Similar presentations:
Institut de Physique et Ingénierie
1. Mechanics-L1
Institut de Physique et Ingénierie2. Kinematics
•Coordinate systems and motions1)Units
2)Position-velocity-acceleration-cartesian coordinates
3)Polar and Cylindric coordinates
4)Introduction to Ellipse -Examples
5)Spherical coordinates
Institut de Physique et Ingénierie
3. Length
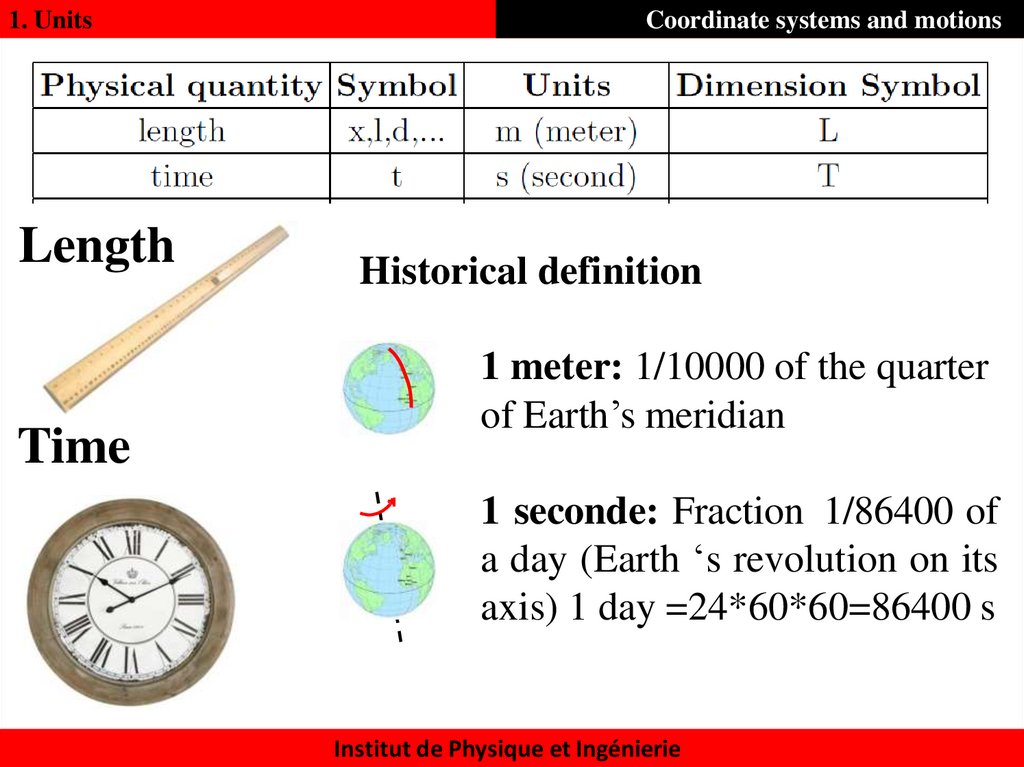
1. UnitsLength
Time
Coordinate systems and motions
Historical definition
1 meter: 1/10000 of the quarter
of Earth’s meridian
1 seconde: Fraction 1/86400 of
a day (Earth ‘s revolution on its
axis) 1 day =24*60*60=86400 s
Institut de Physique et Ingénierie
4. 1. Units
Coordinate systems and motionsModern definition with the speed of light:
c= 299 792 458 m/s
1 meter: distance that travels light during 1/c
seconds =3.34… ns
1 second: duration of 9 192 631 770 periods of the
radiation corresponding to the transition between
the two hyperfine levels of the ground state of
the cesium 133 atom”
Institut de Physique et Ingénierie
5. Kinematics
•Coordinate systems and motions1)Units
2)Position-velocity-acceleration-cartesian
coordinates
3)Polar and Cylindric coordinates
4)Introduction to Ellipse -Examples
5)Spherical coordinates
Institut de Physique et Ingénierie
6.
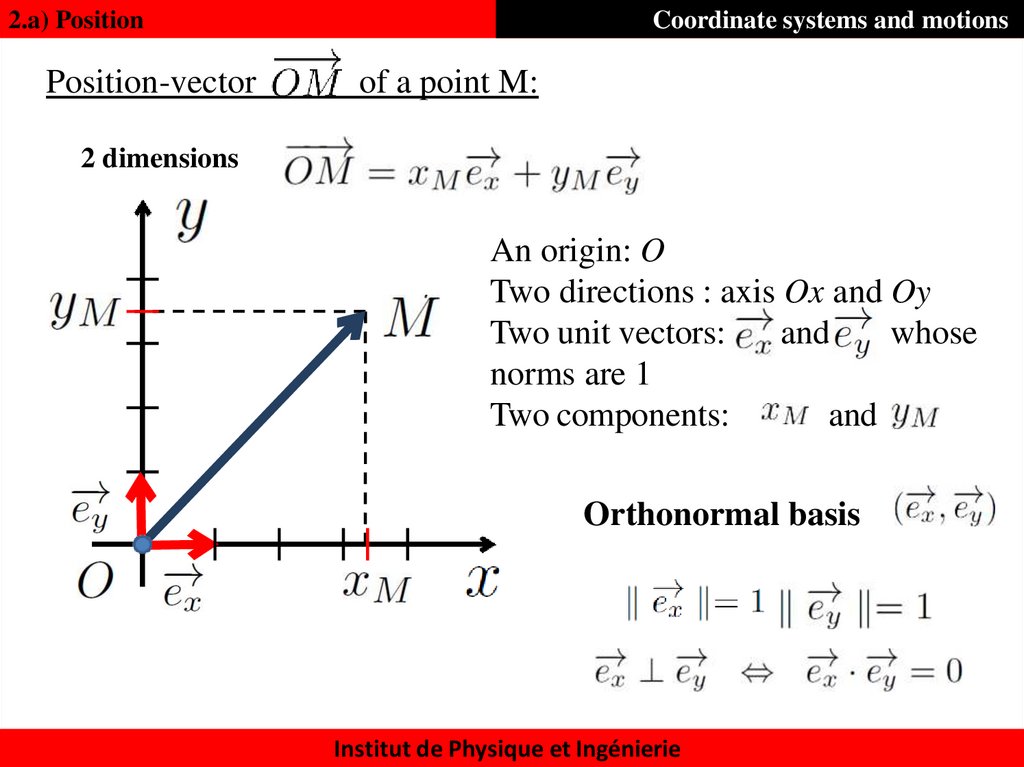
2.a) PositionPosition-vector
Coordinate systems and motions
of a point M:
1 dimensions
An origin: O
A direction : axis Ox
A unit vector:
whose norm is 1: A
component :
Institut de Physique et Ingénierie
7. Position-vector of a point M:
2.a) PositionPosition-vector
Coordinate systems and motions
of a point M:
2 dimensions
An origin: O
Two directions : axis Ox and Oy
Two unit vectors:
and
whose
norms are 1
and
Two components:
Orthonormal basis
Institut de Physique et Ingénierie
8. Position-vector of a point M:
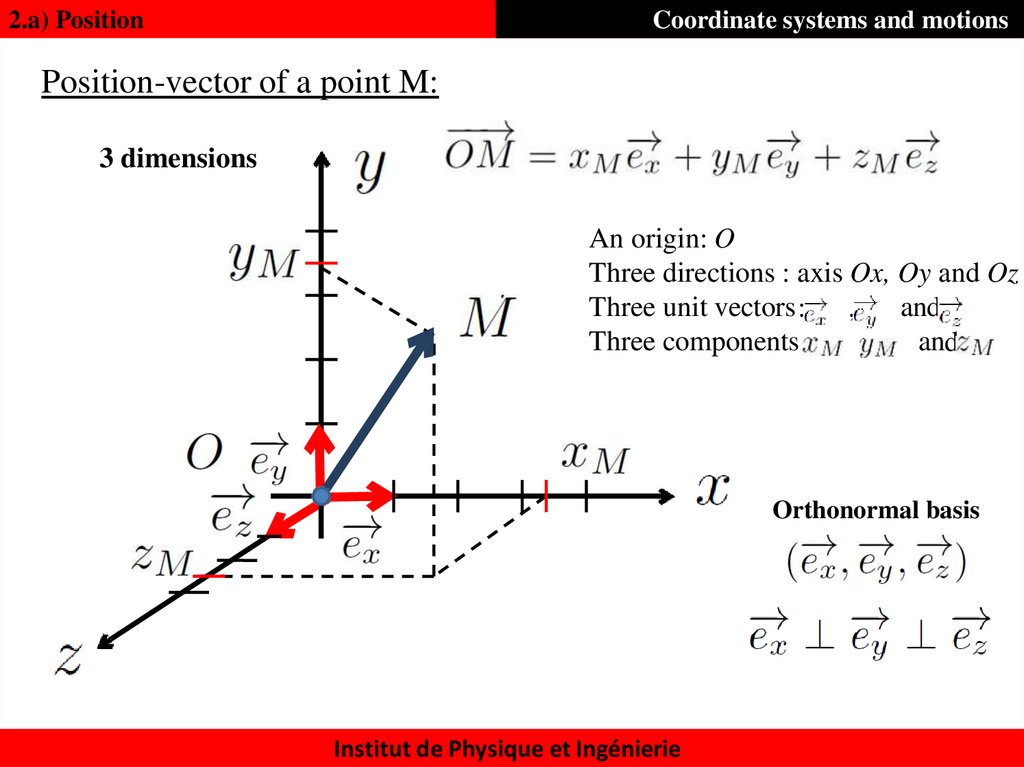
2.a) PositionCoordinate systems and motions
Position-vector of a point M:
3 dimensions
An origin: O
Three directions : axis Ox, Oy and Oz
Three unit vectors :
and
,
Three components:
and
,
Orthonormal basis
Institut de Physique et Ingénierie
9. Where is Wally ?
InterludeCoordinate systems and motions
Where is Wally ?
Institut de Physique et Ingénierie
10.
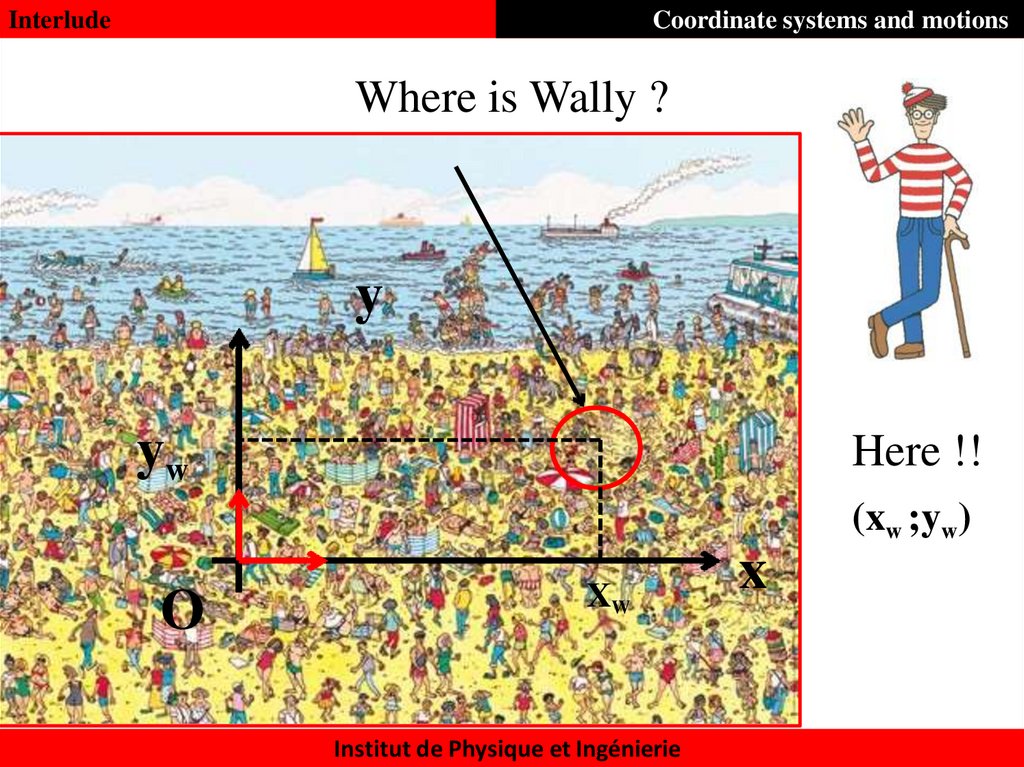
InterludeCoordinate systems and motions
Where is Wally ?
y
yw
Here !!
(xw ;yw)
O
XW
Institut de Physique et Ingénierie
x
11.
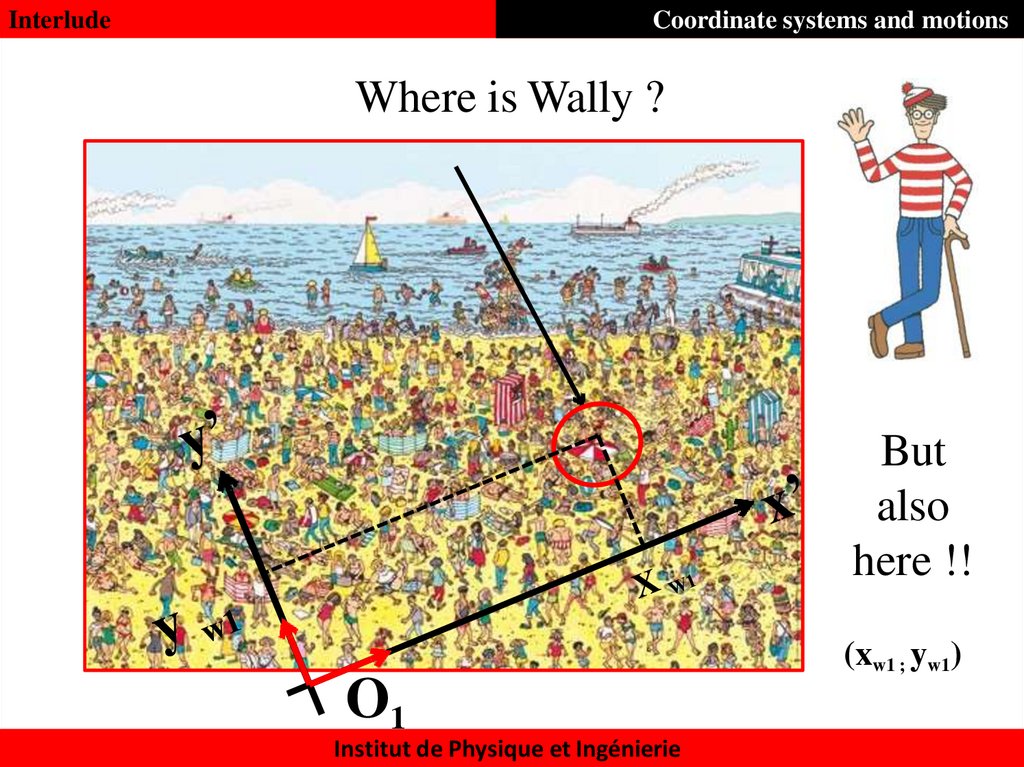
InterludeCoordinate systems and motions
Where is Wally ?
But
also
here !!
(xw1 ; yw1)
O1
Institut de Physique et Ingénierie
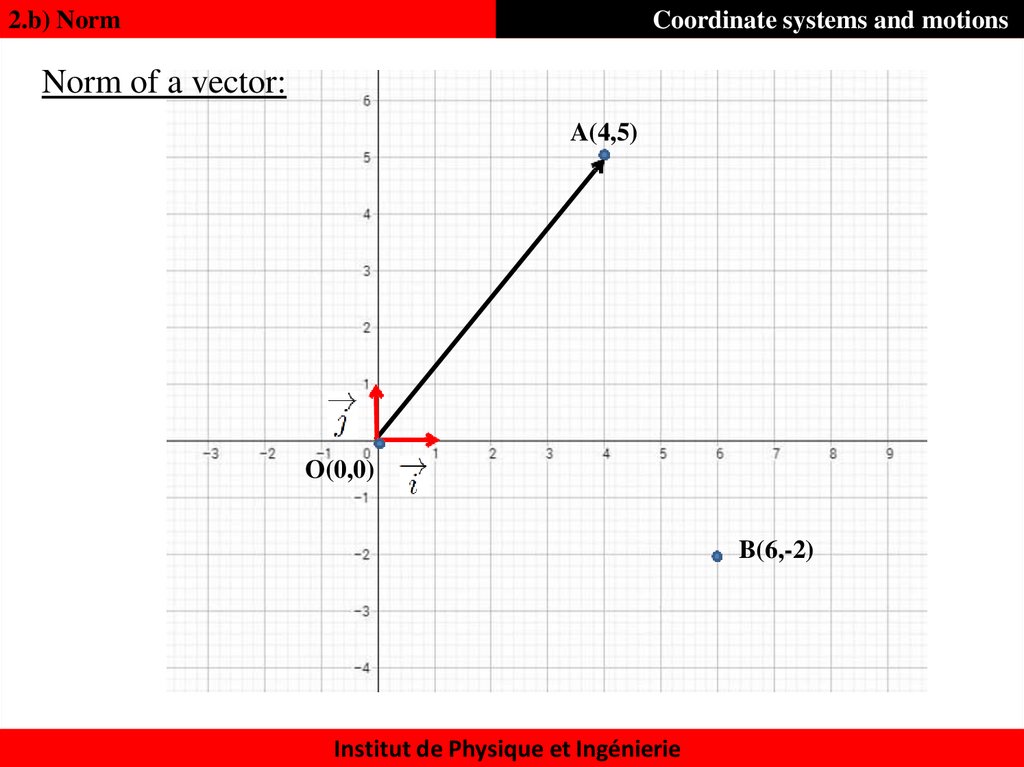
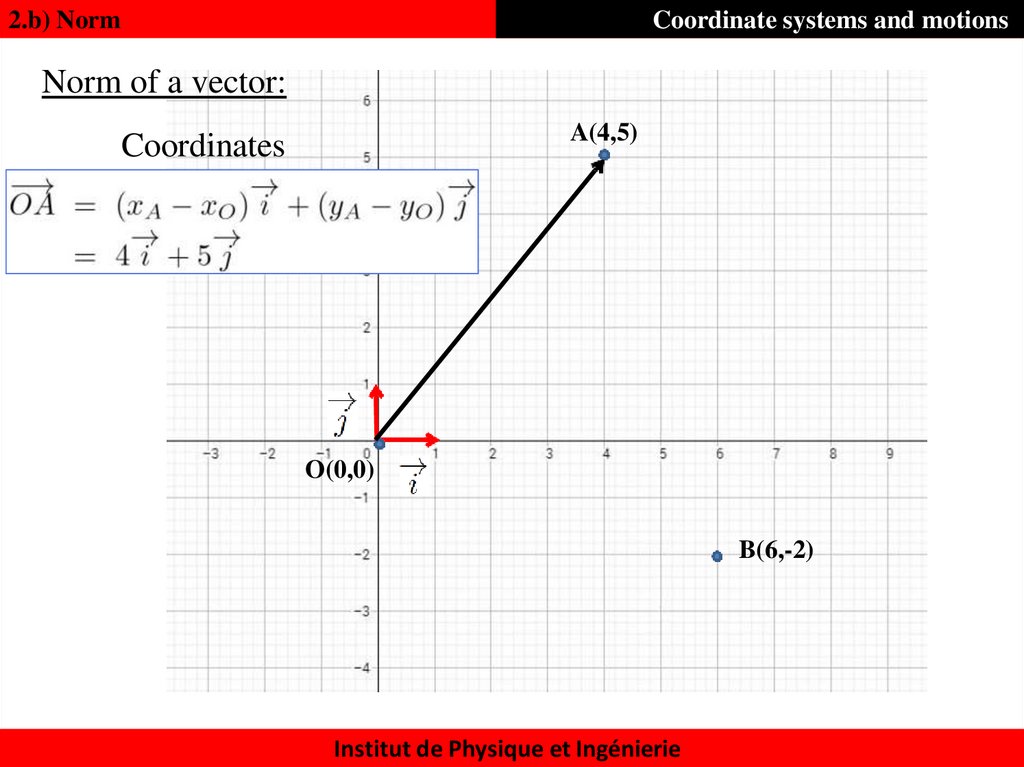
12. Norm of a vector:
2.b) NormCoordinate systems and motions
Norm of a vector:
A(4,5)
O(0,0)
B(6,-2)
Institut de Physique et Ingénierie
13. Norm of a vector:
2.b) NormCoordinate systems and motions
Norm of a vector:
A(4,5)
Coordinates
O(0,0)
B(6,-2)
Institut de Physique et Ingénierie
14.
2.b) NormCoordinate systems and motions
Norm of a vector:
Pythagoras
A(4,5)
Coordinates
Norm (scalar quantity)
O(0,0)
B(6,-2)
Institut de Physique et Ingénierie
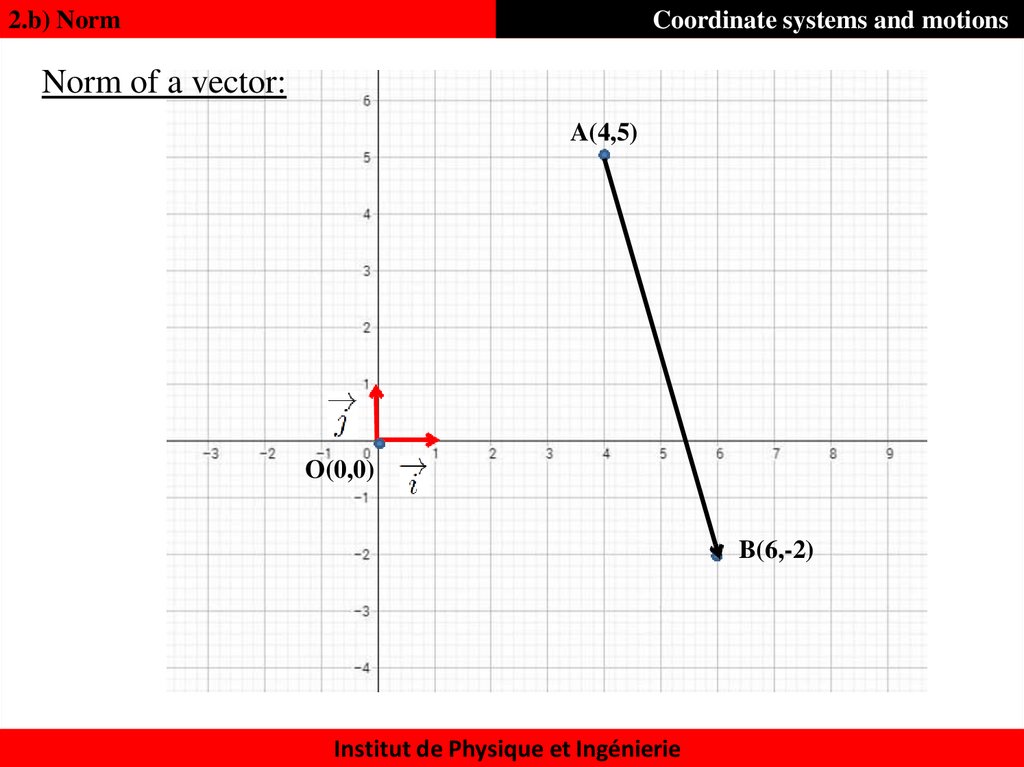
15. Norm of a vector:
2.b) NormCoordinate systems and motions
Norm of a vector:
A(4,5)
O(0,0)
B(6,-2)
Institut de Physique et Ingénierie
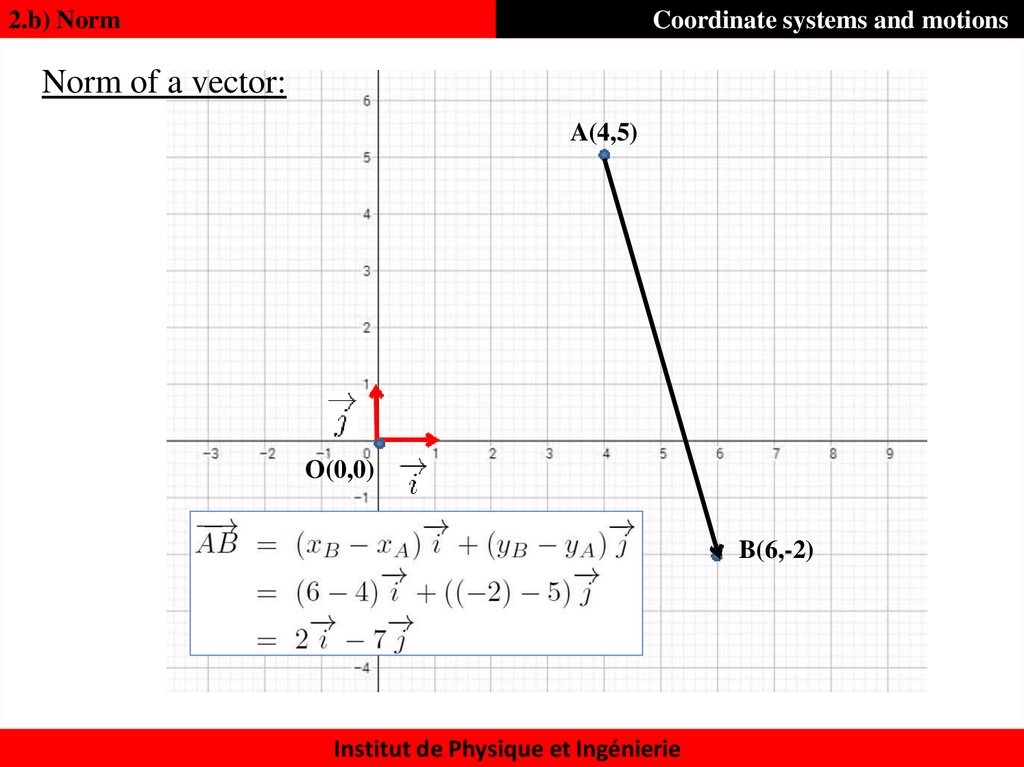
16. Norm of a vector:
2.b) NormCoordinate systems and motions
Norm of a vector:
A(4,5)
O(0,0)
B(6,-2)
Institut de Physique et Ingénierie
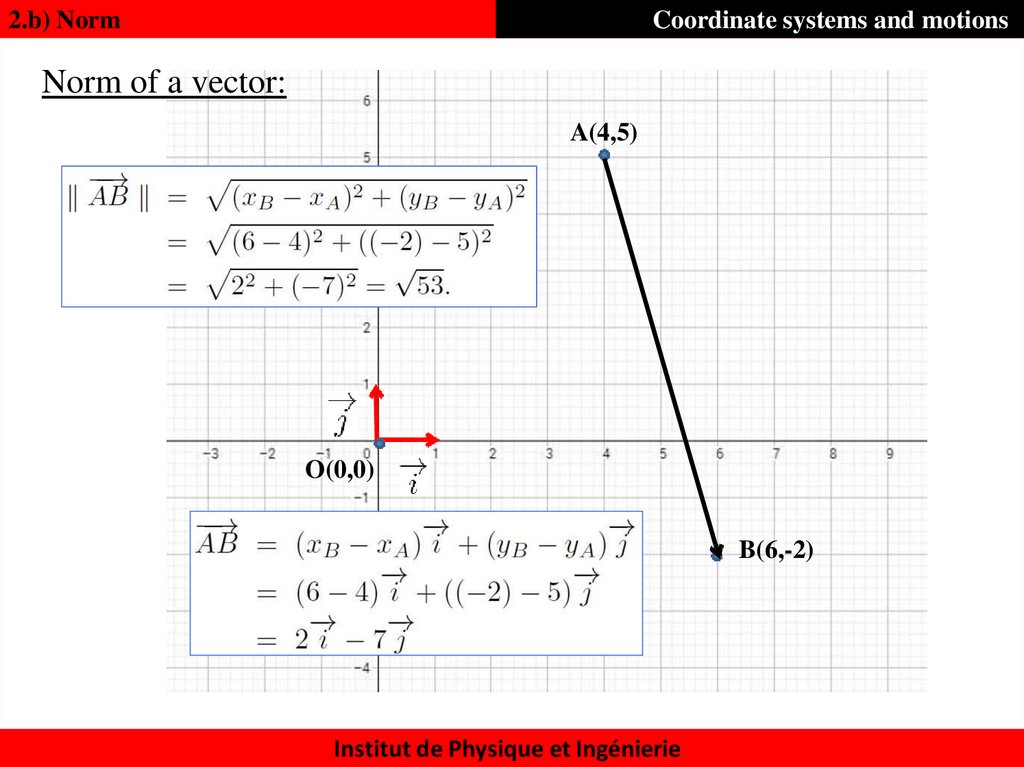
17. Norm of a vector:
2.b) NormCoordinate systems and motions
Norm of a vector:
A(4,5)
O(0,0)
B(6,-2)
Institut de Physique et Ingénierie
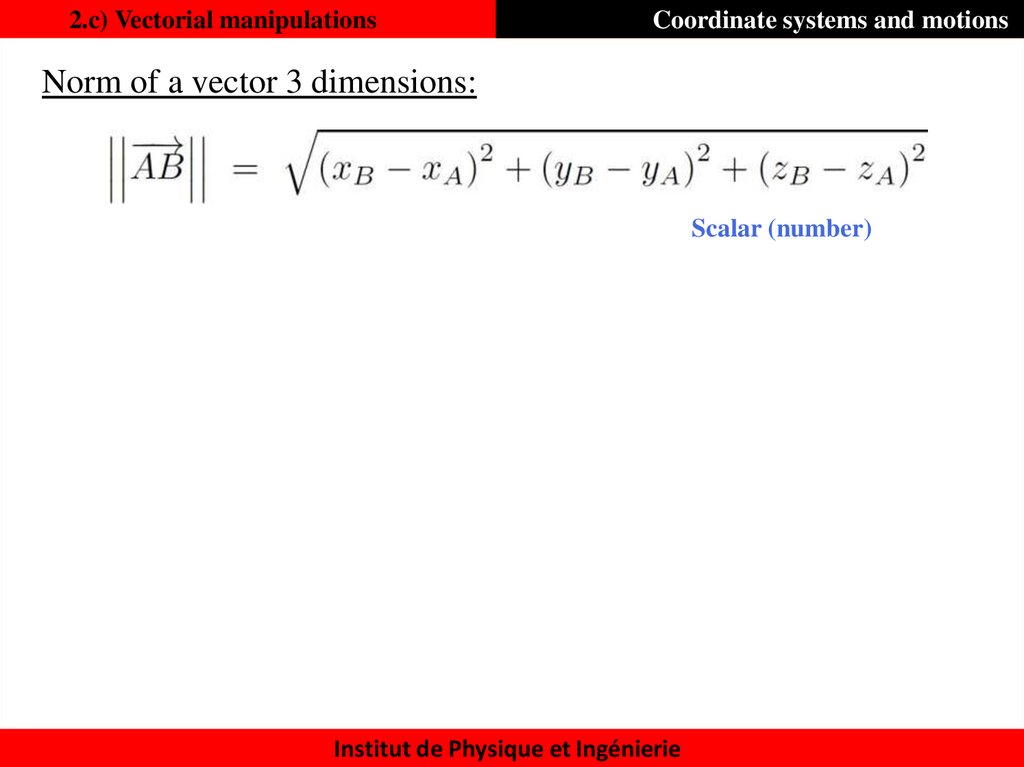
18. 2.c) Vectorial manipulations
Coordinate systems and motionsNorm of a vector 3 dimensions:
Scalar (number)
Institut de Physique et Ingénierie
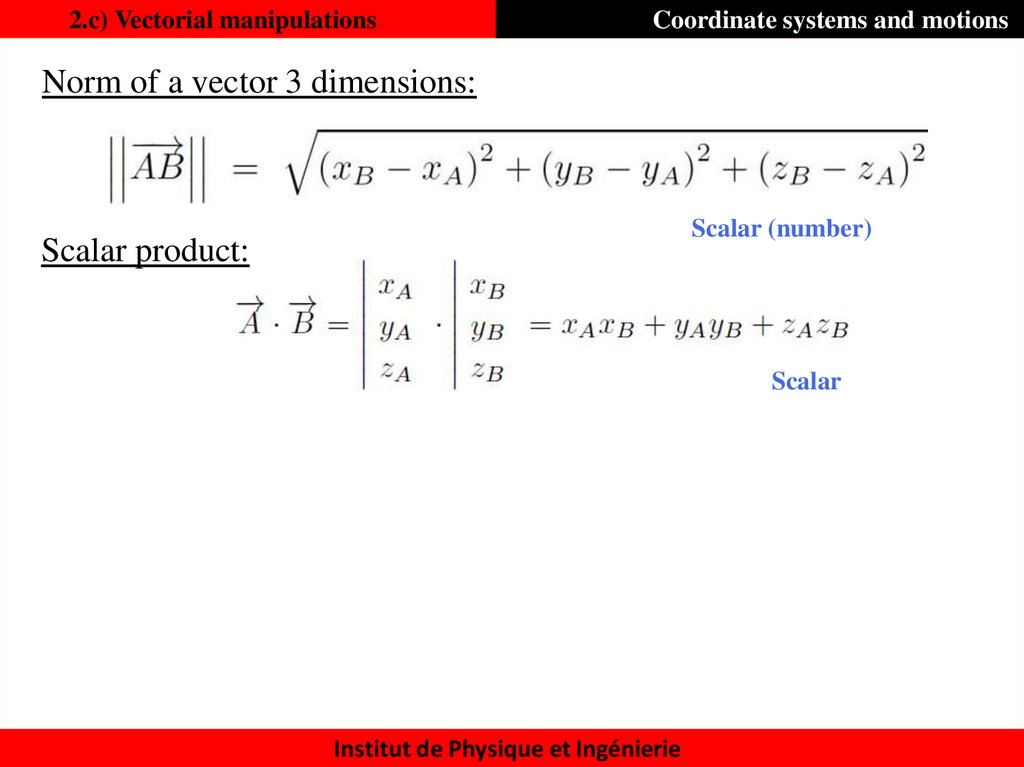
19. 2.c) Vectorial manipulations
Coordinate systems and motionsNorm of a vector 3 dimensions:
Scalar (number)
Scalar product:
Scalar
Institut de Physique et Ingénierie
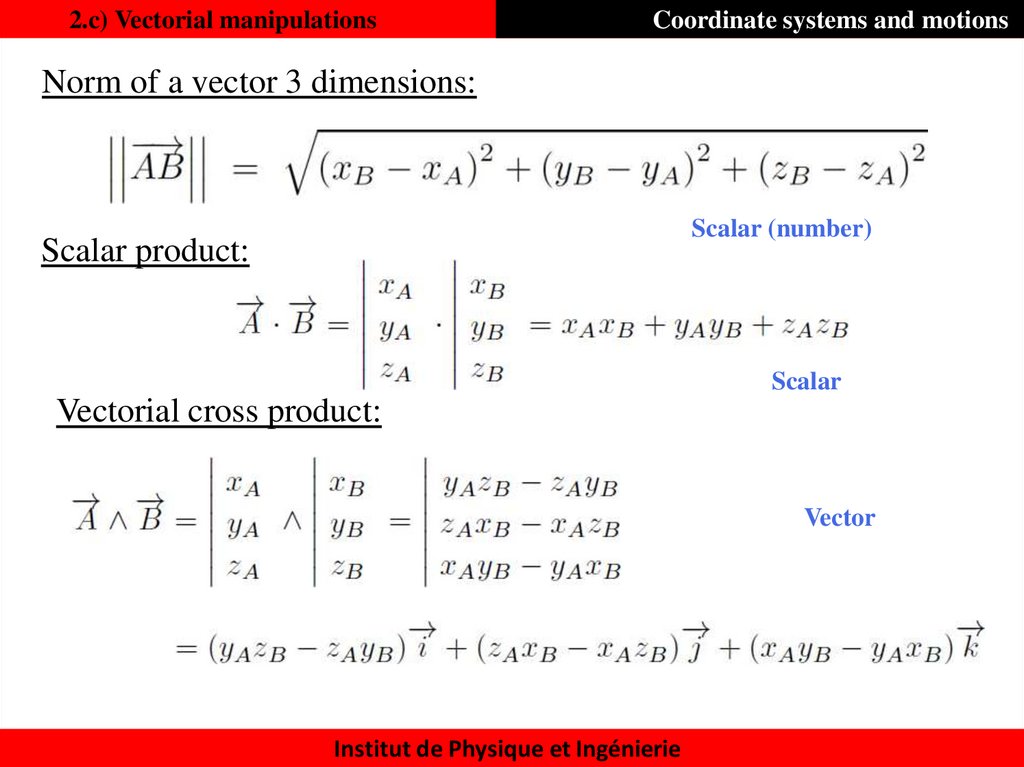
20. 2.c) Vectorial manipulations
Coordinate systems and motionsNorm of a vector 3 dimensions:
Scalar (number)
Scalar product:
Scalar
Vectorial cross product:
Vector
Institut de Physique et Ingénierie
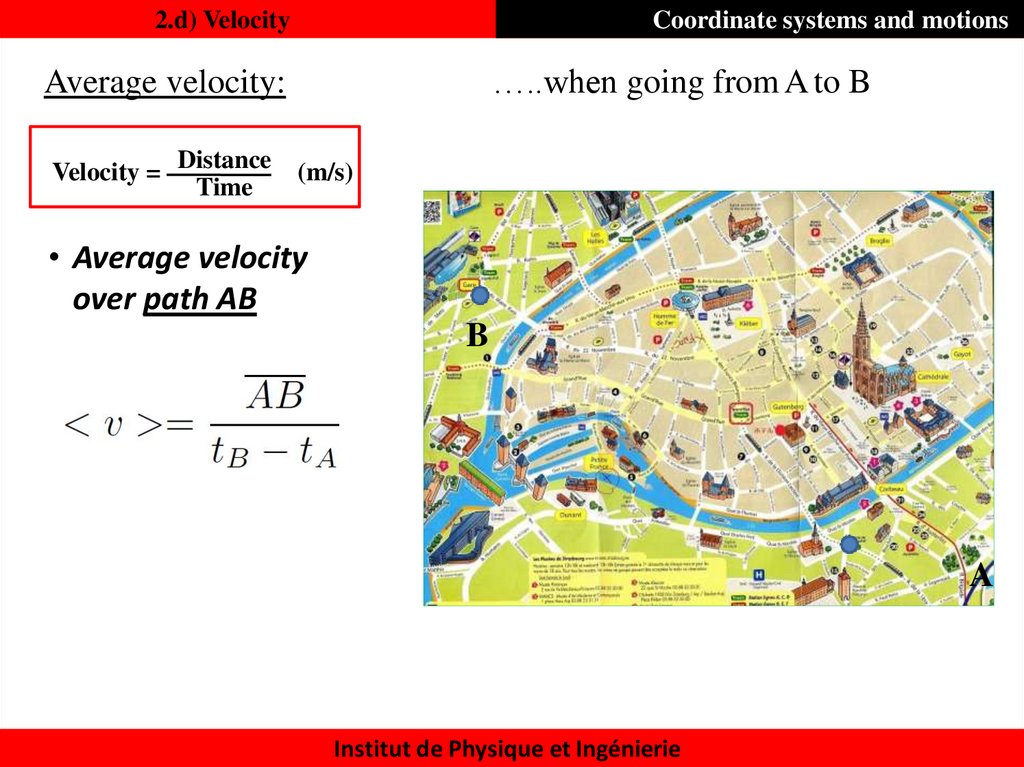
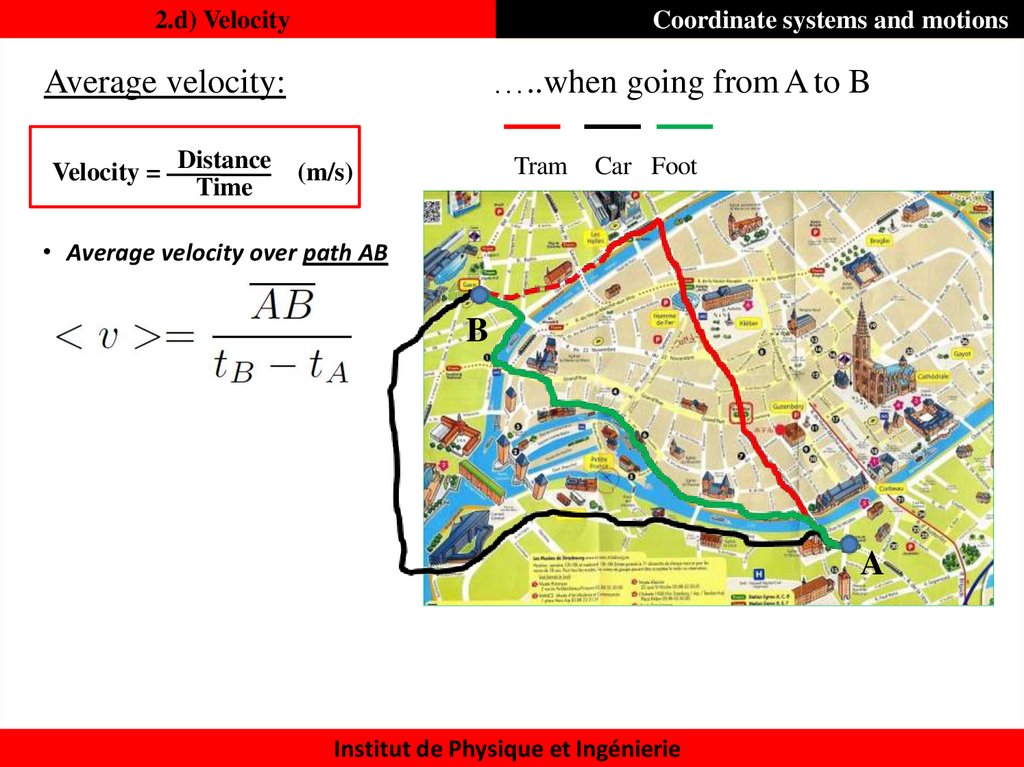
21. 2.d) Velocity
Coordinate systems and motions…..when going from A to B
Average velocity:
Velocity = Distance
Time
(m/s)
• Average velocity
over path AB
B
A
Institut de Physique et Ingénierie
22. 2.d) Velocity
Coordinate systems and motions…..when going from A to B
Average velocity:
Velocity = Distance
Time
Tram
(m/s)
Car Foot
• Average velocity over path AB
B
A
Institut de Physique et Ingénierie
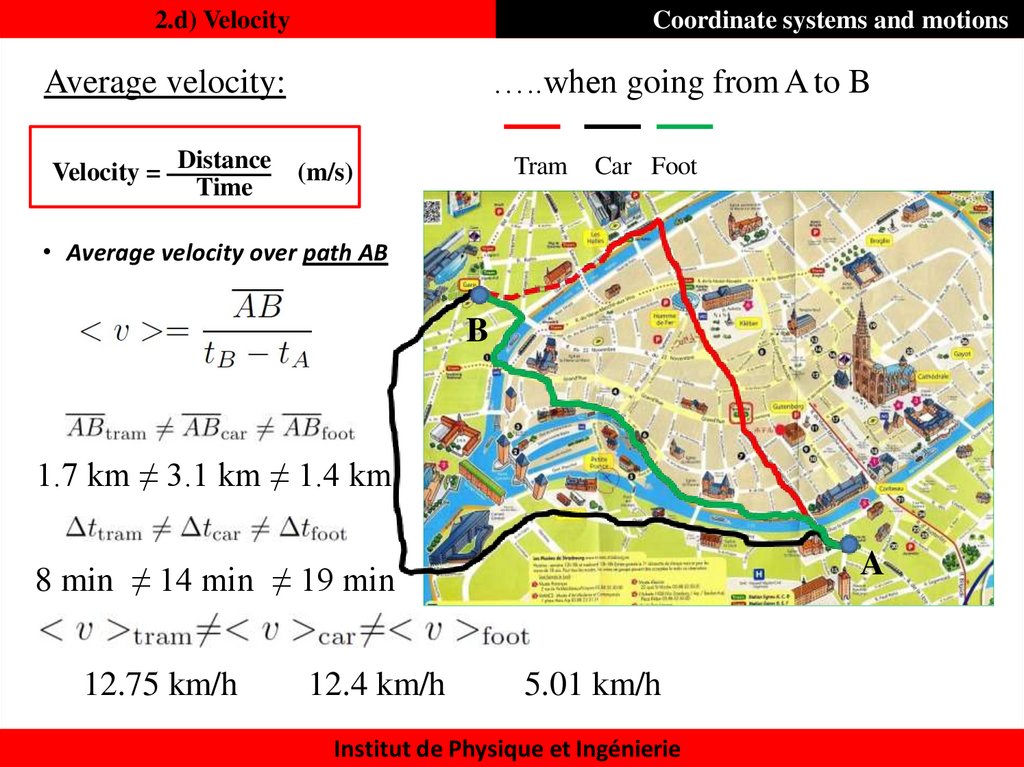
23. 2.d) Velocity
Coordinate systems and motions…..when going from A to B
Average velocity:
Velocity = Distance
Time
Tram
(m/s)
Car Foot
• Average velocity over path AB
B
1.7 km ≠ 3.1 km ≠ 1.4 km
A
8 min ≠ 14 min ≠ 19 min
12.75 km/h
12.4 km/h
5.01 km/h
Institut de Physique et Ingénierie
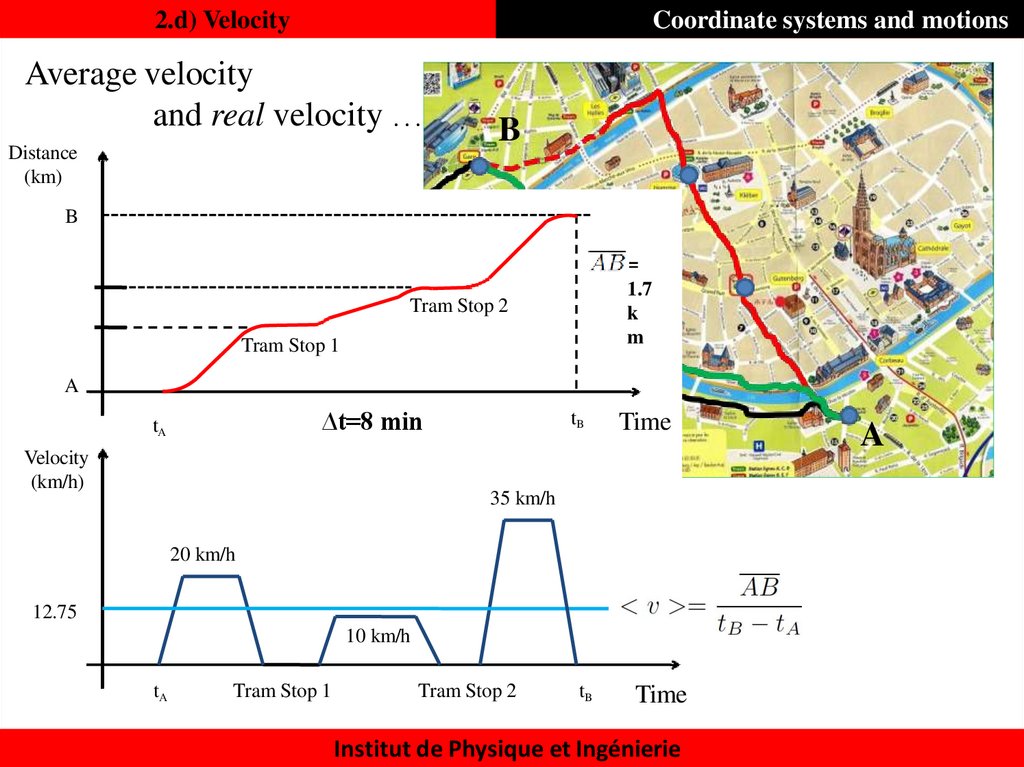
24. 2.d) Velocity
Coordinate systems and motionsAverage velocity
and real velocity …
B
Distance
(km)
B
B
AB =
1.7
k
m
Tram Stop 2
Tram Stop 1
A
∆t=8 min
tA
Velocity
(km/h)
tB
Time
35 km/h
20 km/h
12.75
10 km/h
tA
Tram Stop 1
Tram Stop 2
tB
Time
Institut de Physique et Ingénierie
A
25. 2.d) Velocity
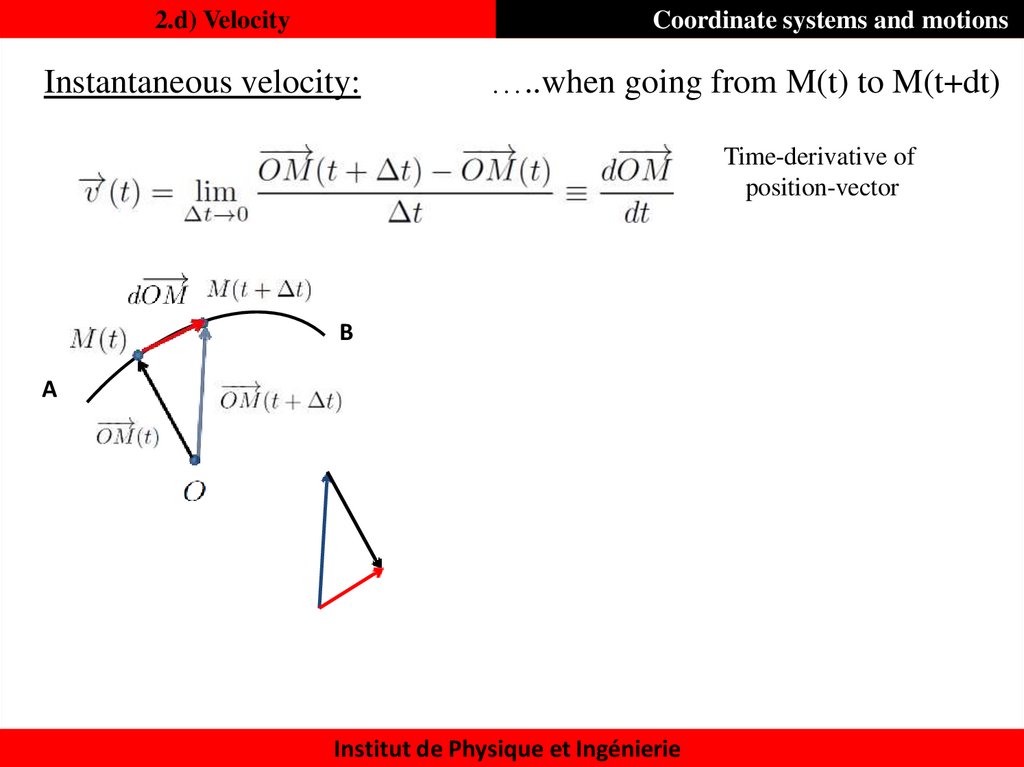
Coordinate systems and motionsInstantaneous velocity:
…..when going from M(t) to M(t+dt)
Time-derivative of
position-vector
B
A
Institut de Physique et Ingénierie
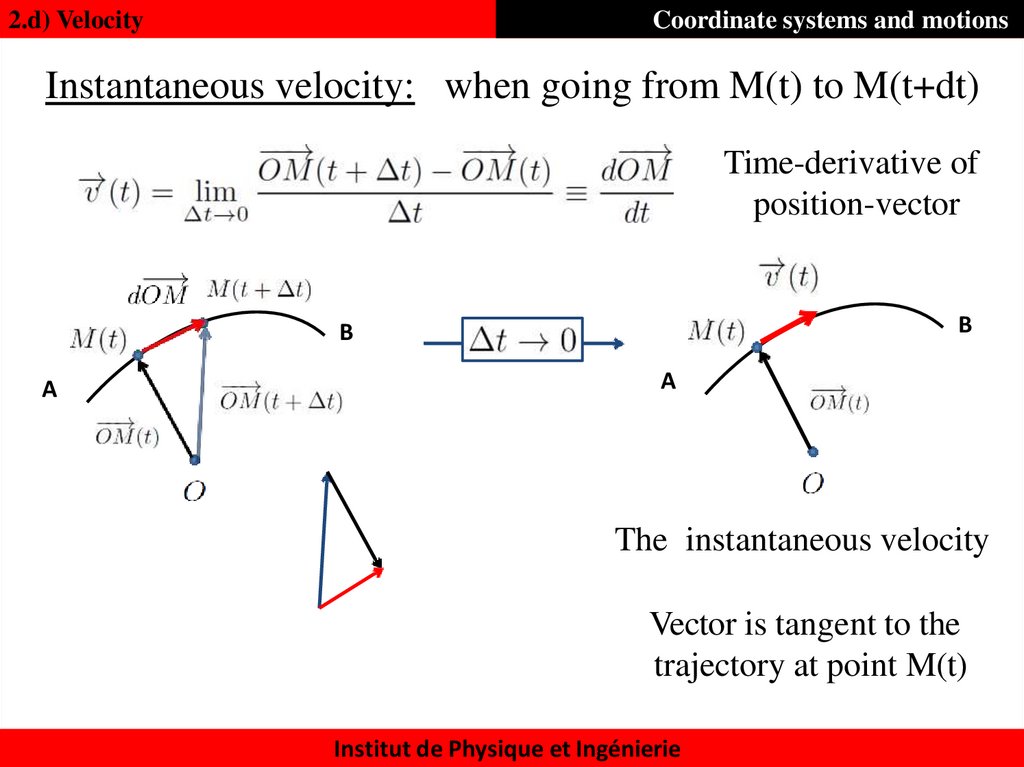
26. Instantaneous velocity:
2.d) VelocityCoordinate systems and motions
Instantaneous velocity: when going from M(t) to M(t+dt)
Time-derivative of
position-vector
B
B
A
A
The instantaneous velocity
Vector is tangent to the
trajectory at point M(t)
Institut de Physique et Ingénierie
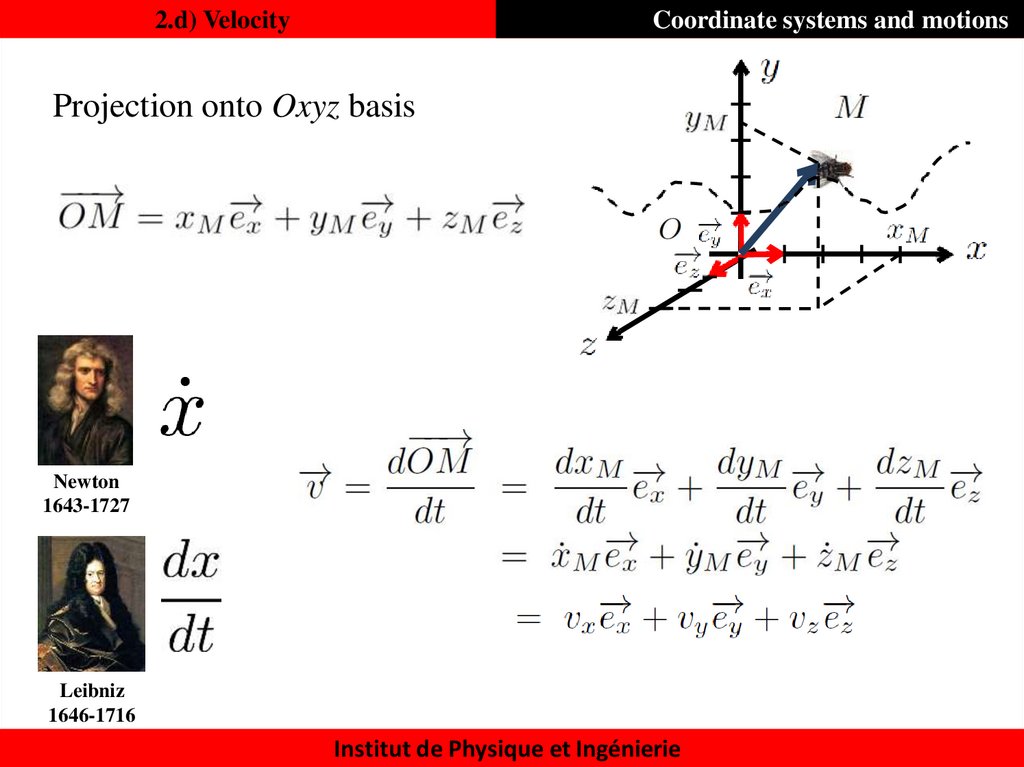
27. 2.d) Velocity
Coordinate systems and motionsProjection onto Oxyz basis
Newton
1643-1727
Leibniz
1646-1716
Institut de Physique et Ingénierie
28.
2.e) AccelerationCoordinate systems and motions
Acceleration = Velocity (m/s2)
Time
Average acceleration over path AB
Importance of vectors: example
uniform rotation with
constant.
A
Institut de Physique et Ingénierie
B
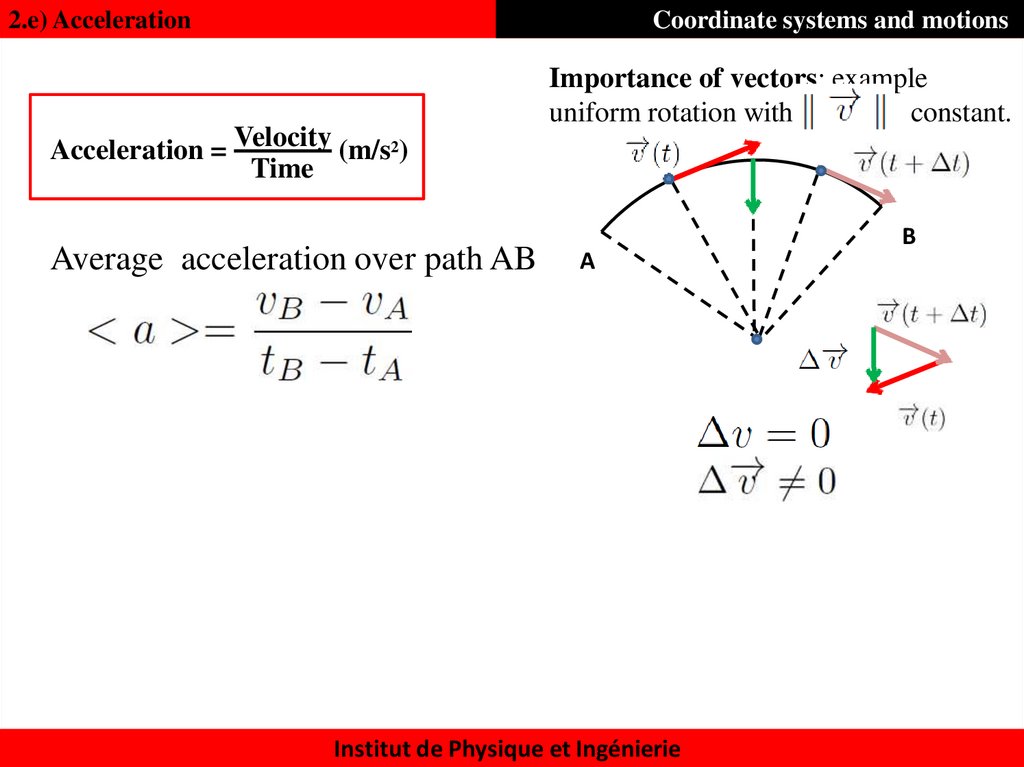
29. 2.e) Acceleration
Coordinate systems and motionsImportance of vectors: example
uniform rotation with
constant.
Acceleration = Velocity (m/s2)
Time
Average acceleration over path AB
A
Instantaneous acceleration at point M
Institut de Physique et Ingénierie
B
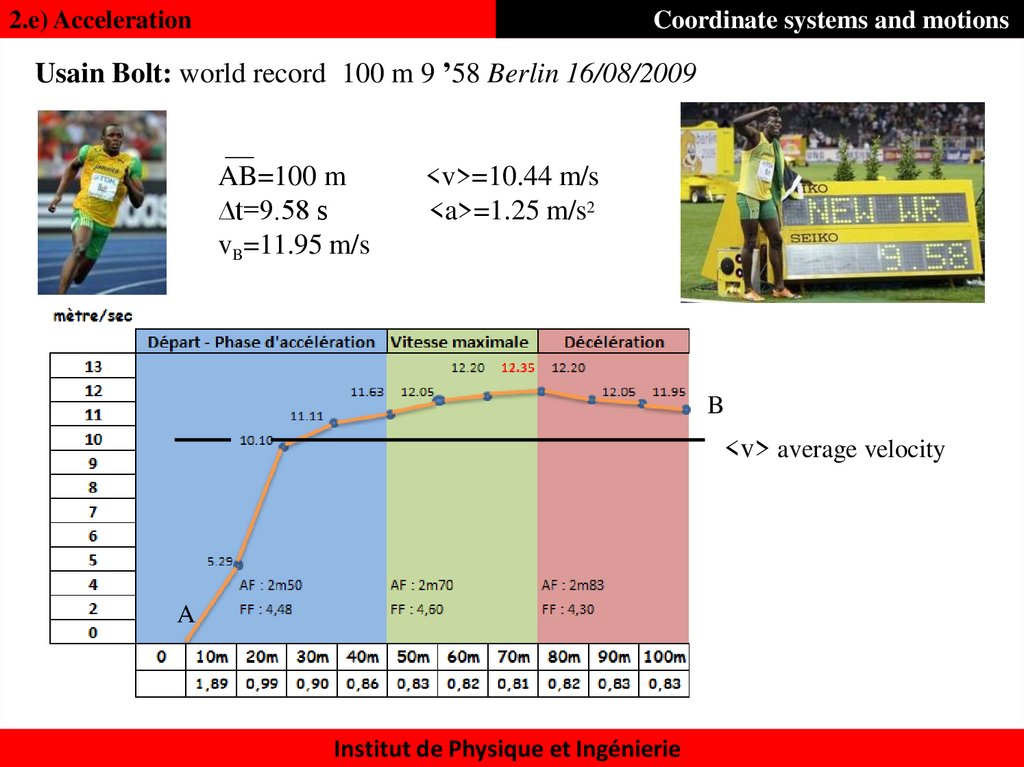
30. 2.e) Acceleration Coordinate systems and motions
Usain Bolt: world record 100 m 9 ’58 Berlin 16/08/2009AB=100 m
∆t=9.58 s
vB=11.95 m/s
<v>=10.44 m/s
<a>=1.25 m/s2
B
<v> average velocity
A
Institut de Physique et Ingénierie
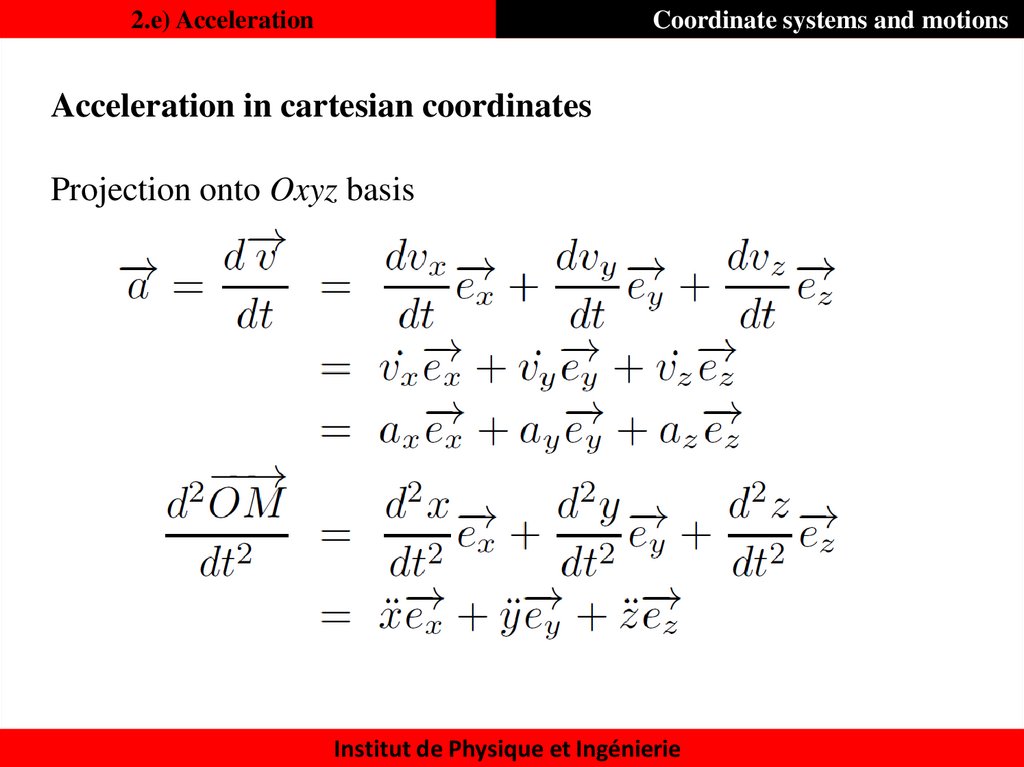
31. 2.e) Acceleration
Coordinate systems and motionsAcceleration in cartesian coordinates
Projection onto Oxyz basis
Institut de Physique et Ingénierie
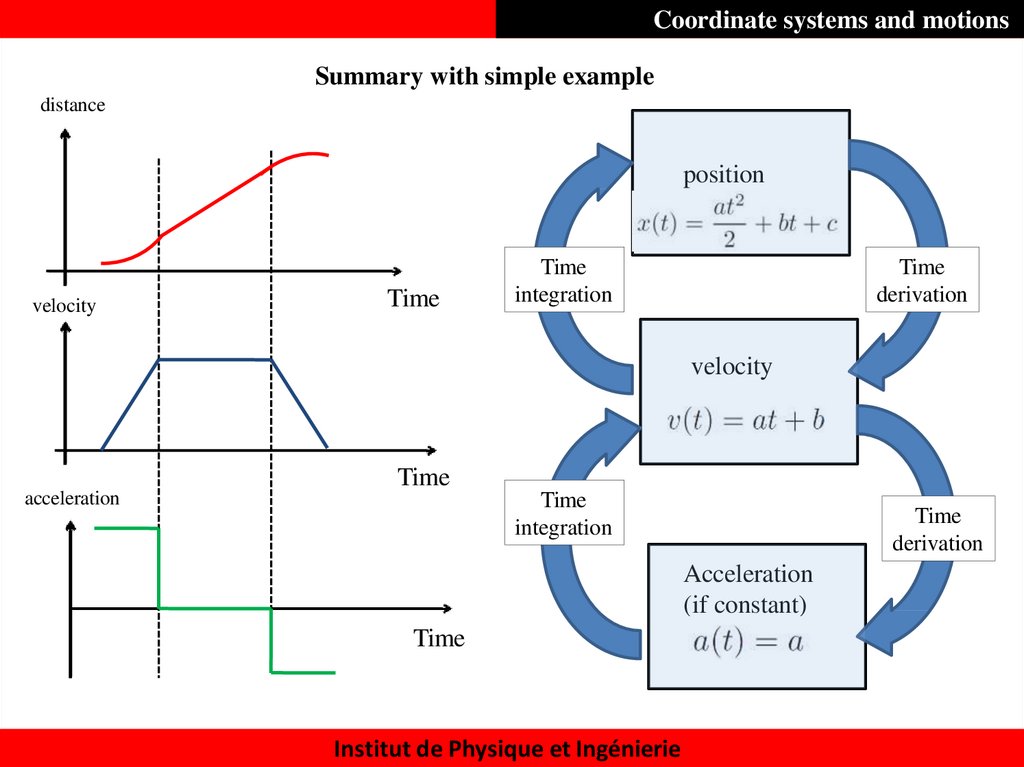
32. Coordinate systems and motions
Summary with simple exampledistance
position
velocity
Time
Time
integration
Time
derivation
velocity
acceleration
Time
Time
integration
Time
derivation
Acceleration
(if constant)
Time
Institut de Physique et Ingénierie
33. Kinematics
Coordinate systems and motions1)Units
2)Position-velocity-acceleration-cartesian coordinates
3)Polar and Cylindric coordinates
4)Introduction to Ellipse -Examples
5)Spherical coordinates
Institut de Physique et Ingénierie
34. 3.a) Polar basis Coordinate systems and motions
Polar basis and time-derivation of unit vectors!!!
angular velocity
radial, orthoradial
orthonormal direct basis
Institut de Physique et Ingénierie
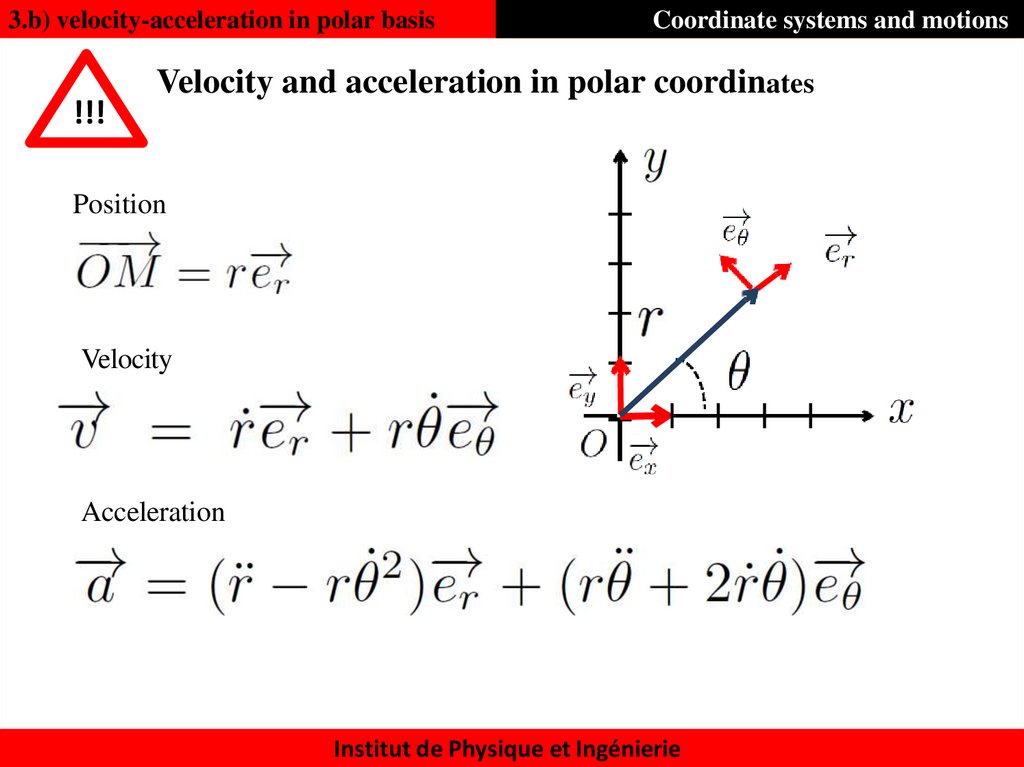
35. Velocity and acceleration in polar coordinates
3.b) velocity-acceleration in polar basis!!!
Coordinate systems and motions
Velocity and acceleration in polar coordinates
Position
Velocity
Acceleration
Institut de Physique et Ingénierie
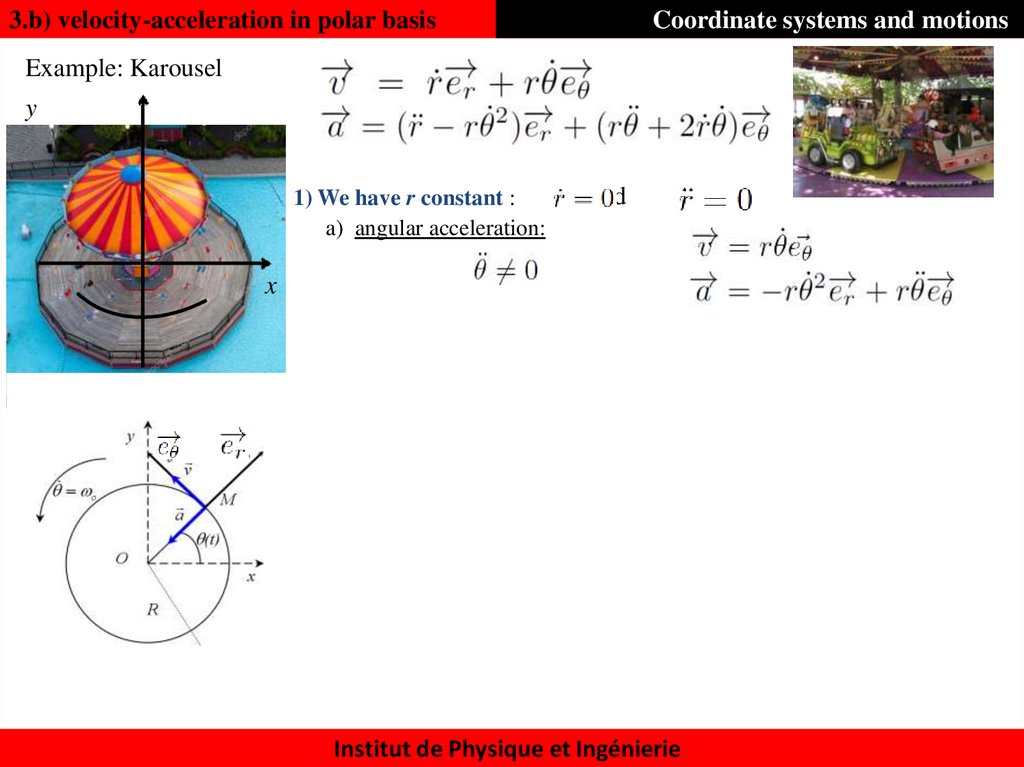
36. 3.b) velocity-acceleration in polar basis
Coordinate systems and motionsExample: Karousel
y
1) We have r constant :
a) angular acceleration:
and
x
Institut de Physique et Ingénierie
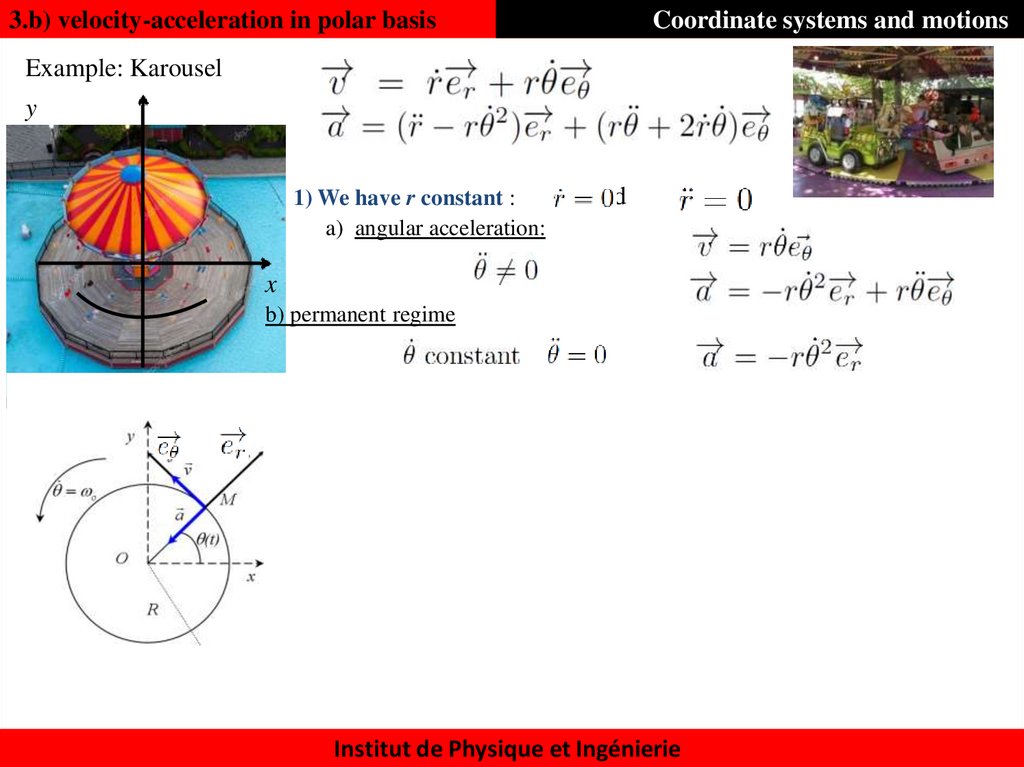
37. 3.b) velocity-acceleration in polar basis
Coordinate systems and motionsExample: Karousel
y
1) We have r constant :
a) angular acceleration:
and
x
b) permanent regime
Institut de Physique et Ingénierie
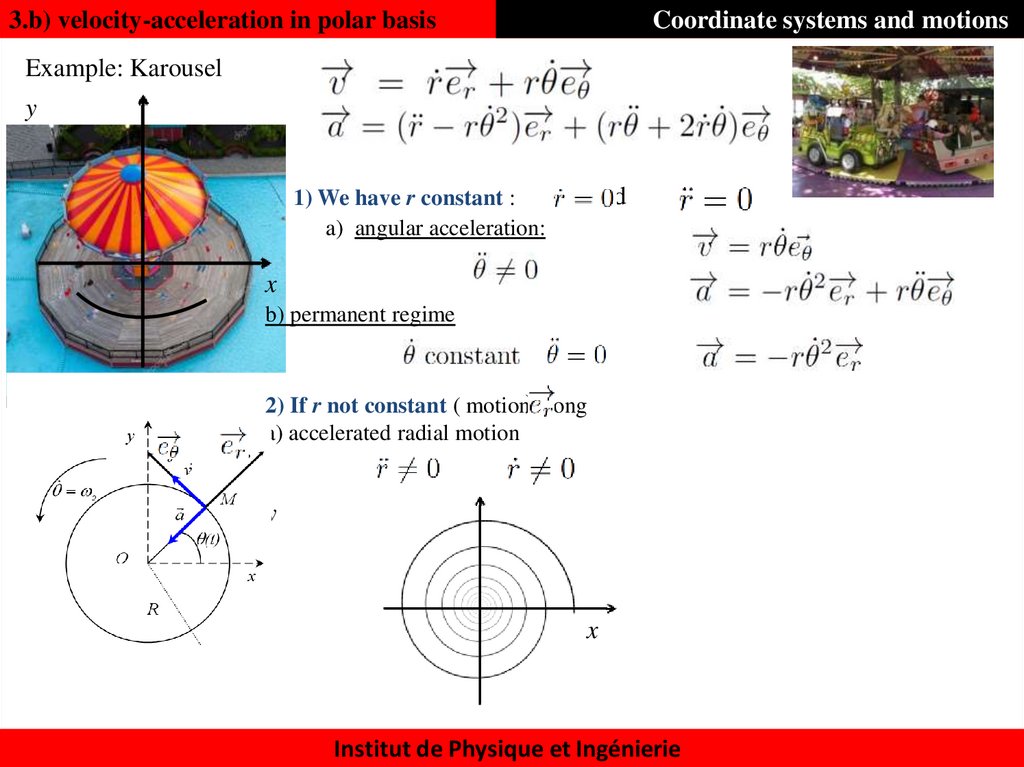
38. 3.b) velocity-acceleration in polar basis
Coordinate systems and motionsExample: Karousel
y
and
1) We have r constant :
a) angular acceleration:
x
b) permanent regime
2) If r not constant ( motion) along
a) accelerated radial motion
y
x
Institut de Physique et Ingénierie
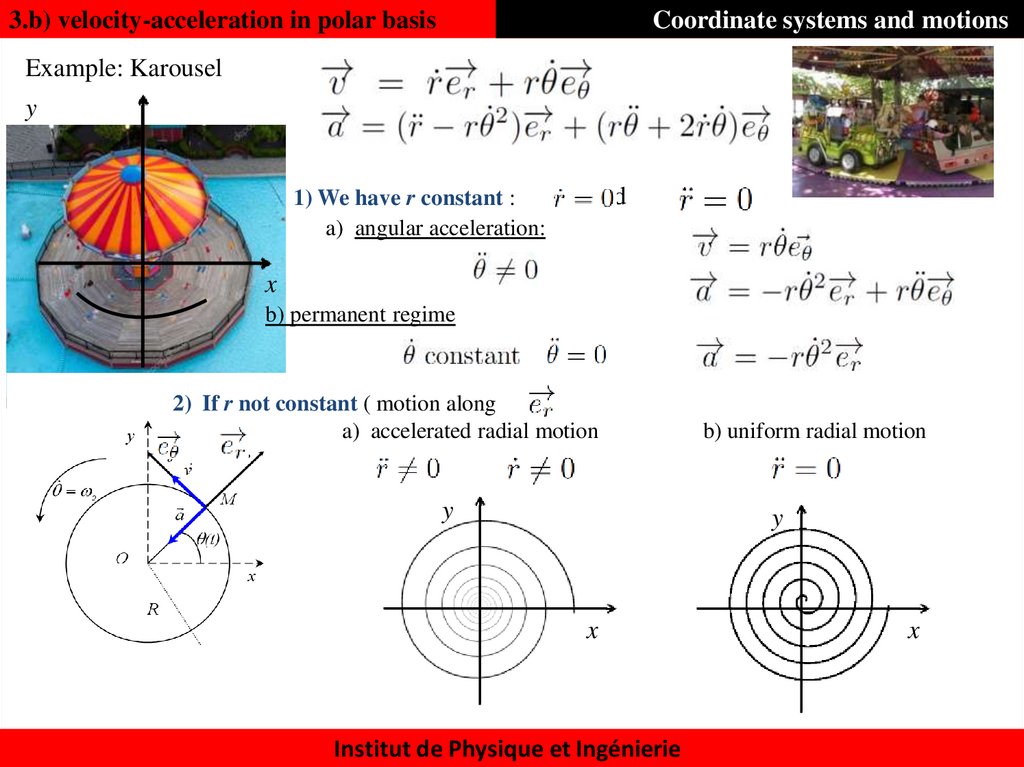
39. 3.b) velocity-acceleration in polar basis
Coordinate systems and motionsExample: Karousel
y
1) We have r constant :
a) angular acceleration:
and
x
b) permanent regime
2) If r not constant ( motion along
)
a) accelerated radial motion
y
b) uniform radial motion
y
x
Institut de Physique et Ingénierie
x
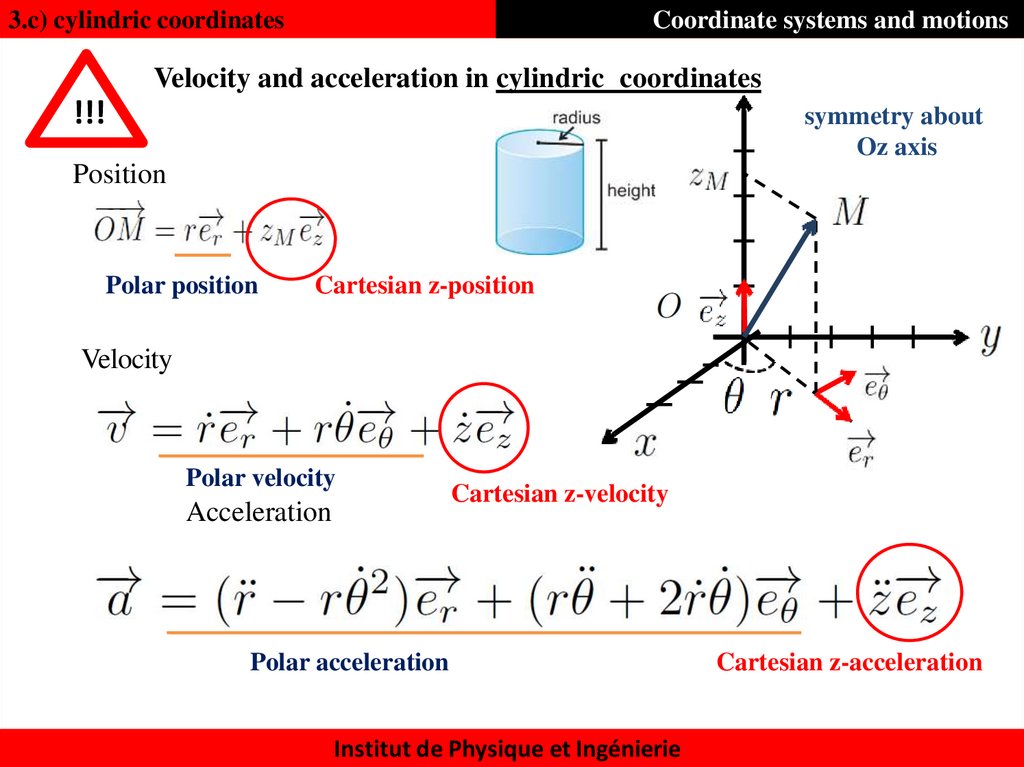
40. Velocity and acceleration in cylindric coordinates
3.c) cylindric coordinatesCoordinate systems and motions
Velocity and acceleration in cylindric coordinates
!!!
symmetry about
Oz axis
Position
Polar position
Cartesian z-position
Velocity
Polar velocity
Acceleration
Cartesian z-velocity
Polar acceleration
Institut de Physique et Ingénierie
Cartesian z-acceleration
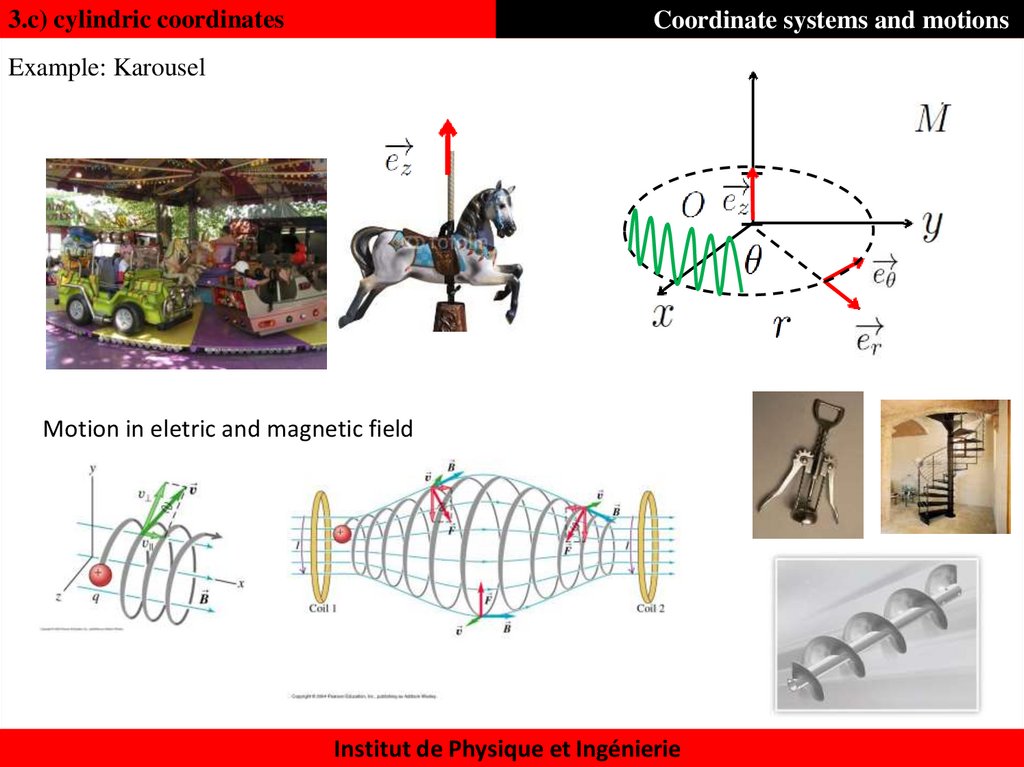
41. Coordinate systems and motions
3.c) cylindric coordinatesCoordinate systems and motions
Example: Karousel
Motion in eletric and magnetic field
Institut de Physique et Ingénierie
42. Kinematics
•Coordinate systems and motions1)Units
2)Position-velocity-acceleration-cartesian coordinates
3)Polar and Cylindric coordinates
4)Introduction to Ellipse -Examples
5)Spherical coordinates
Institut de Physique et Ingénierie
43.
4.a) EllipseCoordinate systems and motions
Hello Ellipse
M
semi-minor
axis b
Focus F(0,c)
Focus F’(0,-c)
c
eccentricity e
semi-major axis a
Institut de Physique et Ingénierie
44. 4.a) Ellipse
Coordinate systems and motionsWhere can we find ellipses ?
Planet orbits in the solar system
In gardens…..
….and in the metro
Propagation of ellipticaly polarized light
How many ellipses ?
Institut de Physique et Ingénierie
45. Kinematics
Coordinate systems and motions1)Units
2)Position-velocity-acceleration-cartesian coordinates
3)Polar and Cylindric coordinates
4)Introduction to Ellipse -Examples
5)Spherical coordinates
Institut de Physique et Ingénierie
46.
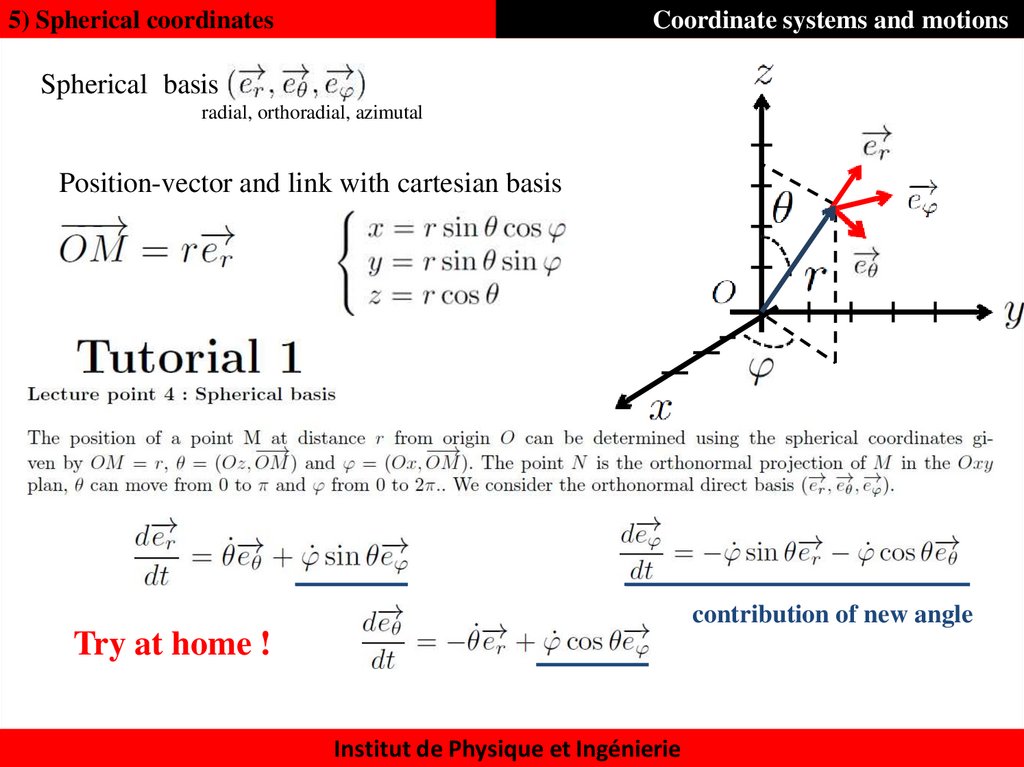
5) Spherical coordinatesCoordinate systems and motions
Spherical basis
radial, orthoradial, azimutal
Position-vector and link with cartesian basis
contribution of new angle
Try at home !
Institut de Physique et Ingénierie
47. Velocity and acceleration in Spherical coordinates
5) Spherical coordinatesCoordinate systems and motions
Velocity and acceleration
in Spherical coordinates
Velocity
Acceleration
Try at home !
Institut de Physique et Ingénierie
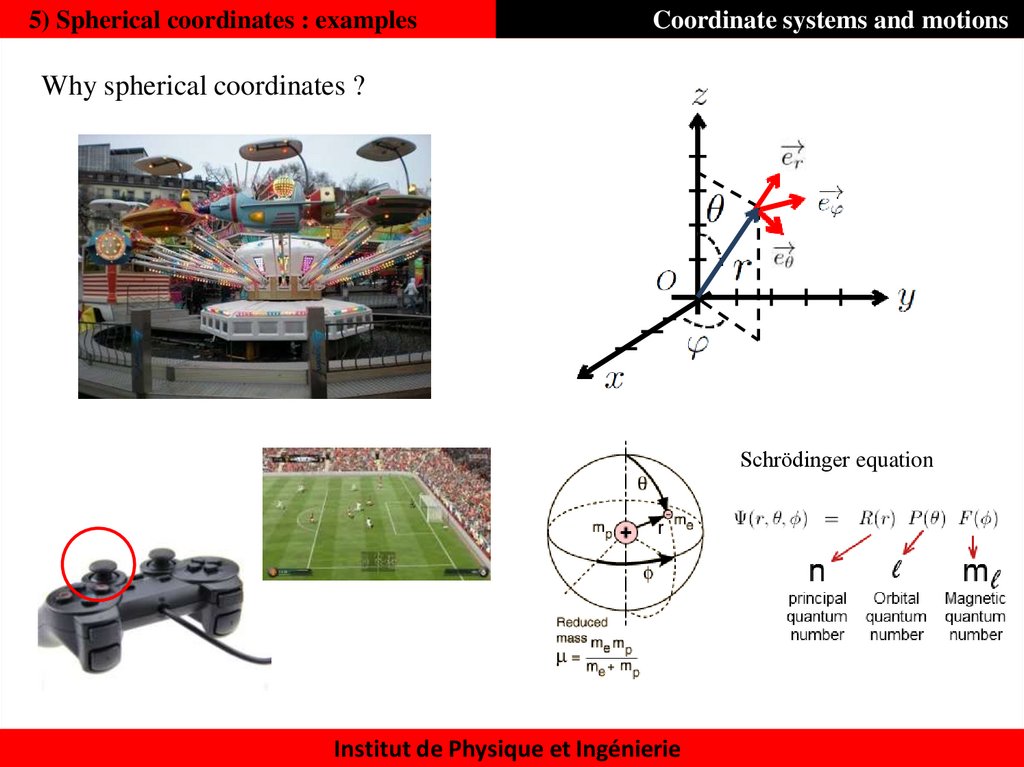
48. 5) Spherical coordinates : examples
Coordinate systems and motionsWhy spherical coordinates ?
Schrödinger equation
Institut de Physique et Ingénierie










 physics
physics








