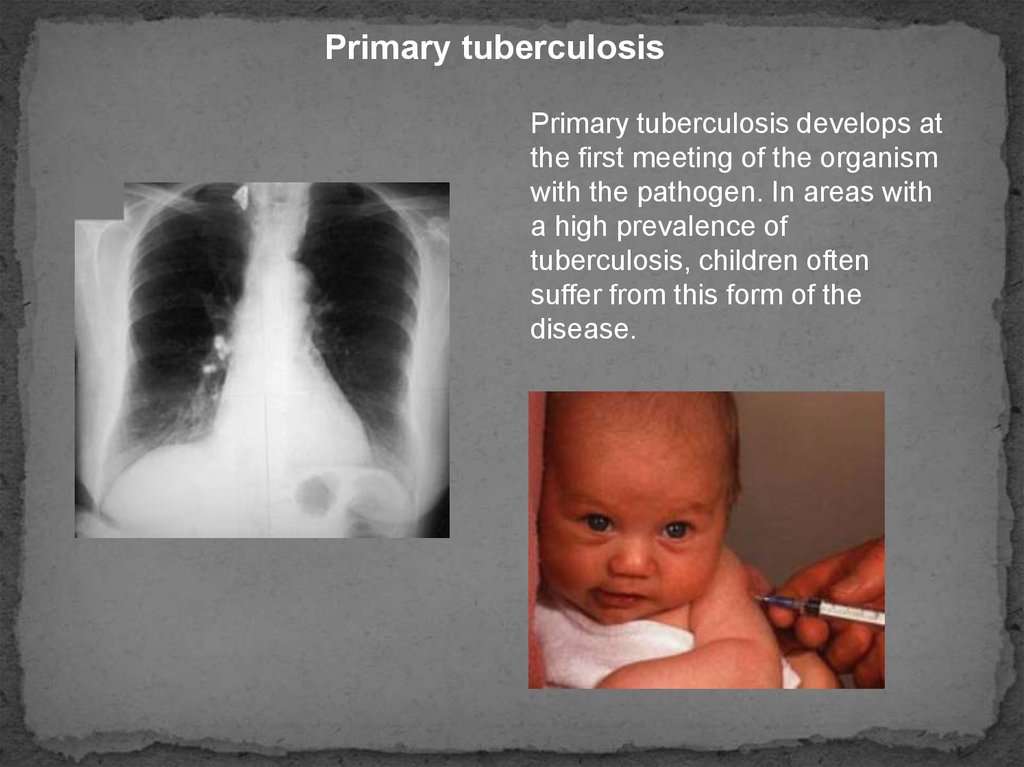
Primary tuberculosisPrimary tuberculosis develops at
the first meeting of the organism
with the pathogen. In areas with
a high prevalence of
tuberculosis, children often
suffer from this form of the
disease.
6.
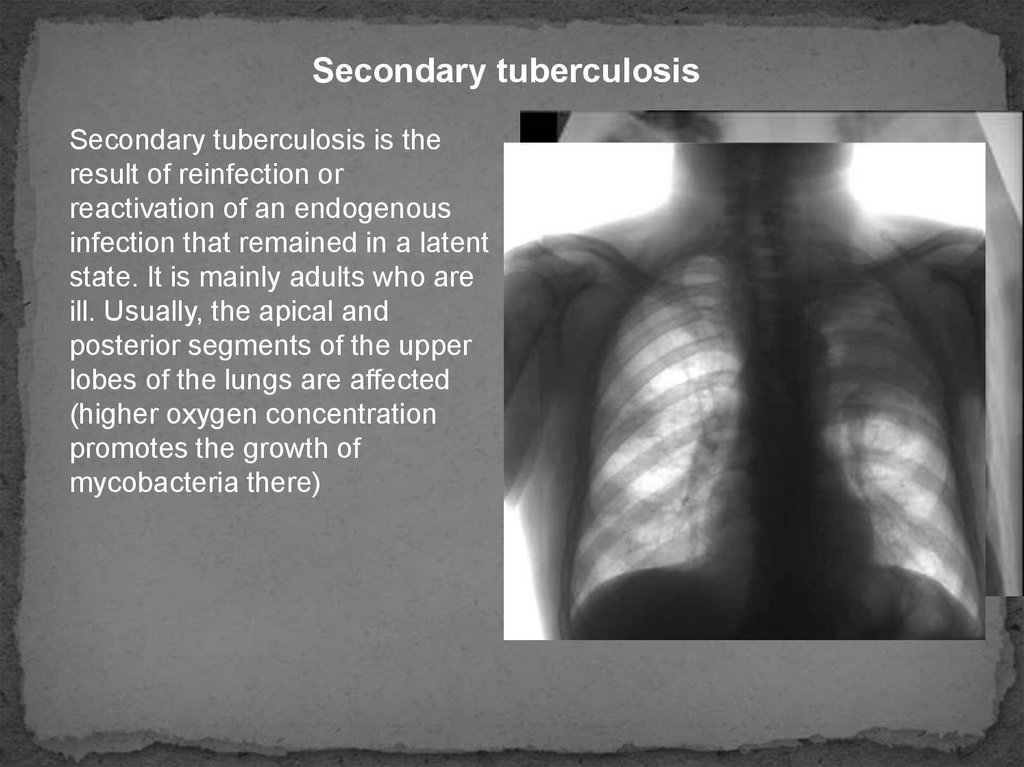
Secondary tuberculosisSecondary tuberculosis is the
result of reinfection or
reactivation of an endogenous
infection that remained in a latent
state. It is mainly adults who are
ill. Usually, the apical and
posterior segments of the upper
lobes of the lungs are affected
(higher oxygen concentration
promotes the growth of
mycobacteria there)
Рентгенограмма органов грудной клетки в
прямой проекции больного вторичным
туберкулезом.
7.
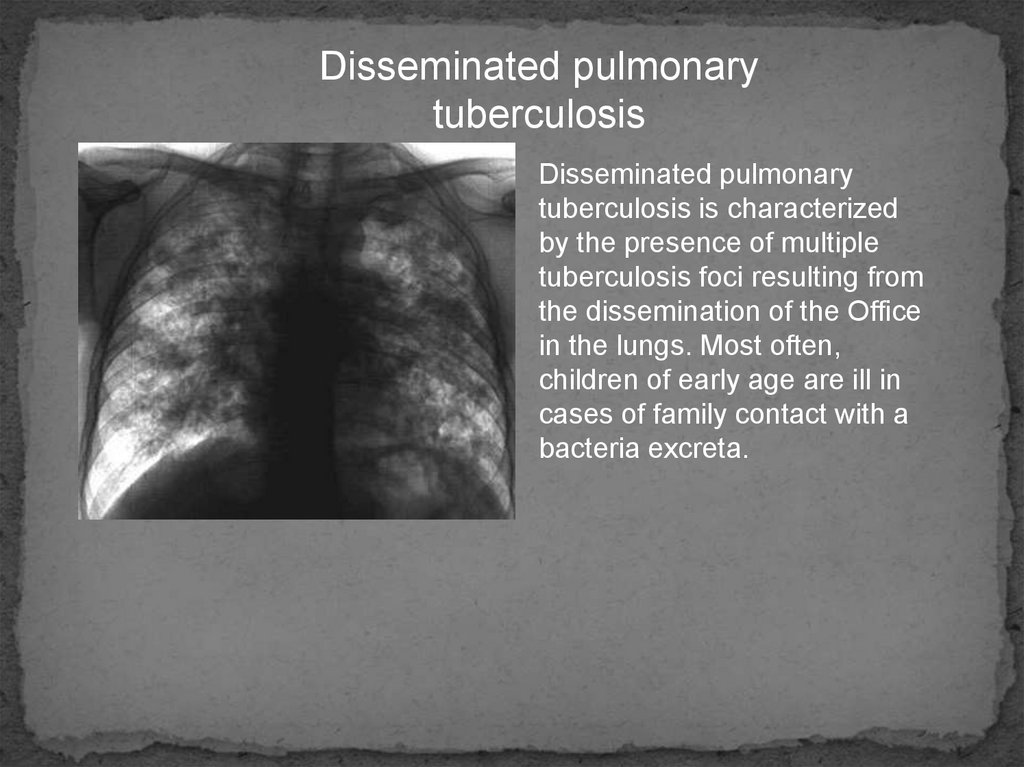
Disseminated pulmonarytuberculosis
Disseminated pulmonary
tuberculosis is characterized
by the presence of multiple
tuberculosis foci resulting from
the dissemination of the Office
in the lungs. Most often,
children of early age are ill in
cases of family contact with a
bacteria excreta.
8.
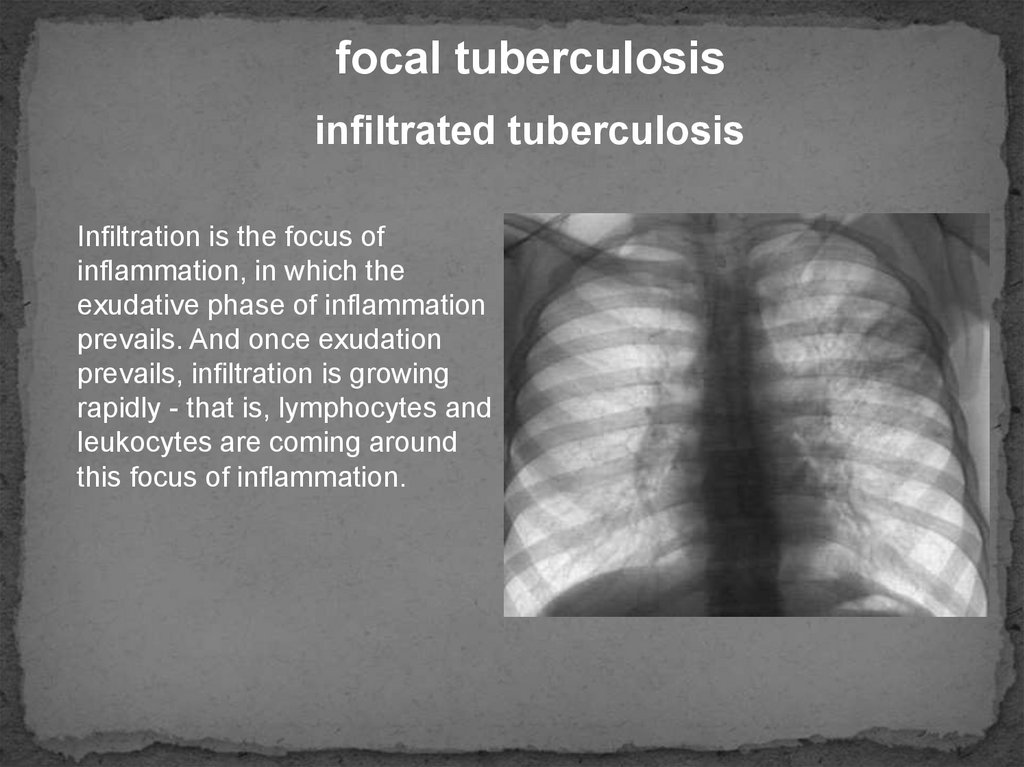
focal tuberculosisinfiltrated tuberculosis
Infiltration is the focus of
inflammation, in which the
exudative phase of inflammation
prevails. And once exudation
prevails, infiltration is growing
rapidly - that is, lymphocytes and
leukocytes are coming around
this focus of inflammation.
9.
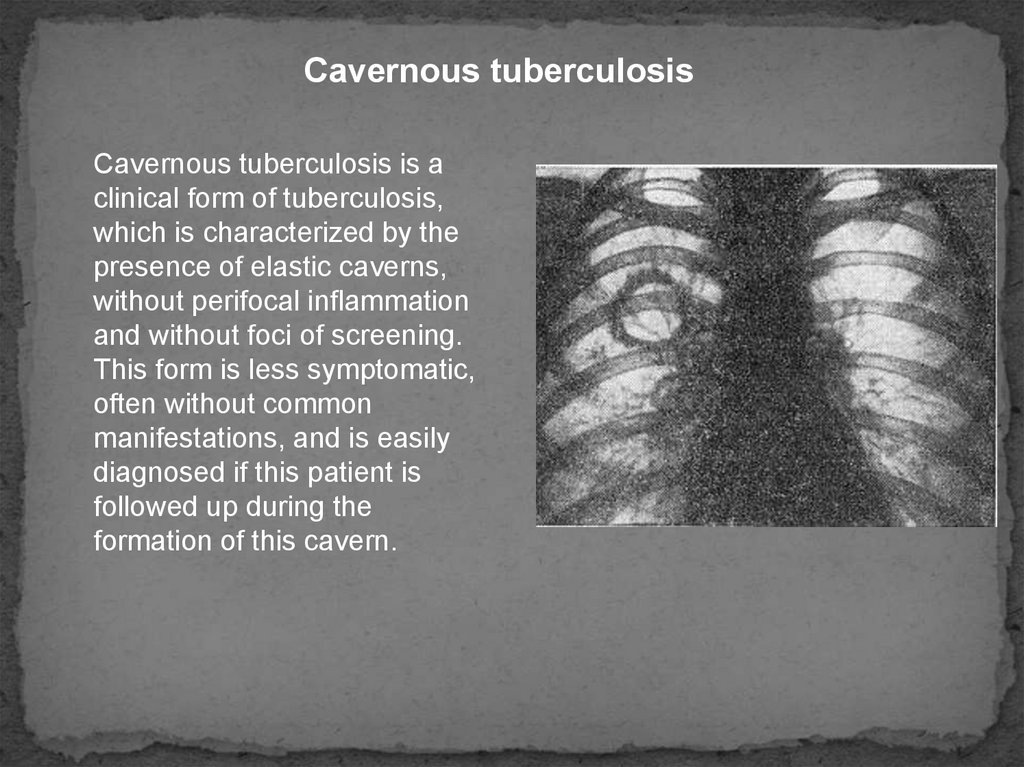
Cavernous tuberculosisCavernous tuberculosis is a
clinical form of tuberculosis,
which is characterized by the
presence of elastic caverns,
without perifocal inflammation
and without foci of screening.
This form is less symptomatic,
often without common
manifestations, and is easily
diagnosed if this patient is
followed up during the
formation of this cavern.
10.
Особенности клинического течениятуберкулеза у ВИЧ-инфицированных
Интоксикационный
синдром длится недели и
месяцы.
Стойкая и
длительная анемия
(гемоглобин < 90 г/л).
Периферические
лимфатические узлы
увеличены неравномерно,
несимметрично
Гепатомегалия (всегда
при милиарном
туберкулезе).
Интоксикационный
синдром появляется раньше,
чем.бронхолегочный



 medicine
medicine








