Similar presentations:
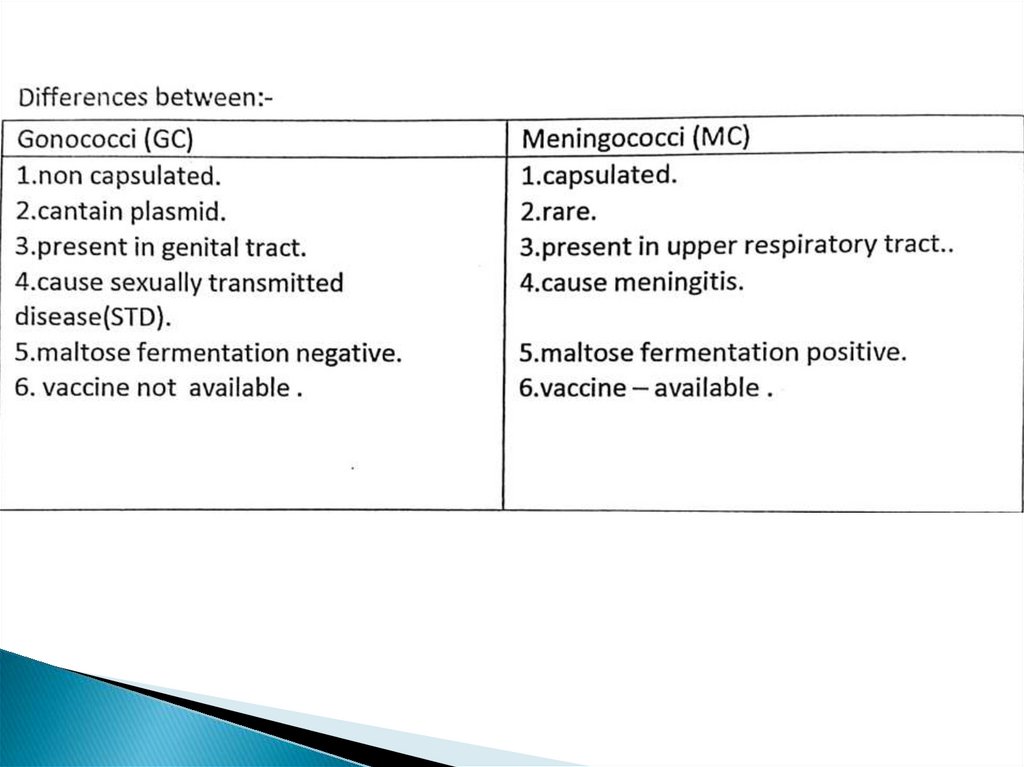
Neisseriae. Neisseria gonorrhoeae (Gonococci) GC
1.
2.
NeisseriaeCharacters :Gram-negative diplococci, individual cocci are kidney-shaped, non motile non
hemolytic and non pigmented, Colonies are opaque or transparent.
There are two pathogenic species for humans :
1. Neisseria gonorrhoeae (Gonococci) GC, the causative agent of gonorrhea,
neonatal conjunctivitis (ophthalmia neonatorum) and pelvic inflammatory
disease (PID).
2. Neisseria meningitidis (Meningococci) MC, the causative agent of meningitis
and meningococcemia.
3.
all N. Spp. Are oxidase-positive (ie. Produce oxidase enzyme ).The oxidase is a key test for identifying them. When bacteria are spotted on a
filter paper soaked with tetramethylpara phenylenediamine (oxidase reagent),
The Neisseriae rapidly run dark purple.
The growth of both organisms(GC and MC) is inhibited by toxic trace metals
and fatty acids found in certain culture media e. g., blood agar plate, they are
therefore culture on chocolat agar containing blood heated to 80°c. The
organisms are rapidly killed by drying, sunlight, moist heat and many
disinfectants. (they are fastidious).
Non pathogenic e. g. Moraxella catarrhalis was previously named
Branhamella catarrhalis (Neisseria catarrhalis).
4.
Neisseria gonorrhoeae (Gonococci) GC.Classification :On the basis of morphology and their colonial mutation, there are four biotypes :
(T1, T2) virulent small brown colonies (pilitated gonococci) posses pili which are
adherence factors.
(T3, T4) a virulent large non pigmented colonies (no pilitated gonococci).
Virulence factors (antigenic structure) :1. pili acts as adhesions.
2. porprotien.
3. opaproteins.
4. Rmp(protein111).
5. Iipopolysaccharide(in gonococei is called a lipooligosaccharide, LOS, as
endotoxin).
6. IGA1 protease.
5.
Pathogenesis :Gonococci cause--gonorrhea (sexually transmitted disease STD or veneraldisease)
-Ophthalemia neonatorum.
Gonorrhea (example urithritis, cervicitis)
Gonorrhea is usually symptomatic in men but often asymptomatic in women.
Gonococci are sexually transmitted.
The transmission of these bacteria is through direct contact of mucous membrane
-to mucous membrane, usually sexually contact ; mother-to-neonate during
birth.
GC attack mucous membrane of genitourinary tract, eye, rectum and-throat.
6.
Clinical finding :-Gonococci caused both localized infection in the genital tract and disseminated
infections with seeding of organs, GC reach these organs via the
bloodstream(gonococcal bacteremia),
gonorrhea
-ln men is characterized primarily by urethritis accompanied by dysuria (painful
urination) and purulent discharge complication include (Epididymitis and
prostatis).
-In women cervicitis and the most frequent complication is an ascending
infection of the uterine tubes (salpingitis, PID) which can be result in sterility and
ectopic pregnancy as a result of scarring of the tubes.
Disseminated gonococci infections (DGI) arthritis, skin lesion.
In newborn infant GC. Can cause ophthalemia neonatorum, an infection of the
eye of the newborn, is acquired from the mother during passage through an
infected birth canal.
Other sexually transmitted infections, example, syphilis and non gonococcal
urithritis (NGU) caused by Chlamydia trachomatis, can coexist with gonorrhea
therefore appropriate diagnostic and therapeutic measures must be taken.
7.
Lab. Diagnosis :1. Specimens, pus, secretion from urethra, cervix, conjunctiva, throat andrectum.
2. Gram stained smear, then we look intracellular Gram-negative diplococci in
PMNs )polymorphoneuclear cells) from urethral discharge in men is sufficient for
diagnosis while in women false positive because of the normal flora interference
3. Culture, on
A. Chocolate agar.
b. Thayer-Martin agar. (selective medium) which is chocolate agar containing
antibiotics (vancomycin, colistin and nystatin to suppress the normal flora found
in the specimen.
C. Modified Thayer-Martin agar. same as(Thayer-Martin agar plus trimethoprim)
The culture is incubated in an atmosphere containing 5% COZ (candle extinction
jar) at 37°c.
4. Oxidase test positive.
5. Sugar fermentation the differentiation between GC and MC is made on the
bases glucose and maltose.
6. Nucleic acid amplification test.
7. Serology by ELISA, antibodies against pili. These test are not useful for
diagnosis.
8.
TreatmentCeftriaxon plus doxycyclin.
Some strain of GC called penicillinase producing gonorrheae or (PPNG) possess
plasmids containing the gene for penicillinase production(resistant to penicillin).
Control and prevention :Treatment of symptomatic patient with contact, cases on gonorrhea must be
reported to the public health department to ensure proper follow up.
Gonococci conjunctivitis is preventive by the use of erythromycin ointment.
Silver nitrate drops are use less frequently.
No vaccine is available.
9.
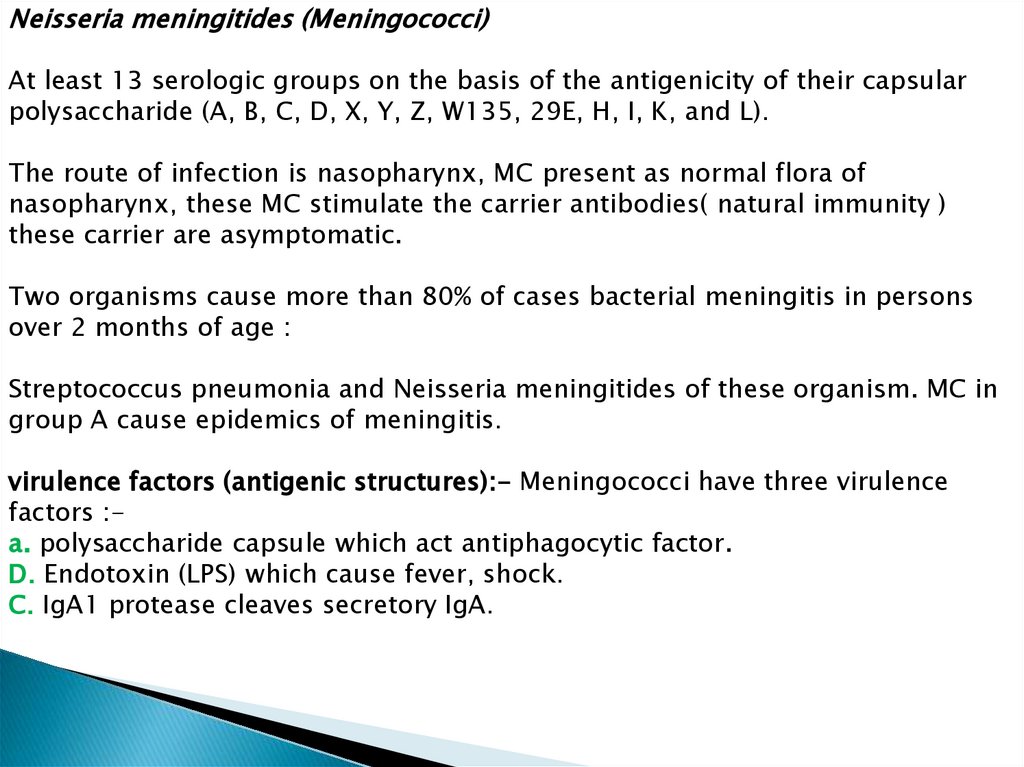
Neisseria meningitides (Meningococci)At least 13 serologic groups on the basis of the antigenicity of their capsular
polysaccharide (A, B, C, D, X, Y, Z, W135, 29E, H, I, K, and L).
The route of infection is nasopharynx, MC present as normal flora of
nasopharynx, these MC stimulate the carrier antibodies( natural immunity )
these carrier are asymptomatic.
Two organisms cause more than 80% of cases bacterial meningitis in persons
over 2 months of age :
Streptococcus pneumonia and Neisseria meningitides of these organism. MC in
group A cause epidemics of meningitis.
virulence factors (antigenic structures):- Meningococci have three virulence
factors :a. polysaccharide capsule which act antiphagocytic factor.
D. Endotoxin (LPS) which cause fever, shock.
C. IgA1 protease cleaves secretory IgA.
10.
Pathogenesis and clinical finding :Disease meningitis and meningococcemia,MC spread via respiratory secretions, MC via nasopharynx-blood stream
bacteremia (meningococcemia) intravascular coagulation and spread-meningitis
most common complication of meningococcemia-fulminant meningococcemia
(septic shock).
Meningitis most common disease in children less than 1 year.
11.
Lab. Diagnosis :1. Specimens from blood, CSf and nasopharyngeal swap.2. Direct-Gram stain smear of centrifuged CSF shows MC as typical Neisseria
within polymorphonuclear leukocyte or extracellularly.
3. Culture, CSF specimen are plated on Choclate agar and incubated at 37oC
with 5% CO2. Also culturing in Thayer martin agar and modified TM.
4. Biochemical test :--Oxidase test-positive.
--Sugar fermentation test, ferment maltose and glucose.
5. Serology, antibodies to meningococcal polysaccharides can be measure by
latex agglutination test or by measuring the bactericidal activity. These
antibodies give
12.
Treatment :Penicillin G is the drug of choice.Prevention and control :Vaccine contains capsular polysaccharide of strains A, C, Y and W-135, rifampin
or ciprofloxacin given to clos contact to decrease oropharyngeal carriage.
Moraxella catarrhalis :-normal flora of the upper respiratory tract, it causes
bronchitis, pneumonia, otitis media and conjunctivitis, this spp. Produce
beta-lactamase so its resistant to peniciliin.
It produces butyrate esterase.











 medicine
medicine