Similar presentations:
Peptic ulcer
1.
Peptic ulcerRustanov A.
2.
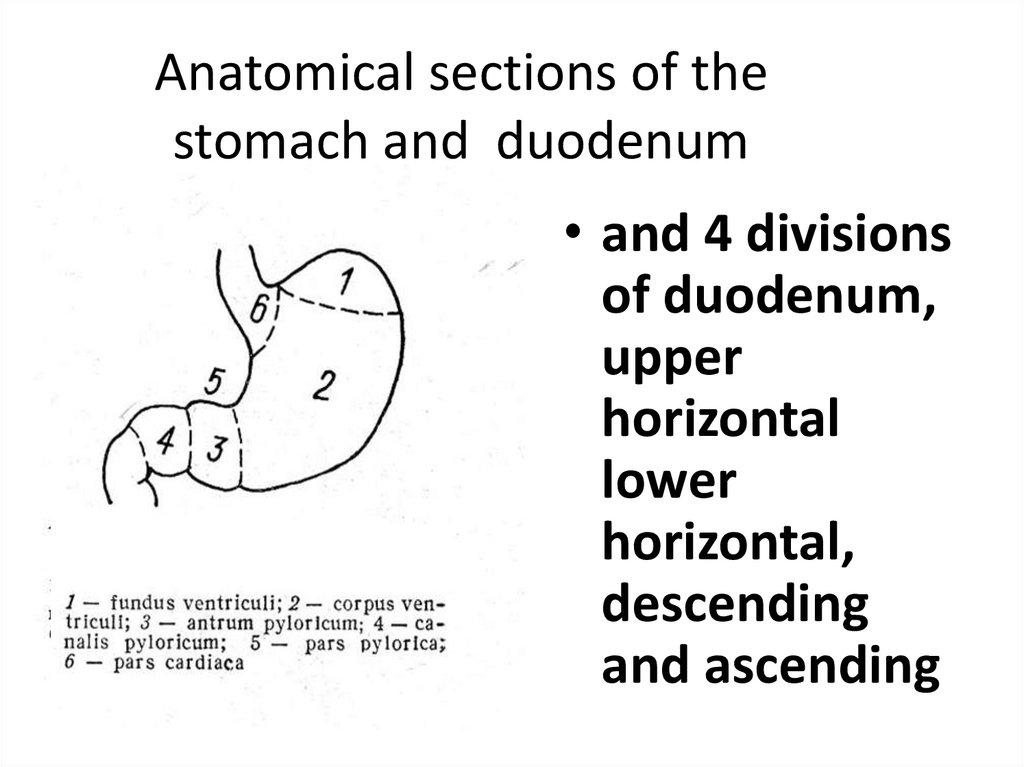
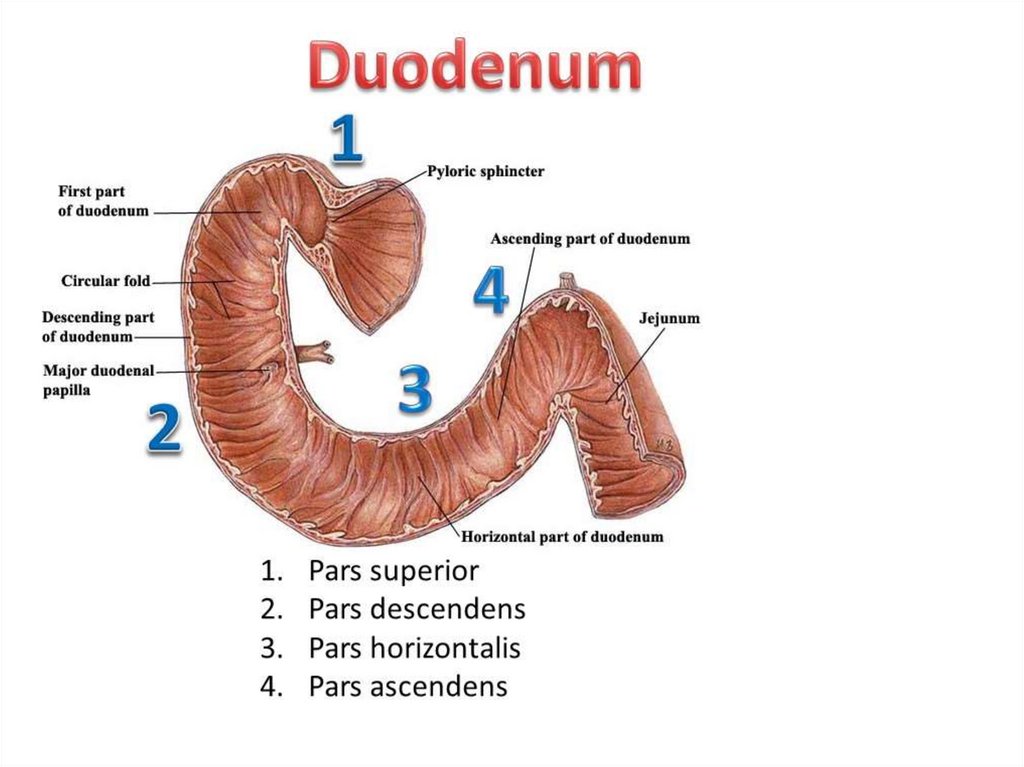
Anatomical sections of thestomach and duodenum
• and 4 divisions
of duodenum,
upper
horizontal
lower
horizontal,
descending
and ascending
3.
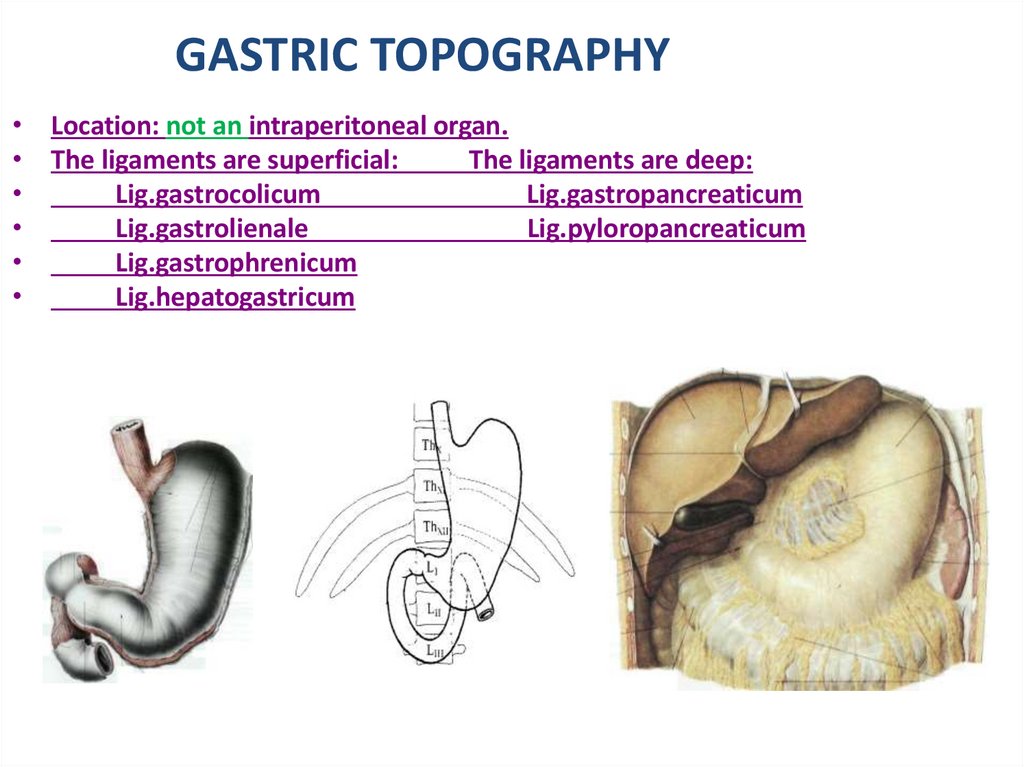
GASTRIC TOPOGRAPHY• Location: not an intraperitoneal organ.
• The ligaments are superficial:
The ligaments are deep:
Lig.gastrocolicum
Lig.gastropancreaticum
Lig.gastrolienale
Lig.pyloropancreaticum
Lig.gastrophrenicum
Lig.hepatogastricum
4.
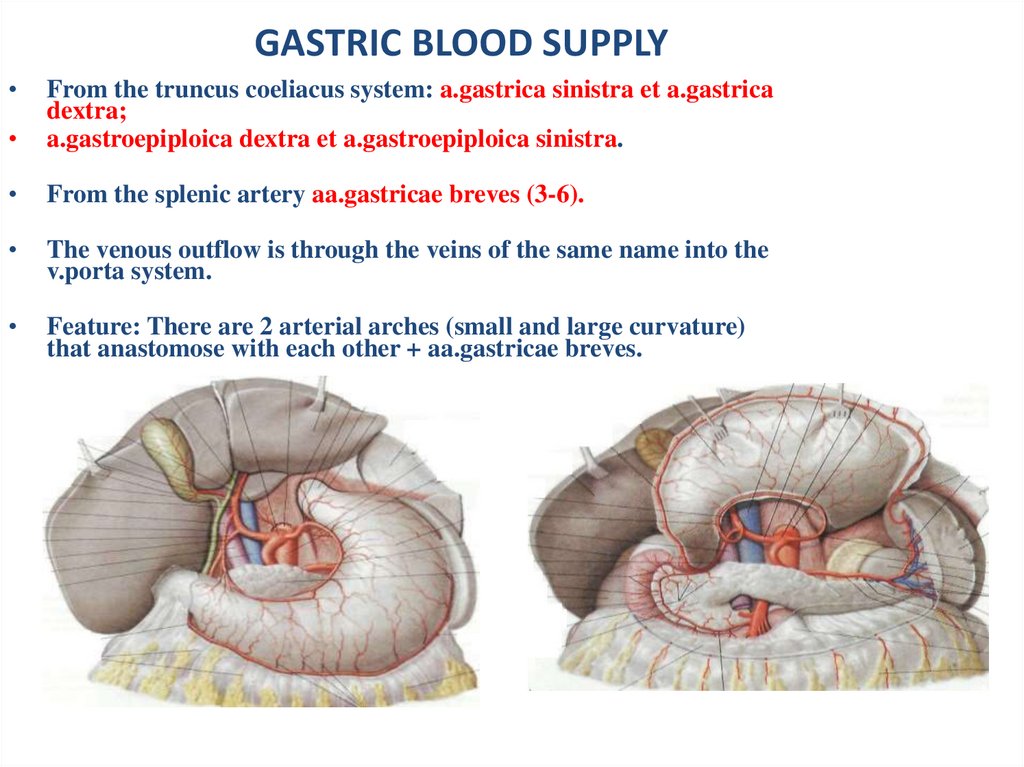
GASTRIC BLOOD SUPPLYFrom the truncus coeliacus system: a.gastrica sinistra et a.gastrica
dextra;
a.gastroepiploica dextra et a.gastroepiploica sinistra.
From the splenic artery aa.gastricae breves (3-6).
The venous outflow is through the veins of the same name into the
v.porta system.
Feature: There are 2 arterial arches (small and large curvature)
that anastomose with each other + aa.gastricae breves.
5.
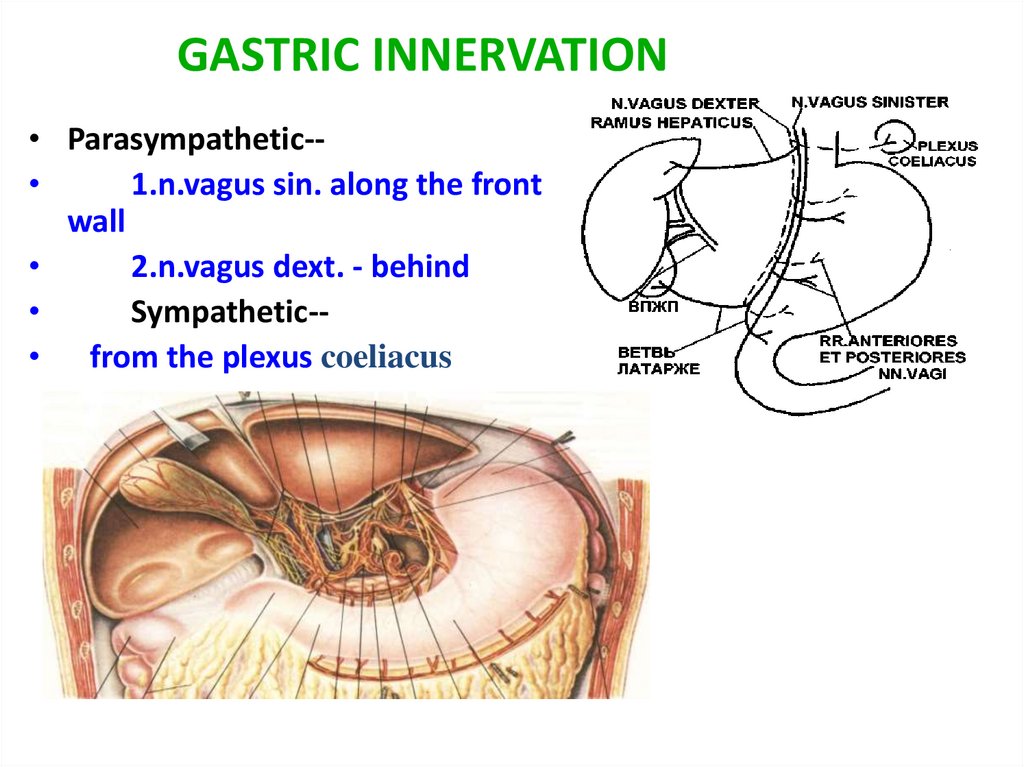
GASTRIC INNERVATION• Parasympathetic-
1.n.vagus sin. along the front
wall
2.n.vagus dext. - behind
Sympathetic-• from the plexus coeliacus
6.
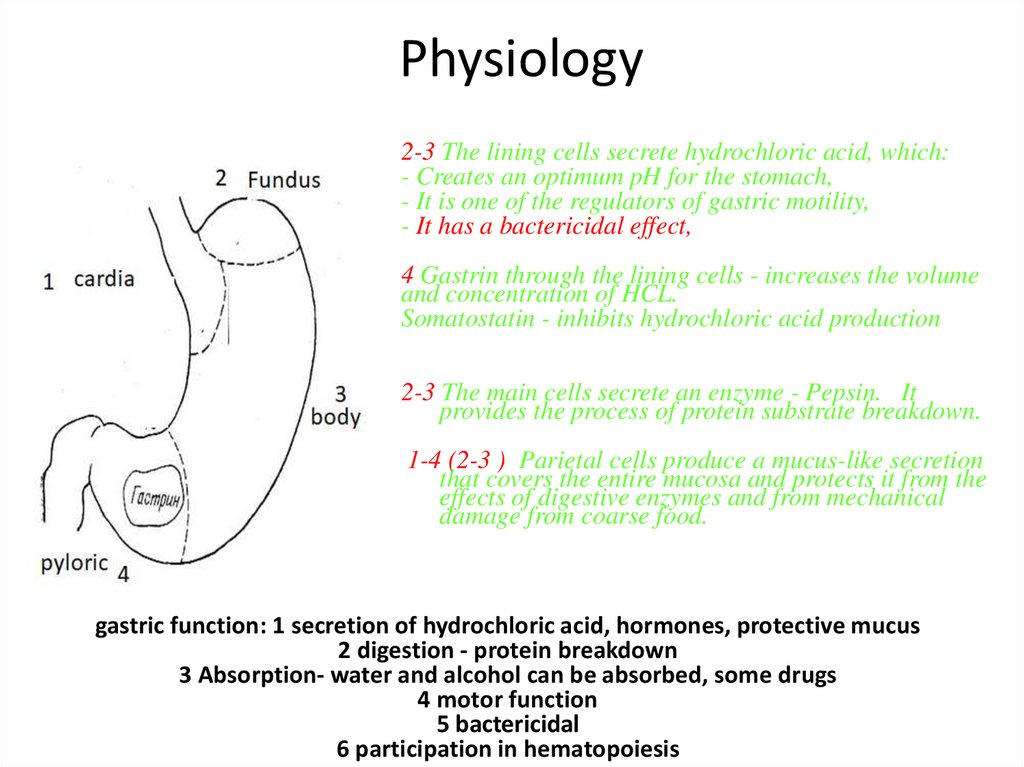
Physiology2-3 The lining cells secrete hydrochloric acid, which:
- Creates an optimum pH for the stomach,
- It is one of the regulators of gastric motility,
- It has a bactericidal effect,
4 Gastrin through the lining cells - increases the volume
and concentration of HCL.
Somatostatin - inhibits hydrochloric acid production
2-3 The main cells secrete an enzyme - Pepsin. It
provides the process of protein substrate breakdown.
1-4 (2-3 ) Parietal cells produce a mucus-like secretion
that covers the entire mucosa and protects it from the
effects of digestive enzymes and from mechanical
damage from coarse food.
gastric function: 1 secretion of hydrochloric acid, hormones, protective mucus
2 digestion - protein breakdown
3 Absorption- water and alcohol can be absorbed, some drugs
4 motor function
5 bactericidal
6 participation in hematopoiesis
7.
DUODENUMСостоит из : луковицы, нисходящего, горизонтального и восходящего
отделов.
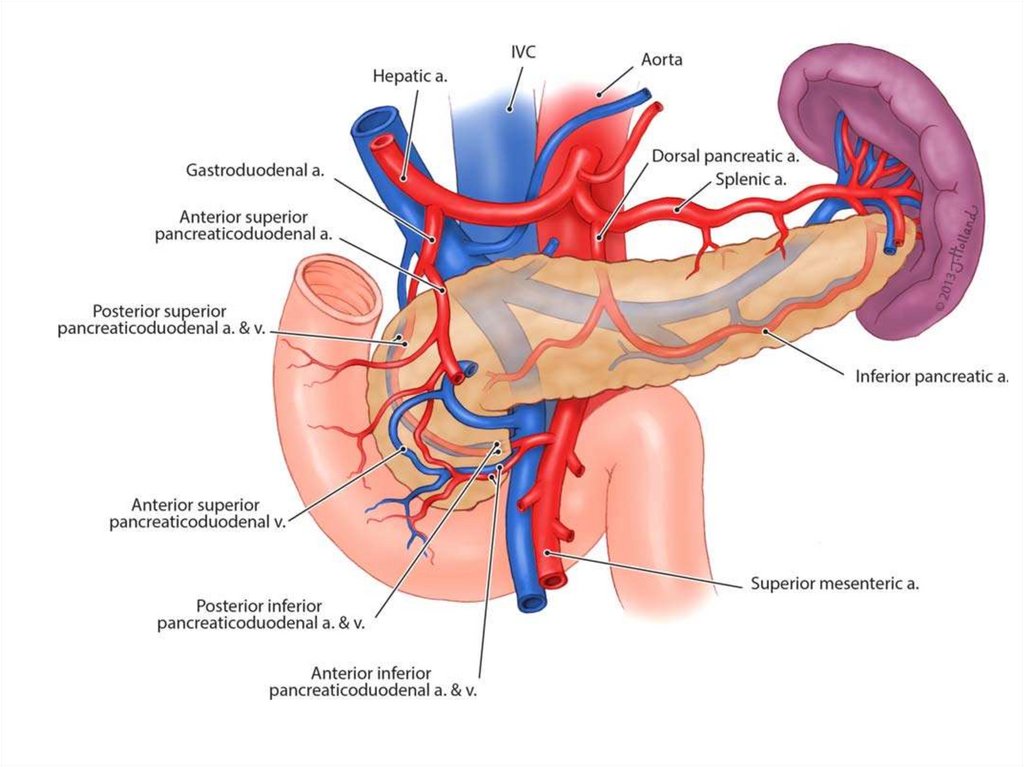
• Кровоснабжение:
A.pancreaticoduodenalis superior ) – делится на переднюю и заднюю.
A.pancreaticoduodenalis inferior (из a.mesenterica superior) – делится на
переднюю и заднюю.
• Вены следуют ходу артерий, вливаясь в систему v.porta.
• Лимфоотток: - передние и задние 12перстно- поджелудочные узлы;
8.
9.
Peptic ulcer diseasePrimary chronic recurrent disease
of upper gastrointestinal tract
associated with circumscribed
ulcers within stomach and
duodenum
9
10.
Ulceris disruption of the mucosal integrity of the
stomach and/or duodenum leading to a
local defect or excavation due to active
inflammation
10
11.
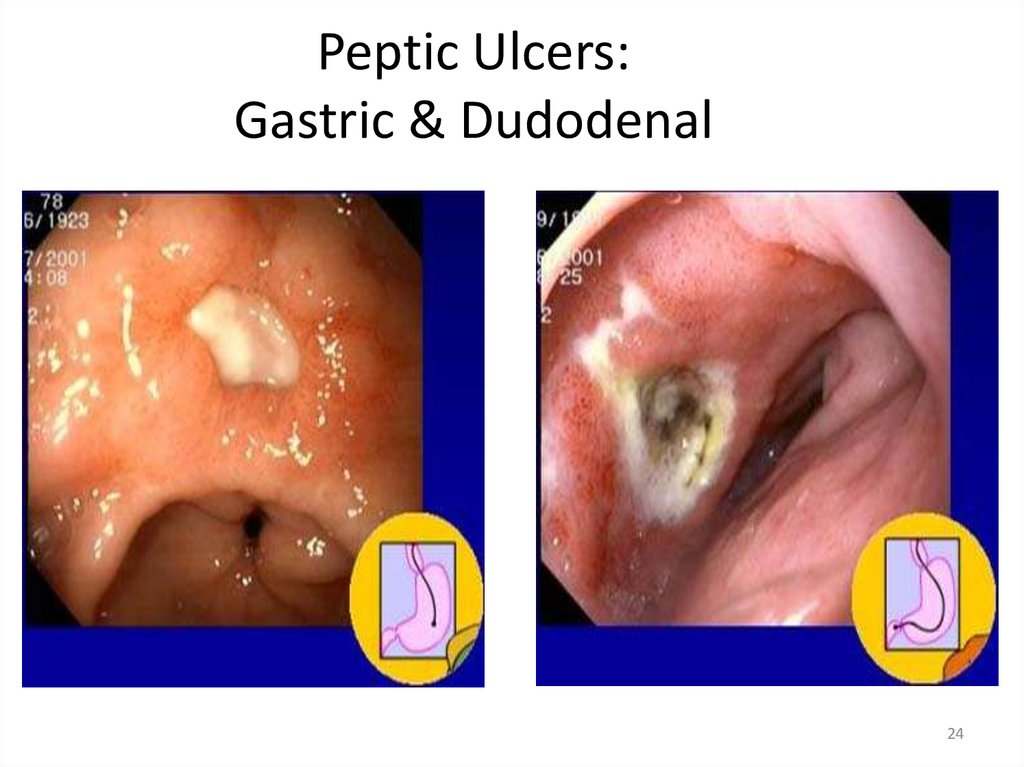
Peptic Ulcers:Gastric & Dudodenal
11
12.
13.
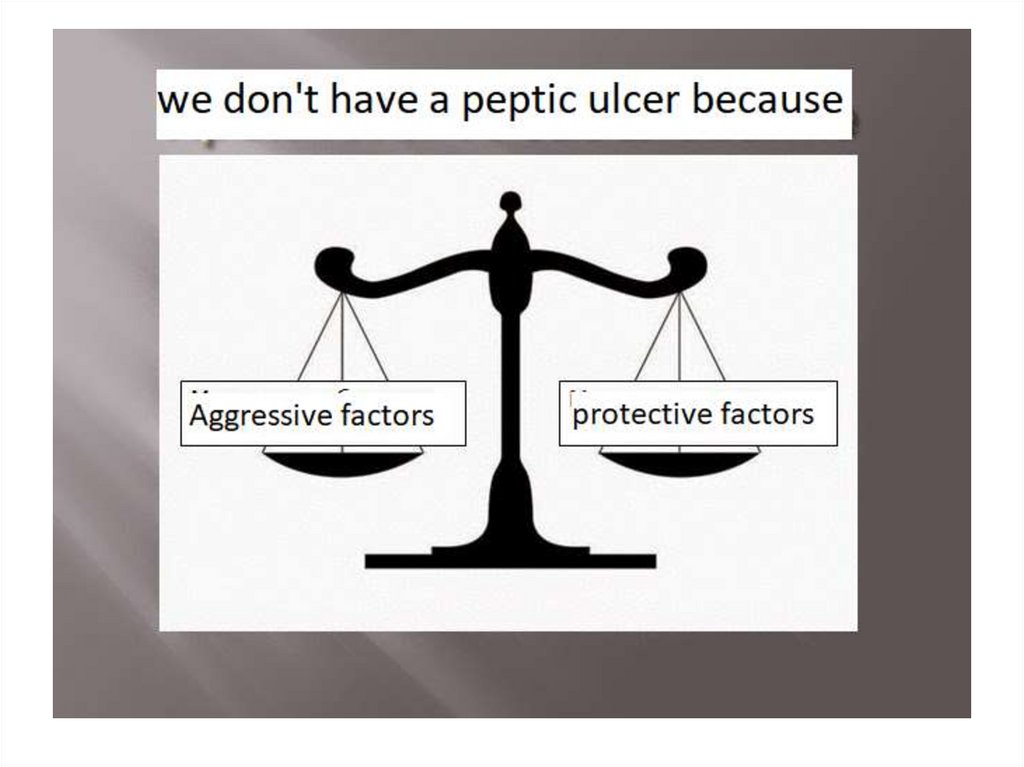
Aggressive factors• bad habits (smoking, alcohol)
• Stress (psychological and physical)
• H/Pylory
• Hyperproduction of HCL
• Prolonged use of NSAIDs and SAIDs
• After gastric surgery, trauma.
14.
Protecrive factors• Good regenerative function of epithelium
• Good blood supply to the stomach
• Protective bicarbonate mucus
• Prostaglandins
15.
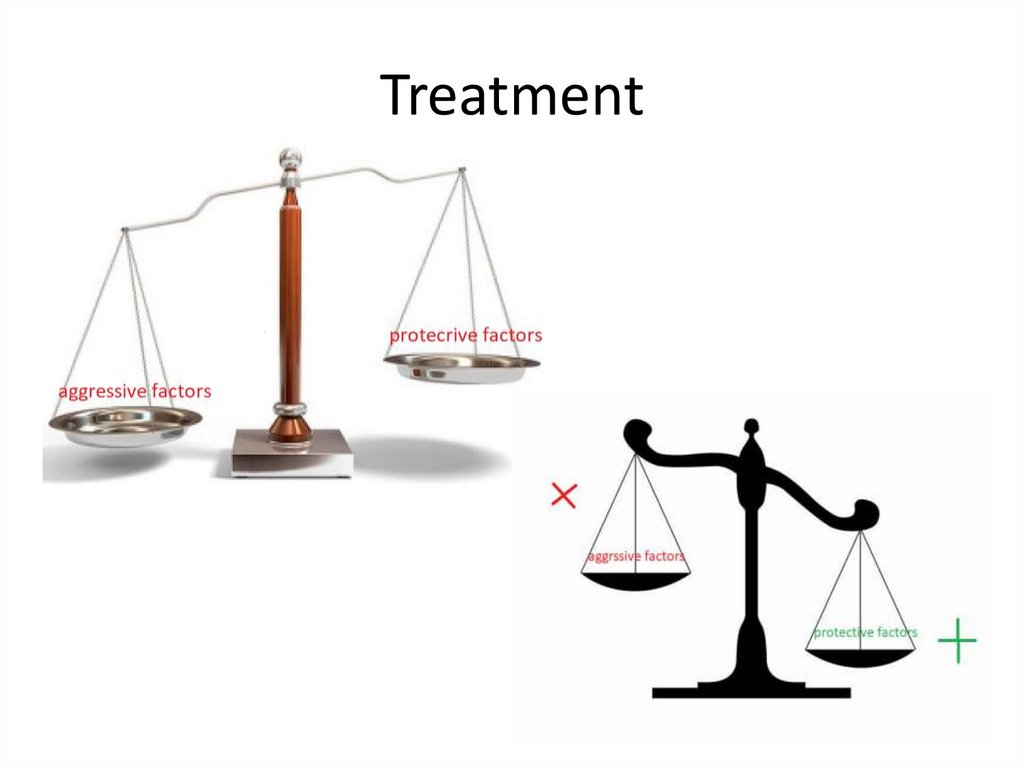
Etiology• the cause of peptic ulcer disease is the
predominance of agressive factors over
protective ones.
16.
Epidemiology• Duodenal ulcers (5x) > gastric ulcers
• ♂ (4x) > ♀
• Urban resident > rural resident
16
17.
Locations of ulcers• Any area where pepsin and acid are present
• Prevailing locations
– Duodenum: duodenal bulb
– Stomach: over lesser curvature
17
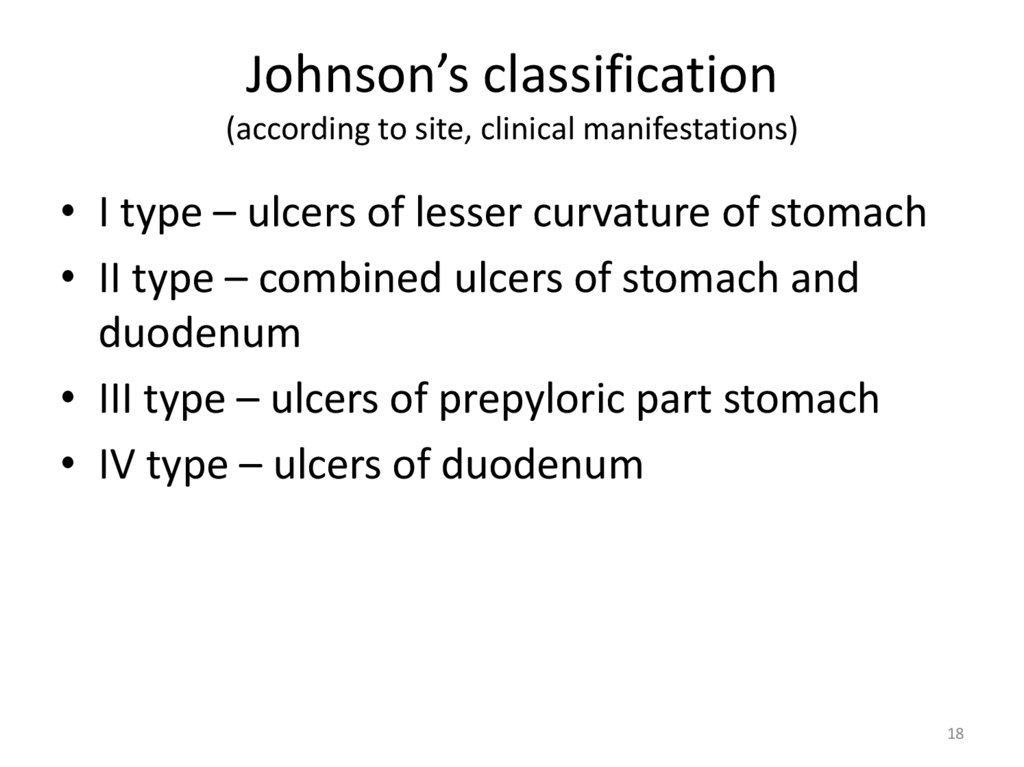
18.
Johnson’s classification(according to site, clinical manifestations)
• I type – ulcers of lesser curvature of stomach
• II type – combined ulcers of stomach and
duodenum
• III type – ulcers of prepyloric part stomach
• IV type – ulcers of duodenum
18
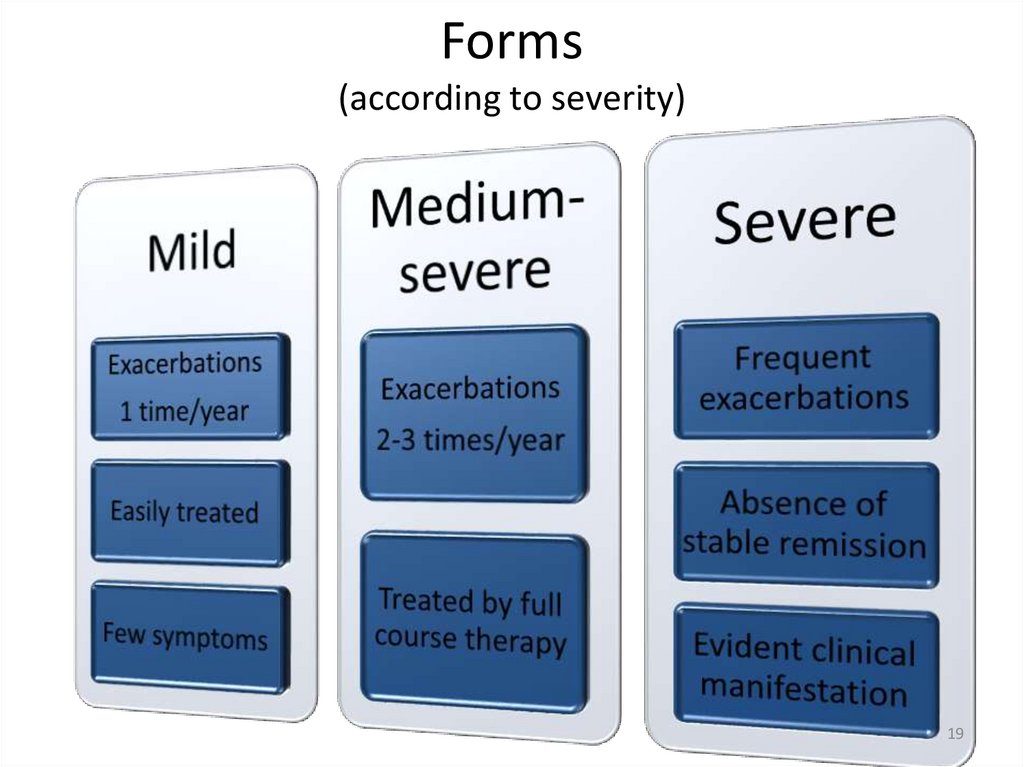
19.
Forms(according to severity)
19
20.
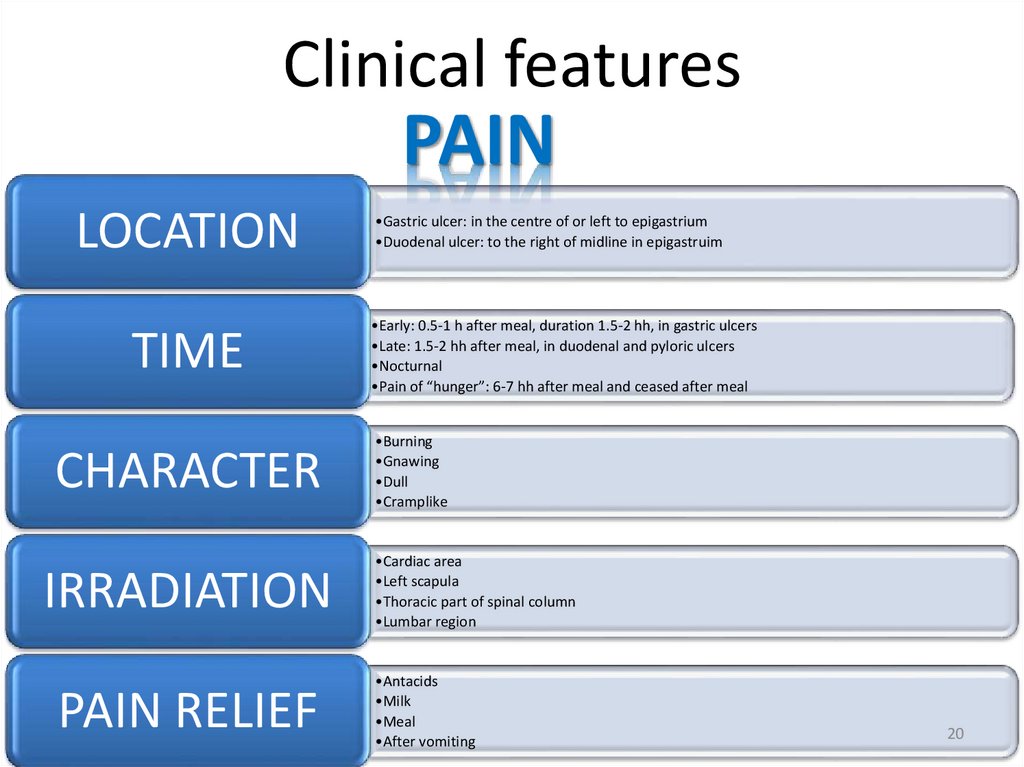
Clinical featuresPAIN
LOCATION
TIME
CHARACTER
IRRADIATION
PAIN RELIEF
•Gastric ulcer: in the centre of or left to epigastrium
•Duodenal ulcer: to the right of midline in epigastruim
•Early: 0.5-1 h after meal, duration 1.5-2 hh, in gastric ulcers
•Late: 1.5-2 hh after meal, in duodenal and pyloric ulcers
•Nocturnal
•Pain of “hunger”: 6-7 hh after meal and ceased after meal
•Burning
•Gnawing
•Dull
•Cramplike
•Cardiac area
•Left scapula
•Thoracic part of spinal column
•Lumbar region
•Antacids
•Milk
•Meal
•After vomiting
20
21.
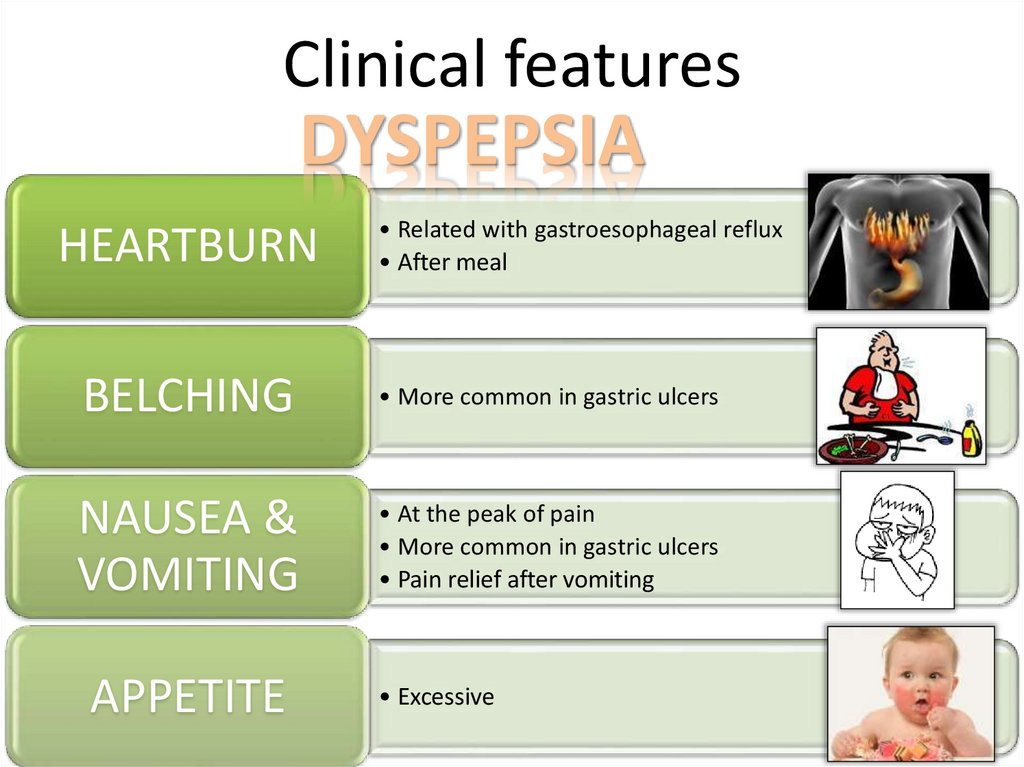
Clinical featuresDYSPEPSIA
HEARTBURN
• Related with gastroesophageal reflux
• After meal
BELCHING
• More common in gastric ulcers
NAUSEA &
VOMITING
• At the peak of pain
• More common in gastric ulcers
• Pain relief after vomiting
APPETITE
• Excessive
21
22.
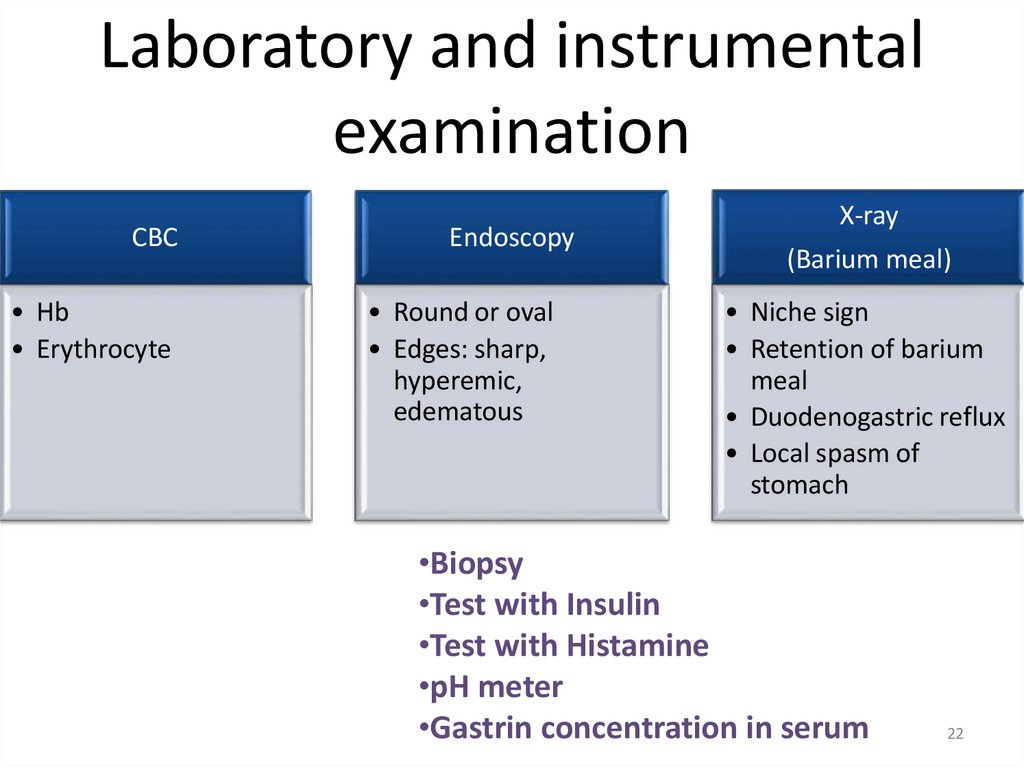
Laboratory and instrumentalexamination
CBC
• Hb
• Erythrocyte
Endoscopy
• Round or oval
• Edges: sharp,
hyperemic,
edematous
X-ray
(Barium meal)
• Niche sign
• Retention of barium
meal
• Duodenogastric reflux
• Local spasm of
stomach
•Biopsy
•Test with Insulin
•Test with Histamine
•pH meter
•Gastrin concentration in serum
22
23.
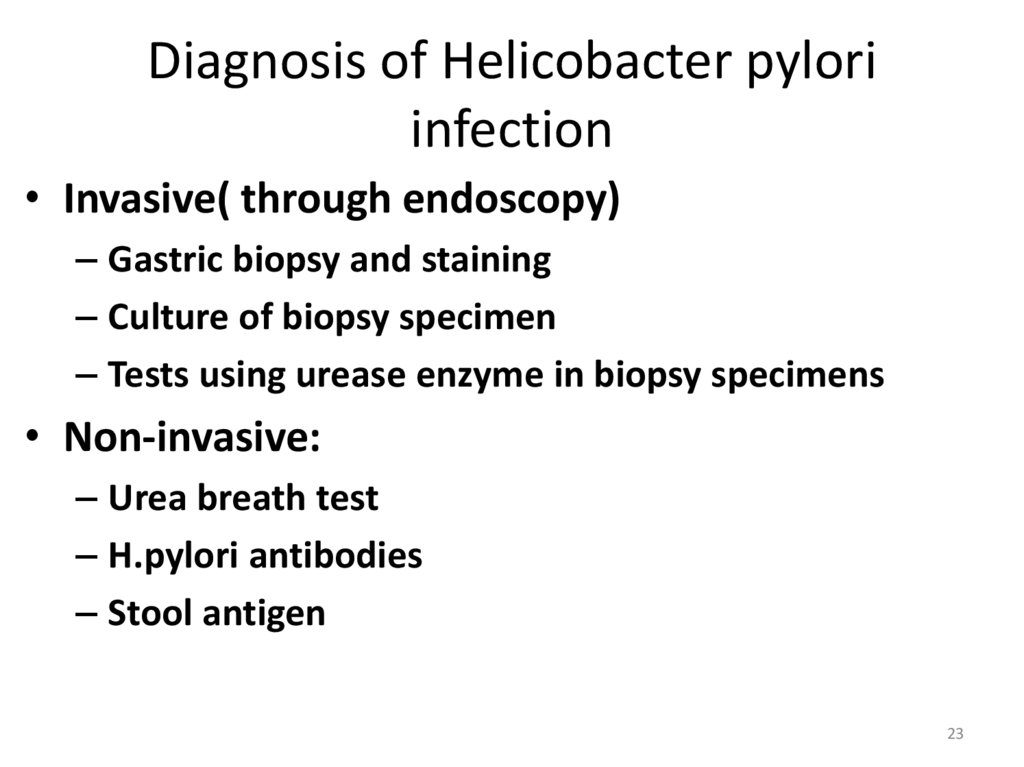
Diagnosis of Helicobacter pyloriinfection
• Invasive( through endoscopy)
– Gastric biopsy and staining
– Culture of biopsy specimen
– Tests using urease enzyme in biopsy specimens
• Non-invasive:
– Urea breath test
– H.pylori antibodies
– Stool antigen
23
24.
Peptic Ulcers:Gastric & Dudodenal
24
25.
• В развитии язвы желудка основными факторами являютсятрофические нарушения в стенке желудка, расстройства
микроциркуляции и инфекционный фактор - Helicobacter pylori
(НbР). Эта бактерия является причиной развития хронического
гастрита и язвенной болезни желудка и двенадцатиперстной
кишки.
• По локализации язвы:
• 1. Желудок: кардиальная и субкардиальная часть, малая
кривизна, большая кривизна, тело желудка, передняя и задняя
стенка, антральная часть.
• 2. Двенадцатиперстная кишка: луковица, постбульбарный
отдел, передней, задней, верхней, нижней стенок.
• 3. Сочетанные язвы желудка и ДПК.
26.
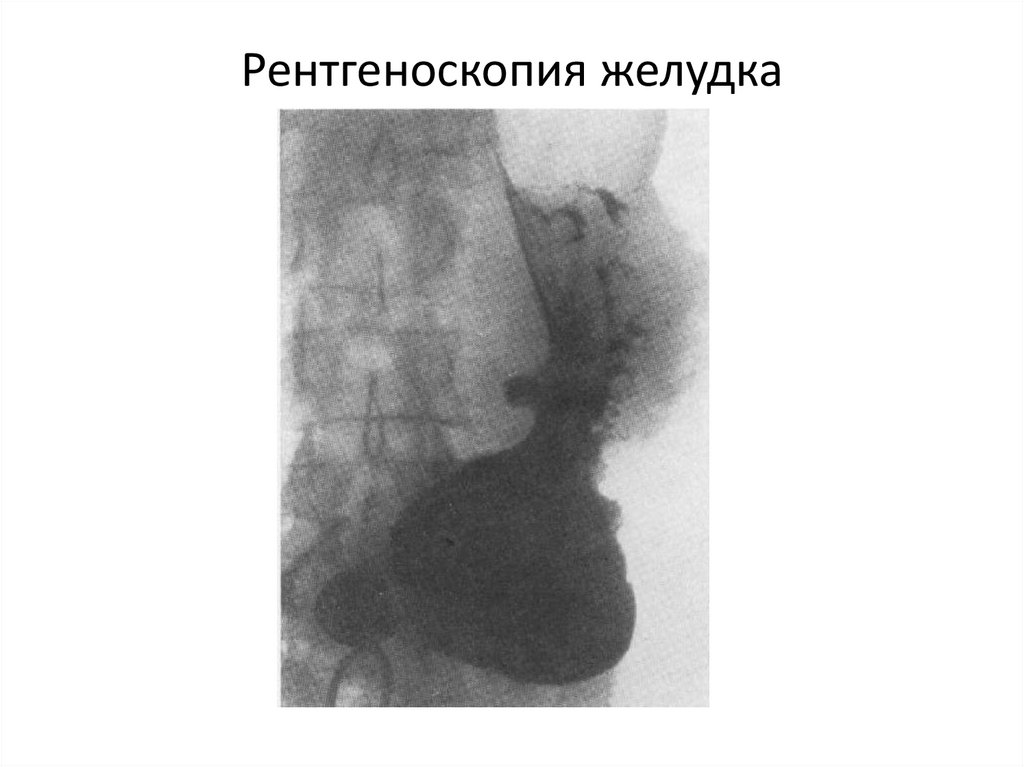
Рентгеноскопия желудка27.
Treatment28.
• how to deal with aggressive factors and howto help the protective factors we will talk in
practice class











 medicine
medicine biology
biology








