Similar presentations:
Muscle tissue
1.
PhD Inna A. Demyanenko2.
3.
4.
- According to morphologic and functional features:1. striated (skeletal, cardiac)
2. smooth
- According to development ( histogenetic
classification):
1. Mesenchymal ( smooth muscle- visceral and
vascular)
2. Myoepithelial (from ectoderm)- in acini of some
exocrine glands;
3. Neural ( from neural tube)- in iris of eye ( m. sphincter
pupilla, m. dilatator pupilla) and ciliary body of eye;
4. Coelomic (from myoepicardial plate of
splanchnotome)- in myocardium;
5. Somatic ( from myotome)- in skeletal muscle
5.
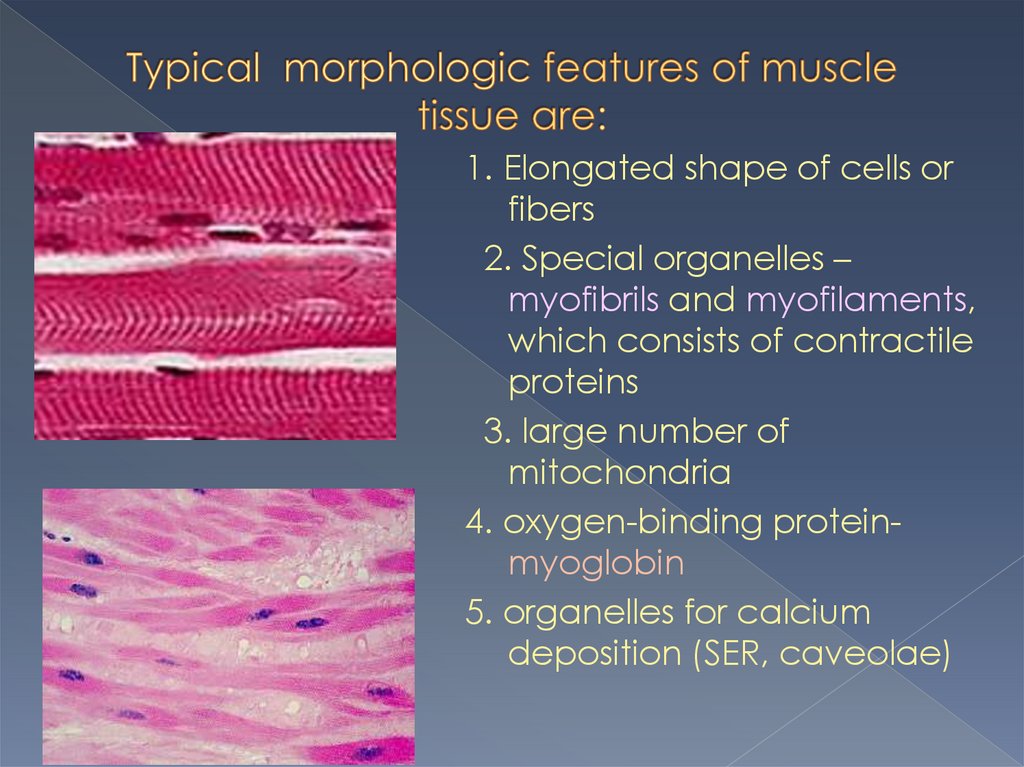
1. Elongated shape of cells orfibers
2. Special organelles –
myofibrils and myofilaments,
which consists of contractile
proteins
3. large number of
mitochondria
4. oxygen-binding proteinmyoglobin
5. organelles for calcium
deposition (SER, caveolae)
6.
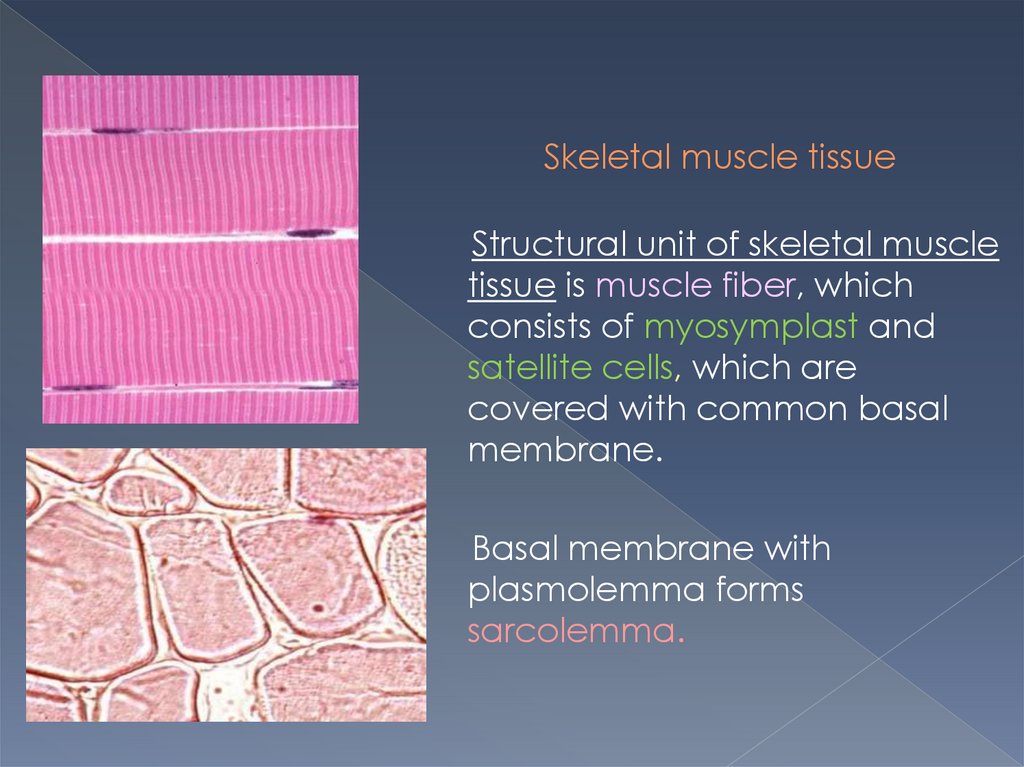
Skeletal muscle tissueStructural unit of skeletal muscle
tissue is muscle fiber, which
consists of myosymplast and
satellite cells, which are
covered with common basal
membrane.
Basal membrane with
plasmolemma forms
sarcolemma.
7.
Length of myosymplast – from several micromitersup to several santimiters; diameter: 50-100
micromiters.
In peripheral portion of myosymplast there are nuclei
(from several dozens up to several tens of thousands);
in its central portion there are myofibrils.
8.
9.
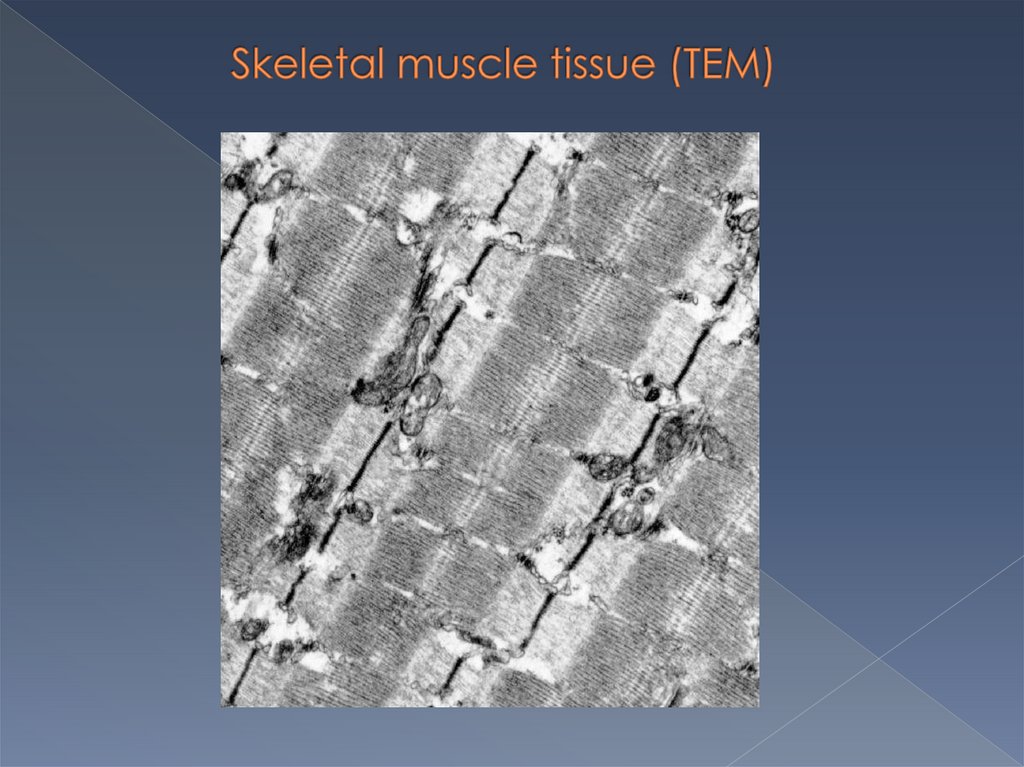
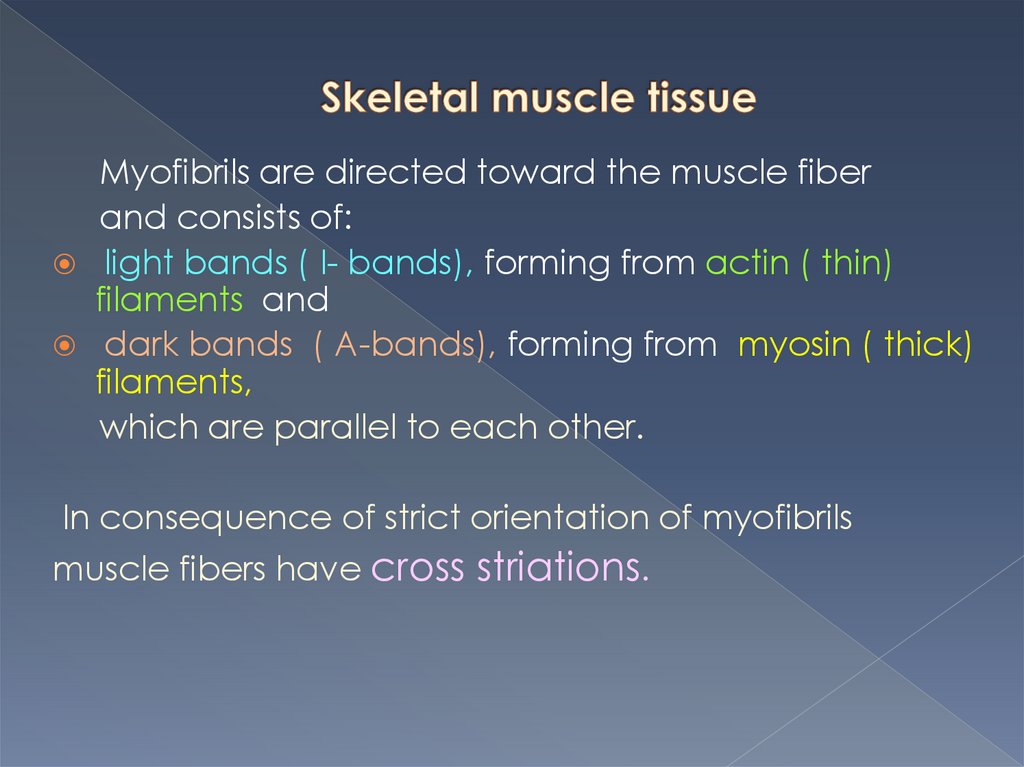
Myofibrils are directed toward the muscle fiberand consists of:
light bands ( I- bands), forming from actin ( thin)
filaments and
dark bands ( A-bands), forming from myosin ( thick)
filaments,
which are parallel to each other.
In consequence of strict orientation of myofibrils
muscle fibers have cross striations.
10.
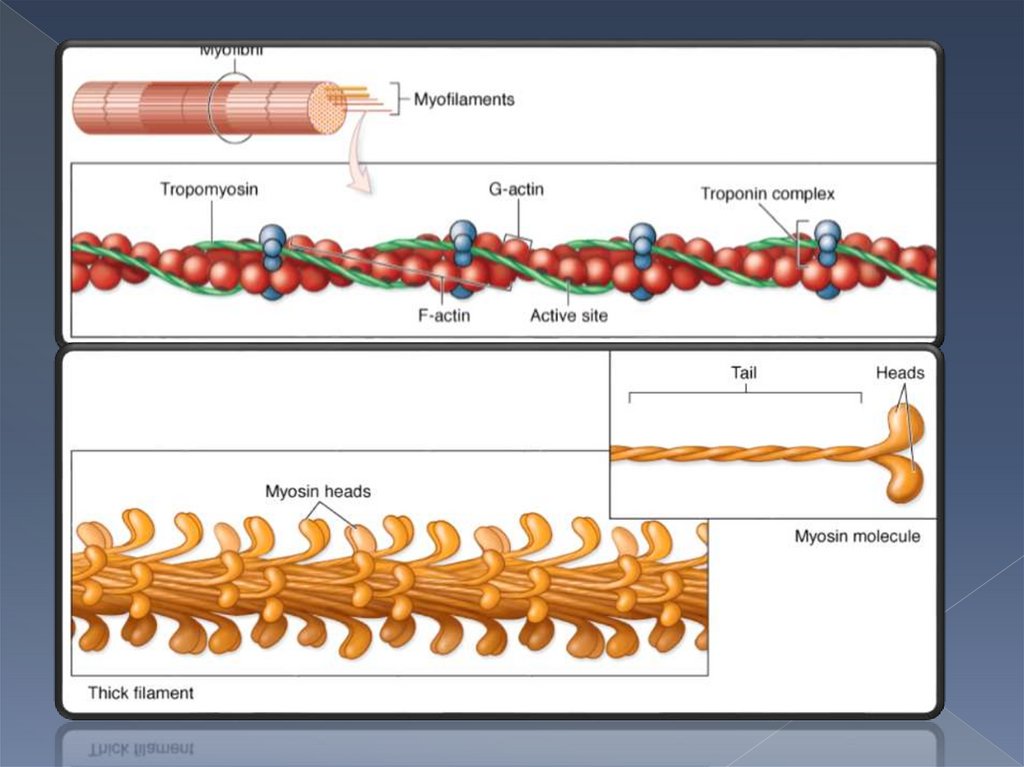
Thin filaments contain contractile protein- actinand two regulatory proteins- troponin and tropomyosin
Thick filaments are formed with fibrillar proteinmyosin
Myosin filaments penetrate into the spaces between
actin filaments.
11.
12.
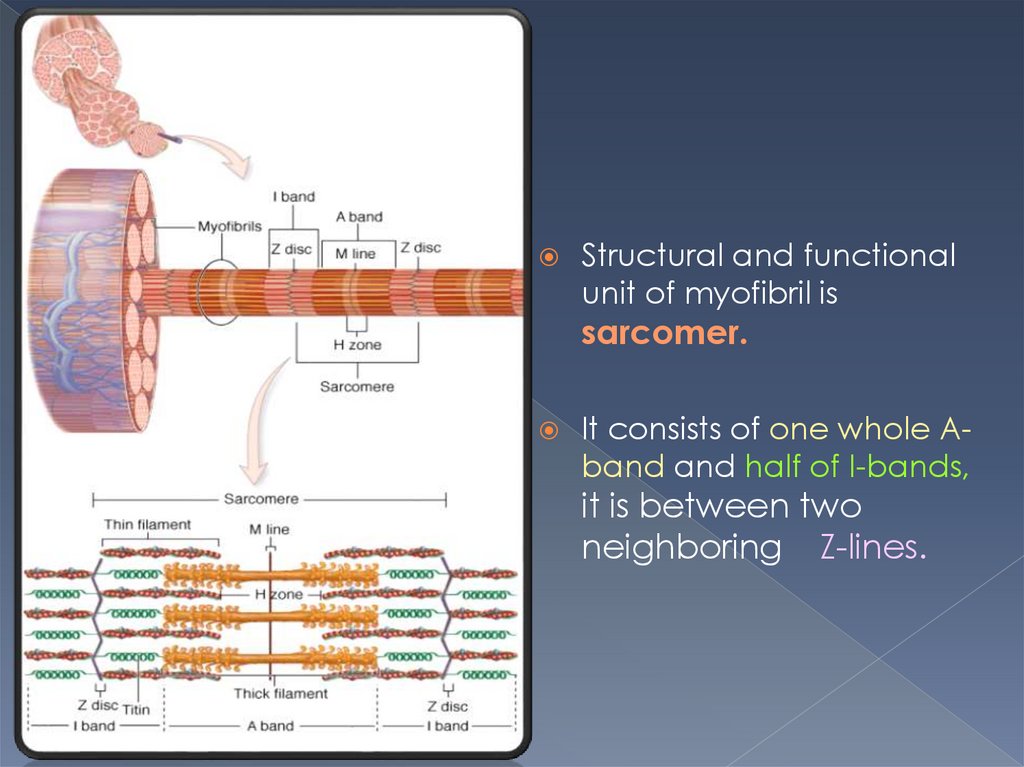
Structural and functionalunit of myofibril is
sarcomer.
It consists of one whole Aband and half of I-bands,
it is between two
neighboring Z-lines.
13.
14.
Basic types of skeletal muscle fibers:1. Red (contain much of myoglobin and
mitochondria)
2. Intermediate have structural and functional
characteristics between those of red and
white fibers
3. White fibers (contain less of myoglobin and
fewer mitochondria)
15.
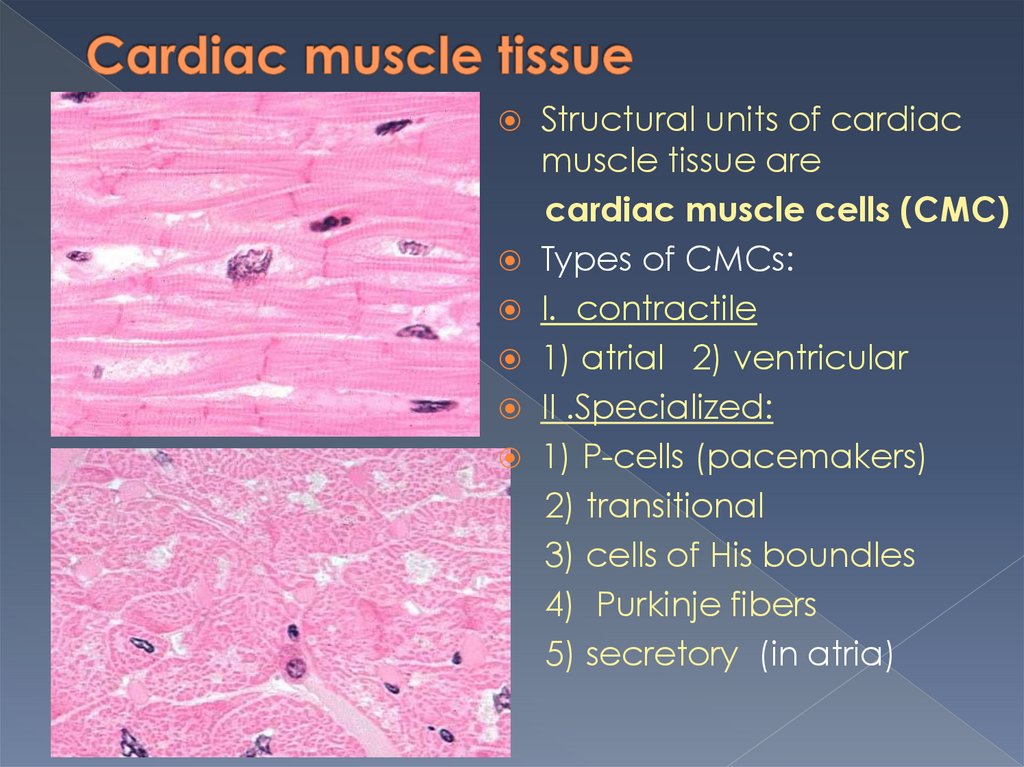
Structural units of cardiacmuscle tissue are
cardiac muscle cells (CMC)
Types of CMCs:
I. contractile
1) atrial 2) ventricular
II .Specialized:
1) P-cells (pacemakers)
2) transitional
3) cells of His boundles
4) Purkinje fibers
5) secretory (in atria)
16.
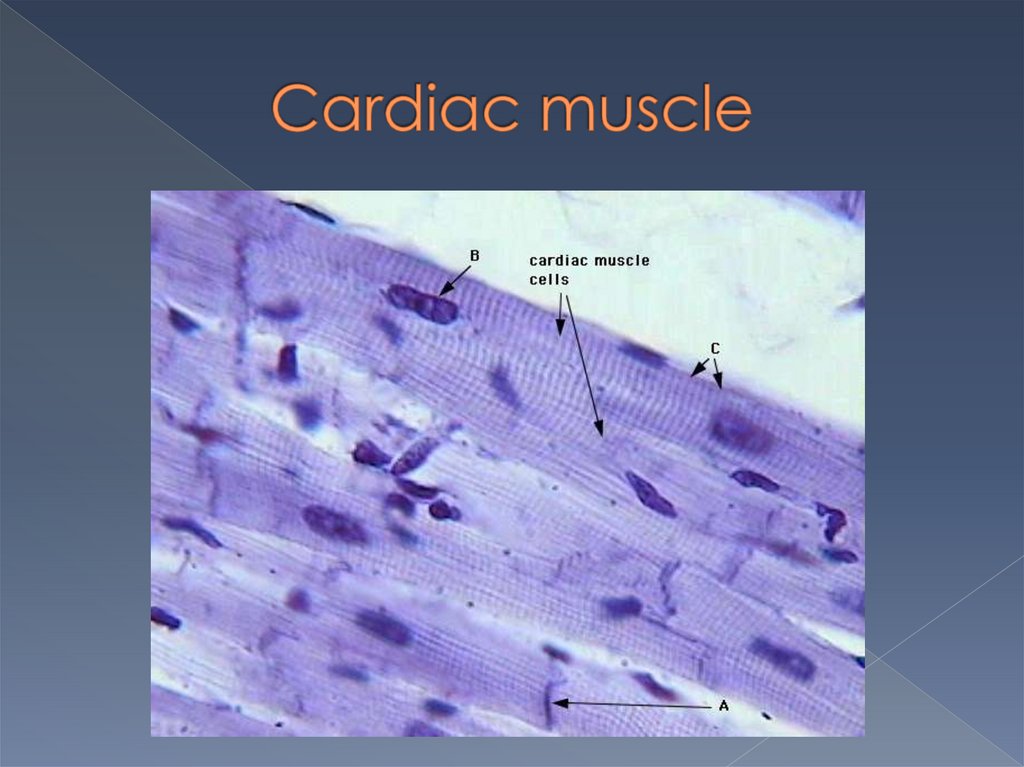
They are cylindrical in shape, theirlength about 100-150 mcm and
diameter up to 20 mcm.
They contain one, seldom two nuclei
in the center of cell; groups of
myofibrils dispose around the nuclei .
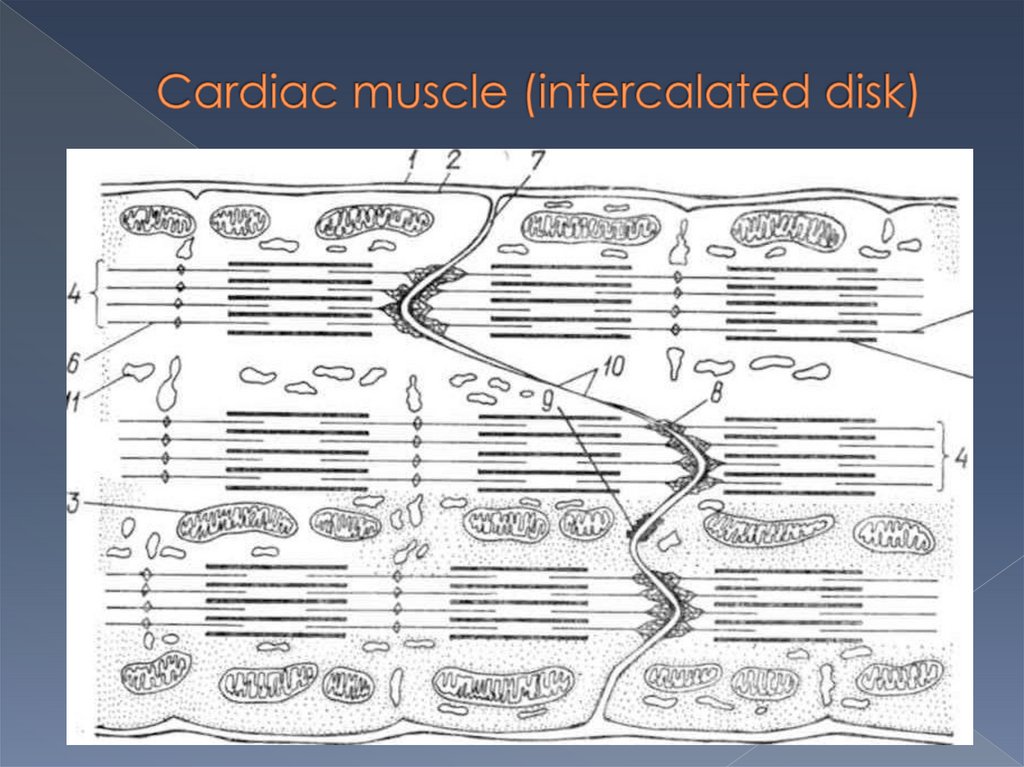
Cells join to one another with
intercalated disks forming muscle
fibers.
17.
18.
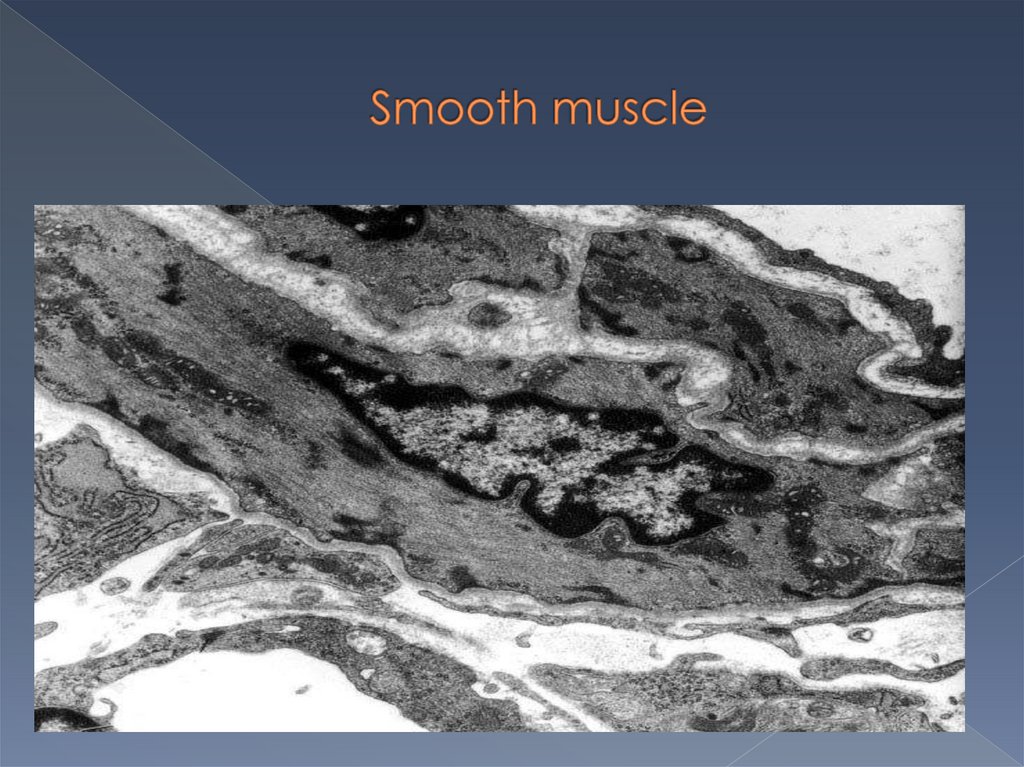
19.
20.
Its structural unit issmooth muscle cell, which
is spindle in shape with
single central ovoid
nucleus.
Its length 20-500 mcm, аnd
diameter 5-8 mcm.
21.
22.
23.
24.
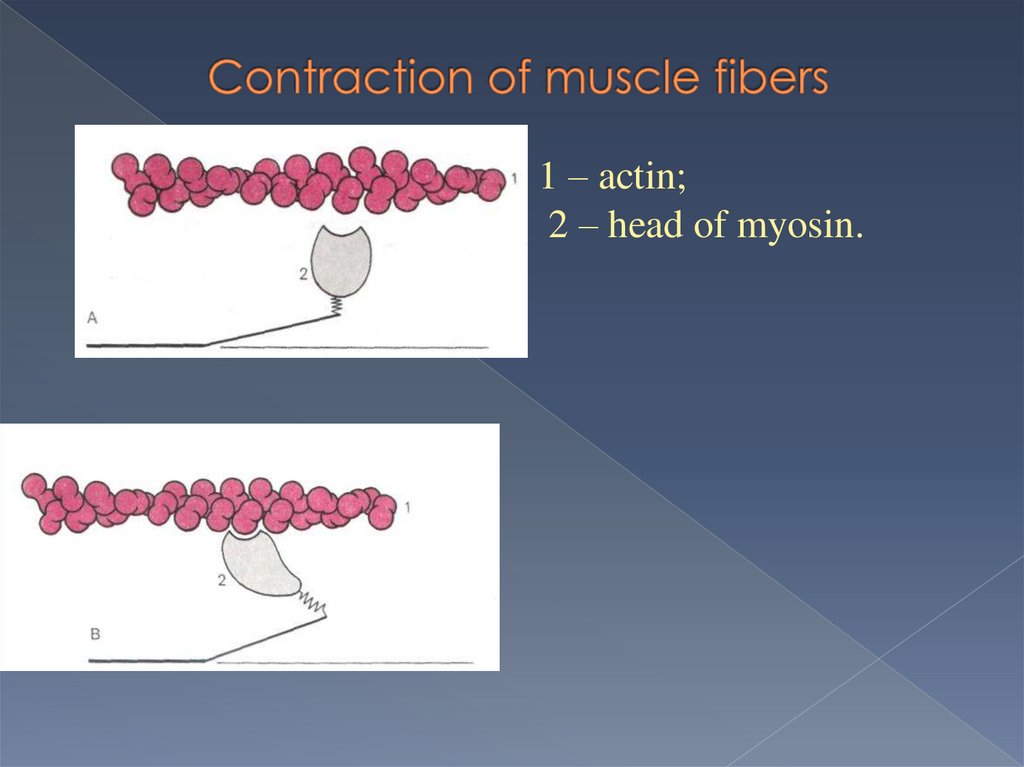
1 – actin;2 – head of myosin.
25.
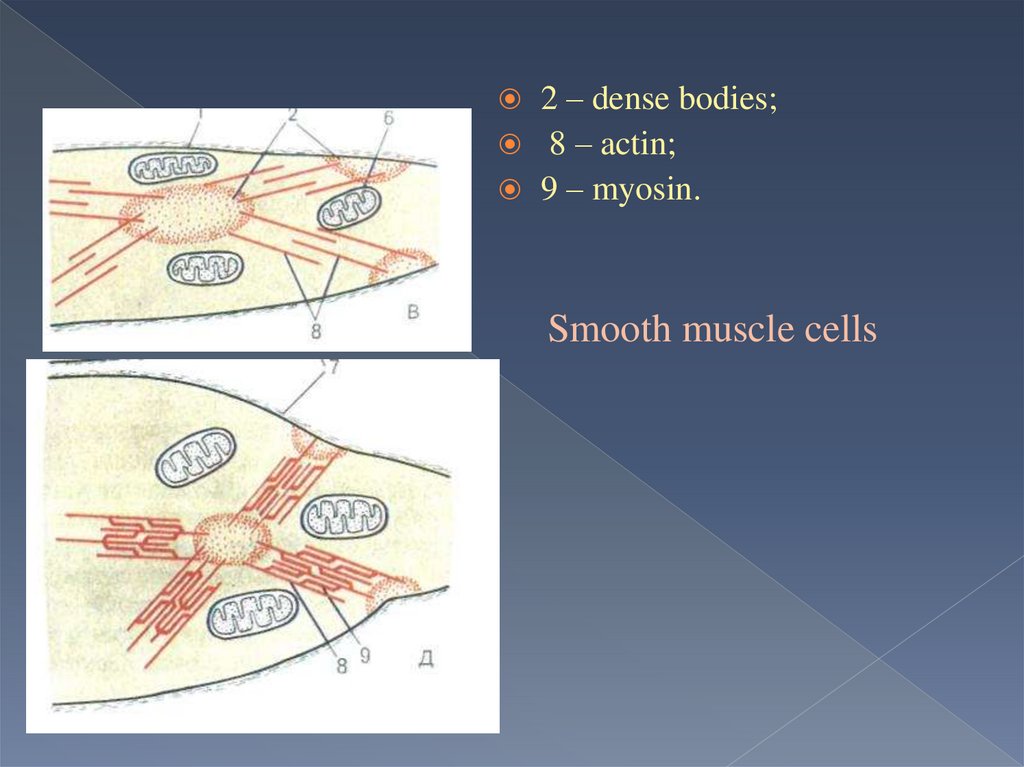
2 – dense bodies;8 – actin;
9 – myosin.
Smooth muscle cells
26.
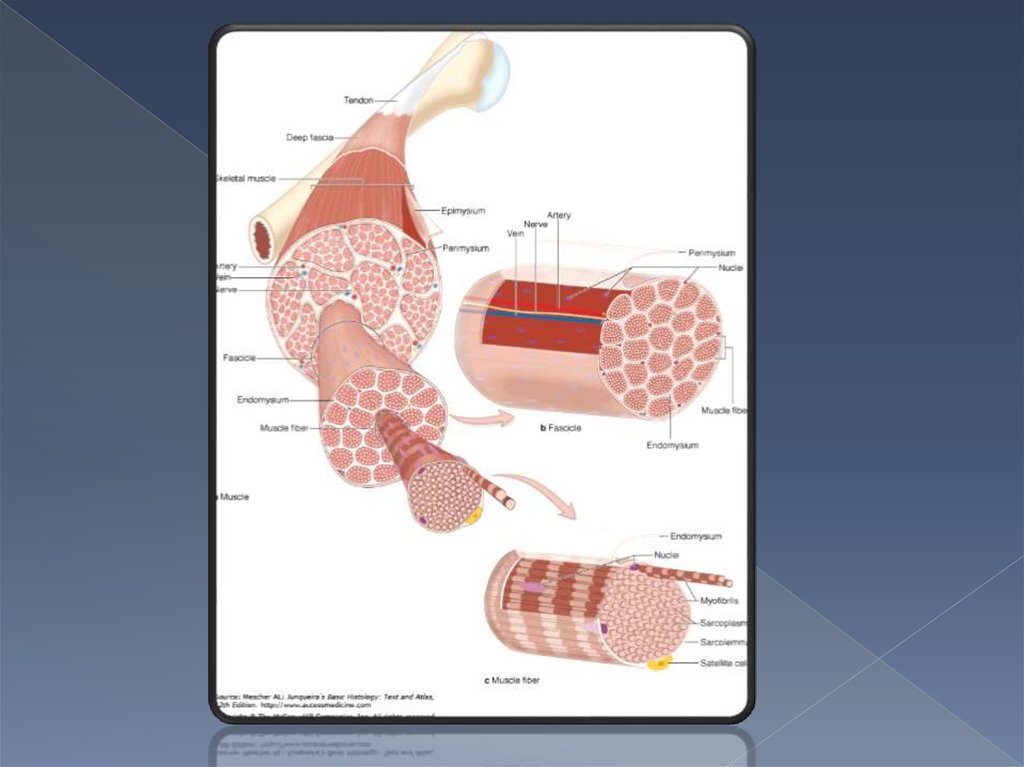
Each muscle fiber is surrounded with asheath of delicate loose connective tissue
- endomysium
Each fascicle is a boundle of muscle fibers
surrounded with a dense connective tissue
sheath - perimysium
Each skeletal muscle is a boundle of
muscle fascicles surrounded with a sheath
of dense connective tissue - epimysium














 biology
biology