Similar presentations:
Peptic ulcer disease
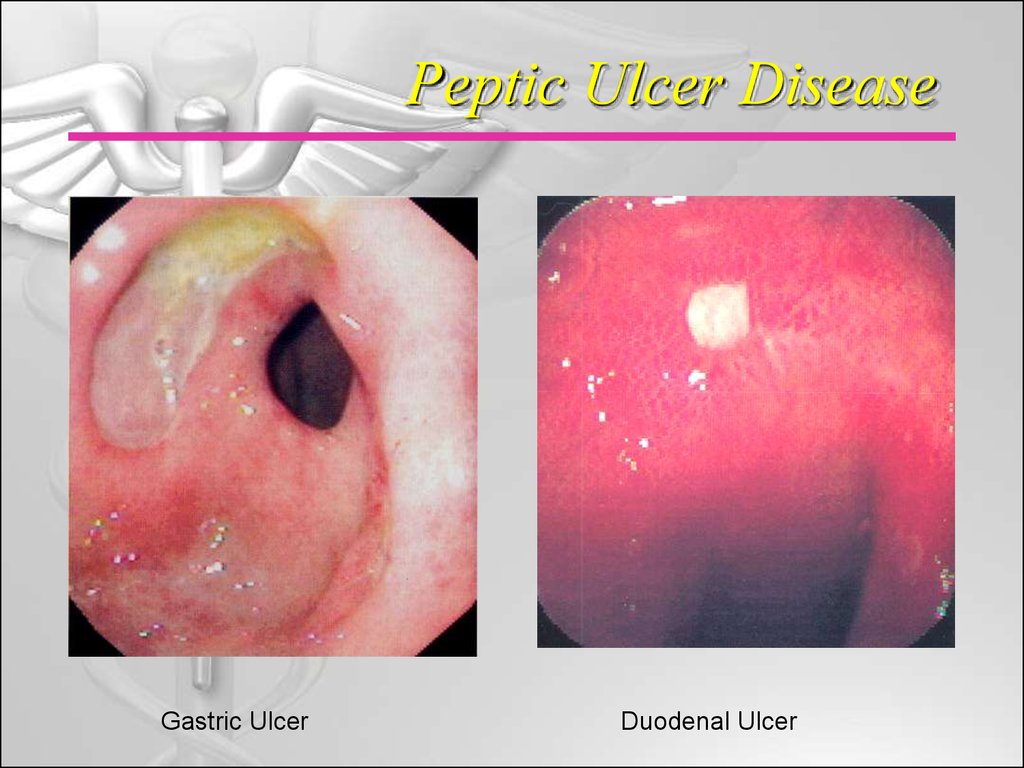
1. Peptic Ulcer Disease
Gastric UlcerDuodenal Ulcer
2. Ulcerogenic Factors
Nonspecific
Endogenous :
1. Hyper secretion of HCl and pepsin
2. H. pylori
3. Chronic gastritis “B” and metaplasia into
duodenal mucosa
4. Failure of gastroduodenal movement
5. Genetic susceptibility
3.
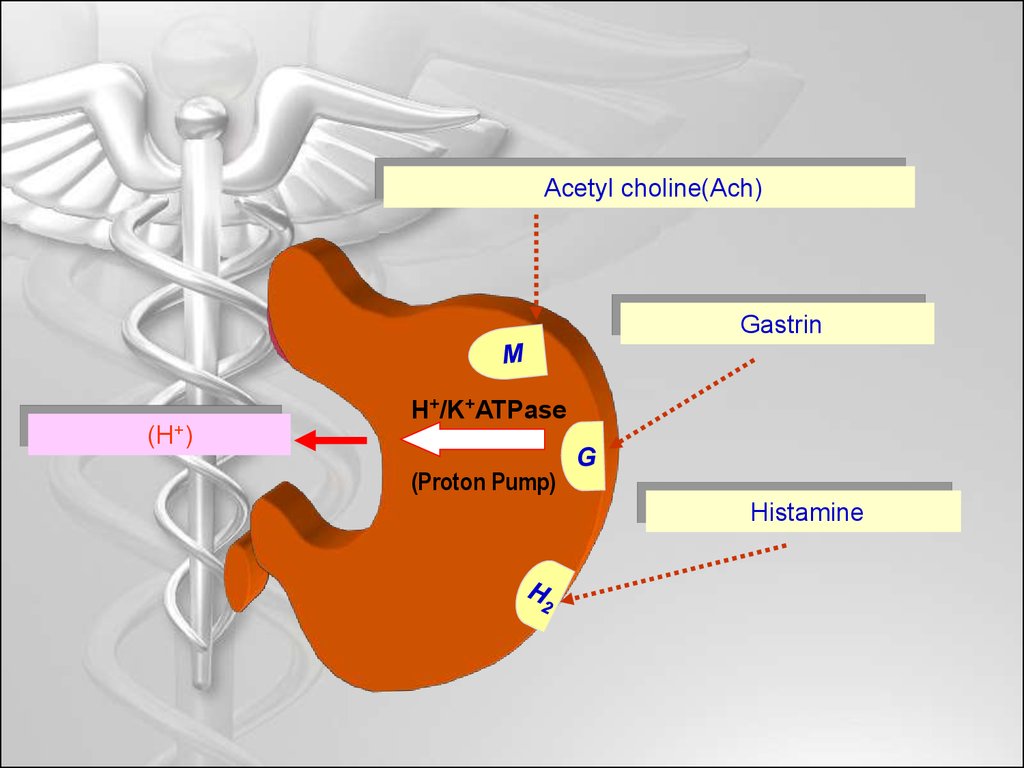
Acetyl choline(Ach)Gastrin
H+/K+ATPase
(H+)
(Proton Pump)
Histamine
4. Pathophysiology of peptic ulcer disease
Abnormalities in the secretion of gastric acidand pepsin,and on the suppression of acid as a
treatment strategy.
Gastric hypersecretion-associated with
gastrinoma in Zollinger-Ellision syndrome,antral
G-cell hyperplasia,an increase in parietal-cell
mass and physiological imbalance between the
antagonistic gastric hormones gastrin and
somatostatin-is still an important issue in peptic
ulcer disease.
5. Management and Prevention of NSAID-associated peptic ulcer
Misoprostol, a mucosal-protectiveanalogue of prostaglandin E2 reduces
the risk if ulcer complications,but only at
the recommended dose of 800 ug/day.
Lower doses of misoprostol are not
effective
6.
А.А. Shalimov, V.V. Sajenko, 1972, 1987.1.
Direct indications:
Perforation of ulcer.
Decompensating pyloroduodenal stenosis.
Profuse GIT bleeding.
2. Indirect indications:
Penetration into contiguous organs.
Giant ulcer.
Recurrence bleeding.
Long –term medical history with recurrences of ulcer
Unsuccessful drugs therapy .
Indirect indications are changeable according trials.
7.
According to our experience indications forduodenal ulcer surgery are:
Perforation of ulcer;
Decompensating pyloroduodenal
stenosis;
Profuse GIT bleeding after
unsuccessful endo-hemostasis;
Penetration into contiguous organs;
Recurrence bleeding;
Long –term medical history with
recurrences of ulcer with
unsuccessful drug therapy.
8.
According to our experience indications for gastric ulcersurgery are:
1) Complicated ulcer (perforation, bleeding,
penetration);
2) no effect drug therapy fro three months;
3) Long –term medical history with recurrences of
ulcer with unsuccessful drug therapy;
4) Chronic ulcer with epithelial dysplasia IIIst or
/and metaplasia
subcardial [juxtacardial, type IV gastric] ulcer.
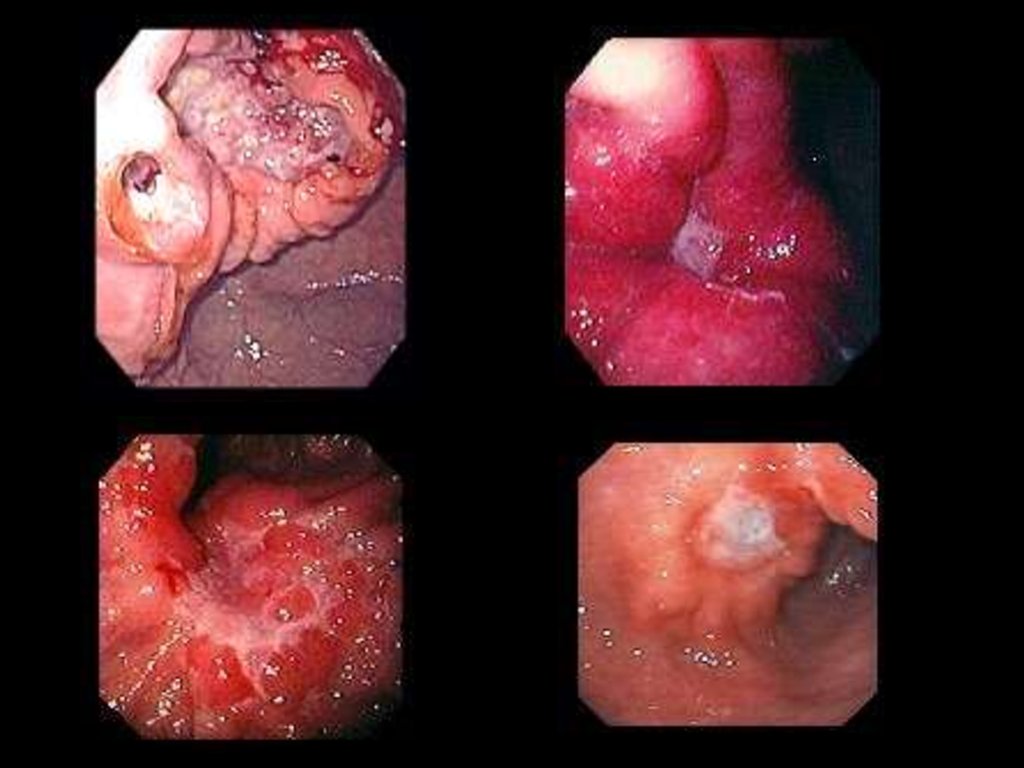
9. Johnston` s classification of gastric ulcer (1965):
I type — ulcer of lesser curvature of stomach ( 3 sмunder pylorus),
II type — combined ulcer`s of duodenum and
stomach,
III type — ulcer`s of pylorus ( up to 3 sм).
IV type - subcardial ( juxtacardial ) ulcer
2 sм from esophagus sphincter)
V type — drug related ulcers
(up to







 medicine
medicine








