Similar presentations:
Staphylococcus. Classification
1.
2.
Staphylococcus3. Classification
• FamilyMicrococcaceae
• Genus
Micrococcus and Staphylococcus
• Species
more
than 20
specie
s
S. aureus
S. saprophyticus
S. epidermidis
M. luteus
4.
Gram-Positive CocciFAMILY Streptococcaceae (catalase negative)
Group A: -hemolytic Streptococcus pyogenes
Group B: -hemolytic (occasionally or ) S. agalactiae
Group C: -hemolytic ( or ) S. anginosus, S. equismilis
Group D: or hemolytic ( ) S. bovis
Group F: -hemolytic S. anginosus
Group G: -hemolytic S. anginosus
Viridans streptococci: (no group specific CHO)
or hemolytic S. mutans and
S. salivarius, S. sanguis, S. mitis and S. milleri groups
Streptococcus pneumoniae (no group CHO)( -hemolytic)
Enterococcus (Group D CHO) hemolytic ( or )
Enterococcus faecalis, E. faecium
FAMILY Micrococcaceae (catalase positive)
Coagulase-positive Staphylococcus aureus
Coag.-neg. Staphylococcus epidermidis, S. saprophyticus
5.
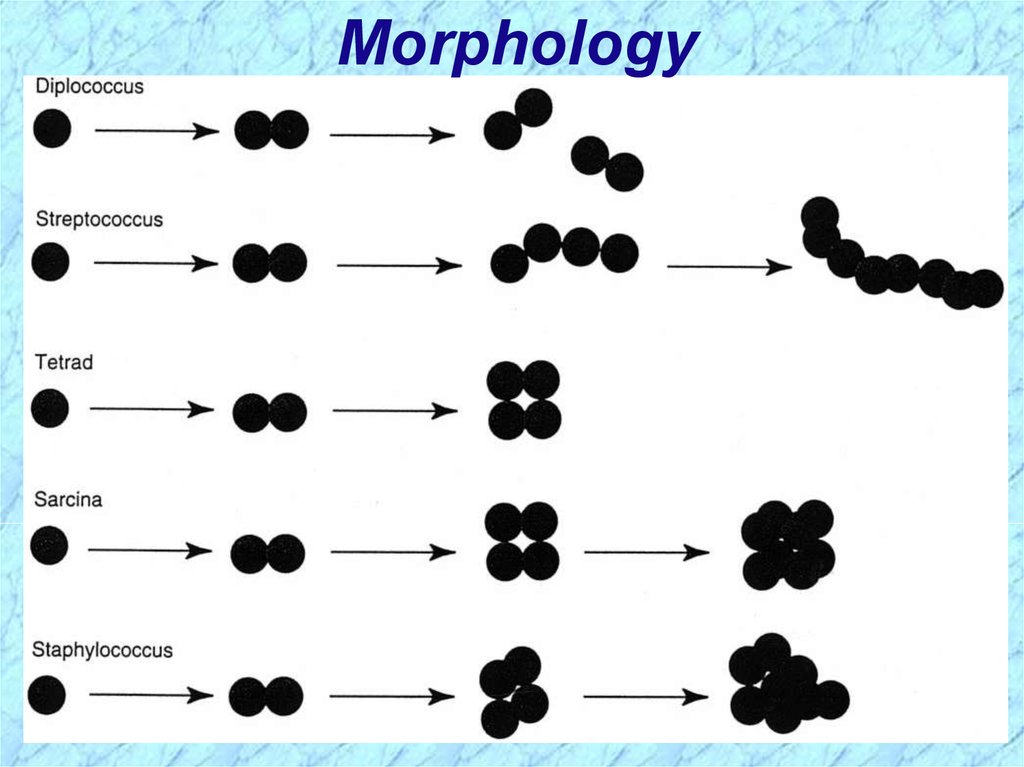
Morphology6.
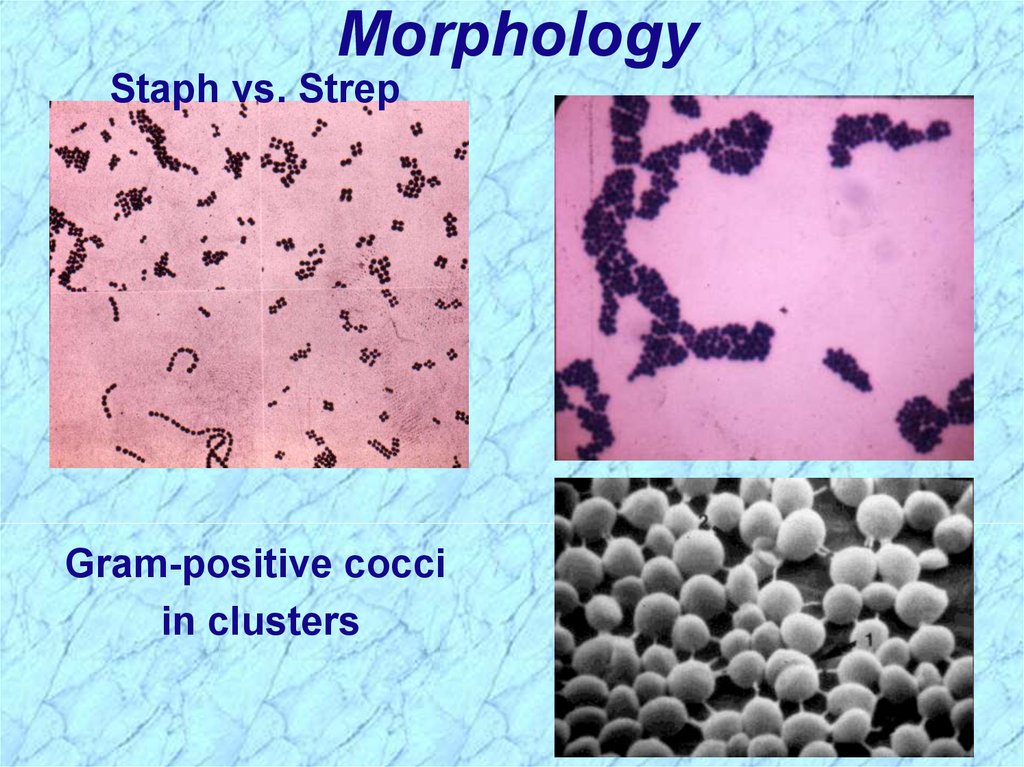
MorphologyStaph vs. Strep
Gram-positive cocci
in clusters
7.
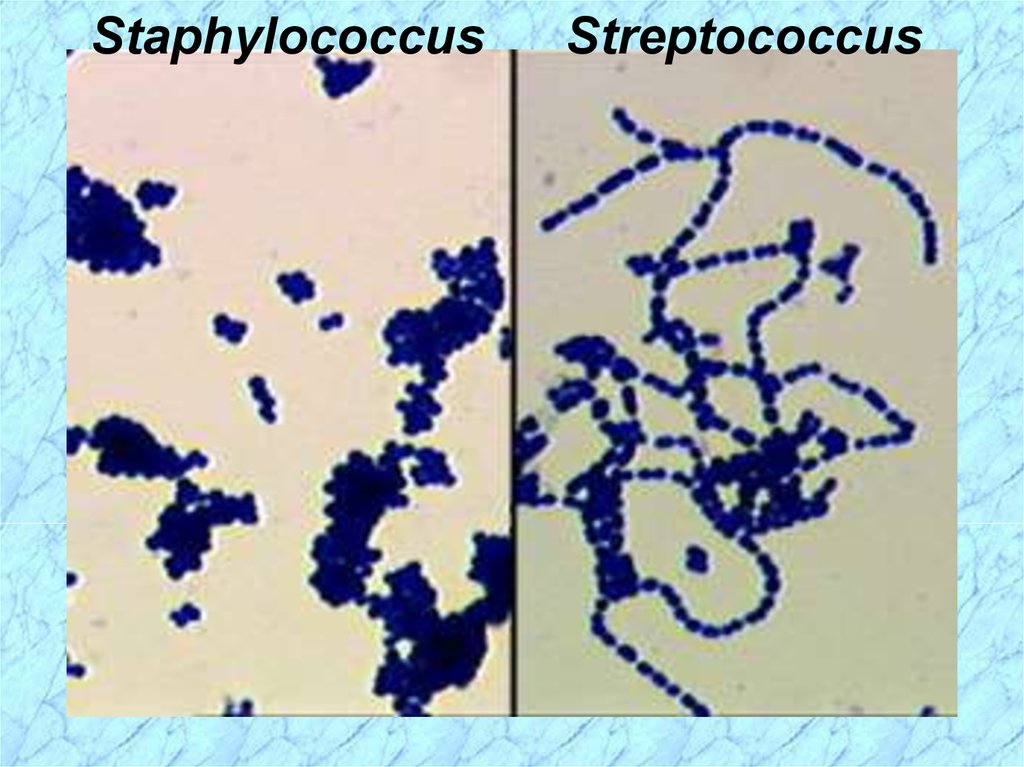
StaphylococcusStreptococcus
8.
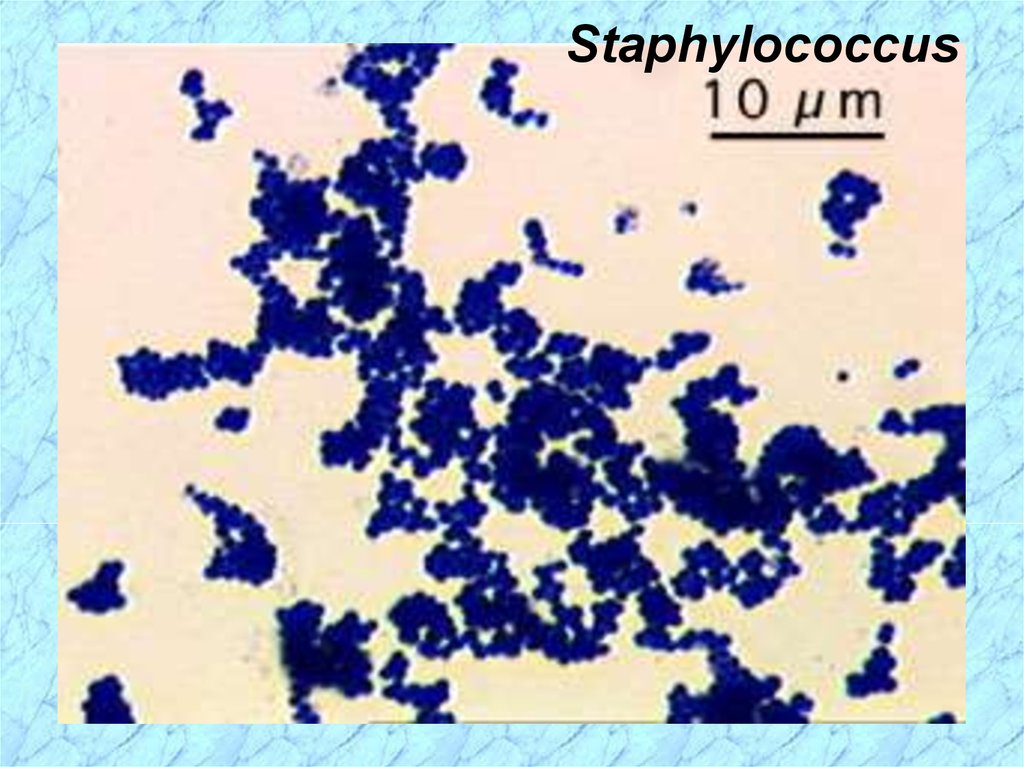
Staphylococcus9.
10.
11.
12.
See Overheads~~~~~~~~~~
TSS
Foodborne Intoxication
~~~~~~~~~~
13.
14.
MICROBIALPATHOGEN
Staphylococcus aureus
Staphylococcus spp.
Group A Streptococcus
Streptococcus pneumoniae
Escherichia coli
Other Enterobacteriaceae
Neisseria gonorrhoeae
Treponema pallidum
Chlamydia spp.
Mycoplasma pneumoniae
Vibrio cholerae
ADHESIN
RECEPTOR
Lipoteichoic acid
Unknown
Slime layer
Unknown
LTA-M protein complex Fibronectin
Protein
Type 1 fimbriae
CFA 1 fimbriae
P fimbriae
Type 1 fimbriae
Fimbriae
P1, P2, P3
Cell surface lectin
Protein P1
Type 4 pili
N-acetylhexosamine-gal
D-Mannose
GM ganglioside
P blood grp glycolipid
D-Mannose
GD1 ganglioside
Fibronectin
N-acetylglucosamine
Sialic acid
Fucose and mannose
15. Cell-Associated Virulence Factors
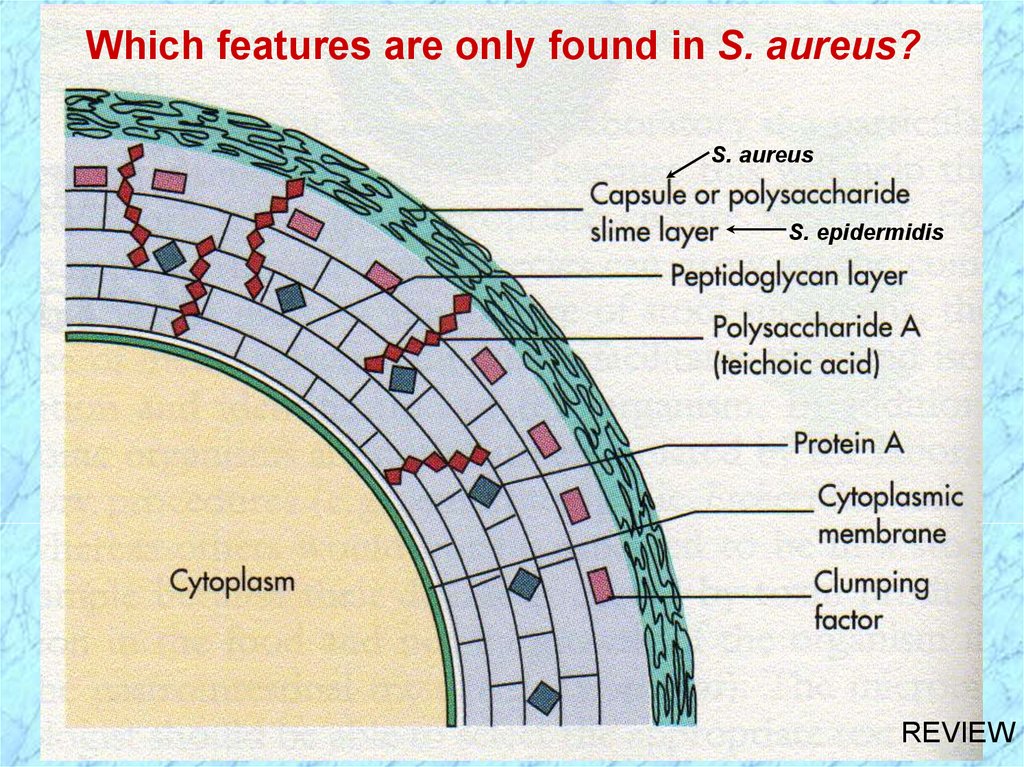
• Capsule or slime layer (glycocalyx)• Peptidoglycan (PG)
• Teichoic acid is covalently linked to PG
and is species specific:
S. aureus
S. epidermidis
ribitol teichoic acid
(polysaccharide A)
glycerol teichoic acid
(polysaccharide B)
• Protein A is covalently linked to PG
• Clumping factor (bound coagulase)
16. Virulence Factors Extracellular Enzymes
• Coagulases (bound or free)Antigenic
• Hyaluronidase
“spreading factor” of S. aureus
• Nuclease
Cleaves DNA and RNA in S. aureus
• Protease
Staphylokinase (fibrinolysin)
• Lipases
• Esterases
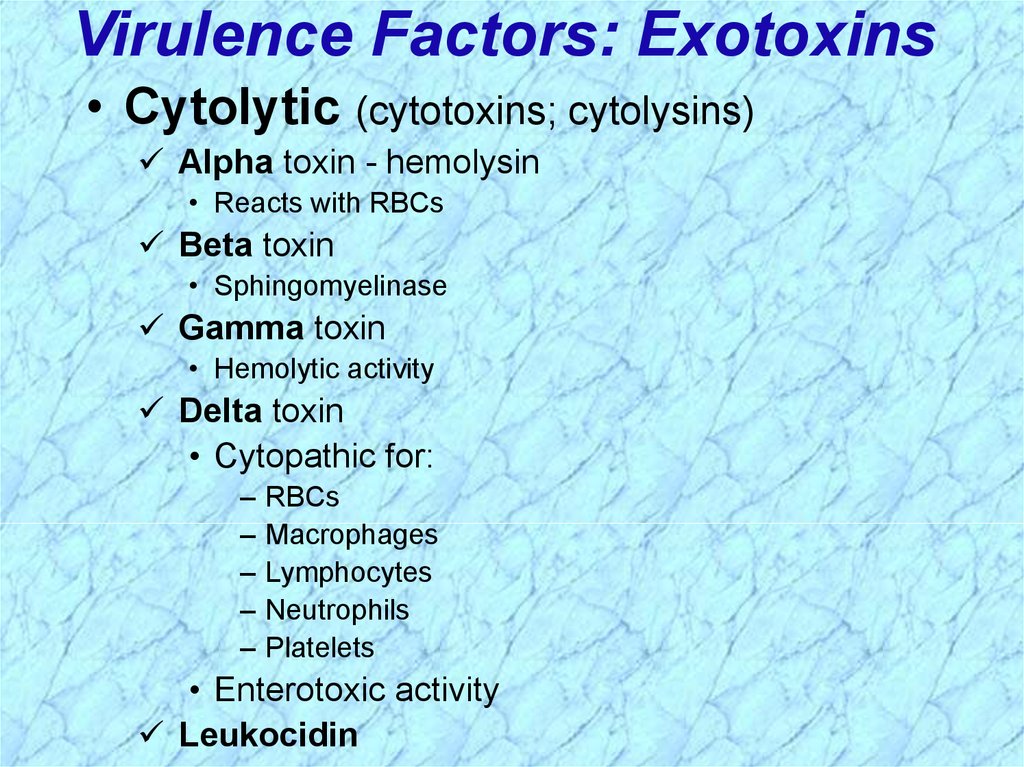
17. Virulence Factors: Exotoxins
• Cytolytic (cytotoxins; cytolysins)Alpha toxin - hemolysin
• Reacts with RBCs
Beta toxin
• Sphingomyelinase
Gamma toxin
• Hemolytic activity
Delta toxin
• Cytopathic for:
–
–
–
–
–
RBCs
Macrophages
Lymphocytes
Neutrophils
Platelets
• Enterotoxic activity
Leukocidin
18.
Virulence Factors: Exotoxins• Enterotoxin
• Exfoliative toxin (epidermolytic toxin)
• Pyrogenic exotoxins
19. Pathogenesis
• Pass skin – first line of defenseBenign infection
• Phagocytosis
• Antibody
• Inflammatory response
Chronic infections
• Delayed hypersensitivity
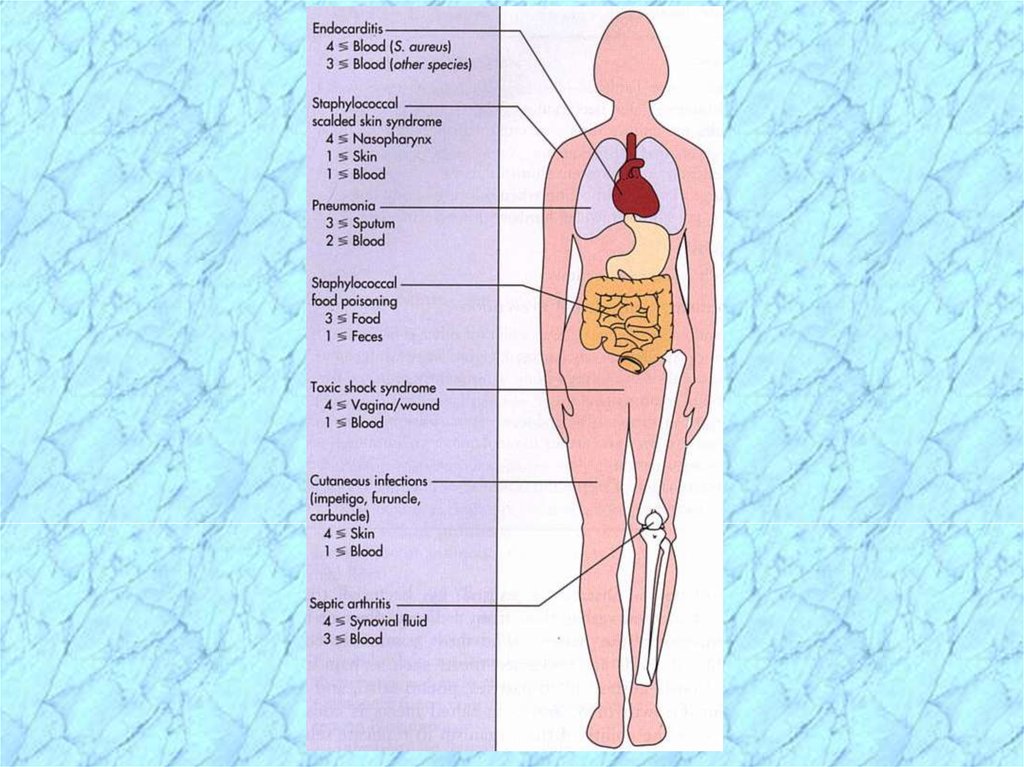
20. Clinical Manifestations/Disease
• SKINfolliculitis
boils (furuncles)
carbuncles
impetigo (bullous & pustular)
scalded skin syndrome
•Neonates and children under 4 years
21. Clinical Manifestations/Disease
• Other infectionsPrimary staphylococcal pneumonia
Food poisoning vs. foodborne disease
Toxic shock syndrome
22. Metastatic Infections
•Bacteremia•Osteomyelitis
disease of growing bone
• Pulmonary and cardiovascular
infection
23.
24. Coagulase-Negative Staphylococci
• Staphylococcus epidermidis• S. saprophyticus
25.
26.
27. Staphylococcal Lab ID & Diagnostic Tests
Staphylococcal Lab ID & Diagnostic Tests• Microscopic
• Lab isolation
• Coagulase positive
S. aureus
28.
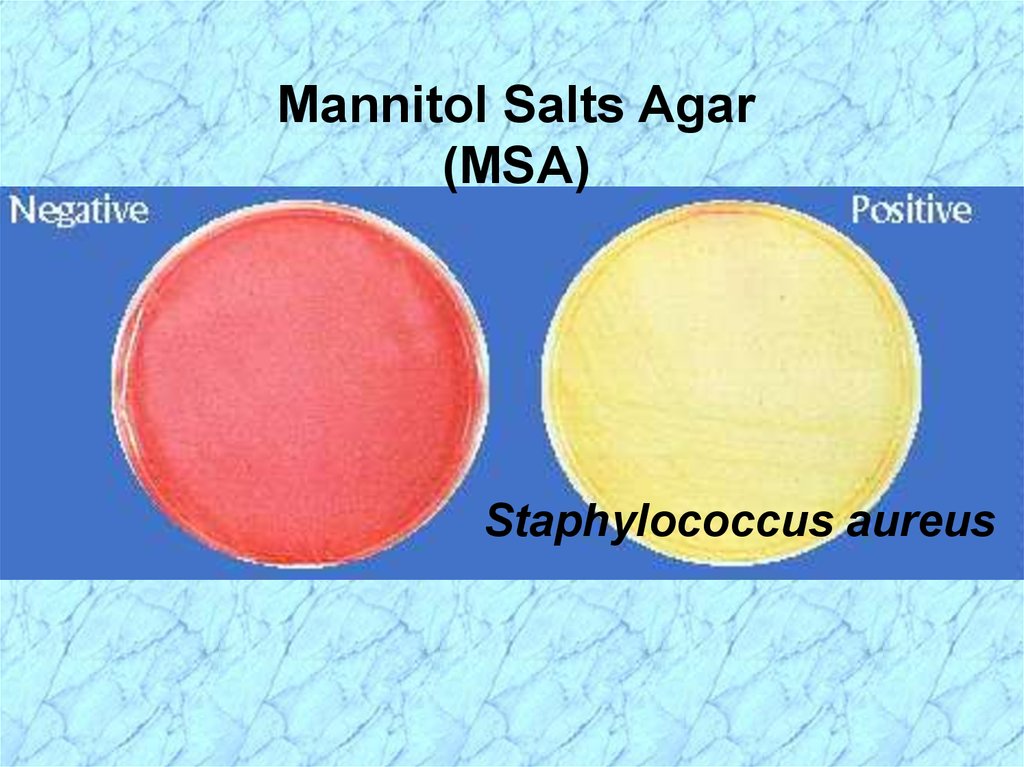
Mannitol Salts Agar(MSA)
Staphylococcus aureus
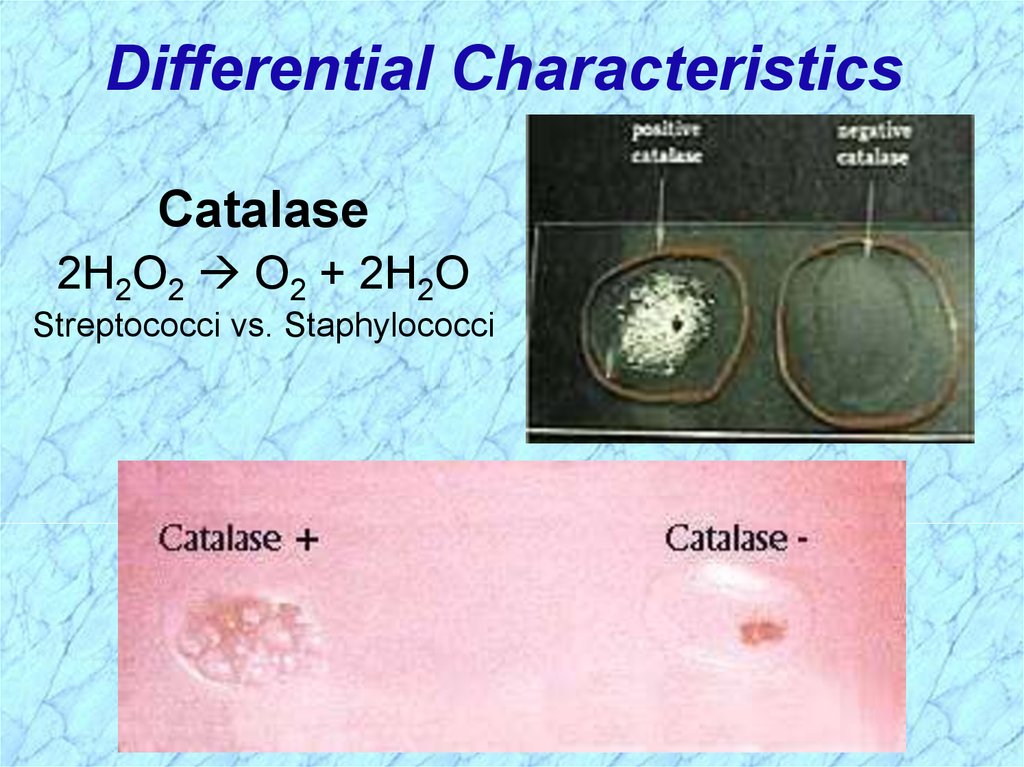
29. Differential Characteristics
Catalase2H2O2 O2 + 2H2O
Streptococci vs. Staphylococci
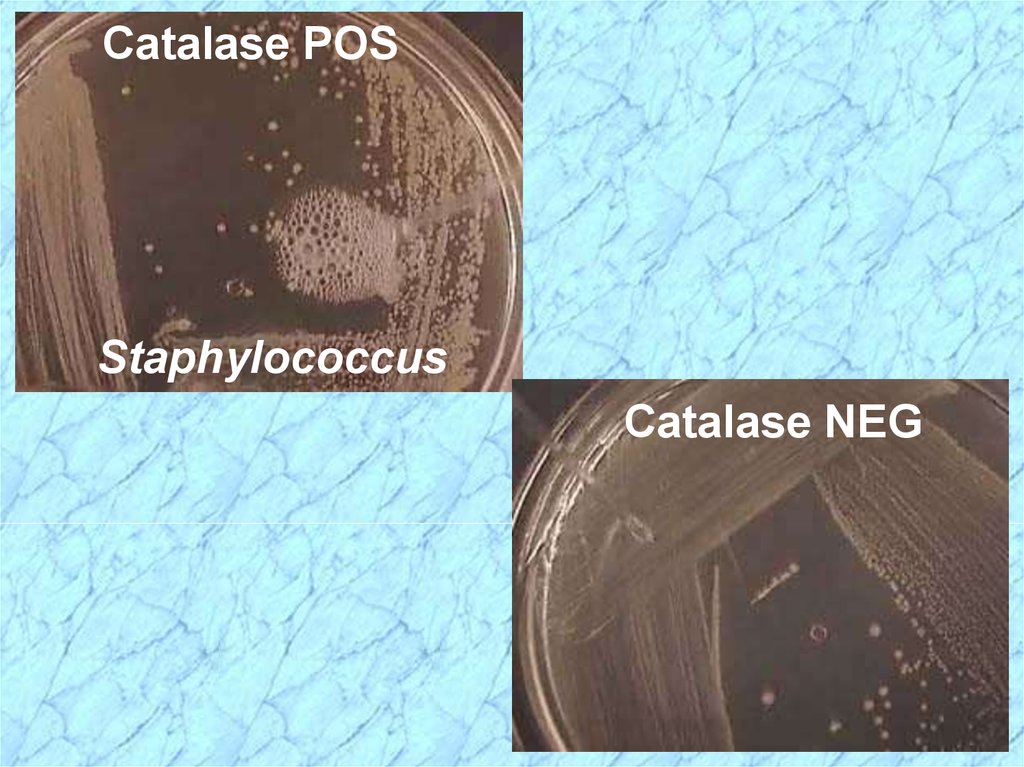
30.
Catalase POSStaphylococcus
Catalase NEG
31.
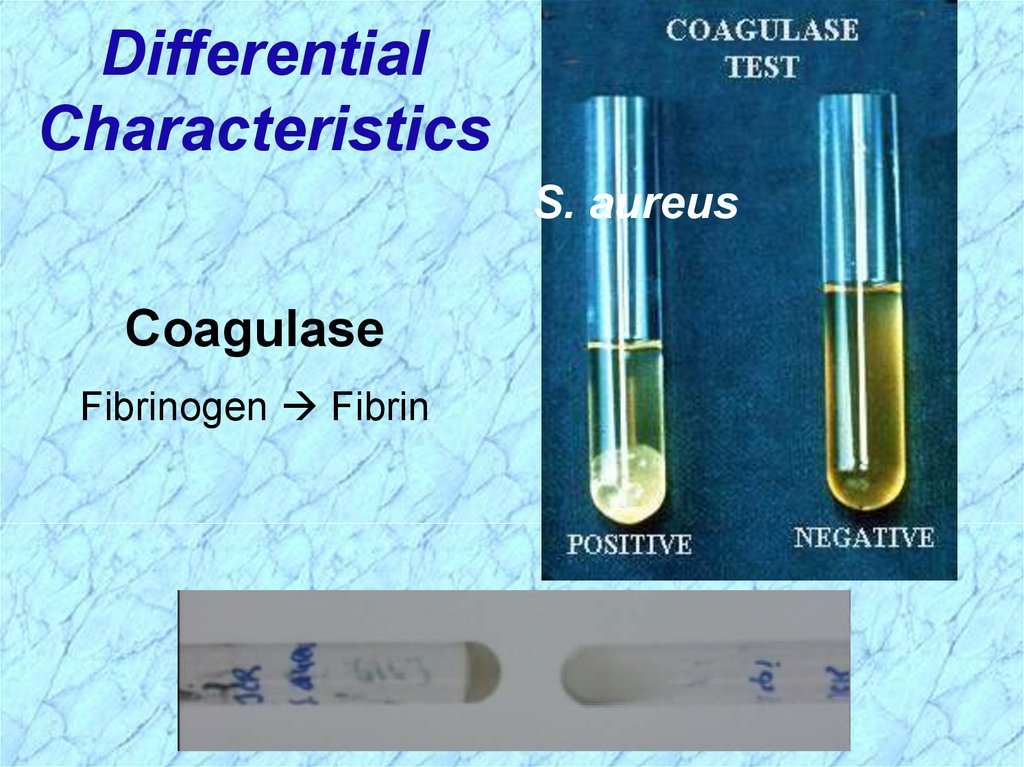
DifferentialCharacteristics
S. aureus
Coagulase
Fibrinogen Fibrin
32.
Staphylococcusaureus
Coagulase POS
Coagulase NEG
33. Treatment
• Drain infected area• Deep/metastatic infections
semi-synthetic penicllins
cephalosporins
erythromycin
clindamycin
• Endocarditis
semi-synthetic penicillin + an aminoglycoside
34. Prevention
• Carrier status prevents complete control• Proper hygiene, segregation of carrier
from highly susceptible individuals
• Good aseptic techniques when
handling surgical instruments
• Control of nosocomial infections
35.
36.
REVIEW37.
Gram-Positive CocciFAMILY Streptococcaceae (catalase negative)
Group A: -hemolytic Streptococcus pyogenes
Group B: -hemolytic (occasionally or ) S. agalactiae
Group C: -hemolytic ( or ) S. anginosus, S. equismilis
Group D: or hemolytic ( ) S. bovis
Group F: -hemolytic S. anginosus
Group G: -hemolytic S. anginosus
Viridans streptococci: (no group specific CHO)
or hemolytic S. mutans and
S. salivarius, S. sanguis, S. mitis and S. milleri groups
Streptococcus pneumoniae (no group CHO)( -hemolytic)
Enterococcus (Group D CHO) hemolytic ( or )
Enterococcus faecalis, E. faecium
FAMILY Micrococcaceae (catalase positive)
Coagulase-positive Staphylococcus aureus
Coag.-neg. Staphylococcus epidermidis, S. saprophyticus
REVIEW
38.
Which features are only found in S. aureus?S. aureus
S. epidermidis
REVIEW
































 medicine
medicine








