Similar presentations:
Methods and computer modeling technologies
1.
Presentation materials on the discipline“Methods and computer modeling technologies”
Compiled by: Ph.D., Associate Professor, Department of Information Systems and Mathematical
Methods in Economics, Perm State National Research University
Shimanovsky Dmitry Viktorovich
Contact Information:
Dmitry-Shimanovsky@mail.ru(if the question is important and
not very urgent);
https://vk.com/id11435153(if the question is urgent and not very
important);
Auditorium 109 of the economic building of Perm State National
Research University(come during consultation hours or by prior
arrangement).
Perm 2024
2.
Macroeconomics as a scienceMacroeconomics studies economic processes or phenomena at the state level. Unlike microeconomics
which studies the behavior of households and firms, this scientific discipline focuses on the study of
concepts such as inflation,unemployment, economic growth, level of interest rates, volume of investment in
physical capital, etc.
Traditionally, Western economic theory distinguishes two approaches to the analysis of macroeconomic
processes: classical and Keynesian. Meanwhile, there are also less well-known economic schools
(institutional, Marxist and etc.).
According toclassical approach, market economy is self-regulating system. In other words, if during a crisis
the economy of a country is out of balance (for example, demand is not equal to supply), then it is able to
return to an equilibrium state using market mechanisms without serious intervention from the state.
3.
Macroeconomics as a scienceKeynesianthe approach does not share this point of view. According to the principles of the Keynesian school,
without government intervention, a market economy can remain in a disequilibrium state for a long time and work
inefficiently. Economists of this movement recommend developing special mechanisms for state regulation of
market systems, which become especially relevant during a crisis.
Meanwhile, both representatives of the classical school and supporters of the Keynesian approach recognize that
market mechanisms are more effective than a complete state monopoly on economic decision-making at all
levels.
An American scientist is considered the founder of macroeconomics as a science.John Maynard Keynes, who
laid down its basic concepts in his work “The General Theory of Employment, Interest and Money,” published in
1936. This scientific discipline received significant development in the works M. Friedman, published in the
1960s. The further development of macroeconomics occurred under the influence of the worksR. Lucas,
published in the 1970s.
4.
Main macroeconomic indicatorsCurrently, the most well-known macroeconomic indicator isgross domestic product(abbreviated GDP). It
reflects the final cost of all goods and services produced in the country. The methodology for calculating
gross domestic product is regulated by a special document “System of National Accounts”, developed and
improved by international organizations under the auspices of the UN. The latest edition of this document
was published in 2008.
At the same time, GDP reflects only final the cost of all goods and services produced within the country. For
example, according to Rosstat, the total revenue of all Russian companies in 2022 amounted to274.21
trillion. rubles. However, GDP for the same period is approximately153.43 trillion. rubles. Rest120 trillion
rublesamounts tointermediate consumption.
Example.Let a farmer sell grain worth 10 million rubles to a flour mill in 2022. He, in turn, made flour from it
and sold it to a bakery for 20 million rubles. The bakery, in turn, made bread from it and sold it for 40 million
rubles. In this case, only 40 million rubles will be used to calculate GDP. The remaining 30 million rubles will
beintermediate consumption.
5.
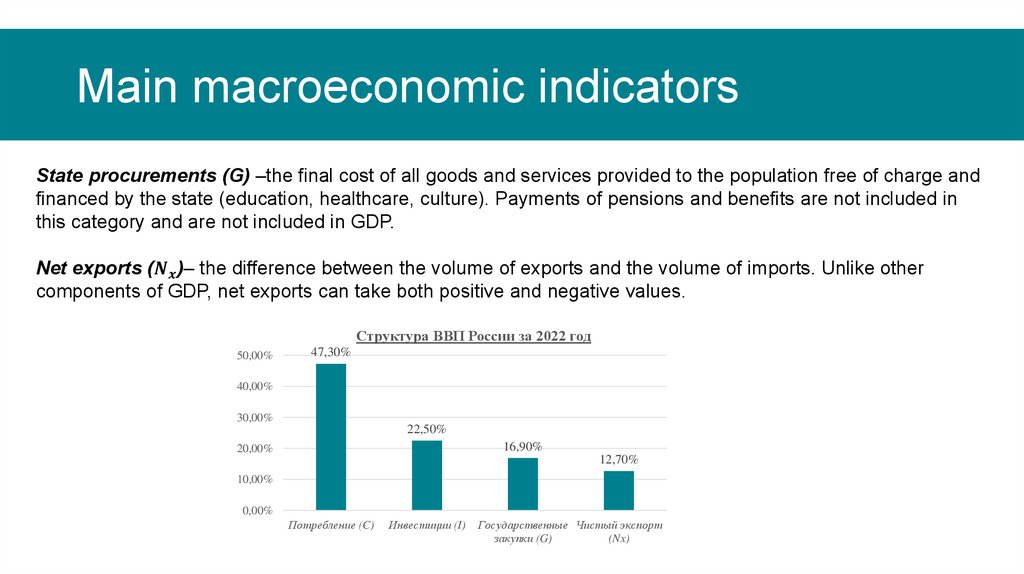
Main macroeconomic indicatorsAccording to one classification, the volume GDP can be divided into four subgroups:
Household consumption (denoted by C);
Investments (denoted by the letter I);
Government procurement (denoted by the letterG);
Net exports (denoted







 informatics
informatics








